Plants to grow with strawberries
13 Companion Plants For Strawberries (And What Not To Plant Nearby)
Time to add some strawberries to your garden or plant around an existing strawberry patch? Strawberries are perfect for companion planting as they can be particularly fussy about what’s planted nearby.
Good companion plants for strawberries include spinach, lettuce, peas, beans, onions, clovers, thyme, garlic, and borage. Avoid planting brassicas like kale, cauliflower, and broccoli near your strawberries, as well as all types of fennel.
Read on to learn all about companion plants for strawberries!
13 companion plants for strawberries (and what not to plant nearby)Strawberry Companion Plants: The Basics
1. White Clover
2. Crimson Clover
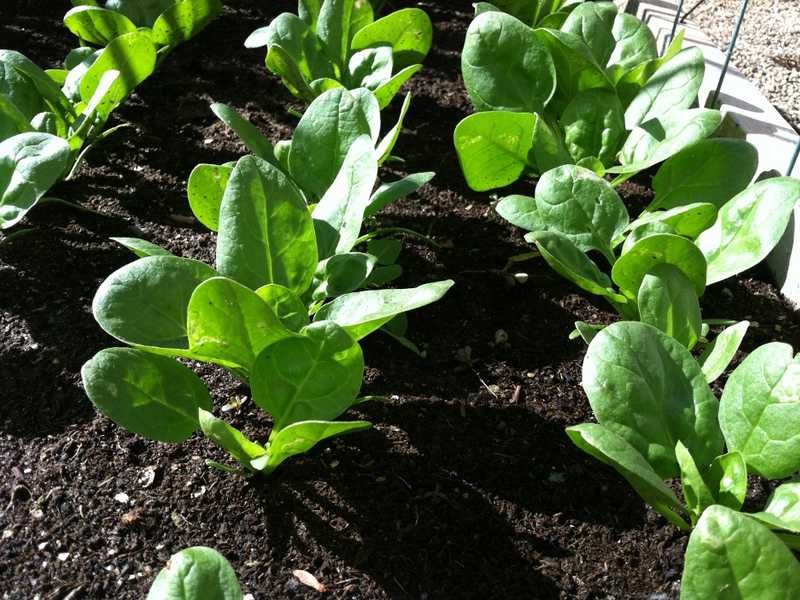
3. Spinach
4. Lettuce
5. Peas
6. Beans
7. Onions
8. Chives
9. Garlic
10. Thyme
11. Borage
12. Marigold
13. Asparagus
Bad Companions To Avoid Planting Nearby Strawberries
Resources
Strawberry Companion Plants: The Basics
Strawberries are a widely grown hybrid species of the genus Fragaria (flowering plants in the rose family). They are a popular fruit because of their bright, red color and sweet, juicy taste. Give your strawberries the best chance to become sweeter and brighter by companion planting them with their most Strawberry-friendly plant friends.
1. White Clover
White clover can be an excellent mulch plant around a strawberry bed. This is because the white clover draws nitrogen in from the air and down into the soil. It also helps keep weeds at bay and attracts beneficial insects as it flowers (just don’t let it grow too many seeds). The plants are usually (or should be) mowed down before they get to the point of growing seeds.
It’s best to plant around the strawberry patch rather than between the strawberry plants so that the strong roots of the white clover don’t create too much competition for the strawberry plants.
2. Crimson Clover
Crimson Clover is a good host plant for minute pirate bugs which are beneficial insects that feed on thrips—ideally drawing unwanted bugs away from your strawberry garden bed.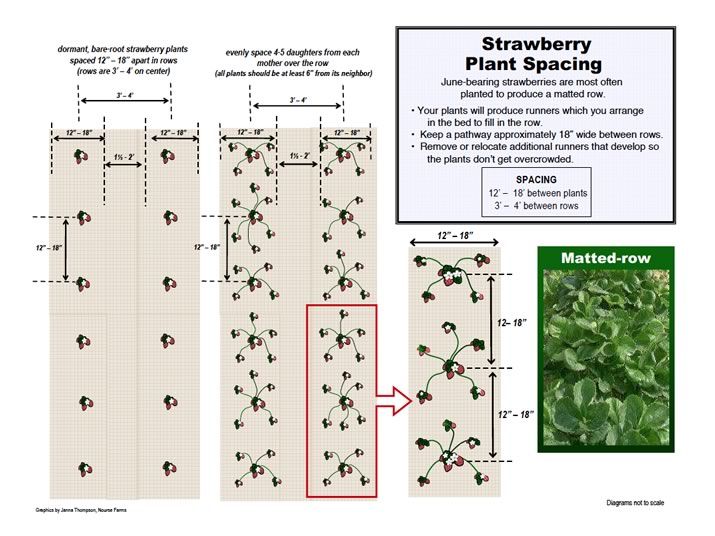 These pirate bugs love crimson clover because it gives them nectar and habitat. Crimson clover also attracts and supports other beneficial insects like lacewings and parasitic wasps.
These pirate bugs love crimson clover because it gives them nectar and habitat. Crimson clover also attracts and supports other beneficial insects like lacewings and parasitic wasps.
Crimson clover not only attracts pollinators but also naturally fix nitrogen—allowing it to help itself and other plants around it that may need or benefit from it—like strawberries.
3. Spinach
Spinach is sometimes planted in strawberry patches between strawberry plants. The spinach plants leave a substance called saponin which can improve the soil for the strawberries by lessening fungal and bacterial plant disease from affecting the strawberry plants—making them ideal companions if you plant them strategically amongst your garden layout.
4. Lettuce
Lettuce is another cool-season crop that works well with strawberries. The beauty of growing spinach or lettuce with your strawberry plants is that their larger leaves can help shield the bright red berries from the hungry sight of birds or other unwanted pests. These leafy greens, both lettuce and spinach, are said to be especially beneficial when grown together so creating a garden space for these three friends is likely a good idea!
These leafy greens, both lettuce and spinach, are said to be especially beneficial when grown together so creating a garden space for these three friends is likely a good idea!
5. Peas
Peas are a great companion plant to grow near your strawberry plants because they will help improve the surrounding soil due to their nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Creating ideal soil conditions for your strawberry crop will enhance the flavor of strawberries.
6. Beans
Beans are also good companion plants to grow near your strawberries because they help improve the soil and are natural nitrogen fixers as well—allowing it to give the strawberry plants what it needs to healthily grow to their fullest potential.
7. Onions
Onions are one of those extremely useful ingredients in the kitchen but an even more useful ingredient in the garden because their strong scent will deter birds and pests that will typically want to consume your juicy berries before you get a chance to pick them from your own garden.
8. Chives
Chives also have a strong scent that will cover the sweet scent of your desirable berries and therefore tricks pests who typically want to dine from the strawberry plant.
9. Garlic
Garlic’s strong smell makes it a good neighbor for strawberry plants. As mentioned prior, this is a great way to dissuade birds and other unwanted pests from devouring your beautiful berries. While the pungent smell of garlic is great for the kitchen, it’s even greater for your strawberry beds!
13 companion plants for strawberries (and what not to plant nearby)10. Thyme
Thyme is a great addition to include between your strawberry plants as they will help prevent weed growth, deter unwanted worms, and help your soil hold onto its moisture. Overly dry soil is a quick way to ensure your strawberries won’t grow into their prime and produce a nice harvest of juicy berries. A popular variety to consider, is Red Creeping thyme, which is known for its affinity for attracting pollinators. This will be great for your strawberry plants as it will encourage pollination and stronger growth.
This will be great for your strawberry plants as it will encourage pollination and stronger growth.
11. Borage
Borage is said to be one of the best companion plants for strawberries because this herb attracts both pollinators and pest predators. These predatory insects will then prey on the harmful pests that can do major damage to your beautiful strawberry plants—making them the best, natural pest control you can find.
12. Marigold
Marigolds are beautiful—and they also make excellent companions for the strawberry plant. Planting marigolds are a great way to keep unwanted insects and pests away from your beloved strawberries. They may also help deter harmful soil nematodes.
13. Asparagus
Asparagus is said to be an excellent companion plant to pair with strawberry plants because their roots both grow differently and don’t interfere with one another—allowing each to thrive as needed for an optimal growing season (and the best strawberries).
13 companion plants for strawberries (and what not to plant nearby)Bad Companions To Avoid Planting Nearby Strawberries
Avoid planting brassicas like kale, cauliflower, broccoli, bok choi, and cabbage near your strawberries. When attempting to grow members of the Brassicas family with strawberries, you will find this is an awful combination because they will compete for nutrients and not allow either to thrive to their full potential.
When attempting to grow members of the Brassicas family with strawberries, you will find this is an awful combination because they will compete for nutrients and not allow either to thrive to their full potential.
Planting potatoes, tomatoes, or eggplants with your strawberries can also be a bad idea because these nightshades tend to be prone to pests and disease. Growing them nearby may lead to a higher chance of fungal disease spreading.
Fennel can be great for repelling pests, however, it can potentially inhibit growth—making it less than ideal for strawberries you want to grow with plenty of nutrients, vitamins, and sweet, juicy flavor. If you’re keen on fennel you’ll want to plant it entirely separate from your nearest and dearest (and from most food crops in general).
Resources
- The Best-Tasting Strawberry Varieties to Grow
- Recommended Fertilizer for Strawberries
- Mulch Options for A Small Strawberry Patch
- Alpine Strawberries: A Gardener’s Guide
- 10 Strawberry Garden Ideas
MORE STRAWBERRY ARTICLES
Mary Jane Duford
Mary Jane Duford is a gardening expert and founder of Home for the Harvest. She's also an engineer and certified permaculture garden designer. Mary Jane has been featured by publications such as Real Simple, Mother Earth News, Homes & Gardens, Heirloom Gardener, and Family Handyman.
She's also an engineer and certified permaculture garden designer. Mary Jane has been featured by publications such as Real Simple, Mother Earth News, Homes & Gardens, Heirloom Gardener, and Family Handyman.
Strawberry companion plants: what to grow with strawberries
(Image credit: Getty Images)
By growing strawberry companion plants alongside your fruit bushes you can help to boost the crop of these delicious soft fruits.
Try taking a lesson from nature and grow plants alongside your strawberries that will be beneficial for a great harvest. Companion planting is a great way of ensuring a bumper strawberry crop and has been used by gardeners and farmers for many years.
Companion planting strawberries is just one of the elements worth trying if you're learning how to grow strawberries and a way to achieve the best results from your vegetable garden ideas.
Read on for more details of the best strawberry companion plants to grow.
Why grow strawberry companion plants?
(Image credit: Unsplash)
When you are planning a kitchen garden, companion planting is one of the factors to consider.
'Companion planting strawberries can enhance growing conditions, attract pollinators, control pests, and make good use of available space,' says Claire Ransom from Lazy Flora .
The benefits of companion planting strawberries can include improving their flavor, or increasing their resistance to pests, such as slugs. Sometimes the strawberry companion plant will do both. Select the right companion plants and you may also improve pollination and boost the nutrients in the soil. These are all excellent results for permaculture gardening and if you want to create a sustainable garden with less reliance on chemical pesticides and lots of soil maintenance.
'Strawberries, in particular, are prone to a number of pests. Strawberry companion plants will also provide shade in the afternoon light. In return, strawberry plants serve as a mulch, keep weeds at bay and keep the soil cool and moist,' adds Claire Ransom.
Strawberry companion plants include everything from vegetables to other fruits, and herbs, and can be used whether you are growing strawberries under cover in a greenhouse, as vegetable garden container ideas, or in a small vegetable garden. These are the best to grow side-by-side.
These are the best to grow side-by-side.
Strawberry companion plants – herbs
(Image credit: Future / Tim Young)
There are many herbs that can be grown as herb garden ideas that make useful strawberry companion plants.
If you grow thyme, chives, mint and borage, they are all excellent companion plants for strawberries.
Borage, in particular, is a long-established and much valued strawberry companion plant. The deep blue flowers of this plant for pollinators attract pollinating insects, which then draw in insects that prey upon them, such as predatory wasps. The predators also prey on insects that can damage the strawberry plants.
Borage adds trace minerals to the soil, which help strawberry growth. Some people also claim that borage improves the strawberries' flavor.
Vegetable companion plants for strawberries
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Whether you are growing strawberries in raised garden beds, in containers or in the vegetable patch, there are many crops that make good strawberry companion plants to grow alongside them.
Try growing asparagus, beans, peas, spinach, lettuce, garlic, horseradish, and rhubarb – yes, strictly speaking, rhubarb is a vegetable. All work well planted alongside strawberries. Strawberries are good for onion companion planting.
Legumes – beans and peas – grown next to strawberries will improve the soil, fixing nitrogen and thus feeding the strawberry plants.
Asparagus and strawberries are compatible neighbors as their roots spread in different ways, so they don't compete for space or nutrients.
Flower companion plants for strawberries
(Image credit: Unsplash)
Growing ornamentals among your edible crops not only looks lovely, adding color and scent, but also brings a number of benefits.
The humble marigold (tagetes) is valued by gardeners just as much for its pest repellant properties as for its cheery blooms. Strawberries and marigolds are a classic combination in many mixed garden planting schemes.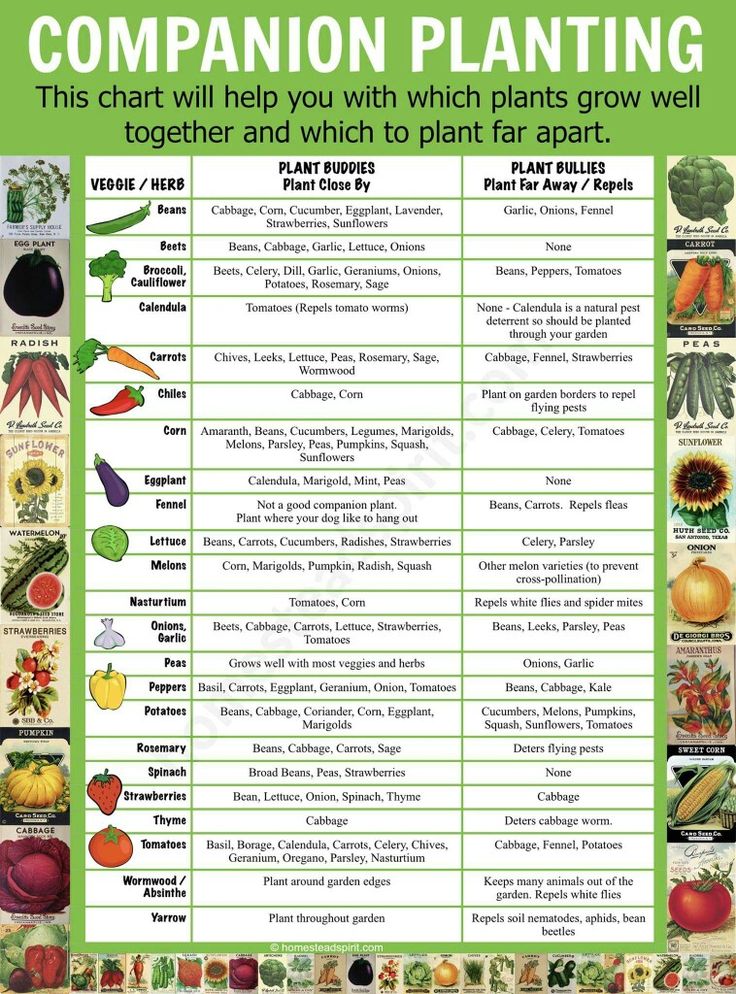
You'll often find marigolds used as cucumber companion plants, for tomato companion planting, with beans, lettuce and many other popular vegetables. Many gardeners swear by the marigold's ability to keep pests, bugs, and even invasive weeds at bay.
'Although there is limited scientific research surrounding companion gardening, many gardeners find it extremely beneficial,' says Sue Sanderson of Thompson & Morgan .
Indeed, Sarah Raven has written about the success she's had in her own garden with Tagetes minuta, the Mexican marigold, which she says 'is effective against perennial weeds such as bindweed, couch grass and ground elder as it gives out a chemical from its roots that is toxic to them. It sounds far-fetched,' she continues, 'but I can vouch for its efficacy: it cleared ground elder from my rose garden and yet had no effect on my roses. They’ve gone from strength to strength, yet the ground beneath them is now clean.'
Marigolds are just one of the flowers useful as strawberry companion plants, with others including borage, lupins and white clover.
(Image credit: Faba Photography/GettyImages)
What should not be planted with strawberries
There a various crops you should not plant with strawberries. These include: cauliflower, cabbages, broccoli, fennel, potatoes, melons, peppers and mint.
Plants from the brassica family – cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli – would compete with the strawberry plants for nutrients.
Plants from the Nightshade family, including tomatoes, potatoes and eggplant, or aubergine, may spread fungal disease to strawberry plants.
What is good to plant with strawberries?
Onions are a great companion plant for strawberries. Their smell creates an unappealing deterrent to many garden pests, especially slugs and snails.
Bob Lawson from Kellogg Garden advises: 'These pungent vegetables make great strawberry companion plants. Their unappealing odor is a natural deterrent of many garden pests that feed on the leaves and fruits of the strawberry plant.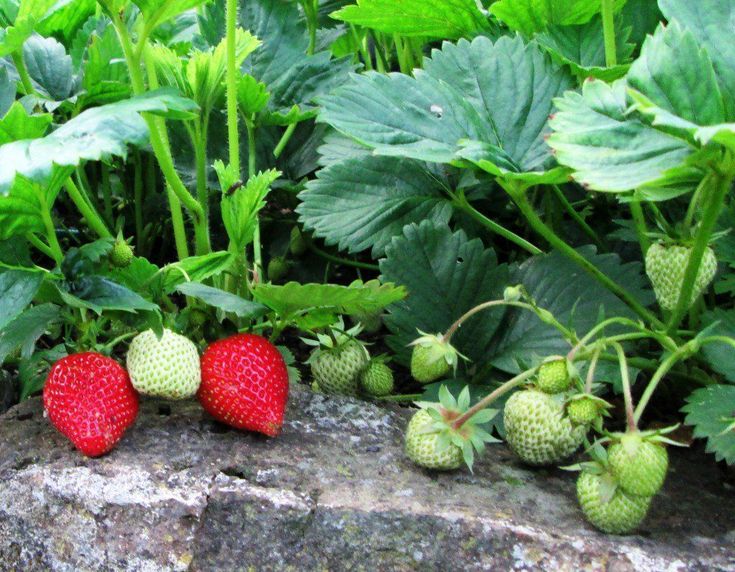 '
'
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Do tomatoes and strawberries grow well together?
Tomatoes are not the most productive companion plant you can choose for your strawberries.
According to Lawson, strawberry plants are prone to a disease called verticillum. 'Plants like tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes, melons, peppers, roses and okra may actually contribute to this deadly disease in strawberry plants. It is essential to note that strawberries should not even be planted in beds that have recently housed those plants on this list,' he explains.
Does basil grow well with strawberries?
It is a great choice to grow basil alongside strawberries. The plants work really well side by side. They also taste great together in a salad and are definitely something worth trying.
Karen is the houses editor for homesandgardens.com and homes editor for the brand’s sister titles, Period Living and Country Homes & Interiors, and an experienced writer on interiors and gardens. She loves visiting historic houses for Period Living and writing about rural properties for Country Homes & Interiors, and working with photographers to capture all shapes and sizes of properties. Karen began her career as a sub editor at Hi-Fi News and Record Review magazine. Her move to women’s magazines came soon after, in the shape of Living magazine, which covered cookery, fashion, beauty, homes and gardening. From Living Karen moved to Ideal Home magazine, where as deputy chief sub, then chief sub, she started to really take an interest in properties, architecture, interior design and gardening.
She loves visiting historic houses for Period Living and writing about rural properties for Country Homes & Interiors, and working with photographers to capture all shapes and sizes of properties. Karen began her career as a sub editor at Hi-Fi News and Record Review magazine. Her move to women’s magazines came soon after, in the shape of Living magazine, which covered cookery, fashion, beauty, homes and gardening. From Living Karen moved to Ideal Home magazine, where as deputy chief sub, then chief sub, she started to really take an interest in properties, architecture, interior design and gardening.
What to plant next to strawberries? These plants will stimulate its growth
- Details
- Anatoly Vorontsov
Proper planting of strawberries will allow us to enjoy abundant harvests of sweet fruits. When planning this task, it is necessary to take into account not only the soil and the requirements for caring for fruit plants, but also the appropriate neighborhood.
When planning this task, it is necessary to take into account not only the soil and the requirements for caring for fruit plants, but also the appropriate neighborhood.
What can be planted next to strawberries and why is it so important? It turns out that some plants (including popular vegetables and herbs) can significantly reduce the number of chemical sprays, and at the same time effectively protect the crop from attack by pests and diseases.
Importance of other plants in strawberry cultivation?
For many of us, juicy strawberries are a delicious symbol of the beginning of summer. They taste best straight off the bush, so you need to take care of every step of the growing process yourself.
Proper positioning, watering and fertilizing isn't everything. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that strawberries grow better in the neighborhood with some types of plants, and worse with others. What is it coming from?
They can compete for soil nutrients. In addition, some plants (especially cruciferous plants) secrete substances that inhibit the growth of strawberries. Therefore, we will tell you what to plant next to strawberries so that it grows by leaps and bounds.
In addition, some plants (especially cruciferous plants) secrete substances that inhibit the growth of strawberries. Therefore, we will tell you what to plant next to strawberries so that it grows by leaps and bounds.
Planting strawberries next to vegetables
Growing strawberries with vegetables can bring many benefits. Of course, provided that we choose the right neighborhood for the berries. What vegetables can we safely include in strawberry beds?
- Garlic, onion, leek and green onion : Probably, each of us associates them with a characteristic taste and aroma, as well as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It turns out that they have a positive effect not only on the human body, but also on strawberries! These vegetables release phytoncides, i.e. volatiles. Their presence protects fruit bushes from attack by pests and fungal diseases, especially gray rot.
- Legumes : It is highly recommended to plant beans and peas next to strawberry beds.
 They have the ability to fix nitrogen from the air and supply it to the soil. This results in bountiful strawberry growth and a more bountiful harvest of larger fruits.
They have the ability to fix nitrogen from the air and supply it to the soil. This results in bountiful strawberry growth and a more bountiful harvest of larger fruits. - Leafy greens : lettuce and spinach also pair well with strawberries. They can positively affect the taste of fruits. Thanks to this, we can grow a variety of vegetables on the same plot, which will enrich our menu with essential minerals and vitamins.
What greens to plant next to strawberries?
Among the greens that should be next to strawberries, thyme deserves special attention. It will be useful not only for seasoning dishes, but most of all it will be useful in scaring off pests that could eat strawberries. Some herbs further enrich the taste of strawberries, including:
- coriander ,
- garden savory ,
- cumin ,
- sage ,
- peppermint .

Plants known for their healing properties, chamomile and borage, should be found in flower beds with strawberries. They act as a magnet for the insects that pollinate the flowers and also cause strawberries to be pollinated.
What's not to love about strawberries?
It has already been mentioned that in the infamous group of plants there are cruciferous plants, with which strawberries will not be friends. Especially avoid planting strawberries with cabbage, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and kohlrabi. Cucumbers also negatively affect their growth.
Strawberry bushes will not bear fruit in the company of raspberries and blackberries. The main reason for this is that plants are attacked by the same diseases and pests. If one of them falls ill, all the rest will also be in great danger.
 Recommended climate for indoor/greenhouse cultivation
Recommended climate for indoor/greenhouse cultivation  For growing strawberries in protected ground, planting material is used from mustaches formed in the last vegetative season (the best, i.e., seedlings obtained from biennial plants are considered to be the best, i.e., abundantly fruiting; before the onset of frost, the plants are transferred to a greenhouse or tunnel). Moreover, the better the mustache-rosettes, the better their root system is developed, the more chances for successful cultivation in protected ground. Rosettes are rooted in open ground in July-August, then in October-November they are transplanted into a heated greenhouse.
For growing strawberries in protected ground, planting material is used from mustaches formed in the last vegetative season (the best, i.e., seedlings obtained from biennial plants are considered to be the best, i.e., abundantly fruiting; before the onset of frost, the plants are transferred to a greenhouse or tunnel). Moreover, the better the mustache-rosettes, the better their root system is developed, the more chances for successful cultivation in protected ground. Rosettes are rooted in open ground in July-August, then in October-November they are transplanted into a heated greenhouse. 
 In the greenhouse, artificial pollination of strawberries will have to be carried out. In small greenhouses, this can be done with a soft brush 2-3 times during the day. A few days later, the procedure is repeated. A beneficial effect on strawberries is provided by additional lighting for eight hours a day.
In the greenhouse, artificial pollination of strawberries will have to be carried out. In small greenhouses, this can be done with a soft brush 2-3 times during the day. A few days later, the procedure is repeated. A beneficial effect on strawberries is provided by additional lighting for eight hours a day. 

 Before the onset of frost, the plants are transferred to a greenhouse or tunnel (this usually happens in November).
Before the onset of frost, the plants are transferred to a greenhouse or tunnel (this usually happens in November).  4
4  m, when grown on agromats, plants are fed with complex water-soluble fertilizers at the rate of 150-200g / 100 liters of water. NPK 19/9/27 - during the growing season and 5/11/32 during fruit set + Micro, PH keep 6.0-6.2.
m, when grown on agromats, plants are fed with complex water-soluble fertilizers at the rate of 150-200g / 100 liters of water. NPK 19/9/27 - during the growing season and 5/11/32 during fruit set + Micro, PH keep 6.0-6.2.  They also fill the soil with organic or mineral fertilizers. Seedlings from the mother plantation are planted in a permanent place in early August (planting pattern - 25x30 cm). If there is no rain, the plants need to be watered.
They also fill the soil with organic or mineral fertilizers. Seedlings from the mother plantation are planted in a permanent place in early August (planting pattern - 25x30 cm). If there is no rain, the plants need to be watered.  5
5 










