How much baking soda to raise ph
How to Raise the pH in Your Pool Using Baking Soda
Maintaining your pool can be a costly and challenging undertaking. However, there are things you can do to make the process easier and less expensive. For example, by not squandering your hard-earned cash on commercial alkalinity-increasing products when you can use a common, inexpensive compound to do the job: baking soda.
Common, inexpensive compounds do the job too
In this article, I’ll cover these points:
- Using baking soda to solve common pool problems
- The difference between pH levels and total alkalinity
- Why pH balance is so important
Let’s dive in!
What are Pool pH Levels?
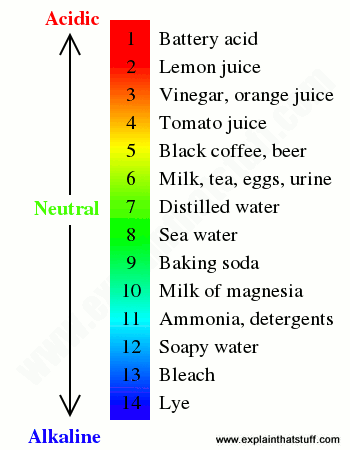
pH, or “potential hydrogen,” is how well a solution attracts hydrogen ions. It can tell us how alkaline or acidic a liquid is. You measure pH on a scale from zero to 14. Zero means the solution is acidic, while 14 indicates the solution is basic or containing more OH – ions than H + ions.
A neutral solution such as pure water falls in the middle of the scale with a pH of seven. A good level for pool water is a pH of 7.5, which means it’s slightly basic. Low pH can be caused by:
- Rainwater
- Debris such as leaves, bugs, and grass clippings
- Human secretions such as body oils, sweat, saliva, and urine
The difference Between pH and alkalinity
Lots of pool owners get hopelessly confused by the difference between alkalinity and pH. As I already discussed, you measure pH using a scale. On the other hand, you measure total alkalinity in parts per million. This means that total alkalinity is an absolute measure of the concentration of all alkaline substances in a solution.
The most common alkaline substances in a pool are bicarbonate, carbonate, and hydroxides. Alkaline substances are important because of how they affect pH. They act as buffers, preventing pH levels from rising or falling. They do this by neutralizing acids. So, in the end, total alkalinity is a measure of how strongly pool water resists changes in pH levels.
So, in the end, total alkalinity is a measure of how strongly pool water resists changes in pH levels.
Why pH Balance is Important
Maintaining the correct pH balance not only keeps your swimming pool sparkling clean but also helps preserve your pool finish’s aesthetic appeal by preventing it from getting stained. pH balance is also essential to ensuring the longevity of your pool and its components.
Pools need to have a pH level of between 7.2 and 7.8. Pool water with pH levels that are low is acidic. This kind of water is corrosive and can lead to pumps and other equipment breaking down. Basically, everything that acidic water touches gets worn away, including accessories, plumbing, and other parts of the pool system.
Unbalanced pH levels can also wear down pool liners and ladders, causing them to become brittle and crack. Improper pH levels can even strip the copper right out of heat exchangers.
The Relation of pH Levels to Chlorine
Everyone knows that chlorine is vital in keeping pool water healthy and safe for swimmers. However, elevated pH levels can decrease chlorine’s effectiveness, leading to unsanitary swimming conditions.
However, elevated pH levels can decrease chlorine’s effectiveness, leading to unsanitary swimming conditions.
On the other hand, adding too much chlorine can lower your pool’s pH balance. This can cause health problems for swimmers, including irritated skin, eyes, and the nasal cavity’s mucous membranes. This is because acidic water strips away the body’s natural oils.
When your pool water’s alkalinity is too low, any chemicals you add can create a condition known as pH bounce. pH bounce is when the water rapidly cycles between acidic or basic pH levels, making the water unsafe for swimmers. pH bounce means you’ll have to keep adding more chlorine to achieve the same sanitizing effect.
How to Raise pH in Pool
Adding baking soda, an ingredient commonly found in most kitchens, to your pool water raises both its pH and alkalinity. Many commercial pool products have baking soda as their primary active ingredient. This means you can save yourself wads of cash by purchasing baking soda instead of an overpriced commercial pool product.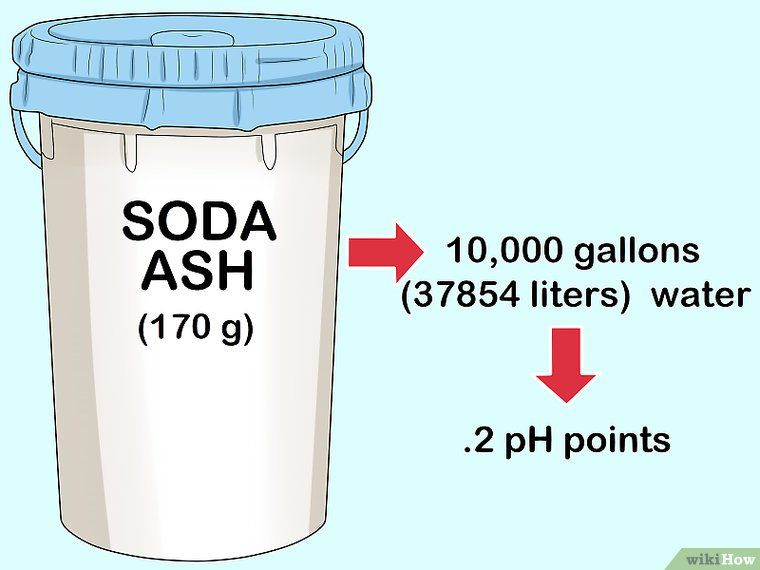 Because you’ll be adding up to 10 pounds of baking soda to your water, it’s more cost-effective to buy your baking soda in bulk.
Because you’ll be adding up to 10 pounds of baking soda to your water, it’s more cost-effective to buy your baking soda in bulk.
However, you’ve got to be careful because it’s easy to go overboard. If you do, you’ll go from a low pH problem to a high pH problem in a matter of no time. Here are the steps you’ll need to follow to keep your pool’s alkalinity at optimal levels by using baking soda:
- Test your pool’s alkalinity every day. The optimal pH level is between 7.2 and 7.8, and the ideal alkalinity range is between 100 and 150 parts per million. If your alkalinity level is lower than 80 ppm, you need to raise it.
- Determine how much baking soda to add. 1.5 pounds of baking soda per 10,000 gallons of water raises alkalinity by approximately 10 ppm. Start by adding only one-half of the recommended amount. Retest to find out if you need to add more.
- Spread the baking soda across the entirety of your pool’s surface. Avoid dumping it all in one spot. It’s not advisable to do this on a windy day because the powder will get into the air.

- Wait at least six hours for the powder to dissolve. Turning on your pool’s circulation system will help it disperse.
- 24 hours after adding the sodium bicarbonate, retest your pool’s pH and total alkalinity levels. If the pH is under 7.2 and the alkalinity is below 110 ppm, repeat these steps.
Common Pool Problems
AlgaeIf your pool water is dull green, pool surfaces are slippery, and walls and the pool bottom are slimy, you have a severe algae problem on your hands. This means you’ll need to use an algaecide to kill all the aquatic scum. After applying algaecide, test your pH and alkalinity. Add a little sodium bicarbonate to raise alkalinity levels to at least 100 ppm and pH to between 7.2 and 7.8.
CorrosionSay your ladder is corroded, or you see pits on your pool tiles or liners. In that case, the alkalinity level of your water is abnormally low. Add sodium bicarbonate to get the levels back up to where they should be. You’ll probably need eight pounds or more if the levels are low enough to cause corrosion.
You’ll probably need eight pounds or more if the levels are low enough to cause corrosion.
Cloudy pool water can be caused by a couple of things. Start by checking your pool’s filtration system.
If that isn’t the culprit, test the hardness level of your household water supply. If it’s hard, immediately stop using any pool products that contain calcium.
The easiest remedy for cloudy pool water is by super chlorinating it. This means temporarily increasing the chlorine levels in your pool to boost its sanitizing power. Test the water after adding the chlorine, and slowly add baking sodium to get the pH level to between 7.2 and 7.8.
Final Thoughts
So, there you have it—all the ways you can use baking soda to save money on pool maintenance. It’s hard to believe that such an inexpensive and commonplace compound can make such a big difference in both the way your pool looks and how clean it is. If you’d like more assistance in the battle to keep your pool sparkling, clean, check out these skimmers. What part of this article did you find most helpful? Let me know in the comments!
What part of this article did you find most helpful? Let me know in the comments!
Author
Our pool maintenance expert, Luke Reed, earned his BS in Civil Engineering from Georgia Tech in 1998. Since then, he’s worked in a variety of industries, including design and construction of luxury swimming pools.
Maintain Your Pool with Baking Soda
Baking Soda to Raise pH and Alkalinity in Pools
Most people know that chlorine is an important chemical in keeping pool water safe for swimming. But adding too much chlorine can lower your pool’s pH as well as its total alkalinity. When alkalinity falls, it is more difficult to maintain a stable pH. Plus, a lower pH and alkalinity of your pool water creates several negative effects, from itchy skin and stinging eyes for swimmers to corrosion of your pool ladders, liner, or other components.
When your water’s alkalinity is too low, any chemicals you add will exponentially affect the pH, creating a condition known as pH bounce. You’ll also need to add more chlorine to get the same sanitizing effect, and your swimmers will complain. Overall, pool water with inadequate alkalinity levels can be frustrating and costly.
You’ll also need to add more chlorine to get the same sanitizing effect, and your swimmers will complain. Overall, pool water with inadequate alkalinity levels can be frustrating and costly.
Fortunately, there is a simple and cost-effective way to maintain your pool’s alkalinity and pH. You might use it in your cookie recipes or to freshen your fridge. This handy tool for pools is none other than Arm & Hammer baking soda, although you’ll need pounds of it rather than a pinch.
What Does Baking Soda Do For a Pool?
Baking soda, also known as sodium bicarbonate is naturally alkaline, with a pH of 8. When you add baking soda to your pool water, you will raise both the pH and the alkalinity, improving stability and clarity. Many commercial pool products for raising alkalinity utilize baking soda as their main active ingredient. You can maintain your pool for a fraction of the cost by going straight to the source and using pure baking soda in your pool.
Using Baking Soda to Increase Alkalinity
Follow these steps to test and raise your pool’s alkalinity and pH with baking soda.
- Test your pool’s alkalinity daily. Ideally, your pH is between 7.2 and 7.8 and the alkalinity is between 110 and 150 ppm (parts per million). If your alkalinity level is lower, and especially if less than 80 ppm, then you need to raise the pool water alkalinity.
- Purchase baking soda in bulk (available in pouches up to 15 lbs.). You will be adding anywhere from 1.5 lbs. to as much as 8-10 lbs. of baking soda to your pool, depending on how low your alkalinity is.
- Determine amount to add. You’ll need to figure out how much baking soda to add to your pool. Pool chemical measurements are based on 10,000 gallons of water. If your pool is larger or smaller, you’ll need to adjust your math. A rule of thumb is 1.5 lbs. of baking soda per 10,000 gallons of water will raise alkalinity by about 10 ppm.
 If your pool’s pH tested below 7.2, add 3-4 pounds of baking soda. If you’re new to adding pool chemicals, start by adding only one-half or three-fourths of the recommended amount. After retesting, you can always add more if the level is still low. Otherwise, you could swing too far in the delicate pH balance and need to add an acid.
If your pool’s pH tested below 7.2, add 3-4 pounds of baking soda. If you’re new to adding pool chemicals, start by adding only one-half or three-fourths of the recommended amount. After retesting, you can always add more if the level is still low. Otherwise, you could swing too far in the delicate pH balance and need to add an acid. - Add baking soda to the pool. Sodium bicarbonate is packaged in powder form and can be sprinkled directly into your pool water. Spread in wide arcs across the pool’s surface to avoid dumping it all in one spot. Beware of adding baking soda on a windy day, as the powder can go airborne.
- Wait at least six hours. Let the baking soda dissolve into the water. Turn on your pool’s circulation system to help it disperse.
- Retest and repeat if needed. Between 6 and 24 hours after you added the baking soda, retest your pool’s pH and total alkalinity. If the pH is below 7.2 and the alkalinity below 110 ppm, then repeat these steps.

Correcting Common Pool Problems with Baking Soda
Baking Soda and Green, Blue, or Yellow Algae
If you have algae in your pool, you’ll notice dull green water, slimy walls and pool bottom, and a slippery pool surface. You’ll need to use an algaecide to kill the algae and superchlorinate your pool to clear the water. After this treatment, test your pH and alkalinity and add baking soda to raise alkalinity to at least 100 ppm and pH to between 7.2 and 7.8.
Baking Soda and Pool Corrosion
If you’re noticing corrosion on your pipes or ladders, or pits on your pool liner or tiles, you have very low water alkalinity. Test and add Arm & Hammer baking soda according to the instructions. You will typically need at least 8 lbs. if your levels are low enough to cause corrosion.
Scaling Buildup on Pool Surfaces
Too much calcium and pH as well as high alkalinity levels are culprits for pool scaling. So, too, is hard water. Stop using calcium-based disinfectants and keep your pool’s alkalinity between 80 and 110 ppm. Test your levels and carefully add a pool acid, such as muriatic acid to lower pH to below 7.8. If you go too far, add baking soda sparingly to reach the appropriate levels.
Stop using calcium-based disinfectants and keep your pool’s alkalinity between 80 and 110 ppm. Test your levels and carefully add a pool acid, such as muriatic acid to lower pH to below 7.8. If you go too far, add baking soda sparingly to reach the appropriate levels.
Cloudy Pool Water
If your pool water is cloudy or murky, there could be a number of causes. Check your pool’s filtration system; often the problem lies there. Also test your water’s hardness. If your water is naturally hard, or contains a lot of minerals, you will want to stop using any products containing additional calcium and keep your alkalinity levels lower than 110 ppm (but higher than 80 ppm). To cure cloudy pool water, superchlorination is usually the easiest fix. Be sure to test your pH levels after the hyper-chlorination treatment, and slowly add baking soda to your pool water, if needed, to get to between 7.2 and 7.8. Higher pH levels can lead to cloudiness.
For a more complete guide to pool care and rectifying common issues, see our comprehensive Arm & Hammer Pool Care Guide.
How to Clear a Cloudy Pool with Baking Soda
For a simple method to keep your pool crystal clear, we developed Arm & Hammer Clear Balance™ Pool Maintenance tablets. Our scientists have done the math for you, and 1 to 4 tablets per week, depending on the size of your pool, will keep your water clear all summer. Follow the package directions and dispense through your skimmer or floater. Tablets dissolve in about 15 minutes and will help keep your pool’s pH and alkalinity at proper levels. It’s super easy to use and Clear Balance™ can help prevent pH rebound and other pool problems all season.
Baking Soda for Pools: An Easy Way to Raise pH and Alkalinity
Don’t waste money on commercial alkaline-increasing pool products when you can use baking soda to raise your pool’s pH and alkalinity instead. Follow the procedure above and the guidelines in our Pool Care Guide to correct common pool issues. And use Arm & Hammer Clear Balance™ Pool Maintenance tablets to keep a clear, clean, safe pool without a lot of hassle.
Resources
https://www.swimuniversity.com/household-products-clean-pool/
https://www.hunker.com/13415244/how-to-lower-the-ph-in-a-swimming-pool-with-baking-soda
https://www.armandhammer.com/-/media/aah/feature/articles/baking-soda/baking-soda-articles/pool-owners-guide.pdf
https://www.armandhammer.com/articles/diy-pool-maintenance-tips
https://www.armandhammer.com/baking-soda/pool-maintenance/pool-maintenance/clear-balance-pool-maintenance-tablets
http://poolforthought.com/raising-pool-alkalinity/
My Vegan Way | Cleansing
Acid-base balance or pH regulates respiration, circulation, digestion, excretion, immunity, hormone production and more. Almost all biological processes proceed correctly only when a certain level of pH is maintained. The acid-base balance is constantly maintained in the body, in all its approximately one hundred trillion cells. In each of these cells, carbon dioxide is constantly produced during energy production.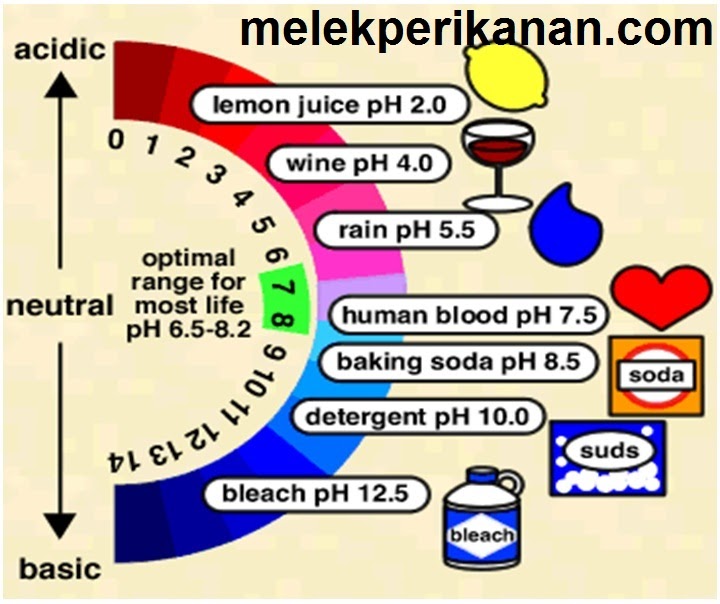 At the same time, other acids appear, which are formed during the processing of food.
At the same time, other acids appear, which are formed during the processing of food.
There is a pH scale that can be used to determine how acidic or basic any solution, liquid, including blood, saliva and urine, is. The measuring scale of the pH level goes from 0 to 14. Moreover, the sequence of values here is logarithmic. This means, for example, that pH 6 indicates an acid strength ten times greater than pH 7, and pH 5 is already a hundred times greater than pH 7. Accordingly, pH 4 is already a thousand times greater than pH 7.
Blood has a constant pH of 7.35 to 7.47, i.e. it is slightly alkaline.
Urine pH can range from pH 4 in patients to pH 8 in infants. The urine pH of infants is in part even above pH 8. This pH is an indicator of the highest degree of health.
The pH of the human body, its cells and its urine is getting smaller and smaller from year to year, further and further away from the value at the beginning of life. An infant 9 months before birth is in the mother's alkaline amniotic fluid, where the pH is greater than 8.
Acids and alkalis are in the body in a very close relationship, like day and night. They should be in balance, and the advantage should be on the alkaline side. Human vitality and health lie in alkaline compounds - minerals and trace elements. The normal pH level of the blood can only be slightly disturbed, otherwise a critical life-threatening condition may occur.
To prevent large fluctuations in this pH, the human metabolism has various buffer systems. One of them is a hemoglobin buffer. The kidney is the most important organ of the buffer system, removing excess acid. The lung regulates the acid-base balance by exhaling carbon dioxide. The liver is also an important organ for pH regulation. Its full biochemical strength also lies in the alkaline region.
What does the body do if, despite the smooth functioning of all these organs, acids remain in the metabolic process?
These acids are neutralized according to all the laws of chemistry: alkali metals such as sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium replace hydrogen in acids, entering into compounds with an acidic residue, resulting in compounds that are called salts. Salt is chemically neutral, no more reaction takes place with it. Such salts, that is, neutralized acids, are supposed to be excreted by the kidneys, but due to the general peroxidation of the blood, they are not completely excreted, and then the body is forced to deposit these salts inside itself (primarily in the connective tissue), these forcedly deposited salts are colloquially and are called slag.
Salt is chemically neutral, no more reaction takes place with it. Such salts, that is, neutralized acids, are supposed to be excreted by the kidneys, but due to the general peroxidation of the blood, they are not completely excreted, and then the body is forced to deposit these salts inside itself (primarily in the connective tissue), these forcedly deposited salts are colloquially and are called slag.
The process of salt deposition is similar to the behavior of sugar in a cup of water, coffee or tea. One spoon dissolves without residue. The second and third remain mostly undissolved and settle at the bottom of the cup. The fourth will not be able to dissolve at all. And, remember, if the cup stands like this for a day or two, then the sugar at the bottom will cake, compact in such a way that it will become a dense mass that will be very difficult to wash off. This is exactly what happens in our body. The more acidic the blood becomes, the less salts can dissolve. Accordingly, the more they are deposited throughout the body and the more difficult it is to remove them.
Unfortunately, in our time, the deposition of toxins in the connective tissue has moved from an intermediate position to a final one, and slagging of the body begins, in other words, the process of poisoning, which underlies aging and all age-related diseases. Chemically, the aging process of our body is nothing more than the removal of minerals from tissues and organs in order to neutralize acids.
Especially disruption of the acid-base balance affects the work of the heart. This is a very strong muscle, which in the process of constant work consumes a large amount of energy. Thus, a good metabolism is essential. In this case, the resulting carbon dioxide and lactic acid must be very quickly removed from the area of \u200b\u200bthe heart muscle. If the vehicle (blood), as a result of its own acidification, has exhausted its ability to collect acids, then this can lead to stagnation of acids in the heart muscle. The worst consequence of this is a heart attack.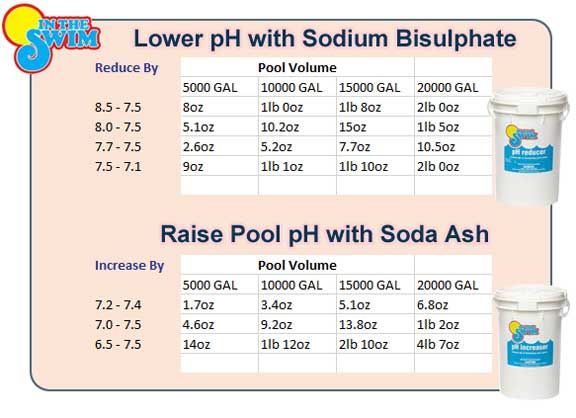 In the working muscles of the arms and legs, we feel muscle pain during overload. The same thing happens in the heart muscle. There are heart pains, weak pulse, palpitations and other problems.
In the working muscles of the arms and legs, we feel muscle pain during overload. The same thing happens in the heart muscle. There are heart pains, weak pulse, palpitations and other problems.
The basic functions of human metabolism must be in balance. These are: water balance, electrolyte balance and acid-base balance. Of these, it is the acid-base balance that is key. Restoration of impaired metabolism is impossible without the correction of basic functions. And in the first place here is, of course, an understanding of the meaning of water. Water is the most important solvent of organic substances, which only in dissolved form enter into the necessary chemical exchange reactions with each other, and the quality of water primarily depends on the pH level.
On a pH scale of 0 to 14, an average value of 7 indicates a neutral level, the blood pH of a healthy person lies in the slightly alkaline zone. When the blood pH is below 7.35, in other words, with increased acidity, acidosis occurs. With today's lifestyle and diet, shifts towards acidosis occur very often and lead in most cases to serious disorders. Therefore, alkalization of the body is necessary to maintain health.
With today's lifestyle and diet, shifts towards acidosis occur very often and lead in most cases to serious disorders. Therefore, alkalization of the body is necessary to maintain health.
Causes of acidosis are animal products, tobacco, alcoholic beverages, poisons in food, water and air, drugs, pesticides, stress. Often there is a self-poisoning of people with mental poisons in stressful situations, the body is strongly acidified by feelings of fear, anxiety, irritation, discontent, envy, anger, hatred. The loss of psychic energy always leads to the loss of alkalis.
In humans, the pH of the blood should be within the normal range of 7.35-7.47. If the pH is less than 6.8 (very acidic blood, severe acidosis), then death of the organism occurs. Nowadays, most people suffer from hyperacidity of the body (acidosis), having a blood pH below 7.35. At pH less than 7.25 (severe acidosis), alkalizing therapy should be prescribed: taking soda dissolved in water.
The pH of saliva can be used as a diagnosis of the general condition of the body:
4.5 - 5.5 Most likely you are sick
6.0 - 6.5 The body is weak
7.0 - 7.5 You are healthy
to overcome acidosis, you must, firstly, eat right, do not use (or limit) foods that strongly acidify the body, do not smoke, do not drink alcohol, think positively, control emotions. Secondly, ordinary baking soda dissolved in water helps to alkalize the body and remove toxins from it.
By using baking soda, we can save on powerful drugs that often have side effects. Medications are by no means a substitute for properly selected nutrition, as they acidify the body even more.
Baking soda is a white powder that is chemically alkaline. It has weak antiseptic properties, can reduce water hardness. The role of soda is to neutralize acids, increase the body's alkaline reserves, and maintain a normal acid-base balance.
General recommendations
It is necessary to take soda on an empty stomach, 20-30 minutes BEFORE a meal, not immediately after a meal - there may be a reverse effect. Soda and food should not touch in the stomach.
Soda and food should not touch in the stomach.
Start with small doses - 1/5 teaspoon, gradually increase the dose, bringing to 1/2 teaspoon.
Soda should be diluted in one glass of water: first pour half a glass of boiling water, dissolve soda, then add cold water, you will get warm alkaline water (closer to hot). Take 1-3 times a day.
You can analyze the acidity and determine its pH value using a special test strip. It costs a penny and is sold in pharmacies. The test strip is wetted with urine or saliva. Comparing the color of the test strip with a color standard allows you to determine the pH level.
Urine pH. A few centuries ago, human urine had an alkaline reaction, its pH was approximately 7.5-9.0. In modern people, this indicator is in the slightly acidic range: from 6.0-6.4 in the morning to 6.5-7.0 in the evening. On average, it is 6.4-6.5. Urine pH is best measured on an empty stomach, 2 hours before and after meals 2 times a day several times a week.
Soda, neutralizing excess acids, increases the alkaline reserves of the body, makes urine alkaline, which facilitates the work of the kidneys (saves energy), saves glutamine amino acid, and prevents the deposition of kidney stones. Excess soda is easily excreted by the kidneys, giving an alkaline urine reaction. But the body should be accustomed to soda gradually, since alkalization of the body with soda leads to the dissolution of stones and the removal of a large amount of poisons (slags) accumulated by the body over many years of acidic life. In an alkaline environment with activated water, the biochemical activity of amine vitamins increases many times: B1 (thiamine, cocarboxylase), B4 (choline), B5 or PP (nicotinomide), B6 (pyridoxal), B12 (cobimamide). In the acidic environment of a poisoned organism, even the best plant vitamins cannot bring out all their qualities.
Saliva pH. The optimal time to measure the pH of saliva is from 10 am to 12 noon. According to the rules for using the test, it is recommended not to eat or drink anything for half an hour before testing. Before using litmus paper, swallow it several times, then moisten it with saliva. Not later than in 2-3 seconds, compare the test with the proposed scale. Repeat the test several times during the day.
Before using litmus paper, swallow it several times, then moisten it with saliva. Not later than in 2-3 seconds, compare the test with the proposed scale. Repeat the test several times during the day.
In an acidic organism, saliva is acidic, pH = 5.7-6.7, which leads to a slow destruction of tooth enamel. In an alkaline organism, saliva is alkaline, pH = 7.2-7.9and the teeth are not destroyed. To treat caries, you need to take soda twice a day so that saliva becomes alkaline.
So, if the pH deviates to the acid side, it is necessary to alkalize the body: drink soda, increase the content of alkaline foods in the diet and do more aerobic exercise, for example, 30-40 minute walks at a fast pace 4-5 times a week are good.
Various applications of soda
1. Prevention and treatment of cancer.
2. Treatment of all types of poisoning: drug addiction, substance abuse, alcoholism, smoking cessation.
For quitting smoking: rinsing the mouth with a thick solution of soda or smearing the oral cavity with soda with saliva: soda is placed on the tongue, dissolves in saliva and causes an aversion to tobacco when smoking. Doses are small so as not to disrupt digestion.
Doses are small so as not to disrupt digestion.
3. Removal of harmful substances from the body: lead, cadmium, mercury, thallium, barium, bismuth and other heavy metals, radioactive isotopes and prevention of radioactive contamination of the body. Soda is used for poisoning with methanol, ethyl alcohol, formaldehyde, karbofos, chlorophos, white phosphorus, phosphine, fluorine, iodine, mercury and lead. A solution of soda, caustic soda and ammonia is used to destroy (degas) chemical warfare agents.
4. Leaching, dissolution of all harmful deposits in the joints, in the spine; stones in the liver and kidneys, that is, the treatment of radiculitis, osteochondrosis, polyarthritis, gout, rheumatism, urolithiasis, cholelithiasis; dissolution of stones in the liver, gallbladder, intestines and kidneys. A healthy body produces highly alkaline digestive juices for digestion. Digestion in the duodenum occurs in an alkaline environment under the action of juices: pancreatic juice, bile, juice of the Bruttner gland and juice of the mucous membrane of the duodenum. All juices have a high alkalinity. Pancreatic juice has pH = 7.8-9,0. Enzymes of pancreatic juice act only in an alkaline environment. Bile normally has an alkaline reaction pH = 7.50-8.50. The secret of the large intestine has a strongly alkaline environment, pH=8.9-9.0. With severe acidosis, bile becomes acidic, pH = 6.6-6.9 instead of the normal pH = 7.5-8.5. This impairs digestion, which leads to poisoning of the body with products of poor digestion, the formation of stones in the liver, gall bladder, intestines and kidneys. Therefore, soda is necessary for restoring the processes of digestion.
All juices have a high alkalinity. Pancreatic juice has pH = 7.8-9,0. Enzymes of pancreatic juice act only in an alkaline environment. Bile normally has an alkaline reaction pH = 7.50-8.50. The secret of the large intestine has a strongly alkaline environment, pH=8.9-9.0. With severe acidosis, bile becomes acidic, pH = 6.6-6.9 instead of the normal pH = 7.5-8.5. This impairs digestion, which leads to poisoning of the body with products of poor digestion, the formation of stones in the liver, gall bladder, intestines and kidneys. Therefore, soda is necessary for restoring the processes of digestion.
5. Purification of the body to increase attention, focus, balance and performance in an active learning process.
6. Purification of the body from poisonous substances that came with food and developed with negative emotions: irritation, anger, hatred, envy, resentment, doubt, discontent and other negative feelings and thoughts of a person.
Soda, destroying acidosis, increases the body's alkaline reserves, shifts the acid-base balance to the alkaline side. In an alkaline organism, water is activated, that is, it dissociates into H+ and OH- ions due to amine alkalis, amino acids, proteins, enzymes, RNA and DNA nucleotides. All biochemical processes improve in activated water: protein synthesis is accelerated, poisons are neutralized faster, enzymes and amino vitamins work more actively.
In an alkaline organism, water is activated, that is, it dissociates into H+ and OH- ions due to amine alkalis, amino acids, proteins, enzymes, RNA and DNA nucleotides. All biochemical processes improve in activated water: protein synthesis is accelerated, poisons are neutralized faster, enzymes and amino vitamins work more actively.
7. Antiparasitic effect. In an acidic environment, opistarchosis worms, pinworms, roundworms, tapeworms and other interesting life forms live quietly. In an alkaline environment, they die. To combat roundworms and pinworms, piperazine amine alkali is used, supplementing it with soda enemas.
8. Baking soda helps with headaches and migraines.
9. Treatment of thrush caused by Candida yeast. It is recommended to douche 2 times a day for 2 weeks and drink alkaline water.
10. Used for rinsing and washing with tonsillitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, throat and eyes: 1-2% solution of baking soda. It relieves the manifestations of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
It relieves the manifestations of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
11. Cosmetic care: for peeling, skin cleansing, hair washing, brushing teeth, as an anti-cellulite agent. You will find more information about this on the Natural Hygiene Products page.
ALKALIZING AND ACIDIFYING FOOD
With the advent of agrarian civilization, man began to eat a lot of refined grains, dairy products and meat from domesticated animals. Especially dramatic shifts in nutrition occurred in the late 20th century, when the diet was flooded with industrially processed foods. These dietary changes are risk factors in the pathogenesis of civilization diseases, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, and type 2 diabetes. The diet of a modern person is rich in saturated fats, simple sugars, table salt, but poor in fiber, magnesium and potassium. It is dominated by refined and processed foods, sugar, flour products, and many semi-finished products. What is the food of modern man? These are dumplings, kebabs, steaks, pizza, mashed potatoes, chips, glazed curds, newly appeared miracle dairy products, trans-fat confectionery, white flour flour products, sweet soft drinks, tea, coffee, chocolate.
What is the food of modern man? These are dumplings, kebabs, steaks, pizza, mashed potatoes, chips, glazed curds, newly appeared miracle dairy products, trans-fat confectionery, white flour flour products, sweet soft drinks, tea, coffee, chocolate.
Watch your diet consciously.
To maintain the acid-base balance, 2/3 of the diet should be foods that alkalize the body.
I wish you good health!
How to raise Ph in an aquarium. Or downgrade?
6 Ways to Raise Aquarium pH
You can use any of the following methods to raise and maintain pH.
Add bicarbonate
The addition of bicarbonate to the aquarium shows a significant increase in pH.
You can add the following to raise the pH level in your aquarium:
- Aquarium buffers : Aquarium buffers are available from aquarium and pet stores. They are rich in bicarbonates and sodium carbonate.
 Aquarium buffers raise the pH level much more effectively than baking soda - on this resource you can find Photos from around the world on the Gaz-Kvas.Com website.
Aquarium buffers raise the pH level much more effectively than baking soda - on this resource you can find Photos from around the world on the Gaz-Kvas.Com website. - Baking soda : Baking soda contains bicarbonates and you may already have it in your home. Generally, the recommended ratio is 1 teaspoon of baking soda per 5 gallons. To raise the pH consistently, dissolve the baking soda in a small amount of water rather than adding it directly to the aquarium water. Adding baking soda is not a one-time solution, you will need to constantly adjust the pH level in the aquarium.
Be aware of how you add bicarbonates.
Adding too much baking soda or buffers can cause a sudden pH spike that can kill your fish.
It's best to take your time so as not to shock or stress your fish with a sudden change in environment.
Add rocks and substrates
You can raise the pH in your aquarium by adding some rocks and substrates - How to choose the right sink faucet
Some of the options:
- Limestone
- Shredded corals
- Texas holey rock as substrate
These stones are readily available from pet stores. Make sure you remove the fish from the tank before adding any rocks or substrate to prevent harm to their gills.
Make sure you remove the fish from the tank before adding any rocks or substrate to prevent harm to their gills.
If you don't want these stones displayed in your aquarium, you can put them in a small bag and add it to the filter.
Again, be aware of the sudden rise in pH and make sure you don't overdo it.
Add shells
Sea shells are naturally high in carbonates, which play an important role in raising the pH of the water.
You can collect shells from the beach or buy them from the shop. Be sure to rinse them before adding them to the aquarium.
Add two shells to every gallon of water. It may take several days for the pH to rise as the shells slowly dissolve.
Also avoid colored shells as they can be harmful to your fish.
Change the water regularly
A very easy way to prevent a drop in pH in an aquarium is to change the water regularly.
Consider changing it at short intervals instead of one big shift so as not to shock the fish with constantly changing pH.
Regular vacuuming of food and waste particles is also essential to keep the pH from dropping over time.
Increase the aeration in the aquarium
Increasing the aeration in the aquarium is of great importance. It increases the oxygen content, which leads to a decrease in carbon dioxide.
The less carbon dioxide, the higher the pH.
Therefore, aeration is a great way to maintain a higher pH.
Remove pH lowering items
Many items will lower pH if you are not paying attention.
For example, a piece of driftwood can have a significant impact on the pH of your aquarium.
Most people use driftwood for ornamental purposes, but they contain tannic acid, which lowers the pH of the water.
Removing objects that lower the pH in the aquarium will help you maintain the pH level.
How to check the pH level in an aquarium?
To determine if your aquarium needs a pH increase, you first need to measure the correct pH.
pH indicates the amount of hydrogen ions in water. You can dilute the water to lower its pH.
Similarly, the addition of bicarbonates, hydroxides and other compounds increases the pH.
pH can be calculated using aquarium test kits. These pH test kits are available at local pet stores and online (you can buy this one).
Different test cases use different testing methods. Some test kits change the color of water samples to represent a specific characteristic.
While others can be immersed directly in the aquarium. The color on these strips is matched against the supplied pH color chart.
Digital testers are another pH testing device that gives fast readings. They are easy to use and calibrate. Digital testers are readily available online.
You should check the pH of your aquarium daily, weekly or every other week, depending on its alkalinity.
It is important to remember that test kits do not always give accurate readings.
Make sure you calibrate your test kit before using it.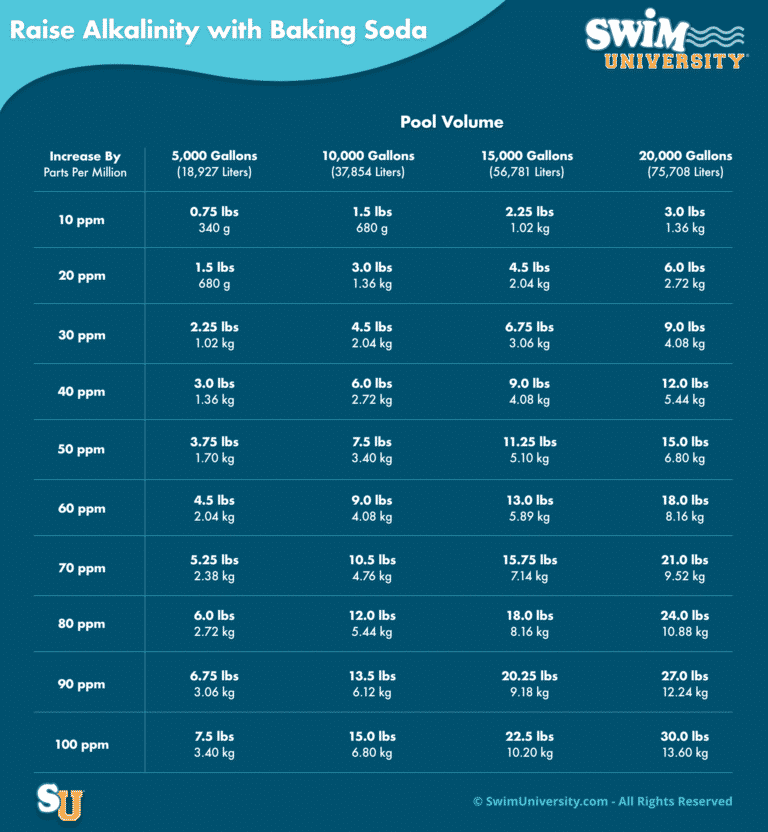 If it shows an unusually high or low pH, you should double check it with a new kit, just to be on the safe side.
If it shows an unusually high or low pH, you should double check it with a new kit, just to be on the safe side.
Which pH level is right for your aquarium?
The appropriate pH level of the aquarium varies and it depends on the type of fish you have. There is no one solution for everyone. Freshwater fish require a different environment than marine fish.
If you are not sure which environment your fish is in, you should check with the pet shop where you bought it.
You can also continue to maintain the same pH as the previous owner, as the fish are already adjusted to it.
There is also a lot of information on the Internet about each type of fish. Several resources are available on social media groups, communities, and local libraries.
See also: How do fish react to low pH in an aquarium?
How to lower the pH level in an aquarium?
Just as low pH is bad for your fish, extremely high pH can also be deadly.
If your aquarium shows a high pH, you can lower it by adding the following things:
- Peat Moss : Adding peat moss to an aquarium can effectively lower the pH level.
 You can add it as a substrate or put it in a filter.
You can add it as a substrate or put it in a filter. - Carbon Dioxide : As we mentioned earlier, a high concentration of carbon dioxide is the main cause of low pH. Thus, by adding or increasing the carbon dioxide content, you will be able to lower the pH.
- Driftwood : The tannins in driftwood lower the pH level in the aquarium.
Make sure you keep checking the pH to make sure it stays within limits.
How does pH affect the water quality in an aquarium?
Water pH affects the water quality and chemistry in your aquarium in several ways.
Maintaining a healthy pH for your fish should be a top priority, as failure to do so can be fatal.
For example, if the pH of an aquarium falls below 6.0, the bacteria in the water will die.
These bacteria play an important role in keeping ammonia and nitrate concentrations low.
Nitrates and ammonia are extremely toxic to fish. This will force your aquarium to recycle so the toxic elements can be eliminated.










