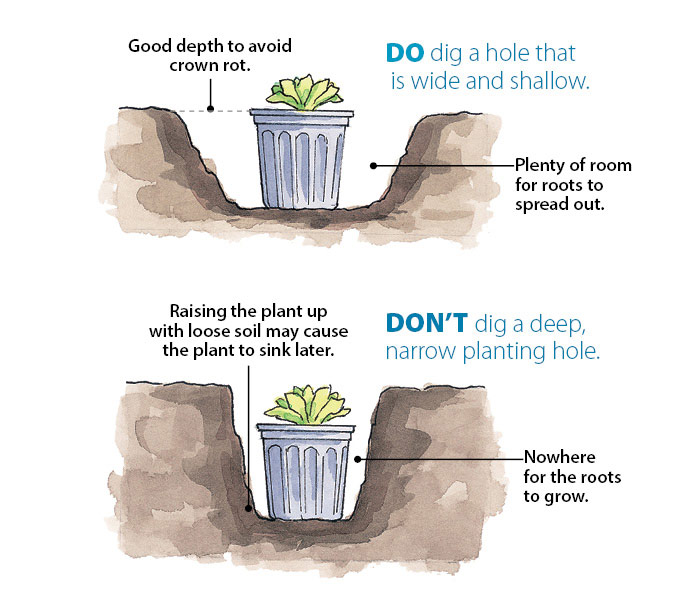
How deep to plant leeks
Seed to Harvest to Table ~ Homestead and Chill
In all our years gardening, and with a seemingly endless list of veggie varieties we’ve grown, we discovered leeks later in our gardening game. But once we started growing leeks, I was like: where have you been all my life? Leeks are delicious, beautiful, fun and easy to grow (albeit a tad slow). Yet their journey to maturation is a laid back one, as very few pests bother leeks, and they’re also frost-tolerant.
Ready to become a certified leek geek? Read along to learn how to grow leeks, from seed through harvest and beyond. We’ll talk about the best time of year to grow leeks, starting seeds, transplanting seedlings, ongoing care, and different varieties of leeks to grow. After harvest, we’ll also cover several ways to store, preserve, and eat fresh leeks – including leek greens!
What are Leeks?
Leeks are part of the Allium family, alongside onions, scallions, and garlic. They have an onion-like flavor, but are far more mild and sweet. Unlike many alliums, leeks don’t form bulbs. Instead, they’re easily recognized by their long, thick, cylindrical white stalk. Atop their stalk, leeks grow a fan of wide, flat, blue-green leaves – which can be a bit tough but are also edible! Leeks are considered a cool-season crop, though they are adapted to growing in a wide range of temperatures, much like onions.
Nutritionally speaking, leeks are rockstars! While low in calories, they boast an impressive amount of vitamins and minerals including manganese, iron, folate, vitamin K, vitamin B6 and vitamin C. Like the rest of the allium family, leeks also contain an high amount of flavonoid antioxidants. According to WebMD “Flavonoids are antioxidants and may have anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and anticancer properties, as well as other health benefits.”
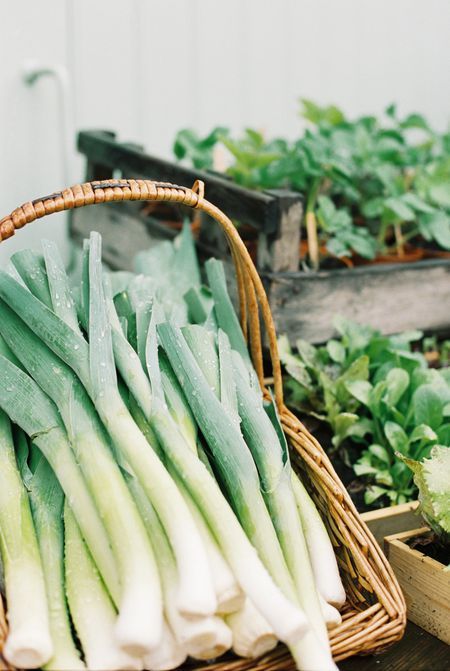
A harvest of Jumper leeks from our gardenGrowing Leeks: At a Glance
- Days to maturity: 55 to 180 days after transplanting, depending on variety.
- Temperature: Leeks thrive in temperatures 55-75°F. They can tolerate hotter weather, though their growth rate may decline.
- Planting time: Spring in northern climates. Spring or late summer to fall in mild southern climates.
- Direct sow or transplant: starting leek seeds indoors to transplant later is preferable in most cases.
- Plant spacing: 6 inches apart, plant seedlings 3-6 inches deep.
- Growing preferences: full sun, ample consistent water, well-draining soil, moderate nitrogen and organic matter.
- Frost tolerant: Yes, once mature (seedlings are not).
- Pests: few, including thrips, maggots, and fungal diseases.
Types of Leeks: Short vs Long Season
Leek varieties fall into one of two general categories: long season or short.
Short season leeks, also known as “early season” leeks, are ready to harvest within 50-100 days of planting seedlings. Short season leeks are generally smaller, more mild-tasting, and less hardy than long season leeks. Yet they are ideal for gardeners with a short cool-season growing window. Popular short season leek varieties include King Richard, Varna, Rally and Lancelot.
Yet they are ideal for gardeners with a short cool-season growing window. Popular short season leek varieties include King Richard, Varna, Rally and Lancelot.
On the other hand, long season leek varieties need more than 100 days to reach maturity – some up to 180 days after transplanting! Even more, long season leeks can often be left in the ground for “storage” after they reach maturity, for up to 210 days (or until the ground freezes). These leeks are larger, more cold-tolerant, and can be stored longer – including in the ground or after harvest. Long season leeks also benefit from blanching, described more to follow.
Notable long season leek varieties (100-150 days on average) are Comanche, Bandit, Runner, Carentan, Tardorna, Giant American Flag and Giant Musselburgh.
Sometimes you’ll also see a third “mid-season” leek category, capturing the leeks that take 90-120 days to mature in their own intermediate group. The vast majority of leek varieties are mid to long season types.
The vast majority of leek varieties are mid to long season types.
When to Plant Leeks
When is the best time to plant leeks, you wonder? Most gardeners plant short season leeks in the spring to harvest in summer to early fall. In the north, long season leeks are also planted in spring, but can be harvested up until the ground freezes. Mature leeks are frost-tolerant.
Southern gardeners with mild, virtually frost-free winters have more flexibility. They too can plant leeks in spring, as well as in late summer or fall as part of their winter garden. Fall-planted leeks can overwinter to harvest in late winter or spring. Here on the temperate Central Coast of California, we grow leeks year-round!
For spring planting, start leek seeds indoors in late winter about 8 to 10 weeks before your area’s last spring frost date. Transplant leek seedlings outside after the last risk of spring frost has passed. See more tips about growing leeks from seed below.
Transplant leek seedlings outside after the last risk of spring frost has passed. See more tips about growing leeks from seed below.
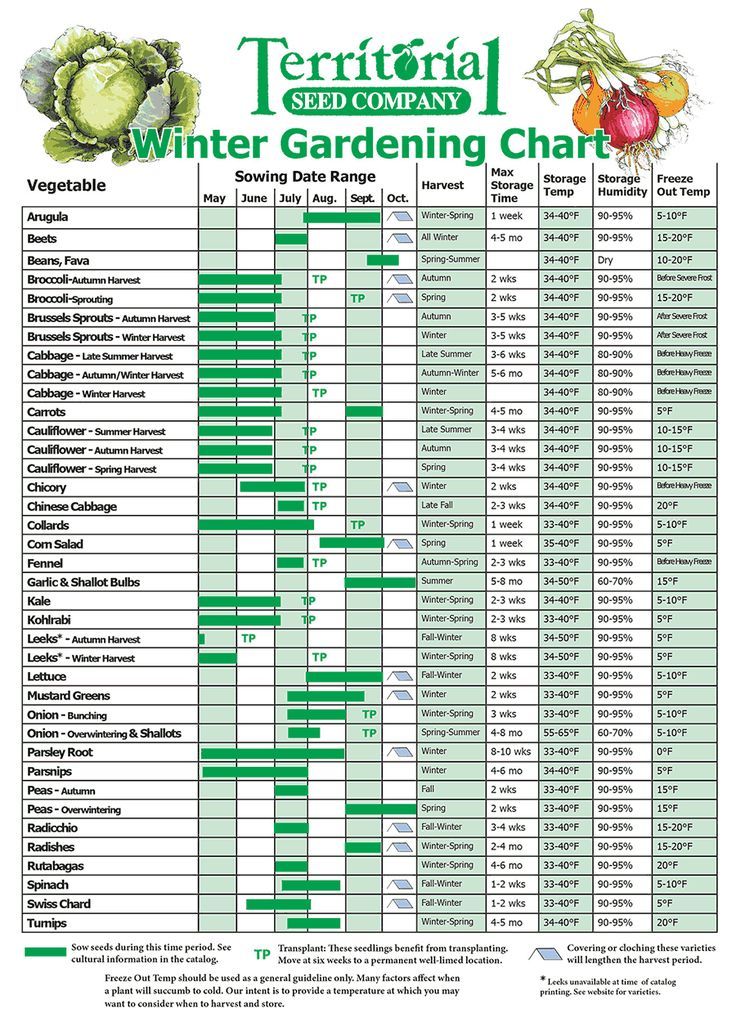
To determine the best time to start leek seeds and transplant them outdoors for your particular zone, check out the Homestead and Chill planting calendars – available for every USDA hardiness zone!
An example of the Homestead and Chill planting calendars, zone 9. Get a printable planting calendar for every zone as part of our free garden planning toolkit for email subscribers!Growing Leeks from Seed or Seedlings
There are two ways to grow leeks: start them from seed yourself, or purchase already-started seedlings to plant. We have done both, but usually prefer to start from seed.
One key benefit of growing leeks from seed is the ability to choose specific varieties that sound intriguing or most suitable for your climate. For instance, we look for leek varieties that are naturally resistant to rust – a fungal disease that affects the allium family, which is fairly common in our area.
Yet there is nothing wrong with growing leeks from nursery seedlings either! (If you can find them at your local garden center, that is.) Nursery seedlings are especially convenient if you don’t have seed starting supplies, have a short growing season, and/or didn’t start seeds on time.
Should I start leek seeds indoors or direct-sow leeks outside?
To grow leeks from seed, you’ll find the most success by starting the seeds indoors (or in a greenhouse) in containers and transplanting seedlings outside later.
While you technically can direct-sow leek seeds outside, I don’t usually recommend it since the seeds can be finicky to germinate. Plus, long-season leek varieties will greatly benefit from the jump start they’ll get inside – much sooner than you could start them outside in colder climates. Last but not least, starting leeks from seed in a container allows you to bury the leek stem deeper come transplant time, which helps promote the most upright, tender, and delicious leeks.
Tips for Starting Leek Seeds Indoors
- Start spring leek seeds indoors about 8 to 10 weeks before your area’s last frost date (usually in mid to late winter). For fall planting in mild climates, start leek seeds in late summer.
- Plant leek seeds in fresh, sterile, fluffy seed-starting mix.
- You can start leek seeds in traditional seedling cell trays or “6 packs”, planting a few seeds per cell. Or, scatter seeds (not too heavily) across a single large shallow tray of seedling soil, and thin/separate the seedlings later – also known as the multi-sow method.
- Sow leek seeds ¼” deep, covered only lightly with soil (not compacted).
- Spacing leek seeds at least 1/4″ to 1/2″ apart will make it easier to separate the seedlings later.
- Ideal soil temperature for leek seeds to sprout is around 70°F. They can germinate in cooler temperatures, though at a much slower rate.
 Use a seedling heat mat to promote quick and even germination.
Use a seedling heat mat to promote quick and even germination. - Maintain the seedling soil damp (but not soggy) at all times. Keep the trays covered with a humidity dome before germination to prevent the soil from drying out. Uncover once they sprout.
- Leek seeds are fairly slow to sprout, so be patient! They should germinate within 2 weeks, or about 10 days on average.
- As soon as they sprout, provide ample bright light for at least 12 to 16 hours per day. Grow lights are highly recommended when starting seeds indoors.
- When in doubt, follow the instructions provided on your seed package.
- See our seed starting guide for more detailed information on starting and caring for seedlings indoors.
How to Plant Leeks (Transplant Leek Seedlings)
Once the leek seedlings are at least 7 to 8 inches tall and about as thick as a pencil, it’s time to plant your leeks outside! Whether you are growing leeks from seed or purchased seedlings, the following transplanting tips apply:
- Before transplanting, ensure indoor-raised seedlings have been hardened off first.
 The hardening off process reduces the risk for transplant shock or injury. Learn more here.
The hardening off process reduces the risk for transplant shock or injury. Learn more here. - Transplant leek seedlings outdoors in spring after the last risk of frost has passed. Keep an eye on the weather forecast and be prepared to protect seedlings from frost if needed. Mature leeks can withstand a light frost (especially long-season varieties) but tender seedlings are far more susceptible to frost damage.
- Gently separate or pull apart any leek seedlings that may still be clustered in the same seedling pot or tray. Remove the root ball from the container, gently loosen the soil, and slowly untangle the leeks – taking care to not to break the roots or seedlings.
- Plant, space or thin each leek seedling about 6 inches apart. Adequate spacing is essential for leeks to grow to their potential size!
- Dig a trench approximately 6 inches deep, or use a dibble or small trowel to create 3 to 6-inch deep holes.
- You can plant leek seedlings deep, with a majority of the stem buried and only a couple inches of green tips showing above the soil line (see depth discussion below).

- Gently and loosely backfill, but don’t compact the soil around the seedling stem. Or, don’t backfill at all and let the holes fill in on their own with time.
How deep should I plant leek seedlings?
This deserves it’s own discussion because there is a lot of confusion and conflicting information out there about transplanting leek seedlings. Most garden experts recommend planting leek seedlings deep (up to 6″, with most of the stem buried) to reduce the need for blanching. Planting leeks deep will result in a longer white stalk, which some folks find more desirable. Yet deeply-planted or hilled leeks may also harbor more dirt inside this way – so there’s a tradeoff.
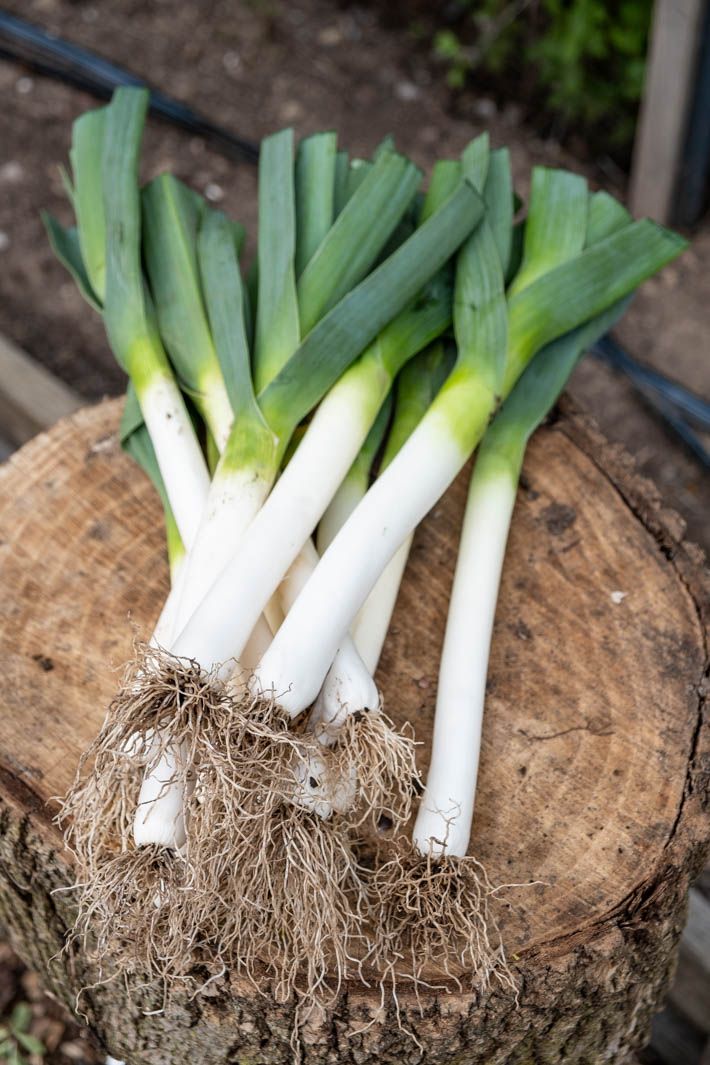
However, you don’t have to bury them so deep. Leeks grow just fine if only minimally buried, planted 2-3″ deep. Their stalk color will simply be light green instead of pearly white. If you desire extra-white leeks, you can always blanch them later after planting (read more below). Or, simply let them grow au natural like we usually do!
Or, simply let them grow au natural like we usually do!
Leek Growing Requirements: Sun, Soil, Fertilizer, Water & Mulch
- To grow the best leeks, choose a location that receives ample sun. Leeks will tolerate partial shade but grow most vigorously in full sun.
- You can grow leeks in the ground, in raised garden beds, or even in large grow bags.
- Leeks grow best in well-draining soil that is rich with organic matter. If needed, amend clay or heavy soils with quality potting soil and/or horticulture sand to promote good drainage.

- Leeks are fairly heavy feeders and enjoy ample nitrogen. Before planting, add a couple inches of well-aged compost to the soil. We also add a sprinkle of slow-release organic fertilizer, gently scratched into the top of the soil. Long season leeks may benefit from a mid-season feeding of compost tea, dilute seaweed extract, fish fertilizer, or a side dressing of mild slow-release granular fertilizer. Avoid strong fertilizers mid-season, as it could trigger leeks to bolt.
- Leeks thrive with consistent moisture. Therefore, water leeks regularly enough to maintain the soil damp (though not soggy) at all times.
- Mulch around the base of leeks (once they’re no longer tender seedlings) to help with moisture retention and insulate against temperature extremes. One to two inches of mulch is adequate for leek seedlings that were initially buried 4 to 6” deep. Provide a deeper layer of mulch for shallowly-planted seedlings (see ‘blanching’ below) or when freezing conditions are expected.
Blanching Leeks
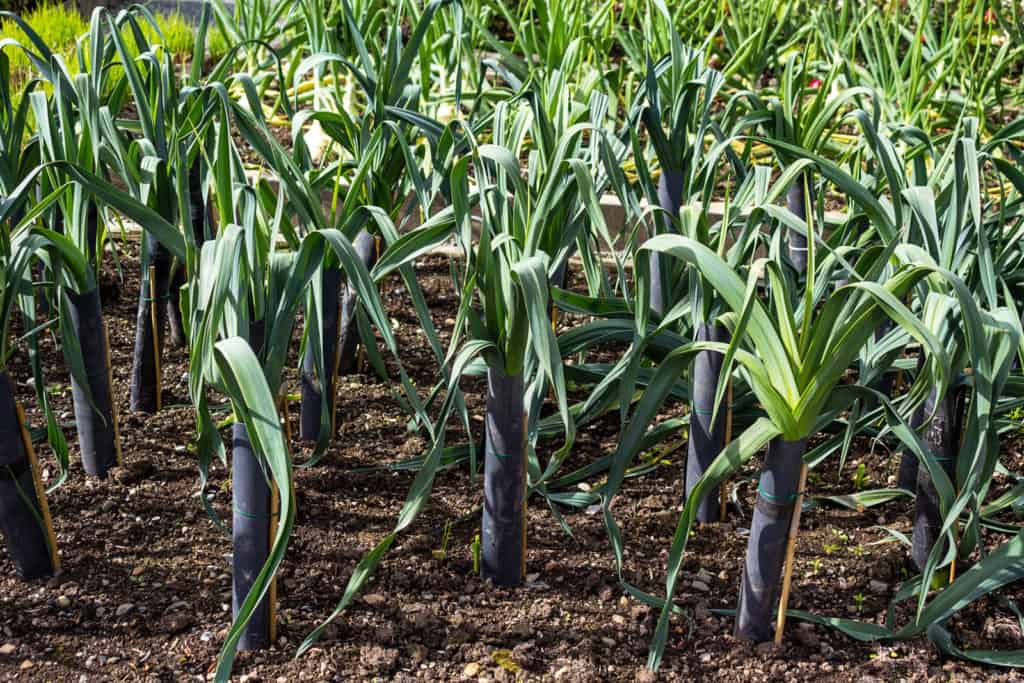
Blanching is the act of covering or hilling soil around leek stalks as they grow, blocking sunlight from the lower portion. It encourages the leaves to grow higher up the plant and results in a longer, whiter stalk. Un-blanched leek stalks are light green instead. Certain leek varieties are “self-blanching” and produce white stalks even when exposed to the sun while growing.
Some folks claim that the more white and blanched the stalk, the more tender and sweet the leek is. However, this claim has also been repeatedly refuted in blind taste tests when comparing blanched to un-blanched leeks. So, it seems blanching is more about aesthetic than anything.
To blanch leeks, simply hill up soil or mulch around the base of the plant, burying a couple inches of the stalk (but not too high or dirt will end up between the leaves). Do this two or three times throughout the growing season, hilling higher each time.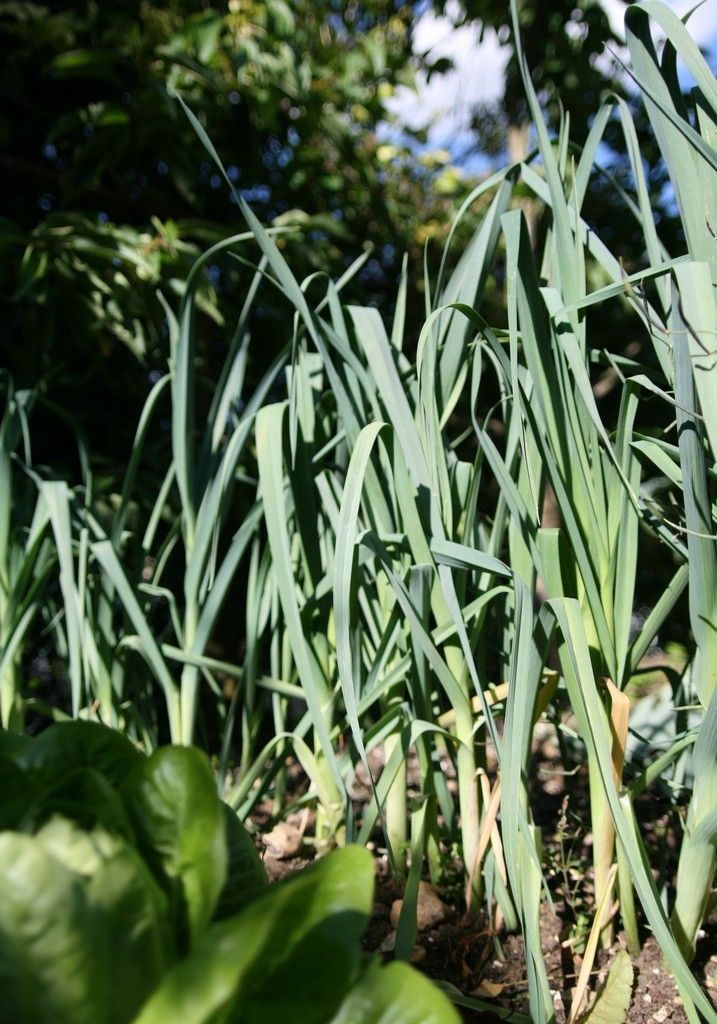 Another way to blanch leeks is to cover or wrap their stalks, such as with cut cardboard tubes made from toilet paper or paper towel rolls.
Another way to blanch leeks is to cover or wrap their stalks, such as with cut cardboard tubes made from toilet paper or paper towel rolls.
Blanching is most useful when leek seeds are directly sown outside, or if seedlings are buried shallowly when they’re first transplanted. When leeks seedlings are transplanted deeply with the “dibble method” or in deep trenches, the need for hilling is reduced or eliminated. It’s also less necessary when growing short-season leek varieties.
Rather than hilling soil to blanch leeks, the base of these stalks have been wrapped to block the sun.Another example of blanching leeks.One of our homegrown leeks, left to grow without blanching. The stalk is light green in color instead of white (minus the tip) but are still plenty tender and delicious.Leek Pests & Diseases
Thankfully, leeks are inflicted by few pests compared to most garden crops, making them relatively fuss-free to grow. Rather, leeks, onions, and other members of the allium family naturally deter many pest insects! Leeks are most susceptible to pests or diseases that affect onions.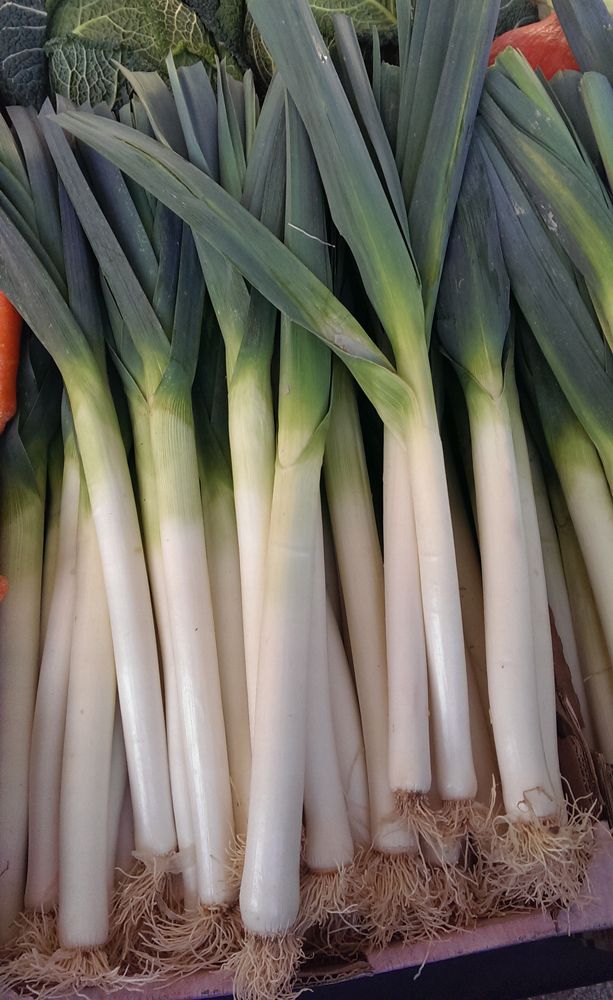
The most common leek pests include:
- Onion thrips are tiny yellow-brown colored leaf-sucking insects. They are fairly common but most prolific in hot, dry conditions. They concentrate in tight folds between leaves and focus their feeding on new succulent growth. Organic management strategies include neem oil spray, biological control with beneficial insects (such as lacewing larvae and predatory thrips) and the removal of heavily infested plants.
- Onion maggots are the larvae from the onion maggot fly. Similar size to a housefly, onion maggot flies lay eggs near the base of allium plants, where their larvae will emerge and begin to feed. They feed on allium seedlings, roots and bulbs, causing wilting or reduced growth. Onion maggots thrive in cooler damp conditions (especially coastal climates) and are not as bothersome in hot arid climates. As natural predators to maggots and grubs, the application of beneficial nematodes is an excellent and effective organic onion maggot control option.

- Allium Leaf Miners are invasive insects from Poland, and are currently only found in the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic regions of the U.S. The fly-like pests pierce and feed on plant sap, and lay eggs within the plant tissues.
- Leek moth is found in Canada, Asia, Europe and Africa, though not yet in the continental United States.
- Fungal diseases such as allium rust, downy mildew, pink rot, white rot, and Botrytis leaf blight. Homemade neem oil spray can help reduce the spread and damage caused by most fungal diseases. Dilute potassium bicarbonate spray is another effective organic fungicide. Check out our article on powdery mildew control for more details on using both solutions.
Flowering or Bolting Leeks
Us gardeners grow leeks as annual crops, though they’re technically biennials. That means if they’re left long enough in the ground (beyond their prime harvest time), they will form a center flowering stalk and eventually produce seeds. Leeks may also form a flowering stalk prematurely, referred to as “bolting” or “going to seed”.
Leeks may also form a flowering stalk prematurely, referred to as “bolting” or “going to seed”.
Leeks may bolt when presented with unfavorable growing conditions, such as too little or irregular water, too much fertilizer (especially high phosphorus fertilizer), or too little sunlight. Unlike many garden veggies that bolt due to hot weather, consistently cold conditions (e.g. daytime temperatures regularly under 45°F) can cause leeks to bolt instead. The best way to prevent leeks from bolting is to grow leeks at the right time of year for your climate, and transplant seedlings before they become too large or root-bound.
Once leeks begin to flower, their stalks and leaves become increasingly tough, woody and bitter (though still technically edible). Therefore, if you notice your leeks start to flower, harvest them as soon as possible since the quality will only continue to decline. That is, unless you want to leave the flowers to enjoy! They’re quite beautiful, and popular with the pollinators too.
When and How to Harvest Leeks
Harvest leeks once they’ve reached the desired size. Check the description of the particular leek variety you are growing to determine their expected maturation time and size. Like onions, you can harvest leeks early and enjoy them as tender premature versions of their adult selves if you’d like!
One of the beautiful things about growing leeks is that you don’t have to harvest them all at once. Long season leek varieties can be left and stored in the ground until you’re ready for them – as long as they don’t begin to flower and aren’t exposed to a hard freeze (though they’re frost tolerant). When hard freezing conditions are expected, either harvest the leeks or protect them with mulch and horticultural fleece.
When it comes time to harvest leeks, remember: DIG, don’t pull! Leeks can be deep-rooted in the soil, and pulling up on them risks breaking the precious stalk. Instead, carefully insert a small trowel or spading fork straight down into the soil near the stem to gently loosen and lift the leek upwards from below.
Instead, carefully insert a small trowel or spading fork straight down into the soil near the stem to gently loosen and lift the leek upwards from below.
Storing Fresh Leeks
After harvest, avoid washing or trimming the leeks until you’re ready to use them. (That is, unless you intend to use them within the next few days). You can trim off the dirty roots, but don’t cut into the stalk itself. Store fresh leeks in the refrigerator tucked inside a plastic bag (or two, if they’re extra tall). Refrigerated leeks should stay good for at least a week or two, sometimes longer.
Another option to store fresh leeks is in a root cellar, ideally between 32 and 40°F. After harvest, transfer the leeks (unwashed, roots still intact) into a bucket of horticulture sand or fresh potting soil. Stand them upright in the sand/soil and cover several inches of the bottom stalk. Certain leek varieties can stay good for several months in a root cellar!
Stand them upright in the sand/soil and cover several inches of the bottom stalk. Certain leek varieties can stay good for several months in a root cellar!
Ways to Eat Leeks (and Leek Greens)
Leeks are a wonderful mild substitute for onion in any recipe. The tender stalks are fantastic thinly-sliced on top of pizza, sourdough focaccia, in stir-fry, pasta or rice dishes, omelets and quiche, soups, sauces, and more. They’re also fantastic grilled, or turned into pesto. Then of course perhaps leek’s most renowned use: potato leek soup! Try our creamy vegan potato leek soup recipe here.
How to Prepare Leeks
The cylindrical stalk is the most edible, tender, and delicious portion of the leek. To prepare leeks, cut off the firm root end as well as the upper leafy green portion. (But don’t discard those just yet!) Peel away a few outer layers of the stalk if needed; they may be more tough or dirty. Finally, thinly slice the stalk into rounds to use in your recipe of choice.
Finally, thinly slice the stalk into rounds to use in your recipe of choice.
Since leeks are grown partially underground they can be quite dirty, including hiding between the layers of leaves. In addition to running them under water, you can clean leeks by soaking cut leeks in a bowl of water if needed. The dirt will settle to the bottom of the bowl, while the leek pieces will float and can be scooped out. (I’ve found commercially grown leeks to be far more dirty than our homegrown leeks, and don’t usually need to soak ours).
Can you eat leek greens?
Yes, you absolutely can eat leek greens! Yet they can be quite tough and chewy, especially the uppermost portion. Therefore, I suggest using the lower leek greens (closer to the white stalk) for cooking applications. Thinly-sliced, those leek greens make a great addition to soup or other recipes where they can cook long enough to soften. Or, if they get blended up – like added to our besto pesto recipe. Yet our favorite way to use leek greens is to dehydrate and turn them into leek powder. We use some of the toughest top leek greens for that!
Yet our favorite way to use leek greens is to dehydrate and turn them into leek powder. We use some of the toughest top leek greens for that!
Can you eat leeks raw?
Sure can! Just as you can eat raw onions, raw leeks offer an even more mild (and more enjoyable, in my opinion) pop of flavor to many meals. Add thinly-sliced raw leek stalks mixed into salads (including potato or pasta salad), dips, pesto, or homemade salad dressings. They’re also great as a garnish on top of roasted veggies, sandwiches, egg dishes, soups, salads, and more. I personally would not eat tough leek greens raw.
Preserving Leeks
Fresh leeks can be frozen, dehydrated, canned, fermented or pickled. We love to preserve leeks by drying them to make leek powder. The result is a delicious sweet onion-like seasoning powder. Learn how to make and use leek green powder here. Freezing leeks is also easy, explained below. Another great way to preserve leeks is to freeze potato leek soup!
Freezing Leeks
Freezing leeks is a great way to preserve leeks when you have more than you can eat fresh. Later, frozen leeks can be added to soups, sauces, or other recipes that call for cooked leeks. However, their texture won’t be quite as great as fresh leeks.
To freeze leeks, cut them into thin rounds so they’re ready to use without further preparation after thawing. Line a baking sheet or other tray that can fit in your freezer with parchment paper, then lay the cut leeks out in a single layer. Next, freeze the tray until the leeks are frozen solid (overnight or 24 hours).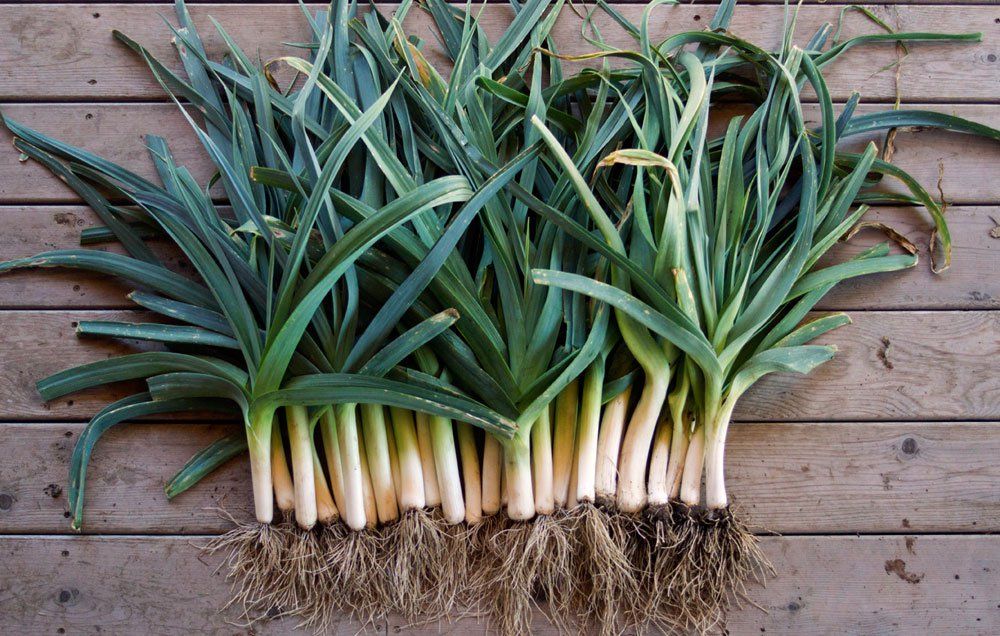
Finally, transfer the individually-frozen leek pieces into a freezer safe storage container and place back in the freezer for final storage. Move quickly so they don’t defrost while you work. This way, the leeks won’t stick together into one solid clump, making it easier to pull out just a portion of them as needed.
And now you know how to grow leeks – and then some!
In closing, I hope this article boosted your confidence and excitement about growing leeks. Between their easy care, unique appearance, and versatility in the kitchen, they’ve certainly become a staple in our garden! Please let me know if you have any lingering questions that I didn’t address in the comments below. If you found this article to be helpful, please feel free to spread the leek love by pinning or sharing this post. Thank you so much for reading!
Ready to learn more? Don’t miss these awesome grow guides:
- Onion Grow Guide
- Kale Grow Guide
- Tomato Grow Guide
- Green Bean Grow Guide
- Garlic Grow Guide
- Carrot Grow Guide
- Basil Grow Guide
- Potato Grow Guide
- Zucchini Grow Guide
Growing Leeks | Tips for Planting Leeks in your Garden – Bonnie Plants
Grace your dinner table with an easy-to-grow, elegant onion cousin: the leek. Sweet and mild, leeks are gentle on the digestive system and play the role of onion in dishes, only toned down. Unlike onions, leeks don't produce bulbs but stash their flavor in thick, juicy stems that look similar to giant scallions. Leafy stems are pretty, and growing leeks doesn't require much room in the garden.
Sweet and mild, leeks are gentle on the digestive system and play the role of onion in dishes, only toned down. Unlike onions, leeks don't produce bulbs but stash their flavor in thick, juicy stems that look similar to giant scallions. Leafy stems are pretty, and growing leeks doesn't require much room in the garden.
In the supermarket, leeks cost a premium; harvested from the garden, they're a bargain. Leeks are most famous for leek and potato soup, but they're also good steamed like asparagus, oven-roasted, chopped in quiche, or wrapped in ham and baked (perhaps with a little cheese on top).
Frost-tolerant leeks thrive in cool weather. In zones 7 and warmer, plants can overwinter in the ground, making them perfect for fall planting. In northerly zones, tuck plants into beds in early spring, as soon as soil can be worked.
Quick Guide to Growing Leeks
- Plant leeks during the cool weather of early spring and fall. They grow well in raised beds, containers, and in-ground gardens.
- Space leeks 6 inches apart in an area that gets 6 or more hours of sun daily and has nutrient-rich, well-drained soil.
- Improve native soil by mixing in several inches of aged compost or other rich organic matter.
- Leeks aren't fussy, but they do require moist soil, so check soil moisture often and use a soaker hose if necessary.
- One week after planting, begin regularly feeding with a water-soluble plant food.
- Harvest leeks at any time once they are large enough to eat.
Soil, Planting, and Care
Plant leeks in a sunny spot in soil that is fertile and well-drained. Leeks thrive in traditional garden beds, raised beds, or even in tall containers, so choose whatever works best for you. Space leeks 6 inches apart when planting.
Leeks need two things to thrive: lots of nitrogen and consistent soil moisture. If possible, add compost to the leek bed the season prior to planting. To improve the soil if you haven't thought that far ahead, mix in a few inches of Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® All Purpose In-Ground Soil with your native soil. Or, if planting in raised beds or containers, be sure to fill them with the right type of soil for that growing environment, such as Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® Raised Bed Mix for raised bed gardens and Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® All Purpose Container Mix for pots.
Or, if planting in raised beds or containers, be sure to fill them with the right type of soil for that growing environment, such as Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® Raised Bed Mix for raised bed gardens and Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® All Purpose Container Mix for pots.
To produce a succulent white stem, leeks must be blanched — in other words, covered or hidden from the sun. To do this, plant leeks into deep holes. (Deeper planting yields a more drought-resistant plant, too.) Create a narrow trench 6 to 8 inches deep, then tuck seedlings into the trench, adding soil back so it comes up to the base of the first green leaf. Water well.
After planting, mulch the bed with straw or some other organic material to help soil retain moisture. Feed newly planted leeks with Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® Edibles Plant Nutrition every seven days. Water leeks as needed until plants are established. After that, plants require an inch of water a week, either through rainfall or irrigation. Inconsistent moisture yields tough stems.
Inconsistent moisture yields tough stems.
As leeks grow, mound the soil from the trench around stems, beginning when stems are 1 inch thick.
Troubleshooting
Soil that tumbles into leaf folds can wind up trapped between skin layers in the stem. To keep this from happening you can slip a section of paper tube, such as from toilet tissue or paper towels, over the plants while they are still young as early as planting time. The tube will rot over the growing season, but will help prevent soil from getting into leaf bases during early growth.
On young plants, slugs can be devastating. Gather them at night, set traps, or use biological control. If there is a lot of rain in winter or early spring, leaf rot can set in. Rot shows as white spots on leaf tips that eventually shrivel. At this point there is not much you can do except pull the rotted plants and thin the planting to increase air circulation.
In summer, orange pustules on leaves indicate leek rust, which is worse in wet growing seasons. Remove affected foliage; later maturing foliage will be healthy.
Remove affected foliage; later maturing foliage will be healthy.
Because they are so cold-hardy, you could find that you still have leeks left in the garden that have made it though the winter, planted many months before. At this point, dig them because they will throw up a bloom stalk that ruins the fleshy texture of the stem.
Harvest and Storage
You can start pulling leeks from the ground just about anytime. Typically, you'd let them get least 1 inch or larger in diameter for the big white stems, but you can dig young ones to eat like scallions. If the soil is moist, they may just pull right out of the ground. If they resist, use a spading fork to loosen soil and then gently pull leeks by grabbing them at their base.
In zones 7 and warmer, you should be able to harvest leeks all winter long.
In colder areas, extend the harvest season by mulching deeply around plants (up to 1 foot deep) before a hard freeze. You could continue harvesting leeks until they are locked frozen into the ground, but don't let that happen. Dig them first and store.
Dig them first and store.
Wash the stems thoroughly to remove soil and grit that may have collected between the leaves.
For short-term storage (up to one week), tuck stems into an airtight plastic bag and place in the refrigerator crisper. For longer storage in coldest zones, dig leeks with roots attached. Cut leaves back until just an inch of green remains on each leaf. Place stems in a box (root side down) and pack with sawdust, clean sand, or vermiculite. Keep the packing moist and store in a cool place. Stems will keep up to 8 weeks.
To freeze leeks, wash, slice, and blanch for 1 minute in boiling water. Drain, drip dry, and toss into plastic freezer bags. Add the frozen leeks to soups, stews, and other dishes.
Bury the plants up to the point where the foliage arises from the stem, but not so deep that soil gets into the folds between the leaves.These leeks could stand to have the soil mounded up around their stems more deeply for better blanching.Even though our biodegradable pot directions indicate planting the whole pot, in the case of leeks, you need to remove the plant from the pot and very gently coax the clump of seedlings apart so that you can plant each leek seedling separately.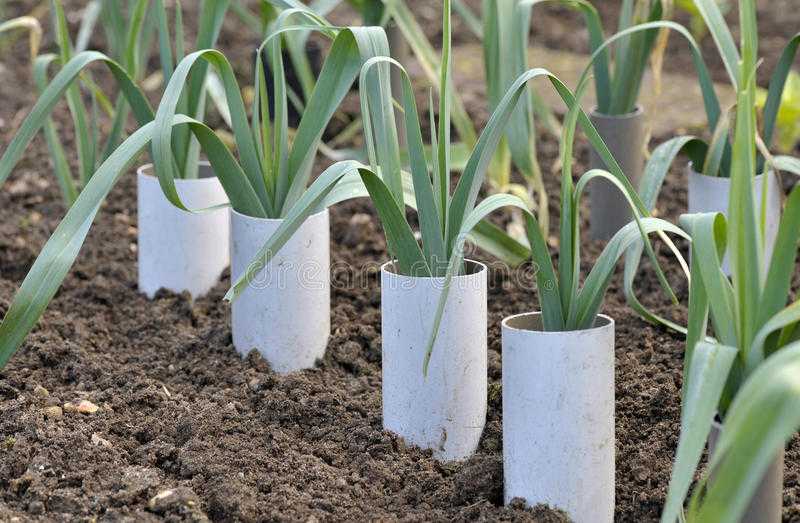 Ideally, leek stems will be long and white at harvest time. The white part is where the stem was blanched underground, hidden from sunlight.This winter scene shows kale alongside leeks in a display of two of the garden's most cold-hardy vegetables.
Ideally, leek stems will be long and white at harvest time. The white part is where the stem was blanched underground, hidden from sunlight.This winter scene shows kale alongside leeks in a display of two of the garden's most cold-hardy vegetables.FAQs
Should I just plant the pot of leeks like I do with other Bonnie plants?
No, this is an exception to our plant-the-pot rule. Our pots are sown thickly with leek seedlings, which means you get a lot in one pot. Gently separate the seedlings to plant.
Will leeks grow in pots?
Yes, you can grow them in containers. Use a container about 18 inches deep and fill it only about 2/3 full of soil to begin with. Continue filling as the stems grow so that they will blanch. Make sure to water and fertilize regularly. Use a liquid plant food when you water to encourage fast growth that will result in tender stems.
Just how cold hardy are leeks?
American Flag, the heirloom variety that we offer, is one of the most cold hardy. You will also run into what is called a "summer leek" which is intended to plant in spring and harvest before cold weather. However, American flag will over winter in Zones 7 and warmer, easily tolerating temperature in the teens.
You will also run into what is called a "summer leek" which is intended to plant in spring and harvest before cold weather. However, American flag will over winter in Zones 7 and warmer, easily tolerating temperature in the teens.
If I don't blanch my leeks are they still edible?
You can strip away the leaves and eat what white part of the stems is left below the leaves. The green portions are actually edible, but they won't be as tender.
outdoor planting and care
Some gardeners find it easier to grow onions than leeks. However, it is worth knowing that the gastronomic qualities and rich vitamin composition of leeks are significantly superior in their subtlety of taste (not spicy, but even slightly sweet) of their onion counterpart. Nevertheless, even a novice summer resident can plant and grow leeks on his site, which you will definitely see by reading this material to the end.
Well, then you will learn when and how to plant leeks for seedlings (including whether it is possible to plant leeks immediately in the ground, so to speak, grow in a seedless way), how to properly care for a decent harvest.
Contents
- 1 How to plant leeks for seedlings: timing, preparations and staged planting
- 1.1 Sowing dates
- 1.2 Required planting containers and soil 9.33 seed preparation0016
- 1.4 Planting seeds for seedlings
- 2 Leek seedling care after planting
- 2.1 Picking
- caring for leeks in the garden after planting
- 5 Seedless cultivation of leeks
- 6 When to harvest and how to store
How to plant leeks for seedlings: timing, preparatory measures and staged planting
In the South, due to earlier warming of the earth and a long summer, leeks are planted with seeds directly into the ground, i.e. they use a seedless planting method, which is in no way suitable for the Middle Strip (the same suburbs) due to the fact that return frosts and a relatively belated onset of stable warm weather are not uncommon in these latitudes. Therefore, due to the fact that the growing season of leeks is very long (about 6 months), it is better to grow leeks through seedlings in this region. nine0005
nine0005
Sowing dates
As for the approximate planting dates, as a rule, seedlings are planted for leek seedlings from the end of February to the end of March .
By the way! The site already has a separate material on how to determine when to plant leeks for seedlings , including favorable days according to the lunar calendar in 2023.
Required planting containers and soil
The choice of containers for sowing leeks for seedlings is not limited to purchased options, you can always make a planting container yourself. nine0005
By the way! An excellent option would be planting and growing leeks in peat tablets without a pick.
In order for a leek to sprout successfully and quickly grow, it needs light and nutritious soil. Heavy (dense) or excessively clay soil does not suit him.
Heavy (dense) or excessively clay soil does not suit him.
You can buy ready-made soil for seedlings at the garden store, while ready-made soil mixtures for eggplants, peppers and cucumbers are excellent for this. nine0005
Recipe for self-preparation of soil mixture for growing seedlings of leeks:
- 1/4 peat;
- 1/4 garden (garden) land;
- 2/4 humus.
Before sowing, it is desirable to decontaminate the prepared soil using one of the methods , spilling a warm solution of potassium permanganate, and even better Fitosporin .
Preparation and treatment of seeds before sowing
Before planting leek seeds, they must be treated for better germination, and it does not matter if you plant the leeks first in seedlings or directly in the ground. nine0005
Remember! The optimal shelf life and, as a result, the germination of leek seeds is 3 years, then the chances for friendly seedlings of crops are significantly reduced.
There are many ways to prepare leek seeds before planting.
For example, you can simply soak seeds in lukewarm water, soak for 24 hours, and then dry.
Another processing option can be keeping the planting material in a thermos at a water temperature of about 40 degrees for 3-5 hours. After that, the seeds must be rinsed in cold water and dried. nine0005
It is possible to dress leek seeds in a special solution, for example, Phytosporin .
Planting seeds for seedlings
Sowing seeds of leek occurs differently depending on the size of the planting container: if it is a separate container, for example, cups, then it is better to place 1 seed in each (although, for better further selection can be sown in 3-4, so that later only the strongest seedling is left).
So, step-by-step instructions for planting leeks for seedlings:
- Fill containers with moistened substrate.

- Make small grooves 1-1.5 cm deep.
- Sow the seeds at a distance of 4-5 centimeters from each other and cover lightly with soil.
- Then sprinkle the whole surface with an additional 0.5 cm layer of sand and pour over.
- Now you can cover the crops with a lid or plastic wrap, or you can use the most ordinary shoe covers (to create the effect of a greenhouse) and put them in a warm place where the air temperature is around + 21-25 degrees throughout the day. nine0016
Video: planting leeks for seedlings
You can also sow leeks in snail or non-woven napkin. How to do this, see the following video:
Care of leek seedlings after planting
cooler place. There the temperature in the room at night should be at the level of + 10-12 degrees, in the daytime - + 15-17 degrees. Under such conditions, planting should live for 1 week. Then the temperature must be raised again to + 13-15 degrees at night and + 18-20 degrees during the day. It is in this mode that you need to keep the seedlings until they are finally transplanted into open ground. nine0005
Video: care of leek seedlings
Onion seedlings require 12 hours of daylight to grow normally .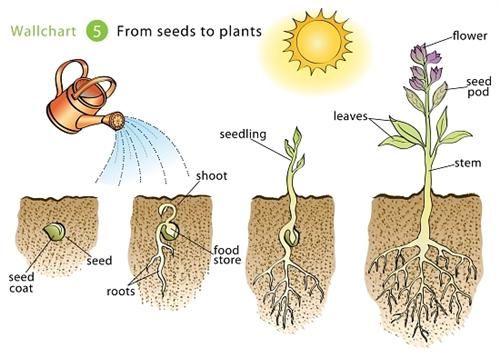 Therefore, when sowing early, you need to immediately think about how you will illuminate the leek: these will be more expensive fitolamps or economical LED counterparts.
Therefore, when sowing early, you need to immediately think about how you will illuminate the leek: these will be more expensive fitolamps or economical LED counterparts.
Leek needs frequent and heavy watering . The soil should not be allowed to dry out, the leek germinates well only in moist soil. nine0005
Important! Due to the fact that the stalks of young leek seedlings are very tender, they need to be watered very carefully. That is why a constant additional sprinkling of earth into the seedlings is required, which ensures the correct formation of the leek bulb.
After 1 month from the moment of seedling formation, it is necessary to start thinning so that the distance between seedlings is somewhere 3-4 cm.
also stem thickening by pruning plants every 14 days, while maintaining the height of the onion at a level of 10 cm from the ground.
Video: leek seedling care - pruning (cutting)
Leek seedlings need fertilizer to grow best. So, it is desirable to carry out exactly 2 top dressings. The first - a couple of weeks after germination and the second - about a week before transplanting to the garden. Can be used as ready-made fertilizers (for example, Kemira-universal or Nitroammophoska). nine0005
nine0005
A week or more before planting the leek in the ground (that is, 7 weeks after the first shoots appear), the seedlings need to be hardened first. Therefore, gradually begin to take out planting containers with seedlings on the street (preferably left in partial shade), every day increasing the time of his stay in the open air.
Pick
Please note! Picking leek seedlings is undesirable, so plant seeds immediately in spacious containers. nine0005
If you have planted the leek too thickly, then transplanting young seedlings must be carried out very, very carefully, in no case damaging the small roots.
Method of planting leek seedlings in open ground: terms, rules and rules for further care As a rule, this occurs approximately 50 to 60 days from the moment of germination, depending on the variety chosen. nine0005
If you haven't prepared the soil since autumn, it's okay, you can do it in the spring. Mark out the bed in advance, dig the ground and apply fertilizer (for digging).
Mark out the bed in advance, dig the ground and apply fertilizer (for digging).
Leek does not favor or grow in acidic soils. Therefore, if you are not sure that we have a soil of neutral acidity, then add, for example, lime or dolomite flour to the garden bed.
Tip! Leek grows very well next to beets, carrots, strawberries and celery, so they can be planted side by side, for example, in alternating beds. nine0005
According to the crop rotation, if you plant a leek in a bed where legumes (peas) were previously grown, as well as potatoes, tomatoes, cabbage or green manure , then it will grow well.
By the way! Do not plant onions in the same place 2 years in a row.
Just before planting, lightly (1/3 or 1/4) pinch off the roots and top of the leek seedlings. Such shortening will have a positive effect on the speedy rooting and on the further production of better greenery. nine0261
Such shortening will have a positive effect on the speedy rooting and on the further production of better greenery. nine0261
By the way! To improve the survival rate of seedlings, leek roots are recommended to be dipped in a clay mash with mullein (1 to 1).
Leek seedlings are planted in small V-shaped grooves 10-12-13 cm deep and at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other and at a distance between rows of 35-45 cm. This planting pattern will be ideal for subsequent hilling of beds.
Leek can be planted from individual containers and into individual holes. nine0005
Important! Do not forget to lightly sprinkle the grooves (furrows) with a mixture of humus and ash before planting onions (1 bucket of humus per 0.5 liter jar of ash).
Video: planting leek seedlings outdoors
How to care for leeks in the garden after planting
Aftercare of leeks is not very difficult, but to get a rich harvest, you have to follow exactly the basic procedures of agricultural technology for growing leeks. nine0005
Leek care includes the following agrotechnical measures:
- hilling;
- loosening and weeding;
- watering;
- groundbait;
- treatment for diseases and pests.
After the young seedlings take root, and the stalks reach a thickness of 0.5-0.7 cm (so to speak, they become like pencils), then you can already start doing light hilling, namely: little by little pour the earth under the stems. Real hilling can be started only after 45-60 days from the date of planting the seedlings. nine0005
nine0005
Please note! Hilling is the most important part of leek care. it is this that leads to the bleaching of the lower parts of its stem.
If you ignore regular hilling (it should be done 4 to 5 times throughout the season), then you will grow a tasteless green “trunk”.
leek should be watered frequently, about once every 4-6 days. Naturally, if the days are hot and the weather is dry, then it is necessary to increase the amount of watering. You can water with cold water, somewhere at the rate of 1 bucket of water per 1 sq. garden meter. nine0005
Important! It is necessary to monitor the moisture content of the soil, as constant moisture stagnation adversely affects the growth and development of onions, and can also contribute to its diseases. However, the same applies to the lack of moisture in plantings.

By the way! The site already has a general article on the rules for watering onions .
Leek responds very well to feeding chicken manure with the addition of phosphate and potash fertilizers. It is necessary to breed in the following proportion: 1 part of litter and 20 parts of water. nine0005
In addition to hilling, top dressing and watering, regular loosening and weeding of plantings from weeds should definitely be included in the care of leeks.
Seedless leeks
As mentioned earlier, seedless leeks are only suitable for southern regions.
With the onset of April-May, when the earth warms up enough and stable warm weather sets in, the time for sowing leek seeds in open ground is also suitable. This is due to the fact that onion seedlings do not tolerate frost, although they are quite resistant to cold. nine0005
nine0005
The basic requirements for a bed for planting leeks with seeds in open ground are as follows:
- the soil must in no case be acidic and heavy, leeks grow well only on light and neutral soils;
- a place for a bed on the site is better to choose well-lit and moisture-retaining.
Step-by-step instructions for planting leek seeds outdoors are as follows:
- Treat the seeds (of course, you can use the same methods as for sowing seedlings)
- Preparing a garden bed. First dig the soil to a depth of 20-25 cm (shovel bayonet), and then add fertilizer to it, and then dig again and lightly tamp.
- Now you need to make grooves and sow seeds in them at a distance of 10 cm and sprinkle with earth.
Further care of the leek is fundamentally no different from the care of onions grown from seedlings. nine0005
nine0005
When to harvest and how to store
The harvest time of leek is determined by its variety: certain varieties can be harvested already in late summer - August, others created for long storage - only in mid-autumn, that is, starting from October .
How to harvest leeks for storage? First you need to dig the plant, and then pull it out, holding the stem with both hands. Loose earth makes it easy to pull out the stems without resorting to the use of additional funds. Now the onion needs to be cut to 20-30 centimeters in length, while shortening the roots to 1.5-2.5 cm. Be careful not to cut the roots completely, otherwise the leek will simply rot during storage. nine0005
Leek can be stored in a basement or cellar, perhaps even a shed or garage. It is only important that the air temperature is at least 0 degrees.
Pearl onions, subject to the optimal storage temperature, have every chance and opportunity to lie like this until spring and not lose their useful properties.
By the way! Leek has one very distinctive feature: during storage, the level of ascorbic acid in it rises by 150%. nine0005
Video: growing, harvesting and storing leeks
As you already understood, growing strong and healthy leek seedlings and planting them competently in open ground will not be difficult even for a beginner vegetable grower and summer resident. It is only necessary to properly care for the seedlings, and then you will be pleased with a fragrant and juicy harvest.
Video: leeks from A to Z - sowing, picking, planting in the garden, harvesting and storing the crop
planting and care in the open field, sowing for seedlings, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/en/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: garden plants reprinted: Last amendments:
Content
- Planting and Leak-Leam
- Luke-Porings-Description
- Growing Luke-Pores from seeds
- leek seeds for seedlings
- Caring for leek seedlings
- When to plant leeks outdoors
- Soil for leeks
- Then how to plant leeks leek outdoors
- How to grow leeks
- Watering leeks
- Feeding leeks
- Processing of leeks
- onion Useful properties Leek - contraindications
Leek (lat.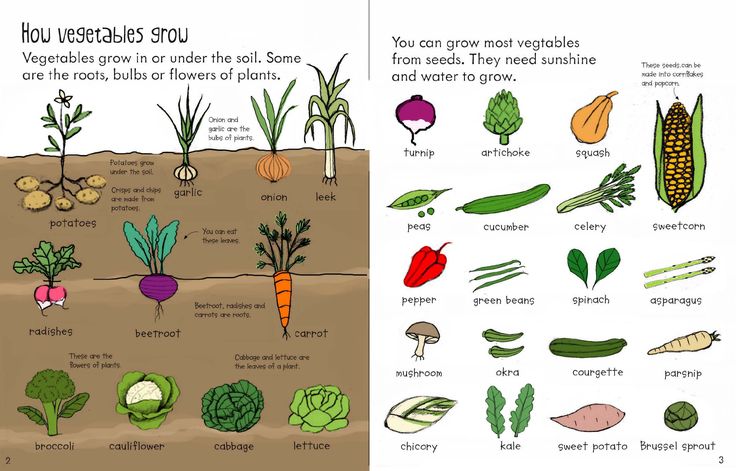 Allium porrum), or pearl onion - a herbaceous plant belonging to the genus Onion. The leek comes from Western Asia, but later it ended up in the Mediterranean, where you can still find its original wild form in nature - grape onion. Leek was well known in the countries of the ancient world - Egypt, Rome and Greece, and since the Middle Ages it has already been grown throughout Europe, it is especially popular in France - Anatole France called the leek asparagus for the poor. nine0005
Allium porrum), or pearl onion - a herbaceous plant belonging to the genus Onion. The leek comes from Western Asia, but later it ended up in the Mediterranean, where you can still find its original wild form in nature - grape onion. Leek was well known in the countries of the ancient world - Egypt, Rome and Greece, and since the Middle Ages it has already been grown throughout Europe, it is especially popular in France - Anatole France called the leek asparagus for the poor. nine0005
Today this type of onion is ubiquitous.
Planting and caring for leeks
- Planting: sowing seeds in open ground - before winter, in November. Sowing seeds for seedlings - in late February or early March. Sowing seeds in the greenhouse - in mid-April. Sowing seeds under the film - at the end of April. Planting seedlings in open ground - in early or mid-May.
- Lighting: bright sunlight.
- Soil: fertile, breathable, neutral reaction.

- Watering: regular. The first days after planting the seedlings, the bed is not watered, and then the soil is moistened on average once every five days, spending 10 to 15 liters of water per m².
- Top dressing: 3-4 times per season with organic and mineral fertilizers. The first time - three weeks after landing.
- Hilling the main procedure for the culture, which is carried out 3-4 times per season from mid-summer. nine0016
- Propagation: seeds.
- Pests: onion flies.
- Diseases: downy mildew, rust, viral mosaic.
- Properties: medicinal and dietary plant.
Read more about the cultivation of leeks below.
Leek – description
Leek is a herbaceous biennial growing from forty centimeters to one meter in height. In the first year of life, the leek forms a powerful root system, a false white bulb with a diameter of 2 to 8 cm and a length of 10-12 cm, turning into a false stem, and a large number of linear-lanceolate, fan-shaped green or bluish-green leaves. In the second year, in June-July, the plant develops a peduncle up to 2 m high with pink or white flowers forming an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, and in August or September, seeds similar to onion seeds ripen and remain viable for two years. nine0005
In the second year, in June-July, the plant develops a peduncle up to 2 m high with pink or white flowers forming an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, and in August or September, seeds similar to onion seeds ripen and remain viable for two years. nine0005
Leek is a cold-resistant culture demanding moisture. In the central and northern regions, it is grown in seedlings, and in the south it is sown directly into the ground.
Growing leeks from seeds
Sowing leeks for seedlings
The vegetation period of the crop is from 150 to 200 days, and to speed up the ripening process, leeks are grown in seedlings. If you decide to sow onions for seedlings at home, you need to do this in late February or early March. Sowing in the greenhouse is done in mid-April, and if you are going to grow on a bed under a film, then you need to sow leek seeds at the end of April. nine0005
For sowing, you will need containers at least 10-12 cm deep, as leeks have long roots. The dishes must be disinfected by washing in a strong solution of potassium permanganate, and the seeds should be kept in a thermos with warm water (40-45 ºC) for several hours, and then immediately lowered into cold water, and then dried to flowability.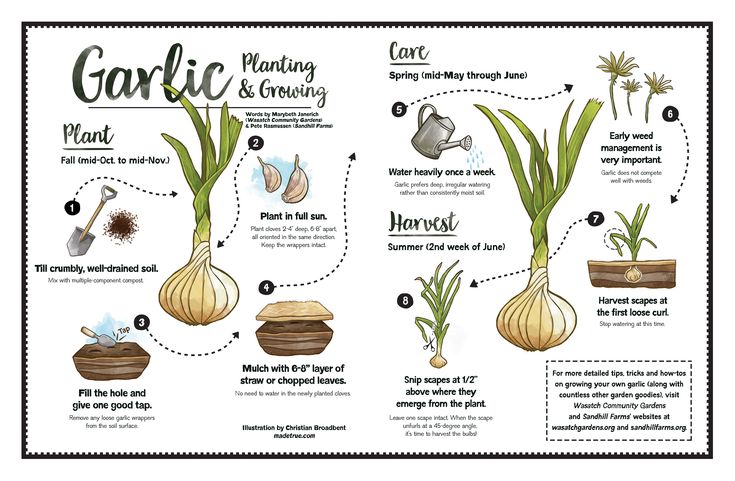 Fill the containers (it is better that they are separate pots or cups) with light sod-humus soil. Lightly tamp it and water well, then sow the leek seeds, cover them with a layer of sand 5 mm thick, cover with a film and keep at a temperature of 22-25 ºC until germination. nine0005
Fill the containers (it is better that they are separate pots or cups) with light sod-humus soil. Lightly tamp it and water well, then sow the leek seeds, cover them with a layer of sand 5 mm thick, cover with a film and keep at a temperature of 22-25 ºC until germination. nine0005
Care of leek seedlings
Plants should be aired daily, and to keep the soil slightly moist all the time, it is sprayed with a spray bottle. The first shoots appear after 10 days, and as soon as this happens, the cover is removed from the crops, they are exposed to bright diffused light, and the temperature is lowered during the day to 18-20, and at night to 12-14 ºC. The roots of the plants should be warm, so place a sheet of drywall or foam under the container with crops. Protect seedlings from direct sunlight and drafts. If the leek seedlings have sprouted too thickly, thin them out. Water the seedlings with warm water. nine0005
When the seedlings grow up and get stronger, they are fed with a solution of 20 g of ammonium nitrate, the same amount of potassium chloride and 40 g of superphosphate in a bucket of water per 1 m² of crops.
Planting leeks in open ground
When to plant leeks in open ground
From early days to mid-May, at the age of 50-60 days, leek seedlings are planted in the garden. On the eve of the leek seedlings, they should be watered abundantly, and in the process of transplanting, the leaves and roots of the seedlings are cut by one third. Planting leeks in the ground should be done in the late afternoon or on a cloudy day. nine0005
- How to grow a bumper crop of green beans
Soil for leeks
Choose an open and sunny site for cultivation, away from trees and shrubs that block the light. The soil needs fertile, neutral reaction, water and breathable. Too acidic soils need to be limed. A plot is being prepared for planting leeks in the fall: for each m², a couple of tablespoons of Nitrophoska, a teaspoon of urea and a bucket of compost or humus are added for digging. In the spring, you need to scatter compost and humus over the site at the rate of 3 kg per m², but you do not need to dig it up - fertilizer will fall into the soil when planting seedlings and subsequent watering. nine0005
nine0005
Leeks can then be planted
Leek grows well after crops such as peas, beans, soybeans and other legumes, green manure, cabbage, tomatoes and early potatoes, but leeks should not be planted in areas where the latter for three years some kind of onion grew.
How to plant leeks outdoors
On the sixth or seventh week after germination, the seedlings begin to harden off, taking them out into the open air for a short time during the day, but gradually increasing the duration of the procedure. Seedlings prepared for outdoor life will be ready for transplanting. nine0005
The area prepared for the leek is leveled and grooves are made on it with a depth of 10-15 cm at a distance of 20-30 cm from each other. The soil taken out of the furrows is fixed so that it does not crumble into the furrow. Leek planting is carried out in grooves at a distance of 10-25 cm between seedlings - depending on the variety. Before planting, the roots of the seedlings should be shortened to 4 cm and dipped in a mash, consisting in equal parts of clay, cow dung and water. Seedlings are lightly dug in the furrow, without filling it completely, and watered abundantly so that there is no air left around the roots. nine0005
Seedlings are lightly dug in the furrow, without filling it completely, and watered abundantly so that there is no air left around the roots. nine0005
Planting leeks before winter
Leek is often grown by sowing directly into the ground before winter. The site is prepared in advance, in the summer they dig up and fertilize, and in November the seeds are laid out every 8-12 cm into grooves located at a distance of 20 cm from each other. Keep a close eye on the weather forecast: if it is too warm, the onion will have time to sprout, which will almost certainly die in the subsequent cold snap. Crops for the winter are mulched with peat and humus, and then covered with snow - the more it is on the site, the better: the snow will melt for a long time, and the leek will sprout when the return frosts have passed. nine0005
How and when to plant leeks outdoors in autumn
Caring for leeks
How to grow leeks
Growing and caring for leeks involves following procedures that are familiar to every gardener.
So how do you grow leeks? It is necessary to carry out regular watering, weeding and loosening of the soil in the rows, to fertilize, to protect against diseases and pests, but the most important procedure that allows you to get a bleached stem - and this is the main value of the leek - is the hilling of plants, which must be carried out 3-4 times during the growing season. Hilling begins in the middle of summer, and after each procedure, the site is mulched with chopped straw, dry grass or dry manure. nine0005
- What are GMOs and how do such vegetables differ from varietal and hybrid vegetables?
As for loosening the soil around the plants, it should be carried out at least once every two weeks. As soon as the onion stalk reaches the thickness of a pencil in diameter, begin to gradually add the earth taken out of them during planting into the furrows during the loosening procedure. As soon as the furrow is completely closed, you can start hilling the plants.
Leek watering
Moisture is the basis for the growth of leeks, but the first three days after planting the seedlings in the garden, they should not be watered. In the future, watering is carried out approximately once every five days, spending from 10 to 15 liters of non-cold water for each m².
Top dressing of leeks
Feed 3-4 times per season. Three weeks after planting seedlings in open ground, it is necessary to water the soil with a solution of 20 g of ammonium nitrate and 15 g of potassium salt in 10 liters of water - this amount will be enough for you for 4 m² of beds. Leek also responds well to organic top dressing - a solution of mullein (1:10) or bird droppings (1:20). Before each hilling, sprinkle wood ash under the onion stalks at the rate of 1 glass of fertilizer per 1 m² of land. nine0005
Pests and diseases of leeks
Mosaic, a viral disease transmitted by aphids, is the most dangerous disease for leeks. You can identify the mosaic by the longitudinal yellow spots on the leaves of the onion. Affected plants are stunted.
Affected plants are stunted.
Leek also suffers from fungal diseases, downy mildew and rust. Peronosporosis, or downy mildew, is manifested by fast-growing oval spots on onion leaves. Affected plants become inedible. nine0005
Rust is also a fungal disease. It can be recognized by the bright yellow pads of fungal spores that appear on onion leaves. As the pads mature, they darken, then blacken, and the affected leaves dry up.
The main pest of leek is the onion fly, capable of causing irreparable damage to the crop. The onion fly can be seen already in mid-May - at this time it lays eggs in the soil and on the leaves, and after a couple of days larvae will appear that feed on the central part of the onion, which makes it rot and wither. nine0005
- Microgreens - fashionable and useful: what plants are suitable for growing microgreens?
Treatment of leeks
To protect the crop from the onion fly, the site is pollinated with wood ash at the rate of one glass of ash per m² of beds. Instead of ash, tobacco dust or a mixture of tobacco dust and ash can be used. The treatment of soil and plants with ground pepper repels the fly (one teaspoon of pepper per m² of plot). Whatever you pollinate the leeks, after processing, be sure to loosen the soil to a depth of 2-3 cm.
Instead of ash, tobacco dust or a mixture of tobacco dust and ash can be used. The treatment of soil and plants with ground pepper repels the fly (one teaspoon of pepper per m² of plot). Whatever you pollinate the leeks, after processing, be sure to loosen the soil to a depth of 2-3 cm.
Tobacco infusion has proven itself in pest control. It is prepared as follows: a tablespoon of liquid soap and 200 g of tobacco are added to 10 liters of hot water, insisted for several hours, then the infusion is filtered and the plants are sprayed with it.
In order to definitely scare away the onion fly from the leek, you can plant celery between its rows.
How to deal with leek diseases? The causative agents of fungal diseases are destroyed by treating plants and soil in the area with a solution of Fitosporin or copper oxychloride. Unfortunately, viral diseases, like a mosaic, are incurable, so they are only controlled by agrotechnical methods:
- crop rotation;
- weed and pest control;
- using disinfected seeds for sowing;
- immediate removal of diseased plants from the bed;
- cultivation of resistant varieties of leeks.

Harvesting and storing leeks
Harvest leeks before the temperature in the garden drops to -5 ºC, as the plant can only tolerate frost down to -7 ºC. Dig up the leek with a shovel and leave it for a while at the edge of the furrow to dry. Then the plants are cleaned of the earth, trying not to get between the leaves, the onion roots are cut a little and sent for storage. Don't cut the leaves! - this will lead to the rapid withering of plants. nine0005
Leek is stored in different ways. For example, in a cellar at a temperature of -1 to +1 ºC and an air humidity of about 85%. A layer of wet river sand about 5 cm thick is poured at the bottom of the box, leek stalks are placed vertically on it, and sand is again poured between them - in this form, the onion is stored for up to six months.
You can store the leek in a box with damp sand on the balcony - if the box is well covered, the leek will easily survive frosts down to -7 ºC.
To store leeks in the refrigerator, choose the best quality plants, cut their roots and leaves, cool to 0 ºC, then quickly lay out 6-8 stems in perforated plastic bags and store at -5 ºC for 4- 5 months. nine0005
nine0005
Leek is also stored in chopped form: washed, dried and chopped onion leaves and stalks are placed in a layer of up to 5 cm in plastic bags and stored in a freezer.
Types and varieties of leeks
According to the ripening time, leek varieties are divided into early, or summer, which are harvested in August or early September, mid-ripening, or autumn, ripening by October, and late, or winter.
Onion stalks of early varieties, which take from 130 to 150 days to ripen, weigh from 200 to 350 g, and reach 3 cm in diameter. by the end of July they become rough. nine0003 The most popular early maturing leek varieties are:
- Columbus is one of the best early maturing varieties of Dutch selection with excellent taste. In adulthood, the plant reaches a height of only 70-80 cm, and forms a leg 20 cm high, 6 cm in diameter and weighing 400 g. The advantage of the variety is that it does not need hilling to bleach the stem;
- Vesta is a productive variety, the plants of which reach a height of 150 cm, and the product stem, with constant hilling, can reach 30 cm in height and 350 g in weight.
 Vesta is distinguished by a wonderful sweetish taste; nine0016
Vesta is distinguished by a wonderful sweetish taste; nine0016 - Elephant's trunk - the leg of this variety is formed up to 30 cm high, but only as a result of repeated hilling. The Elephant Trunk is distinguished by a good sweetish taste and the ability to be stored for a long time;
- Goliath - a plant with a bleached part up to 30 cm tall, up to 6 cm in diameter, weighing up to 200 g, with broad green or grayish-green leaves and a weak bulb;
- Kilima is a high-yielding mid-early variety, in which the bleached part reaches a height of 10 to 25 cm and 3-4 cm in diameter, weighing about 150 g.
Mid-season leek varieties are not as productive as the early ones, but they are superior in quality. These varieties need 150 to 180 days to mature. Mid-season plants have blue-green leaves up to 7 cm wide and a stem weighing up to 200 g and up to 25 cm high. The best leek varieties in this group: up to 35 cm, with a weakly expressed bulb and narrow, grooved, vertically arranged leaves of dark green color with an anthocyanin tinge; nine0016 Late varieties of leek ripen for a long time - more than 180 days. Their productivity is the same as that of mid-season varieties, but they are stored longer. The leaves of the late onion are wide, blue-green in color, often with a waxy coating. They are very densely located on a false stem and depart from it at almost a right angle, which makes the plants look squat. Their legs are dense, thick and short. nine0003 Popular late varieties of leek are:  5 cm in diameter;
5 cm in diameter;
- Karantansky - the height of the bleached leg of this variety reaches 25 cm, the diameter is 4 cm with a weight of 200 or more grams.
 The leaves are wide, sprawling, dark green with a strong wax coating;
The leaves are wide, sprawling, dark green with a strong wax coating; - Elefant – frost-resistant and drought-resistant, spicy-tasting variety of Czech selection with stem up to 25 cm long and weighing about 200 g, blue-green leaves with a strong wax coating and a weak bulb; nine0016
- Bandit is a beautiful tall plant, bred by Dutch breeders, with a short thick stem of excellent taste. The variety is cold resistant;
- Autumn Giant is another variety of Dutch selection, which forms a large stem up to 40 cm high and up to 8 cm in diameter. The main advantage of the variety is its excellent keeping quality;
- Asgeos - winter-hardy variety with wide dark bluish-green leaves, weak bulb and stalk of semi-sharp taste up to 20 cm high, but weighing up to 350 g; nine0016
- Mercury – virus-resistant plant with dark green leaves, semi-acute stalk up to 25 cm high and weighing up to 200 g.

Properties of leeks - harm and benefits
Useful properties of leeks
Leek has a high content of vitamins (B2, B1, E, C), carotene, as well as protein substances, potassium salts, magnesium, iron, phosphorus, calcium and sulfur. This type of onion has the ability to increase the content of ascorbic acid by more than one and a half times during storage. nine0005
The healing properties of leek have been known since antiquity: it was used in the treatment of gout, scurvy, rheumatism, obesity, metabolic disorders, beriberi, exhaustion, urolithiasis, mental and physical fatigue.
Clinical studies have found that leeks have a choleretic and diuretic effect, increase appetite, improve liver function.
Leek is also used to slow down the development of oncological diseases, such as cancer of the intestines, prostate and uterus. In addition, it restores the body, gives strength and improves tone during the spring beriberi. nine0005
Leek is also used to heal abrasions and scratches, as well as to increase hemoglobin in the blood, in the treatment of tuberculosis and anthrax, streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, diarrhea, insomnia, chills, asthma attacks, arthritis and other diseases and disorders of the body.
Leek has a minimum calorie content, so it can be classified as a dietary product and recommended to anyone who watches their figure or fights obesity. Leek is used to prepare mashed soups, borscht, pickles, it is used as an ingredient in multi-component dishes - vegetable stew, scrambled eggs, casseroles, salads, leeks are also added to pizza. Braised leeks seasoned with lemon dressing are used as a side dish. nine0005
Leek - contraindications
Fresh leek is not recommended for diseases of the stomach and duodenum, but after heat treatment it will not cause harm. The product is contraindicated in diseases of the kidneys and bladder. Leek should be used with caution in people suffering from kidney stones, as it contains the substance oxalite. And overeating a leek can cause a headache even in a perfectly healthy person.
Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Learn more
- Quick home makeover ideas

- Efficient toaster oven

- Stairs balusters pictures

- 2023 kitchen design

- Trimming peonies after bloom

- Reading nook ideas living room
- New house interior ideas

- What should i use to clean walls
- What grows with cucumbers

- How to pick a hardwood floor color
.jpg)
- Cottage living room pictures
