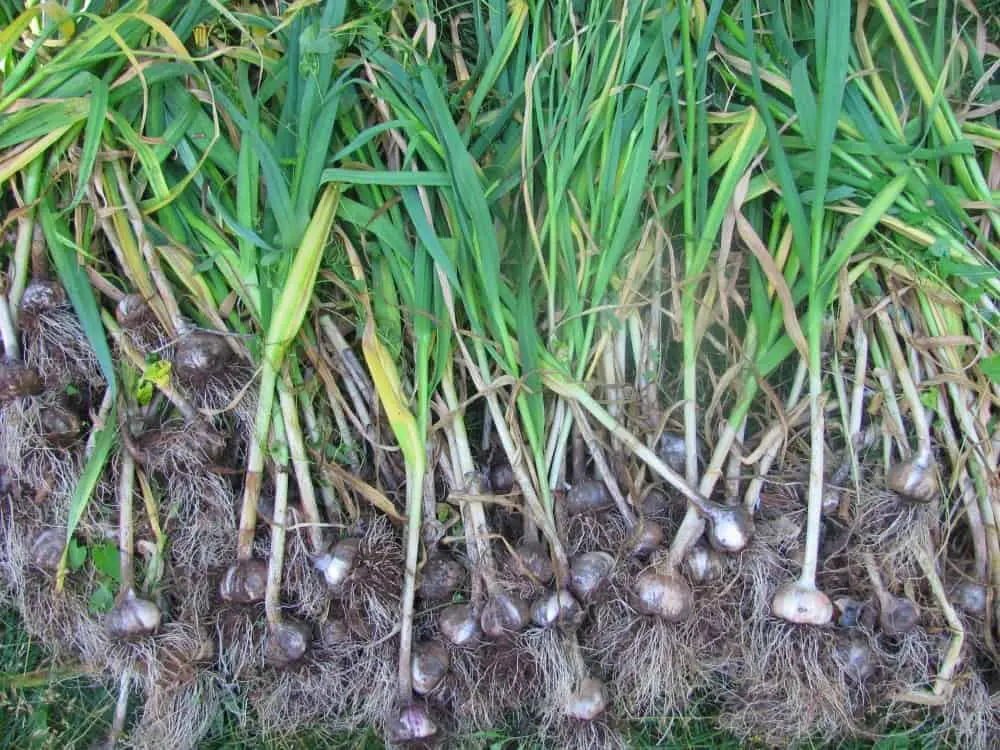
Home grown garlic
Grow Your Own Garlic - FineGardening
Fine Gardening Project Guides
Garlic isn’t hard to grow. In fact, growing garlic plants is almost ridiculously easy. It has a few important requirements that are easily met: decent soil, adequate moisture, and, of course, planting and harvesting at the right time.
When is the right time for planting garlic? Plant garlic four to six weeks before the ground freezes in your area. You can fudge the planting time a little. I have planted as early as September (by mistake) and as late as Thanksgiving (to experiment) and have had decent crops. Roots will start to grow soon after you plant. Your aim is to get good root development before the plants go dormant. Green shoots may appear in the fall, which is fine.
1. Prepare the soil
To grow nice, big heads of garlic, you need loose, fertile soil. Loosen the soil with a digging fork, spread a 2- to 3-inch-deep layer of organic matter over the area, and dig it in. For organic matter, I use a well-aged mixture of compost, leaf mold, and aged rabbit manure. To avoid disease problems, don’t plant garlic in the same spot two years running. Prepare several shallow furrows in the soil that are 6 inches apart.
2. Choose your varieties
| Hardneck garlic. Photo: Ruth Lively | Softneck garlic. Photo: Ruth Lively |
There are two main types of garlic: hardneck and softneck. Hardnecks have cloves growing around a hard central stalk. This stalk forms a curling scape (or flower stem) on top, which many growers cut off to redirect energy to the bulb. Softneck garlics form more cloves, with big ones around the outside of the head and numerous small ones at the center. Softnecks also tend to keep longer once harvested than hardnecks. Break apart a large head of garlic, and plant only the biggest cloves. The bigger the clove, the greater the likelihood it will yield a nice, big head of garlic. Save the smaller cloves to use in the kitchen.
3.
 Plant a clove, get a head
Plant a clove, get a headTo plant, place the cloves 4 inches apart in a furrow. Hold each clove pointed end up, and push it into the soil about 2 inches deep. After all the cloves are in the ground, smooth the soil surface using your fingers or a rake to fill in the holes, and water well. If you’re planting more than one variety, be sure to label each one clearly. I also make a map of my planting, in case the labels go astray. I wait to mulch for a month or more after planting to give the soil a chance to cool down. When it’s leaf-raking season, I put several inches of chopped leaves over the bed.
4. Fertilize and water
Photo: Melissa LucasTop growth starts in earnest in spring when the weather warms and the days lengthen. I fertilize twice with a solution of liquid kelp and fish emulsion: once, when the garlic has started growing strongly—about mid-April in my area—and, again, a month later. Garlic isn’t greedy for water, but it doesn’t like to dry out, either. When the soil feels dry an inch below the surface, it’s time to water. In mid-to-late June, I stop watering. By that time, the garlic has sized up and the heads are starting to form cloves.
When the soil feels dry an inch below the surface, it’s time to water. In mid-to-late June, I stop watering. By that time, the garlic has sized up and the heads are starting to form cloves.
5. Time the harvest carefully
Photo: Michelle GervaisHarvest in late spring or early summer when the plants have five or six green leaves, with no more than one or two beginning to turn brown. Each green leaf represents a wrapper layer surrounding the head. During harvest, you’re liable to damage the outer layer. Later, while cleaning the heads, you’re apt to lose another one or two layers. Your goal is to end up with two or three tight, papery layers enclosing each bulb. To harvest, drive a garden fork beneath the plants (be careful not to damage the bulbs), gently pry them loose, and then pull them out. Shake off any excess soil, and lay the plants in a pile. As soon as you’ve finished harvesting, move the plants to an airy location that is protected from sun and rain. If you’re growing more than one variety, keep each variety separate and well labeled so that you know what’s what.
If you’re growing more than one variety, keep each variety separate and well labeled so that you know what’s what.
6. Cure, clean, and store the heads
Photo: Michelle GervaisTo cure garlic in preparation for storage, hang the bare bulbs with their foliage in bundles or spread them out on a table or rack. You can begin eating them right away, but bulbs intended for storage must be cured.
After a few weeks of curing, it’s bulb-cleaning time. Trim the stalks to 12 inches above the bulb, and trim the roots close to the bulb. Rub off the outer layer of skin around the bulb, and use a nailbrush or toothbrush to gently remove any soil clinging to the base. Try not to remove more wrapper layers than you have to. Store the bulbs in a well-ventilated, dark spot. If you want, set aside the biggest bulbs for planting in the fall.
• ‘Georgian Crystal’—hardneck; four to six immense cloves per head; smooth, mild flavor
• ‘Gypsy Red’—hardneck; five to six large cloves; hot flavor
• ‘Inchelium Red’—softneck; 10 to 20 cloves; stores well; tops for taste, not too strong
• ‘Siberian’—hardneck; five to seven good-size cloves with beautiful, pinkish brown skins; rich flavor
—Ruth Lively is a former senior editor for Kitchen Gardener.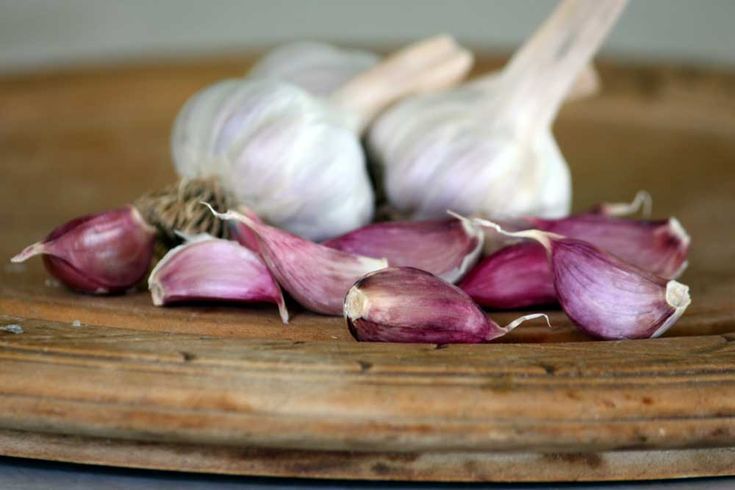 She grows garlic by the dozens in her garden in New Haven, Connecticut.
She grows garlic by the dozens in her garden in New Haven, Connecticut.
All photos, except where noted: Jennifer Brown
More on garlic:
How to Plant Garlic
Garlic Begets Garlic
Garlic as an Herbal Medicine
Previous: Plant an Asparagus Patch Next: Plant Garlic as a Fall Crop
View Comments
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and Vegetables
Growing your own food is easy with the help of this comprehensive step-by-step guide
View Project Guide
View All Project Guides »
Become a member and get unlimited site access, including the Fruits and Vegetables Project Guide.
Start Free Trial
Basics
- Planning
- Plant Collections
- Techniques
- Pests and Diseases
- Regional Advice
- Seasonal Extenders
Tomatoes
- Varieties
- Care
- Harvest
Cool-Season Crops
- Lettuce
- Peas
- Assorted Greens
- Carrots and Radishes
- Brassicas
- Rhubarb and Asparagus
- Garlic
- Root Vegetables
- Onions
Warm-Season Crops
- Peppers
- Corn
- Potatoes
- Eggplant
- Beans
- Cucumbers
- Squash, Pumpkins, and Melons
Herbs
- Perennials
- Basil
- Annuals
- Container Growing
- Edible Flowers
Fruits
- Trees
- Berries
- Citrus and Grapes
How To Grow Garlic | BBC Gardeners World Magazine
- March: sow varieties suitable for spring sowing
- April to June: water
- July or August: harvest garlic
- November or December: sow most varieties of garlic
It’s easy to think of garlic as a Mediterranean plant and therefore a tender crop that needs lots of warmth to grow well. However, if you choose a good variety and give it the right conditions, you can produce a decent crop no matter where you live in the UK.
However, if you choose a good variety and give it the right conditions, you can produce a decent crop no matter where you live in the UK.
Garlic needs a long growing season to do well, and autumn through to early winter is the perfect time to sow so that plants develop roots and shoots before the heavy frosts. Some varieties can be sown in spring.
Home-grown garlic takes up little space and requires hardly any effort to get a good crop. It's an easy crop to grow – it's sown from garlic cloves as opposed to seeds. The certified garlic bulbs are sold at garden centres or online.
There are two types of garlic to grow: softneck garlic and hardneck garlic.
Softneck varieties
The most common type in supermarkets. It produces the greatest number of cloves per bulb – up to 18. It has a white, papery skin, stores well and rarely produces a flower stalk. Softneck garlic is less tolerant of prolonged cold temperatures and is therefore best suited to growing in mild southern counties, though it can be grown elsewhere with protection in the winter.
Hardneck varieties
Hardneck garlic has fewer cloves per bulb – usually 10 or less. They are generally hardier than softneck types and can be grown throughout the UK. Hardneck types will often produce a curling flower stalk or ‘scape’. This straightens out as it matures, to carry a head of tiny clove-like bulbils. It is best to remove the scape as soon as it appears (use it in stir fries) so that the plant will divert its energies into producing a larger bulb. If left to develop on the plants, you can harvest and plant the bulbils, but it may take 2-3 years to form a decent bulb.
There's also elephant garlic, which bears giant, mild-flavoured bulbs, which you can grow for a lighter garlic taste.
Growing garlic
Grow garlic in a warm, sunny spot, in fertile, well-drained soil that doesn't get too wet in winter. Garlic is usually planted in late autumn or early winter (although some cultivars can be planted in early spring). It can be sown directly in the ground, or started off in small pots if you have heavy soil.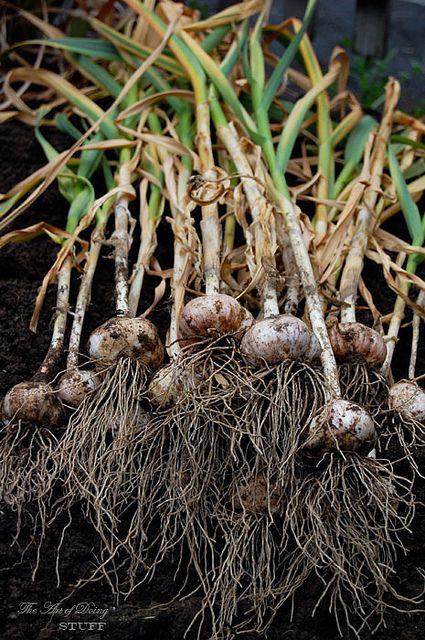 It can also be grown in a large container.
It can also be grown in a large container.
More like this
Whichever way you decide to grow garlic, always buy bulbs at the garden centre or order from a seed supplier – don't use bulbs from the supermarket. Break up the bulbs into separate cloves and plant the large ones with the fat end downwards and the pointy end 2.5cm below the soil surface. Harvest from July onwards, once the top growth has begun to die back. Leave the bulbs to dry in the sun for a few days before storing.
Growing garlic: jump links
- Planting garlic
- Caring for garlic
- Growing garlic: problem-solving
- Harvesting garlic
- Buying garlic
- Garlic varieties to grow
How to plant garlic
How to grow garlic - planting garlic cloves
Most varieties of garlic are best planted in late autumn or early winter, as the cloves need a period of cold weather to develop into bulbs.
Make sure your soil is cleared of weeds and the remains of summer crops.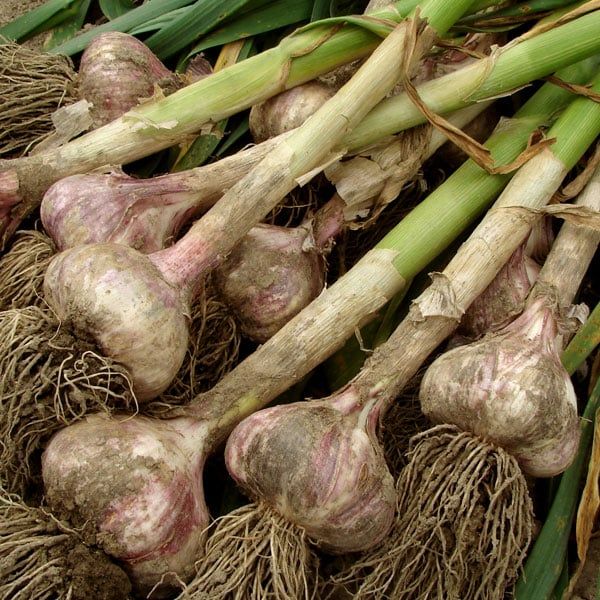 Before planting, dig in some home-made compost or well-rotted manure and rake over well. Push cloves in, or use a dibber to make holes 15cm apart, leaving 30cm between rows. Birds have a penchant for the bulbs and will pull them out of the soil, so lay bird netting or horticultural fleece over new plants until the shoots are 5cm tall. In cold areas, you may need to cover plants with cloches over winter. This extra protection will encourage root growth, so plants are ready to grow next spring.
Before planting, dig in some home-made compost or well-rotted manure and rake over well. Push cloves in, or use a dibber to make holes 15cm apart, leaving 30cm between rows. Birds have a penchant for the bulbs and will pull them out of the soil, so lay bird netting or horticultural fleece over new plants until the shoots are 5cm tall. In cold areas, you may need to cover plants with cloches over winter. This extra protection will encourage root growth, so plants are ready to grow next spring.
Here, Monty Don demonstrates how to plant garlic, with advice on planting depth and varieties to grow:
If you have heavy clay soil, you can start garlic off by planting cloves singly in module trays in autumn and growing them on in a cold frame. This prevents the bulbs rotting off in very wet soil during winter. You can then plant these out in spring, when the soil has dried out a little. You could also try growing garlic in mounds 15cm tall and 20cm wide at the base. Plant the garlic cloves into these mounds, 15-20cm apart and 7-10cm deep. Because the soil is slightly raised, it doesn't get as wet, so the garlic is less likely to rot.
Because the soil is slightly raised, it doesn't get as wet, so the garlic is less likely to rot.
How to grow garlic – starting garlic off in pots
How to grow garlic in a container
If you have no space, or your plot has been affected by onion white rot in the past, then growing in containers is for you. Use any pot that's at least 15cm wide and deep, filled with multipurpose compost. Sow three cloves in a 15cm wide pot, six in a 30cm one. Feed from April when you see strong spring growth, using a high nitrogen feed such as dried chicken manure pellets, or fill the container to the top with more compost. Stop feeding in mid May.
Watch Monty plant garlic in a container, with advice on drainage and feeding:
Where to buy garlic online
- Dobies
- Thompson & Morgan
- Van Meuwen
- Suttons
- You Garden
How to care for garlic
Garlic needs little care. Water regularly in spring and early summer, but reduce once you see the foliage turning yellow – this is a sign that the bulbs are reaching maturity. Weed between the plants to reduce the competition for water and nutrients. This is best done by hand, as hoeing could damage the developing bulbs. Remove any flowers, or 'scapes' the plants produce – you can eat these in stir-fries.
Weed between the plants to reduce the competition for water and nutrients. This is best done by hand, as hoeing could damage the developing bulbs. Remove any flowers, or 'scapes' the plants produce – you can eat these in stir-fries.
Growing garlic: problem solving
Garlic is generally pest free and is only affected by a few problems.
Birds
Birds, especially pigeons, will take freshly sown garlic cloves from the ground and will also eat recently germinated plants. Cover the area with netting or horticultural fleece immediately after sowing and don't remove until the young plants are at least 5cm tall.
Onion white rot
Onion white rot is hard to detect until it's too late – the first sign that anything is wrong is usually yellowing, wilting foliage but this is usually around harvest time, when you'd expect the leaves to be dying back anyway. When you dig up the plant, you'll notice a white fluffy fungus on the base of the bulb, along with tiny black growths. In severe cases, the bulb will be black and rotten.
In severe cases, the bulb will be black and rotten.
Onion white rot is a soil-borne disease, so there is no control and the problem can persist for years. Avoid spreading the problem around the garden on boots and tools, as the disease can affect the whole allium family, including onions and leeks. Dig up all of the affected plants and bin or burn them – do not add them to the compost heap. You may be able to salvage some of your crop to eat, but it won't store well. In future, grow garlic in containers, in fresh soil that does not come from the garden.
Leek rust
Garlic can be affected by leek rust, a fungal infection that is more common in wet weather. There is no cure. Orange pustules appear on the leaves in summer, which then begin to die back. The bulbs are perfectly safe to eat but it's a good idea to harvest affected plants immediately, to prevent the disease spreading, and to eat them straightaway. Dispose of the rest of the plant material (bin or burn it, don't add to the compost heap) and avoid growing garlic, leeks and onions in the same place for three years. Choose a variety that has some resistance to rust, and space plants out to reduce humidity.
Choose a variety that has some resistance to rust, and space plants out to reduce humidity.
Watch Monty Don's video guide to dealing with rust on garlic:
How to harvest garlic
How to grow garlic - harvesting garlic
Harvest garlic in summer when the leaves turn yellow. Gently lift out bulbs with a fork or trowel, taking care not to damage the bulbs. Leave the garlic to dry out for a couple of days, by laying it out on a table or tray, in full sun.
Watch Monty Don's video guide to harvesting garlic:
How to store garlic
How to grow garlic - plaiting garlic
Once the bulbs are dry and feel papery to touch, you can either store them loose or plait their foliage to make a traditional string of bulbs. Store in a cool, dry place. Take care not to bruise the bulbs, as any damage can make them deteriorate in storage. Bear in mind that Softneck garlic varieties store better than hardneck garlic and should keep for several months, so eat the hardneck varieties first.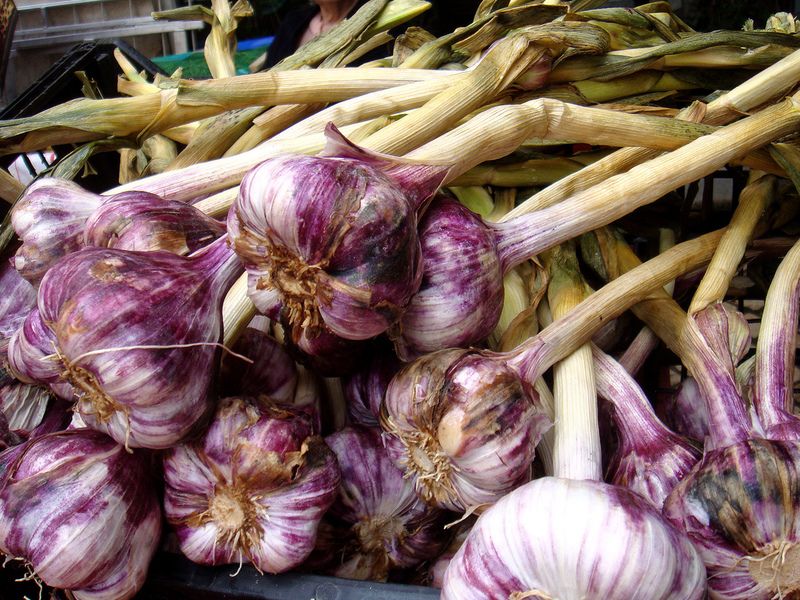
How to prepare and use garlic
Crush, slice or finely chop, or roast cloves whole, to add flavour to many dishes. Hardneck varieties tend to have more flavour than softnecks, so work well when roasted whole.
- Try BBC Good Food's recipe for garlic butter
Watch this 20-second video demonstration from our friends at olive magazine on how to chop and crush garlic.
Can you plant supermarket garlic?
It is possible to grow garlic from supermarket bulbs, but it's not recommended as there's a risk of virus infection. If you buy from proper planting stock, it should be virus free. And you can also choose a variety that has been bred especially for our climate.Advice on buying garlic
Here’s our guide to buying garlic, including where to buy garlic.
- Always buy from a garden centre or online seed supplier – do not use bulbs from the supermarket
- Choose from softneck or hardneck garlic.
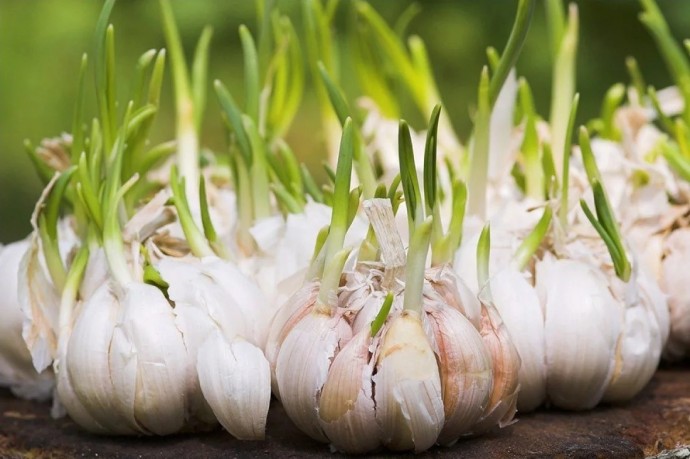 Softneck varieties tend to be hardier and last longer, but hardnecks are said to have more depth of flavour
Softneck varieties tend to be hardier and last longer, but hardnecks are said to have more depth of flavour - Check the garlic bulbs to make sure they have no signs of mould, and are firm to touch
Where to buy garlic online
- Dobies
- Thompson & Morgan
- Van Meuwen
- Suttons
- You Garden
Great garlic varieties to grow
1
Garlic 'Albigensian Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Albigensian Wight'
A heavy cropping, softneck variety from south west France. It has large bulbs and is a heavy cropper.
- Buy garlic 'Albegisian Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
2
Garlic 'Chesnok Red'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Chesnok Red'
This hardneck variety hails from the Ukraine and has attractive purple stripes. It’s said to be the best variety for garlic bread.
- Buy garlic 'Chesnok Red' from Thompson & Morgan
3
Garlic 'Early Purple Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Early Purple Wight'
This softneck variety produces mild, purple-tinged bulbs. As its name suggests, it crops very early, from mid May. It doesn’t store well, so use within three months.
As its name suggests, it crops very early, from mid May. It doesn’t store well, so use within three months.
- Buy garlic 'Early Purple Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
4
Garlic 'Iberian Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Iberian Wight'
This softneck variety from Spain has large bulbs with plump cloves. Good for plaiting, it stores well.
- Buy garlic 'Iberian Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
5
Garlic 'Solent Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Solent Wight'
This softneck variety was bred on the Isle of Wight, so is well suited to the UK climate. It has small bulbs with a strong flavour and keeps well.
- Buy garlic 'Solent Wight' from Crocus
6
Garlic 'Christo'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Wight Christo'
This softneck variety is reliable and easy to grow and produces large bulbs. It can be planted in autumn or spring stores well.
- Buy garlic 'Christo' from You Garden
cultivation, planting, care in the open field
There are 2 varieties of garlic: winter and spring (1).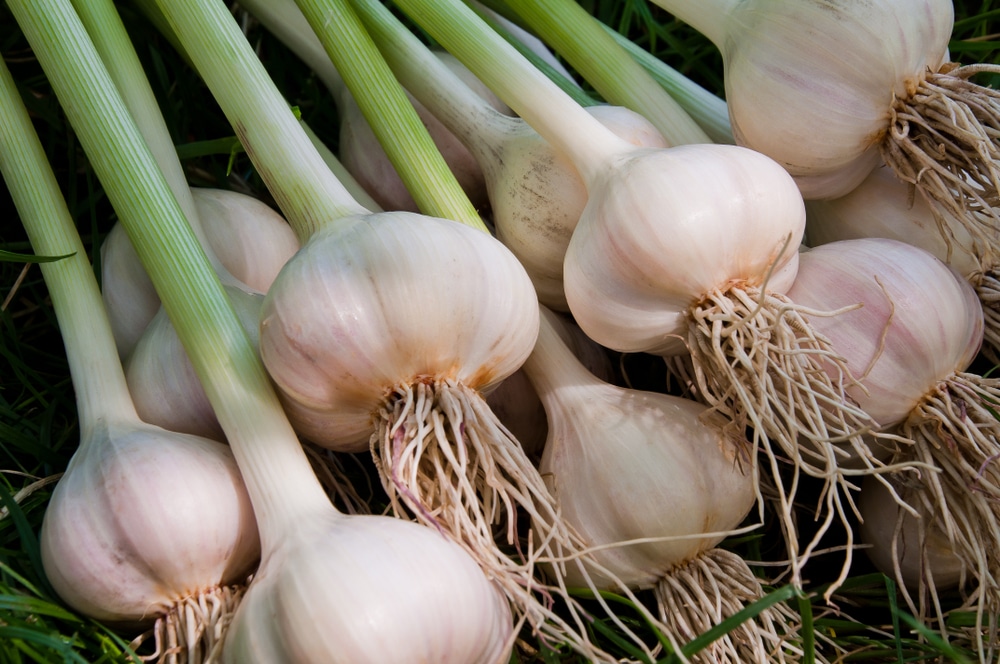 You can tell them apart by the bulbs.
You can tell them apart by the bulbs.
Winter garlic. It has an even number of cloves in the head - from 4 to 10. They are large and arranged in a circle. And in the center there is always a stem - the rest of the stem. The problem with winter garlic is that it does not store well.
Spring garlic. His teeth are arranged in a spiral, and they are of different sizes - larger on the outside, closer to the center - smaller. And there are many more - up to 30 pieces. And there is no stem in the center. This variety of garlic is perfectly stored - it can easily lie for a whole year until the next harvest.
Winter garlic is planted before winter, spring - in the spring, respectively, their care has differences.
Cultivation of garlic
Garlic is a rather unpretentious crop; in many gardeners it grows almost without care and gives good yields. But still, he has one requirement - the soil must be pedigree. Therefore, before planting on the site, fertilizers must be applied (calculation per 1 sq. M):
M):
- humus - 1/2 bucket;
- rotted sawdust of deciduous trees - 1/2 bucket;
- ash - 5 glasses;
- fluffy lime - 5 cups.
Fertilizers should be mixed, spread evenly over the area and dug up by 10 cm. And he does not like urea and potassium chloride.
Place for garlic should be sunny - this is a light-loving crop.
Planting garlic
The timing of planting garlic depends on its variety.
Winter garlic. It is traditionally planted 2 - 3 weeks before the onset of hard frosts, in late September - early October (2), when the soil temperature drops below 15 °C.
Planting pattern is as follows:
- row spacing - 25 cm;
- in a row - 10 - 15 cm;
- planting depth - 8 - 10 cm.

Spring garlic. It is planted in the spring, no later than the end of April (3). He is not afraid of frosts, therefore, the earlier you plant, the more likely it is that the crop will have time to ripen - this is especially true in regions with a short summer. The optimum soil temperature is 5-6 °C.
Planting pattern:
- row spacing - 25 - 30 cm;
- in a row - 8 - 10 cm;
- planting depth - 2 cm.
The cloves are planted at a depth of 3 - 4 cm, and when they begin to take root, they themselves go deep into the soil by 6 - 8 cm (4).
Outdoor garlic care
Watering. It should be regular, but up to a certain point:
- in April-May - once a week: 10 liters per 1 sq. m
- in June-July - 1 time in 2 weeks: 10 liters per 1 sq. m;
- from August it is not possible to water.
In rainy summers, garlic does not need watering.
Top dressing. As a rule, in fertile areas of this crop, it is enough that they were applied to the soil before planting. On poor soils, it is useful to additionally feed it with phosphorus and potassium - fertilizers must be applied between the rows 2 weeks after planting the cloves:
As a rule, in fertile areas of this crop, it is enough that they were applied to the soil before planting. On poor soils, it is useful to additionally feed it with phosphorus and potassium - fertilizers must be applied between the rows 2 weeks after planting the cloves:
- double superphosphate - 30 g (2 tablespoons) per 1 sq. m;
- potassium sulfate - 20 g (1 tablespoon) per 1 sq. m.
- Winter garlic is important to cover in the winter - mulch with humus, compost or peat with a layer of about 5 cm, - advises agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova. - This should be done in late autumn, at the end of November. The mulch will help keep the bulbs from freezing if the winter turns out to be snowless and the frosts are severe. In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, the mulch must be removed so that the cloves in the soil do not get wet.
“Caring for spring garlic also has its tricks,” continues Svetlana Mikhailova. - It happens that in the cold summer, the ripening of the bulbs slows down, and they may not have time to ripen before the autumn frosts. In this case, in mid-August, you can collect the leaves in a bunch and tie them in a knot - then they will stop growing, the plants will direct all their forces to the ripening of the bulb.
In this case, in mid-August, you can collect the leaves in a bunch and tie them in a knot - then they will stop growing, the plants will direct all their forces to the ripening of the bulb.
Garlic harvesting
Garlic harvesting time also depends on the variety.
Winter garlic. It is usually harvested at the end of July. There are three signs that it is already ripe:
- the covering skin begins to crack on the inflorescences, and the bulbs are exposed, but this only applies to arrow varieties - yes, garlic arrows usually break out (5), but you can always leave a couple of plants with inflorescences to use as beacons;
- lower leaves turn yellow;
- The outer, covering scales of the bulb become dry - this can be seen if you dig up one plant.
Spring garlic. It is removed later - around the end of August. Most varieties of this group do not form arrows, so yellowing of the leaves and lodging of the tops can serve as a visual signal for harvesting.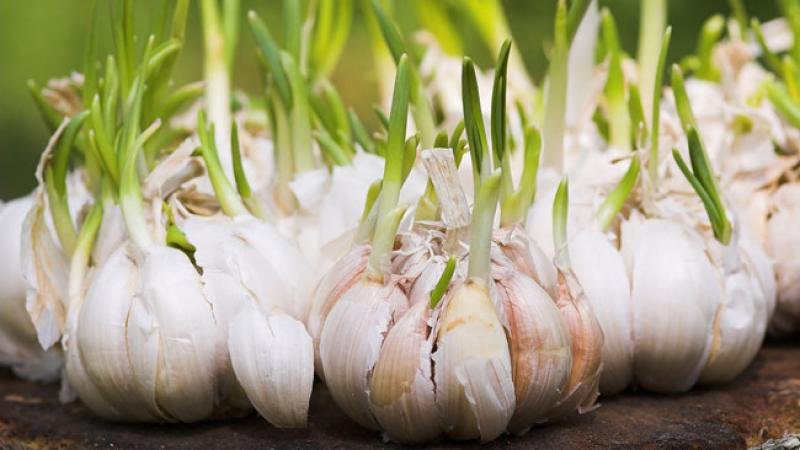
– It is better to dig up garlic with a pitchfork – this way there is less chance of damaging the bulb, recommends agronomist Svetlana Mikhailova. - You need to dig in dry weather. After harvesting, the garlic, together with the tops, is removed to dry - for about a week it should lie under a canopy.
After drying, cut off the roots and stems of the bulbs, leaving a stump of about 10 cm (if the garlic is to be stored in braids, the stems are not cut).
Garlic storage rules
There are many ways to store garlic, but practice shows that almost all of them are unreliable. The best way is to braid the plants in the same way as you do with onions.
But there are nuances here:
- garlic stalks are hard and brittle, it is difficult to braid them, so you need to weave straw or twine there;
- Braids should be stored at a temperature of 1 - 2 °C - onions are stored at room temperature, and garlic dries quickly in heat.

Large heads are stored longer, so the small ones should be eaten first.
Popular questions and answers
agronomist Svetlana Mikhailova answered our questions about growing garlic.
Should garlic cloves be peeled before planting?
No way! Covering scales - reliable protection of teeth from mechanical damage, diseases and pests. Peeled cloves will rot rather than germinate.
Should winter garlic be watered after planting?
No. It will be enough for him to take root in the autumn rains. Over watering can cause tooth decay.
Can winter garlic be planted in spring?
It makes no sense. For winter varieties, it is important that there are low temperatures after planting. And the spring is too warm. If planted in April, the bulbs will grow inferior and will not be stored. And besides, underdeveloped teeth cannot be used for planting - they form roots very slowly and freeze out in winter.
Is it possible to plant spring garlic before winter?
It is possible, but spring varieties, when planted in autumn, take root worse and often freeze, therefore, they will give a crop much less than winter varieties.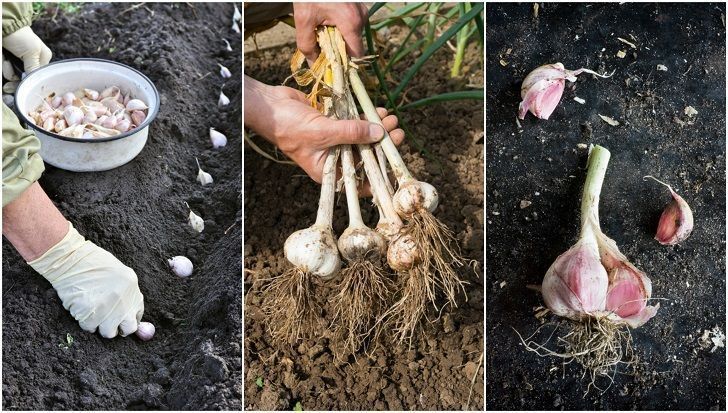
Why does winter garlic turn yellow in spring?
There may be 4 reasons:
- cold spring - in such a situation, the leaves begin to grow, and the roots cannot yet extract nutrients from the soil;
- lack or excess of moisture in the soil;
- acidic soil;
- Fusarium disease.
Sources
- Fisenko A.N., Serpukhovitina K.A., Stolyarov A.I. Garden. Handbook // Rostov-on-Don, Rostov University Press, 1994 - 416 p.
- Pantielev Ya.Kh. ABC vegetable grower // M .: Kolos, 1992 - 383 p.
- Group of authors ed. Polyanskoy A.M. and Chulkova E.I. Tips for gardeners // Minsk, Harvest, 1970 - 208 p.
- Shuin K.A., Zakraevskaya N.K., Ippolitova N.Ya. Garden from spring to autumn // Minsk, Uradzhay, 1990 - 256 p.
- Yakubovskaya L.D., Yakubovsky V.N., Rozhkova L.N. ABC of a summer resident // Minsk, OOO "Orakul", OOO Lazurak, IPKA "Publicity", 1994 - 415 p.
everything about it, what does the plant and crop look like in the photo, vegetable, fruit or not, whether it is a root crop, and what family it belongs to
- Growing (67)
- Varieties of garlic (11)
- Healing properties and harm (45)
Surely many have heard that garlic can help get rid of many diseases, infections and viruses. It is known in many countries for its beneficial properties and for its spicy, piquant taste. The culture can be consumed in different forms, added to dishes and snacks, tinctures or healing masks can be made. But they should not be abused, as negative consequences may appear.
It is known in many countries for its beneficial properties and for its spicy, piquant taste. The culture can be consumed in different forms, added to dishes and snacks, tinctures or healing masks can be made. But they should not be abused, as negative consequences may appear.
Garlic is a vegetable crop that belongs to the genus Onion and the Amaryllis family. It is a perennial herbaceous plant, which is characterized by a sharp taste and a sharp specific smell due to organic sulfides in the composition.
Appearance, photo and botanical description
The culture bulb is rounded ovoid, consisting of 2-8 cloves depending on their size. With the help of these "teeth" a new vegetable crop is planted.
Photo of garlic heads
At the bottom of the white or pink-purple bulbous root is the root system. An even stem often twists at the top into a ring. There is a dome-shaped peduncle, which is covered with a transparent film. But this crop gives seeds in rare cases; they are not suitable for planting a new crop.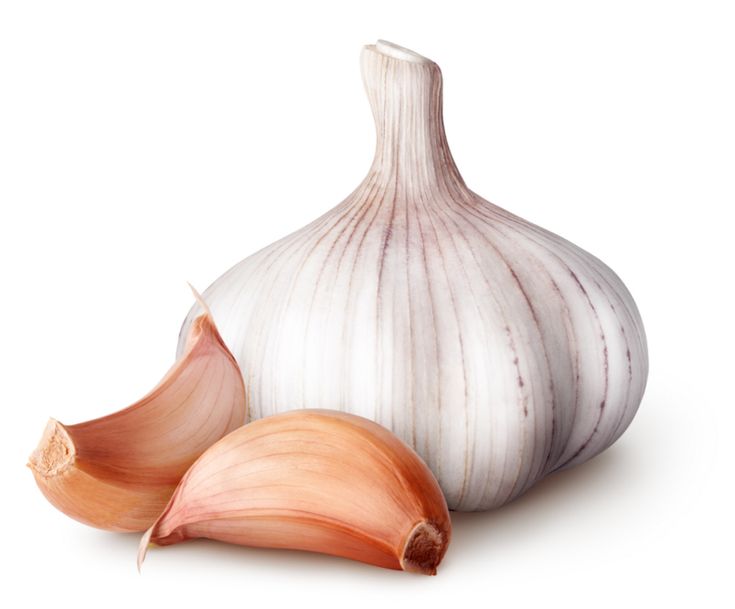
The length of the flat linear green leaves can be up to one meter. The top leaf grows from the inside of the previous one, which allows the stem to be stronger than that of onions.
Garlic blooms, like all of the Onion family: the flower is collected in a spherical shape and has bulbs, in which small vegetable cloves are formed.
Help
There are those that have large purple or lilac "balls" of flowers.
Origin
Asia is considered to be the birthplace of vegetables. The first to grow it were Uzbeks, Turkmens, residents of Afghanistan and Iran.
Ancient Egypt and Greece not only used the plant to add spice to dishes, but also believed that garlic had mystical powers, or rather, protected from many troubles and angry spirits. During excavations, even in the tomb of Pharaoh Tutankhamen, this useful culture was discovered.
Nowadays, China and India occupy the first places in cultivation. Russia took an honorable fourth place. The amount of harvest in our country exceeds even the United States.
Russia took an honorable fourth place. The amount of harvest in our country exceeds even the United States.
Structure
The plant consists of aboveground and underground parts.
Above the ground are:
- leaves are flat and bright green, which reach 1 meter in length, their width is up to 1 cm;
- peduncle or arrow is a dense stem that grows almost one and a half meters in length, the spiral top ends with an umbrella inflorescence;
- inflorescence similar to a spherical umbrella with many small white or pink flowers;
- the fruit is a small boll on an arrow that forms after flowering. Seeds rarely ripen, so they are not suitable for propagation.
The underground part is divided into:
- the bulb is round and slightly flattened, may be yellowish, white, pinkish or purple in color, consists of 3-20 cloves, each of which is covered with a hard shell;
- rhizome is tufted, arranged in a circle and grows to a depth of 60-70 centimeters.

Spring and winter varieties
Exists . One of the main ones is the time of planting - the spring variety is planted in the spring, and the winter variety is planted in late autumn or early winter. Hence, the latter has a well-developed root system, which manages to develop during cold weather. The spring species takes at least ten days to root, it matures for a long time.
The average gardener prefers the winter variety because its yield is much higher than the spring variety. Also, the ripening period for a winter vegetable is shorter.
But since garlic, which is planted before winter, grows arrows with bulbs, and they take away the nutrients of the vegetable, this makes the bulb smaller. If you remove the peduncle, then everything will work out, but this is quite a laborious job when entire crop fields are grown. Hence the price for such a product is much higher. Therefore, large farms prefer spring garlic, it also has much more cloves.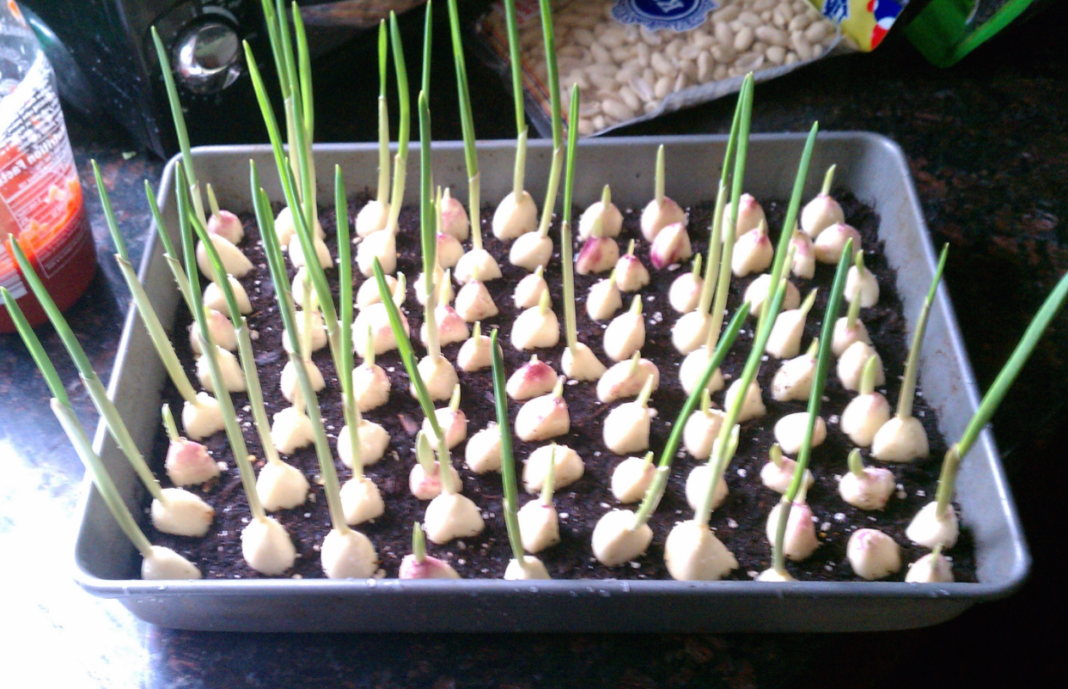
The leaves of each plant are also different, in the winter variety they are large and few, in the spring variety there are a large number of narrow leaves.
Benefits and harms
Benefits of garlic:
- strengthens the immune system;
- fights viruses and infections;
- treats arthritis;
- cleanses the liver;
- removes toxins from organisms;
- improves the activity of the gastrointestinal tract;
- lowers blood pressure;
- reduces the level of cholesterol in the body;
- reduces the amount of sugar in the blood.
Harm can be manifested in diseases such as:
- anemia;
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- hemorrhoids;
- allergy.
Attention!
There were cases when garlic in large quantities led to spasms of cerebral vessels.
There are a number of contraindications to the use of vegetables. They are:
They are:
- Low blood pressure.
- Cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
- During lactation, introduce the product gradually and consume no more than one clove per day.
- The presence of gastritis requires medical advice.
- During pregnancy, only the first two trimesters can be consumed.
- Garlic is not recommended for children under three years of age. Fresh can be consumed from 3-4 years old, and thermally processed - from 8 years of age.
Could it be an allergy?
There are cases when an allergy to garlic has manifested itself. Often this is due to the content of aplicin in the composition of the vegetable or to chemicals that the crop has absorbed during fertilization or pest control and infection.
Allergic reaction occurs due to erroneous perception of the garlic protein by the immune system.
Allergy manifests itself with skin rashes, redness and watery blisters. May be accompanied by sneezing, choking cough, nasal congestion and copious mucus, as well as diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain and fever.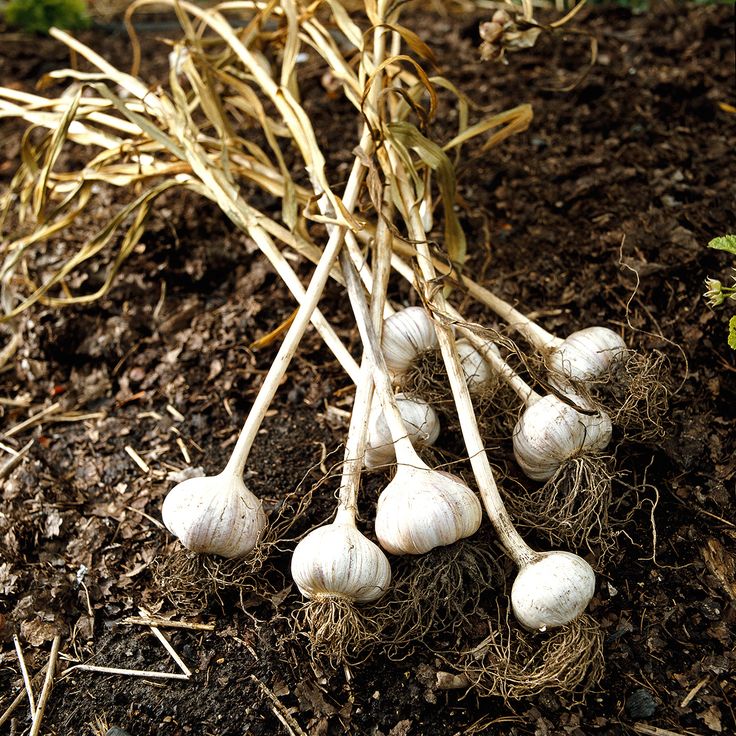 The worst is swelling of the entire face and Quincke's edema (swelling of the airways).
The worst is swelling of the entire face and Quincke's edema (swelling of the airways).
Important!
If the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor or provide first aid.
Treatment
Garlic can help treat diseases such as:
- infections;
- oncology;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- liver diseases;
- problems with the nervous system;
- the appearance of blood clots in the vessels;
- obesity.
Recipes for general health
For the first recipe you will need:
- 4-6 spice cloves;
- 1 lemon.
Two ingredients to be crushed and mixed. You need to eat 1 teaspoon before meals twice a day.
The second strengthening recipe is prepared from the same ingredients, only in a different quantity:
- lemon - 4 pieces;
- garlic - 4 cloves.
The juice is squeezed out of the lemon, the garlic is minced.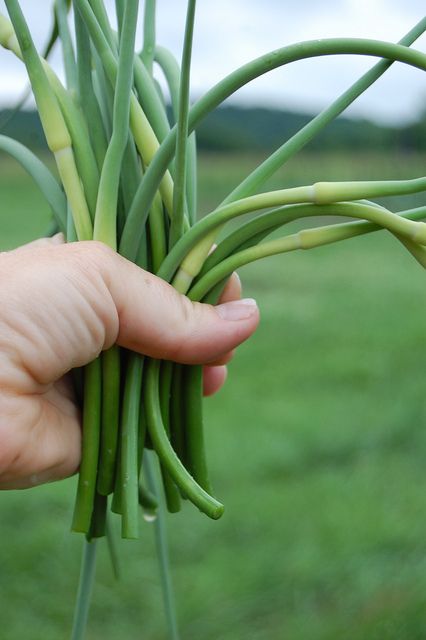 Everything is placed in a three-liter jar, poured with boiling water and infused for three days in a dark, cool place. Then everything is filtered and poured into a bottle, stored in the refrigerator. A quarter cup is taken three times a day.
Everything is placed in a three-liter jar, poured with boiling water and infused for three days in a dark, cool place. Then everything is filtered and poured into a bottle, stored in the refrigerator. A quarter cup is taken three times a day.
The third recipe is prepared from:
- lemon - 1 piece;
- garlic - 5 cloves;
- ginger root - 100 g;
- honey - 50 g.
All ingredients are crushed, mixed and infused for 24 hours. For strengthening, you need 1 tablespoon twice a day.
Varieties should be selected according to planting time, climate, soil and end result. The most popular spring varieties are Abrek, Aleisky, Gulliver, Yelenovsky, Degtyarsky and Flavor.
Winter garlic is represented by such species as Komsomolets, Alkor, Garkua, German, Moskal, Lyubasha, Messidor, Sofievsky, Parus and Spas.
Important! When choosing a vegetable variety, you need to pay attention to the growing season and the amount of harvest at the end.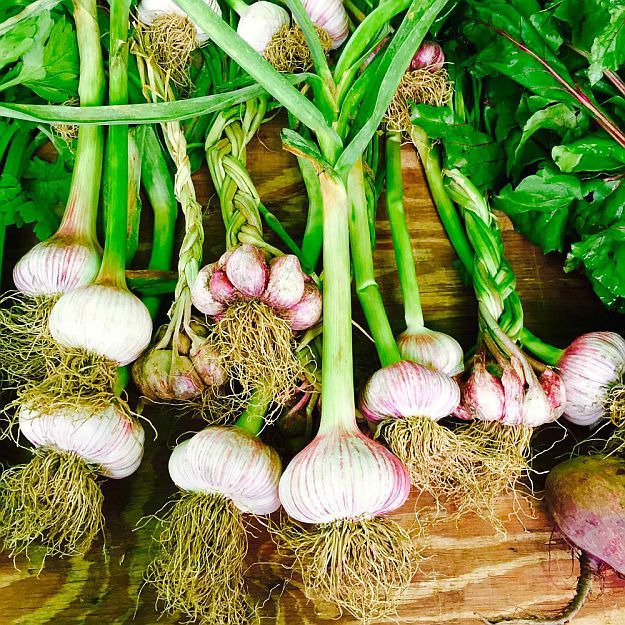
is an unusual variety. It is characterized by a fragrant and rich taste. It is easy to grow and the flowers of this plant are also used in cooking.
is a fermented herb that has been re-tasted to be sweet and does not have a strong garlic odor.
Wild garlic, wild garlic or "bear's onion" is used in cooking and for medicinal purposes. In Russia, it is popular in pickled form. It is an onion with a garlic smell.
Planting
Planting of cloves begins in autumn or spring, depending on the variety. So winter varieties are planted in September-October, and spring varieties - in April. The soil must be prepared in advance by fertilizing with humus.
For planting it is necessary to select large and healthy cloves, which must first be disinfected in a weak solution of potassium permanganate before planting. With a sharp end up, the teeth of the culture are placed in the grooves at a distance of 10-15 cm and at the same depth. To prevent diseases, you can pour ashes at the bottom of the groove. Then everything is covered with earth and watered.
Then everything is covered with earth and watered.
Care
Garlic care consists of weeding once every two weeks, top dressing as soon as the bulb begins to branch, and watering when the soil dries out. Over-watering can lead to crop rot. We must not forget to pull out the weeds, and fertilize several times a season.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting begins when the leaves turn dry and yellow (late summer-early autumn). It is best to do this on a cloudy day in the morning or evening. The winter variety is ready for harvest already in July, the spring variety - in August-September.
Carefully remove the bulbs from the ground, clean them from the ground and put them to dry. Then you can trim the roots and leaves. Read more here.
Store garlic in a box or braid in the pantry. It is important to remember that the room air temperature should not exceed +5 degrees. Also, the vegetable can be stored dried, pickled or frozen.
Diseases and pests
Garlic, like any crop, can be affected by various pests such as onion flies, root mites, weevils and many others.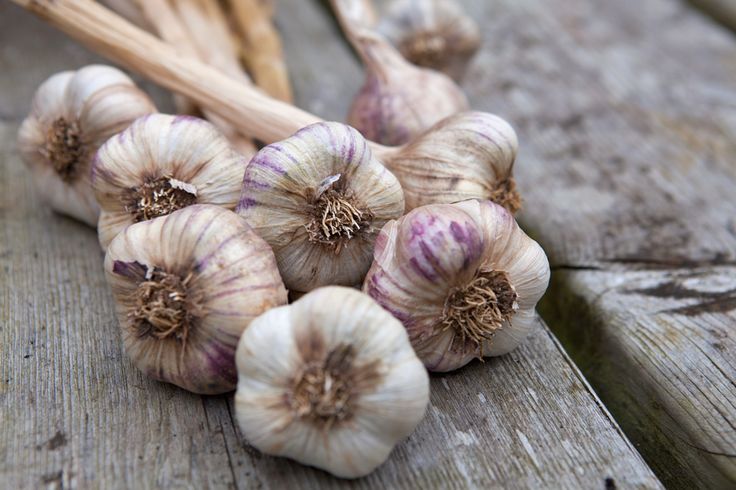 These "unwanted guests", as well as improper care, can lead to infections and diseases, such as mosaic, rot or fungus.
These "unwanted guests", as well as improper care, can lead to infections and diseases, such as mosaic, rot or fungus.
How to get rid of the smell after drinking?
can be with sour fruits and juices, spicy herbs (parsley), milk, coffee, green tea or mint tea, mints, heavily menthol gum or by brushing your teeth. Rinsing your mouth with a salt and baking soda solution will also help get rid of this odor.
Garlic ingestion by animals
It is best not to give garlic to pets such as cats to avoid poisoning. But green vegetables to prevent the appearance of worms.
In addition, garlic and its infusion can help get rid of small rodents, as well as birds that intend to eat fruits.
Garlic is widely used in many countries. And this is not surprising, because he is not whimsical in care, if you follow the basic rules, and the beneficial properties of this vegetable are simply excellent. But you should always remember that it is impossible to abuse this plant in order to avoid the manifestation of negative consequences.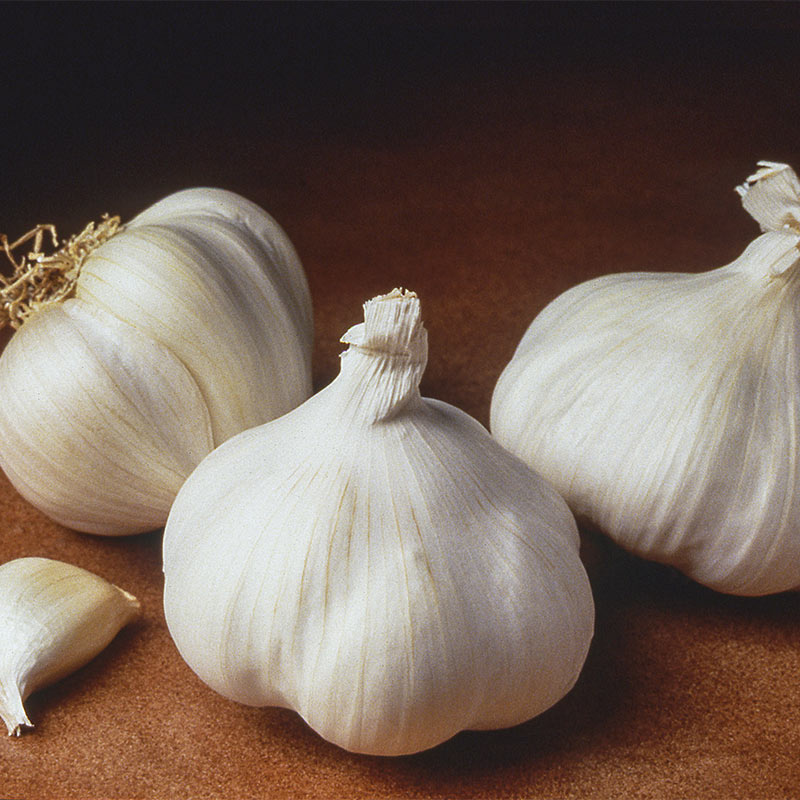
Articles from the heading "Garlic"
Garlic is an unpretentious crop; it is grown both in the southern regions of Russia and in colder regions, including the Urals and Siberia. Siberia occupies a considerable part of the territory of our ...
Garlic is winter and spring. The first is planted in spring or autumn. It is spicier in taste and propagated by bulb cloves. Spring garlic is planted in the spring to get ...
Characteristics of varieties of winter garlic are given. The main differences between this type of crop and spring crop, the predominant characteristics, and selection criteria are indicated. The terms of planting depending on the area are described, lists of varieties by cultivation regions are given.
The winter garlic variety Dobrynya, which has recently appeared on Russian fields and gardens, has already managed to attract the attention of gardeners and farmers. Let's figure out what are the advantages and disadvantages of this variety, and how to properly grow Dobrynya.
Let's figure out what are the advantages and disadvantages of this variety, and how to properly grow Dobrynya.
Garlic variety Grigory Komarov is a relatively new selection result. What are its advantages and disadvantages?
Agat is a new Russian variety of winter arrow garlic. Let's figure out when it is useful when growing.
The climate of the Urals is favorable for the cultivation of garlic both in winter and spring planting. Agrospecialists recommend cultivating proven, cold-resistant and disease-resistant varieties.
Varietal characteristics of garlic Rocambole. The benefits and harms of the product, its use in cooking and medicine are given. A step-by-step instruction for growing a plant and storing a crop is considered.
Large varieties have become very popular among gardeners and consumers. Their diversity allows you to choose the right one for everyone individually, depending on the taste and properties. It is only necessary to properly care for the culture and observe all storage conditions so that such a healthy vegetable is always on the table.
It is only necessary to properly care for the culture and observe all storage conditions so that such a healthy vegetable is always on the table.
Let's talk about a new unique variety of garlic - Lyubasha. We will describe in detail the care and cultivation of the crop, as well as ways to preserve the crop.
Grow a cool crop of garlic and make money from it. Everyone can afford their own business. Maximum profitability and minimum risks.
All about winter garlic "Komsomolets". Complete information about the variety, planting technology, care, harvesting and storage of the crop.
Variety Bogatyr, its advantages and disadvantages. Instructions for planting and further care of the culture are given. Diseases and pests affecting garlic, as well as preventive measures are considered.
We tell you how to feed winter and spring garlic correctly and at what time, how to prepare the beds before planting.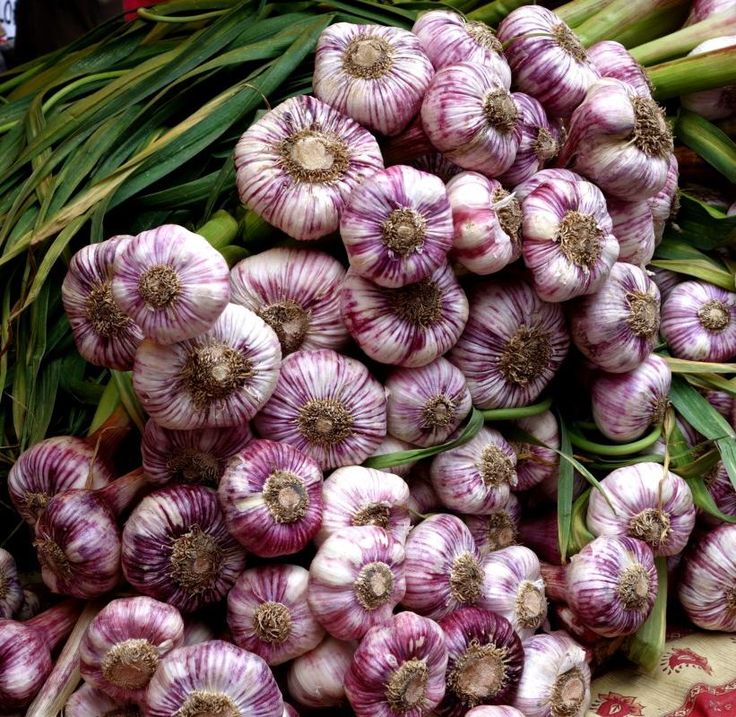
Learn more
- Preparing hydrangea for winter

- Best non slip bathroom flooring

- How tall does nasturtium grow

- How to plant corn from seedlings
- Biggest homes in california

- How to remove clover from a lawn

- French country look interior decorating

- Weed killer with epsom salt and vinegar

- Seeding lawn grass

- Hallway table decorating ideas

- Little kids bedroom
