Fruit from a tree
27 Different Types of Fruit Trees (Plus Fruitful Facts)
Interested to know and learn about all the different types of fruit trees? Here's a massive list of them with photos and detailed descriptions.
All cultures have hundreds of cultural connections to their local fruits and various legendary myths about their magical healing or restorative qualities. Even if not magical, fruits are an essential part of the human diet, and fruit-producing trees have evolved over billions of years, alongside every other species, beautifully linked with the ecosystem.
Fruits are an important part of nearly every type of cuisine in the world; in many places, native fruits are even made into expensive delicacies. The Densuke watermelon from Japan, for example, is said to have a ‘special kind of sweetness’ that makes people pay thousands of dollars for one. Farmed on a northern island of Japan, only a hundred grow every year!
Fruits are also a vital source of nutrition. Almost all vitamins that we need for the healthy functioning of our bodies can be found in fruits. However, trees do not produce fruits just for us. Fruits are seed houses for trees; they are a mechanism through which plants can spread their genes as far and wide as possible so more of their kind populate the land.
The ovaries of flowering trees turn into fleshy, dry, or ripe fruits. Seeds are the fertilized ovum of a tree, therefore when they are planted, a new tree is born. Fruits are not found exclusively on trees, but also shrubs, small plants, or ground vegetations. The main objective of fruit trees is to attract various land animals, birds, insects, and humans to their fruits so that they can be consumed and their seeds replanted. That is why fruits taste delicious.
So what makes a fruit tree and how many types of fruit trees are there exactly? Read this article to find out all about the fruit trees that supply important vitamins and enzymes to our diet. Interestingly, this article on the different varieties of fruit trees also reveals the many different types of fruit you can eat – but not all (such as berries which don’t grow on trees).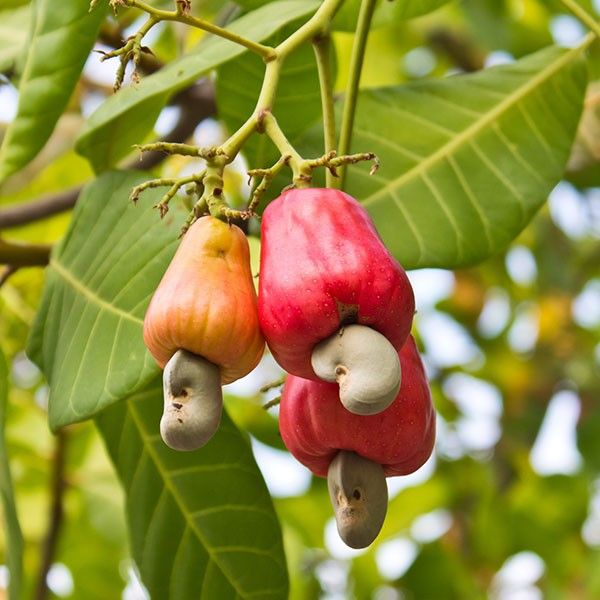
Related: Types of Trees | Types of Ficus Trees | Fruit Trees for Growing Indoors | Fruit Tree Flowers | Backyard Fruit Tree Ideas | Types of Figs | Types of Palm Trees
Fruits in Our DietThe fruits we eat genuinely seem like a gift from nature. A small bowl of pineapple, for example, fulfill 131% of our daily requirement for vitamin C, and 76% for manganese. Grapefruits are known for their ability to reduce insulin levels in the blood while balancing your cholesterol and preventing kidney stones.
Avocados consist mainly of healthy fats but are also packed with loads of potassium and magnesium. All of these nutrients are known to promote heart health. Blueberries, on the other hand, are rich in antioxidants that reduce the risk of heart disease and Alzheimer’s while giving the immune system a boost. Pomegranates have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce the risk of cancer.
Besides these, there are many other fruits that are a source of dietary fiber, rare vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants which makes them an indispensable part of the human diet.
430 million years ago in the Devonian period, the first seed-producing trees came about. Through the entire Carboniferous period to the quarternary period today, trees have been flourishing on the earth. Trees evolved further with every generation, adapting more and more to the environment. Just by existing, they provided enough oxygen and temperature balance to the planet. It is because of the sublime relationship of trees with the planet that complex organisms came about, who paved the way for human life to evolve as well.
Since trees rely on their fruit to disseminate their seeds, their fruits evolved to be edible to birds and other animals. Some fruits are even selectively edible. The jalapeno fruit, for example, has a chemical called capsaicin, a pepper that scares of all animals except humans, who know better. Birds are however immune to capsaicin, so they can feast on these peppers and send out their seeds as far as they can fly.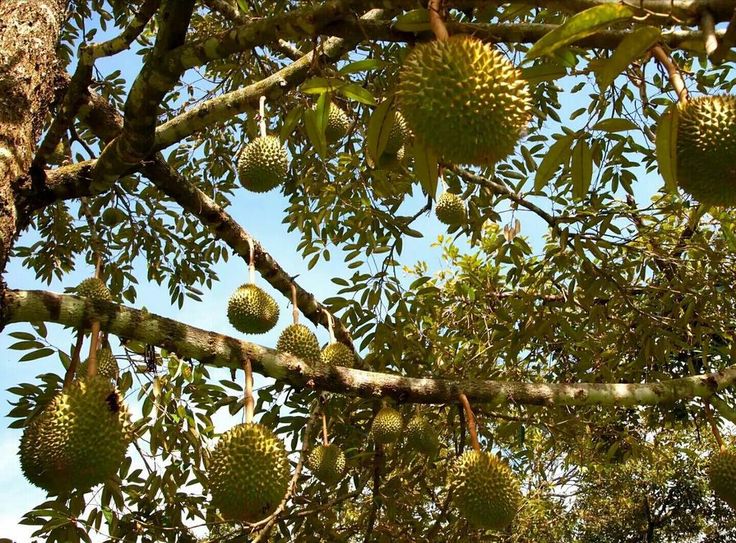
Source: Royal Forestry Society
Fruit Trees in the EcosystemAn important role that fruit trees play in the ecosystem is the primary conversion of sunlight into food for other secondary members of the food chain. Photosynthesis is not only beneficial to plants as it produces food for them, but also stores excess energy in fruits, leaves, stems, and sometimes even roots. When we incorporate plants in our diet, the nutrients in them benefit us immensely.
All ecosystems are built on a system of energy transfer. Planet Earth is powered by its sun, but animals usually do not have the tools to convert this energy into a usable form. So plants do their job for them, and the energy transfer continues in the form of food webs. Many animals such as birds, lizards, and invertebrates depend on plants for their food, which in turn are preyed on by other tertiary animals.
Trees are taller for the very purpose of harboring as much sunlight as possible to convert into functional energy; this gives them plenty of raw materials to produce delicious and nutritious fruits for us.
Source: Science Learning Hub
Habitat and Geographical OccurrenceFrom the forests of the Amazon to deserts and savannahs, fruit trees are found everywhere in their different forms and variations. Each continent has several specialized species that have evolved suited to the climate and landscape. Except for Antarctica, which has very low plantation level in general, fruit trees are a common feature of every continent.
Source: LibGuides
Fruits in Different CulturesFruits are usually considered a symbol of abundance, fertility, and reward. Some common fruits have been around for so long that they have become part of the local mythology and culture.
Many such myths and stories seem to surround apples. In Greek mythology, Hercules had to acquire a special type of apple as one of his twelve great labors. In Norse mythology, apples represent eternal youth, and Adam and Eve were banished for heaven for eating the apple of ‘knowledge’. Even Snow White was poisoned by her stepmother through an apple.
Even Snow White was poisoned by her stepmother through an apple.
There are interesting origin stories for some fruits as well, like Tahiti, where legends claim that the first coconut came from the head of an eel called Tuna. To the Romans, the pomegranate was a symbol for marriage, and earlier brides wore pomegranate plant wreaths on their heads. The Greeks also considered them a symbol of beauty, love, marriage, and fertility. For Muslims around the world, pomegranates are fruits from heaven.
Types and SubtypesPome FruitsPome fruits are members of the plant family Rosaceae, and subfamily pomoideae. These are fruits that have a tough, fleshy, edible membrane on the outside covering the core of small seeds in the center.
Some main pome fruits are apples, pears, and quince, which are harvested in late summer to late autumn months.
Source: Department of Primary Industries
Stone Fruits or DrupesDrupes or stone fruits are indehiscent, which means that they have an outer fleshy part that surrounds the single shell inside housing the seeds.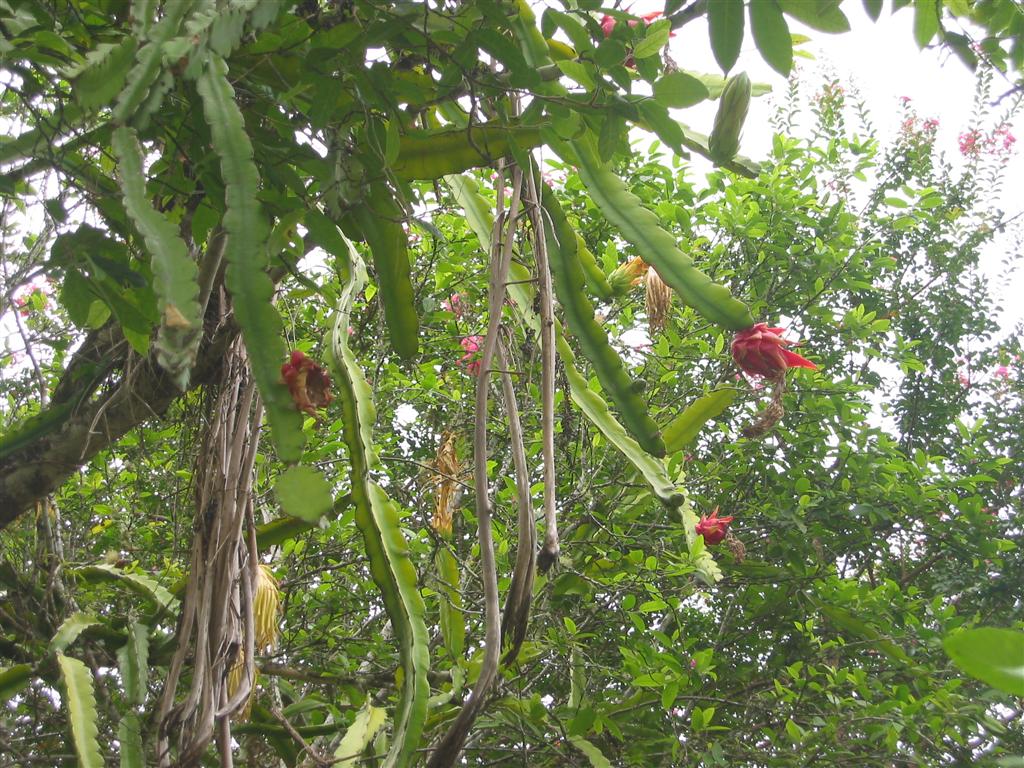 They usually develop from a single carpel and include fruits as mango, olive, coconut, apricot, cherry, peach and plum amongst many others.
They usually develop from a single carpel and include fruits as mango, olive, coconut, apricot, cherry, peach and plum amongst many others.
Source: University of California
Common Fruit TreesBelow we list, explain and provide pictures of the many common fruit trees throughout the world.
ApplesApple trees are extremely popular to plant because of their value as nutritious snacks. There are various species of apple trees found in different parts of the world. They have huge amounts of fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, and potassium. They reduce the risk of diabetes and cancer, even Alzheimer’s in older people.
The pectin content in apples is another notable health benefit. Pectin is a fiber that feeds the good bacteria in your gut, which in turn helps in improving your metabolic health
OrangesOranges are one of the most popular and nutritious fruits in the world.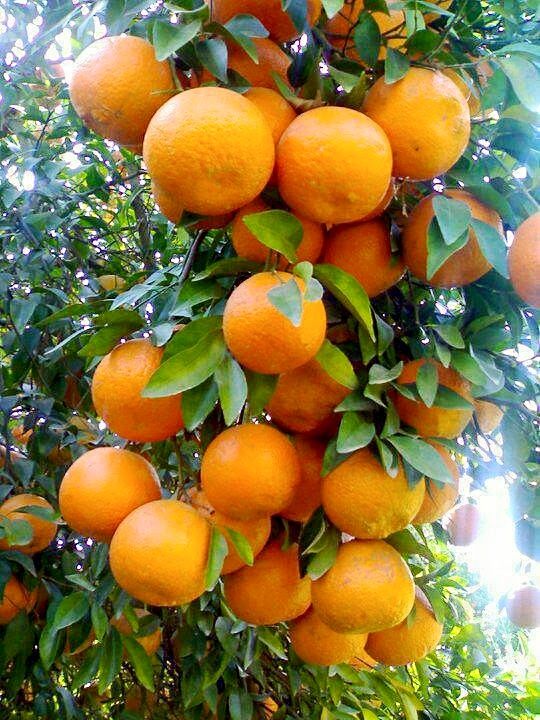
Orange trees are not only aesthetically pleasing to plant in your garden, but also provide a large quantity of vitamin C and potassium. They supply vitamins such as thiamine and folate as well
The citric acid found in oranges may help in the dissolution of kidney stones and a healthy hydration supply in the body.
Source: Healthline
MangoesThere are many variations of the delicious mango fruit, and they are especially found in the SouthEast Asian region. Mangoes are an excellent source of vitamin C, and they also contain soluble fiber with several health benefits.
Mangoes also contain antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that lower the probability of contracting diseases, especially diabetes.
LemonsLemons are similar to oranges in the impressive amount of vitamin C and citric acid they contain. In the human body, lemons help in increasing iron absorption, which helps in the prevention of anemia.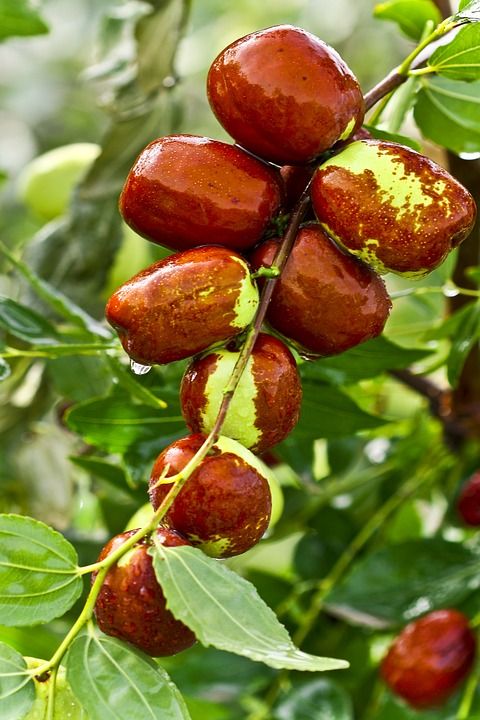 Lemons are also known to help in curbing nausea, improving metabolism, and improving skin conditions.
Lemons are also known to help in curbing nausea, improving metabolism, and improving skin conditions.
Once planted, lemon trees take at least 3-5 to produce fruit, so choose something else if your time is constrained.
Source: Nature and More
PearsIf you choose to plant a pear tree in your backyard or garden, you may be in for a rewarding experience. If taken care of properly, a pear tree can grow to be up to around forty feet tall! They can be grown in a variety of regions in Europe, Asia, and northern Africa.
Not only is the pear fruit full of protein and fiber, but the tree itself can also be a wonderful addition to your garden because of its character, and its ability to survive for over 50 years.
Source: Harvest to Table
ApricotsApricot trees, when not producing fruit, are decorated by the blooming pink and white flowers. This tree in your garden will add vibrant beauty to the surroundings. Some care is required to make sure the fruit you obtain is healthy, but the tasty apricot yield will convince you to expend some labor on these trees.
Some care is required to make sure the fruit you obtain is healthy, but the tasty apricot yield will convince you to expend some labor on these trees.
Apricots have lots of vitamin A and copper, which are rare vitamins to be found in fruits. They can also strengthen your heart and bones if eaten every day.
Source: Gardening Know How
CoconutsCoconut trees or more commonly palm trees, belong to family Arecaceae and are an important addition to any beach atmosphere. Although there are over 150 species spread in over 80 countries, coconut trees only grow in a tropical climate.
Coconuts as fruits are highly beneficial to humans. From their water and their flesh to oil and milk, coconuts are versatile. As foods, they provide us with a rich source of fatty acids, ascorbic acid, proteins, and other B vitamins. Taking them in abundance can also help in restoring damaged tissues in the body.
Having all this fascinating information about fruit trees can help you decide what you would like to plant in your backyard. A fruit tree is an investment that does not only provide shade and oxygen to the environment but also gives you and children plenty of healthy food to eat. It’s spring season, get planting!
A fruit tree is an investment that does not only provide shade and oxygen to the environment but also gives you and children plenty of healthy food to eat. It’s spring season, get planting!
Source:
OwlcationPlumPlums are said to be some of the first fruits humans domesticated. They have many types, but the one commonly found is purple in color. It is differentiated from similar fruits like peaches because of the shoots possessing a terminal bud and non-clustered solitary side buds. If the weather is not humid enough, the fruit will stop growing past a certain point and fall from its tree while still in small, green form. Moreover, if the humidity is too much, plums need to be harvested as soon as possible, otherwise the fruit can develop brown rot, which is a fungal condition.
Some different plum species are damson, which has purple skin, greengage which is bright green in color, the Mirabelle which is tinted dark yellow, the Satsuma red plum, and the Victoria plum which has yellow flesh while its skin is red or mottled.
Plums consist of 87% water, some vitamin C, and plum juice can be made into plum wine.
AlmondAlmond is a drupe fruit, which has an outer hull and a hard shell that contains seed. This makes almond a fruit and not a true nut, inside. The twigs are green when they are young; taking on a purplish hue on the sides exposed to sunlight, and then turning grey in another year. The best places to grow almonds are Mediterranean climates where there are warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The most favorable temperature for almond trees is between 59 and 86 °F.
Almonds are sold with or without their shell, and ‘shelling’ almonds refers to removing the shell to reveal the seed in order to make the fruit edible.
Some researchers have managed to develop hybridized variations of almond trees that are self-pollinated and have a high nut quality, in order to accelerate growth and improve worth.
Source: Wikipedia
Indian GooseberryThe leaves of the Indian gooseberry tree are simple, sub-sessile and narrowly spaces; they are light green in color and resemble pinnate leaves.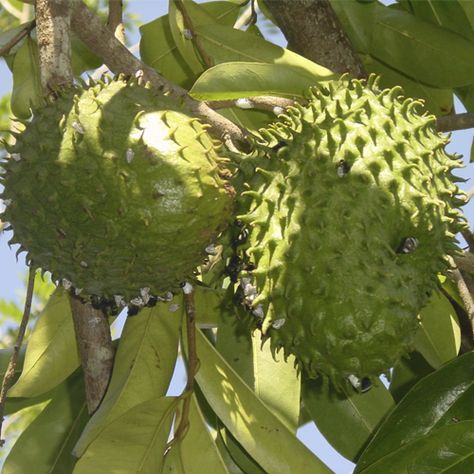 The flowers in full bloom are tinged greenish-yellow, and the fruit is quite round, greenish-yellow, smooth and hard to the touch.
The flowers in full bloom are tinged greenish-yellow, and the fruit is quite round, greenish-yellow, smooth and hard to the touch.
The berries ripen in autumn, when they are picked by hand as harvesters climb to high branches that bear fruits. The taste of this berry is sour and bitter, and the texture fibrous. In India, the berry is submerged in salt water and red chili powder is added to make it more appetizing.
Source: Wikipedia
CherryCherry trees grow in temperate climates of high latitude; and like most trees of this nature, cherry trees need a cooling period each year to avoid dormancy and bear fruit. How much cold is required is dependent on the variety, but because of this condition, no species of Prunus can successfully grow in tropical places.
In the Middle East, Europe, North America, and Australia, there are many varieties of the cherry tree that are harvested and exported. The genus contains more than 40 members, some of which are Prunus apetala, Prunus avium (sweet cherry), Prunus campanulata (Taiwan cherry, Formosan cherry or bell-flowered cherry), Prunus canescens, Prunus caroliniana Aiton, amongst many others.
The Morus genus comprises of about 10–16 kinds of deciduous trees that are known as mulberries. Mulberries can grow in the wild and under cultivation in temperate climates
Southern Europe, the Middle East, northern Africa and the Indian subcontinent are all home to mulberries in their various forms, particularly black, red, and white.
The ripe fruit is used in pies, tarts, wines, and teas. The black mulberry and the red mulberry, native to southwest Asia and eastern North America respectively, have the strongest flavor that is often describes as ‘fireworks’ on the tongue.
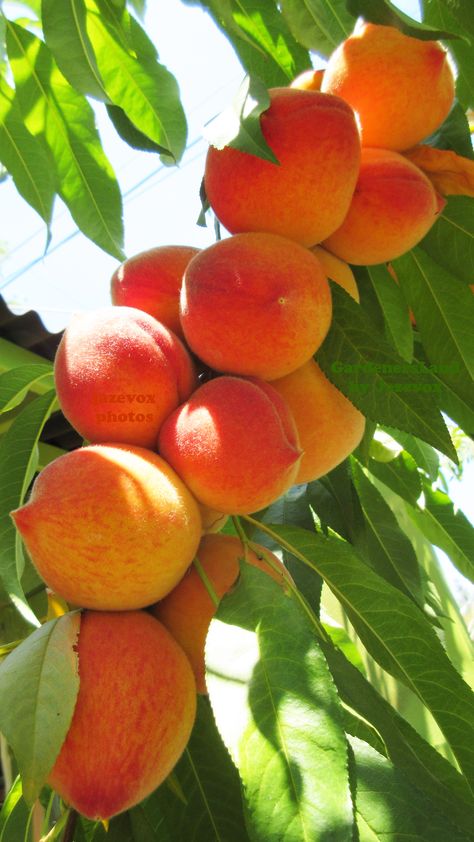
PeachThe Prunus persica is another deciduous tree native, hailing from the Northwestern Chinese region, where it was first and cultivated. The edible juicy fruit is named persica, referring to its extensive cultivation in Persia, modern-day Iran.
Peaches require a fairly specific type of climate to thrive: dry, continental or temperate, the reason for this is a chilling requirement that tropical climates cannot satisfy, except in certain high altitude places such as certain areas in Ecuador, Colombia, Ethiopia, India, and Pakistan.
In areas where it is grown commercially, fig is an important crop that can generate a lot of revenue. It is native to the Middle East and western Asia, where it has been cultivated for centuries. Figs are now grown globally, for its fruit and for its ornamental value.
Fig trees grow wild in areas that are dry and sunny, with fresh soil. It can also be found in rocky areas, at sea level up to 1,700 meters. It favors a comparatively light soil, and can easily grow in nutritionally poor conditions.
Source: Good Housekeeping
PersimmonFrom the genus Diospyros comes the edible fruit called Persimmon. The tree grows to be around 4.5 to 18 meters in height with a round top. It is not uncommon for the tree to sometimes be crooked or have a willowy look. The fruit ripens in late fall and can stay safe and edible on the tree come winter.
The color of the matured fruit ranges from shiny light yellow to dark red or orange depending on habitat and variety. The flesh is hard textured until it ripens and becomes soft, taking on a yellow, orange, or dark-brown hue.
The flesh is hard textured until it ripens and becomes soft, taking on a yellow, orange, or dark-brown hue.
The pomegranate, or Punica granatum, is a fruit born in a deciduous shrub from family Lythraceae. The tree is quite small, growing to be about 5 and 10 meters high.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the tree bears fruit in fall and early spring, and in the Southern Hemisphere in mid spring season. Pomegranates have several culinary uses, such as baking, juice blends and smoothies, meal garnishes, and even alcoholic drinks can be made through fermentation.
Originally, the pomegranate tree came from modern-day Iran and northern India, ever since cultivated everywhere in the Mediterranean region. By the late 16th century, pomegranates had come to Spanish America, and in 1769 brought to California by Spanish settlers.
GrapefruitGrapefruit is a citrus fruit known for its sour to somewhat bitter flavor.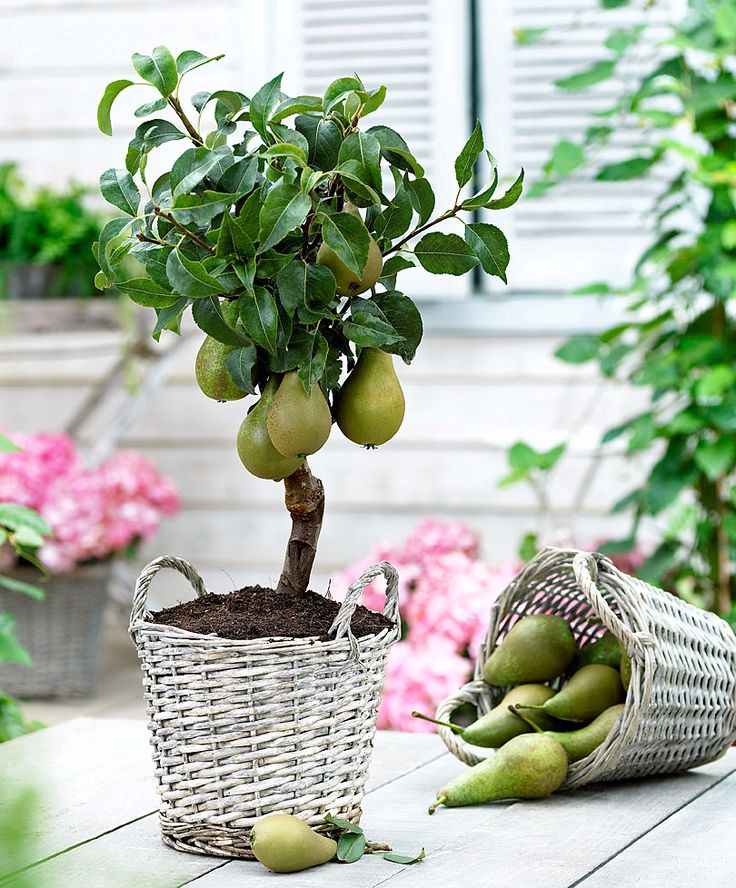 The citrus fruit is a hybrid that was created as an accidental cross between the sweet orange and pomelo, which are both native to Asia and were introduced to the west in the seventeenth century. It is frequently misidentified as one of its parent species, pomelo.
The citrus fruit is a hybrid that was created as an accidental cross between the sweet orange and pomelo, which are both native to Asia and were introduced to the west in the seventeenth century. It is frequently misidentified as one of its parent species, pomelo.
There are several varieties of grapefruit, but some Texas and Florida grapefruit species are Rio Star, Oro Blanco, Ruby Red, Pink, Thompson, White Marsh, Flame and Star Ruby.
AvocadoThe avocado tree is most likely to have originated from South Central Mexico. The fruit is actually a large berry that has one big seed. The species is has adapted a lot due to selection pressure by humans to produce better with a thinner outer shell and therefore has many varieties.
Avocados need a climate that is warm with less wind, since high winds reduce humidity, dehydrating flowers, and harming the pollination process. When the weather becomes chilly, the fruit may drop prematurely, even though some species can tolerate low temperatures.
The Plinia cauliflora, commonly known as the Brazilian grapetree, belongs to the family Myrtaceae, and is native to some states in Brazil. The fruit is well-known for its purplish-black color with white flesh, and it interestingly grows directly on the trunk. The jaboticaba fruit can be enjoyed raw, or it can be made into culinary delights such as jellies, jams, juices and wine.
Even though the tree grows slowly, it is an evergreen and can grow as high as 15 meters if not pruned. The leaves have a salmon-pink tinge when young, and turn green in adulthood.
In order for the tree to grow well, a moist, rich, slightly acidic soil is required. It is quite adaptable and grows suitably even on different kinds of soils, as long as they are well taken care of.
LemonLemon is a species of a short evergreen tree, native to South Asia, and primarily north eastern regions of India. The tree’s spherical or ellipse-shaped yellow fruit is used in many cuisines and recipes in the world.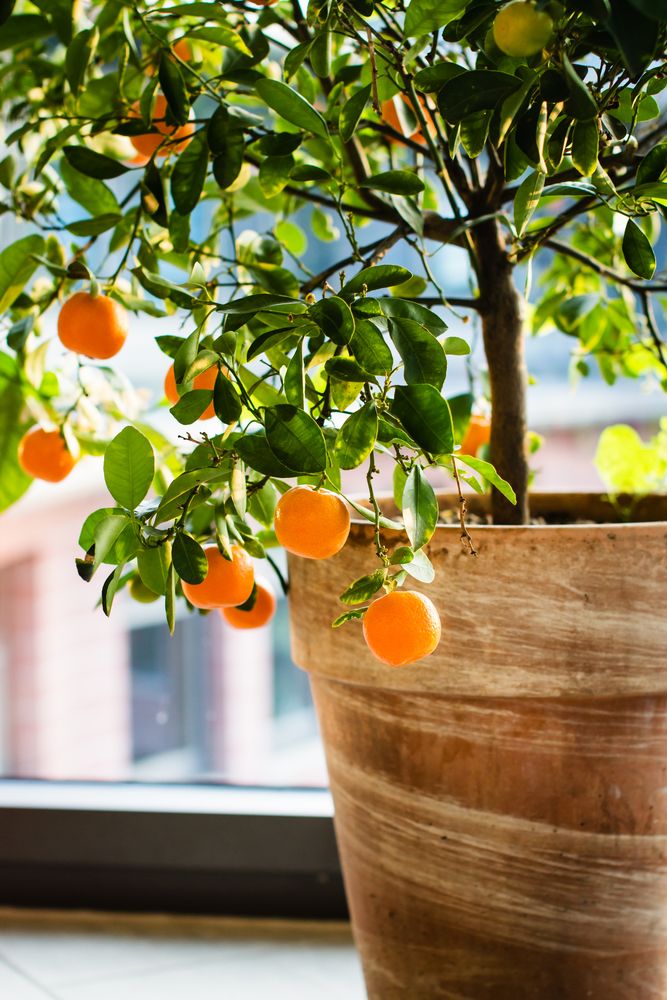
Its sour juice has both culinary and cleaning uses. The zest can also be used when cooking or baking. Lemon juice contains 5% to 6% citric acid, which gives it its flavor. This flavor is what makes lemon an important addition to beverages and foods such as mint lemonades and lemon meringue pies.
LimeA lime is a citrus fruit typically round and green in color. The size is about 3–6 centimeters in diameter. There are several species that are referred to as lime and belong to the same family, including the Key lime (Citrus aurantifolia), the Persian lime, kaffir lime, and the desert lime.
These fruit are similar to lemons in their abundance of vitamin C, and so they are often added to food to accentuate the flavors. Grown all year round, limes have various genetic origins and do not come from one monophyletic cluster.
GuavaIn many tropical and subtropical regions, the guava is a commonly cultivated tropical fruit.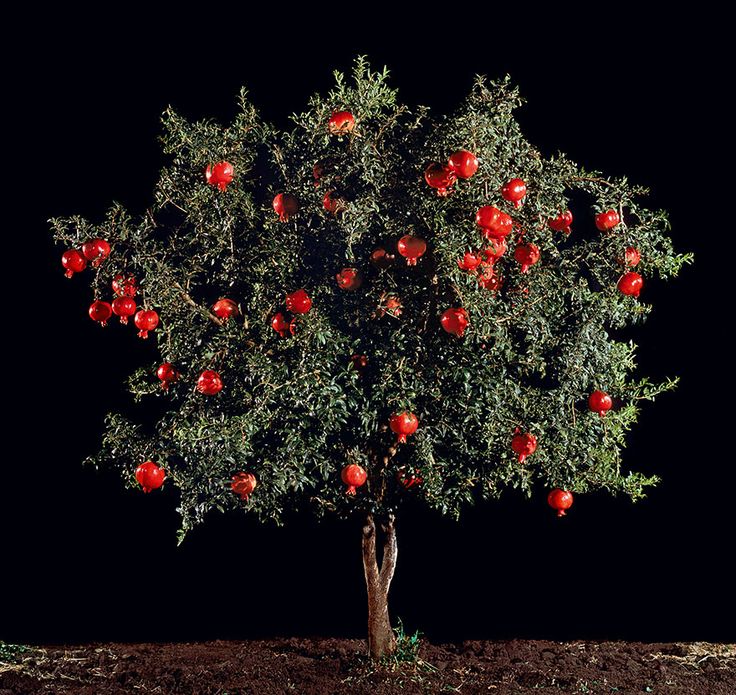 The guava tree is a small, and native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America.
The guava tree is a small, and native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America.
Several related species may also be termed guavas, but they usually belong to other genera. India was the biggest cultivator of these fruit trees with 41% of the world total in 2014.
Source: Hunker.com
OliveOlives, also known as Olea europaea (that stands in for “European olive”) come from a small tree in the Mediterranean Basin. The fruit is grown in many places and is now considered naturally occurring in all countries of the Mediterranean. It is also grown in Argentina, Norfolk Island, California, Bermuda, and Saudi Arabia
The olive’s fruit, also called the olive, is of major agricultural importance in the Mediterranean region as the source of olive oil; it is one of the core ingredients in Mediterranean cuisine.
Source: Olive Tree Growers
Lychee
Lychee is a tropical tree that comes from the Guangdong and Fujian provinces of China.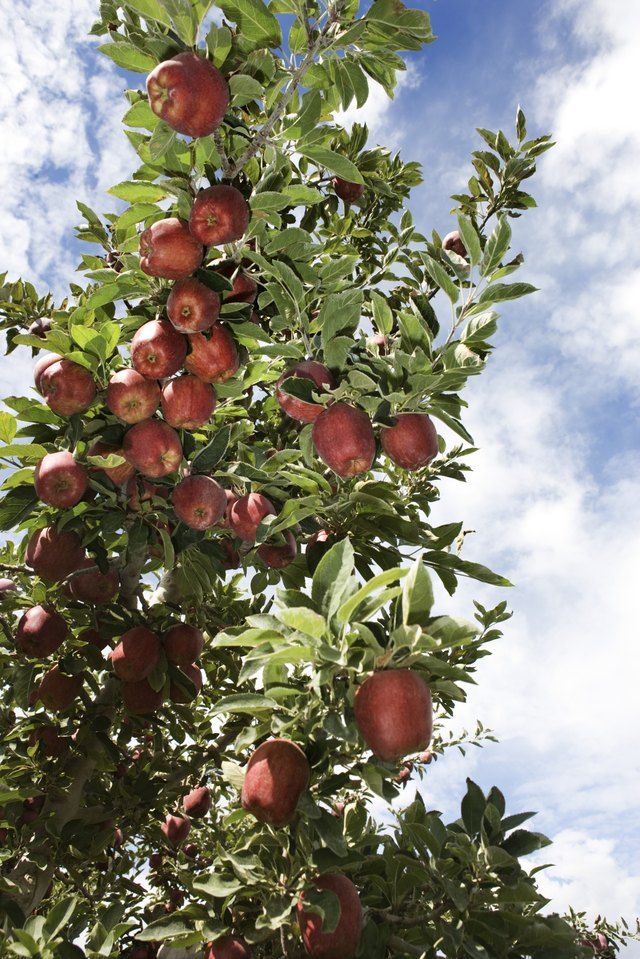 Here, its cultivation is documented for a thousand years. The main producer of lychee fruit is China, then other countries in Southeast Asia, such as India and Nepal. The evergreen lychee tree grows small fruits, the outside of which is pinkish red, with a rough texture. The outer layer is inedible, while the sugary flesh is eaten in many different countries as dessert.
Here, its cultivation is documented for a thousand years. The main producer of lychee fruit is China, then other countries in Southeast Asia, such as India and Nepal. The evergreen lychee tree grows small fruits, the outside of which is pinkish red, with a rough texture. The outer layer is inedible, while the sugary flesh is eaten in many different countries as dessert.
The seeds of the fruit contain a particular chemical that has been known to cause hypoglycemia in malnourished Indian and Vietnamese kids, who eagerly consume it.
DurianThe exotic Durian fruit is famous for its taste and very unusual and often unbearable smell. The unusual flavor and odor of the fruit have made many people express passionate views ranging from profound approval to intense dislike and even disgust.
Durian trees are quite large (25–50 meters in height), and the leaves are evergreen, have an elliptic shape and several centimeters long. Durian trees only produce fruits and flowers once a year, although the timing differs depending on the species, particular harvesting techniques, and geography.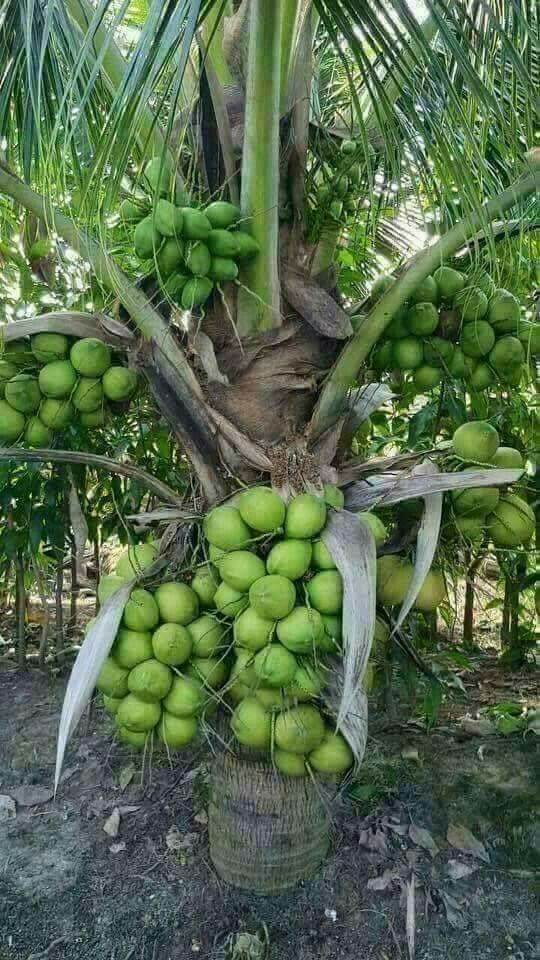
The jackfruit (scientific name Artocarpus heterophyllus), is called the jack tree, and is a species related to the fig, mulberry, and breadfruit family. It is unclear where these fruits hail from, but most botanists consider its native areas to be Western provinces of India, or the Borneo rainforests.
The jackfruit tree is best grown in tropical lowlands, and the fruit is considered the largest grown on any tree. A fully-aged jackfruit tree can grow about 100 to 200 fruits in a single year.
CashewThe cashew tree is an evergreen tree that grows in tropical climates. It produces the cashew seed and the cashew apple, which grow together as one fruit. The tree can reach as high as 14 meters, but the dwarf varieties prove to be more profitable, and hence, are cultivated in abundance.
The species comes from Central America and the Caribbean Islands. The cashew apple is light reddish to yellow in color, and its pulp can be made into fruit or fermented into alcohol.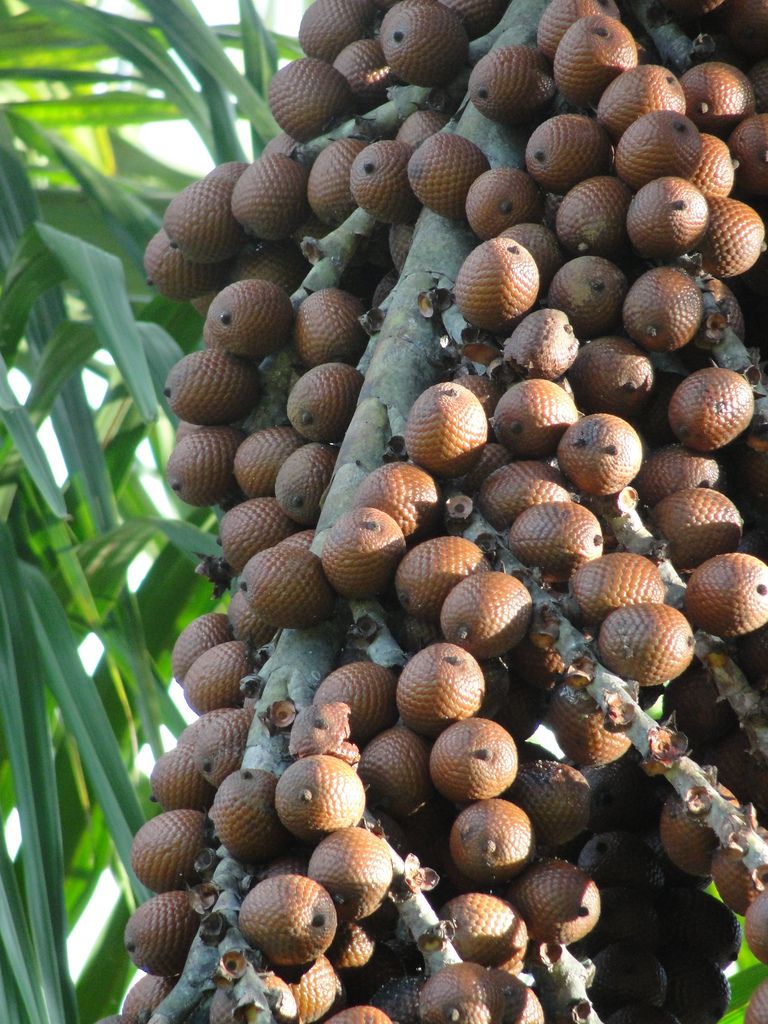 The cashew nut is sold widely and exported to all corners of the world.
The cashew nut is sold widely and exported to all corners of the world.
Having all this fascinating information about fruit trees can help you decide what you would like to plant in your backyard. A fruit tree is an investment that does not only provide shade and oxygen to the environment, but also gives you and children plenty of healthy food to eat.
It’s spring season, get planting!
Nectarine TreesNectarines are the same species as peaches, Prunus persica, with the only difference that the outer skin of the former lack what we have come to know as peach fuzz.
Even though they usually grow in any warm climate, nectarines will grow better and faster if they are exposed to more sun. On the other hand, they can easily become dormant, or even die, in frosty weather. These trees prefer sandy loam soils but can usually grow quite well in other soils too.
Source: Chestnut Hill Tree Farm
Dwarf Fruit TreesIf you want your very own fruit tree but are constrained by space, dwarf fruit trees can be your choice of houseplant. A dwarf tree is a small cultivar of full sized fruit trees that can yield many mature fruits in a year without taking up the usual growing space occupied by trees. In fact, these tiny versions of trees can grow in containers 12-15 wide.
A dwarf tree is a small cultivar of full sized fruit trees that can yield many mature fruits in a year without taking up the usual growing space occupied by trees. In fact, these tiny versions of trees can grow in containers 12-15 wide.
All they need to grow well is fertile potting, a good water drainage system, and plenty of sun exposure. One of the most famous varieties is the dwarf peach plant, aptly named the Prunus persica ‘Bonanza’ which bears fruit as early as within a year and has self-fertilizing properties.
Source: HGTV Outdoors
Columnar Fruit TreesUnlike regular trees, columnar trees grow upwards, not out. The best thing about them is that they consume so little horizontal space that they can be grown anywhere you wish, if sufficient conditions are fulfilled.
Not only is it extremely pleasing to the eye, it also enables passionate gardeners with little outdoor space to have the experience of growing a fruit tree under their belt.
The fruit from columnar trees is full sized, and just as delicious as any other variety. Fruits like cherries, plums, and peaches are also available in this variety; however, they may need to pruned and plucked at certain points to maintain the spiral structure as well as other fruits.
Source: Luv2Garden
Having all this fascinating information about fruit trees can help you decide what you would like to plant in your backyard. A fruit tree is an investment that does not only provide shade and oxygen to the environment, but also gives you and children plenty of healthy food to eat.
It’s spring season, get planting!
FAQ
What should you put on fruit trees to keep bugs off?
If you have noticed bugs on your fruit trees lately then you need to get an insecticide spray that offers a variety of ingredients to fight these pests. Because you could have different pests on each tree, you want a spray that will target all of them at once.
Which fruit trees can grow in pots?
There are a few fruit trees that can grow in large pots. They include apple, peach, fig, and nectarine trees. They are ideal for patios in pots that give you the shade you need and the fruit you want.
They include apple, peach, fig, and nectarine trees. They are ideal for patios in pots that give you the shade you need and the fruit you want.
What size of pot for patio fruit trees?
If you are planning to pot your fruit trees, you want a patio pot that is at least 10 gallons in the smaller size. For best practice and a chance at healthy trees, a 20 or 25 gallon will give your fruit tree the room it needs for substantial root development.
What fruit trees are deer resistant?
While there are some fruit trees that will attract deer to your property, there are some that are deer resistant. These trees include fig, ginkgo Biloba, sugar maple, persimmons, and honey locust trees.
Can you use grey water on fruit trees?
It is absolutely safe to use grey water or use laundry water on your fruit trees. Reusing grey water for your fruit trees keeps them hydrated and reduces the amount of water you use regularly. This water will include detergent and soaps, but there is no adverse effect to the fruit trees from this grey water unless you use a strong chemical like bleach which could burn the roots.
When to plant fruit trees?
The best time of the year to plant your fruit trees each year is in the spring. This is because the trees have an opportunity to get acquainted with the soil and adjust to rising temperatures. Planting any other time in the year could shock the tree and cause it to die.
When to prune fruit trees?
If you are concerned about pruning your fruit trees, plan to do this late in the winter. The last two weeks of February are great for pruning because it encourages new growth in the tree. Like planting in the spring, these pruned trees have the opportunity to become familiar and comfortable with the changing temperatures.
Are fruit trees fast-growing?
Fruit trees tend to grow faster than hardier trees. In most cases, your fruit trees will grow within 3-5 years, depending on which tree it is and the environment where it is growing.
Will fruit trees grow in rocky soil?
Rocky soil is not the ideal option for growing fruit trees, but there are a few varieties that are more tolerable in these conditions. If you have rocky soil, consider growing cherry, olive, fig, peach, apricot, or plum trees.
If you have rocky soil, consider growing cherry, olive, fig, peach, apricot, or plum trees.
Do fruit trees lose their leaves in winter?
Since the majority of the fruit trees in your garden are deciduous, you can expect them to lose their leaves in the winter months. This is why pruning is a great idea at the end of winter just before spring.
Page not found - Home Stratosphere
We didn't find the posts for that URL.
Latest Posts
Researched and written by experienced contractor Alan Roberts. With a good plan and meticulous attention to detail, you can save thousands of dollars by refinishing your hardwood floors instead of calling in a professional flooring contractor. DIY hardwood floor sanding and finishing is definitely something you can do, but you’re going to need the proper …
Read More about 5 Best Sanders For Hardwood Floors In 2022
Architects: OOIIO Arquitectura Area: 250 m² Year: 2019 Photographs: josefotoinmo Manufacturers: Daikin, Baumit, Donaire Solar, Grupo Halcón Cerámicas, Hormigón y Pavimento s. l. Lead Architect: Joaquín Millán Villamuelas Design Team: Joaquín Millán Villamuelas, Natalia Garmendia Cobo, Irene Muñoz Fernández, Alessio Runci, Pilar Bolaños Almeida, Marta Muñoz Hermoso, Paolo Mercorillo, Mario Gómez de Agüero Client: Private Specialized …
l. Lead Architect: Joaquín Millán Villamuelas Design Team: Joaquín Millán Villamuelas, Natalia Garmendia Cobo, Irene Muñoz Fernández, Alessio Runci, Pilar Bolaños Almeida, Marta Muñoz Hermoso, Paolo Mercorillo, Mario Gómez de Agüero Client: Private Specialized …
Read More about Albania House by OOIIO Arquitectura
Location: Risør Program: Cabin Area: 117 m² BRA Architect: Fjord Arkitekter The prerequisites for the design of the cabin have been to take care of the fine qualities of the plot, and to process it as little as possible. This is for both economic and aesthetic reasons. The shape and construction of the cabin has been …
Read More about Risør by Fjord Arkitekter
Yes, you can wash feather pillows. It can seem like they are the impossible household chore because feather pillows are made of natural fibers, and it is always difficult to understand how to wash those. However, you don’t want to avoid washing them because they can be prone to mites and bacteria more than other …
Read More about Can You Wash Feather Pillows? How?
If you are interested in getting a new fireplace for your home, you have most likely looked at all the options available.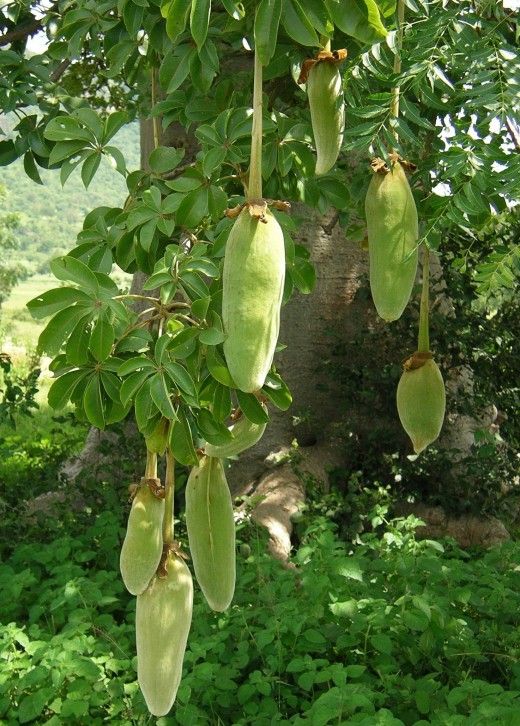 You may feel overwhelmed by all of the choices available to you. One of those options is an electric fireplace. They are more flexible than their traditional counterparts. They can be used in …
You may feel overwhelmed by all of the choices available to you. One of those options is an electric fireplace. They are more flexible than their traditional counterparts. They can be used in …
Read More about How Do Electric Fireplaces Work? How Do the Flames Work?
One of America’s spectacular castle homes was once owned by Harry H. Frazee, the Boston Red Sox owner who traded Babe Ruth to the New York Yankees in 1920 for $120,000 – the most lopsided American trade since the Dutch bought Manhattan in the 1600s for $24 worth of trinkets. The Ruth trade was the …
Read More about Historic New England Castle Sold for ($10.4 Million) – Connected To ‘Curse of the Bambino’
Specifications: Sq. Ft.: 2,456 Bedrooms: 3-4 Bathrooms: 3.5-4.5 Stories: 1 Garage: 2 Welcome to photos and footprint for a 4-bedroom single-story transitional home. Here’s the floor plan: This single-story transitional home exudes a timeless charm with its stately brick exterior, graceful gables, a shed dormer, and rustic timbers accentuating the windows and entry.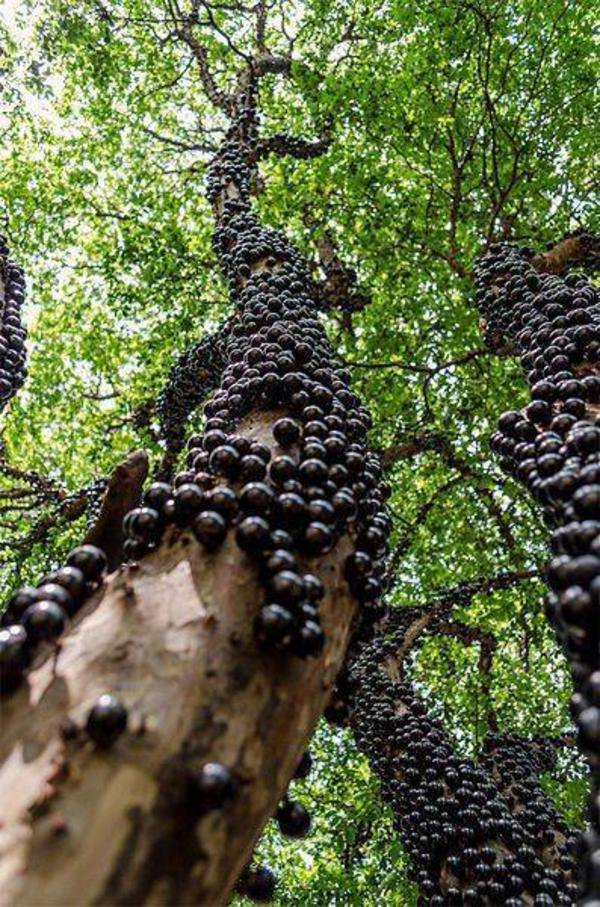 As you …
As you …
Read More about 4-Bedroom Single-Story Transitional Home with Covered Porch and Optional Bonus Room (Floor Plan)
Specifications: Sq. Ft.: 4,238 Bedrooms: 3-5 Bathrooms: 4.5-5.5 Stories: 2 Garage: 3 Welcome to photos and footprint for a two-story traditional style 5-bedroom home. Here’s the floor plan: A mixture of stone and horizontal siding along with metal roof accents and wood columns surrounding the covered porch and deck adorn this two-story traditional home. Inside, …
Read More about Two-Story Traditional Style 5-Bedroom Home for a Wide Lot with Loft, Balcony, and a Drive-Through RV (Floor Plan)
You might be in the middle of home remodeling or just sprucing things up a bit. If so, it usually means out with the old and in with the new. When it comes to your window treatments, you might be looking at your aging blinds and wondering what to do with them. Before sending your …
Read More about What Can You Do with Old Blinds? 4 Options
Office Name: JYJ Architects Social Media Accounts: @jyj_architects Contact e-mail: kyungmo-jung@naver. com Firm Location: 10.603, City Hall-ro 160beon-gil, Namyang-eup, Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea Completion Year: 2022 Gross Built Area (m²/ ft²): 311 m² Project Location: Saesol-dong, Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea Program / Use / Building Function: Private House Lead Architects: Jung Kyungmo Lead Architects …
com Firm Location: 10.603, City Hall-ro 160beon-gil, Namyang-eup, Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea Completion Year: 2022 Gross Built Area (m²/ ft²): 311 m² Project Location: Saesol-dong, Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea Program / Use / Building Function: Private House Lead Architects: Jung Kyungmo Lead Architects …
Read More about Saesoldong House I by JYJ Architects
Location: Asker Programme: Detached house Project Owner: Private Completed: Autumn 2015 Area: 293 m² + garage Architect: Fjord Arkitekter Interior: Fjord Arkitekter Supplier: Sköna Hus Contractor: Visjonsbygg Villa Flaterud is a detached house and garage of 293 square meters over three floors. The home and garage are located to the north-east in the steeper part …
Read More about Haugboveien 3 by Fjord Arkitekter
Choosing the Perfect Reading Sofa Living in a world that is so dedicated to consuming information from screens, everyday it becomes more and more important to dedicate some of your day towards reading. Whether it be a magazine, a good book, a comic, or your own journal entries from 6 years ago (yikes), reading is …
Whether it be a magazine, a good book, a comic, or your own journal entries from 6 years ago (yikes), reading is …
Read More about 15 Best Sofas for Reading (2022)
Do you have pillows you are no longer using? You may think that Goodwill is the perfect place to donate your used pillows, but this may not be the case. Goodwill actually has very strict rules on what they will and will not take. They do take some pillows, but not others. Does Goodwill Take …
Read More about Does Goodwill Take Pillows?
Specifications: Sq. Ft.: 3,156 Bedrooms: 3-4 Bathrooms: 4.5 Stories: 2 Garage: 3 Welcome to photos and footprint for a 4-bedroom two-story modern farmhouse. Here’s the floor plan: Clapboard and board and batten siding embellish this modern farmhouse. It is further enhanced with metal roof accents, a cupola, and a welcoming porch framed with rustic timbers. …
Read More about 4-Bedroom Two-Story Modern Farmhouse for a Wide Lot with an Open Floor Plan and Side-Loading Garage (Floor Plan)
Specifications: Sq.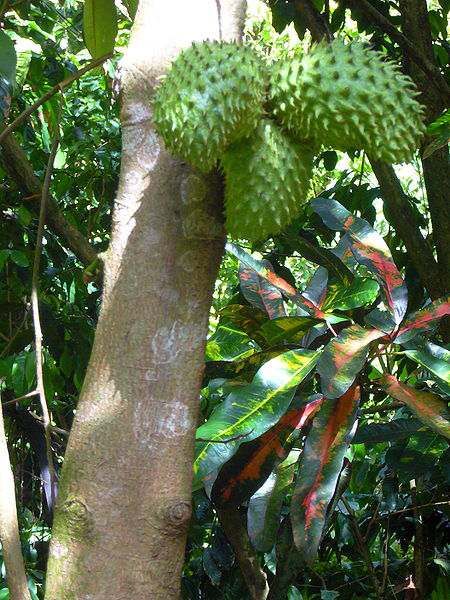 Ft.: 4,090 Bedrooms: 3 Bathrooms: 3.5 Stories: 2 Garage: 2 Welcome to photos and footprint for a modern two-story 3-bedroom farmhouse. Here’s the floor plan: This two-story modern farmhouse boasts an exquisite curb appeal with its horizontal and vertical siding, stone accents, and a welcoming front porch adorned with three gable dormers, exposed …
Ft.: 4,090 Bedrooms: 3 Bathrooms: 3.5 Stories: 2 Garage: 2 Welcome to photos and footprint for a modern two-story 3-bedroom farmhouse. Here’s the floor plan: This two-story modern farmhouse boasts an exquisite curb appeal with its horizontal and vertical siding, stone accents, and a welcoming front porch adorned with three gable dormers, exposed …
Read More about Modern Two-Story 3-Bedroom Farmhouse for a Wide Lot with Open Concept Design (Floor Plan)
Crackling wood in the fireplace is one of the most notable scenes in all of domestic bliss. Nothing says coziness like cuddling up with a warm blanket in front of a roaring fire. Just ask any romance novel cover designer. Not everyone has the option to enjoy throwing logs on a fire, though. If I’m …
Read More about Electric Fireplace vs Gas vs Wood (Differences? Similarities?)
Do you have old pillows that you hate to throw away? They look clean, so you consider recycling them or donating them to a local thrift shop or a local charity.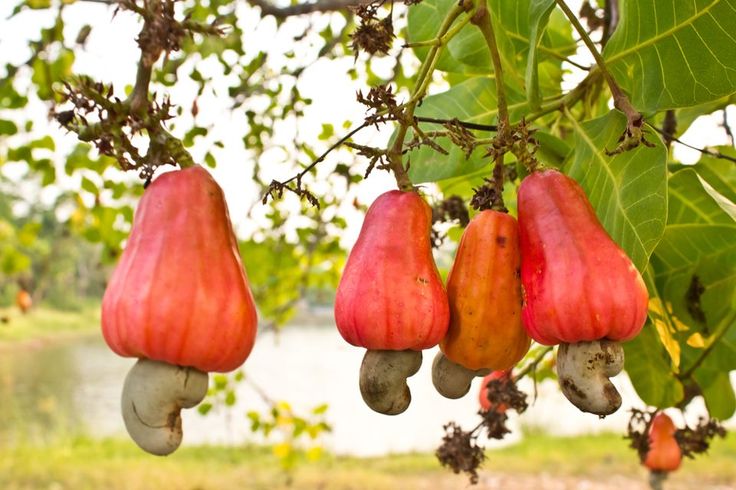 Do you want to get rid of them but do not know what to do with the old pillows now that you purchased new …
Do you want to get rid of them but do not know what to do with the old pillows now that you purchased new …
Read More about What to Do with Old Pillows? (Your Options)
The first time I ever saw an electric fireplace was in 1983, when my best friend’s single dad moved to a new condo. I couldn’t get over the fact that you could flip what looked like a light switch and suddenly there was a full-blown, fairly realistic-looking fire in the fireplace. And, just as easily, …
Read More about What is an Electric Fireplace?
Most don’t think much about throw pillows, since they simply sit on your sofa or bed and tie the room together. Many distinct types of throw pillows exist, however, each with different qualities. The only time individuals think about throw pillows is when in the market to make a new purchase. This could be sprucing …
Read More about 19 Different Types of Throw Pillows
Winter is always either here or right around the corner.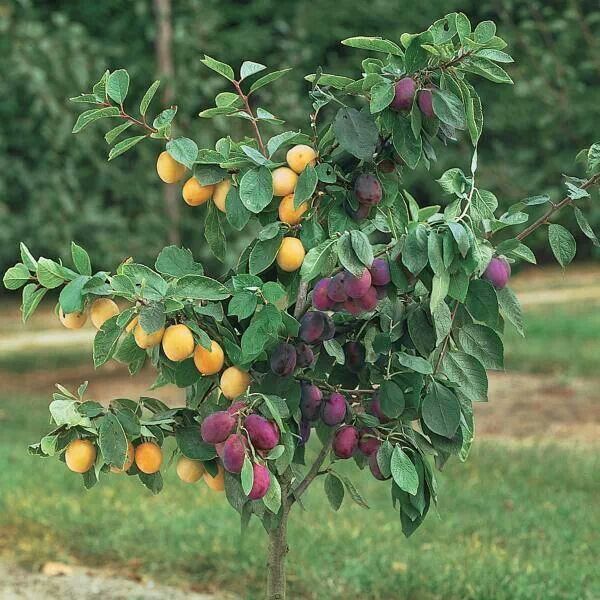 Advances in wood stove design have made the appliances more efficient for heating compared to the older models. According to Penn State University, a wood stove could provide a massive discount compared to electricity or natural gas. A wood stove is a major appliance that …
Advances in wood stove design have made the appliances more efficient for heating compared to the older models. According to Penn State University, a wood stove could provide a massive discount compared to electricity or natural gas. A wood stove is a major appliance that …
Read More about How Hot Do Wood Stoves Get?
UNUSUAL FRUITS | Science and life
Truly paradise flora grows in the tropics. There are trees with food names: breadfruit, sausage, candy, spinach, dairy (their milky juice, the shape or taste of the fruit resembles the corresponding products), trees with fruits that look like cannonballs, and many other curious plants.
ARTOKARPUS "BREAD"
Durian fruits (Durio zibethinus) are covered with hard conical spikes and weigh about 3 kilograms. They are slightly smaller than a basketball.
Ripe durian fruit.
Kigelia flowers and fruit hanging on a long stem.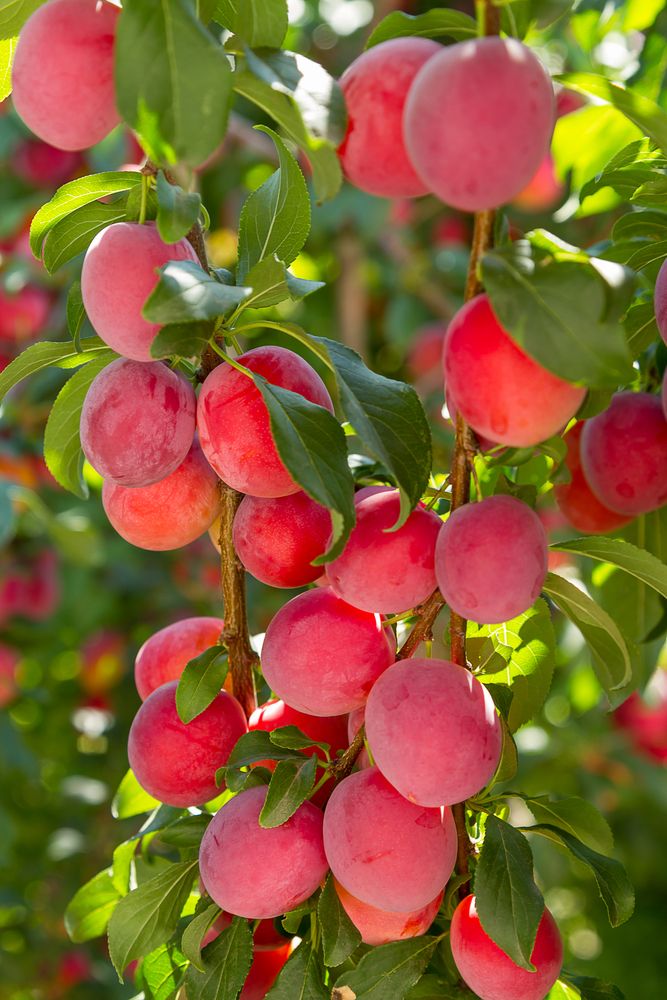
Couroupita guianensis flowers bloom directly on the bark of a massive trunk. They are unusually beautiful and emit a delicate, pleasant aroma.
Kigelia (Kigelia pinnata) is called the sausage tree (1).
Science and Life // Illustrations
Huge round fruits of the Guianan couroupita (Couroupita guianensis) - "cannonballs" - hang in clusters on trunks (2, 3).
Breadfruit Artocarpus altilis is native to Polynesia. Its starch-rich fruits are used by locals to make puddings, breads, pies, and are fried like potatoes (4).
The breadfruit Artocarpus heterophyllus, or jackfruit, is the largest fruit in the world (5).
The chocolate tree (Theobroma cacao) reaches a height of 4-8 meters. Its fruits grow directly on the trunk.
‹
›
View full size
All types of trees (and there are about 50 of them) of the genus Artocarpus of the mulberry family are called breadfruit trees. They are famous food plants of the tropics. They were mentioned in their manuscripts by the ancient Greek botanist, student and friend of Aristotle - Theophrastus, and later - Pliny.
They were mentioned in their manuscripts by the ancient Greek botanist, student and friend of Aristotle - Theophrastus, and later - Pliny.
"If someone during his life plants ten breadfruit trees, he can consider what he has done in order to feed himself, his family and his offspring, more than an inhabitant of the temperate zone, who works his whole life in the sweat of his brow. field...", wrote the English navigator James Cook in his diary.
Breadfruit trees are evergreens. On one copy there are unusually diverse leaves: whole, pinnately dissected, pinnately compound - with varying degrees of pubescence. Flowers and fruits are formed directly on the trunk. Male flowers are arranged very simply and do not shine with beauty. But the female ones are combined into large inflorescences. After pollination, their perianths and bracts, as well as the fleshy axis of the inflorescence, grow and merge into one large seed, suspended from the trunk, as if on a rope, and shaped like a large greenish-yellow or brown knobby melon.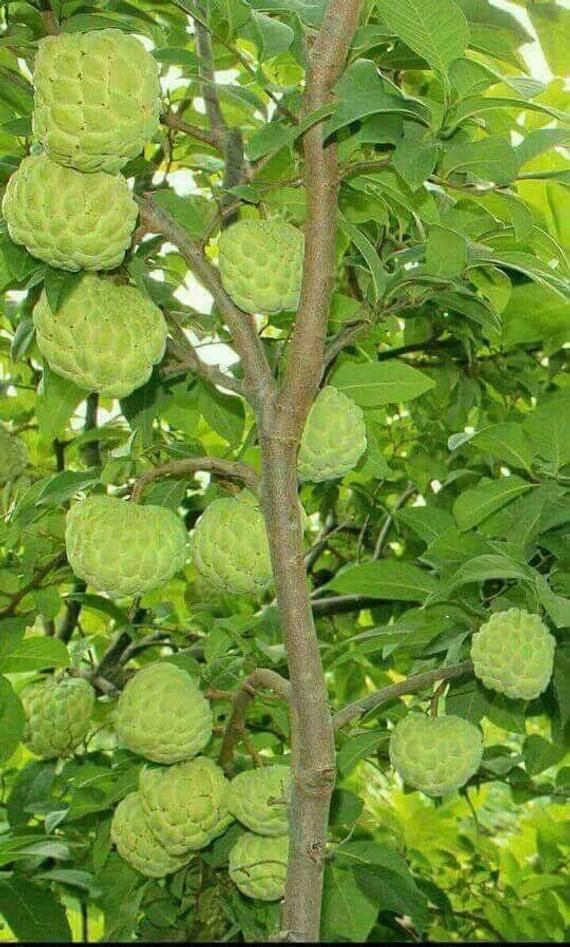 Simultaneously with the ripening of the fruit, new flowers continue to appear on the tree trunk.
Simultaneously with the ripening of the fruit, new flowers continue to appear on the tree trunk.
Normally breadfruit trees bear fruit for nine months of the year and then rest for three months. And so for 70-75 years. On one tree, 700-800 "breads" ripen annually. The fruits are filled with sweet pulp.
Polynesia is considered to be the birthplace of the common breadfruit Artocarpus altilis. But now it is grown in almost all countries of Southeast Asia, Oceania and other areas of the tropics. On oceanic islands, it plays an important role in the nutrition of the local population. This tree reaches 35 meters in height and 1 meter in diameter, has palmate-lobed leaves, and its seed weights from 3 to 4 kilograms.
Breadfruit seeds are roasted like chestnuts. And the fruits are canned, baked, boiled, fried, dried and eaten raw. When fully ripe, they have a doughy flesh that tastes more like potatoes than bread. But you need to eat this pulp quickly, otherwise it will become tasteless in a day.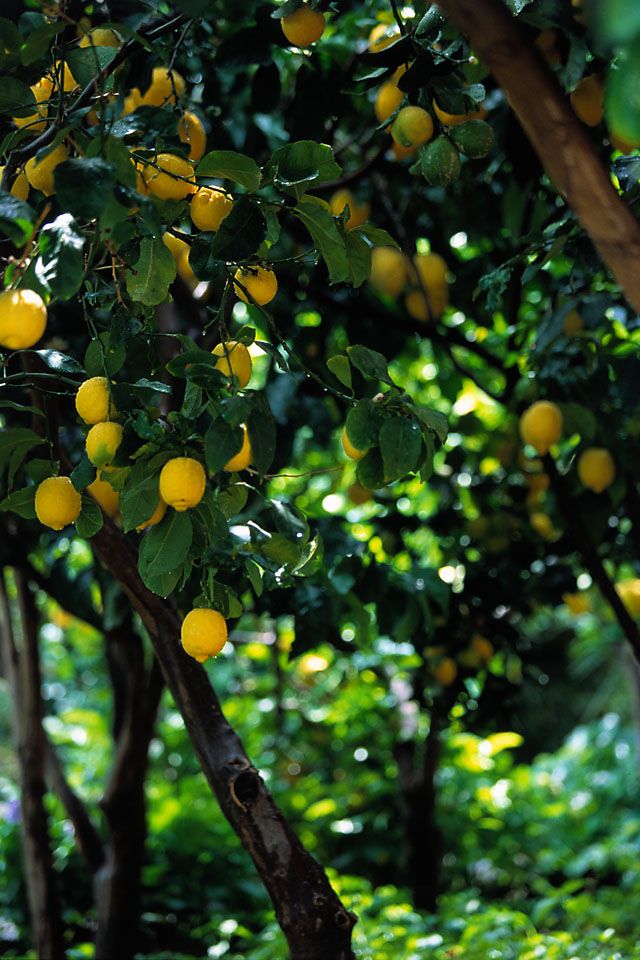 The easiest cooking method is fire treatment. Freshly picked, still green fruits are buried in ashes and baked in a fire like potatoes. After ten or fifteen minutes, the green crust turns black, cracks, and a milky-white inside peeps through the cracks, which tastes like sweetish wheat bread.
The easiest cooking method is fire treatment. Freshly picked, still green fruits are buried in ashes and baked in a fire like potatoes. After ten or fifteen minutes, the green crust turns black, cracks, and a milky-white inside peeps through the cracks, which tastes like sweetish wheat bread.
Inhabitants of the Marquesas usually crush peeled and cored fruits in a mortar, turning them into a homogeneous mass, to which coconut juice is added to improve the taste. Then it is divided into briquettes, wrapped in several layers of leaves, tightly tied with bark fibers and buried in large pits, from where it is subsequently removed as needed. In the ground, such a semi-finished product can lie for years, becoming even tastier with time. Prepare it as follows. The bottom of the pit is lined with stones and a large fire is lit. When the stones are warm enough, the ashes are raked out, the bottom is covered with a layer of leaves, a wrapped dough block is placed there, covered with another layer of leaves on top.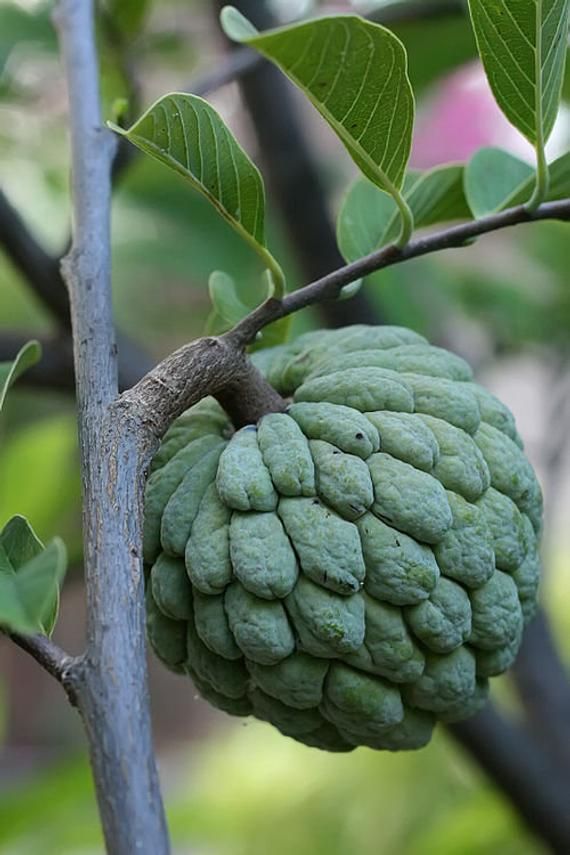 Then all this is quickly covered with earth so that a slide is obtained. Baked dough is a plump yellow cake that tastes good. If such a cake is soaked in water and mixed to a uniform consistency, you get a kind of pudding.
Then all this is quickly covered with earth so that a slide is obtained. Baked dough is a plump yellow cake that tastes good. If such a cake is soaked in water and mixed to a uniform consistency, you get a kind of pudding.
The closest relative of the common breadfruit tree is the jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) - the plant with the largest seedlings in the world. Their diameter can reach 30-40 centimeters, length - 60-90 centimeters, and weight - about 34 kilograms. This tree is up to 15 meters high, with whole leaves - a native of India. Currently, jackfruit is bred in many countries of South and Southeast Asia - from India to Indonesia. Its fruits are very tasty, similar to melon, mango and papaya, but have one drawback - a specific cologne smell. The juice is sweet, yellow, brownish or pink, depending on the maturity of the fruit.
Unripe jackfruit is cooked like a vegetable, while ripe jackfruit is eaten raw or canned in syrup. The seeds are boiled or roasted.
In Asia, they say about jackfruit: "If jackfruit grows in your yard, you will not die of hunger."
DURIAN - THE KING OF FRUIT
Durian (Durio zibethinus) belongs to the Bombax family. This large (up to 45 meters high) evergreen tree grows wild in the tropical forests of Kalimantan, Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula, cultivated in Southeast Asia and southern India. Outwardly, it has no special advantages. But the fruits give rise to unusual ones: very tasty, but foul-smelling. It is no coincidence that in most hotels of those countries where durian grows, a poster with a crossed-out image of the fruit hangs. When ripe, the fruits fall to the ground, crack and begin to spread a disgusting smell of rot, which attracts insects and animals: ants, beetles, rhinos, tigers, elephants. They feast on the fruit, and then take away and spread its seeds. Through such a pilgrimage, the tree flourishes.
Durian, if not overripe, smells only when cut, and the smell does not appear until half an hour after the fruit has been cut.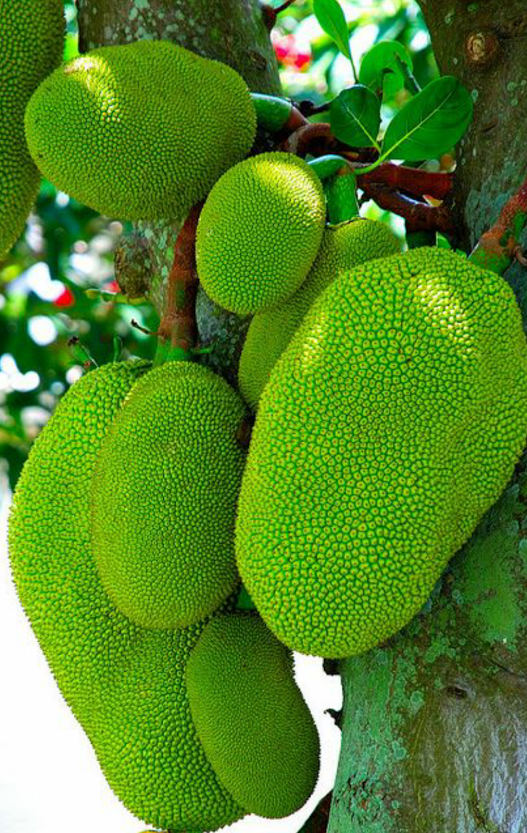 At room temperature, the pulp stays fresh for up to five days. If the fruits are frozen, then after thawing and storage in the refrigerator, they are recommended to be used within two days.
At room temperature, the pulp stays fresh for up to five days. If the fruits are frozen, then after thawing and storage in the refrigerator, they are recommended to be used within two days.
This fruit is recommended to be eaten in the same way as drinking vodka: exhale the air, quickly put the durian in your mouth, and only then inhale. Its taste is reminiscent of sweet almond cream with the addition of cream cheese, onion sauce, cherry syrup and other products that are difficult to combine.
Durian is considered the king of fruits in Southeast Asia. It is eaten fresh, added to baked goods, ice cream, drinks, fried as a side dish, or mixed with rice. In Thailand, during the ripening period of durian fruits (from May to August), even special festivals are held, which attract people from all over the world. Exotic fruit leaves few people indifferent. Those who tried it are divided into two camps - passionate fans and haters.
KIGELIA SAUSAGES
In tropical Africa and Madagascar you can admire Kigelia pinnata - a beautiful tree from the bignoniaceae family, with a wide shady crown and bizarre fruits.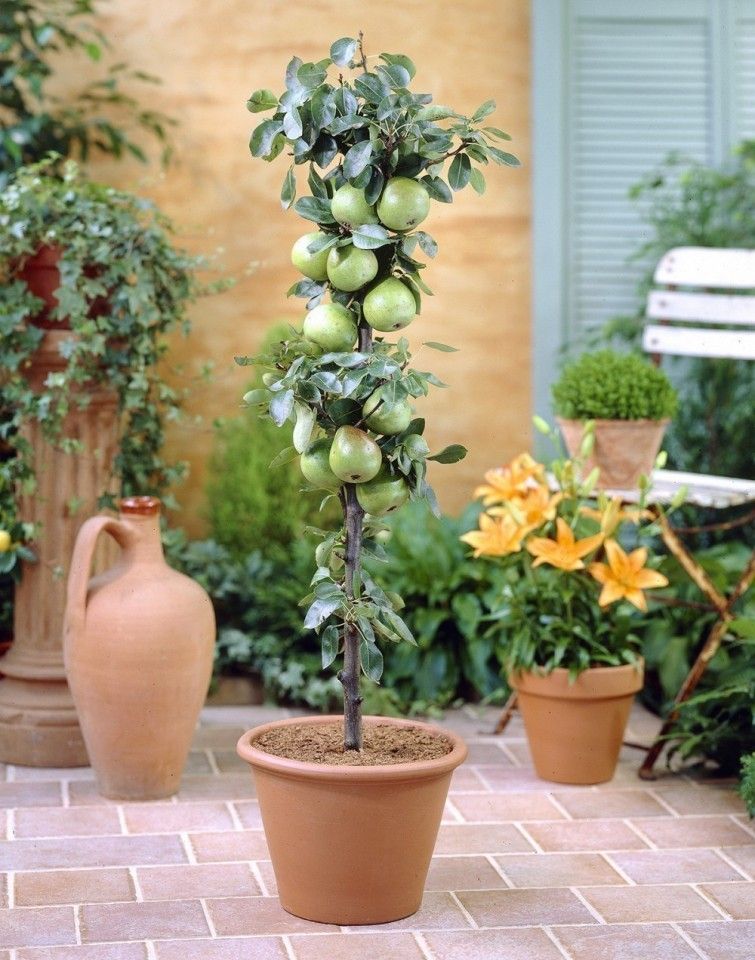 It is called sausage because it carries on its branches a lot of brownish, sausage-shaped fruits randomly hanging on long stalks. Each such "sausage" can be a little over half a meter long and about 10 centimeters in diameter. But, alas, these fruits are inedible neither for man nor for the beast.
It is called sausage because it carries on its branches a lot of brownish, sausage-shaped fruits randomly hanging on long stalks. Each such "sausage" can be a little over half a meter long and about 10 centimeters in diameter. But, alas, these fruits are inedible neither for man nor for the beast.
The flowering of the sausage tree is amazing. Large, dark red funnel-shaped flowers appear in inflorescences during the dry season. They open in the evening and bloom at night. Small bats in search of nectar stumble upon them and pollinate them. Birds of the nectary also participate in pollination. By morning, many flowers fall off. The ovaries form only those that were pollinated at night.
CANNONBALLS COUROPITES
Couroupita guianensis, native to the tropical forests of South America and South Asia, is called the cannonball tree. Its perfectly round, edible fruits are truly reminiscent of cast-iron cannonballs in size and shape.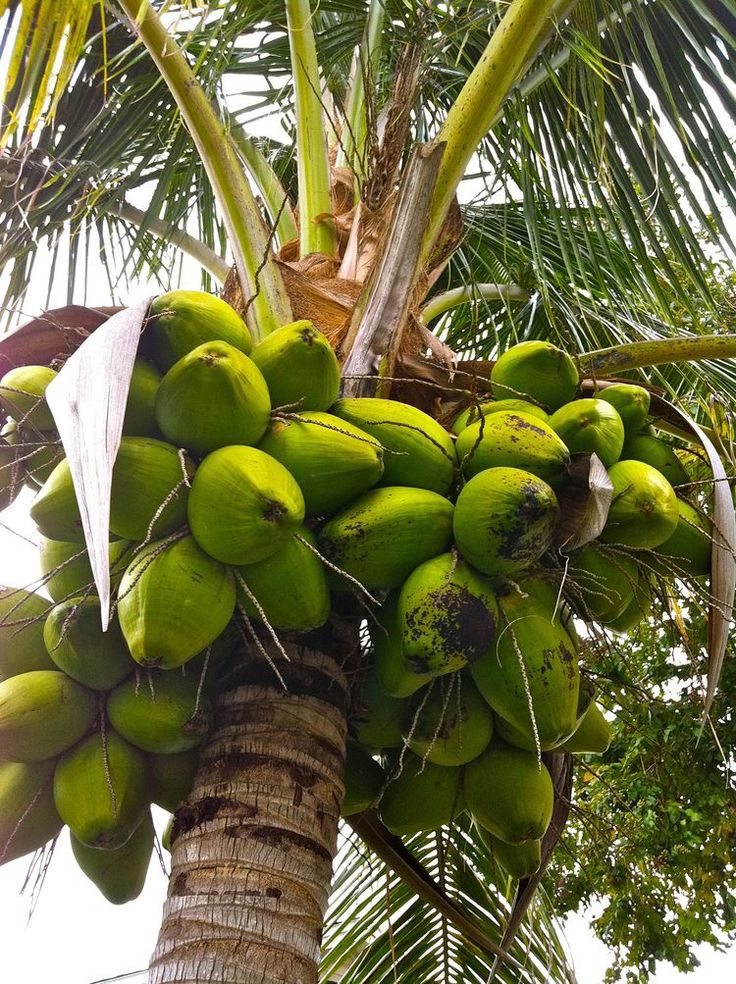 They hang in clusters on thick stems around the trunk. In some countries, this rather tall (15 to 25 meters) deciduous tree, related to the Brazil nut, was at one time planted along the roads. But very soon they abandoned this idea. To get a round ripe fruit at full speed under the wheels of a car, although it is not cast iron, is not a pleasant prospect.
They hang in clusters on thick stems around the trunk. In some countries, this rather tall (15 to 25 meters) deciduous tree, related to the Brazil nut, was at one time planted along the roads. But very soon they abandoned this idea. To get a round ripe fruit at full speed under the wheels of a car, although it is not cast iron, is not a pleasant prospect.
"Cannonballs" couropites develop from flowers that appear on thick pedicels right on the trunk of a tree, striking with their beauty and subtle, like expensive perfumes, aroma. Because of the delicious aroma, the flowers are used in the perfume and cosmetic industries.
The white flesh of the fruit is soft and very fleshy and tastes like a nut. Unlike flowers, it has an unpleasant smell. Therefore, not every person decides to try it. Hard shells of fruits are adapted by local residents for containers.
Every tropical park considers it their duty to purchase at least one couropita. Once this tree was planted at his country villa near Havana by E. Hemingway. Now it constantly attracts the attention of tourists.
Hemingway. Now it constantly attracts the attention of tourists.
The article is illustrated with photographs from the Internet and the electronic "Encyclopedia of Cyril and Methodius".
In the tropics, many trees have flowers not at the ends of the shoots, but directly on the trunk and on thick branches. Later, the flowers develop into fruits. This phenomenon is called "caulifloria", which literally means "stem blossom".
Many researchers of tropical nature have tried to explain why in warm climates flower buds are formed deep in the tissues of the trunk and then break out through the bark.
Some believe that this is due to the economy mode. In a rainforest where flora crowd each other, the expenditure of energy pushing nutrient juices through a complex system of branches to fruits is an unnecessary luxury. Isn't it easier to directly feed them from the trunk to the fruits?
Others find it beneficial for trees with very large fruits that, due to their weight, could easily break branches.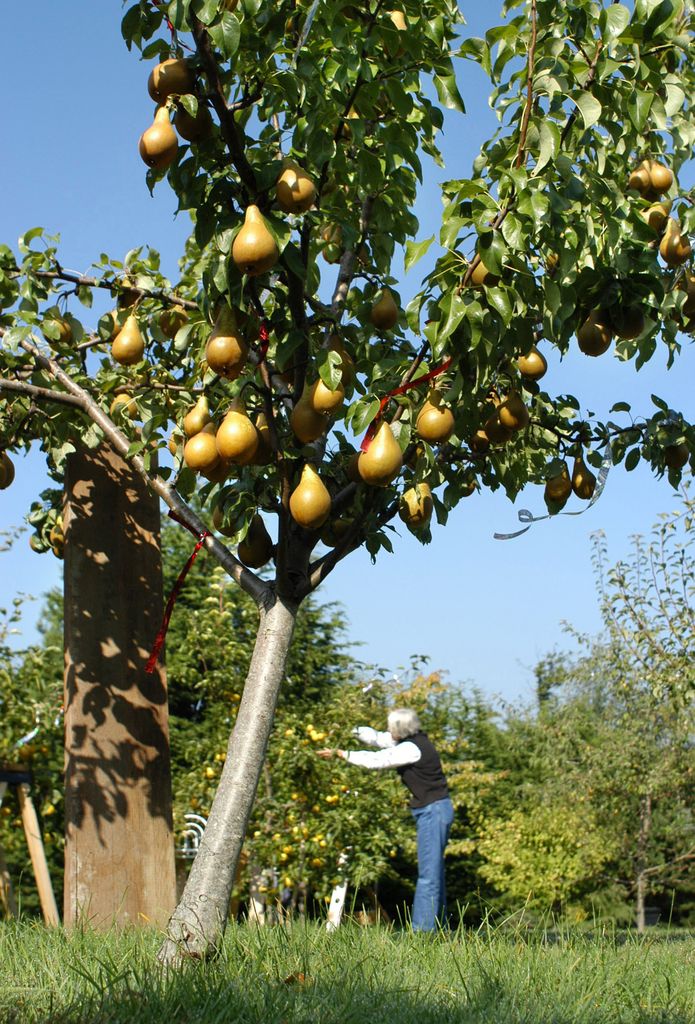
In 1878, the English naturalist Alfred Wallace suggested that caulifloria made it easier for pollinators to find flowers in the dusk of the rainforest.
Pronounced cauliflory is observed in cocoa (Theobroma cacao), couroupita (Couroupita guianensis), breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) and its closest relative, jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus). This phenomenon is also characteristic of some ficuses and various representatives of the Annon and Sapot families.
In the tropics, many trees have flowers not at the ends of the shoots, but directly on the trunk and on thick branches. Later, the flowers develop into fruits. This phenomenon is called "caulifloria", which literally means "stem blossom".
Many researchers of tropical nature have tried to explain why in warm climates flower buds are formed deep in the tissues of the trunk and then break out through the bark.
Some believe that this is due to the economy mode. In a rainforest where flora crowd each other, the expenditure of energy pushing nutrient juices through a complex system of branches to fruits is an unnecessary luxury.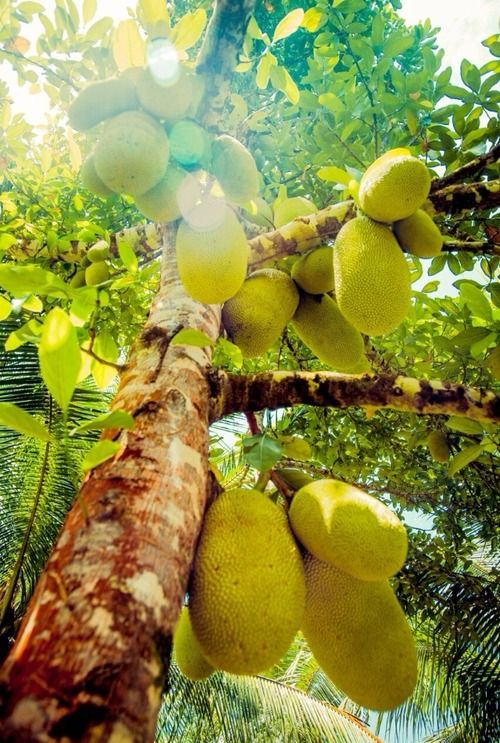 Isn't it easier to directly feed them from the trunk to the fruits?
Isn't it easier to directly feed them from the trunk to the fruits?
Others find it beneficial for trees with very large fruits that, due to their weight, could easily break branches.
In 1878, the English naturalist Alfred Wallace suggested that caulifloria made it easier for pollinators to find flowers in the dusk of the rainforest.
Pronounced cauliflory is observed in cocoa (Theobroma cacao), couroupita (Couroupita guianensis), breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) and its closest relative, jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus). This phenomenon is also characteristic of some ficuses and various representatives of the Annon and Sapot families.
15 fruits we eat but don't know how they grow — Botanichka
Thanks to world trade and the rapid development of transport flows, today we can enjoy the fruits of plants that do not grow in our climatic conditions. At the same time, some of them are so fond of that they have firmly entered our daily diet. And what do we know about how these "overseas dishes" grow?
Pear-shaped peduncle (so-called kazh apple). Below is a real fruit - a cashew nut. © Amar Bangladesh
Below is a real fruit - a cashew nut. © Amar Bangladesh Our publication will tell you the fruits of which plants are 15 products that are well known to everyone. At the same time, it should be noted that some of them, from the point of view of biology, are not considered fruits.
1. Capers
CapersCapers, for example, are not fruits at all, but the unblown buds of the herbaceous plant Caper prickly. If they are allowed to bloom, then you can admire the white flowers of stunning beauty for a long time, and then collect the fruits. True, they are considered less tasty than buds, therefore, usually, when purchasing canned capers, we buy exactly unblown flower buds of prickly caper.
Collection of prickly caper buds. © Bellina Alimentari Prickly caper is an extremely hardy plant. Its roots reach groundwater, growing up to 20 meters, the length of the branches reaches 1.5 meters. He lives in nature on stones, in cracks in walls, therefore he brings significant trouble to historical architectural monuments in his homeland - in Central Asia. It is grown on an industrial scale today, mainly in the Mediterranean countries of Europe, whose cuisines are rich in dishes with capers. The original recipe for the famous Olivier salad, by the way, used capers, not pickles. It grows in the wild in the Caucasus, Crimea, Kazakhstan.
It is grown on an industrial scale today, mainly in the Mediterranean countries of Europe, whose cuisines are rich in dishes with capers. The original recipe for the famous Olivier salad, by the way, used capers, not pickles. It grows in the wild in the Caucasus, Crimea, Kazakhstan.
2. Figs
Figs, fruits of the fig tree. © MaximilianFigs originate from India and the Mediterranean. These fruits grow in the subtropics on trees or large shrubs, reaching a height of ten meters. On the banks of the rivers, fig trees or fig trees (other names for figs) form impenetrable thickets. These plants are also loved by the southern slopes of the mountains, where they can grow at an altitude of up to 2000 meters above sea level.
Fig, or Fig, or Fig tree (Ficus carica). © Get Horty In Russia, figs are cultivated only in the southern regions, and the main industrial plantations of fig trees are located in Turkey, Greece, Tunisia, South America, Portugal and Italy. This plant does not withstand frosts below -12 degrees Celsius.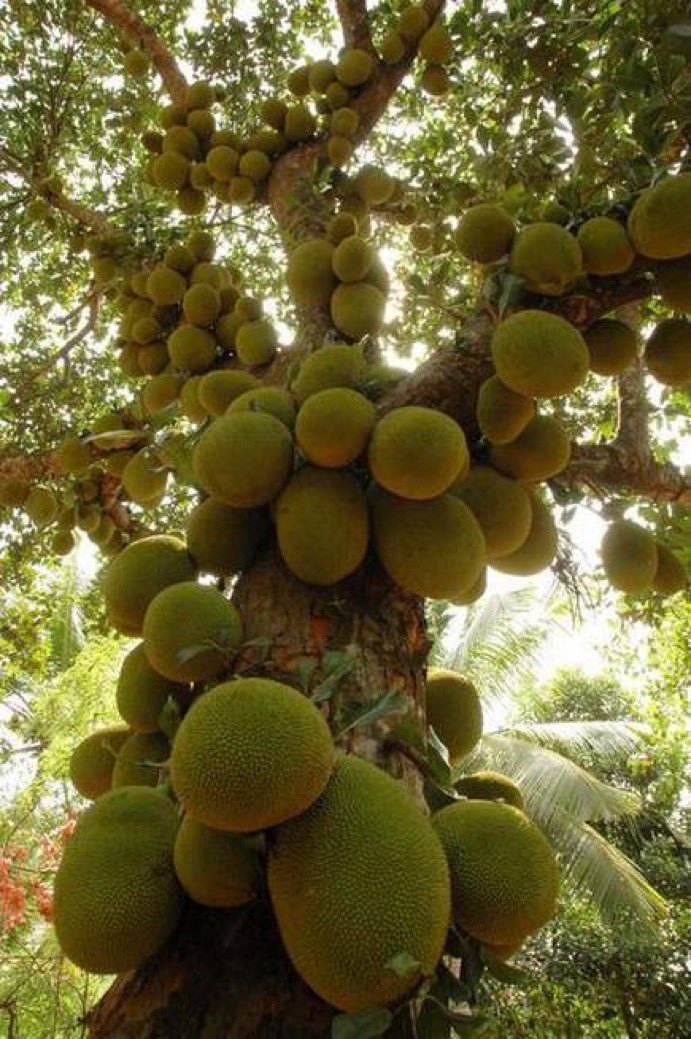 But you can grow figs successfully at home, as an ornamental crop. Tub fig trees grow no higher than 3 - 4 meters.
But you can grow figs successfully at home, as an ornamental crop. Tub fig trees grow no higher than 3 - 4 meters.
How to grow figs, read the article: Figs - figs.
3. Papaya
Ripe papaya fruitMelon tree, also known as the plant on which the papaya fruit grows, is native to Central America and Mexico. Papaya absolutely does not tolerate sub-zero temperatures, even the most minimal ones, therefore it grows only in the tropics. The plant looks like a palm tree, but it is not. It is a tree reaching 15 meters in height. The diameter of the hollow inside the trunk at the base is 30 cm, and the side branches are completely absent.
Cultivation of papaya or melon tree on a plantation (Carica papaya). © cnseed Papaya leaves are formed only at the top of the trunk and can grow up to 90 cm in length. Interestingly, the plant has male and female flowers. In this case, more often flowers of only one sex grow on one tree. But during high summer temperatures, the sex of flowers can change from female to male and vice versa.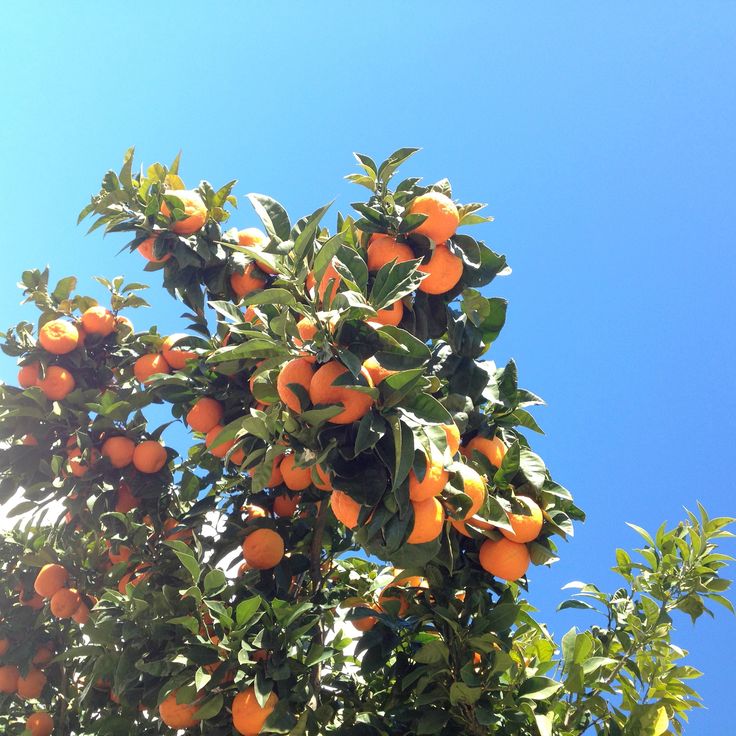
4. Brazil nut
Brazil nut. © zoom50The Brazil nut is a tree that grows in the wild forests of Brazil, but also in Peru, Colombia, Bolivia and Venezuela. This plant has two features that, like its fruits, deserve great attention. Firstly, Bertoletia (another name for it) is one of the largest plants on our planet. It reaches a height of 30-45 meters, and the diameter of the brazil nut trunk can be about two meters. Secondly, this tree is an absolute long-liver. Although it is officially believed that the bartoletia lives only half a millennium, the Brazilians claim that this tree grows and bears fruit for up to 1000 years. And they even show such specimens to tourists, although, of course, it is difficult to verify the accuracy of this information.
Bertholletia, Brazil nut (Bertholletia). © Aspruder Another feature of the Brazil nut is that it only bears fruit in the wild. And the richest crops are harvested not in Brazil, as one might think, but in Bolivia. The fruit itself looks like a large box, reaching 15 cm in diameter and two kilograms of weight. And the so-called nuts are the grains of this fruit.
The fruit itself looks like a large box, reaching 15 cm in diameter and two kilograms of weight. And the so-called nuts are the grains of this fruit.
5. Pitahaya (dragon fruit)
Pitahaya (dragon fruit). © Jordan SteadmanDragonfruit grows on a cactus. True, not quite ordinary. Pitahaya is a vine-shaped climbing cactus, successfully grown today in Central and South America, Australia and Southeast Asia. It is interesting that these cacti are very prolific - about thirty tons of crop can be obtained from one hectare of plantations per year. Pitahaya bears fruit up to six times a year!
Plantation of hylocereus, plants that produce pitahaya fruits. © thejakartapostAnother feature of the plant that gives us these sweet fruits with incredibly tender creamy pulp is that it blooms only at night. Large white flowers have a very pleasant persistent smell.
6. Wasabi
Wasabi paste and eutrema japonica root. © maguro Eutrema japonica is a perennial herbaceous plant, from the rhizome of which the world-famous seasoning for Japanese cuisine - wasabi is prepared, grows up to half a meter in height. It is noteworthy that the rhizome itself grows very slowly, at most, gaining a length of 3 cm per year. It is customary to consider the root as mature only in the 3rd - 4th year. Wasabi is popularly called Japanese horseradish, although this plant has little in common with horseradish - only belonging to the same family.
It is noteworthy that the rhizome itself grows very slowly, at most, gaining a length of 3 cm per year. It is customary to consider the root as mature only in the 3rd - 4th year. Wasabi is popularly called Japanese horseradish, although this plant has little in common with horseradish - only belonging to the same family.
Another peculiarity of wasabi is that the rhizome has different sharpness in different parts. But this is a feature of only real wasabi - a plant that grows exclusively in the flowing waters of mountain streams. A vegetable grown in the garden does not have even a tenth of the beneficial properties that “honwasabi” (as the Japanese call real wasabi) has, however, such garden wasabi costs much less.
How to grow Japanese eutherma - wasabi, read the article: Japanese eutherma - "Japanese horseradish" wasabi.
7. Turmeric
Turmeric root and dried powder Turmeric, a perennial plant from the ginger family, can reach a height of up to one meter.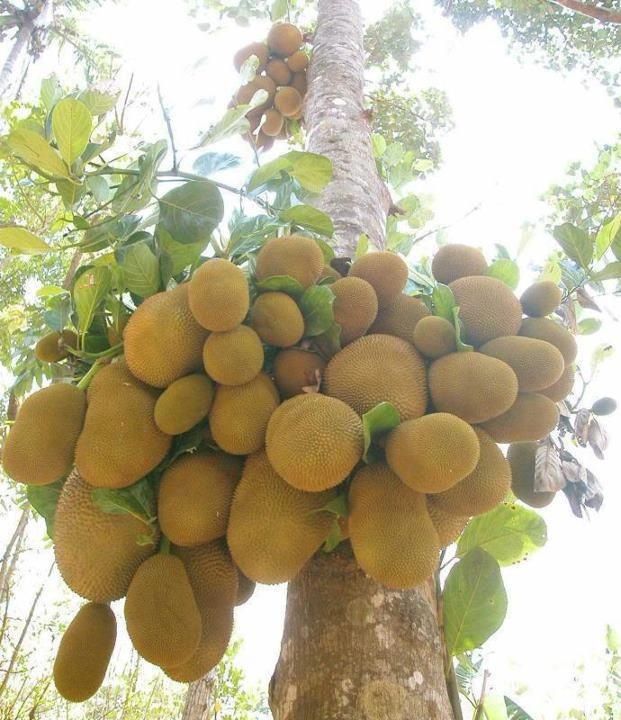 On an industrial scale, it is now grown in Japan and China, India and Indonesia. In these parts, turmeric is considered the most popular seasoning.
On an industrial scale, it is now grown in Japan and China, India and Indonesia. In these parts, turmeric is considered the most popular seasoning.
For the preparation of spices, only the rhizome of Indian saffron (the second name of the plant) is used, but the plant itself is quite decorative. Small flowers are combined into large (up to 20 cm in length) inflorescences and boast very beautiful bracts. One turmeric bush (long leaves grow straight from the soil) can have several of these inflorescences. At the same time, the flowering of turmeric is very long - up to three months. Therefore, today this plant is gaining popularity in home floriculture.
To learn how to grow turmeric, read the article: Daring forms of indoor turmeric.
8. Clove
Clove is a spice. © Thamizhpparithi Maari The world-famous clove spice is the unopened flower buds of a large evergreen tree (up to 20 meters high), which grows mainly on the islands of Pemba and Madagascar.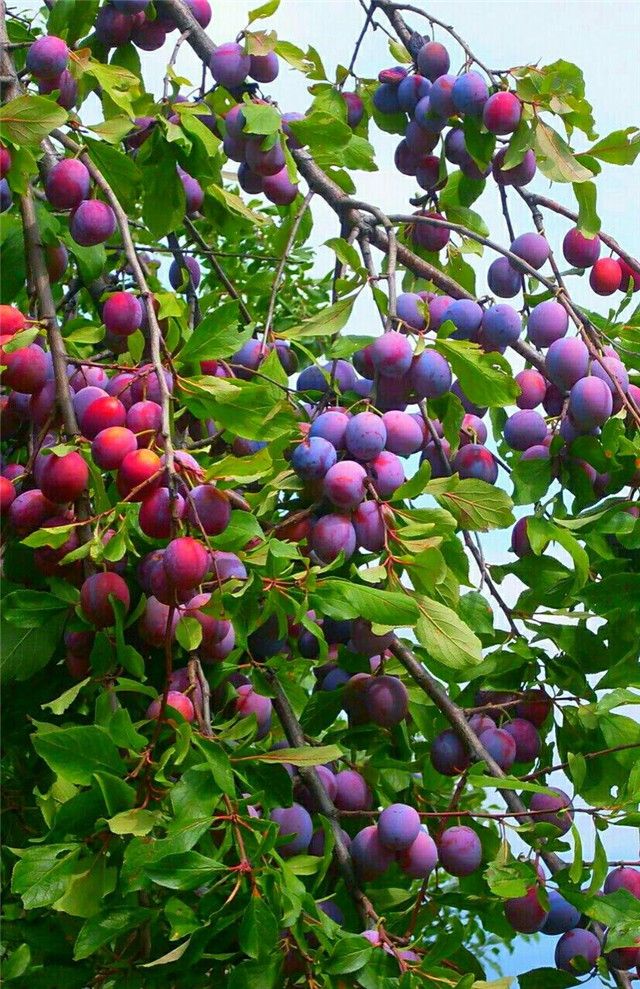 A third of the world's supply of cloves comes from there.
A third of the world's supply of cloves comes from there.
Carnation blooms and, accordingly, “fruits with buds” twice a year. The assembly process is simple, so this spice is relatively inexpensive. In greenhouse conditions, cloves are also grown, but this is a rather troublesome process. However, as well as caring for any exotic house plants.
9. Avocado
Avocado fruitAvocado is biologically a drupe. It grows on an evergreen tropical tree with a wide crown and a height of up to 15 meters. Most growers regularly trim avocado trees to about 5 meters to make harvesting easier.
Avocado inflorescences and fruits on a Persea americana tree branch. © agric.wa.gov Avocados are unique in that they never fully ripen on the tree. After picking the fruits, at least 1-2 weeks pass, during which they reach the desired condition at room temperature. Therefore, if you bought an unripe avocado, this is normal. Just put it in a dark locker for a few days.
How to grow avocados, read the article: Secrets of growing avocados at home.
10. Black pepper
Black pepper: green, dried without peel and dried with peel. © Liliana UsvatThe most widespread spice on the planet Earth is black pepper. These are the fruits of a perennial evergreen tree vine of the pepper family.
Malabar berry (also called black pepper) grows in tropical forests, twisting around trees and reaching 15 meters in length. On an industrial scale, black pepper is grown on special trellises or supports.
Black pepper plantation (Piper nigrum). © Liliana UsvatAt the beginning of ripening, the fruits of the plant have a green color, darkening with time and acquiring a more intense aroma. If the pepper berries are overripe, the peel is removed from them, leaving only the white core. Such black pepper is called commercially "white". Its taste is not so sharp, but the smell is more intense.
How to grow black pepper, read the article: Black pepper, or "Malabar berry".

11. Quinoa
Quinoa SeedsThe quinoa plant looks like tall grass. It grows up to four meters, has a rigid branching stem, large round leaves and large inflorescences. Biologists classify the culture as pseudocereal, due to the absence of a hard shell on the fruit. Hundreds of varieties of quinoa are known today, but only three are commercially grown.
Quinoa plantation. © Michael HermannQuinoa has been proven to be a staple of the ancient Indian diet. "Golden grain", as the Incas called it, who considered these fruits as important a product as potatoes and corn. At the beginning of the 21st century, quinoa became popular all over the world thanks to the adherents of healthy eating. However, this product must be introduced into your diet very carefully: it is a strong allergen.
To learn how to grow quinoa, read the article: Quinoa is a diet crop in your garden.
12. Vanilla
Vanilla powder and pods.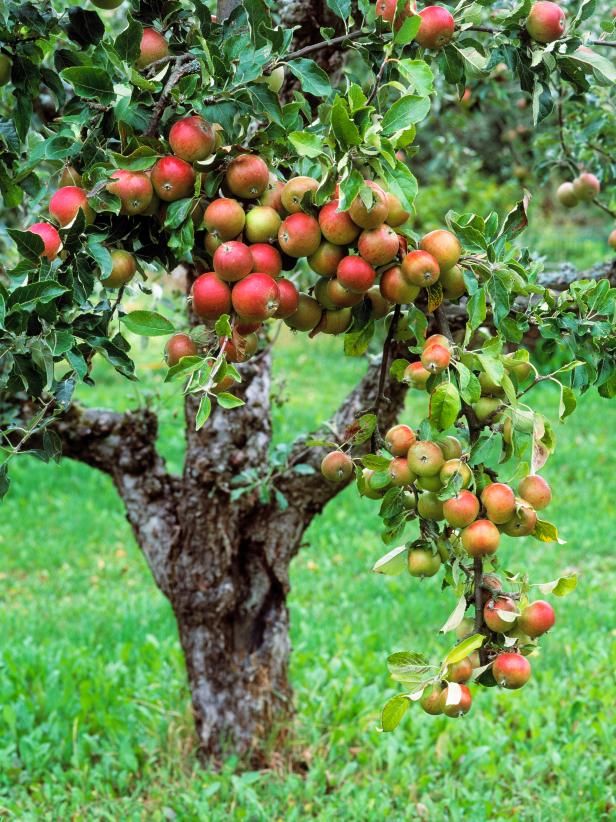 © lafaza
© lafaza Real vanilla has little in common with vanilla or vanilla sugar, which we buy in supermarkets for baking. It is obscenely expensive, because its cultivation is very difficult, and the yields are meager - a maximum of two centners per hectare. Vanillin is a product of the chemical industry, and vanilla is the dried and powdered fruits of a perennial liana of the orchid family.
Vanilla orchid (Vanilla): flower, green and dried pods. © Aveter This plant, wrapping around a tree, climbs to a height of up to 15 meters. The vanilla stem is very thin and the leaves are fleshy and flat, long and oval. They grow directly from the stem, which does not branch. Vanilla flowers bloom no more than one day. After fertilization, the ovary is found only on the 7th - 9th month! Vanilla fruit is a narrow oblong cylinder about 25 cm long and one and a half cm wide with small seeds inside. Difficulties with the cultivation of vanilla are associated, first of all, with the problems of its pollination. Oddly enough, but in the wild, only one species of hummingbird and bees of the same genus, which live only in Mexico, can pollinate it. Commercially, vanilla is pollinated by hand. To do this, use a special brush. This is a very lengthy and not always effective process. Only half of the flowers pollinated artificially produce an ovary.
Oddly enough, but in the wild, only one species of hummingbird and bees of the same genus, which live only in Mexico, can pollinate it. Commercially, vanilla is pollinated by hand. To do this, use a special brush. This is a very lengthy and not always effective process. Only half of the flowers pollinated artificially produce an ovary.
13. Ginger
Ginger rootGinger, a perennial herbaceous plant with long narrow leaves and a valuable rhizome, is now rarely found in the wild. What we eat is a crop grown mainly on plantations in India and Southeast Asia. Ginger flowers are slightly reminiscent of the well-known irises.
Rooted ginger plant (Zingiber officinale). © EricInterestingly, in the Middle Ages, ginger was brought to Europe, where it became famous as the most effective prophylactic against the plague. Its price was simply fabulous. In cooking, ginger began to be used much later than in medicine.
To learn how to grow ginger, read the article: Ginger is a seasoning and medicine.
Growing methods.
14. Pistachios
PistachiosWe are accustomed to consider pistachios as nuts, although the science of Botany claims that these are the seeds of a fruit - a drupe. They grow on small trees, often called bushes, with a dense crown. The pistachio tree blooms in April, the fruits ripen by September-November, depending on the variety and region of growth.
Plantation of real pistachio or pistachio tree (Pistacia vera)In the wild, pistachios grow almost everywhere in Asia, in areas of North-West Africa. The nature of Syria, Mesopotamia, Iran and Central America is rich in pistachios. This plant is cultivated in southern Europe.
Pistachio trees are long-lived. It is believed that in favorable conditions they live for at least 400 years.
Read more about how pistachios grow in the article: How do pistachios grow?
15. Cinnamon
Cinnamon stick and cinnamon powder The spice cinnamon is not a fruit, but the dried inner part of the bark of the Ceylon cinnamon tree, which belongs to the laurel family and the cinnamon genus.