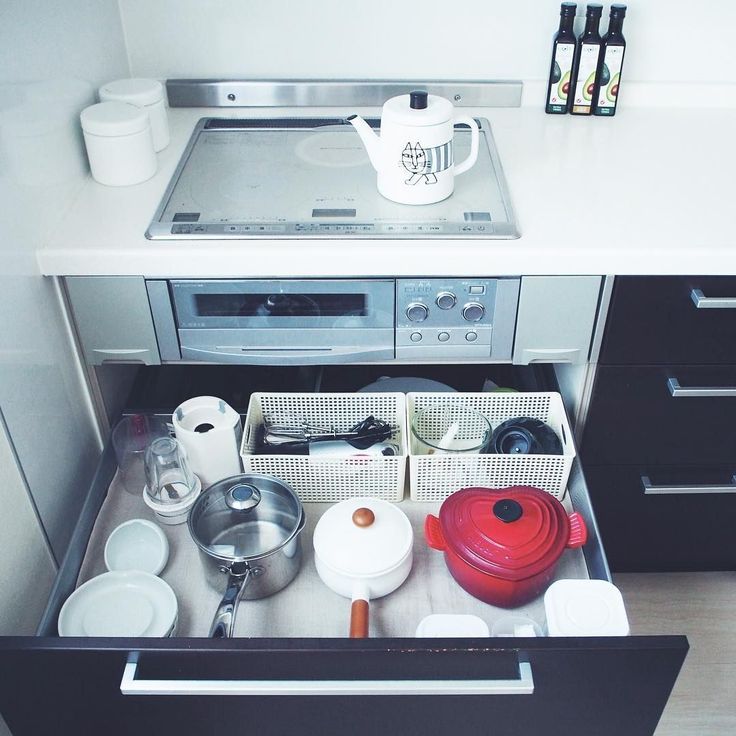
Best time to plant sunflowers
3 Options for Lots of Beautiful Blooms
Sunflowers are among the most colorful and cheerful plants for gardens. They are quick to grow, attractive to pollinators, and downright beautiful. If you’re wondering when to plant sunflowers for the greatest chance of success, you’ve come to the right place. This article introduces three different planting times for sunflowers and discusses the pros and cons of each method. You’ll also find step-by-step instructions for getting the job done.
There are many different varieties of sunflowers. All can be started from seed by planting at one of three times.Sunflower planting times
As a horticulturist and former cut flower farmer, I’ve grown dozens of different varieties of sunflowers. Over the years, I’ve found that knowing when to plant sunflowers can mean the difference between a large and successful show of blooms and one that’s less than ideal. If you plant them at the wrong time, the seeds could rot or they could fail to germinate. Did you know that there are three different times to plant sunflowers? Each one occurs in a different location, demands a different level of effort, and requires different tools and equipment for getting the job done.
Your options for when to plant sunflowers include:
1. Early spring – sow sunflowers indoors, under grow lights
2. Mid spring – sow sunflowers outdoors, directly into the garden
3. In winter – sow seeds in plastic milk jugs outdoors using a method known as winter sowing.
Let me share the ins and outs of each of these three sunflower growing options.
Option 1 – Early Spring: When to plant sunflowers indoors
Admittedly, this is my least favorite time and method for planting sunflowers, simply because it requires special equipment and more attention from the gardener.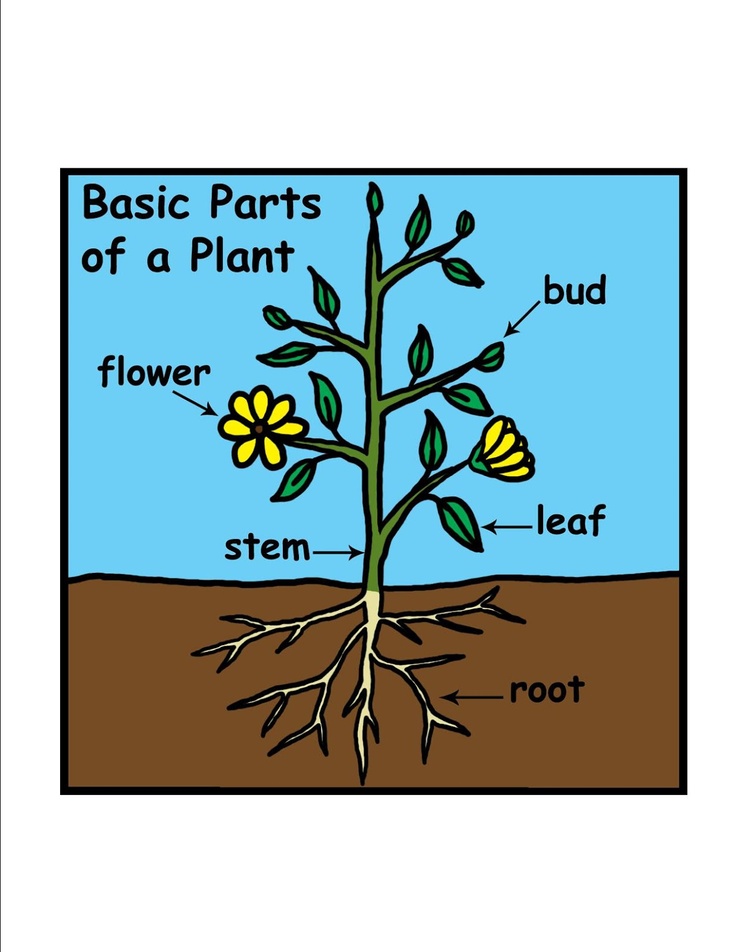 However, it’s probably the safest way to grow sunflowers since the young seedlings are protected from the elements and grown in a very controlled environment. Watering and fertilizing chores are carefully managed, and you have better control over how and when the plants are eventually placed out into the garden. This timing involves sowing sunflower seeds indoors under grow lights and then transplanting the seedlings out into the garden when the danger of frost has passed for your growing zone.
However, it’s probably the safest way to grow sunflowers since the young seedlings are protected from the elements and grown in a very controlled environment. Watering and fertilizing chores are carefully managed, and you have better control over how and when the plants are eventually placed out into the garden. This timing involves sowing sunflower seeds indoors under grow lights and then transplanting the seedlings out into the garden when the danger of frost has passed for your growing zone.
Tools you’ll need:
- Sunflower seeds
- Peat pellets or pots filled with potting soil
- Plant labels
- Hose or watering can
- Grow lights with a timer
Step 1: Decide on the proper timing
When to plant sunflowers indoors depends on when your last spring frost occurs.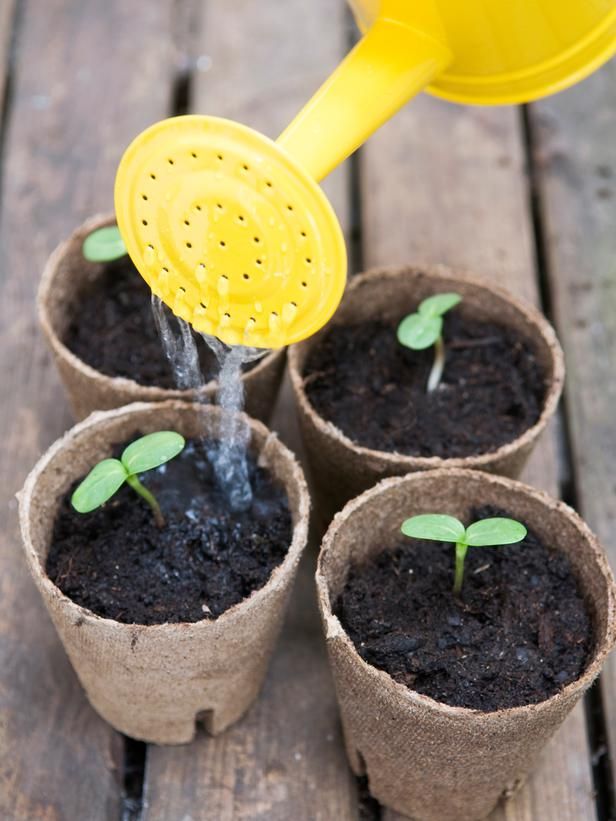 Here in Pennsylvania, our last spring frost is usually around May 15th. From your own region’s last frost date, subtract 4 weeks; that’s your target date for planting sunflower seeds indoors. If you plant too early, they’ll be leggy and weak. If you plant too late, they won’t be large enough when it’s time to move the plants out into the garden.
Here in Pennsylvania, our last spring frost is usually around May 15th. From your own region’s last frost date, subtract 4 weeks; that’s your target date for planting sunflower seeds indoors. If you plant too early, they’ll be leggy and weak. If you plant too late, they won’t be large enough when it’s time to move the plants out into the garden.
Step 2: Sow the seeds
I like to use peat pellets for planting sunflower seeds indoors because there is no root disturbance when you move them out into the garden. Plus, peat pellets are easy to use. But a pot of potting soil works just as well for starting sunflower seeds. Sow one seed per peat pellet or small pot. Plant to a depth of a half inch. Cover the seed with soil and water it in.
Step 3: Turn on the grow lights
Growing sunflowers indoors means you’ll need grow lights. Sunflower seedlings get very leggy when grown with just window light, even if it’s a bright window. Leggy seedlings often result in mature plants with weak stems that don’t stand up straight in the garden. Use grow lights and keep them 4-5 inches above the tops of the plants. Run them for 16-18 hours per day.
Leggy seedlings often result in mature plants with weak stems that don’t stand up straight in the garden. Use grow lights and keep them 4-5 inches above the tops of the plants. Run them for 16-18 hours per day.
Step 4: Care for the seedlings
Keep the seedlings watered and fertilize once a week with a liquid organic fertilizer.
Step 5: Move the plants outside
Another downside of using this method of when to plant sunflowers is the need to slowly acclimate the seedlings before transplanting them outdoors full time. About a week before your last frost is expected, take the seedlings outside for a few hours every day. Start them in the shade, and then gradually increase the amount of sunlight they receive every day, as well as the amount of time the plants are outdoors, until they’re outside day and night. Now it’s time to plant them into the garden.

Option 2 – Mid Spring: When to plant sunflowers outdoors
For me, this is the easiest and most practical way to grow sunflowers. If you’re wondering when to plant sunflowers with the least amount of effort, this is it! The seeds are sown directly out into the garden. You get to skip the grow lights, acclimatization, transplanting, and general babying your sunflower plants. This is the tough-love version of growing sunflowers. The biggest downside to sowing sunflowers outdoors is the pests. Birds, chipmunks, and mice enjoy eating the seeds, and slugs, bunnies, and deer sometimes nibble on the plants themselves (more on managing these pests later). I always over-plant, knowing that I may lose some of the plants to these critters.
Tools you’ll need:
- Sunflower seeds
- Labels (optional)
Step 1: Decide on the proper timing
When to plant sunflowers outdoors depends on your last average frost date, just like it does when starting the seeds indoors. Except you can delay the process by a month or more. I start planting sunflower seeds within 7-10 days of my last frost date, and I continue to sow more seeds for several weeks beyond that date. This gives me a staggered bloom time and keeps my garden colorful for the longest amount of time.
Except you can delay the process by a month or more. I start planting sunflower seeds within 7-10 days of my last frost date, and I continue to sow more seeds for several weeks beyond that date. This gives me a staggered bloom time and keeps my garden colorful for the longest amount of time.
Step 2: Prepare the planting site
When planting sunflower seeds outdoors, choose a site that receives a minimum of 8 hours of full sun per day (They don’t call them sunflowers for nothing!). Remove any weeds and cultivate or turn the soil over a bit to loosen it. If you’d like, you can amend the planting area with a few shovels full of compost, but you don’t need to. Average garden soil is just fine for these tough plants.
Step 3: Plant the seeds
Sow the sunflower seeds directly into the garden soil. Use a trowel to dig individual holes about 1-inch-deep, or dig a trench or furrow to plant a row of seeds. Plant the seeds about 6 to 8 inches apart for dense plantings or 12 to 15 inches apart for wider spacing (this is ideal for branching sunflower varieties that produce multiple flowering branches, rather than those that produce a single flower on a tall, upright stalk). Don’t sow the seeds deeper than 1 inch or they could fail to germinate.
Don’t sow the seeds deeper than 1 inch or they could fail to germinate.
Step 4: Thin the seedlings if necessary
If you sowed the seeds a little too thick, don’t be afraid to thin out some of the seedlings. Try to dig them out carefully because if there is a decent root system intact, you can move the thinned seedlings to a new spot in the garden.
Option 3 – Winter: When to plant sunflowers using winter sowing
The third time to plant sunflowers is in winter. Yep, winter. Using a technique known as winter sowing to start your sunflowers is fun and simple. If you’ve ever had volunteer sunflower plants pop up from seed dropped around a bird feeder, you’re already familiar with an unplanned version of winter sowing. But intentional winter sowing allows you to control the process more carefully, ensuring you grow the varieties you love, instead of just the black oil sunflowers found in most birdseed blends. The process can take place any time during the winter. Another big plus of planting sunflower seeds in winter this way is that they’ll germinate at exactly the right time, and there will be no need to acclimatize the seedlings to outdoor growing conditions because they’ll already be living there.
The process can take place any time during the winter. Another big plus of planting sunflower seeds in winter this way is that they’ll germinate at exactly the right time, and there will be no need to acclimatize the seedlings to outdoor growing conditions because they’ll already be living there.
Tools you’ll need:
- Sunflower seeds
- Plastic milk jugs with caps removed
- Potting soil
- Scissors
- Duct tape
- Labels
Step 1: Prepare the jugs for planting
Use the scissors to cut the top of the jug off about one-third of the way up from the bottom. Cut it almost all the way around, leaving a two-inch-wide section uncut to keep the top and bottom of the jug connected. Then, use the scissors to pierce several drainage holes into the bottom of the jug.
Step 2: Fill the bottom of the jug with soil and plant the seeds
Hold the top of the jug off to the side while you fill the bottom of the jug with potting soil. Once filled, sow the seeds 1 inch deep, spacing them 1-2 inches apart. Sowing thickly is fine because you’ll be transplanting them out into the garden when they’re very small. Water the seeds in.
Step 3: Close the jug
Use a piece of duct tape to reattach the top of the jug to the bottom. This makes a mini greenhouse to protect the seedlings.
Step 4: Wait
Put the jugs in a sheltered spot in the garden for the rest of the winter. Snow, rain, or sleet won’t negatively impact the seeds nestled inside. When spring arrives, the seeds will sprout at exactly the right time. Remove the duct tape and open the top of the jug on very warm days (over 70°F), just remember to close it back up at night. Water if necessary.
Step 5: Transplant
Around the time of your last expected spring frost or when the plants reach 2 inches in height (whichever comes first), transplant the seedlings out into the garden. Sunflower seeds grown through winter sowing are more tolerant of cold temperatures than those grown indoors. They’ll tolerate a few light spring frosts without issue.
Sunflower seeds grown through winter sowing are more tolerant of cold temperatures than those grown indoors. They’ll tolerate a few light spring frosts without issue.
Why aren’t my sunflowers growing?
Knowing when to plant sunflowers is only part of your success. Knowing how to overcome possible problems is also an important factor. If you’ve done everything right, and your sunflowers either don’t germinate or something nibbles them off, the list below should help.
- Failure to germinate: Purchase fresh, high-quality seeds; don’t plant too early or in very wet soil
- Very young seedlings nibbled off just above the ground: Probably slugs; use an organic iron phosphate-based slug bait
- Entire leaves go missing: deer; spray the leaves with a liquid repellent every three weeks
- Tops of young plants are eaten off: rabbits; use a granular repellent sprinkled around the plants
- Seeds disappear before they germinate: birds; cover the planting area with floating row cover until the seedlings are an inch tall
- Seeds disappear and the area is dug up: chipmunks or mice; cover the planting area with cage of hardware cloth until the seedlings germinate
 Just be sure the site receives full sun.
Just be sure the site receives full sun.You’re now fully prepared to get started growing your own collection of cheerful sunflowers. Knowing when to plant sunflowers and the best techniques for each different time is key to growing a beautiful sunflower garden, no matter which varieties you decide to grow.
Want to learn more about growing flowering plants? Please visit the following articles:
- Rudbeckia: A powerhouse perennial
- When to plant zinnias: 3 options for lots of beautiful blooms
- Growing sweet alyssum from seed
- Purple perennials
- When to plant sweet peas
- Shasta daisies and how to grow them
- Lilies for the garden
How Late Can You Plant Sunflowers? Things to Know!
Sunflowers love warmth, so it’s only natural that they thrive under mild weather. This is why if you read gardening guides, you’ll see that the growing season for these plants is late spring.
But what if you forget to plant them then? Do you have to wait until next year to enjoy sunflower blooms?
The answer is no. It’s possible to sow sunflower seeds in summer, up until August and possibly even later, depending on when your fall frost begins.
Read on to know how late can you plant sunflowers.
Table of Contents
- How Late to Plant Sunflowers?
- Other Things to Keep in Mind When Planting Late Season Sunflowers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
How Late to Plant Sunflowers?
When is it too late to plant sunflowers? The answer depends on the sunflower varieties you choose and the first frost where you live. In detail, it is too late to start growing these plants if there isn’t enough time for them to bloom before frost arrives.
To illustrate, if you live in Danville in Illinois, your first fall frost will be on October 15.
- Residents who grow Teddy Bear sunflowers in this city will need to do so 65 to 75 days before freezing temperatures come.

- That means planting sunflower seeds on August 1 or 11 at the latest. In this case, sowing seeds in September or mid and late August would be impossible.
Meanwhile, people in Big Rapids, Nichigan will have their expected frost earlier on September 28.
- If they grow Big Smile sunflowers, which take 50 to 60 days to produce bright yellow blooms, their planting times will be August 9 or, to be safe, July 30.
From these examples, it’s clear that if you plant late season sunflowers, it’s best to find the variety with the quickest development, especially if you’re expecting a light frost soon.
Generally, the latest time for planting sunflowers will be in July or late August. You can use 100 days as your benchmark for calculating when to sow seeds, since this is the upper limit of sunflower plants’ maturation period.
Other Things to Keep in Mind When Planting Late Season Sunflowers
Whether you grow sunflowers in late summer or in the fall, you can put them in your garden bed or in pots.
- If you plant sunflower seeds directly into the garden outdoors, you’ll have to follow the rule on early fall frosts we mentioned above. Make sure your sunflowers bloom before winter arrives, or cold weather will kill them.
- In contrast, if you have an indoor yard with temperature control, you can ignore the first frost date and plant sunflowers inside anytime you want. Sow the young seedlings in pots or directly into the garden bed, though I recommend direct seeding, as sunflowers are hard to transplant.
- Alternatively, you can plant seeds in pots outdoors and move them inside before the first early frost date. This way, you won’t have to worry about low air and soil temperatures ruining your yellow flowers.
- In terms of the sunflower planting season, some regions have more extended growing periods than others. Specifically, warmer parts of Australia and other tropical or subtropical regions allow growing sunflowers year-round.
- However, if you don’t live in these climates, remember this: Though sunflowers are cold-hardy down to zone 2, zone 8 and up have better chances of growing these flowering plants during summer.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. When is the best time to plant sunflowers?
Sunflowers growing is best done after the last spring frost if you sow the seeds outdoors. For young plants to survive and sprout, the soil’s temperature should also measure 55 to 60 degrees at the minimum.
Indoor gardening, on the other hand, can begin earlier, about four to six weeks before the last frost date.
These rules apply to both the US and UK. And if you wonder what month to plant sunflowers in spring, the growing season will often start in March or April in the US and end in June. For the UK, April and May are when people plant sunflowers.
To give you an example, Indianapolis in Indiana has its last frost on April 26. Therefore, residents here can have their sunflowers planted on April 27 outdoors, or on March 15 to 29 indoors.
Read more: Best time to plant sunflowers in North Carolina.
2. Where to plant sunflowers or sunflower seeds?
Whether you put sunflowers in the garden or in containers, keep in mind the following criteria when selecting your planting location:
- Place the sunflower seedlings or seeds in well-drained soil with a pH of 6 to 7.
 5.
5. - Give them full sun exposure (6 to 8 hours of sunlight per day) and put them in rows that are 30 inches apart.
- Avoid planting in locations with strong winds.
- Pick a spot with fertile soil (i.e., soil rich in nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus, plus organic matter and other minerals).
3. What happens if you plant sunflowers late?
If you stick to the guideline above, your sunflowers will still grow, though there’s a chance they will have fewer flower heads. You may wonder why this is the case.
As fall and winter approach, the day will get shorter, giving sunflowers less sunlight to absorb. We also know from research that following the sun helps these plants develop and produce bigger leaves, so if you’re deciding when to plant sunflowers, stick to mid or early spring if possible.
4. What are the hardiness zones for sunflowers?
Sunflowers will grow best in hardiness zone 2 to 11. In practice, this means you can plant them in pretty much all parts of the United States, given that the country only has thirteen main hardiness zones.
If you want to know whether your climate is suitable for sunflowers, go to planthardiness.ars.usda.gov and look up the map for your locality.
- For example, if you live in CT or other states in the Northest, you’ll have no trouble growing tall sunflowers, considering you’ll be in zone 3 to 7.
- Places in the Midwest, namely, Ohio, Indiana, and Missouri, can accommodate sunflowers as well because they’re in zone 5, zone 6, and 7.
- Similarly, zone 5 to 8 in Virginia and zone 7 to 9 in Alabama (both Southeast states) all suit sunflower growing.
Using hardiness zones, you can find more examples of places for sowing sunflowers, such as in California. This information can also be used to pick your plant variety, since seed packages will usually list the zones or regions they best grow in.
5. Which pests should I look out for when planting sunflowers?
Below are some pests that will attack sunflowers:
- Aphids
- Bugs (such as harlequin and left-footed varieties)
- Sunflower moths (or Homoeosoma ellectellum)
- False and true wireworms
- Thrips
- Loopers
- Field crickets
Conclusion
How late can you plant sunflowers? Hopefully, you now have the answer.
It’s essential to avoid frosts when choosing your planting date. Only by doing so will you have flower petals to decorate your home with and sunflower seeds to use as a tasty snack.
And if you have a bird feeder, know that sunflowers produce edible seeds that attract avians as well.
Have you sowed sunflowers yet? If you haven’t, why not start this year and brighten up your home with vases of cut flowers?
Categories Planting CalendarA Few Words From the Author
Hi, I am William – Floridayards’ digital content creator. My job is to find answers to all your concerns with thorough research and our team’s expert advice. I will also bring you honest reviews on the best products and equipment for raising your beautiful garden. Please look forward to our work!
Please look forward to our work!
– William Golder
growing from seeds, planting and care in the open field, types and varieties, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/en/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden plants Reissued: Last edited:
Contents
- Planting and caring for sunflowers
- Planting a sunflower - description
- Growing a sunflower from seed10012
Sunflower (lat. Helianthus) is a genus of the Compositae family, numbering about fifty species that grow naturally in North, Central America and Peru. Sunflower cultivation was carried out by the Indians, who used the plant to relieve chest pains and treat fever, baked bread from it, and the pollen and petals of the plant served in those days as raw materials for purple-violet paint, which the natives made on the body of a tattoo.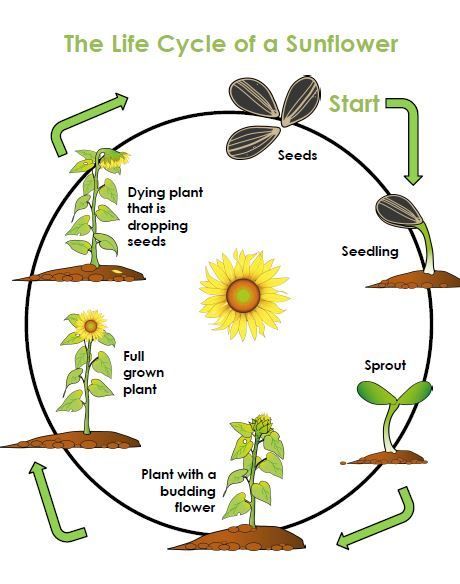 Sunflower oil was used to smear hair, and altars and temples were decorated with inflorescences.
Sunflower oil was used to smear hair, and altars and temples were decorated with inflorescences.
Some species of the genus, representing oil plants or ornamental plants, were exported to Spain in the 16th century, then they came to France and Italy, and by the end of the century they were already grown in Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, Holland and England. In Russia, sunflower became widespread after the Orthodox Church recognized it as a lenten food product. Today, the sunflower plant is the most valuable agricultural crop and is grown all over the world.
Planting and caring for sunflowers
- Planting: sowing seeds in open ground - in late April or early May, when the soil at a depth of 10 cm warms up to 8-12 ˚C.
- Lighting: bright sunlight.
- Soil: any, except acidic, swampy and saline, but fertile soils with clay content are more suitable.
- Watering: frequent and plentiful.
 Most of all, moisture is needed before the plant forms 4 pairs of leaves, and then during budding, flowering and seed filling. In the heat, watering should be daily, and in drought, the site should be watered 2-3 times a day.
Most of all, moisture is needed before the plant forms 4 pairs of leaves, and then during budding, flowering and seed filling. In the heat, watering should be daily, and in drought, the site should be watered 2-3 times a day. - Top dressing: regular throughout the growing season with the use of both organic and mineral fertilizers. The method of introducing the main elements is root, the plant is supplied with microelements during foliar top dressing.
- Propagation: seed - seedlings and non-seedlings.
- Pests: steppe crickets, weevils, scoops, sandy lingers, meadow moths, wireworms, May beetles and their larvae, herbivorous bugs, aphids.
- Diseases: downy mildew, embellisia (black spot), phomopsis (grey spot), stem phomosis, coal (ash) rot, dry rot, verticillium wilt, gray mold, alternariosis (brown spot), sclerotinia ( white rot), ascochitosis, powdery mildew, rust, broomrape, bacteriosis, viral mosaic and greening of flowers.

Read more about sunflower cultivation below
Sunflower plant - description
Oil sunflower (lat. Helianthus annuus) is an annual plant up to 2.5 m high with a tap root system penetrating to a depth of 2-3 m. core. The leaves are alternate, long-petiolate, with the upper ones sessile, and the lower ones opposite, oval-heart-shaped, with pointed tops. The length of the leaf plate with serrated edges, pubescent with a hard pile, reaches 40 cm. The flowers are collected in very large baskets, surrounded by wrapping leaves. Buds and young heads turn with the sun, changing orientation from east to west during the day, but with maturity, the plant fixes the position of the head, although the leaves still turn with the sun. Marginal flowers of baskets from 4 to 7 cm long are reed, barren, and numerous internal flowers are tubular, bisexual.
Usually oilseed sunflower produces only one inflorescence, but sometimes additional shoots with small heads appear. Sunflower blooms for a month - from July to August, cross-pollinated with the help of wind and insects. The fruits are oblong, slightly compressed achenes with weakly pronounced edges, 8 to 15 mm long and 4 to 8 mm wide, with a leathery pericarp and a gray, white, striped or black peel (husk). Inside the seeds are white kernels in the seed coat. Sunflower is an excellent honey plant.
Sunflower blooms for a month - from July to August, cross-pollinated with the help of wind and insects. The fruits are oblong, slightly compressed achenes with weakly pronounced edges, 8 to 15 mm long and 4 to 8 mm wide, with a leathery pericarp and a gray, white, striped or black peel (husk). Inside the seeds are white kernels in the seed coat. Sunflower is an excellent honey plant.
Growing sunflower from seeds
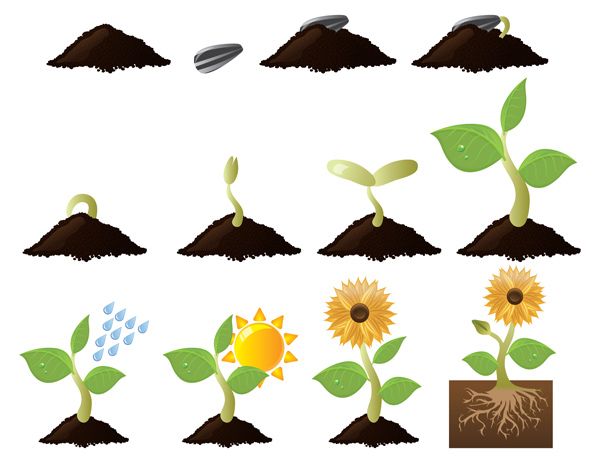
Sowing sunflower seeds
Growing sunflower seeds from seedlings does not make sense, because its seedlings can tolerate light frosts. But if you still decide to grow sunflower seedlings, then sow the seeds 20-25 days before planting in the garden immediately in separate containers - in pots or, for example, in cut plastic bottles 28-30 cm high with drainage holes made in the bottom. Mix fertile soil with humus in equal proportions, fill containers with a wet mixture, plant one or two seeds in each to a depth of 3-4 cm and be sure to press the soil so that it embraces the seeds from all sides. Place the seeds in a warm place and cover them with cling film.
Place the seeds in a warm place and cover them with cling film.
Growing sunflower seedlings
As soon as shoots appear, the crops are moved to a bright windowsill. Seedling care consists in moistening the substrate, carefully loosening the soil and regular airing. A week before planting in open ground, the seedlings are hardened, exposing them daily to the open air and gradually increasing the duration of the procedure.
Sunflower picking
The fact is that sunflower does not tolerate transplantation well, so it is better not to pick seedlings. Sunflower seedlings are planted in open ground in early June along with an earthen clod by transshipment. The sunflower planting scheme involves placing seedlings at a distance of a meter from each other. Be very careful not to damage the root system when transplanting.
Sowing sunflowers in open ground
When to plant sunflowers in the ground
Sow sunflowers in late April or early May, when the soil warms up to 8-12 ºC. The culture is unpretentious to growing conditions - seedlings can withstand both frosts down to -5 ºC and drought. However, there are a few caveats:
The culture is unpretentious to growing conditions - seedlings can withstand both frosts down to -5 ºC and drought. However, there are a few caveats:
- do not grow sunflower for several years in one place, take a break of 3-4 years;
- do not plant sunflowers where tomatoes, beets or legumes were grown last season;
- The best predecessors for sunflower are corn and cereals;
- when planting sunflower, keep in mind that no crop can fully grow in the diameter of its root system.
Sunflower Soil
Fertile soils with some clay in the roots and moisture underneath will be optimal for sunflowers. In general, sunflower is able to adapt to any type of soil - both light and heavy. Acid, marshy and saline soils are not at all suitable for culture.
- Coriander: cultivation, properties, application
Before sowing sunflower, prepare the site: free it from weeds and apply complex mineral fertilizers for digging. Some gardeners do not consider it necessary to fertilize the soil specifically for this crop, believing that if other vegetables grow well on the site, then sunflower will also grow.
Some gardeners do not consider it necessary to fertilize the soil specifically for this crop, believing that if other vegetables grow well on the site, then sunflower will also grow.
How to plant sunflowers in open ground
Before sowing, sunflower seeds must be calibrated and then pickled for 14 hours in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or kept overnight in garlic-onion infusion, to prepare which 100 g of garlic are crushed, mixed with onion peel, pour two liters of boiling water, insist for a day and filter through gauze. The use of garlic infusion for seed dressing will not only kill all pathogens, but for the first time will scare away pests and rodents from seeds.
Sunflower is sown in moist soil to a depth of about 8 cm, leaving 2-3 seeds per nest. Between large sunflowers, a distance of about a meter is kept, and between varieties of medium height - about 60 cm. The greater the distance between plants, the larger the seeds of the new crop will be.
What to plant after sunflower
Growing sunflower greatly depletes the soil, so it is pointless to plant vegetables after it, it is better to plant some legumes - soybeans, beans, peas, vetch, lupins. Legumes will allow the soil to rest and saturate it with nitrogen. The following year, after legumes, cucumbers can be grown in this place.
Caring for sunflowers
How to grow sunflowers
If you want to get large seeds, you have to take care of sunflowers. What does it mean? It is necessary to regularly water, remove weeds and loosen the soil around the plants and between rows, apply top dressing, protect plants from diseases and pests.
Watering sunflowers
Water sunflowers as needed. Especially the plant needs moisture until the formation of 4 pairs of leaves. The next stage of increased demand for moisture falls on the formation of inflorescences, and then - during the period of flowering and seed filling. When moistening sunflower, not only the frequency of watering is important - it is necessary to soak the soil to the depth of the plant's roots. In the summer heat, sunflowers are watered daily, but if drought sets in, you will have to moisten the soil two or even three times a day - sunflowers are very moisture-loving.
In the summer heat, sunflowers are watered daily, but if drought sets in, you will have to moisten the soil two or even three times a day - sunflowers are very moisture-loving.
Sunflower top dressing
Since sunflower needs a large amount of nutrients, after the formation of the third pair of leaves, it should be fed: 20-40 g of superphosphate is applied per m² of plot, spreading dry fertilizer over the surface. Then the granules are embedded in the soil to a depth of 10 cm, after which the site is watered.
- Yarrow: properties, planting and care, types and varieties
As soon as the baskets are formed, apply a potassium-nitrogen fertilizer to the soil: add a tablespoon of potassium sulfate to a bucket of mullein solution (1:10). Re-fertilize the plants with the same solution during seed maturation.
Sometimes sunflower leaves develop blistering distortions, cracks form on the stems and become brittle. These are signs of a lack of boron in the soil. In this case, it is necessary to treat the plant along the leaves with a boron-containing preparation.
In this case, it is necessary to treat the plant along the leaves with a boron-containing preparation.
Pests and diseases of sunflower
Diseases of sunflower
Sunflower with improper care and non-compliance with agricultural technology can infect many diseases.
Downy mildew, or downy mildew, is a fungal disease caused by the Plasmopara fungus. The diseased plant looks underdeveloped, its stems become thin and brittle, and the leaves are small and chlorotic, with a white coating on the underside of the plate. But there is a form of the disease in which the stems are shortened and thickened. In one season, it is possible to re-infect with peronosporosis a sunflower that has almost completed its development. In this case, small irregularly shaped oily spots appear on the leaves, a whitish coating forms on their underside, and the stems become light green. Then the infection penetrates into the basket, which, due to the lesion, ceases to develop.
Embellisia, or black spot is a harmful disease affecting not only sunflowers, but even very resistant weeds. Signs of the disease appear on plants at the stage of development of 5-6 leaves: dark necrotic spots 3-5 mm in size appear on the plates, which grow and merge, forming spots 4-5 cm in size, surrounded by a yellow border. Dark elongated spots of irregular shape appear on the petioles, numerous cracks appear at the point of attachment of the petiole to the stem, and black necrosis forms on the stem around the petiole. On baskets affected by embellisia, dark brown spots can also be seen.
Signs of the disease appear on plants at the stage of development of 5-6 leaves: dark necrotic spots 3-5 mm in size appear on the plates, which grow and merge, forming spots 4-5 cm in size, surrounded by a yellow border. Dark elongated spots of irregular shape appear on the petioles, numerous cracks appear at the point of attachment of the petiole to the stem, and black necrosis forms on the stem around the petiole. On baskets affected by embellisia, dark brown spots can also be seen.
Phomopsis, or gray spot is one of the most dangerous fungal diseases that affects all parts of the plant. Dark brown angular necroses appear on the leaves, as if from a burn, and the leaves, together with the petioles, dry out and die. On the stems around the affected petioles, brown necroses with a clear contour are also formed, which after a while turn gray and become covered with pycnidia. The stems become brittle and break easily. The disease progresses with high humidity in warm weather.
Stem blight is caused by a fungus and occurs on young plants in the developmental stage with 6-8 leaves. Brown spots with a bright yellow rim appear on the leaves, they increase, covering the entire leaf and even the petiole. Then the fungus infects the tissues of the stem, and if infection occurs during flowering, brown spots of irregular shape soon form on the basket, the seeds develop poorly, turn out to be half empty, and then turn brown too.
- Jerusalem artichoke: growing in the garden, types and varieties
Coal, or Ash Rot is a fungal disease that also affects beets, potatoes and corn. The infection gathers on the neck of the root and, developing, moves up the stem, blocking the flow of useful substances through it, which is why the leaves and top begin to wither, dry out, and the plant may die. The disease progresses in the heat with a long absence of precipitation.
Dry rot is caused by a fungus and is ubiquitous. Rotting dark brown spots are found on the front side of the basket, which gradually dry out and harden. With a strong defeat, cells with grains easily move away from the base in whole layers. The seeds look flat, underdeveloped, stuck together, and they taste bitter. Most often, the disease develops in a prolonged drought and after sunflower damage by hail.
Gray mold is also caused by a fungus that can survive for a long time in the soil, on seeds, plant roots and in crop residues. The infection becomes active in humid weather against the background of a decrease in temperature. Brown spots appear on young plants, soon covered with a grayish coating. Dark strokes with the same bloom form on the stems. It affects the fungus and ripening baskets, which is why oily spots appear on their back side, the tissue in these places softens, becomes coated, rots and dies. Under favorable conditions for the fungus, it can adversely affect the yield of sunflower.
Verticillium wilt can cause gradual tissue wilt and even plant death. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus that affects the vascular system of sunflower. The first signs of the disease are already noticeable during flowering, then verticillium appears on leaves that lose turgor between the veins, after which they wrinkle and die, but may not fall off for a long time. The infection affects the vessels of the stem, worsening the quality of the generative organs - if you cut the stem of the affected plant, you can see the flesh that has become brown. The fungus is activated during prolonged drought and heat.
Alternaria blight, or brown spot, caused by a fungus, affects sunflower stems, leaves and seeds. First, brown necrotic dots appear on the leaves, which increase and acquire irregular shapes. Sometimes Alternariosis appears only at the end of the growing season. The disease develops against the background of high humidity and air temperature.
Sclerotinia, or white rot affects sunflower during the entire growing season, but may manifest itself in different ways. The rapidity of development is characteristic of this disease. Seedlings affected by white rot die immediately. In young plants with 5-6 leaves, at an air temperature of 16-18 ºC, against the background of high humidity, a white felt coating forms on the leaves. With the development of the disease, diseased tissues die off, the stems break and the plants die. Wet light brown spots appear on the back of the basket, the fabric under which becomes soft. Root damage of sunflower with white rot reduces the supply of nutrients to the leaves and stems, which brings the death of the plant closer.
Ascochitosis may appear during the entire growing season, but symptoms become more pronounced in the second half of summer: very dark, almost black spots of round or irregular shape, 1-2 cm in diameter, appear on leaves, stems and baskets, and over time pycnidia appear in the center of the spots. The infection is of fungal origin.
- Chili pepper (bitter): growing from seeds in the garden
Powdery mildew is widespread in the southern regions. It appears as a white powdery coating on the surface of the leaves, which gradually darkens and turns into a dense brown film. With the intensive development of the disease, the yield of plants decreases and the oil content in the seeds decreases.
Rust is a fungal disease found in all areas where sunflowers are grown. In spring, convex orange formations in the form of pads appear on the lower, and sometimes on the upper side of the leaves - pustules, when cracked, a rusty powder, which is a fungus spore, scatters. Rust causes the death of leaves, and with severe infection, other organs also suffer. In the affected plants, moisture loss, metabolic disorders and developmental delay are observed.
Broomrape is a single stem parasite with light purple flowers and capsule-shaped fruits. The broomrape sprout is attached to the sunflower root, penetrates into it and lives off the plant, greatly reducing its yield.
Bacteriosis, as it is clear from the name of the disease, has a bacterial nature. Sunflower tissues affected by the disease rot and become slimy, wither and dry.
Mosaic is caused by the tobacco curl stripe virus and is manifested by a change in sunflower leaves - they become variegated, then deformed and lag behind in growth and development.
Greening of flowers is manifested by leaf chlorosis, dwarfism, the formation of thin secondary shoots and sterility of flowers that acquire a green color. The disease is caused by mycoplasma bodies carried by leafhoppers.
Sunflower pests
Not only diseases, but also pests can affect the sunflower yield. For example:
- Goldenrod: properties, cultivation, types
- steppe crickets are adult insects that damage the plant during the period of the first leaves and destroy the growing point. Most of the pests are concentrated on the edges of the plots;
- gnawing scoops - the danger is the first generation of pests: caterpillars in the soil gnaw the stem at the root collar;
- sandy slowworms - these beetles gnaw through seedlings and eat them;
- weevils - the most dangerous species are the southern gray, gray and gray beet weevils, which eat cotyledon leaves, bite the stems and harm sprouts that have not yet emerged from the ground;
- Meadow moths are highly gluttonous and omnivorous: the larvae can eat the entire leaf surface, leaving only large veins, they also destroy the epidermis in the baskets and stems;
- herbivorous bugs suck the juices out of the plant.
The most dangerous thing is the defeat of achenes by pests, which leads to their death;
- aphid damages young leaves, causing the plate to wrinkle, turn yellow and turn brown. Plants affected by aphids lag behind in development;
- wireworms - larvae of the click beetle - eat away the sown seeds, sprouts, gnaw seedlings underground. Wireworms are dangerous until the sunflower develops 2-3 pairs of leaves;
- Maybug - its larvae, while in the ground, damage sunflower and other crops, feeding on the roots of plants at the first stage of their development.
Sunflower treatment
In order to protect sunflower crops from diseases and pests, it is necessary:
- observe crop rotation;
- select disease and pest resistant sunflower varieties for cultivation;
- before sowing, it is mandatory to treat sunflower seeds with fungicides and insecticides;
- comply with the terms and scheme of sowing;
- regularly destroy weeds in the area;
- carry out preventive treatments of plants with fungicides and insecticides;
- remove plant debris from the site after harvest;
- carry out deep plowing or digging of the site in autumn.
If signs of fungal diseases appear on the plants during the growing season, the infection should be destroyed with systemic fungicide solutions, for example, Apron or Cruiser. Stop processing at least a month before harvest. Viral diseases are incurable, so specimens affected by the mosaic should be immediately removed and burned.
Seed treatment with insecticides before sowing protects seedlings from pests for 5-7 weeks, but then preventive spraying of sunflowers with broad-spectrum insecticides and acaricides, such as Zalp, Akarin, Actellik or Agravertin, should be carried out from time to time. Especially dangerous are sucking insects - aphids and bedbugs, because they not only damage plants and suck juices out of them, but are also carriers of incurable viral diseases.
Harvesting and storage of sunflowers
When and how to harvest sunflowers
Sunflowers are harvested in the period of their full maturity, when the leaves and baskets dry up and turn brown - it is at this time that the process of oil accumulation in the seeds is completed, the kernels of the seeds harden, the peel acquires a characteristic varieties of color, and the seeds split when squeezed from the sides with teeth. When no more than 15% of sunflowers with yellow reed flowers remain on the site, you can start harvesting.
But sometimes the seed ripening coincides with the beginning of the rainy season, and the baskets do not have time to dry on the vine. Do not store seeds with high humidity. In such cases, on the eve of the start of rains, the plants in dry weather are treated with desiccants that ensure rapid ripening - the seeds in the baskets sing a week earlier. This measure increases the yield of sunflower, the seeds are of high quality, and their moisture content does not exceed 9%.
Sunflower harvesting must be completed within six days, otherwise the seeds will start to fall off. When harvesting, the heads are cut off 2-3 cm down the stem, then the seeds are removed from them with the help of friction and the debris is blown off.
Without cutting, you can tilt the heads over the bucket and knock out the seeds from the baskets by tapping something heavy on the back side. Mature seeds themselves slip out of the nests into the bucket.
The third method of harvesting allows you to save the crop completely without loss: the heads are cut from 10 cm of the stem when only 2/3 of the seeds are ripe. Cloth or paper bags are put on the heads and hung from the ceiling for 2-3 weeks in a well-ventilated area, after which ripe and dry seeds are easily peeled from the nests.
The stems remaining on the plot must be pulled out and burned, and the plot should be plowed or dug up to the depth of a shovel bayonet.
Methods of sunflower storage
The keeping quality of sunflower seeds depends on the integrity of their shells - grains with damaged skins are not protected from infection and quickly deteriorate. They reduce the shelf life of seeds and organic impurities, since they have an increased hygroscopicity compared to seeds.
For long-term storage, only seeds that have been de-littered and winnowed with a moisture content of not more than 7%, cooled to 10 ºC, can be stored. Dry the seeds in a dry place with good ventilation. If the humidity exceeds 12%, it is necessary to increase ventilation during drying.
Dry seeds can be stored for half a year. Keep them in a clean, dry, unheated room in cloth bags suspended from the ceiling.
Sunflower species and cultivars
Commercially, sunflowers are classified according to the color of the husk. For example, varieties of sunflower with black husks are classified as oily, since they contain up to 50% oil, and varieties with striped skins are used for food production, including confectionery. Oil varieties, in turn, depending on the quantity and quality of acids contained in the seeds, are divided into polyunsaturated, monounsaturated and medium oleic.
According to the length of the growing season, sunflower varieties and hybrids are divided into early ripening, mid-early, mid-ripening and mid-late. We offer you an acquaintance with the best varieties of sunflower:
- Lux is a highly productive, large-fruited, resistant to diseases, drought and weeds confectionery variety of early ripening.
Plants of this variety reach a height of 185 cm, the diameter of their basket is 25-27 cm, large nuclei do not adhere tightly to the walls of the achenes;
- Nut is a high yielding, early maturing, versatile variety that is resistant to weather, weeds and some diseases and pests. In plants up to 170 cm high, large oval-oblong black seeds with a peel in a longitudinal dark gray stripe;
- Lakomka is a large-fruited mid-season productive universal variety resistant to weeds, drought, some diseases and pests. The plant reaches a height of almost 2 m, its basket is convex, lowered, the seeds are large and elongated;
- Oliver is a high-yielding early maturing oily hybrid of Serbian selection, resistant to disease and drought. The plant is low - up to 145 cm, not branched, with powerful roots. Medium-sized baskets have a flat shape, ovoid dark seeds are also medium in size;
- Forward - resistant to various rot, sclerotinia, phomopsis, peronosporosis and weeds, high-yielding oil-bearing hybrid of medium early ripening, up to 190 cm high, with convex shape lowered down baskets with a diameter of 15-20 cm and dark striped achenes;
- Rimisol is a lodging-resistant mid-early oilseed hybrid with immunity to some diseases and pests.
These are plants up to 160 cm high with a thick, densely leafy stem, developed root system, inclined convex baskets up to 22 cm in diameter with elongated black seeds;
- Flagman is an early maturing oily variety resistant to powdery mildew and weeds, but susceptible to Phomopsis. Plants of this variety up to 2 m high with elongated oval seeds;
- Prometheus is an extra early and high yielding oil variety that is resistant to drought, weeds, rust and powdery mildew. The height of the plant of this variety is not more than 140 cm, and the diameter of their baskets is 18-22 cm;
- Atilla is also an extra-early and high-yielding oil variety, resistant to almost all fungal diseases and adverse conditions. Plants up to 165 cm high with semi-inclined flat baskets up to 24 cm in diameter;
- Vranac is a high-yielding confectionery mid-late hybrid resistant to diseases, drought, lodging and shedding.
Plants of this variety are tall and powerful, baskets of medium size, very convex, wrapped downwards, achenes broadly ovate, large, black with dark gray stripes along the edges;
- Almaz is an early maturing productive confectionery variety, relatively resistant to lodging, drought and fungal diseases. Its stem is up to 190 cm high, the baskets are convex, large, inclined, the achenes are large, black with gray stripes;
- Zaporizhia confectionery is a mid-season highly productive variety resistant to weeds, shedding, verticillium and downy mildew. The height of the stem reaches 210 cm, the baskets with a diameter of 20-25 cm are flat or barely convex.
Properties of sunflower - harm and benefit
Useful properties of sunflower
The composition of sunflower seeds includes the following substances:
- carotene, which increases the body's defenses by neutralizing the harmful effects of free radicals;
- betaine, which activates lipid metabolism, promotes energy production, normalizes the acidity of the stomach, improves the activity of the digestive system and prevents the deposition of fat;
- choline, which promotes the absorption of fats, lowers cholesterol, strengthens the central nervous system, stimulates the heart and slows down aging;
- resins that have a bactericidal, bacteriostatic, astringent and antiseptic effect;
- fatty oils involved in tissue regeneration, eliminating foci of inflammation, accelerating the process of wound healing, protecting the body from exposure to carcinogens;
- flavonoids, which strengthen and improve the elasticity of capillaries and vessel walls, neutralize the action of free radicals and lower blood pressure;
- organic acids that increase appetite and immunity, activate metabolic processes, remove toxins and normalize digestion;
- tannins with bactericidal, bacteriostatic and astringent action;
- glycosides having diuretic, sedative, expectorant, vasodilating, antimicrobial and disinfectant effects;
- anthocyanins that reduce the fragility of capillaries and blood vessels, slow down the aging process, stop bleeding, strengthen the heart muscle, normalize metabolism and the functioning of the central nervous system, relieve inflammation;
- bitterness that stimulates appetite, normalizes digestion, strengthens the immune system and helps to restore the body in case of weakness, fatigue, exhaustion, loss of strength and neurasthenia;
- phytin, which stimulates the liver, lowers cholesterol, normalizes the state of the nervous system and activates fat metabolism;
- lecithin, which accelerates oxidative processes, provides fat metabolism, improves brain function, normalizes the cardiovascular system, stimulates bile secretion;
- pectin, which removes radionuclides and salts of heavy metals, suppresses putrefactive flora in the intestine;
- saponins that thin sputum, remove mucus from the bronchi and lungs, and prevent DNA synthesis in tumor cells.
In addition to the listed substances, the seeds contain proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, calcium and zinc.
Sunflower seeds - contraindications
The use of sunflower seeds can be not only beneficial, but also harmful. For example, tooth enamel suffers from them, gradually being destroyed by a strong peel covering the seeds. Sunflower grains are high in calories, therefore, in large quantities they are contraindicated for those who seek to reduce their weight. In addition, usually fried seeds are used for food, in which there is almost nothing useful left.
The use of seeds negatively affects the voice data - a greasy film forms in the throat, which interferes with singing and speaking. If you buy sunflower seeds for food, you should understand that the long roots of sunflower absorbed not only useful substances, but also poisons and toxins, so you should make sure that the plant was grown in an ecologically safe area, and the seeds were cleaned of dust and dirt before frying.
Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Peculiarities and other plants of the Asteraceae family
- List of all species on The Plant List
- More information on World Flora Online
Lighting for seedlings - how can you get by with inexpensive fluorescent lamps?
Tomatoes in a greenhouse: planting, care, difficulties
Sections: Compositae (Asteraceae) Garden plants Honey plants Plants on P
People usually read after this article
Add a comment
sowing dates, full cultivation and care
To get a good sunflower harvest, it is not necessary to purchase seeds in stores or from hands, it is enough to grow a crop in a personal plot or cottage, focusing on useful tips and recommendations. The beginning of work falls on sowing seeds in open ground or seedlings, depending on the region of cultivation. Germination of seed material is an optional but recommended process necessary to obtain 100% germination. During selection, seeds that are damaged or differ in size, having a changed color or the presence of inclusions on the husk, are discarded. Revision of last year's collection, allows you to exclude the appearance of diseases and pests at an early stage of the growing season. To strengthen immunity, agronomists advise exposing sunflowers to disinfection and stratification before planting. 9Ol000
Complete and correct planting
Care of seedlings
Dive or not
Sowing sunflower in open ground
When to plant and at what time is better
What kind of soil is better to plant in
Optimal sowing according to all the rules
Sunflower care after germination in open ground
How to grow
Proper watering
Fertilization
The best varieties of sunflower, varieties in the photo
First grade - Rimisol
Second grade - Almaz
Third grade - Zaporozhye Confectionery
Fourth grade - Flagman
Fifth grade - Oliver
Sixth grade - Lux
Seventh grade - Lakomka
Eighth grade - Nut
Ninth grade - Forward
Tenth grade - Prometheus
Eleventh grade - Vranac and Atilla
Common diseases
Common pests and their control
Harvesting time and storage rules
Winter storage methods
Video
Interesting! Sunflower is not only a useful product for making up a daily diet, including the addition of oil and seeds, but also a beautiful flower that adorns the garden landscape.
On its basis, unusual compositions are often made up, combined in color. Sunflower is also an excellent remedy, whose use is widespread in cosmetology and traditional medicine.
How to choose sunflower seeds
When choosing one or more varieties for planting, manufacturers recommend focusing on the characteristics and description of the species. Each variety is interesting and unique in its own way, it belongs to early ripe, medium or late varieties. Some seeds are better suited for germination in southern regions, where there is abnormally hot weather from mid-spring, excluding frequent rainfall. Others prefer temperate climates, being immune to common diseases and pests.
Stem height and head size play an equally important role. To date, both decorative compact and tall plants have been proposed, reaching a height of up to 4.5 meters. If planting is planned in a small area, it is better to give advantages to options that form a single stem, instead of several outlets.
Before sowing work, special attention is paid to the following points:
- packing time and expiration date;
- seed size and integrity;
- uniform color;
- no lesions.
Auspicious days for sunflower sowing in 2023 according to the Lunar calendar
Despite the fact that many doubt the positive influence of the heavenly body on seed germination and their further strength, experienced gardeners try to follow the calculations of astrologers. The reason for this is my own experience and comparison between plants grown according to the lunar calendar and without it.
Sowing on favorable days falls on the following numbers of warm months (spring and early summer): Unfavorable and prohibited days for sunflower sowing in 2023
In each of the months of planting, there are bad periods for sowing. Throughout the coming year, astrologers advise to exclude any gardening manipulations related to sowing and planting, feeding on the following days:
- in March - 7, 17 (c) -19 (y), 21-23;
- in April - 6, 14-15, 19-21;
- in May - 5, 11-12, 15-17 (y), 19;
- in June - 4, 7-9 (y), 11 (c) -13, 18, 21-23 (y).
For sunflower cultivation for industrial purposes, not only sowing and planting dates play an important role, but also full-fledged care, including: watering and feeding, agricultural technology necessary for accelerated vegetation, compliance with the planting scheme, both between rows and beds. The more care the summer resident gives to cultivation, the greater the yield of sunflower seeds he receives by the end of the growing season.
Planting seedlings
Having determined the estimated time, every gardener will be able to understand how to plant sunflower seedlings. Every year, sowing work is carried out with the calculation - minus 25 days from the scheduled date of planting in open ground. A simple addition allows you to reduce the vegetation period of plants to 2 to 3 weeks, eliminating the freezing of seeds when sowing during unstable weather, when frosts are still possible.
Seedling method of cultivation is mandatory in cold regions where there is a deviation in temperature indicators, both in spring and summer. The technique is widespread in the Urals and in Siberia, the Leningrad region, Karelia, the Moscow region and the Far East, within Murmansk and Norilsk.
Despite the cold air giving way to warm later than usual, cultivation in the above regions of heat-loving culture is still possible. Preference is given to frost-resistant and early-ripening varieties that have time to ripen before the start of a cold snap.
8 recommendations for full cultivation:
1) it is better to give preference to sowing seeds in peat containers or snails. Plastic cups quite often become the root cause of damage to the root system during transshipment, before planting in the garden;
2) variety selection is the basis of cultivation. Preference should be given to varieties that have advantages in a particular region of cultivation. For example, if the garden plot is located in the southern part of Ukraine or Russia, it is recommended to give preference to varieties that have protection from fading in the sun, subject to minimal watering;
3) growing seedlings is allowed in several ways: at home or in an apartment on a windowsill or table, subject to additional illumination with a phyto-lamp, in a greenhouse if daylight hours exceed 10 hours;
4) feeding seedlings after the formation of 2-4 full-fledged leaves will allow the plant to form correctly, excluding stem deformation;
5) if possible, the soil for sowing seeds should consist of several parts: half of the purchased and garden soil, wood ash and vermiculite;
6) to prevent the appearance of pests, 14 days after the appearance of the first shoots, carry out preventive treatment using a weak solution of potassium permanganate or cinnamon water. The natural composition will protect against aphids and other ill-wishers that easily appear at home;
7) with high-yielding varieties, it is not easy to collect large volumes from the garden. In order for expectations to be met, it is important to follow the plants, adhering to the work schedule according to the lunar calendar. It is worth watering and feeding the crop on time, taking care of loosening and removing weeds that germinate quite often;
8) if the soil does not have time to fully warm up when the sprouts are transferred to the bed, the sunflower will suffer from a lack of nitrogen absorbed through the root system.
How to choose the right variety
When choosing seeds in a gardening shop or hypermarket, you should pay attention to the F1 mark. Today, seeds are divided into two groups: classic and hybrid, which have a corresponding mark. The former allow the collected seeds to be used as seeds for the next year, while the latter do not. When sowing hybrid seeds from last summer's harvest, the summer resident will not achieve seedlings. However, there are still advantages among F1. As many breeders note, the hybrid sunflower is immune not only to diseases, but also to pests. It is easy to grow even for a beginner summer resident who does not have many years of experience in gardening and experience with sunflower.
Obvious advantages of hybrid varieties remain depending on the variety:
- resistance to waterlogging or vice versa, drought;
- high immunity to diseases and pests;
- high resistance to low temperatures or extreme heat;
- increased yield associated with the size of the head or branches on a single stem;
- no shedding of previously calculated variety;
- seed germination up to 90%, subject to a fresh packing date.
When choosing from the best varieties of sunflower, it is advised to give preference to varieties that have a lot of positive reviews. On gardening forums, the following options are most often praised: Nut, Attila, Lux, Rimissol, Lakomka, Jason F1, Vranac, Flagman.
Planting container
Despite the range of planting containers, you should choose only high-quality cups that do not require picking. Peat cells, glasses and tablets are the best option. An alternative would be egg cells made of cardboard. The second solution is the shell, which is a natural fertilizer that dissolves easily in open ground.
The optimal depth of the seed cell is from 8 to 12 cm. A suitable depth will prevent picks during the formation of seedlings, waiting for the moment of planting in open ground.
Important! Excessive injury during picking, affects the slowdown of vegetation, the condition of seedlings and the quality of the crop itself.
Snails remain a new method that has become established among gardeners in recent years. With their help, it turns out to grow good strong roots, without harming each sprout when diving into open ground. You can study the technique in a photo or video shown as a good example on the Internet.
Important! In order not to damage the window sill, it is recommended to use a suitable pallet. Materials that allow settled water to pass through can easily spoil the interior of an apartment in a month, damaging the surface.
Complete and correct planting
As practice shows, fresh seeds germinate a week after sowing, provided that a mini-greenhouse is created. You can germinate seed material immediately after disinfection and stratification, preferring one of the best methods to date:
1) sowing in soil consisting of half purchased soil and part garden soil, with the addition of wood ash;
2) sprouting on cotton pads or napkins placed on the bottom of a convenient plastic container. Before laying out, the material is well irrigated with warm water. The end is the stretching of the cling film;
3) in a single container, seeds are sown, observing intervals of 5-6 cm. Two seeds are dropped at once into a hole 2 centimeters deep to prevent the absence of seedlings. For the full development of seedlings, it is necessary to use most of the soil borrowed from the garden.
After the first sprouts appear, additional lighting is used to prevent improper sprout formation. With its help, it is possible to achieve uniform growth and the formation of true leaves.
Seedling care
As soon as the seeds germinate, you can begin to fully care for the crop. If possible, if the planting containers are located on the east or north window, it is worth adding phyto-illumination and warm mats that speed up the growing season and prevent the thin stem of the plant from stretching. A warm base will protect the kids from drafts, contributing to the proper drying of the soil in the planting containers.
First of all, you should take care of full and regular watering. It is worth sticking to the schedule drawn up according to the lunar calendar. The exclusion of unfavorable days and a clear visual inspection of the topsoil will not allow overflowing or overdrying the soil.
If it is not possible to purchase a special lamp for additional lighting, you can use a regular table lamp by screwing in the lamp of the required power.
As soon as the plant has a few full leaves, it is allowed to apply complex fertilizers. Ready-made mineral and nitrogen supplements are ideal for starting the growing season. The most important thing is to use a smaller percentage when hovering the solution. The proportion indicated in the instructions should be divided by 2.
Worked well when growing sunflower seedlings, complex fertiliser. It can be used with each watering, reducing the proportion of the induced solution by 2-3 times.
To dive or not
Sunflower, like most heat-loving and capricious crops, has a negative attitude towards diving, showing their dissatisfaction with stopping the growing season. To exclude such a phenomenon, it is recommended to sow in decomposing containers that serve as good fertilizer: peat, shells, cardboard.
If it is not possible to buy peat containers, snails of suitable size can be planted, with the possibility of filling with earth as they grow.
Sowing sunflower in open ground
In the southern regions with a warm climate, which is already established by mid-April, early planting immediately in open ground is allowed, excluding preliminary germination in the form of seedlings. May. By the last month of spring, the soil has time to warm up to 9-13 degrees, contributing to the full growth and development of a heat-loving culture. And although the plant does not belong to the category of the most capricious, capable of withstanding frosts of several degrees while strengthening the sprouts, it is impossible to sow unsprouted seeds in cold soil. Frosts can affect germination, leading to rotting of seeds at an early stage of formation.
To avoid poor germination, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations:
1) avoid planting crops in one area. If possible, it is worth choosing new places that can fully nourish the sunflower with nitrogen. A break in growing on one bed is from 2 to 4 years;
2) it is necessary to exclude crops in the places of germination of such crops as: tomatoes, melons and cereals, beets and corn;
3) it is worth planting natural green manure before winter. Autumn is a favorable time for sowing mustard and other crops that restore the soil;
4) it is worth observing the planting scheme so that the roots are fed favorably, being saturated not only with moisture, but also with complex fertilizers.
What kind of soil is better to plant
Sunflower grows best on chernozem soil with an admixture of clay. But if there are few nutrients, this is not a reason to be upset. According to the practice of many summer residents, if you fertilize the soil before winter, restoring the acid-base balance at the beginning of spring, you will be able to grow a good crop, both for yourself and for marketing.
The only soil that sunflowers do not accept is marshland. Land with a high level of groundwater is also not suitable.
Two weeks before planting, it is recommended to scatter complex fertilizer and wood ash, to dig up the future sowing area. Before planting, the holes are fed with bird droppings, eggshells and superphosphate, filled with water and mixed with a stick.
Optimal sowing according to all rules
First, the seed material is distributed in size, throwing aside damaged and too small seeds, inferior in performance to the rest. Next, the seeds are disinfected and stratified using a weak solution of potassium permanganate or cinnamon water. When pointing the pest control, use settled warm water, which has a beneficial effect on further germination.
Soaking in disinfectant is best done in a gauze bag for 30-40 minutes. The tied knot is lowered into the water, excluding the loss of part of the seeds.
Sowing is carried out in pre-moistened soil so as not to bury the seeds deeper than planned. Regardless of the choice of a classic or hybrid variety, it is recommended to spread 2-3 seeds in each hole for 100% germination.
The distance between the holes should not be less than 55-65 cm. the necessary agricultural technology at different stages of the formation of the formation. Each of the points is repeated regularly, not forgetting the intervals and the lunar calendar.
How to grow
It has already been mentioned above that the cultivation of sunflower is a complete care, which includes a set of regular procedures. If they are not fulfilled, the percentage of obtaining a high yield is reduced to 60%.
Proper watering
Regular watering is carried out as the topsoil dries up, without overflowing and overdrying the plants. Most moisture is required for young seedlings, which have no more than four full-fledged leaves. As the set, watering is reduced, resuming only at the beginning of flowering and seed formation.
![]()
In order to fully nourish the plant, it is worth watering the plant not only superficially, but also deeply, in order to saturate the roots. In the summer months, moisten the soil more often than in spring and autumn.
Fertilization
Sunflower is fed at least 3-4 times during the entire growing season. Complementary foods begin with the formation of several full-fledged leaves, using urea or natural organic matter. By the time of flowering, mineral additives or ready-made complex fertilizers are applied. The next time the procedure is carried out after laying the seeds. The last time - 2-3 weeks before the harvest.
There are also slightly different fertilization options. For example, some agronomists prefer to fertilize when growing seedlings, others when planting in open ground, mixing the complexes immediately in the hole.
If there is a shortage of boron, it is worth feeding the plant with a ready-made preparation.
The best varieties of sunflower, varieties in the photo
When choosing seeds for planting on an industrial scale, they are guided not only by the best variety of sunflower, but also by the color scheme of the seed husks.
For example, a sunflower with seeds that are covered with black husks is classified as oily, ideal for making vegetable oil. Their content contains more than 45% of the oil used to obtain a natural product for cooking. Oil based on a vegetable product, quite often used in the preparation of daily meals. I use it for overcooking, frying and frying various products, both individually and in combination with each other.
Varieties with striped skins are used only for confectionery and ready-to-eat foods available in most stores.
Despite the differences, the seeds are divided according to the growing season. Today there are varieties belonging to early-ripening, mid-ripening and late-ripening varieties. Depending on the region of cultivation, preference is given to one of the options.
First grade - Rimisol
Mid-season F1, unable to give the gardener a harvest for several years. The plant is classified as an early ripe variety with a medium early growing season.
Sunflower growth is medium, reaching 150-170 cm when ready. The basket of fruits is integral, reaching a diameter of 23-24 cm. With proper cultivation, the root system becomes tall, well holding an average stem and a flower stuffed with seeds.
Second grade - Almaz
If you want to grow seeds of a confectionery variety on your plot, you should carefully look at this early ripe variety. In comparison with analogues, it has a high immunity to bacterial and fungal diseases, resistance to hot climates and drought. The height of an adult plant is average, not exceeding 2 meters. Seeds are large, wrapped in striped husks.
Third grade - Zaporozhye Confectionery
Mid-season variety of oily seeds, bearing its owner a high yield with proper care. The variety is resistant to most common diseases that affect the plant at different stages of the growing season. Height - average, exceeding 208 cm. It is unpretentious in leaving, it is ideal for cultivation by the beginning gardener.
The length of the culture is slightly longer than 210 cm.
Fifth grade - Oliver
Oily high-yielding variety, which remains the achievement of Serbian breeders. It is immune to diseases and pests. Excellent for decorating the site, due to its compact size, not exceeding 148-153 cm. Stem height - from 170 to 190 cm. Has a medium basket filled with large seeds covered with black husks.
Seventh grade — Lakomka
Mid-season variety of sunflower, with proper care, high yield. It is resistant to frost, abnormal heat and drought. It tolerates weeds and waterlogging. Able to reach a height of 2.1 meters. Seeds - drop-shaped, large.
Eighth grade - Nut
Universal seeds used not only for oil extraction, but also for the preparation of confectionery. It is resistant to bacterial diseases and pests. The height of the plant does not exceed 180-185 cm. The husk is striped, having a black-grayish tint.
Ninth grade - Forward
Has protection against bacterial diseases, pests.
It belongs to mid-season varieties that tolerate drought and abnormal heat well. Easily takes root on sandy soils, not rich in minerals and trace elements. It has an average size - from 180 to 200 cm.
Tenth grade - Prometheus
A high-yielding variety of seeds that can give its owner good vegetable oil with proper care, cultivation and pressing. Height - small, decorative, not exceeding 135-145 cm.
Eleventh variety - Vranac and Attila
Two different varieties with different variations of use share the last line at the same time. One variety is ideal for pressing oil, the second is ideal for making halva, gozinaki and other oriental sweets.
Common diseases
In order to fully approach the cultivation of sunflower in a summer cottage, you should carefully study the features of care, including protection from diseases. With the right approach, uninvited guests are excluded.
Preventive spraying will prevent the formation of powdery mildew, white rot, phomosis and even rust on the plant.
![]()
The first signs of plant damage in any growing season are changes in the color of leaves and stems. You can detect the first signs of the disease even after the formation of several full-fledged sheets. To exclude invasions, it is worthwhile to pre-disinfect the seeds and treat the first shoots, at least with a natural solution containing water and ground cinnamon.
Affected leaves and the plant as a whole can only be saved with the help of ready-made products that are offered in the store.
The broomrape or parasite remains an alternative disease that occurs a little less frequently. It is much more difficult to deal with it than with common types of bacterial diseases.
Common pests and their control
As with diseases, sunflower pests are numerous. If you do not follow the plants and exclude preventive treatment, you can see such enemies as:
- sunflower moth;
- wireworm;
- spikelet;
- southern weevil.
![]()
To prevent their appearance, it is worth sowing fragrant greens between the beds, which scare off unexpected guests who feed on leaves and stems with their smells. If the plant is already affected, do not waste time and effort on the classic methods of struggle. It is better to prefer proven insecticides.
As strange as it sounds, birds can also become pests during crop formation. Little thieves often eat part of the crop unless the gardener sets up a scarecrow to scare away flying guests. An alternative solution would be a gauze bandage on the sunflower head, which preserves the integrity of the seeds and further vegetation.
Harvesting time and storage rules
In order to avoid bitterness in taste and improper storage, which shortens the laying time, it is necessary to collect the baskets correctly, and most importantly, on time. It is impossible to determine the exact date! The period favorable for seed removal directly depends on the following factors: the date of emergence of the first shoots, the duration of the growing season, the lunar calendar and proper care, which affects the rate of maturation and the absence of stress of a capricious plant.
![]()
Characteristic signs of maturity are:
- hardening of the seeds in the basket;
- changing the color range and coloring to a characteristic shade characteristic of the finished sunflower;
- peeling open when pressed with fingers;
- falling yellow petals.
If the harvest period falls during rainfall, gardeners speed up the growing season by treating each basket with special desiccants. An analogue of the method remains watering with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. The product is poured under the root of each plant, contributing to the speedy readiness of the seeds.
The heads are cut a little earlier than the stated time, so that the seeds do not have time to crumble. Withdrawal period - minus 5-10 days. The seeds are dried and dusted off, left to dry for 14 days at room temperature, spread out on a tray.
Some prefer the classic method of harvesting - knocking out of the basket with a light tap with a hammer.
A deep bucket or basin is placed next to the plant so that the seeds cannot scatter past the container. The procedure is carried out in the garden without removing the top of the stem.
In the Urals and Siberia, harvesting is carried out earlier than usual, without waiting for the seeds to ripen. Baskets are cut with a small part of the stem and hung on the wall in a dry but well-ventilated area. After 3-4 weeks, the seeds ripen and dry out, allowing you to store the crop without additional problems.
After harvesting, the stems are pulled out together with the roots and the soil is dug up, preliminarily scattering mineral complex fertilizers. At will, gardeners sow green manure, restoring the acid-base balance and fertility of the planting land.
Methods of winter storage
The duration of seed preservation depends directly on the variety of seeds and the preservation of the husk. Damaged fruits lie less, losing their taste in a short time. If they are not used before they are supposed to, the fruits will acquire bitterness, acidity and a chemical taste.
![]()