Sweet peas planting time
How to Plant and Grow Sweet Peas
From scarifying seeds to mulching tips and more, professional gardeners share their insight.
Caroline Biggs, Freelance Writer portrait
By Caroline Biggs March 31, 2021
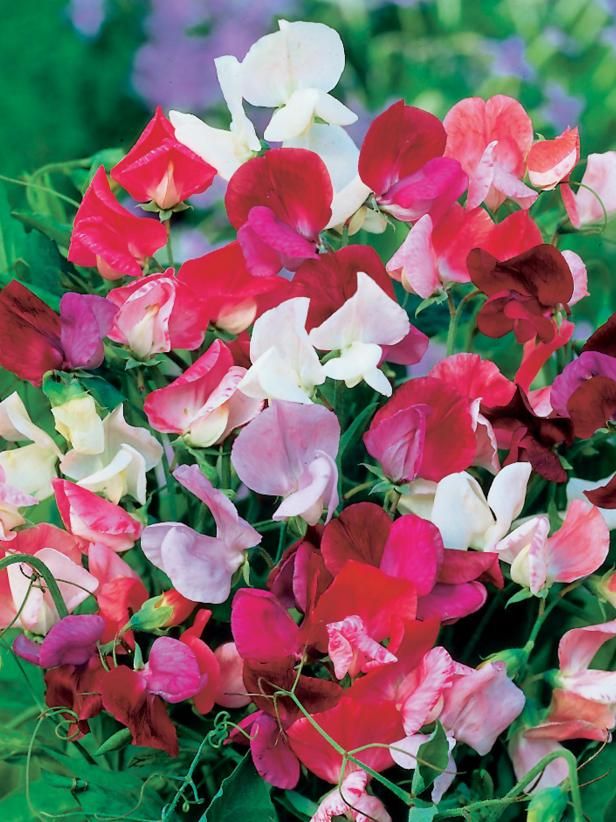
Adored for their profusion of beautiful flowers, sweet peas (Lathyrus odoratus) are typically cultivated as an annual plant—and not a perennial—for a good reason. "As an annual, the climbing variety can grow up to eight feet tall and produce months of flowers," says Benjamin Godfrey, garden manager at Cornerstone Sonoma. "It can also be grown as a short bush."
sweat pea flowers in garden
Credit: Andyd / Getty Images
Along with their bountiful blooms and striking colors, sweet peas are popular for their strong, sweet scent, says gardening expert Melinda Myers. "They bring fragrance to outdoor spaces," she explains. "Whether it's a sweet pea-covered trellis or a hanging basket on your front porch, they provide a colorful and fragrant way to welcome guests to your home. " Interested in incorporating some sweet peas into your home garden? From how to scarify sweet pea seeds to planting tips and more, Godfrey and Myers share their advice, ahead.
Scarify sweet pea seeds before planting.
For as soft and fragrant as their blooms may be, sweet pea seeds have notoriously hard exteriors. To speed up the germination process, which can take up to three weeks, Myers recommends carefully scarifying each seed (this involves weakening the seed coating) before planting. "You can do this by using a nail file or sandpaper to gently scratch the seed coat," she explains. You can also soak sweet pea seeds in water for about eight hours to help soften their "shell." "Soak seeds in damp paper towels overnight and they should be ready to plant the next day," Godfrey says.
Plant sweet peas in full sun and well-drained soil.
Once your sweet pea seeds are scarified, Myers says to plant them in an outdoor spot that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight every day for optimal flowering.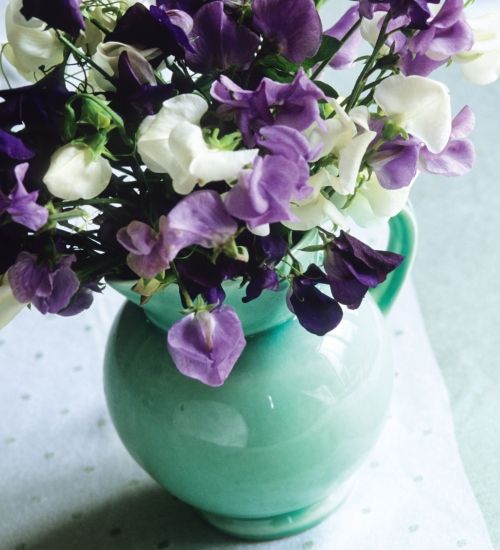 "If you're in a hotter climate, provide some afternoon shade to help extend bloom time," she advises. When planting sweet pea seeds, Godfrey says they should be sown about one-inch deep and spaced three-to-four-inches apart to ensure they have plenty of space to grow. "Plant in rich, well-draining soil," he adds. "Sweet peas won't perform well if the soil is too wet or dry."
"If you're in a hotter climate, provide some afternoon shade to help extend bloom time," she advises. When planting sweet pea seeds, Godfrey says they should be sown about one-inch deep and spaced three-to-four-inches apart to ensure they have plenty of space to grow. "Plant in rich, well-draining soil," he adds. "Sweet peas won't perform well if the soil is too wet or dry."
Start them indoors in colder climates.
If you live in a colder climate where the ground tends to freeze, Myers says you can start sweet pea seeds indoors during the winter. "Sweet peas can be started indoors up to six to eight weeks before the last spring frost, and then transported outdoors in early spring," she explains. "Just remember to space the seeds at least two-inches apart, or twine each plant as they grow, so they're easy to separate when it's time to move them outside."
Provide support for growing sweet peas.
Since most sweet peas are climbing vines, Godfrey says they often need support to grow tall. "When supported with a trellis, against a fence, with mesh or twine, the plant will grasp and hold on with its tendrils (which are like tiny strong ropes)," he explains. To avoid damaging the roots of your growing sweet pea plants, Myers recommends installing a trellis or a similar staking system prior to planting seeds or transplants. "This will make it easier to direct young plants up the support as they grow—instead of forcing them to climb—so they can climb with minimal interference," she explains.
"When supported with a trellis, against a fence, with mesh or twine, the plant will grasp and hold on with its tendrils (which are like tiny strong ropes)," he explains. To avoid damaging the roots of your growing sweet pea plants, Myers recommends installing a trellis or a similar staking system prior to planting seeds or transplants. "This will make it easier to direct young plants up the support as they grow—instead of forcing them to climb—so they can climb with minimal interference," she explains.
Mulch matters.
Sweet peas are heavy feeders, which is why Godfrey says they'll grow best in soil that has been amended with lots of compost. If adding compost isn't an option, "fertilizing can make a big difference," he says. "Granular time released fertilizers are easiest because they can last for months, but diluted liquid fertilizers can be given weekly." Godfrey recommends using a fertilizer with higher levels of phosphorus than nitrogen to help boost flower production. "Too much nitrogen will stimulate the plant to reach for the stars instead of creating stellar flowers," he explains.
"Too much nitrogen will stimulate the plant to reach for the stars instead of creating stellar flowers," he explains.
How to Plant, Grow & Care for Sweet Peas
- Home
- Advice & Inspiration For Your Garden
- how to plant, grow & care for sweet peas
- Written by:
- Sarah Raven
- Last updated:
complete growing guide
We have teepees and arches covered with sweet peas in flower during June and July – they fill the garden, house and life with scent and colour. They are the stars of our summer season. The range of sweet peas to enjoy is huge, from rich, saturated blues and purples, to pastel shades and luscious bi-colours. There are long-flowering ones with whopper stems, as well as compact ones that are good for pots. They all have fantastic fragrance and can be cut and brought in to fill the house with scent.
There are long-flowering ones with whopper stems, as well as compact ones that are good for pots. They all have fantastic fragrance and can be cut and brought in to fill the house with scent.
Browse our range of sweet pea seeds or take a look at our sweet pea seedlings, which are ready to plant out in your garden for gorgeous scent throughout the summer.
details
- Common name: Sweet Pea
- Latin name: Lathyrus odoratus
- Type: Hardy Annual / Hardy Annual Climber
- Height: Some compact varieties are suitable for pots, however most reach around 1.8m (6ft)
- TLC rating: It can take a little patience and dedication to look after sweet peas – but it is worth it
- Aspect: Full Sun
- Planting position: Borders
- Suitable for pots: Compact forms can be grown in pots but most are better in borders
- Good for pollinators: Yes
- Good for cut flowers: Yes
calendar
JAN
FEB
MAR
APR
MAY
JUN
JUL
AUG
SEP
OCT
NOV
DEC
Sow Under Cover/Plant Indoors
Direct Sow/Plant Outdoors
Flowers/Harvest
how to grow sweet peas
where to grow sweet peas
Soil type: A fertile soil which retains moisture but drains well is best for sweet peas.
Aspect & position: Sweet peas love sunshine, so find a position in full-sun.
when to plant sweet peas
Sow sweet pea seeds between October and April. For best results aim for late October/November or late February/March as temperatures and light levels are less than ideal in midwinter. Sweet peas can also be sown direct into the ground in April or May. Plant out your sweet pea seedlings and plants during a mild spell between March and May.
how to plant sweet peas
sowing sweet pea seeds
Sweet peas have a hard seed coat. To aid germination you may find it helpful to leave them on some damp kitchen paper for 24 hours before sowing.
Sow sweet pea seeds undercover between October and April. Rootrainers or loo rolls are ideal as they provide a deep, narrow root run. If you sow into a short, stumpy pot, it doesn’t give the roots as much chance to grow and branch.
To sow the seed, use a peat-free, multi-purpose potting compost and sow two seeds per pot.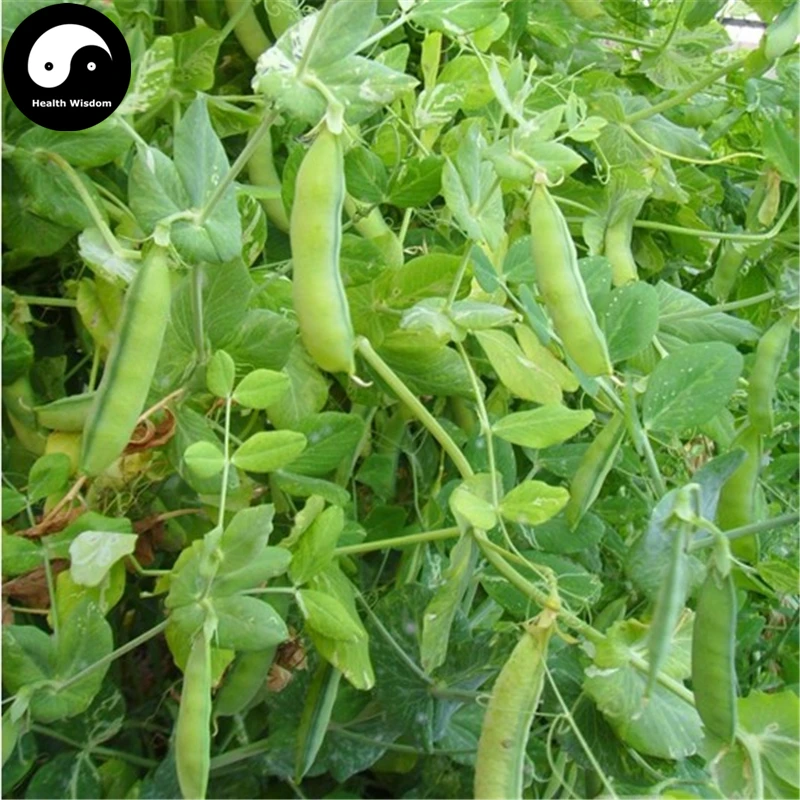 Dampen the compost, then, with your finger, push each seed in 2-3cm below the surface of the compost. Then label the pot if needed.
Dampen the compost, then, with your finger, push each seed in 2-3cm below the surface of the compost. Then label the pot if needed.
If sowing in autumn or spring, sweet peas can be germinated in an unheated greenhouse or cold frame. If sowing in mid-winter, germinate them on a windowsill, heated propagator or very gently heated greenhouse.
Mice love sweet pea seeds and your whole crop may disappear in one go so keep them somewhere mouse-free or try soaking the seeds in liquid seaweed fertiliser before sowing to make them unpalatable.
Check for germination every day and don’t water until you see seedlings start to come through, usually in 10-14 days. Once the seedlings appear, keep them cool at about 5°C (40°F). This promotes root growth, rather than stem growth, which is exactly what you want. An unheated greenhouse or cold frame is usually sufficient.
When there are three or four pairs of leaves, pinch out the leaders – just squeeze off the growing tip between your finger and thumb. This promotes vigorous side shoot formation, with the energy of the plant directed toward growing out, not up.
This promotes vigorous side shoot formation, with the energy of the plant directed toward growing out, not up.
Check your plants regularly and water them lightly if the surface begins to look dry. About a month from germination, check the bottom of the pot for white roots.
If you sowed your sweet peas in spring, they can be planted directly outdoors during a mild spell in March-May. If you sowed them in autumn or winter, you’ll need to pot the plants up in their pairs. Don’t let them get pot-bound in the rootrainers, they will never be quite the same again. A slim, deep, 1 litre pot is ideal. Use a good compost and water them in. Once the roots have filled that pot, it’s time to plant them outside – do this during a mild spell in March-May.
planting sweet pea seedlings
Once your seedlings are ready to plant out, dig plenty of organic material in the planting position. Farmyard manure is good for sweet peas – it helps retain water on a freely drained soil and gently feeds these hungry plants.
Make sure you plant your sweet peas alongside a vertical support such as a teepee, an arch or a tunnel. Plant 2 plants to each rod of a vertical support. Plant them 15cm (6in) apart.
Surround them with slug prevention. I use at least a 30cm (1ft) wide strip of washed inland sharp sand, 5cm (2in) deep.
As the young sweet pea plants begin to grow, tie them into the frame – don’t leave them to flop around. They’ll grow more quickly and make stronger plants tied in regularly. Do this twice in the first month and then more often when they start to romp away.
Feed your sweet pea plants every couple of weeks after the first month in the ground, especially important if the soil is not very fertile. A tomato feed or comfrey feed is ideal.
Once the flowers emerge, pick, pick, pick and fill up your vases. If you see any seed pods as you’re cutting, snip these off as well. You don’t want your plants forming seed or it will stop the plants producing flowers.
The stems on sweet peas get shorter as the season progresses, this is normal due to the energy used to make the flower. Feed, water and deadhead very regularly to encourage more flowers to appear.
Feed, water and deadhead very regularly to encourage more flowers to appear.
growing sweet peas in a pot
Sweet peas can be grown in deep container pots with a climbing frame. Make sure you choose a compact or dwarf variety.
You can buy a small teepee for a pot, or make one. To make one, push birch or hazel twigs about 120cm (4ft) tall firmly into the compost around the perimeter of the pot – push them about 30cm (1ft) down. Gather the ends and tie them in a bundle at the top using twine or flexi-tie. The sweet peas can then scramble over the twiggy teepee.
how to care for sweet peas
watering
Sweet peas need thorough watering. If you let them dry out, they will get stressed. Water them regularly and every day during a drought.
fertilising
Feed your sweet pea plants with a general fertiliser every couple of weeks, or sprinkle on comfrey pellets. A potash-rich tomato feed is ideal. If you maintain a good watering and feeding regime, the sweet peas can go on into August.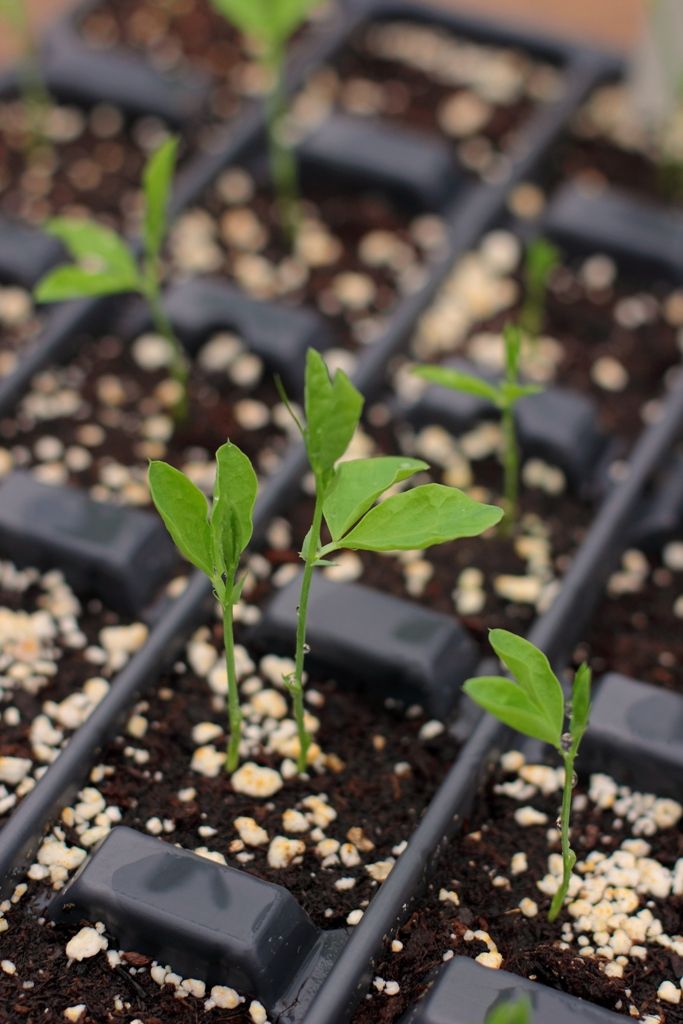
staking
Sweet pea plants need vertical support and will need a frame to clamber and climb over as they often reach over 1.8m (6ft) tall. A teepee or arch is ideal and you can buy these ready made or make these yourself.
As the young sweet pea plants begin to grow, tie them into the vertical support. It's really important to tie in your sweet peas as they’ll grow more quickly and make stronger plants if they are tied in regularly. Do this twice in the first month and then more often when they start to romp away.
We generally tie in our sweet peas every seven to ten days to ensure they're growing vertically, and sometimes even more depending on the season.
For my guide to tying in sweet peas, take a look at the video below.
deadheading
It is very important to deadhead your sweet peas. Look out for seed pods developing and snip them off regularly. This prevents the plants forming seed, which would stop the plants producing flowers.
Professional growers who are going to compete in horticultural shows will tell you to pinch out all the curly stems and tendrils.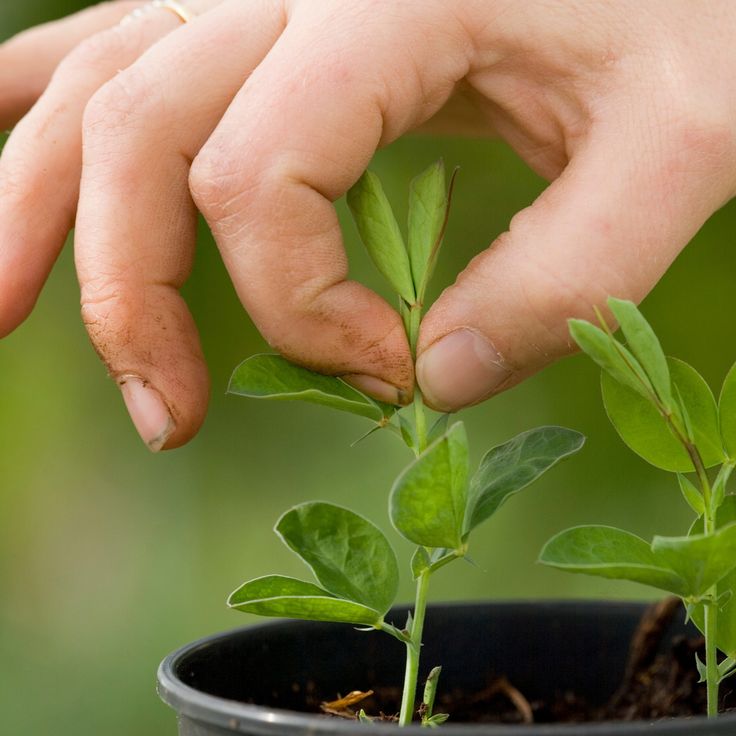 They take energy from the flowers and attach themselves to flower stems and bend them into curves. It’s a lot of work if you are growing a lot of sweet peas. I try to remove any I see while I pick, but I don’t get bogged down.
They take energy from the flowers and attach themselves to flower stems and bend them into curves. It’s a lot of work if you are growing a lot of sweet peas. I try to remove any I see while I pick, but I don’t get bogged down.
propagating
If you have any seed pods at the end of the season, you can collect the seed and store them in a labelled envelope and allow them to dry for a month or so. Then store in a paper bag in a container in the fridge, ready to plant in winter. The resulting plants may well vary slightly from the parent, especially if you grew a mix of varieties.
seasonal checklist
spring
- You can plant your young sweet pea plants directly outside from March–May. Sweet pea seeds sown in autumn or winter will need to be potted on into larger pots before planting out. Those sown in spring can be planted out from their rootrainers.
summer
- Pick your sweet peas and arrange them in vases indoors. Continue to deadhead your sweet peas by removing the seed pods.
 At their peak, you’ll need to pick and deadhead every couple of days.
At their peak, you’ll need to pick and deadhead every couple of days.
autumn
- Cut down your sweet peas when they finish flowering, but leave the roots in the ground as they have little nodules on them which will add nitrogen to your soil.
winter
- You can start sowing sweet pea seeds as early as mid-October and continue through the winter.
pests, diseases & common issues
mildew
Mildew can be a problem for sweet peas, particularly if they are not getting enough water. To help overcome this, water more or try spraying your sweet peas every two weeks with homemade chive tonic. This has a high sulphur content and is a good natural anti-fungicide, which will help slow the spread of mildew. This can be prepared by chopping a large handful of chives into a jug and covering with boiling water. Allow this to steep then strain and use as a spray for your plants.
why are my sweet peas dying?
Sweet peas are thirsty, hungry plants, so make sure you are watering and feeding them regularly.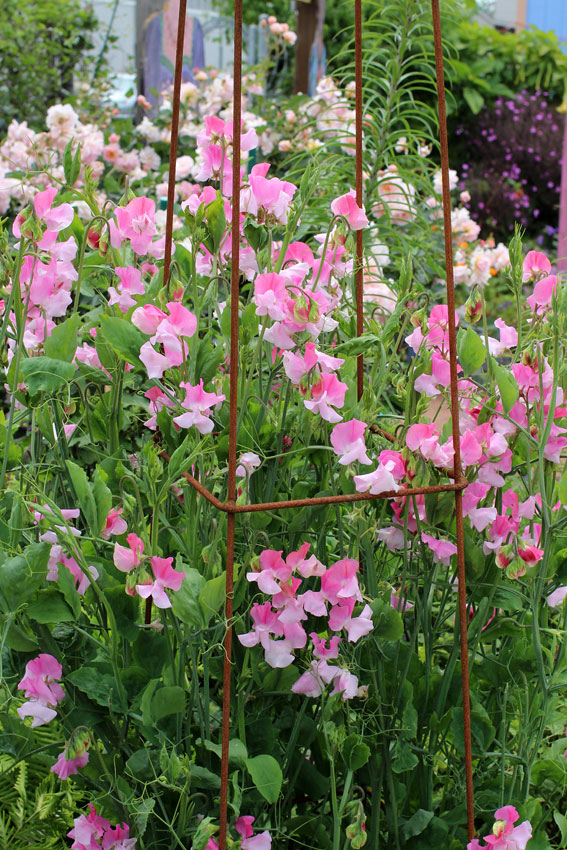 They need plenty of sunlight and will thrive if you continue to tie them in and allow them to grow up a vertical support.
They need plenty of sunlight and will thrive if you continue to tie them in and allow them to grow up a vertical support.
why are my sweet peas not flowering?
Sweet peas need plenty of sunlight to flower prolifically, so make sure they are in full-sun. You also need to deadhead regularly – leaving the seed pods prevents new flowers forming.
why are my sweet peas turning yellow?
Various fungal problems can impact sweet peas and cause leaves to turn yellow. The best way to avoid these is by ensuring your plants are in free-draining soil (that doesn’t get water-logged) and that you mulch around the base.
why are my sweet pea stems so short?
Long stems require the plant’s energy. Tie your sweet peas into their vertical frames so they don’t waste energy holding themselves upright. Water them well so they don’t become stressed in a drought. You can also pinch out all the curly stems and tendrils, allowing the energy to go into growing longer stems and flowers. Towards the end of the growing season the stems tend to become progressively shorter in spite of your best efforts. That said, long stems start with a healthy, happy seedling.
Towards the end of the growing season the stems tend to become progressively shorter in spite of your best efforts. That said, long stems start with a healthy, happy seedling.
why do sweet peas get mildew?
Dry or stressful conditions can cause powdery mildew in sweet peas. Keep them well-watered on free-draining soil, and mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture.
why are my sweet pea buds falling off?
Cold nights can cause sweet peas to suffer and buds to fall off. As the weather settles, the problem should pass.
frequently asked questions
are sweet peas edible?
Sweet peas are not edible and can be toxic.
when are sweet peas in season?
The main flowering season for sweet peas is June and July but they can start earlier or go on later, depending on when you sowed and planted them . Keep watering, feeding and deadheading to prolong their season.
how high do sweet peas grow?
Most sweet peas can grow to around 1.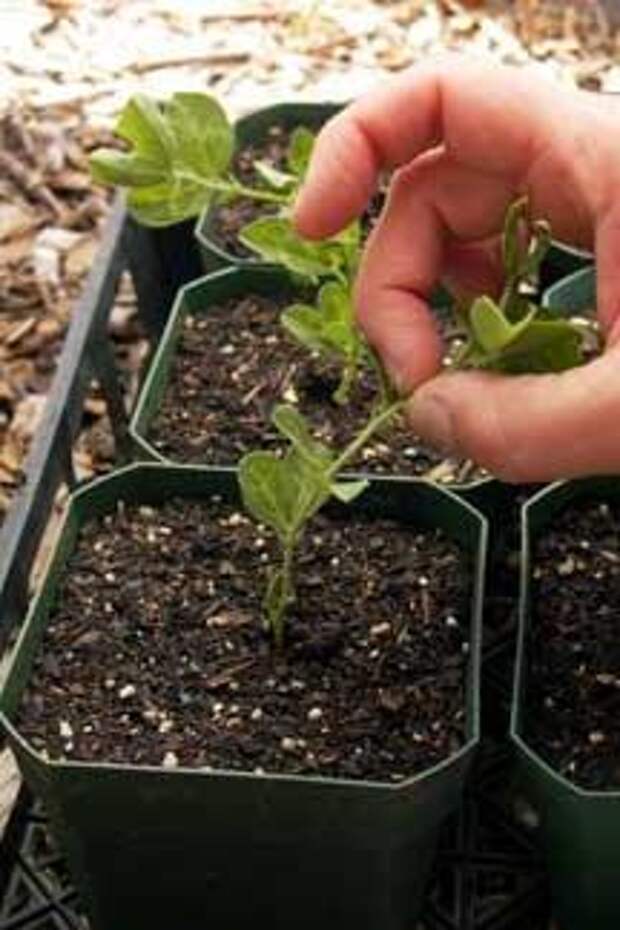 8m (6ft). There are more compact varieties available that are suitable for pots and small spaces.
8m (6ft). There are more compact varieties available that are suitable for pots and small spaces.
how to germinate sweet pea seeds?
Some people suggest soaking sweet pea seeds to help them germinate - you may find it helpful to leave them on some damp kitchen paper for 24 hours before sowing - however, I have found they germinate within 2 weeks with or without soaking.
are sweet peas poisonous to pets?
Yes, sweet peas are poisonous to pets.
can sweet peas grow in shade?
Sweet peas are sun-loving plants and will thrive in a position that receives plenty of sunshine. They may grow in light or dappled shade, but won’t flower as prolifically.
are sweet peas perennial?
Sweet peas are generally annuals, however Lathyrus latifolius (everlasting pea) is perennial.
what to grow with sweet peas
Sweet peas are best grown on their own on a teepee. They look fantastic as punctuation marks in a vegetable or cutting garden, or to give height and scent to a mixed border. Find out how to create your own sweet pea climbing frames in the article below.
Find out how to create your own sweet pea climbing frames in the article below.
how to cut & arrange sweet peas
The wonderful thing about sweet peas is that the more you pick, the more flowers you get. To ensure they have maximum vase life once inside, I add a drop of sugar syrup into the vase water. To make the sugar syrup, use a ratio of 2 parts sugar to 1 part water and place in a pan over a low heat until the sugar is dissolved.
Get more inspiration for displaying your flowers with our flower arranging videos:
learn more
browse our range
learn more
how to cordon train your sweet peasthe sweet pea storylayering sweet peasyou may be interested in growing...
planting and care in the open field, growing with seeds, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/ru/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden Plants Returned: Last amendments:
Content
- Planting and Care for fragrant peas
- Botanical description
- Growing grades from seeds
- how to sewed seeds
- Care for seedlings
- Planting fragrant peas in the ground
- When to plant
- How to plant
- Care for fragrant peas
- Dressing and Diseases
- 9001 9001 9001 9001
Fragrant peas (lat. Lathyrus Odoratus). The scientific name of the plant consists of two words, the first of which is translated as "very attractive", and the second as "fragrant". Some botanists claim that this flowering herbaceous plant comes from the Eastern Mediterranean - its range extends from Sicily east to the island of Crete. Other scientists believe that sweet peas were brought to Sicily by conquistadors from Ecuador and Peru.
Lathyrus Odoratus). The scientific name of the plant consists of two words, the first of which is translated as "very attractive", and the second as "fragrant". Some botanists claim that this flowering herbaceous plant comes from the Eastern Mediterranean - its range extends from Sicily east to the island of Crete. Other scientists believe that sweet peas were brought to Sicily by conquistadors from Ecuador and Peru.
In culture, the plant has been cultivated since the 18th century: in 1699, while walking under the walls of the monastery, the Sicilian monk Francisco Cupani discovered a flower with an unusually pleasant smell, collected seeds from it and sent them to England to his friend, a school teacher. And in England, thanks to the work of breeders, sweet peas eventually became the king of ampels. The first five varieties of the plant appeared in 1800.
Today there are more than 1000 varieties of sweet peas. Gardeners are attracted by bright flowers and a pleasant smell, because of which the plant got its name.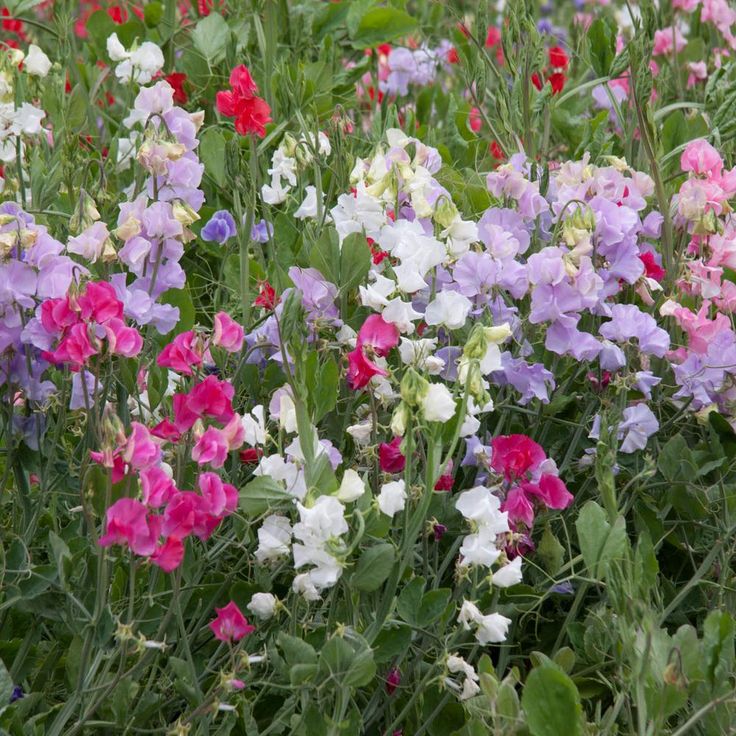 Sweet peas are most often used for vertical gardening of arbors, balconies and terraces. Perennial sweet peas in the middle lane are usually grown in an annual crop
Sweet peas are most often used for vertical gardening of arbors, balconies and terraces. Perennial sweet peas in the middle lane are usually grown in an annual crop
Planting and caring for sweet peas
- Flowering: from July to frost.
- Planting: sowing seeds for seedlings - in mid-March, planting seedlings in the ground - at the end of May.
- Lighting: bright light.
- Soil: moist, well-drained, fertilized, pH 7.0-7.5.
- Watering: regular, on average once a week with a consumption of 30-35 liters of water per m².
- Feeding: is not necessary, but will not interfere: at the beginning of growth - with a solution of 1 tablespoon of Nitrophoska and 1 tablespoon of urea in 10 liters of water, at the beginning of flowering - with a solution of 1 tablespoon of Agricola and 1 tablespoon of potassium sulfate in 10 liters of water , at the height of flowering - a solution of 1 tablespoon of Agricola for flowering plants and 1 tablespoon of Rossa in 10 liters of water.
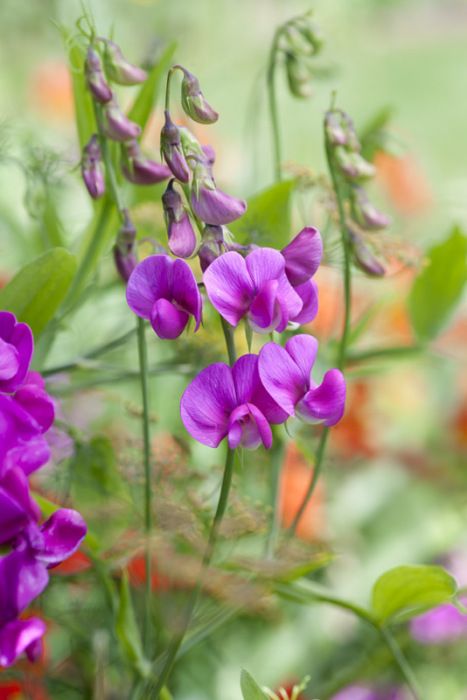

- Tie: tall peas need to be tied to a support.
- Hilling: is carried out regularly to a height of 5-7 cm with adding fertile soil to the base of the stem - this stimulates the development of adventitious roots in the plant.
- Reproduction: seed.
- Pests: nodule weevil and various aphids.
- Diseases: ascochyta, powdery mildew, downy mildew, fusarium, root rot, blackleg, viral mosaic and pea virus mosaic deformans.
Read more about the cultivation of sweet peas below
Botanical description The root system of the plant is highly branched, rod, penetrating into the soil to a depth of one and a half meters. Like most legumes, sweet pea enters into a symbiosis with nodule bacteria that absorb nitrogen from the air. The stems of the rank are climbing, slightly branched, they climb the support, clinging to it with modified leaves - branched tendrils.
 Sweet pea flowers resemble moths, but it seems to the British that they are like a sailboat: the corolla consists of a large petal, similar to a wide oval sail, two side petals (“oars”) and two fused lower petals forming a “boat”. Sweet pea blooms profusely. It begins in July and, with proper care, continues until frost. Sweet pea fruits are small bivalve beans with 5-8 spherical, laterally compressed yellow, greenish or black-brown seeds that remain viable for 6 to 8 years.
Sweet pea flowers resemble moths, but it seems to the British that they are like a sailboat: the corolla consists of a large petal, similar to a wide oval sail, two side petals (“oars”) and two fused lower petals forming a “boat”. Sweet pea blooms profusely. It begins in July and, with proper care, continues until frost. Sweet pea fruits are small bivalve beans with 5-8 spherical, laterally compressed yellow, greenish or black-brown seeds that remain viable for 6 to 8 years. Growing sweet peas from seeds
How to sow seeds
Growing sweet peas begins with sowing seedlings in mid-March. Before sowing, tight seeds of sweet peas should be soaked in water for 10-12 hours or kept in a fifty-degree solution of the Bud preparation (1-2 g per 1 liter of water). Then, within 2-4 days, they are germinated in gauze, wet sand or sawdust at a temperature of 20-24 ºC. As soon as sweet pea seeds have hatched, they should be sown immediately.
Store soils like Saintpaulia, Rosa or a mixture of humus, peat and soddy soil in a ratio of 2:2:2:1 are best suited as a substrate.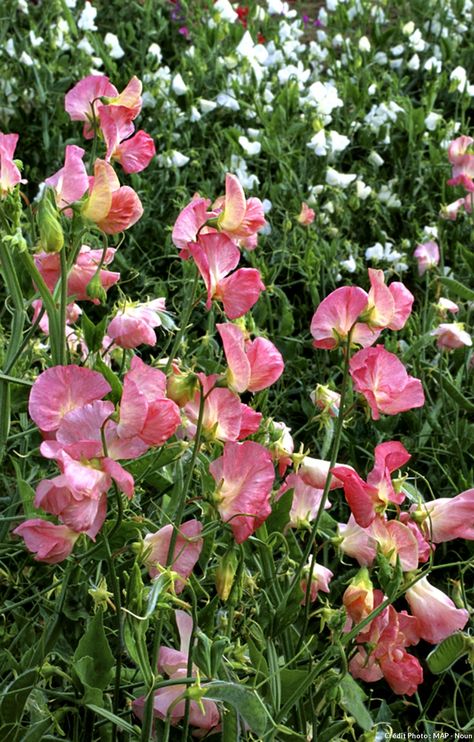 Any of these substrates must be disinfected with a strong solution of potassium permanganate, and it is better to use cups or pots as dishes for growing seedlings. Sowing is carried out in a moist substrate to a depth of not more than 2-3 cm, laying out 2-3 seeds in each cup. If you sow peas in a common box, then the distance between the seeds should be about 8 cm. After sowing, the substrate is watered, the containers are covered with foil and kept on a sunny windowsill at a temperature of 18-22 ºC.
Any of these substrates must be disinfected with a strong solution of potassium permanganate, and it is better to use cups or pots as dishes for growing seedlings. Sowing is carried out in a moist substrate to a depth of not more than 2-3 cm, laying out 2-3 seeds in each cup. If you sow peas in a common box, then the distance between the seeds should be about 8 cm. After sowing, the substrate is watered, the containers are covered with foil and kept on a sunny windowsill at a temperature of 18-22 ºC.
Care of seedlings
When mass germination of seeds begins, and this can happen in a week or two, you need to remove the film from the crops and lower the temperature to 15-16 ºC - this measure contributes to the formation of nitrogen-fixing nodules on the roots of seedlings . Keep the substrate slightly moist at all times and provide seedlings with good lighting: if you cannot keep seedlings in a south window, organize artificial lighting for 2-3 hours daily. To do this, you can use a phytolamp or a fluorescent lamp, fixing them at a height of 25 cm above the seedlings and including, for example, from 7 to 10 or from 17 to 20 hours.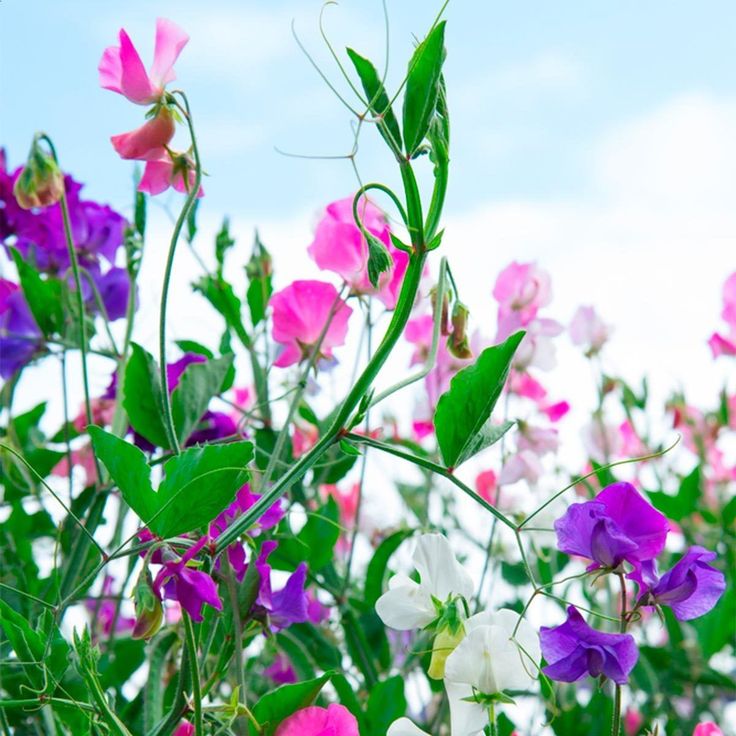
In the phase of development of 2-3 true leaves, seedlings are pinched to stimulate the development of lateral shoots. After pinching, the seedlings are fed with a solution of 2 g of Kemira in 1 liter of water.
Planting sweet peas in the ground
When to plant
Plant sweet peas outdoors from seeds towards the end of May, when the soil has warmed up and the threat of returning frosts has passed. If by that time buds or flowers have already formed on the seedlings, cut them off so that all the energy of the plants is directed to the formation of the root system. 10 days before planting seedlings, it is necessary to carry out hardening procedures with it. To do this, containers with seedlings are taken out into the open air daily, gradually increasing the duration of stay until the sweet pea seedlings can be on the street for a whole day.
- Tulips after flowering: how to dig and store
How to plant
Sweet peas like bright, warm areas and moist, well-drained, fertilized soil with a pH of 7. 0-7.5. Before planting seedlings, dig the area to the depth of a shovel bayonet with compost or humus, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Do not use fresh manure as a fertilizer, as it provokes Fusarium wilt, and do not apply nitrogen fertilizers: sweet peas do not need them.
0-7.5. Before planting seedlings, dig the area to the depth of a shovel bayonet with compost or humus, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Do not use fresh manure as a fertilizer, as it provokes Fusarium wilt, and do not apply nitrogen fertilizers: sweet peas do not need them.
Make holes in a row at a distance of 20-25 cm from each other and plant 2-3 plants in each. For tall varieties of sweet peas, support should be installed immediately. Keep in mind that annual sweet peas must be disposed of in autumn, and it will be possible to re-plant a plant in this area only after 4-5 years.
Caring for sweet peas
Growing conditions
Planting and caring for sweet peas is easy. How to grow sweet peas? He needs watering, weeding, loosening the soil, supports, top dressing and protection from diseases and pests. Watering should be regular and sufficient, because due to lack of moisture, buds and flowers can fall off the plant, and the duration of flowering can be greatly reduced. If the summer is without rain, sweet peas need to be watered weekly, spending 30-35 liters of water per m² of planting. You can prolong flowering by removing wilted flowers in time.
If the summer is without rain, sweet peas need to be watered weekly, spending 30-35 liters of water per m² of planting. You can prolong flowering by removing wilted flowers in time.
Tall varieties of sweet peas need to be tied to supports, which use twine or netting. As the pea grows, its stems are directed in the right direction and tied up.
In order to stimulate the development of adventitious roots, it is necessary to carry out hilling of plants to a height of 5-7 cm with adding a fertile substrate to the base of the stem.
As for top dressings, they are not obligatory, but desirable. At the beginning of growth, sweet peas are fertilized with a solution of 1 tablespoon of Nitrophoska and 1 tablespoon of urea in 10 liters of water. At the beginning of flowering, a solution of a tablespoon of Agricola and the same amount of potassium sulfate in 10 liters of water is used for top dressing, and at the height of flowering, sweet peas are fertilized with Agricola for flowering plants and Rossa, dissolving one tablespoon of fertilizer in a bucket of water.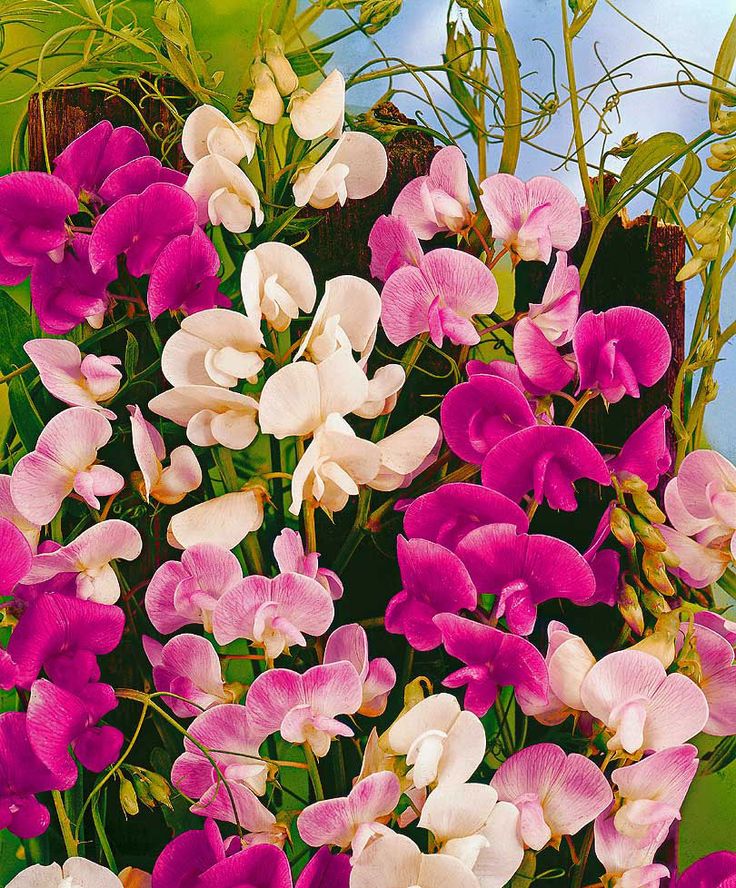
Sweet peas do not need pruning.
- How to sow balsam for seedlings with a pull margin
Pests and diseases
Of the pests for sweet peas, nodule weevil and various aphids are dangerous. At the beginning of the growing season, the weevil gnaws semicircles along the edges of the leaves, and its larvae eat the roots of the plant. As a prophylaxis against a pest, when planting seedlings, pour 100 ml of a 0.1% solution of Chlorophos into each well. The plants themselves must be sprayed with the same solution.
Of all aphids, sweet peas can be attacked by bean, chin and pea aphids. These tiny pests suck the juices from plants, deforming their organs, and infect them with viral diseases. In order to destroy aphids, as well as for the prevention of sweet peas during the growing season, they are treated 2-3 times with Tsineb or Tsiram with a break between sessions of 2-3 weeks.
Ascochitosis, powdery mildew, downy mildew, fusarium, root rot, black leg, viral mosaic and deforming viral mosaic of peas can affect sweet peas.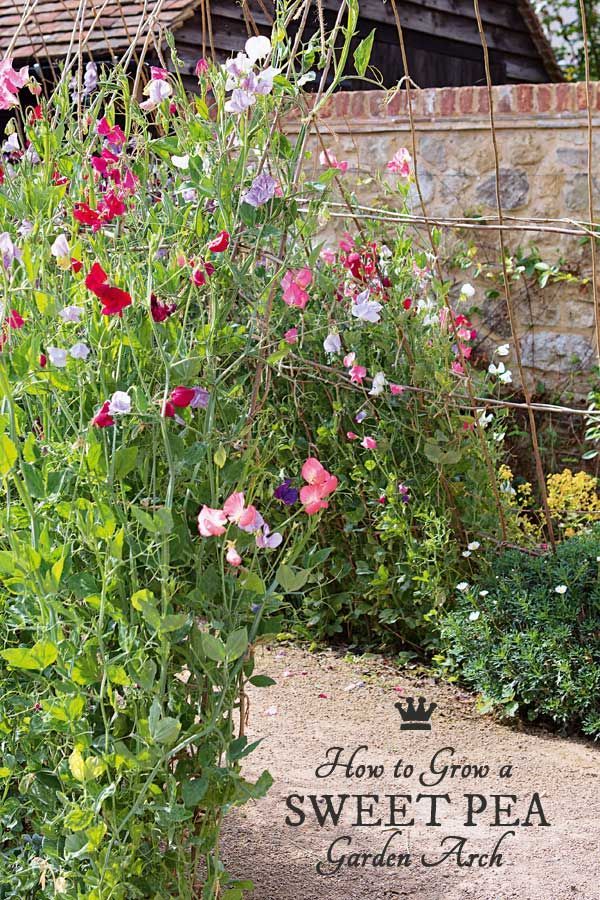
With ascochyta, brown spots with clear boundaries appear on the leaves, beans and stalks of peas. You can fight the infection with two or three treatments of the chin with an interval of 2-3 weeks with a solution of the drug Rogor.
Powdery mildew and peronosporosis (downy mildew) appear in the second half of summer as a loose whitish coating on the leaves and stems of plants. Over time, the leaves turn yellow, turn brown and fall off. Destroy pathogens with a five percent solution of colloidal sulfur, washing the leaves with it.
Signs of Fusarium are yellowing and wilting pea leaves. Diseased plants are not amenable to treatment, they must be removed, and healthy ones must be treated with a solution of the TMDT preparation. As a preventive measure, crop rotation should be observed on the site.
Blackleg and root rot in sweet peas darken the root neck and roots, and the plant dies. Infected specimens cannot be saved, they must be removed, and healthy ones should be transplanted to another place, having disinfected the soil and plant roots before that.
- The Perfect Lawn: What Mistakes to Avoid
The viral mosaic appears as a line pattern on the leaves, and the tops of diseased shoots twist and deform. Plants affected by any of the viral diseases must be removed and burned, as they cannot be cured.
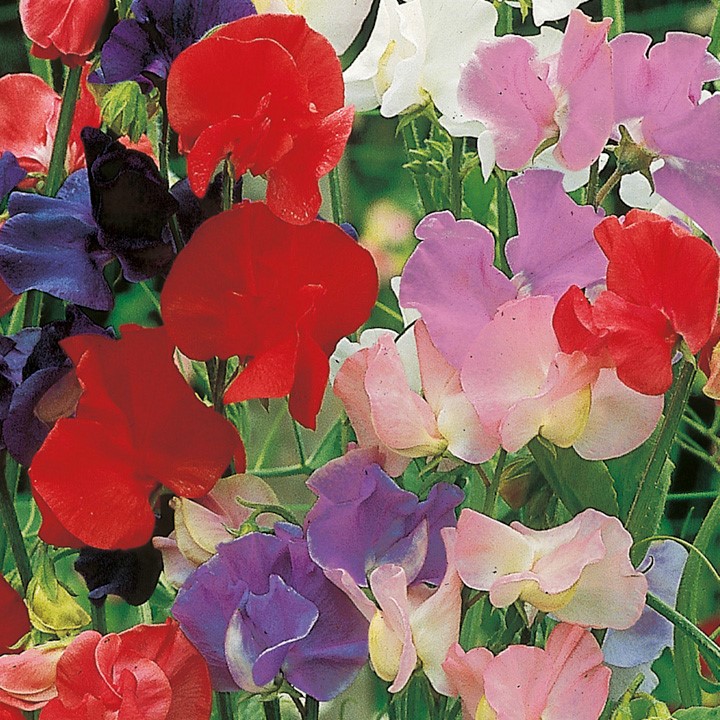
Species and varieties
There are more than 1000 varieties of sweet peas. All of them are divided into 10 garden groups, of which the following are most often grown:
Duplex
Plants with strong stems and double sail flowers, collected in inflorescences of 4-5. One of the best varieties of the group:
- Creamy - a plant up to 90 cm high with fragrant flowers up to 4.5 cm in diameter, light cream in color with a folded or double sail. Inflorescences, located on straight peduncles up to 20 cm high, consist of 3-4 flowers;
Galaxy
Created in 1959, a group of late-flowering varieties over 2 m high with strong inflorescences 30 to 50 cm long with 5-8 corrugated, often double flowers up to 5 cm in diameter.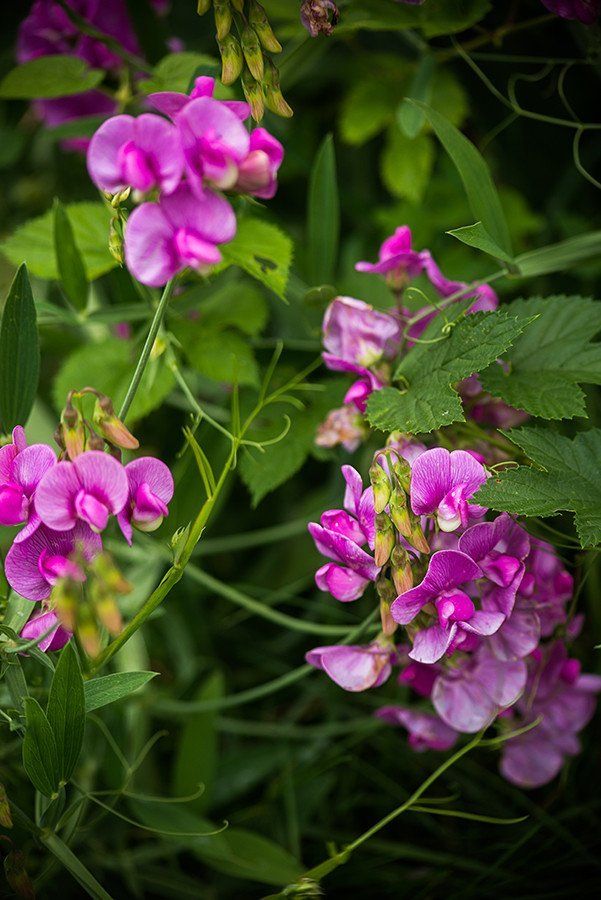 These plants are recommended for landscaping and for cutting. Best varieties:
These plants are recommended for landscaping and for cutting. Best varieties:
- Neptune – a branched variety up to one and a half meters high with strong straight peduncles up to 30 cm high, on which blue flowers, up to 5 cm in diameter, collected in inflorescences of 5-7 pieces, with a white base and often with a double sail, are located;
- Milky Way - branched sweet pea up to 145 cm high with very fragrant pale cream flowers up to 5 cm in diameter with a double sail, which can be 5-6 pieces in one inflorescence;
Bijou
Created by the Americans in 1963, a group of semi-dwarf late varieties up to 45 cm high with strong inflorescences up to 30 cm long, consisting of 4-5 corrugated flowers up to 4 cm in diameter. These plants can be grown without supports, they are recommended for borders and borders ;
Spencer group
which includes powerful multi-stemmed plants up to 2 m high with racemose inflorescences consisting of 3-4 simple or double corrugated flowers up to 5 cm in diameter with wavy petals. The group is represented by varieties of medium flowering period and is recommended for landscaping and cutting. The best varieties of the group:
The group is represented by varieties of medium flowering period and is recommended for landscaping and cutting. The best varieties of the group:
- Warrier - a plant with dark purple flowers with white strokes at the base of the boat, located on straight peduncles. The diameter of the flowers is about 4 cm, the sail is wavy, and the oars are bent;
- Jumbo – variety up to 100 cm high with salmon-pink flowers, white boat, slightly wavy sail and slightly bent oars. The aroma of flowers with a diameter of about 4 cm is weak, the peduncles are straight, strong;
- Charlotte - stems of this variety are up to 150 cm high, flowers are bright crimson, up to 4.5 cm in diameter, the sail is wavy, the oars are widely spaced. Inflorescences of 2-4 fragrant flowers are located on strong peduncles up to 25 cm high;
- Krim Dzhigantik is a plant up to 175 cm high with large creamy fragrant flowers up to 4.
 5 cm in diameter, with a wavy sail and widely spaced, slightly bent oars. Inflorescences, consisting of 3-4 flowers, are located on peduncles up to 30 cm high.
5 cm in diameter, with a wavy sail and widely spaced, slightly bent oars. Inflorescences, consisting of 3-4 flowers, are located on peduncles up to 30 cm high.
In addition to those described, varieties of the Spencer Monty, Mahagony, Flagship, King Lavender, Ayer Warden, Garnet and others groups are popular;
Early Spencer
Created by the Americans at 1910th year, a group of early varieties 120-150 cm high with inflorescences up to 35 cm long, consisting of 3-4 corrugated flowers up to 4.5 cm in diameter. Varieties are recommended for landscaping and for cutting;
Cupido
Created back in 1895, a group of undersized varieties up to 30 cm high with inflorescences up to 7 cm long, consisting of 2-3 medium-sized flowers of various colors. These varieties are recommended for landscaping;
Cuthbertson-Floribunda
A group of varieties created in 1952 in America. These are tall plants up to 2 m high with strong inflorescences up to 40 cm long, consisting of 5-6 large corrugated flowers up to 5 cm in diameter. These varieties of early ripening are recommended for cutting. The best ones are:
These varieties of early ripening are recommended for cutting. The best ones are:
- David - a variety up to 140 cm high with large fragrant dark crimson flowers with a white stroke at the base of the boat and a wavy sail. Inflorescences, consisting of 5-6 flowers up to 5 cm in diameter, are crowned with rigid peduncles up to 30 cm long;
- Kennet - a variety up to 1 m high with large dark red flowers, collected in inflorescences of 5-6 pieces. The diameter of the flowers is about 4 cm, their sail is slightly corrugated, the oars are slightly bent, the peduncles are up to 16 cm long;
- White Pearl - white sweet pea with flowers about 4.5 cm in diameter, collected in inflorescences of 5-6 pieces and located on peduncles up to 30 cm long.
In addition to those described, such varieties of the group as Zhelanny, Peggy, Robert Blain, William and others are widely known;
Royal Family
This group of heat resistant varieties was created in 1964.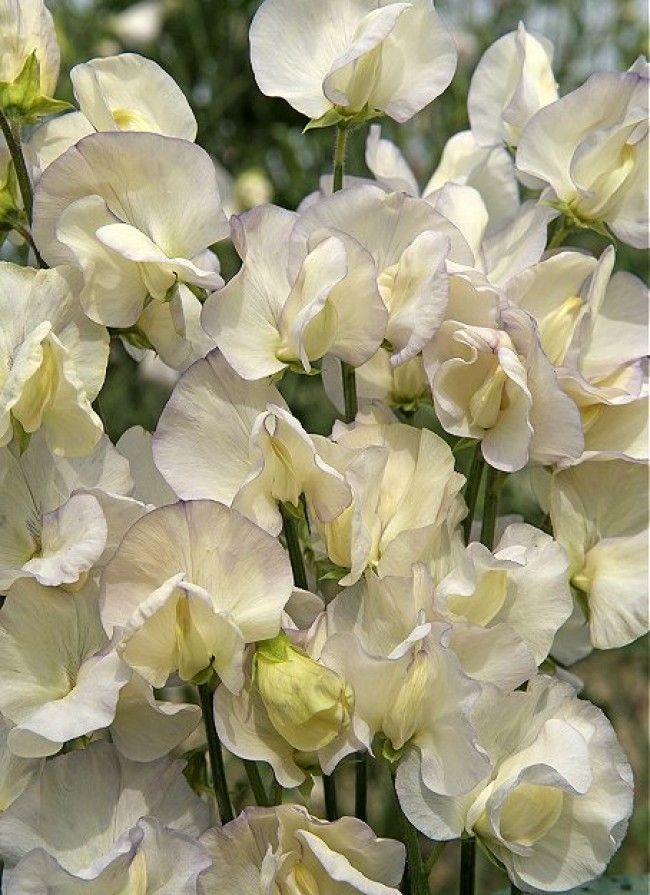 They are an improved version of the varieties of the Cuthbertson-Floribunda group. Inflorescences up to 30 cm long consist of large double flowers of various colors, depending on the variety. The disadvantage of these plants is their increased sensitivity to the length of daylight hours, so they are not grown in winter. Recommended varieties of this group for landscaping and cut;
They are an improved version of the varieties of the Cuthbertson-Floribunda group. Inflorescences up to 30 cm long consist of large double flowers of various colors, depending on the variety. The disadvantage of these plants is their increased sensitivity to the length of daylight hours, so they are not grown in winter. Recommended varieties of this group for landscaping and cut;
Multiflora Gigantea
This group of early varieties up to 2.5 m high was created in 1960 by American breeders. The plants have strong inflorescences from 35 to 50 cm long, consisting of 5-12 corrugated flowers with a diameter of about 5 cm. Varieties are recommended for landscaping and for cutting;
Ruffled
A group of powerful plants with 6-10 large flowers in one inflorescence. Peduncles are long and strong, the sail is wavy. The best varieties of the group:
- Grace is a branchy plant up to 155 cm high with inflorescences consisting of 5-7 fragrant pale lilac flowers about 5 cm in diameter with dark veins and a wavy sail.
 The height of hard peduncles is up to 35 cm;
The height of hard peduncles is up to 35 cm; - Ramona - a variety up to 130 cm high with bright carmine flowers with a white tongue at the base of the boat and a wavy sail. In one inflorescence, located on a rigid peduncle up to 30 cm long, 5-6 flowers up to 5 cm in diameter;
Intergen
A group of early undersized varieties bred in 1991 by Russian breeders that filled a niche between the varieties of the Cupido and Bijou groups. The height of the plants of this group is from 35 to 65 cm, so they can be grown without supports. Inflorescences up to 20 cm long consist of 3-4 simple flowers up to 3 cm in diameter. Best variety:
- Geniana - a plant from 30 to 50 cm high with very fragrant white-lilac flowers;
Lel
Bred in the same year, intermediate between Bijou and Multiflora Gigantea, a group of varieties with a height of 65 to 100 cm with strong inflorescences up to 30 cm long, each of which consists of 7-12 corrugated flowers up to 4.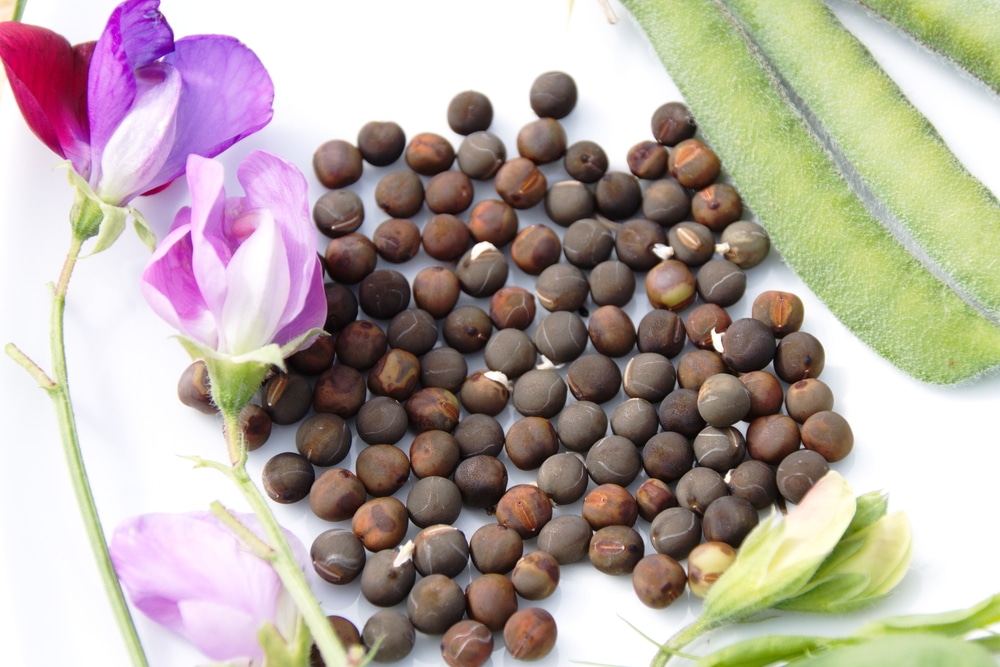 5 cm in diameter. Popular varieties of the group:
5 cm in diameter. Popular varieties of the group:
- Luciena - very fragrant plant 40-60 cm high with light pink flowers;
- Lisetta is a very sweet pea from 40 to 60 cm high with bright red flowers.
In the 70s of the XX century, groups of English varieties Jet Set and German Leisers Koeningspiel were created. Currently, selection work on sweet peas continues.
Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Peculiarities and other plants of the legume family
- List of all species on The Plant List
- More information on World Flora Online
Cocklebur: cultivation, properties, types and varieties
Oregano: cultivation, types and varieties
Sections: Garden plants Garden perennials Garden herbaceous plants Garden flowering plants Garden annuals Plants on D Legumes (Butterflies)
This article is usually followed by
Add a comment
when and how to plant seeds
Everyone knows ordinary peas have a wonderful brother - sweet peas, which is distinguished not only by its decorative effect, but also by its bright, pleasant smell. Many flower growers grow it precisely because of this. In our country, as a rule, an annual flower is grown, but it is also possible to grow a perennial plant. Usually, winter sowing is done in autumn or spring immediately in open ground, however, some summer residents and gardeners practice growing sweet peas from seeds at home. This method allows you to see earlier flowering.
Many flower growers grow it precisely because of this. In our country, as a rule, an annual flower is grown, but it is also possible to grow a perennial plant. Usually, winter sowing is done in autumn or spring immediately in open ground, however, some summer residents and gardeners practice growing sweet peas from seeds at home. This method allows you to see earlier flowering.
Content
- sweet peas for seedlings
When is the best time to plant sweet peas for seedlings? It is optimal to sow the seeds of the culture at home at the end of March, in the first half of April. For example, in the Middle lane (Moscow region) can be planted at the beginning of April , in Siberia, the Urals, Leningrad region - you can plant in mid-April, but in the South you can plant seeds at the end or even in mid March.
You can choose the optimal sowing dates using the Lunar calendar of 2022:
- Auspicious days:
- in January: 1, 10, 11, 15, 16, 19, 20;
- in February: 7, 8, 12, 13, 14, 15;
- in March: 10, 11, 15, 20, 21, 24, 25;
- in February: 1, 16;
- in March: 2, 16, 17, 18, 31.

- Auspicious days:
General rules for preparing for sowing
Container. It is necessary to immediately choose individual cups (plastic, peat), because the plant has a long taproot and does not like picking and transplanting (when choosing such a container, it will be possible to plant it in open ground along with an earthen clod by transshipment). The optimal volume of a glass is 200-250 milliliters. There should be drainage holes at the bottom (with the exception of peat pots), if they are not, then you need to do it yourself.
Primer. You can plant the seeds of this flower crop in a universal soil for seedlings of flowers. Or you can prepare the soil mixture with your own hands, mix: humus (2 parts) + soddy soil (2 parts) + peat (2 parts) + river sand (1 part).
Seed preparation for sowing . To increase germination, you can follow the standard path - soak the seed in a preparation that stimulates growth, for example, Epin-Extra, Energen, Zircon.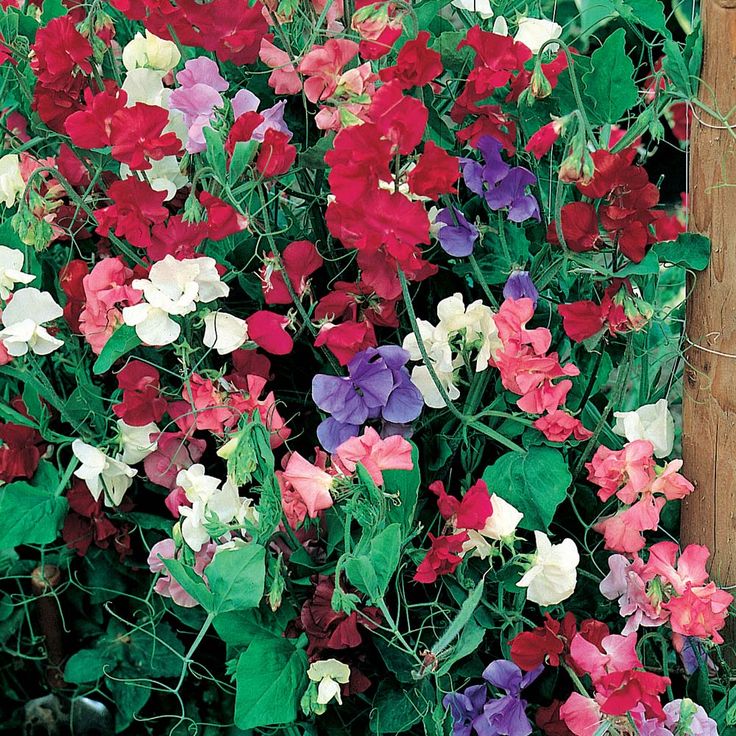 Supporters of organic farming can make an organic solution from aloe juice, honey.
Supporters of organic farming can make an organic solution from aloe juice, honey.
By the way! If you don't want to bother with the preparation, you can simply soak the seeds for 10-12 hours in plain, warm water.
Seeds can be germinated to sprout faster. For germination you need:
- Put the planting material on damp gauze or cotton cloth.
- Wrap cloth or gauze.
- Place material with seeds in a plastic bag.
- Put away for a few days in a warm place (temperature 20-25 degrees Celsius).
- Check daily to see if they have sprouted. Also, do not allow the material to dry out.
Step-by-step photo instructions for planting sweet peas for seedlings
1) Fill cups with drainage.
But this should only be done if you have plastic products. Drainage in peat pots is not necessary, they already pass moisture and air well. You can use perlite (pictured), small expanded clay, broken bricks. The layer thickness is 1.5 cm.
You can use perlite (pictured), small expanded clay, broken bricks. The layer thickness is 1.5 cm.
2) Fill the cups with soil.
Leave a small distance to the edges - 1.5 cm.
3) Moisten the soil liberally with clean water at room temperature.
4) Make a well in the center of the cup.
It is convenient to make it with a finger or a regular pencil, pen. The depth of the hole is 2 cm.
5) Now you need to plant in the holes.
As you can see in the photo, sweet pea seeds are very large, so no additional devices are required for sowing, you can just plant them with your hands.
6) Backfill the holes with soil.
7) Water generously again.
8) Cover the cups with a lid or foil.
This step is necessary to create the greenhouse conditions needed for successful germination.
Seedling care
Caring for sweet pea seedlings at home after sowing is very simple, you must follow the following rules:
- After planting and before germination, it is necessary to maintain a temperature of 20-22 degrees Celsius, regularly moisten the soil, maintaining moderate humidity and avoiding drying out. You should also ventilate the greenhouse every day, removing the lid or film for 15 minutes.
- After the seedlings sprout, you need to remove the covering material, gradually lower the temperature to 15-16 degrees, rearrange the plants on the southern, sunny windowsill. It is required that the plants are well lit (12-14 hours per day), if necessary, illuminate.
- Water regularly, do not allow the soil to dry out, and do not overfill, otherwise the roots may rot. The soil should always be moderately moist.
- When seedlings have 3-5 true leaves, pinch off the top. Manipulation will allow you to achieve a greater number of shoots (i.











