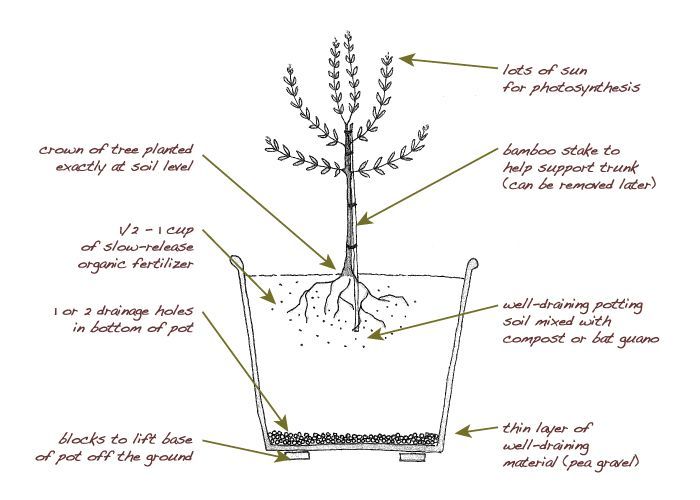
Start basil indoors
How to Grow Basil Indoors
By
Jon VanZile
Jon VanZile
Jon VanZile was a writer for The Spruce covering houseplants and indoor gardening for almost a decade. He is a professional writer whose articles on plants and horticulture have appeared in national and regional newspapers and magazines.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
Updated on 03/23/22
Reviewed by
Kathleen Miller
Reviewed by Kathleen Miller
Kathleen Miller is a highly-regarded Master Gardener and Horticulturist who shares her knowledge of sustainable living, organic gardening, farming, and landscape design. She founded Gaia's Farm and Gardens, a working sustainable permaculture farm, and writes for Gaia Grows, a local newspaper column. She has over 30 years of experience in gardening and sustainable farming.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
The Spruce / Letícia Almeida
In This Article
-
Growing Indoors
-
Care
-
Container
-
Soil
-
Repotting
-
Moving Outdoors
-
Frequently Asked Questions
Basil is one of the easiest herbs to grow indoors, and its delicious flavor and culinary popularity make it a must-have for gardeners and cooks alike. With the proper conditions, basil grown indoors can be just as successful (if not more so) than plants that are grown outdoors. Best planted in early spring outdoors or year-round indoors, basil will grow quickly, establishing in just three to four weeks. The plant features small, shiny green leaves that grow in bunches and possess a very distinct aroma.
| Botanical Name | Ocimum basilicum |
| Common Name | Basil, sweet basil |
| Plant Type | Annual |
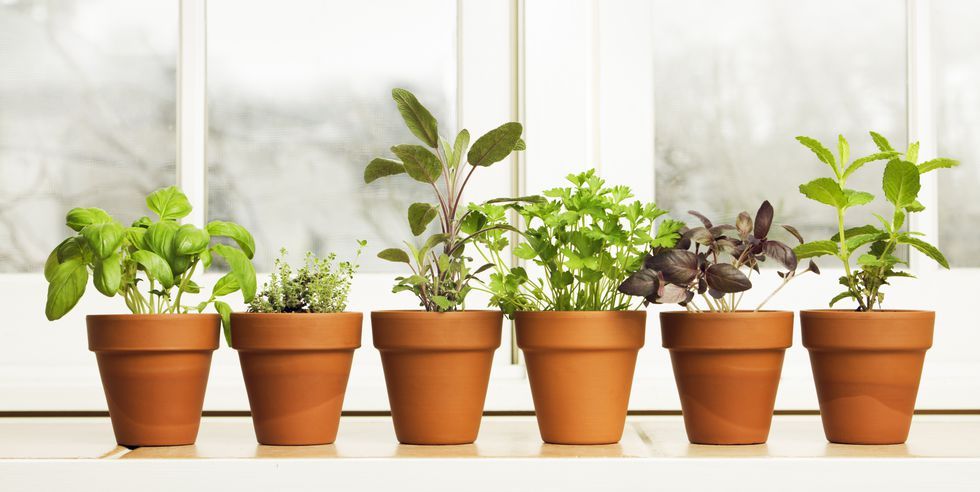
Can You Grow Basil Indoors?
As with many other herbs, basil is a true sun-lover—give it bright light each day, and it will thrive. Alternatively, basil does exceptionally well under grow lights, so you have the opportunity to increase your harvest and grow enough basil to keep your kitchen stocked throughout the year. Basil requires a pot just big enough for the plant, so starter plants can fit quite well in even the smallest apartment space.
Basil requires a pot just big enough for the plant, so starter plants can fit quite well in even the smallest apartment space.
How to Grow Basil Indoors
Basil is a uniquely rewarding plant to grow—it's relatively pest and disease-free and is delicious in both fragrance and taste. Basil's taste will change throughout its life cycle, becoming stronger as the plant flowers—basil that has flowered can still be eaten, but it may be a bit bitter. The herb responds well to pruning and topping, so feel free to use leaves as soon as the plant is established and has branched out.
Sunlight
Whether being grown indoors or outdoors, basil plants need ample light—at least six hours of full sun daily.
Artificial Light
If you're using fluorescent bulbs, keep your basil under them for 12 hours a day, with the lights about 2 to 4 inches away from the top of the plants. Be careful not to let the leaves touch the bulbs to prevent burning.
Temperature and Humidity
Keep your basil somewhere in your home that boasts an average temperature of 70 degrees Fahrenheit or higher. Avoid putting the plant anywhere it may be subjected to a harsh or cold breeze, like in front of an open window in the winter or near an air conditioning unit. Basil plants also like a fair bit of humidity, so mist your plant occasionally, especially if your home is particularly dry. If you find you need an added bit of moisture, you can place your basil container on a bed of wet river rocks to increase the ambient humidity around the herb.
Avoid putting the plant anywhere it may be subjected to a harsh or cold breeze, like in front of an open window in the winter or near an air conditioning unit. Basil plants also like a fair bit of humidity, so mist your plant occasionally, especially if your home is particularly dry. If you find you need an added bit of moisture, you can place your basil container on a bed of wet river rocks to increase the ambient humidity around the herb.
Watering
For best results, aim to keep your basil plants regularly moist. Basil thrives best when it receives about 1 inch of water a week, but plants housed in containers often need a bit more than that. Water your plant once the top layer of soil has dried out, or when the plant shows the first signs of wilting (though it's best to not wait for that as a signal).
Fertilizer
If you've previously amended your soil with organic compost, there's a good chance that your basil plants won't need additional nutrients. However, if you notice your plants aren't experiencing much growth, you can feed your basil plant once a month using a weak liquid fertilizer.
However, if you notice your plants aren't experiencing much growth, you can feed your basil plant once a month using a weak liquid fertilizer.
Pruning and Maintenance
Basil is a hardy plant that needs little maintenance. Well-drained soil, good air circulation, occasional watering, and plenty of sunlight are enough to keep a basil plant in good shape. Harvesting is effectively pruning the plant, as the leaves should be taken from the top down. Cut off individual leaves from smaller plants, or snip stems a few inches down for larger ones.
Container and Size
To avoid potential fungal growth on the plant, basil needs a container that allows for good airflow and excellent drainage. To this end, a fabric pot filled with high-quality potting soil can help basil thrive.
Potting Soil and Drainage
Basil plants prefer a soil mixture that is moist but well-draining. For best results, amend your potting soil with a bit of organic compost before planting your basil indoors. Beyond that, make sure to choose a pot for your plant that boasts ample drainage holes at its base so the soil doesn't get soggy or waterlogged.
Beyond that, make sure to choose a pot for your plant that boasts ample drainage holes at its base so the soil doesn't get soggy or waterlogged.
Potting and Repotting Basil
Most people eat their basil before they can repot it. If you're growing from seed, step up seedlings from a seed starting tray after two weeks into a 4-inch pot, which will likely be their final home. Pinch the herb after the newly repotted plant is established to encourage more leaves. Basil responds well to pruning, but don't expect indoor plants to get quite as large as those grown outdoors.
Moving Basil Outdoors for the Summer
Basil doesn't like the cold. Move it outside only after temperatures are consistently about 50 degrees Fahrenheit. As winter approaches, bring basil inside before the first frost.
Watch Now: How to Grow Basil Indoors
Growing Basil From Seed: A Step-by-Step Guide
Growing basil from seed should be on every gardeners to-do list. Why? Basil is easy to grow from seed and when you buy seeds instead of transplants you can choose from dozens of types and varieties available through seed catalogs. There are two ways to start basil seeds: indoors in a window or beneath a growlight, or by direct seeding outdoors. Keep reading to learn more about the simple steps of growing basil from seed.
Why? Basil is easy to grow from seed and when you buy seeds instead of transplants you can choose from dozens of types and varieties available through seed catalogs. There are two ways to start basil seeds: indoors in a window or beneath a growlight, or by direct seeding outdoors. Keep reading to learn more about the simple steps of growing basil from seed.
What is basil?
Basil (Ocimum basilicum) is a tender annual herb grown for its aromatic leaves that are added to fresh and cooked dishes. Sweet basil, also called Genovese basil is the most widely grown due to its delicious anise clove flavor. There are many other types of basil available through seed catalogs including lemon basil, Greek basil, cinnamon basil, and Thai basil. Each one offers a variety of flavors, forms, leaf sizes, and even colors. Basil is often planted with tomatoes and peppers because they have similar growing conditions – well draining soil and 8 to 10 hours of sunlight. Basil is also used in companion planting as the mid to late summer flowers attract bees and beneficial insects to the garden.
Basil is also used in companion planting as the mid to late summer flowers attract bees and beneficial insects to the garden.
Why you should be growing basil from seed
Wondering if it’s worth your time to grow basil from seed? It absolutely is! Here are my four reasons for starting basil from seeds:
- Basil is easy to grow from seed – It’s true! I’ve been growing basil from seed for over 25 years and it’s generally a fuss-free herb that goes from seed to garden in under two months. You don’t need special equipment either. I start my seeds under grow lights but you can also use a sunny windowsill.
- Save money – I grow a lot of basil each summer so we have plenty of fresh basil and basil leaves for pesto, as well as for the freezer and to dry. With individual basil plants costing $3.00 to $4.00 each at my local nursery, growing basil from seed is a budget-friendly way to get a lot of basil plants for your garden.

- Variety – There are a lot of different types and varieties of basil available through seed catalogs. It’s fun to try new ones each year, but growing basil from seed was also a game changer in my garden when downy mildew wiped out almost all of my basil plants. The plants that weren’t affected? They were Rutgers Devotion DMR, a downy mildew-resistant variety I grew from seed. It can be hard to find disease-resistant basil transplants at garden centres, but they’re easy to source as seeds from seed catalogs.
- Succession planting – I plant basil several times over the course of the growing season to ensure a non-stop supply of high quality leaves. It’s hard to find healthy basil seedlings in mid-summer but starting a few pots of seeds under my grow lights ensures I’ll have basil for successive crops.

Growing basil from seed
There are two ways to grow basil from seed. First, you can start the seeds indoors on a sunny windowsill or beneath grow lights. Eventually the young plants are transplanted into the garden. The second method is to direct sow basil seeds in garden beds or containers. Let’s look closer at each method so you can figure out which one is right for you.
Growing basil from seed indoors
Most gardeners start their basil seeds indoors to get a jump on the growing season. Success begins with sowing the seeds at the right time, 6 to 8 weeks before the last frost date. In my zone 5 garden that’s late May so I start my basil seeds indoors in late March. Sowing the seeds indoors even earlier doesn’t necessarily give you a head start on the basil harvest. It just means you’ll have bigger plants that need to be re-potted into larger containers. And they’ll take up a lot of space on a windowsill or beneath grow lights. Plus, transplanting mature basil plants into the garden often results in bolted plants that begin to flower instead of pushing out lots of fresh leaves. This reduces the overall harvest. Younger seedlings adapt better to transplanting and should be moved to the garden when they’re 6 to 8 weeks old.
This reduces the overall harvest. Younger seedlings adapt better to transplanting and should be moved to the garden when they’re 6 to 8 weeks old.
The best containers for growing basil from seed
Now that we know when to sow basil seeds indoors, we can consider containers. I typically use 10 by 20 trays with cell pack inserts to start most of my vegetable, flower, and herb seeds. They offer an efficient use of space under my grow lights and I re-use them from year to year. However, you can start basil seeds in pretty much any type of container as long as it’s clean and offers good drainage. If you’re up-cycling items like salad containers for seed starting be sure to pole holes in the bottom for excess water to drain away.
To cut down on plastic use I’ve recently bought a soil blocker for seed starting. A soil blocker forms lightly compressed cubes of soil – no container needed. I have several sizes and look forward to experimenting with starting basil seeds this way.
I have several sizes and look forward to experimenting with starting basil seeds this way.
The best soil for growing basil from seed
When starting seeds indoors a lightweight seed starting or potting mix is essential. These mixes are typically made up of materials like peat moss, coconut coir, compost, vermiculite, perlite, and fertilizers. The ideal growing medium for seed starting is one that retains water, but is also quick draining to promote healthy root growth. You can make your own (check out our DIY potting mix recipes here) or buy a bag online or from your local garden centre.
You can use a variety of containers to start basil seeds including soil blocks. Soil blockers form loosely compacted cubes of soil ideal for seed starting.Starting basil seeds indoors
Once you’ve gathered your supplies, it’s time to get planting. Fill your containers with the pre-moistened potting mix. When sowing basil seeds in cell packs, plant 2 to 3 seeds per cell. If starting basil seeds in 4 inch pots, plant 6 to 8 seeds per pot. Whatever type of container you are using for the basil seeds, sow each seed about an inch apart. Plant the seeds a quarter of an inch deep. The exception to this is holy basil whose seeds need light to germinate. Instead of covering holy basil seeds, gently press them into the moist potting mix to ensure good soil-seed contact.
Whatever type of container you are using for the basil seeds, sow each seed about an inch apart. Plant the seeds a quarter of an inch deep. The exception to this is holy basil whose seeds need light to germinate. Instead of covering holy basil seeds, gently press them into the moist potting mix to ensure good soil-seed contact.
After the seeds have been planted place a clear dome or a piece of plastic wrap on top of the trays or pots. This keeps humidity high to promote good germination. Once the seeds sprout, remove any plastic coverings so air can circulate.
When the young plants have developed two sets of true leaves, thin them to one plant per cell, or three to four plants per 4 inch pot. You can carefully prick the surplus seedlings from their containers and transplant them into more pots. Let’s be honest, you can never have too much basil!
There are many advantages of growing basil from seed versus buying transplants.How much light do basil seedlings need?
Providing sufficient light is perhaps the biggest challenge when starting seeds indoors. Most types of vegetables, flowers, and herbs need plenty of light to form strong, stocky seedlings. Relying on natural sunlight from a window can be a challenge, especially for those who live in Northern climates. Seedlings grown in insufficient light are tall, leggy, and tend to flop over. The solution is to use a grow light to start seeds like basil.
Most types of vegetables, flowers, and herbs need plenty of light to form strong, stocky seedlings. Relying on natural sunlight from a window can be a challenge, especially for those who live in Northern climates. Seedlings grown in insufficient light are tall, leggy, and tend to flop over. The solution is to use a grow light to start seeds like basil.
I have two types of grow lights: LED grow lights and fluorescent grow lights. I leave my grow lights on for 16 hours each day using an inexpensive timer to turn them on and off. You can DIY a grow light set up or buy one from a garden supply store. When I’m not starting seeds I use my grow lights to provide light to succulents, culinary herbs, and other indoor plants.
The ideal temperature for basil
Basil is a heat-loving herb and the seeds germinate best in warm soil. The ideal temperature for basil seed germination is 70 to 75F (21 to 24C) with the seeds emerging in about 5 to 10 days. If you have a seedling heat mat you can use it provide bottom heat to both speed up germination and increase germination rates.
Watering and fertilizing basil seedlings
Basil seedlings can be prone to damping off, a soil-borne fungal disease that affects the stems and roots of young seedlings. I’ve found the two best ways to reduce damping off is to water the seedlings properly and provide good air circulation. First, let’s talk watering. Basil seedlings grow best in lightly moist, not wet soil. Water when the soil is dry to the touch, checking seedlings every day to gauge soil moisture. The other consideration for preventing damping off is air movement. I keep a small oscillating fan in the room near my grow lights. Good air circulation helps strengthen the seedlings, reduces mold growth on the soil surface (a sign of overwatering), and dries the leaves after watering.
When basil seedlings have developed their first set of true leaves I begin to fertilize. I use a liquid organic fertilizer diluted to half strength every 14 days. This promotes healthy growth and plenty of bright green leaves.
I use a liquid organic fertilizer diluted to half strength every 14 days. This promotes healthy growth and plenty of bright green leaves.
Hardening off basil seedlings
Hardening off seedlings is the final step when growing basil from seed. This is a step you don’t want to skip. The hardening off process acclimatizes seedlings to the sun, wind, and weather of the outdoor garden. Because basil is sensitive to heat don’t move the plants outside while there is still a risk of cold weather. I begin the hardening off process, which takes about five days, after the last expected date has passed.
Start by moving the seedlings outside on a mild day, placing the trays or containers in a shady spot. Cover them with row cover that night or bring them back indoors. On day two, give the plants some early morning or late afternoon sun, but shade during from mid-morning to mid-afternoon when the sun is most intense. Again, cover them up at night or bring them back inside the house. On days three to five continue to gradually introduce the plants to more light until by day five they are ready for full sun.
Again, cover them up at night or bring them back inside the house. On days three to five continue to gradually introduce the plants to more light until by day five they are ready for full sun.
How and when to transplant basil
Hardened off basil seedlings can be moved into garden beds or containers once the risk of frost has passed and the weather has warmed. Don’t rush basil outside, however, as cold damage can occur when the day or night temperatures fall below 50F (10C). Once the conditions are right, transplant seedlings into a site with direct sunlight and well-draining fertile soil. I add all purpose compost to my beds or containers before transplanting. Space basil plants 8 to 10 inches apart. When the plants have five to six sets of true leaves you can start to harvest basil.
Once your basil seedlings are hardened off they can be moved to garden beds or containers. This Greek basil seedling already has its classic round shape.Growing basil from seed outdoors
The other technique for growing basil from seed is to direct sow seeds outdoors. Because I live in a cold climate, I start my basil seeds indoors to give the plants a head start. Gardeners who live in zones 6 and above, however, can direct sow basil seeds outdoors in a garden bed or container. Choose a sunny site and amend the soil with a thin layer of compost. Plant the seeds in late spring or early summer, about a week or two after the last spring frost. The soil temperature should be at least 70F (21C). Sow the seeds a quarter of an inch deep and one inch apart.
Because I live in a cold climate, I start my basil seeds indoors to give the plants a head start. Gardeners who live in zones 6 and above, however, can direct sow basil seeds outdoors in a garden bed or container. Choose a sunny site and amend the soil with a thin layer of compost. Plant the seeds in late spring or early summer, about a week or two after the last spring frost. The soil temperature should be at least 70F (21C). Sow the seeds a quarter of an inch deep and one inch apart.
Once the seeds are planted, water the seedbed often with a hose nozzle on a gentle setting. You don’t want a hard jet of water which could dislodge or wash away the seeds or young seedlings. Don’t let the soil dry out as the seeds are germinating. Once the basil seedlings have developed two to three sets of true leaves, thin them 8 to 10 inches apart.
For further reading on growing basil, be sure to check out these articles:
- Types of basil to grow
- The secrets of growing great basil
- How to grow basil from cuttings
- How to trim basil for bushy plants
- 7 reasons for basil leaves turning yellow
Are you growing basil from seed this spring?
Basil on the windowsill: how to grow it correctly
Published:
Basil is a vitamin seasoning for various dishes. How to grow a plant in an apartment? Gardeners Anna Zorina, Victoria Karpukhina and Nikolai Zvonarev shared the secrets of growing crops on the windowsill.
How to grow a plant in an apartment? Gardeners Anna Zorina, Victoria Karpukhina and Nikolai Zvonarev shared the secrets of growing crops on the windowsill.
Peculiarities of growing basil on a windowsill
Basil is an unpretentious plant, grows in winter and summer, smells wonderful, contains useful vitamins and microelements, according to the author of the Great Encyclopedia of Spices, Seasonings and Herbs Victoria Karpukhina.
Can you grow basil in a window? Yes. Basil is easy to grow in a pot on a windowsill. The culture does not require special care and actively grows shoots from the main stem. They are used for food.
Secrets of growing basil on the windowsill
How to grow basil on the windowsill? Basil on the windowsill is grown from seeds, by cuttings and transplanting the finished bush into a pot. The best way to grow basil indoors is from seeds. Then it forms a lush bush and yields a green crop for almost a whole year.
How to grow basil on a window sill: Unsplash/Lesly JuarezTo grow basil on a window sill, follow these guidelines:
- Choose small-leaved and low-growing varieties of basil for planting, such as clove aroma, marquise, small-leaf, "beamy".
 Violet and Greek small-leaved develop for a long time and are more demanding in care.
Violet and Greek small-leaved develop for a long time and are more demanding in care. - Prepare green growing containers with drainage holes at least 15 cm deep to avoid picking plants. Basil is difficult to tolerate any manipulation of the root system and is sick for a long time after transplantation.
- Use ready-made universal potting soil. Be sure to mix it with garden soil (1:1) or biohumus (1:4). For long-term cultivation of basil, you will need a lot of nutrients.
- Display basil seedlings in a well-lit window facing south or southwest. Extend daylight hours for the plant in the autumn-winter period up to 12 hours. Author of the book "Spices. Growing, harvesting, application ”Anna Zorina advises using fitolamps to get enough light for plants.
- Keep the temperature in the room at least +20 °C, otherwise the basil will lose its aroma. There should be no drafts on the windowsill, from which the plant is sick and develops poorly.
- Take cuttings from the mother bush in advance to replace the old plant in time.
 A seedling grown from a cutting gives a crop of greenery within 3-4 months.
A seedling grown from a cutting gives a crop of greenery within 3-4 months. - Cut off leaves and shoots after 2 weeks on cuttings. If the basil was planted with seeds, the crop will ripen in a month and a half. Cut the greens, leaving at least 4 leaves on the bottom of the stem, new side shoots will begin to develop in their axils.
- Pinch off the top when the bush is 8-10 cm tall to help it sprout side shoots and keep the flower spike.
When is the best time to plant basil on the windowsill? But this plant is light and heat-loving, therefore, in the autumn-winter months, it requires additional lighting and maintaining the optimum temperature.
When to plant basil on the windowsill? The best time to plant basil in a pot is late February and early March. During this period, there is an active awakening of seeds, and daylight hours increase. Basil seedlings do not have to create artificial conditions for development. By the summer, the bush will grow up, and it will be possible to put it on a balcony or loggia, where there is a lot of light, air and heat.
By the summer, the bush will grow up, and it will be possible to put it on a balcony or loggia, where there is a lot of light, air and heat.
How to plant and care for basil on your windowsill
Basil germinates quickly from seed if you choose varieties suitable for growing indoors. For propagation of basil by cuttings, observe a certain watering regime, optimal indicators of temperature and humidity in the room.
In autumn, the basil bushes are transplanted from the open bed into pots and placed on the windowsill. But such plants very quickly throw out flower stalks. They will have to be cut to get juicy greens in winter.
How to plant basil in pots
Sow basil seeds step by step:
- Soak the seeds for faster germination in warm water for 1-2 days, change the water every 12 hours. Hold them in a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate for 2 hours and dry on a napkin.
- Fill prepared containers or pots with a drainage layer (2-3 cm) of expanded clay or pebbles.
 Lay the soil on top, do not add 3-4 cm to the edges of the container. Level the ground and pour plenty of water.
Lay the soil on top, do not add 3-4 cm to the edges of the container. Level the ground and pour plenty of water. - Sow the seeds in bulk at a distance of 5 cm from each other.
- Sprinkle a centimeter layer of earth on top and cover with foil for a greenhouse effect.
- Place the container in a warm place (+25-28°C) and air the crops every day until germination.
The first sprouts of basil will appear in 7-12 days. After the shoots appear, remove the film, and thin out the seedlings so that a distance of 10 cm remains between them. Place the container on a lighted windowsill. When the stems reach 5 cm, add a layer of earth (2-3 cm) to strengthen the young plants.
How long does basil grow from seeds? The first crop (a couple of top leaves of the top) can be harvested 5-7 weeks after germination, when 5-6 full-fledged leaves appear. A plant grown from seed will take much longer to produce leaves than a seedling from cuttings. It will take 8-12 months for such a bush to fully mature.
It will take 8-12 months for such a bush to fully mature.
When planting basil with cuttings, use the recommendations of Nikolai Zvonarev, author of the book Spicy Herbs. We plant, we grow, we harvest, we treat”:
- Take cuttings from the mother bush, breaking off shoots at least 5 cm long from the top or from the middle of the stem.
- Soak the cuttings in water for 1-2 weeks until roots develop at the broken point.
- Plant the germinated cuttings in pots and cut off the first greens after a couple of weeks.
Pluck out the top shoots in time to keep the bush green longer, then it will not bloom. Flowering basil is not suitable for human consumption.
Planting basil cuttings: YouTube / Yana Fedorova Popular videoHow to care for basil on the windowsill
Basil seedlings take a long time to gain strength until harvest. Plants in pots will need a schedule of watering, fertilizing, a certain temperature regime, proper lighting and humidity regime.
How to water basil on the windowsill? Water the basil correctly:
- in spring and summer - every morning, and on very hot summer days 2 times - in the morning and in the evening. In winter, it is enough to water twice a week;
- use only settled warm water;
- Periodically, and in summer every day, spray the plant with water from a spray bottle.
Basil bushes grow actively at a temperature of +20–25 °C. At the same time, they require direct sunlight for at least 3-4 hours a day and air humidity of at least 60%. When the window is open, basil is not left, because the plant is afraid of drafts.
So that the root system breathes and absorbs moisture, loosen the soil in pots with adult plants once every 2-3 days. If the potted soil is not too fertile, fertilize once a month using complex fertilizers based on humates. Spend the first top dressing when the plant releases lateral shoots.
Cutting of leaves and shoots is being carried out not only in order to use them for cooking various dishes. Frequent early pruning of basil allows you to grow a bushy bush with many succulent branches.
Frequent early pruning of basil allows you to grow a bushy bush with many succulent branches.
Every housewife can grow basil on a windowsill. The correct way of reproduction and care of the plant allows you to create a green garden in the house in a few weeks and use vitamin greens at any time of the year.
Original article: https://www.nur.kz/household/garden/1790656-kak-vyrastit-bazilik-na-podokonnike-sekrety-i-pravila-vyrasivania/
Windowsill basil
Fragrant, healthy, beautiful - this is basil. Spicy greens are universal: they put it in meat, fish, vegetable dishes and even in tea. Whoever chews basil leaves adds health to himself, which is especially valuable during the coronavirus pandemic. The plant is easy to grow on the windowsill, which means saving the family budget. No wonder the “home garden” is becoming more and more popular.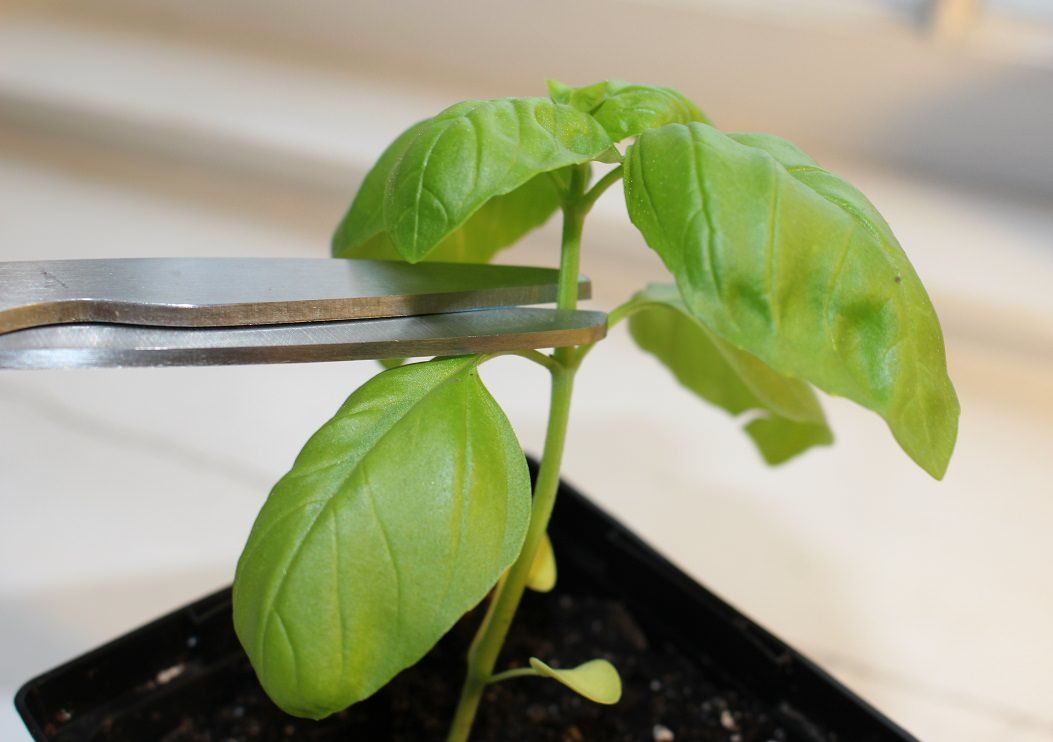
Basil varieties for window sill cultivation
Greens can be grown in the kitchen. What is the best basil to grow at home? For the "bed" on the windowsill, short, fast-growing varieties with green leaves are selected.
Basil on the windowsill
Varieties of purple color are more beautiful, but taller, more demanding in care. With a year-round "green conveyor", the ripening time is taken into account in order to constantly have regrown fresh leaves to the table.
Experts advise choosing well-established varieties for growing basil on the windowsill.
"Lemon" - a wonderful variety with lemon aroma and delicate glossy greens. Strong notes of lemon and lime are also found in Citrus Fresh .
"Marquis" - a bush, similar to a ball, with a mass of small green leaves.
"Dwarf" - a short plant (10-18 cm), decorated with purple or green leaves.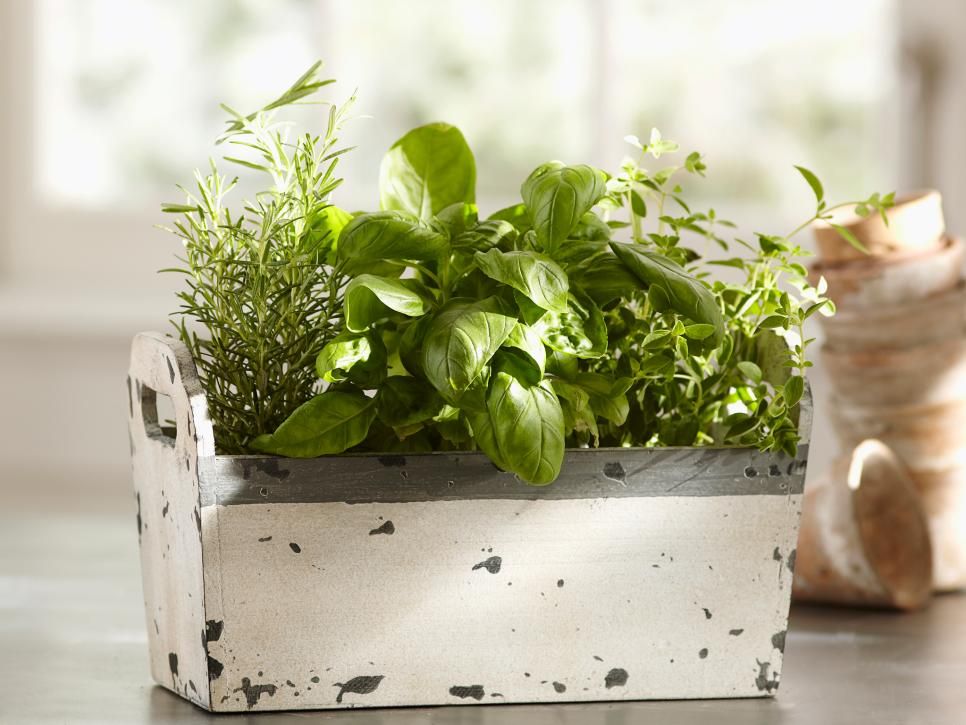 Mid-early variety, with a spicy taste. The company can also take grade "Siberian dwarf" .
Mid-early variety, with a spicy taste. The company can also take grade "Siberian dwarf" .
Caramel Basil
"Carnation" - green-leaved early variety with the smell of cloves and pepper.
"Purple Indoor" - a plant no taller than 30 cm with purple foliage, with a strong aroma. It grows well on the windowsill and "Garnet Bracelet" .
"Osmin" is one of the new varieties of basil with elegant bright purple leaves.
"Yerevansky" - a well-known early ripening tall variety for open ground. Can be grown indoors. Aroma of allspice and tea.
There are also seeds for growing microgreens. They are also great for windowsills.
Soil preparation
What kind of soil does basil prefer if grown on a windowsill? This is a purchased soil for seedlings, indoor plants. Or self-prepared soil from humus and peat (ratio 1 to 2). Mandatory drainage of pebbles, expanded clay 2-3 cm. You can use a pot for growing with a volume of 1-2 liters, containers, any container with a height of at least 15 cm with holes at the bottom. The earth is disinfected before use. Ignite in the oven for half an hour (temperature 70-90 degrees C), scalded with boiling water or spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate (2.5 g per 5 liters of water).
Or self-prepared soil from humus and peat (ratio 1 to 2). Mandatory drainage of pebbles, expanded clay 2-3 cm. You can use a pot for growing with a volume of 1-2 liters, containers, any container with a height of at least 15 cm with holes at the bottom. The earth is disinfected before use. Ignite in the oven for half an hour (temperature 70-90 degrees C), scalded with boiling water or spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate (2.5 g per 5 liters of water).
How to propagate basil
Basil is grown at home by sowing seeds, rooting cuttings, rooted bush.
Sowing seeds and caring for young shoots
When growing basil from seeds, the harvest can be harvested in one and a half to two months. T What kind of plants provide vitamin products and decorate the room for a whole year!
It is advisable to soak basil seeds before sowing, as the essential oils they contain make it difficult to germinate. Soak the seeds in warm water for 1-2 days, change the water after 12 hours. Then they are kept for two hours in a pink solution of potassium permanganate and dried on a paper napkin, cloth. Sowing basil goes like this. Small seeds are picked up with tweezers and embedded in moist soil to a depth of 1 cm. Then they should be sprinkled with earth, watered and covered with glass or film for the greenhouse effect. A pot (another container) with basil is placed in a warm place. Watering is carried out periodically, spraying the crops with warm water (temperature 30 degrees C).
Soak the seeds in warm water for 1-2 days, change the water after 12 hours. Then they are kept for two hours in a pink solution of potassium permanganate and dried on a paper napkin, cloth. Sowing basil goes like this. Small seeds are picked up with tweezers and embedded in moist soil to a depth of 1 cm. Then they should be sprinkled with earth, watered and covered with glass or film for the greenhouse effect. A pot (another container) with basil is placed in a warm place. Watering is carried out periodically, spraying the crops with warm water (temperature 30 degrees C).
After a week or a little more, basil sprouts on the windowsill. Cultivation is continued by removing the glass (film) and thinning out the sprouts. The distance of seedlings from each other is at least 10 cm. When the seedlings reach a “growth” of 5-7 cm, they are sprinkled with earth.
Basil seeds are sown throughout the year with a break from May 25 to July 25. Since the plant blooms quickly with a long daylight hours, the leaves lose their nutritional value.
Since the plant blooms quickly with a long daylight hours, the leaves lose their nutritional value.
Subtleties of propagation by cuttings
It is easier to propagate basil by planting cuttings. Cut apical, lateral shoots from an adult plant. Twigs can be taken even from a store copy. They are put in water for 1-2 weeks (water is changed daily) until roots appear. Then rooted cuttings are planted in a pot. After 2-3 weeks, you can start harvesting. A convenient way to breed in winter. But you can only cut greens from a bush for 3-4 months.
Growing seedlings
This is the same sowing of basil seeds with further picking. Densely sown basil seeds on the windowsill in the phase of 3-4 leaves are transplanted into a separate bowl. When planting, pinch the root to stimulate good growth in the future.
Growing basil from a rooted bush
Plants can be taken from the summer cottage and planted in the room on the windowsill. This prolongs the harvest season, although the basil blooms quickly.
This prolongs the harvest season, although the basil blooms quickly.
Basil Care
Basil, if grown on a windowsill, has a number of requirements. This is especially true for temperature and lighting. Plant care includes watering, fertilizing, bush formation.
Choosing the best location and lighting
The most suitable place in the room for a basil is windows facing southwest, southeast. After all, basil is photophilous. With a lack of light, the plant will stretch out and become weak. In autumn and winter (especially on the northern windows), this spicy-tasting crop should have at least 12 hours of illumination a day. You will need special lamps for plants, which are placed above the plants at a distance of at least 15 cm.
Temperature and humidity
The main feature of basil is thermophilicity. Basil among all annual spicy-flavoring plants is the most demanding to heat. He feels good at a temperature of 20-25 degrees C. At a lower temperature, and even in a draft, the basil sissy will begin to "waste" and lose its aroma. Therefore, it is best to grow it in a room, and take it out to the loggia, balcony only in summer.
At a lower temperature, and even in a draft, the basil sissy will begin to "waste" and lose its aroma. Therefore, it is best to grow it in a room, and take it out to the loggia, balcony only in summer.
But with all the plant's craving for warmth, the room where basil grows can and should be ventilated. And also spray the leaves in the heat and especially during the heating period.
Watering and fertilizing
Watering in summer should be regular, in winter more moderate - at least once a week. But it all depends on the condition of the earth in the tank. If the soil is dry, then you need to water it. If the soil is waterlogged, it should be dried. Overdrying and overflowing are especially detrimental to young seedlings. It is better to water the basil in the morning with settled water. "Having drunk" the plant, loosen the surface of the earth in a pot.
When growing basil on a windowsill, you should not forget about top dressing, because the soil in the pot is depleted. “Feed” the greens with a complex mineral fertilizer for indoor plants once a month, in the spring - twice a month. Dry fertilizer (doses in the instructions) are scattered in a pot and watered over the basil. Liquid top dressing is applied after the main watering.
Can be fed with organic humic fertilizers.
Or use waste from the kitchen. Sprinkle the ground with a little wood ash (rich in potassium, phosphorus) and then water it. Pour the crushed eggshell (a source of calcium) with water, leave for three days and also pour the soil into the container. Many trace elements are contained in the infusion of onion peel. A handful of husks is poured into 1.5 liters of boiling water, insisted for 2 hours, then diluted halfway with water and watered the soil in a pot with basil. A good top dressing is sleeping tea (without flavorings). Dried tea leaves (glass) are poured with 3 liters of boiling water and wait until it cools down. Strain and water. Yeast serves as a growth stimulator. Half a bag of yeast 10-11 g is poured into 5 liters of warm water. They insist a little and water at the rate of 1 cup of yeast sourdough for 5 liters of water. You can add 1 tbsp. l. honey or 2 tbsp. l. Sahara.
Bush formation and harvesting
The correct formation of basil affects the yield and appearance of the bush. By pinching the tops of the shoots, a leafy beautiful "tree" is obtained. The first "circumcision" is carried out when the plant has four to six leaves. Remove two leaves from the top. After that, side shoots will appear. They are pinched in the same way, forming a compact plant. In this case, the plant on the shoots should have four leaves from the bottom.
The first harvest is harvested after a month and a half.
When harvesting, cut off the older side leaves. The most useful and fragrant greens when the basil is just blooming. Then the leaves are cut off, and the buds that have filled the color are removed. Flowering plants are left only to produce basil from seeds.
Greens are used fresh, dried, frozen. Leaves and twigs are used. Leaves give a special taste to salads, pickled vegetables, meat, fish, lemon basil - tea. For drying, the basil is laid out in a thin layer on paper in a ventilated place. A few days later, the dried basil leaf is placed in a tightly closed glass (not plastic!) dish. Store in a dry dark cool place.
Diseases and pests of basil
At home, basil is usually not affected by diseases and pests. Most often, fragile seedlings suffer. Thin sprouts of seedlings can affect the black leg, fusarium. This is facilitated by increased soil moisture, thickened planting, poor ventilation.
A pest that can attack basil in a room is aphid. But this is rare. They observe the agricultural technology of growing basil in order to prevent the appearance of diseases and pests. But if the attack showed up, they take urgent measures. The use of "chemistry" in this case is not recommended. With the defeat of the black leg, Fusarium, the plants will have to be destroyed.