Roses starting from cuttings
Rooting Roses: Growing Roses From Cuttings
Roses
By: Stan V. Griep, American Rose Society Consulting Master Rosarian, Rocky Mountain District
One way to propagate roses is from rose cuttings taken from the rose bush one desires to have more of. Keep in mind that some rose bushes may still be protected under patent rights and thus, are not to be propagated by anyone other than the patent holder. Keep reading to learn more about how to root roses.
The best time to take rose cuttings and rooting roses is in the cooler months, perhaps starting in September, as the success rate is higher for home gardeners at this time. The rose cuttings that one is going to try to root are best taken from the stems of the rose bush that have just flowered and are about to be deadheaded.
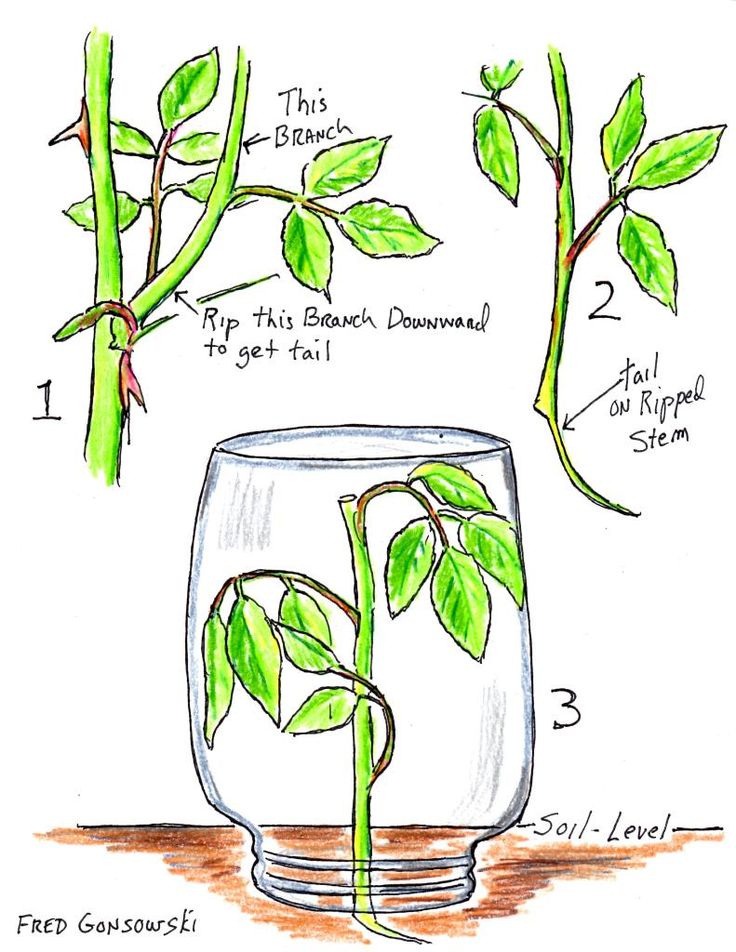
The rose cutting should be 6 to 8 inches (15-20.5 cm.) in length, measuring down the stem from the base of the bloom. I recommend keeping a jar or can of water handy so that the fresh cuttings may be placed directly into the water after making the cutting. Always use sharp, clean pruners to take the cuttings.
The planting site for growing roses from cuttings should be one where they will get good exposure from the morning sun yet be shielded from the hot afternoon sun. The soil in the planting site should be well-tilled, loose soil, with good drainage.
To start rose bushes from cuttings, once the rose cuttings have been taken and brought to the planting site, take out a single cutting and remove the lower leaves only. Make a small slit with a sharp knife on one or two sides of the lower portion of the cutting, not a deep cut but just enough to penetrate the outer layer of the cutting. Dip the lower portion of the cutting into a rooting hormone powder.
The next step when you grow roses from cuttings is to use a pencil or metal probe and push down into the planting site soil to make a hole that is deep enough to plant the cutting up to about 50 percent of its overall length. Place the cutting that has been dipped into the rooting hormone into this hole.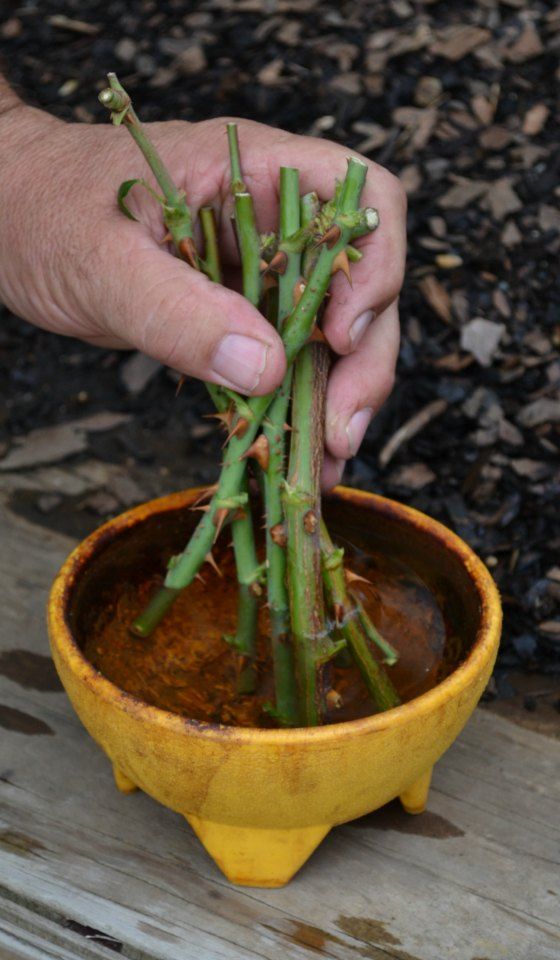 Lightly push the soil in around the cutting to finish the planting. Do the same thing for each cutting keeping them at least 8 inches (20.5 cm.) apart. Label each row of rose cuttings with the name of the mother rose bush it was taken from.
Lightly push the soil in around the cutting to finish the planting. Do the same thing for each cutting keeping them at least 8 inches (20.5 cm.) apart. Label each row of rose cuttings with the name of the mother rose bush it was taken from.
Place a jar over each cutting to form a sort of miniature greenhouse for each cutting. It is extremely important that the soil moisture for the cuttings does not dry out at this rooting time. The jar will help to hold humidity in but can be a problem if it is subjected to a lot of hot afternoon sun, as it will overheat the cutting and kill it, thus the need for shielding against the exposure to the hot afternoon sun when you root roses. Watering of the planting site every other day may be required to keep the soil moist but do not create a standing water or muddy soil situation.
Once the new roses have taken root well and have begun to grow, they may be moved to their permanent locations in your rose beds or gardens. The new rose bushes will be small but usually grow fairly quickly. The new rose bushes must be well protected against the hard winter freezes in their first year as well as extreme heat stress conditions.
The new rose bushes must be well protected against the hard winter freezes in their first year as well as extreme heat stress conditions.
Please keep in mind that many rose bushes are grafted rose bushes. This means that the bottom part is a hardier rootstock that will withstand cold and heat better than the top and more desired part of the rose bush. Starting a rose bush from cuttings places the new rose bush on its own roots, so it may not be as hardy in cold climates or in extreme heat conditions climates. Being on its own root system can cause the new rose bush to be far less hardy than its mother rose bush.
This article was last updated on
Read more about Roses
Did you find this helpful? Share it with your friends!
How to Propagate Roses From Stem Cuttings
By
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti is a life-long gardener and a veteran Master Gardener with nearly three decades of experience.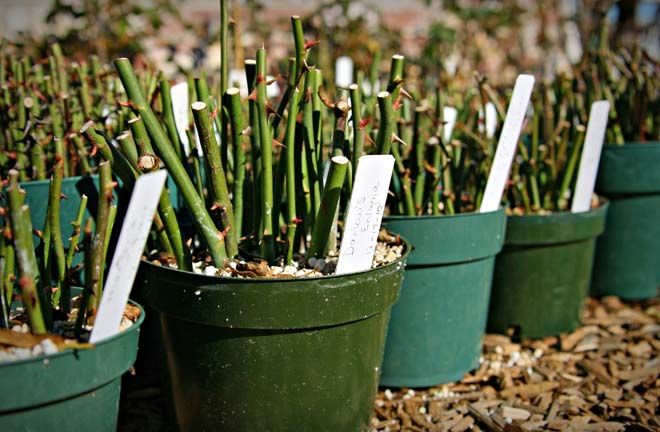 She's also an author of three gardening books, a plant photographer, public speaker, and a former Cornell Cooperative Extension Horticulture Educator. Marie's garden writing has been featured in newspapers and magazines nationwide and she has been interviewed for Martha Stewart Radio, National Public Radio, and numerous articles.
She's also an author of three gardening books, a plant photographer, public speaker, and a former Cornell Cooperative Extension Horticulture Educator. Marie's garden writing has been featured in newspapers and magazines nationwide and she has been interviewed for Martha Stewart Radio, National Public Radio, and numerous articles.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
Updated on 10/18/22
Reviewed by
Julie Thompson-Adolf
Reviewed by Julie Thompson-Adolf
Julie Thompson-Adolf is a master gardener and author. She has 13+ years of experience with year-round organic gardening; seed starting and saving; growing heirloom plants, perennials, and annuals; and sustainable and urban farming.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
In This Article
-
When to Propagate
-
Before Getting Started
-
FAQ
Project Overview
Propagating herbaceous plants is often done by rooting green stem cuttings, but the process can also be successful with woody-stemmed plants, including some roses.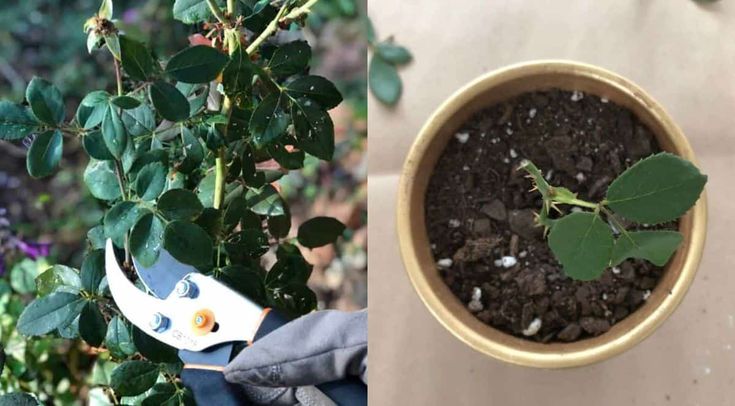 Rooting stem cuttings of roses and other woody plants works best with so-called "wild" or "native" pure species, rather than hybrid shrubs. That's because many hybrids are created through a grafting process in which branches from showy but delicate species are melded onto rootstock from a sturdier species.
Rooting stem cuttings of roses and other woody plants works best with so-called "wild" or "native" pure species, rather than hybrid shrubs. That's because many hybrids are created through a grafting process in which branches from showy but delicate species are melded onto rootstock from a sturdier species.
The result of grafting can be a spectacular plant with exceptional root hardiness. But if you propagate a new plant from a branch clipping, it will lack the parent plant's root hardiness. Thus, it's best to use stem clippings only to propagate non-grafted roses, which include many so-called shrub roses.
The stem clipping method is a bit tricky with woody plants, and you should expect that several attempts will end in failure. Take extra cuttings to ensure you have at least a few viable prospects. Still, if you take your cuttings from a healthy rose plant and follow the proper steps to root them, your odds of developing new plants will be high.
What Is a Shrub Rose?
The term "shrub rose" is defined by the American Rose Society (ARS) as “a class of hardy, easy-care plants that encompass bushy roses that do not fit in any other category of rose bush. ” Many people use the term to refer to any type of non-hybrid rose, but there are several types of hybrid roses that do fit into the ARS's definition of shrub roses, including Moyesi hybrids, hybrid musk roses, Kordesii roses, English roses, and Knock Out roses. These join the many native rose species to form the category of shrub roses. However, any of these hybrid roses described as an "own-root" rose rather than a grafted rose may lend itself to successful propagation from stem cuttings.
” Many people use the term to refer to any type of non-hybrid rose, but there are several types of hybrid roses that do fit into the ARS's definition of shrub roses, including Moyesi hybrids, hybrid musk roses, Kordesii roses, English roses, and Knock Out roses. These join the many native rose species to form the category of shrub roses. However, any of these hybrid roses described as an "own-root" rose rather than a grafted rose may lend itself to successful propagation from stem cuttings.
When to Propagate a Rose by Stem Cuttings
Rooting a stem cutting can be done almost any time, but cuttings taken from new growth that has recently flowered (rather than old, hardened wood) are more likely to root successfully. Spring or fall is the best time to take softwood stem cuttings. Select them in the early morning hours when the plant is well hydrated. Moreover, avoid taking cuttings when your plant is heavily blooming. At this time, the plant is putting most of its energy into flower production rather than root development, so cuttings won't readily root.
Before Getting Started
Sharp pruners are necessary when taking rose cuttings. Dull tools can crush the rose's woody stems instead of forming a clean slice, which can make the cutting susceptible to fungal rot. Furthermore, make sure to clean your pruners before and after each cutting to avoid transmitting any diseases.
Be patient when growing roses from cuttings. It can take several years for your new rose to produce flowers.
Click Play to Learn How to Grow Roses From Cuttings
Equipment / Tools
- Pruning shears
Materials
- Mature rose plant for cuttings
- Powdered rooting hormone
- Plant pot
- Sand and vermiculite or a rose potting mixture
- Plastic bag or plastic wrap
The Spruce / Michela Buttignol
-
Take Cuttings
Start by taking a 12-inch segment of a new stem that has recently bloomed, cutting it from the plant at a 45-degree angle.
 The stem should be about the width of a pencil. The best cuttings for rooting usually come from the sides of the bush, rather than the center.
The stem should be about the width of a pencil. The best cuttings for rooting usually come from the sides of the bush, rather than the center. Remove any flowers or flower buds along the cut stem. Flowers or buds on the cut branch will consume energy, and you want to encourage the stem to refocus its survival energy on sending out new roots. If you're taking multiple cuttings, place them in a container of water to keep them hydrated until you're ready to propagate them.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Remove Most Leaves
Remove all but the top two sets of leaves on the stem. Then, cut off the remaining portion of the stem just above this top set of leaves. Removing the excess leaves will help the cutting divert its energy to root production.
-
Prepare the Stem for Rooting
Using sharp pruning shears, make a fresh cut on the bottom of the stem just below a stem node (a bump where new growth typically forms).
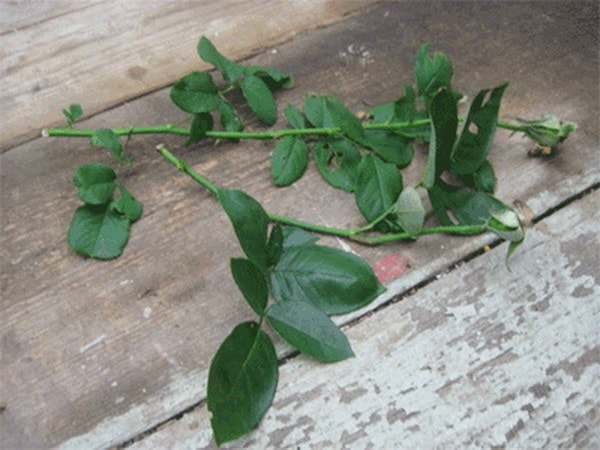 Then, slice into the bottom of the stem about a 1/4 inch up, splitting the stem into open quarters.
Then, slice into the bottom of the stem about a 1/4 inch up, splitting the stem into open quarters. Apply Rooting Hormone
Although not absolutely necessary, applying a rooting hormone can help spur your rose plant into developing new roots. Rooting hormones can be found in powder, liquid, and gel form—you'll have the best success with the powder version when working with roses. To apply, slightly moisten the split end of the rose cutting, and then dip it into the powdered rooting hormone. Shake off any excess.
-
Plant the Cutting
Fill a small pot with at least 6 inches of a potting mix formulated especially for roses. Poke a hole in the potting medium, and then insert the stem sliced-side down, taking care not to rub off the rooting hormone. Gently pack the soil around the stem, and water well.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Cover the Cutting
Loosely cover the cutting, pot and all, with a plastic bag or plastic wrap to help retain soil moisture.
 Be sure not to let the plastic touch any remaining leaves on the stem, which can cause them to remain wet and susceptible to fungal disease. Putting a tall stake into the pot can help hold the plastic away from the leaves. The bag also needs to be slightly vented, so condensation can escape—if you seal the bag too tightly, the stem can rot. Place the cutting under grow lights or near a bright window.
Be sure not to let the plastic touch any remaining leaves on the stem, which can cause them to remain wet and susceptible to fungal disease. Putting a tall stake into the pot can help hold the plastic away from the leaves. The bag also needs to be slightly vented, so condensation can escape—if you seal the bag too tightly, the stem can rot. Place the cutting under grow lights or near a bright window. -
Monitor the Cutting
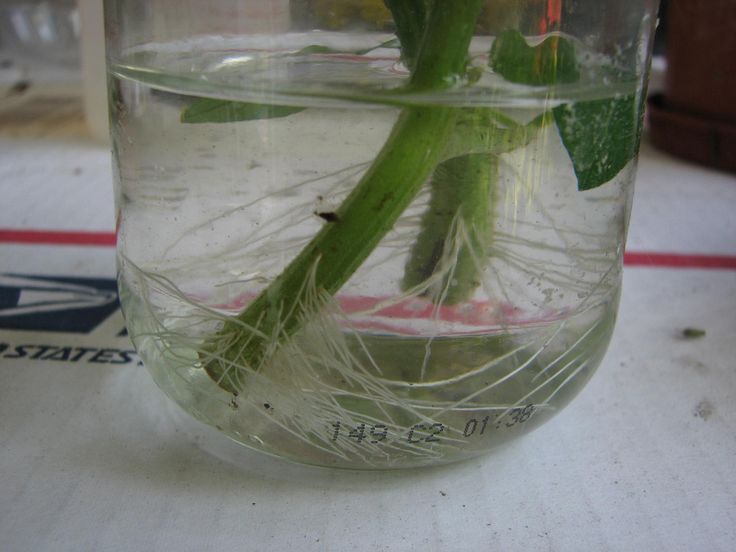
Keep the soil moist until roots begin to form, which usually takes about two weeks. Check for roots by gently tugging on the stem—if there's resistance, roots are probably present.
Your cutting can be transplanted into a pot or the ground as soon as the roots are firmly established or when new leaf sprouts begin to appear along the stem. Make sure to harden off the new rose—i.e., gradually expose it to outdoor conditions—before planting outside.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
How to Prepare for Rose Bloom Season
How to grow a rose from a cutting
Sooner or later, the presented bouquet of roses will wither and will have to be thrown away.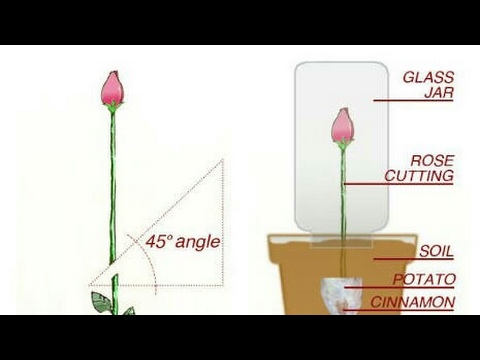 This fate befalls all freshly cut flowers. But, fortunately, you can save the memory of roses not only in photographs, you can breathe new life into a bouquet of roses, and then the flowers will delight you with their beauty and fragrance for a very long time. And for this, roses need to be rooted correctly and on time. If you want to order the Queen of Flowers in Vinnitsa, take a look at our catalog and you will definitely have plenty to choose from. Spectacular roses will not leave anyone indifferent. nine0003
This fate befalls all freshly cut flowers. But, fortunately, you can save the memory of roses not only in photographs, you can breathe new life into a bouquet of roses, and then the flowers will delight you with their beauty and fragrance for a very long time. And for this, roses need to be rooted correctly and on time. If you want to order the Queen of Flowers in Vinnitsa, take a look at our catalog and you will definitely have plenty to choose from. Spectacular roses will not leave anyone indifferent. nine0003
What are the best cuttings to root
Surprise your beloved!
Growing roses is very popular today. A rare summer resident will miss the opportunity to plant a beautiful bush on his site. Moreover, roses are universal holiday flowers. They are given for any reason and without it. As a rule, roses at home are propagated by cuttings (the part of the leaf that connects it to the stem). But in order for everything to work out, you need to know which cuttings are most likely to take root. So, the most important rule is that the fresher they are, the higher your chances of growing new plants, from which then original bouquets will turn out. Secondly, the variety of roses is important. All imported flowers root very poorly, because they undergo multi-stage processing with various chemicals that increase their shelf life. Therefore, you can not try to root a cut rose of Dutch origin. But with local varieties, things are much better. The period of the year when the flower was grown is also important. So, most likely, the summer stalk will take root, then the spring, autumn, and lastly the winter. nine0003
So, the most important rule is that the fresher they are, the higher your chances of growing new plants, from which then original bouquets will turn out. Secondly, the variety of roses is important. All imported flowers root very poorly, because they undergo multi-stage processing with various chemicals that increase their shelf life. Therefore, you can not try to root a cut rose of Dutch origin. But with local varieties, things are much better. The period of the year when the flower was grown is also important. So, most likely, the summer stalk will take root, then the spring, autumn, and lastly the winter. nine0003
How to properly prepare a cutting for planting
Bouquet of roses "Charm"
Planting roses is a delicate matter, and you need to approach it responsibly. So, first of all, take roses that already have formed shoots. Next, carefully cut off the leaves, buds and thorns from them. Now you can cut off the cutting itself (about 10-15 cm will be enough) and immerse it in water. Important: the cut on the handle should be as even as possible. So arm yourself with the sharpest knife. Cut the stem at an angle of 45 degrees, taking into account that the distance from the kidney should be about 1 cm. It is in this part of the stem that a large accumulation of nutrients is located. They then stimulate the growth of a new flower. It will be a huge plus if you treat the cuttings with a special hormone that stimulates the growth of shoots. You can find such a tool in any gardening store, where you will certainly be advised. nine0003
Important: the cut on the handle should be as even as possible. So arm yourself with the sharpest knife. Cut the stem at an angle of 45 degrees, taking into account that the distance from the kidney should be about 1 cm. It is in this part of the stem that a large accumulation of nutrients is located. They then stimulate the growth of a new flower. It will be a huge plus if you treat the cuttings with a special hormone that stimulates the growth of shoots. You can find such a tool in any gardening store, where you will certainly be advised. nine0003
How to grow cuttings in a pot with earth
Bouquet "For my Queen"
First, hold the cuttings in a container of water for about a day. Then plant the lower cut into the ground vertically (it is important that the upper buds are above the soil surface). Water the soil generously with water and place the pot on a windowsill that faces south. The optimum temperature regime is up to 20 degrees above zero. You can insert wooden chopsticks into the pot (unnecessary pencils or Japanese chopsticks will do). In the future, they will become a support for the process on the stem. Then stretch a film or bag over the sticks to create a kind of greenhouse for the cuttings. And that's all. Now we wait about a month and check if the flowers have rooted. It is very simple to do this: slightly pull the stem with your fingers, if there is some resistance, then everything is going according to plan and the stalk has taken root. nine0003
In the future, they will become a support for the process on the stem. Then stretch a film or bag over the sticks to create a kind of greenhouse for the cuttings. And that's all. Now we wait about a month and check if the flowers have rooted. It is very simple to do this: slightly pull the stem with your fingers, if there is some resistance, then everything is going according to plan and the stalk has taken root. nine0003
Method of growing cuttings in potatoes
Bouquet "Gift for a Beloved"
The method of growing roses in potatoes is the most popular and very effective. But it is advisable to use it only in the spring. The meaning of the method lies in the fact that a young potato tuber will create a moist environment for the stem and nourish it with useful microelements. Keep in mind that the length of the handle should be no more than 20 cm, and the potato itself should be medium in size and without “eyes”. We make a hole for the stem, plant the potatoes in the ground, pour water and cover with any unnecessary jar.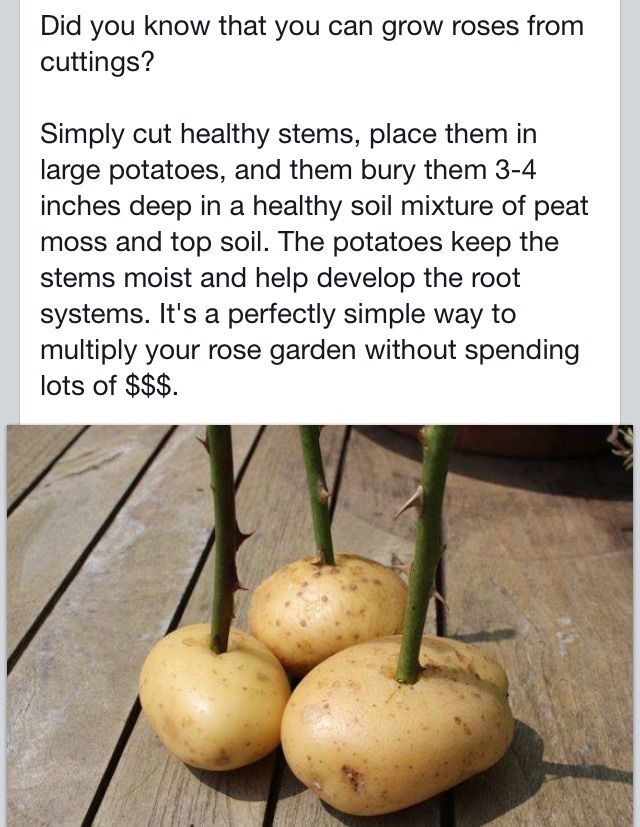 In this form, the stalk will not only receive everything necessary for rapid growth, but will also be protected from pests. Do not forget to periodically moisten the soil (but do not flood), and moisten the cutting itself with water a couple of times a day. Once every five days, it is a good idea to water the shoot with sweetened water (2 teaspoons of sugar per glass of water). nine0003
In this form, the stalk will not only receive everything necessary for rapid growth, but will also be protected from pests. Do not forget to periodically moisten the soil (but do not flood), and moisten the cutting itself with water a couple of times a day. Once every five days, it is a good idea to water the shoot with sweetened water (2 teaspoons of sugar per glass of water). nine0003
Method for growing cuttings in greenhouse conditions
15 red roses
In greenhouses, ripened lignified shoots that have survived the winter indoors are usually rooted. So, take a container and add to it a mixture of fertilizers that are usually used in normal planting in open ground. Plant a prepared cutting there and follow some simple recommendations. So, the temperature regime in the greenhouse should be in the range of 24-25 ° C, the humidity should be high (above 90%), and access to sunlight is limited. The leaves of the cuttings should be regularly moistened, which is why watering will have to be done 10 times a day. When growing roses on a large scale, it is better to get sprinklers for this purpose. After 3 weeks, you can reduce watering, remove shading and start airing the greenhouse (the so-called hardening of cuttings).
When growing roses on a large scale, it is better to get sprinklers for this purpose. After 3 weeks, you can reduce watering, remove shading and start airing the greenhouse (the so-called hardening of cuttings).
Method of growing cuttings in water
Bouquet "Our happiness!"
Growing rose cuttings in water is the easiest method. Carefully cut the stems and place them in a container of boiled water at a temperature of 20-25 ° C. Place the tank in a place with good shade. Change water daily. After three weeks, at the end of the cutting, you can see the beginnings of roots. nine0003
Method for growing rose cuttings in a bag
25 red roses with hearts
This method is also called “burrito”. Now you will understand why. All you need is unnecessary newspapers and a bag. Prepare the cuttings (preferably treated with growth stimulants), lay them on a newspaper and wrap. Now moisten the bundle liberally and place it in the bag. In this form, the cuttings should be stored in a dark place at a temperature of about 20 ° C. About once every ten days, unroll the bundle, inspect the stems, remove the rotten ones, change the newspaper for a new one, treat it with water and put it back in place. After 3 weeks, the root system should germinate on the cuttings. nine0003
About once every ten days, unroll the bundle, inspect the stems, remove the rotten ones, change the newspaper for a new one, treat it with water and put it back in place. After 3 weeks, the root system should germinate on the cuttings. nine0003
Useful tips on how to plant a rose
Basket "In love with you"
In conclusion, we would like to tell you some secrets of cuttings to grow roses at home as efficiently as possible.
- Do not plant more than 3 cuttings in one pot.
- Prefer opaque containers.
- Don't over water to prevent rot.
- When the water begins to evaporate, do not replace it completely, it is better to add a little new water. nine0070
- If there are no leaves on the stems, the root system can also form in the dark. But if at least one leaf has grown, light is needed.
- Roses are light and heat-loving varieties of flowers that do not tolerate drafts and white walls.
If you fail to grow a rose from cuttings the first time, don't give up. This does not mean at all that you are not given to be the owner of the rosary. Keep trying, experimenting and you will definitely succeed. nine0003
This does not mean at all that you are not given to be the owner of the rosary. Keep trying, experimenting and you will definitely succeed. nine0003
How to grow a rose from cuttings from a bouquet and get a luxuriously flowering bush
No one will argue that roses are very elegant and beautiful, so every grower tries to plant at least a few bushes of these beautiful plants on the plot. Often, the passion for this flower turns into a mania - I want to collect all the known varieties on the site, be the first to purchase varietal novelties, and having received a bouquet of exquisite roses as a gift, I feel like rooting the cuttings. By the way, if you do it right, you can get young plants for the garden from a bouquet of roses. Rose propagation is the topic of this article. nine0003
Growing roses from cuttings: planting agrotechnics
A beautiful bouquet, which fascinates with its unusual color or elegant shape, may well serve as planting material for obtaining new plants for the garden.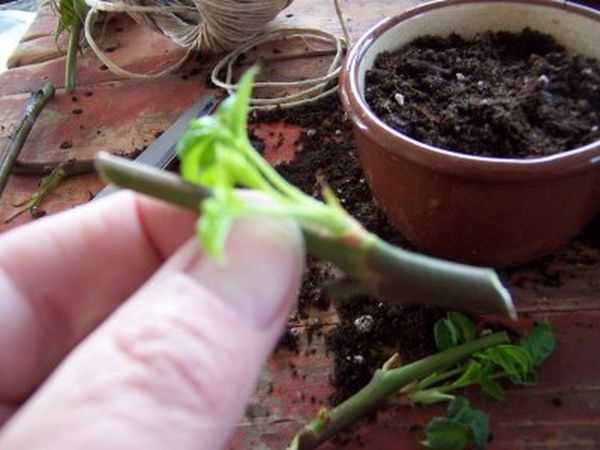 And even a beginner can root a rose cutting from a bouquet.
And even a beginner can root a rose cutting from a bouquet.
The algorithm for planting cuttings is quite simple, but the preparation of the material for planting is of great importance. You should not choose flowers with a completely lignified or weak stem, you must choose strong cuttings for planting that have living leaves and buds that have begun to form a young bark. nine0003
If the bouquet has stood in a vase for several days and the water has not been changed during this time, such cuttings are not suitable for rooting, because pathogenic microbes have already climbed high up the stem. It is best not to delay the procedure by cutting the petioles from a fresh bouquet. Cut off flower heads can be placed in a low vase with water, which will prolong the freshness of the petals for a while and allow you to admire the gift longer.
Huge, magical, imported roses are not suitable for cuttings, because before being sent to the distribution network, these flowers are treated with chemicals to preserve freshness.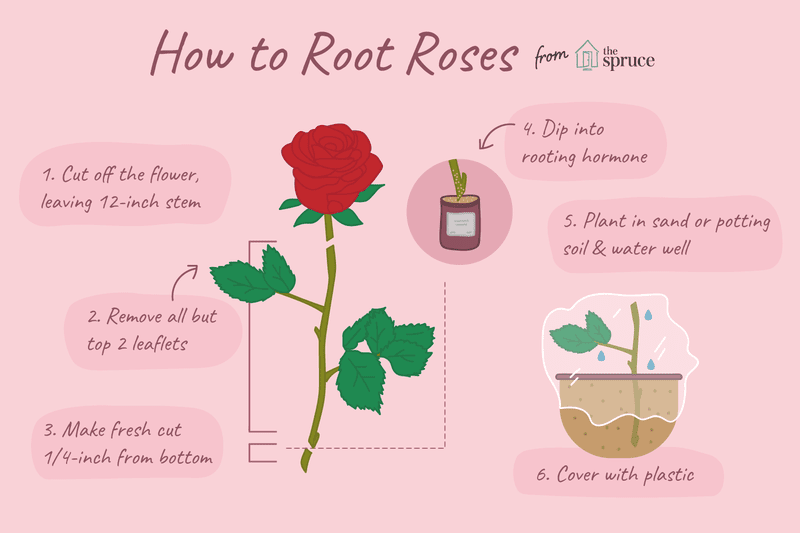 The best option is to cut local fresh roses from a bouquet that has not been in a vase. nine0003
The best option is to cut local fresh roses from a bouquet that has not been in a vase. nine0003
Fresh flowers should be soaked overnight in cold water before cutting. The lower cuttings are cut to 1.2-2 cm. This procedure will allow you to nourish the flowers with moisture, improve the turgor of the leaves.
Important! The best results are achieved when cutting roses with red and pink flowers. Worse cuttings are yellow and white roses.
Bouquet roses can be rooted from the first days of summer until September. It is best to perform the operation in natural conditions. In winter, it is also possible to root bouquet roses, but in this case there are many complications: cuttings of fresh flowers easily freeze, during the rooting period, the rooting material should be highlighted. nine0003
Roses from cuttings from a bouquet: preparation for planting
Roses selected for propagation should be properly prepared for planting:
- Remove buds and flowers.

- Cut cuttings from the middle part of the stem (length from 15 cm, but not more than 30 cm).
- Remove lower leaves completely, cut upper leaves in half.
- Remove spikes.
Important! Cuttings are left with 2-3 buds, the lower part is cut at 45 degrees under the lower bud (indent - 1 cm). The upper cut is straight, directly above the kidney. nine0106
It is useful to soak the lower sections in a solution of biostimulants, for which they use epin, honey, aloe or potato juice, after which the cuttings are planted in water, soil or grown in another way.
Ways of rooting pink cuttings
| Method | Description |
| In potato tuber | nine0139 |
| In water | The lower parts of the cuttings are immersed in a container with clean water, a complete water change is carried out once every 2 days. If putrefactive processes occur, the container is washed, scalded with boiling water and treated with potassium permanganate, after which the cuttings are placed there again. Rooting lasts 15-20 days, the cuttings are transplanted into the ground when a visible callus is formed. |
| In the ground | Choose a fertile garden bed in a quiet, windless place. |
Young overwintered plants are planted in a permanent place with the onset of stable heat. In the middle lane, this time falls on April-early May. In the first year, young roses can give one or two flowers, but to strengthen the bushes, it is better not to bloom, and to cut off the buds.
Planting young plants in the spring has its advantages - during the season the bushes will gain strength, get stronger and prepare themselves for wintering.
What to do if a bouquet of charming roses was given in cold weather, but you really want to get such a variety? It doesn't matter, you can prepare cuttings and save them until better times.
How to keep rose cuttings until spring? The answer is simple - you can use a simple method of storage in the ground.
- Dig a deep hole (up to 70 cm) in a dry spot in the garden.
- Transfer the cuttings with a dry cloth.
- Fill the hole with leaf litter, insulate with foam, boards, insulation films and fill with soil. nine0070
- In winter, you can additionally cover this place with snow.
Under room conditions, cuttings are stored at a temperature of +3+5C in a cellar or refrigerator, they are placed in peat or moss. Humidity must be maintained at about 70-75%.
If everything is done correctly, in a year new roses will thrive in your garden, giving their fragrant graceful flowers. The queen of flowers grown from a bouquet is a reality that will help you get exclusive plants of high decorativeness for mere pennies.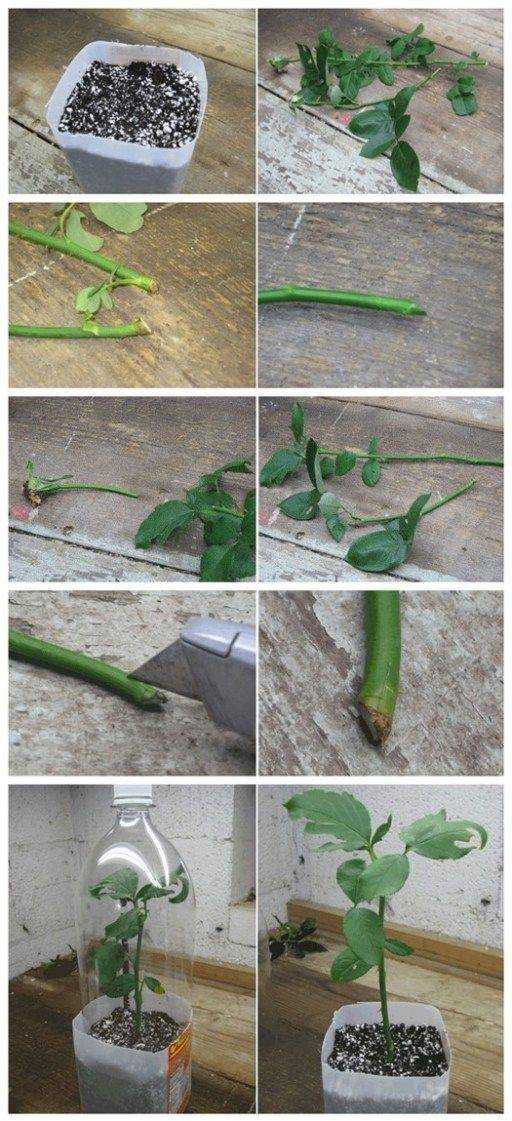

 A trench is prepared, which is covered with sand by 5 cm. The cuttings are placed in the sand and sprinkled with soil, covered with a jar on top or arrange a common greenhouse. Some amateurs leave young plants under a jar for the whole winter, carrying out additional warming, in this case, in the spring, the seedlings are carefully accustomed to fresh air. With this cultivation of young rose bushes from bouquet flowers, planting in the fall is possible, but you should not delay the procedure until frost. nine0003
A trench is prepared, which is covered with sand by 5 cm. The cuttings are placed in the sand and sprinkled with soil, covered with a jar on top or arrange a common greenhouse. Some amateurs leave young plants under a jar for the whole winter, carrying out additional warming, in this case, in the spring, the seedlings are carefully accustomed to fresh air. With this cultivation of young rose bushes from bouquet flowers, planting in the fall is possible, but you should not delay the procedure until frost. nine0003