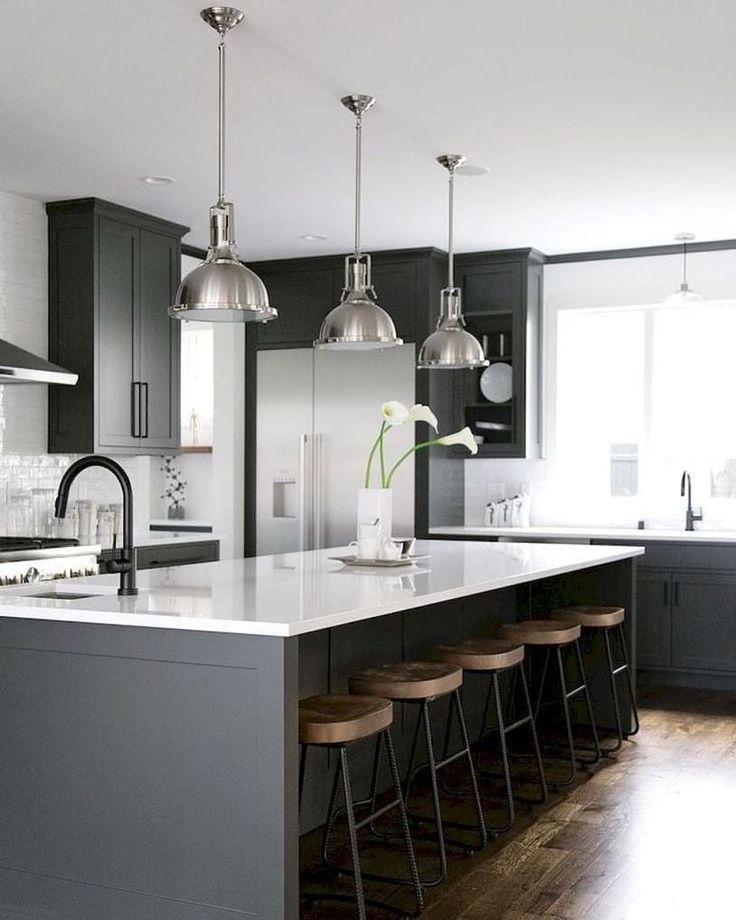
How to build vegetable beds
How to Build a Raised Vegetable Garden
Project details
Skill
1 out of 5 Easy The frame is simple to assemble, but you'll need an adult to run the power saws and fill the bed with soil.
Cost
About $225
Estimated Time
2 hours
Age Range: 6 and up
Here's a great project for the budding gardener in your family. This Old House TV landscape contractor Roger Cook recently showed a few young friends how to make a raised garden. It's a simple frame of rot-resistant lumber that holds soil in place and brings it to a height that's easy for everyone to reach without stepping onto precious plants—plus no more dirty knees (or at least fewer dirty knees).
Plant a vegetable patch in your new DIY raised garden bed. Kids will have tons of fun caring for their seedlings as they mature. And what better reward is there for a garden well tended than a crisp carrot straight from the earth (washed, of course) or a nice ripe tomato right from the vine. Read the following steps to learn how to build a raised vegetable garden.
Step 1
Overview
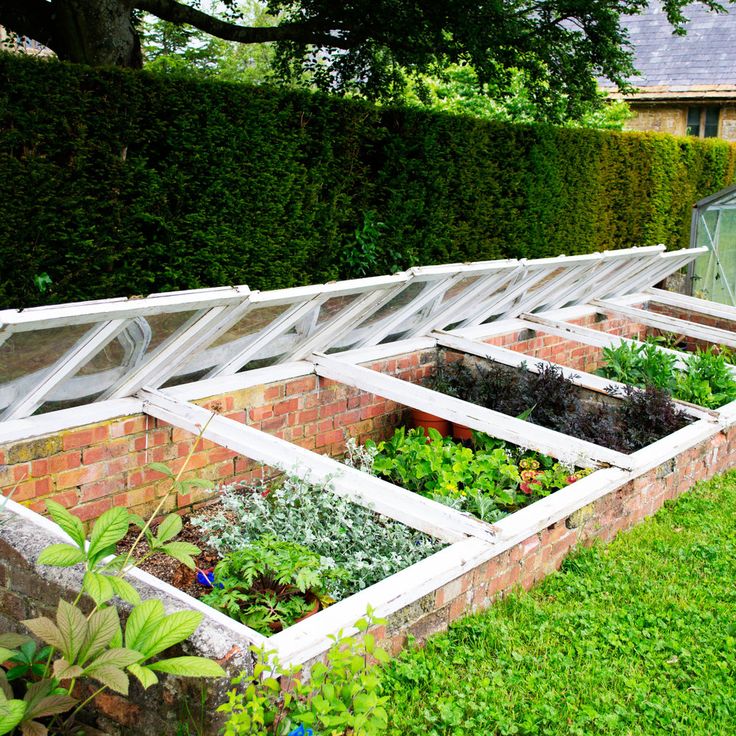
Illustration by Carl WiensRoger and the kids made this bed with rot-resistant cedar, a material that's safe around the edible plants it will contain. Cedar will also turn a nice silvery gray as it weathers.
The bed here is 10 feet long, but you can make yours as long as the lumber allows. However, it should be no more than 4 feet wide so that little arms can reach the plants in the middle. Roger cut stakes from 2x4s and angled one end to a point to hold the frame in place and keep the sides from bowing once it's filled with heavy soil.
Vegetable gardens need a lot of light, so Roger and his helpers placed the bed in an area that gets sun for most of the day. To improve drainage and prevent weeds from growing up into the garden, he removed the grass beneath the bed and tilled the earth before adding soil.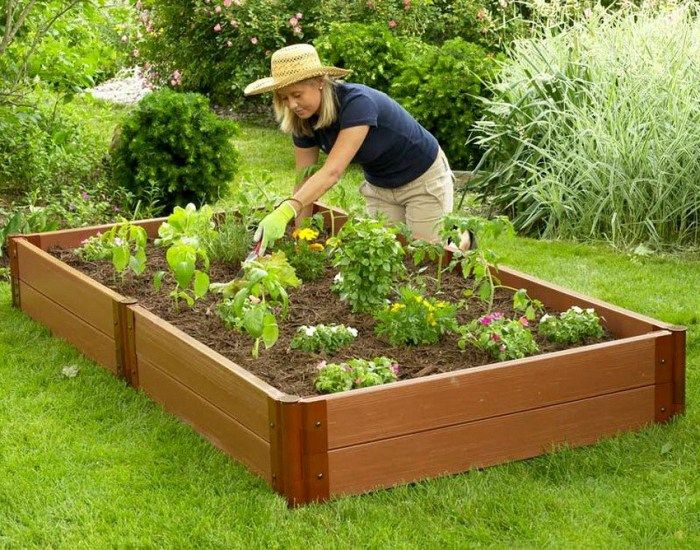
Step 2
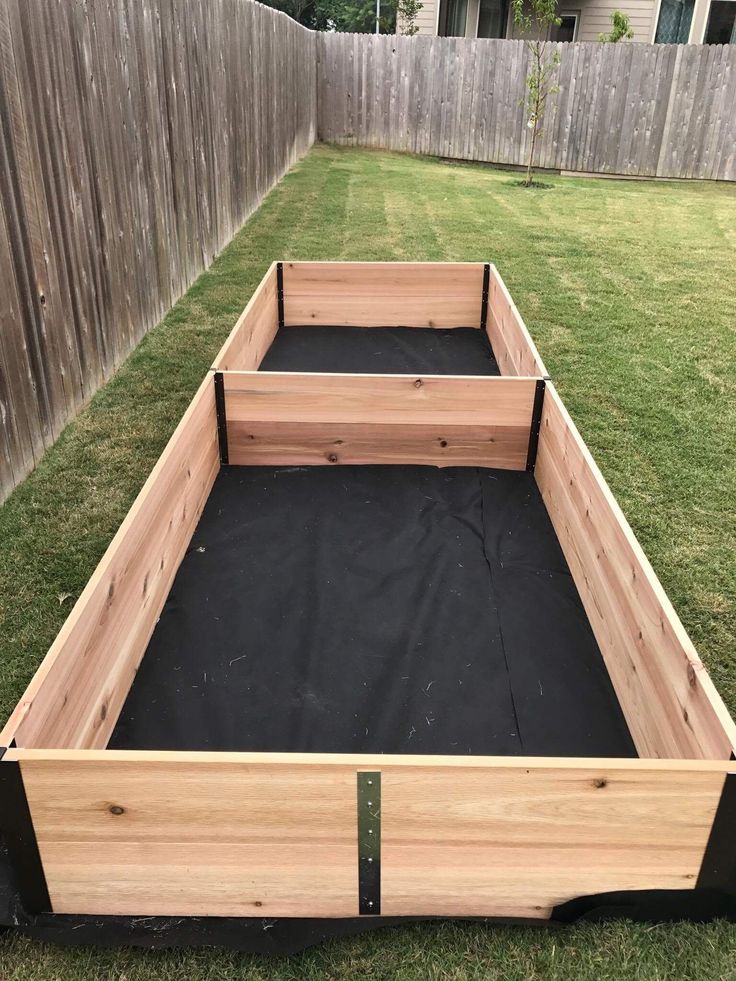
Cut and assemble the frame
Photo by Ask This Old House TVUsing a jigsaw or circular saw, cut an 8-foot length of 2x10 cedar in half.
Hold one of the 10-foot 2x10s on edge, and butt the end of a 4-foot 2x10 up to it so that the face of the longer board overlaps the end of the shorter board. Using the drill/driver, sink three 3-inch screws through the face of the long side and into the end of the short side.
Attach the other sides together, using three 3-inch screws on each corner and overlapping the long sides over the short sides.
Step 3
Square up the frame
Photo by Ask This Old House TVWith the four sides assembled, place a framing square in each corner, one at a time, and adjust the frame until the corner lines up square. After aligning the entire frame, check all four corners again with the framing square.
Roger Cook says: "The great thing about a raised garden is that you can put in the perfect soil for whatever you want to grow.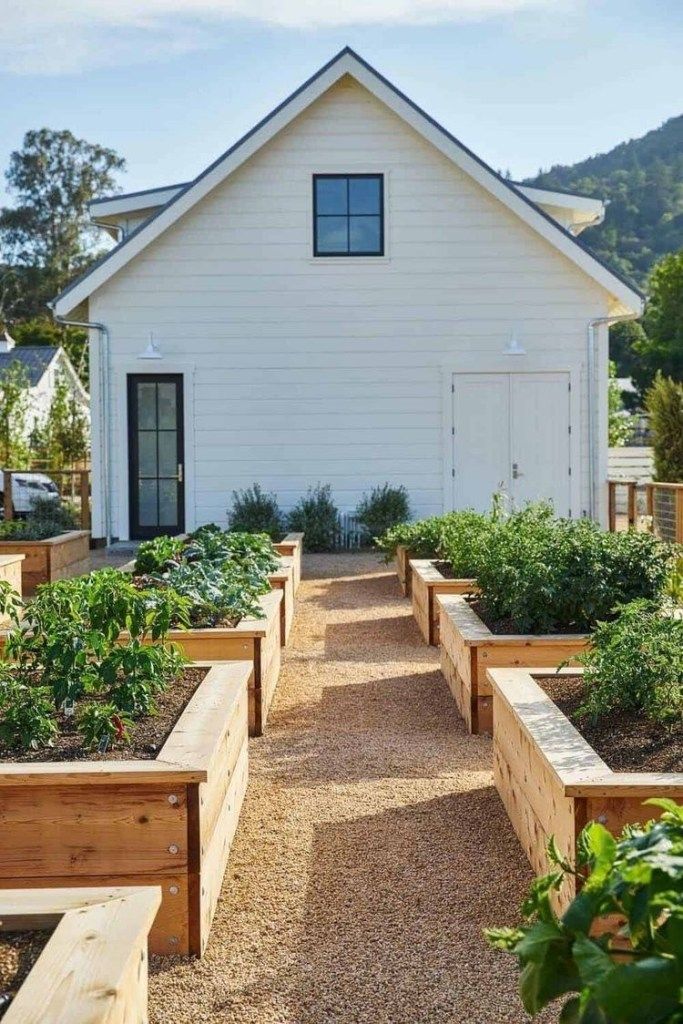 "
"
Step 4
Brace the corners
Photo by Ask This Old House TVLeaving the corners perfectly square, tack scrap lumber across each one with 3-inch screws to hold it in position.
Step 5
Mark the perimeter
Photo by Ask This Old House TVMove the raised garden bed frame to the sunny spot you've picked out for the bed. Using an edger or spade, mark the ground around the perimeter of the frame.
Step 6
Prepare the soil
Photo by Ask This Old House TVSet the raised garden bed frame aside. Using a sod cutter or grub hoe, skim away the grass layer. Increase drainage for your garden by turning the soil beneath the bed area with a pitchfork or rotary tiller.
Step 7
Level the frame
Photo by Ask This Old House TVSet the frame back in place over the tilled area. Using a 4-foot level, check the position of the frame.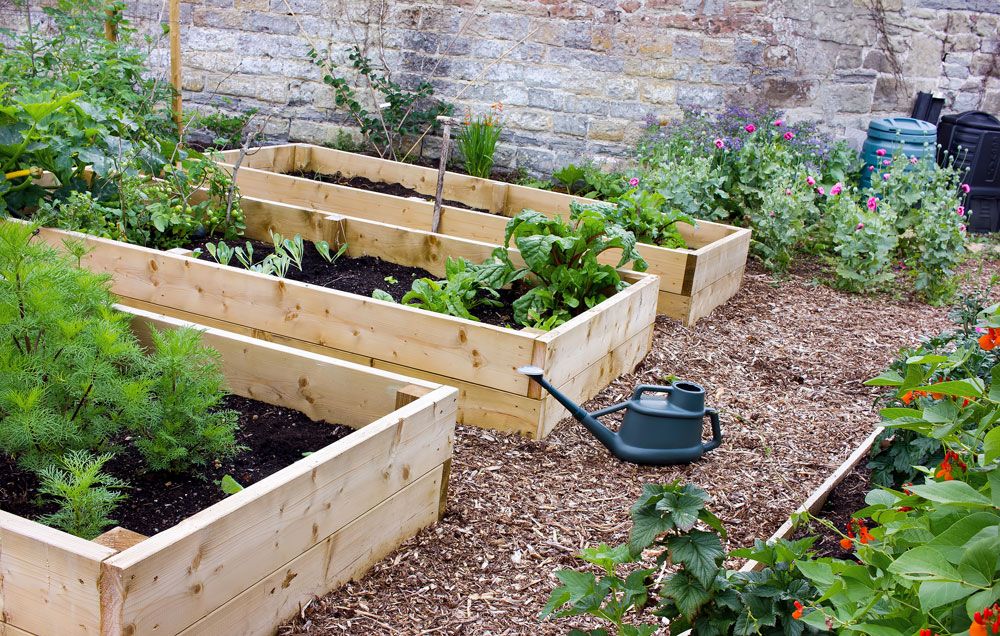 Dig out the soil beneath the frame until it sits level on all sides.
Dig out the soil beneath the frame until it sits level on all sides.
Step 8
Stake the frame
Photo by Ask This Old House TVCut ten 2-foot-long pieces of 2x4. Make two diagonal cuts on one end of each piece to create a point. Using a sledgehammer, drive these stakes at least 18 inches into the ground along the outside of the long sides of the frame at 2½-foot intervals. Using the drill/driver, secure each stake to the frame with three 3-inch screws.
Remove the temporary corner braces. Drive a stake inside each corner. On one short side of the bed, secure the stakes with screws driven through the frame on both sides of each corner. On the other short side, leave the screws off.
Step 9
Fill the bed
Photo by Ask This Old House TVRemove the unscrewed short side of the bed. Using a wheelbarrow, fill the bed with a mixture of soil and compost. Level out the soil and continue filling until it is 2 to 3 inches from the top of the frame.
Step 10
Reassemble the frame
Photo by Ask This Old House TVReplace the short side of the bed and, using a drill/driver, secure it to the long sides and to the corner stakes with 3-inch screws. Using a reciprocating saw or handsaw, cut the top of each stake flush with the top of the frame.
Step 11
Plant the vegetables
Photo by Ask This Old House TVPlant seeds or seedlings for your vegetables. Dig a small hole for each one, mix in the appropriate amount of starter fertilizer, set the seed or seedling into the hole, then cover it with soil.
Step 12
Water and mulch the bed
Photo by Ask This Old House TVOnce the bed is planted, water it thoroughly. Then cover the soil with about an inch of mulch made from grass clippings.
Roger Cook says: “Use grass clippings to mulch around the plants. This will help keep the soil moist and stop weeds from growing.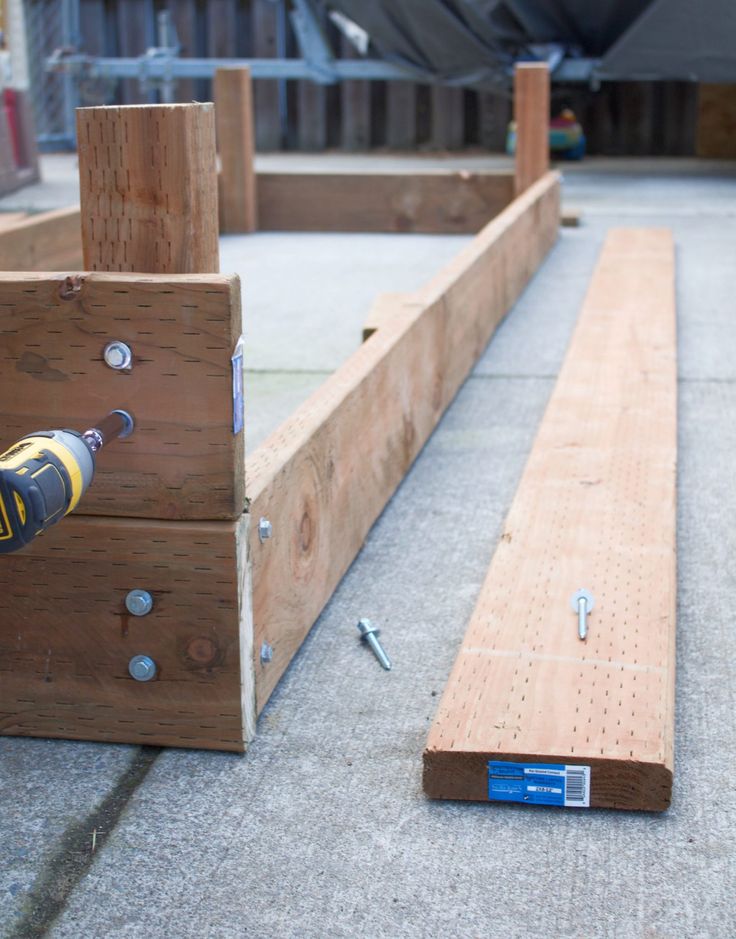 ”
”
Tools:
Tools & Materials
-
Circular saw
-
Drill/driver
-
Edger
-
Grub hoe
-
Pitchfork
-
level - 4-foot
-
Sledge hammer
-
Wheelbarrow
-
Reciprocating saw
How to Build a Raised Garden Bed
We’ve been independently researching and testing products for over 120 years. If you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. Learn more about our review process.
Including what type of wood, soil and plants will work best.
By David Oblas, Zoe Schaeffer and Monique Valeris
Let's face it: Everyone isn't lucky enough to have perfect soil to grow a vegetable garden. Whether your soil is clay-like or way too rocky, at some point, you might have been curious about how to build a raised garden bed as an alternative. The good news is that it's not difficult and can be constructed with a range of materials, including rot-resistant cedar.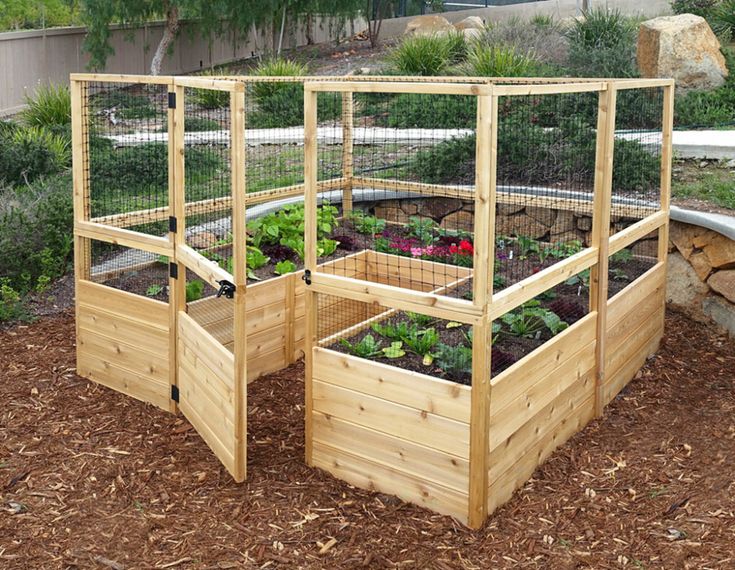
Why consider raised garden beds, which are also known as planter boxes or garden boxes? They offer a slew of benefits to help your plants thrive. Beyond keeping critters at bay, your soil will warm up much earlier in the spring season, meaning that your plants have the chance to grow earlier too. Plus, vegetables, fruits and ornamentals will send their roots deeper in search of water, so they would likely be healthier. And they're just so easy to build on your own! Even if you're new to gardening, you'll
The beauty of this particular raised bed build is that it is cheap and easy to build. The wood and rebar will cost no more than $50 if you're using untreated pine planks, and the entire build can be completed in less than an hour's time. The untreated pine might only last five to 10 years, but due to the nature of this build, each board is easily replaceable without taking apart the entire bed. For a 4-by-8-foot bed, you’ll need:
- Two 2-by-12 planks, each 8 feet long
- Two 2-by-12 planks, each 4 feet long
- 12 pieces of rebar, each 2 feet long
- A rubber mallet
- Newspaper or cardboard
- Soil to fill the finished frame
Step 1: Settle on the right position for your boards.
JOHN BORGOYNE
On a level section of ground, lay the boards down with their inner corners touching. Stand one long board on its side, and, using a rubber mallet, hammer two pieces of rebar 1 foot from each corner, a few inches deep into the ground.
Step 2: Prop up the short sides.
JOHN BORGOYNE
Use a piece of rebar at the center of each for temporary support. Next, prop up the second long side and adjust the alignment of your frame as necessary. Then hammer rebar a few inches deep 1 foot from each corner of the second long side.
Step 3: Reinforce the frame.
JOHN BORGOYNE
Hammer rebar a few inches deep a foot from each corner of the short sides and remove the temporary supports. Add two pieces of rebar 2 feet apart along each long side. These will reinforce the frame when it’s filled with soil. Then hammer in the rebar until 6 to 10 inches are exposed above ground.
Step 4: Fill your bed.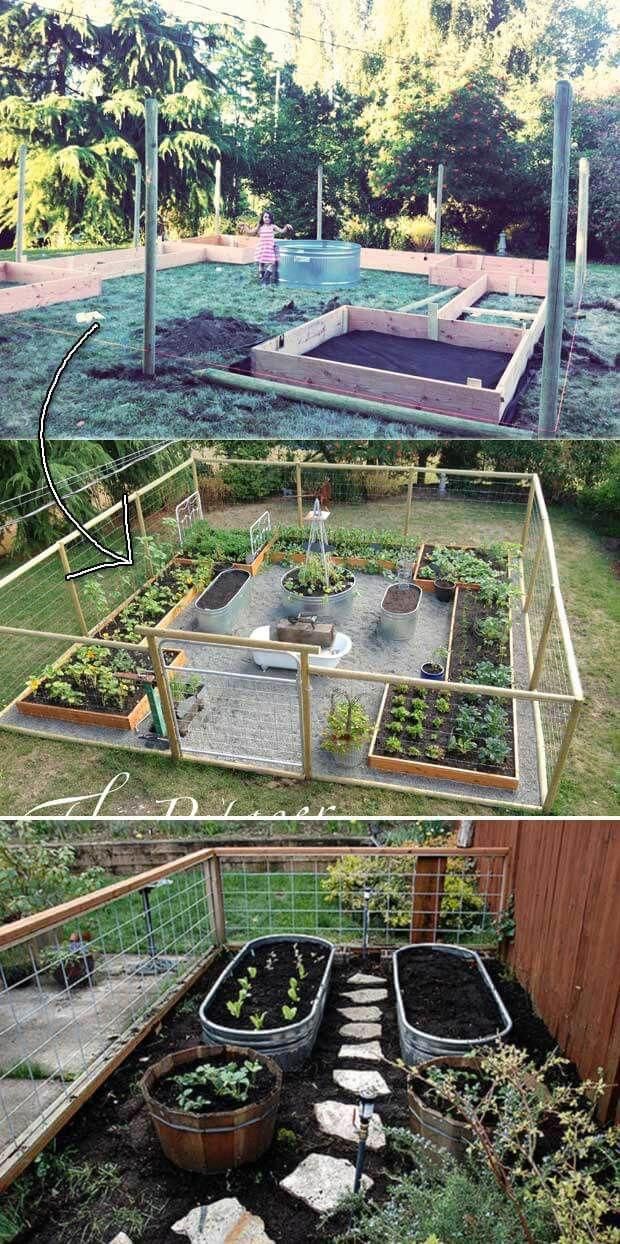
JOHN BORGOYNE
Line the bottom of your frame with newspaper or cardboard and wet it thoroughly. Finally, fill your bed with soil to within a few inches of the top.
Alternative Building Materials
JOHN BORGOYNE
The possibilities for building materials are endless:
Prefab Kits
If you love nothing more than DIY projects, a prefab kit, which can be purchased at home centers and garden suppliers, might be for you. You can find versions made of composite material to resist rot and insects. What's more, they tend to fade better than natural wood over time.
Wattle
Weave a frame with long, flexible sticks. The kids will have fun collecting them, and the results are usually Pinterest-worthy.
Logs
If you’ve recently cleared a tree, logs can be a cost-effective material. Choose pieces that are straight and at least 1 foot in diameter.
Concrete Blocks
Placing the blocks with open ends up provides extra growing room.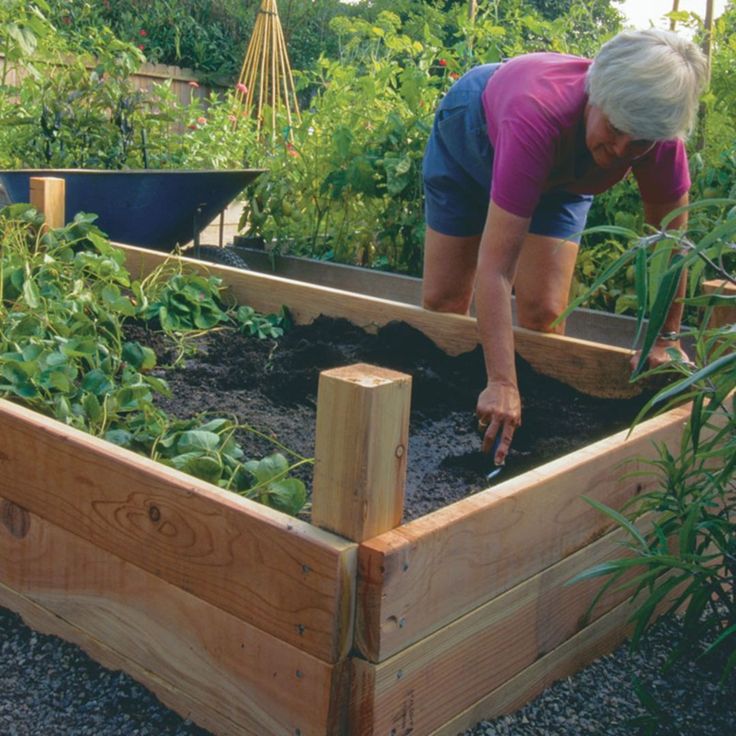 Tuck herbs or decorative flowers into the cavities.
Tuck herbs or decorative flowers into the cavities.
High and Mighty
A waist-high bed is accessible to those with physical limitations.
Other Tips to Consider
Space
Build your beds somewhere that receives at least five to six hours of daily sunlight — the more, the better! Orient them north to south to prevent plants from shading each other out. Beds should be at least a foot wide, though no more than 4 feet across to make weeding and harvesting manageable. Six to 8 feet long is typical and cost-effective. Ten to 14 inches is an ideal height to accommodate strong roots. Leave at least 2 or 3 feet between beds for walking and wheelbarrow access.
And if your garden bed sits low to the ground, be mindful of critters. To keep them out, consider installing a 3-foot wire fence to ensure rabbits, woodchucks and other small invaders stay away. If deer are present in your area, plastic netting (at least 8-feet high) are a good solution.
Wood
The brilliance of a plank-and-rebar design (see above) is that each individual wall is easily replaced. Try naturally rot-resistant varieties of wood, such as oak, cedar, and redwood.
Soil
You want the kind that’s dark, rich, and loaded with microorganisms. Fill your beds with a mix of 50 to 60% good-quality topsoil and 40 to 50% well-aged compost. Before each new growing season, test your soil for pH and nutrient content. You can buy a kit at most home-improvement stores. If your test shows a need for additional nutrients like nitrogen and potassium, raise levels by working in amendments such as bone meal and kelp. Dress beds with an additional ½ inch of compost later in the growing season to increase organic matter and boost soil health.
Plants
If you’re building your beds in high summer, it’s not too late to plant fall crops. Sow seeds like carrots and lettuce directly into the soil, or buy midseason transplants for crops like kale and broccoli. If you’d rather wait until next year to plant, cover the soil in your new raised beds with a mixture of grass clippings and shredded leaves in autumn — the material will compost before you’re ready to start in spring.
If you’d rather wait until next year to plant, cover the soil in your new raised beds with a mixture of grass clippings and shredded leaves in autumn — the material will compost before you’re ready to start in spring.
Water
Raised beds have fantastic drainage, which is great for plant health, but they dry out quickly. Give your plants a long drink in the early evening, but check them again on hot summer afternoons. If the soil is dry, it’s a real scorcher outside, or you live in a hot and arid climate, water again. A programmable drip-irrigation system (try a starter kit from dripworks.com) is inexpensive and convenient, delivering consistent moisture straight to plant roots. Invest in a timer component to save money and water.
Monique Valeris Senior Home Editor Monique Valeris is the senior home editor for Good Housekeeping, where she oversees the brand's home decorating coverage across print and digital.
how to make 10 different beds, pros and cons, for which vegetables
Which bed to make?
Why is it important to think carefully before choosing the shape of a vegetable garden?
There are quite a few factors to consider:
- climatic conditions of the region (average daily temperatures, rainfall and clear days),
- soil composition (for example, what prevails: loam or sand),
- proximity to water and much more.
 nine0010
nine0010
Each of these items affects the moisture content of the soil and its nutritional properties, the rate of air exchange and the reproduction of beneficial microflora.
Only by carefully analyzing each factor, you can decide whether to make a bed high or deepen it into the soil, wide or narrow, what fillers to use for it. And this, of course, will have a positive or negative effect on the yield, taste of vegetables and even the duration of their storage. nine0005
The bed must be warm
The construction of the bed for crops should be started with a natural heating device. Ideally, the bed should be flat and well warmed by the rays of the sun, that is, oriented to the south.
- An excessively high or wide bed should not be made. The smaller it is, the more convenient it is to take care of it, and the plants will receive more heat and moisture.

- The substrate should be moderately dense and loose enough - this is loved by, for example, cucumbers and others. nine0010
Strong fences
Not very thick wooden boards can be used as a fence. They will help to avoid soil erosion, which can occur due to heavy rain or excessive watering.
Planks should be 1/3 deep into the ground for safety.
Fertilization
At the end of the summer season, it is advisable to add 300 g of wood ash, a bucket of humus and 1 tbsp. l. nitroammophoski per 1 m² of beds.
In order not to damage the insulation layer, the soil in the bed can not be dug up. It is enough just to lay a humus slide, sprinkle ash and nitroammophoska on top and distribute it in an even layer. nine0005
What kind of beds are there?
Any garden bed is usually an isolated area of the vegetable garden. Thanks to this isolation, you can take care of each type of vegetable crop according to its requirements, that is, create an optimal moisture regime and provide nutrition at the optimal time.
The beds are created in order to have an individual approach to each crop, because vegetables with a variety of agrotechnical requirements are grown on the site, and if they are violated, then you can forget about a high yield. nine0005
That is why the garden is always divided into zones, which in turn are divided into beds.
There are actually a lot of types of beds, and almost every year new ones are created.
The types of beds
- differ in shape and size,
- in the principle of their formation,
- in the ways of caring for vegetable crops, and so on.
Standard
This is a familiar type of bed: it is about 10 m long and 1 m wide. The width of the paths between such beds is usually 50 cm.
TIP
The marking of the beds is usually done with stakes and a cord stretched between them.
How to make
This garden bed is easy to make. Usually, when digging the soil with a shovel, we discard the earth from future paths, after which we trample down the paths, and carefully level the beds themselves, breaking all the clods with a rake.
Usually, when digging the soil with a shovel, we discard the earth from future paths, after which we trample down the paths, and carefully level the beds themselves, breaking all the clods with a rake.
Pluses and minuses
The advantages of such a garden bed are obvious - this is the elementary nature of their manufacture and the absence of the need for additional investments. nine0005
The disadvantage is often the difficulty in caring for those plants that are located in the very center of the garden. There they often receive less light.
What to grow
Any crop is suitable for standard beds. Naturally, when growing pumpkin crops, cucumbers, tomatoes and similar plants, the distance between the beds must be increased, and when growing root crops, green crops and similar plants, it can be reduced.
Large
Large beds differ only in size - most often their length is at least 12 m². This bed is ideal for growing cucurbits, as they love space. nine0005
nine0005
How to make
The width of a large bed can vary greatly. A large bed is considered to be a bed that exceeds 15 m². The principle of its manufacture, as in a standard bed. The advantages and disadvantages are the same.
What to grow
Usually large beds are made specifically for growing crops such as potatoes, legumes, pumpkins, which do not need careful care.
Box beds
This is also a very common type of bed in vegetable gardens. Thanks to the presence of a bed-box on the site, you can create a place that is most suitable for growing a particular vegetable crop. And at the same time, such places will be separated from one another - isolated. nine0005
Pros and cons
The advantages of these beds are obvious:
- They are very easy to make, since the main excavation work is eliminated.
- These beds are easy to maintain, and if you put decorative walls, they may well become a decoration of the site.

- With capital production, they can last for several seasons (of course, subject to crop rotation).
Box beds are ideal for flooded areas or areas where groundwater is close to the soil surface. nine0005
However, these beds also have their drawbacks .
They need frequent watering, especially at the height of the summer season, and if there is a real heat, the root system of pumpkins can die from overheating.
To prevent this from happening, the walls of the bed must be made of heat-conducting materials or provide for thermal insulation of the walls of the box.
Cons - additional costs of effort, time and money.
- In dry regions, these beds require twice as much watering as standard beds. nine0010
- In addition, in the beds-boxes often arrange nests of the bear, and it will be necessary to provide protection from it.
- And where there are a lot of bears, it is better not to use a layer of humus at all.

IMPORTANT
Box beds allow you to give the garden an interesting, new look, make it unusual.
How to make
To make a box-bed, a fence of 50 cm wide boards is placed on a pre-prepared and already marked area. They are treated with an antiseptic and dug into the ground 25-30 cm. nine0005
The first layer is filled with humus (10–15 cm) into the box, with ordinary garden soil on top. In regions with excessive moisture, drainage can be done at the base - pour a couple of centimeters of broken brick, expanded clay or pebbles, or add sand to the soil.
To prevent the bed from falling apart, it must be reinforced with pegs. Metal rods are more durable, but wooden stakes can also be used. They are driven into the sides of the beds.
What to grow
All vegetable crops without exception can be grown in box-beds, by adjusting the height of the beds, depending on the degree of development of the root system. nine0157 ______________________________________________
WARM BED-BOXES WITH YOUR HANDS: STEP-BY-STEP WITH A PHOTO
______________________________________________
Beds-boxes with high sides
Beds-boxes with high sides are usually made for growing any melons, as well as cucumbers and potatoes. Usually their service life is only one season, because these crops take a large amount of nutrients out of the soil, and the soil will need to be replaced. In addition, the beds during the winter, as a rule, settle heavily. nine0005
Usually their service life is only one season, because these crops take a large amount of nutrients out of the soil, and the soil will need to be replaced. In addition, the beds during the winter, as a rule, settle heavily. nine0005
Pros and cons
Advantages and disadvantages are identical to the advantages and disadvantages of box-beds, but they have an advantage - they are formed for several seasons.
The disadvantage is that these beds often require the installation of additional elements in the form of nets or supports in order for the weaving plants to develop as well as possible.
But to the positive qualities, one can add the fact that they can be easily turned into greenhouses: it is enough to arrange arcs along the length of the beds and cover them with a film or agrofabric. nine0005
Deep trench beds
Trench beds (2 shovel deep) are most often planted in dry areas where plants suffer from desiccation under normal growing conditions. Their structure resembles the structure of high beds, but instead of boxes sewn from boards, plastic or slate, trenches are being dug.
How to make
Deep beds are built on the same principle as high beds. Across the entire width of the intended area allotted for the bed, it is necessary to dig a channel, which should be filled with organic matter. This layer is covered with fertile soil. nine0005
Don't make a bed too wide, but a narrow one won't do much either. The maximum height is 25 cm.
A deep bed is good because it does not freeze in the cold season, and therefore pumpkin crops can be planted on it quite early.
The optimal width of the beds is 1 m, the distance between the beds is 60 cm. The length can be any and depend on your needs. As for the height of the beds, it will be equal to the level of the soil.
A non-woven fabric is laid at the base of the bed, then drainage is a couple of centimeters in a layer, then a layer of 10–15 cm of humus. The bed is covered with fertile soil to the top. The depth of the bed can vary from 0.5 m to 1 m, depending on the type of soil. nine0005
nine0005
Pros and cons
The advantages of beds are durability and high productivity, subject to crop rotation. Especially well deep beds have proven themselves in areas with sandy soils and a lack of moisture.
This type of bed has clear advantages:
- There is no need to build additional fences.
- If you cover the beds with a layer of mulch, they will perfectly retain moisture.
The disadvantage is the additional cost of manual labor in the manufacture. There are also disadvantages:
- Labor-intensive earthworks
- Difficult to maintain.
- Do not use clay soils as they have poor drainage properties. Moisture accumulates in the lower layers, and the pumpkin root system may die.
What to grow
Most vegetable crops are planted in deep beds, but they are especially effective when growing green crops and in areas where there is a lack of moisture in the summer or on sandy soils and sandy loam. nine0005
nine0005
Narrow beds
Narrow beds only 1 m wide, row spacing 0.5 m. Beds can be any length.
TIP
Narrow beds require a mandatory addition of compost or replacement of old soil with new at the end of the season.
What to grow
A variety of vegetable crops can be grown on narrow beds, but it is appropriate to plant in a non-traditional way, but place the plants in a checkerboard pattern. Thanks to this planting, all plants will have enough sunlight. nine0005
Pros and cons
Advantages of narrow beds - ease of manufacture, optimal conditions for the growth of certain vegetable crops.
Disadvantages - additional time required to mark the beds. Lost area that could be occupied with benefit.
Beds according to Mittlider
Mittlider advised making beds no more than 0.5 m wide, placing sides about 10 cm high, but the distance between the beds should be at least 1 m. The length should depend on the size of your plot and on how much volume products you need. nine0005
nine0005
Pros and cons
Disadvantages - these beds are ineffective in lowlands. Maximum attention should be paid to leveling the beds, making them perfectly horizontal, otherwise there may be a strong washout of the soil.
Advantages - relative ease of manufacture, durability, reliability.
What to grow
The most suitable crops for this type of beds are cauliflower and cabbage (best planted in a checkerboard pattern) and root crops (best planted in two rows). nine0005
Mound beds
Mound beds are considered the most common (but also relatively labor-intensive). Average length - up to 1 m.
How to
Start building this bed by laying out layers of organic materials: peat, sawdust, branches, healthy fallen leaves and brushwood.
Ordinary earth removed from the garden bed is suitable as a top layer.
After all the elements have been laid, a small groove (2-3 cm) must be made in the middle of the bed. It greatly increases irrigation efficiency. nine0005
nine0005
What to grow
Cucurbits will thrive in this garden.
Round beds
If you have built a round bed, try to stick to the tiered arrangement of the plants.
Actively growing varieties should be planted in the center, while slow growing varieties should be planted at the edges.
High beds
For high beds, it is better to choose places well lit by the sun, protected from gusts of wind. The length of such a bed can be any, but the optimal length is 1.5 m.
How to make
In order to make such a bed, you need to collect all the garbage in the garden, which can decompose over time. Suitable paper, cardboard, brushwood, small wooden chocks, foliage, grass mulch.
First, a thin mesh is laid (it is better to use plastic, because this material is more durable and easier to work than metal). The bottom layer is large debris, the top layer is small and rapidly decomposing.
After laying all the layers, water the bed well, and then lay a layer of nutrient soil 25–30 cm thick.
Take note
Raised beds need to be watered more frequently as the layers absorb a lot of moisture.
Mixed beds
Mixed beds are slightly more difficult to maintain than conventional beds. They are suitable for dry areas where there is often a lack of moisture, which is very dangerous for pumpkins.
How to make
To begin with, they dig a trench about the depth of a spade bayonet, after which they form a low curb from boards, slate and curb tape. Thanks to this, it is possible to raise the bed above the soil level by about 25 cm.
In a mixed bed, consider thermal insulation of the soil. To do this, you can use plastic bottles: lay them on the bottom or around the perimeter of the garden. This will protect the soil from hypothermia in winter and overheating in summer.
The main thing when laying a layer of thermal insulation is not to forget to make drainage channels.
photos and recommendations for creating a vegetable garden
SHARE
IN SOCIAL NETWORKS
This article discusses beds for the lazy: photos of the easiest structures to manufacture for those who want to get a neat garden with a minimum of effort, the most common materials and technologies for creating structures based on them.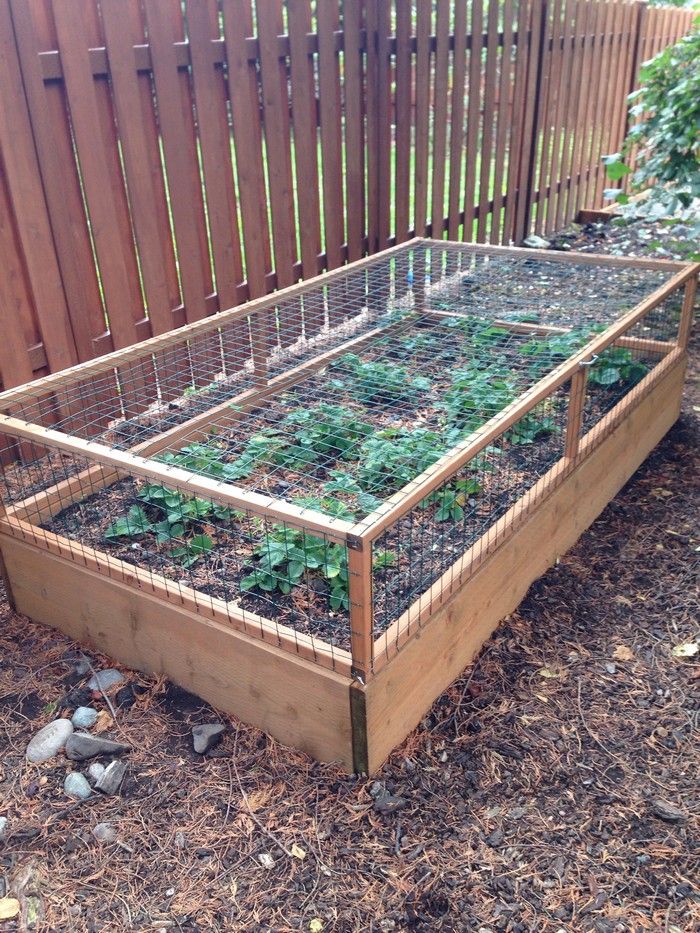 The reader will learn how to combine vegetable crops in one garden and prepare the soil for planting cucumbers. The article contains practical recommendations for beginner gardeners. nine0005
The reader will learn how to combine vegetable crops in one garden and prepare the soil for planting cucumbers. The article contains practical recommendations for beginner gardeners. nine0005
Proper arrangement of beds in the garden will help save time and effort when planting and harvesting
Contents
- 1 Beds for the lazy: photos and basic information for beginner gardeners
- 1.1 Varieties of beds in the garden: how to properly prepare for construction
- 1.2 Making beds with your own hands from improvised materials: photos of high structures
- 1.3 How to arrange the beds in the garden: photos and recommendations for choosing a place
- 1.4 How to make the best beds in the garden: choosing the optimal design
- 2 How to make your own beds from boards: useful tips
- 2.1 Making practical beds from boards: how to make the right choice of material for your own
- 2.2 Making beds from boards hands: photo, dimensions of structures
- 3 Creation of mixed plantings of vegetables in the garden: photo examples and optimal schemes
- 3.
1 Proper neighborhood of vegetables in the beds: compatibility table
- 3.2 Examples of mixed planting of vegetables in the garden: popular schemes
- 3.3 Table of crop rotation of vegetables in the beds by crop groups
- 3.
- 4.2 How to make cucumber beds in the garden with laying
- 4.3 Warm surface cucumber beds in the open field
- 4.4 Raised beds for cucumbers in the open field
- 4.5 How to make beds in the garden: a video review of technology
Beds for the lazy: photos and basic information for beginner gardeners
Designing the right beds in the garden will solve many problems and open up new opportunities for the owner of a summer cottage:
- protection against erosion of the soil in the garden when a large amount of precipitation falls or watering plants. The bed borders will keep the nutrient soil in place, preventing it from washing out onto the paths. In addition, the passages between the structures themselves will remain clean, no dirty puddles and streaks; nine0010
Neat garden beds will make the garden more attractive and organized
- the possibility of forming the basis for the creation of a temporary greenhouse for the spring.
 By installing high sides as fences, inside the structure you can organize a multi-layered garden bed, which can be used as a greenhouse. To do this, it is enough to install special arcs and stretch the film. The result is a neat greenhouse house;
By installing high sides as fences, inside the structure you can organize a multi-layered garden bed, which can be used as a greenhouse. To do this, it is enough to install special arcs and stretch the film. The result is a neat greenhouse house; - improving the appearance of the vegetable garden by orderly and even plantings with beautiful framing; nine0010
- creating boundaries to prevent the spread of weeds.
By planting the plants correctly, you can avoid the growth of weeds on the beds and paths
Making your own beds from boards and other materials allows you to clearly limit the planting area, thanks to which weeds and harmful plants do not have the opportunity to spread widely. If the fence of the garden is dug in to a great depth, the level of protection increases and perennial weeds that are unable to overcome this barrier can no longer penetrate into the garden. nine0005
Please note! With the help of beds with well-buried fences, the spread of plants such as reeds and couch grass is effectively blocked.
Their root system is capable of covering large distances underground if left unchecked.
Tall warm beds made of quality materials can serve the owners for many years
Varieties of beds in the garden: how to properly prepare for construction
Several types of beds are used for gardening:
- standard;
- high;
- narrow.
Wide paths and the optimal size of the beds will allow you not to step on the ground when working with plants
Standard beds are on the same level with the garden, they do not go deep into the ground and do not protrude above it. At the same time, the owner of the territory can independently choose the width, length and nature of the location of the beds in the summer cottage, photos of interesting design options can be seen in this article. As a rule, plantings are placed at a distance of no more than 0.5 m from each other, so that it is easier to care for the plants. To mark the territory, it is recommended to use a rope stretched between the pegs. The use of a special garden marker is allowed. nine0005
The use of a special garden marker is allowed. nine0005
Paths can be planted with lawn grass, but care must be taken to ensure that the beds are well defined.
Before making a bed with a narrow design, make sure that the building area has a level surface and sufficient lighting. This type of product is characterized by increased row spacing. This parameter can sometimes reach 1 m. At the same time, the beds themselves do not exceed 0.45 m in width. The designs of narrow beds slightly rise above the soil level. The difference between the height of the garden and the surface of the plot is 0.2 m.
Many gardeners find it convenient to work with narrow beds
In the area where the beds are planned, the soil should be dug up and fertilized. At the same time, you should not spend nutritional supplements on aisles, you only need to process the planting site. Dolomite flour or a special complex consisting of minerals can be used as fertilizers.
Interesting fact! Narrow structures are also called Mittlider beds (after the man who invented their technology).
According to the agronomist, the garden will bring a good harvest if the plants are regularly watered and nutrient mixtures of industrial production are applied. And he, on the contrary, did not recommend using compost and manure. nine0110
Narrow beds according to the Mittlider method, due to the large amount of light received, give a good harvest
Making beds with your own hands from improvised materials: photos of high structures then proceeds to further planning and construction, since the technology of their creation depends on the physical and operational indicators of the material. Regardless of his choice, the mechanism for manufacturing structures is almost always the same. Construction begins with the installation of the frame. The standard size of such structures is 0.9m (width) and 1.2 m (length). After that, the product is filled with fertile soil.
Beds made from quality wood are more environmentally friendly than concrete or asbestos-cement ones
Designs of self-made beds from improvised materials can be created on the basis of:
- Stone or brick - products from these materials look aesthetically pleasing, while they characterized by a long service life.
 The disadvantages of stone or brick frames include their cost. In addition, the assembly procedure requires a lot of time, the dismantling of a stationary structure can be difficult. nine0010
The disadvantages of stone or brick frames include their cost. In addition, the assembly procedure requires a lot of time, the dismantling of a stationary structure can be difficult. nine0010 - Vines are the most accessible material found in nature. Due to the flexibility, the beds can be given any shape, however, the service life of such a design is limited to a short period of time. In addition, you will need to carefully study the weaving technique and acquire a special tool for cutting branches.
- Metal - the material allows you to create lightweight portable structures that can be painted in any color. However, the cost of such a frame is high, and the operation may require a welding machine and skills in handling it. Products also need anti-corrosion protection. nine0010
- Slate is a relatively inexpensive material that provides easy assembly of the structure, but requires extreme care due to its fragility.
Gabion can also be used to organize a warm bed
How to arrange the beds in the garden: photos and recommendations for choosing a place
Of no small importance in obtaining a rich harvest is the correct choice of a place for the construction of beds and the scheme of their placement. It is desirable that the area chosen for organizing the garden is flat and receives maximum sun exposure throughout the day. nine0005
It is desirable that the area chosen for organizing the garden is flat and receives maximum sun exposure throughout the day. nine0005
Please note! Most plants need a lot of sunlight. In the afternoon, a slight blackout will be useful.
To make the right choice of a place for organizing a garden, it is recommended to spend some time on the site and observe the distribution of light throughout the day. In addition, special attention should be paid to the placement of trees, both on your site and on the territory of your neighbors. This is necessary in order to determine what size the shadow is and where it falls. It should be borne in mind that a site flooded with sun in winter may be shaded in summer, since dense foliage appears on bushes and trees in the warm season. nine0005
Related article:
Beautiful garden beds with your own hands: photo examples and unusual solutions
Photos of interesting designs of beds, recommendations for their creation.
Tips for designing unusual landscape design on the site.
The best place is the area where the sun is present throughout the day. It is allowed to install beds where the shadow is present in the morning or in the afternoon. If the proposed construction zone is dark throughout the day, you should not use this place for arranging a garden. nine0005
How to make the best beds in the garden: choosing the optimal design
Choosing the design of the beds is carried out at an early stage of planning, when the place for the garden has already been selected.
Each type of bed has its own advantages:
- Raised or high beds are the most efficient designs and best suited for growing vegetable crops. Building materials for their creation are not expensive, while the soil does not need to be dug up. The width and height of the structures determine how much effort and time it will take to build them. Most often, summer residents prefer wooden beds made of boards.
 On the network you can find photos of bulk beds with your own hands, such structures do not have a fence. They are also categorized as elevated structures; nine0010
On the network you can find photos of bulk beds with your own hands, such structures do not have a fence. They are also categorized as elevated structures; nine0010
Container beds are very convenient because they can be moved to another convenient location if desired. For organizing such beds, pots of small, large and medium sizes are suitable. Garlic, peppers, lettuce and greens feel especially good in containers. Mobility is another advantage of container beds, which, if desired, can be rearranged to any place; nine0010
Annual plants can be grown in large plastic bottles and placed in a convenient location
Helpful Hint! If crops are planned to be planted outdoors, it is recommended to determine the quality of the soil, fertilize it and check the compatibility of vegetables in the garden against the table.
nine0110
How to make your own plank beds: useful tips
Raised beds are most often made of wood. This material in comparison with others is considered the most practical and environmentally friendly. Similar designs look very aesthetically pleasing in the photo. Do-it-yourself plank beds have other advantages:
- simple maintenance system for easy weeding, harvesting and watering plants;
- the possibility of growing vegetable crops even where the soil is completely unsuitable for these purposes. On the basis of the boards, a frame is made, which is subsequently filled with fertile soil bought in a store, so there is no connection to the quality of the earth and its composition. Thanks to this, plants can be grown even in areas with a rocky surface; nine0010
Sturdy wooden beds can be made on your own or purchased from a garden center
- box constructions keep the soil inside the bed. In addition, the presence of sides simplifies the process of mounting arcs to form a greenhouse.
 It is much easier to fix these elements on the fence than to dig them into the soil;
It is much easier to fix these elements on the fence than to dig them into the soil; - without even knowing how to properly make beds in the garden, any summer resident will cope with the manufacture of wooden structures-boxes. The boards are easy to process, and the construction and assembly of the frame does not require an expensive tool; nine0010
- there is no chance that plants planted near the sides will get burned in the summer heat. Wood, unlike metal, is not prone to overheating.
In order to avoid washing out of soil from high beds, it is necessary to pay special attention to the joints when assembling the box
Please note! The environmental friendliness of the material allows you not to worry that harmful substances will get into the soil. Wood is much safer than asbestos-cement sheets (slate). The exception is boards treated with chemicals designed to double the life of the material. nine0110
Making practical beds from boards: how to make the right choice of material
Summer residents most often create wooden structures based on blanks that they find on the farm.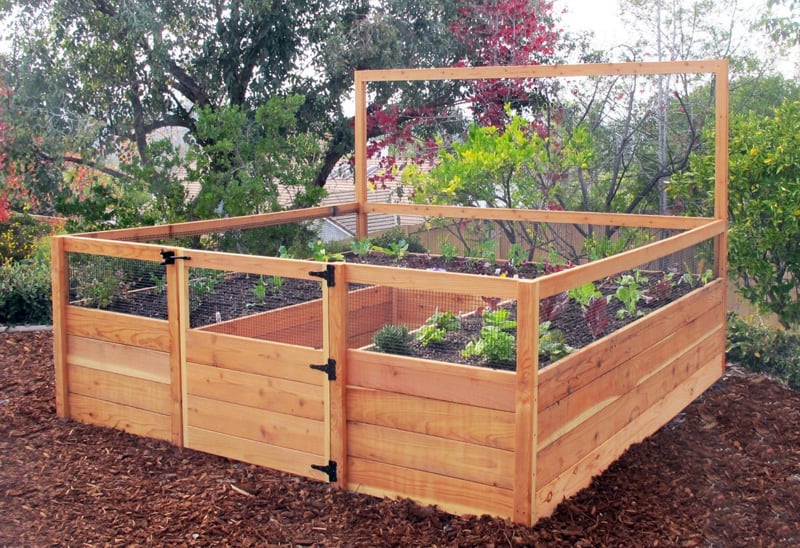 For the manufacture of beds, timber, round timber, slab, lining can be used.
For the manufacture of beds, timber, round timber, slab, lining can be used.
When it comes to purchasing boards in a store, you should pay special attention to the type of wood from which they are made:
- a board made of ash or oak will last a very long time. Although the cost of such products is quite high; nine0010
- pine board remains the most favorable in terms of price and processing. But this type of wood is highly susceptible to decay while in the ground, so its service life is short. Due to impregnations and antiseptic agents, the life of a pine tree can be extended for a couple of years;
- cedar and larch boards are considered the most suitable material for making boxes. Larch has a natural impregnation with resin, thanks to which the product will retain its novelty for many years without the use of additional impregnations. Cedar wood is characterized by a lower resin content, but it is not inferior to larch in terms of durability and at the same time has an affordable price; nine0010
In order to prevent water from stagnating in the boxes, it is necessary to consider a drainage system before planting.
- boards made from acacia feel good in the ground. It is worth noting that this type of wood is durable and has a solid structure, so the process of processing it will be more difficult. To work with acacia, you need a powerful electric tool.
Good advice! It is not recommended to save on the quality of the material. Boards made of bad wood are prone to rapid decay. After a few years, holes will appear on the fences of the beds, through which fertile soil will be washed out during rains and watering plants. nine0110
Shrubs and small fruit trees can also be planted in wooden beds
Making beds from boards with your own hands: photos, dimensions of structures
Beds-boxes have a rectangular shape and are made of boards. The simplest design does not require special knowledge and skills, so any novice summer resident can handle it. The main thing at the same time is to correctly calculate the dimensions of the boxes.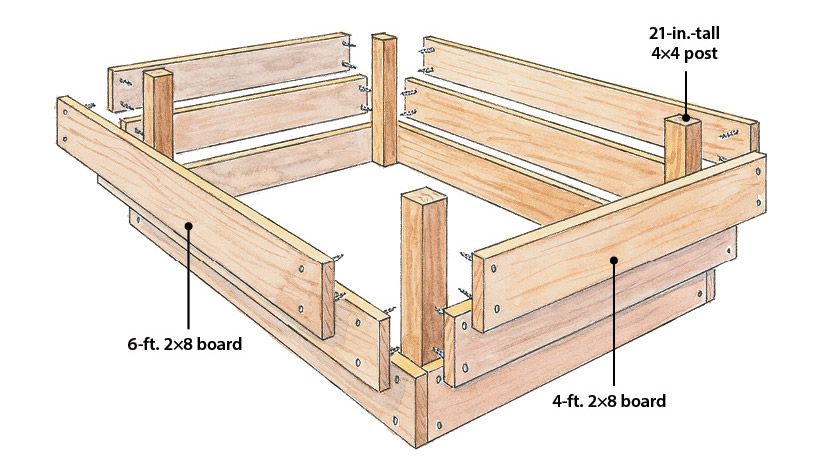
When planting plants, it is necessary to take into account the optimal amount of light and heat for certain crops, since the higher the bed, the faster it heats up
Recommended bed sizes:
- height - many summer residents strive to create the highest possible sides. However, this approach is erroneous if it is not planned to build a warm bed for cucumbers or other types of crops, where a fence height of up to 0.7 m is welcome. The manufacturing technology of such structures requires the laying of a multilayer insulation. For ordinary beds, such high fences are not required, it is enough to limit yourself to 0.15-0.2 m. In addition, wood is susceptible to deformation changes under the influence of moisture, so there is a risk that over time, high fences will swell and lose their attractive shape; nine0010
Long beds made of wood should be reinforced in several places to avoid their deformation. Most often, this parameter is in the range of 0. 9-1.2 m, because in the process of work, a person should be able to reach the middle of the structure from the side of the side rail;
9-1.2 m, because in the process of work, a person should be able to reach the middle of the structure from the side of the side rail;
Good advice! When choosing dimensional parameters for wooden beds, it should be taken into account that between them it is necessary to organize passages 0.4-0.6 m wide. Only after that is the layout of structures on the site considered.
Creating mixed plantings of vegetables in the garden: photo examples and optimal schemes
The method of combining crops in practice is very effective if the companion plants are chosen well. Therefore, site owners calculate according to a special table of the neighborhood of vegetables in the beds before planting. Some types of vegetables have a depressing effect on each other, others can improve the growth and development of neighbors, provide them with protection from pests. nine0005
Some types of vegetables have a depressing effect on each other, others can improve the growth and development of neighbors, provide them with protection from pests. nine0005
When planning the beds, it is worth considering that companion plants give more yield if they are planted side by side
The correct neighborhood of vegetables in the beds: compatibility table
significantly reduced the number of the Colorado potato beetle. Marigolds effectively protect cabbage from white butterflies. Despite this, a certain balance must be maintained. After all, an excessive amount of marigolds in the garden can drown out the growth of cabbage. nine0005
Table of neighboring vegetables in the garden, creating a successful tandem:
| Vegetable crop name | Plants for successful combination |
| strawberry | beans, spinach, marigolds, garlic, lettuce |
| kohlrabi | cucumber, lettuce, onion, beetroot |
| peas | carrot, corn, cucumber, calendula, eggplant |
| bow | tomato, celery, beetroot, savory, carrot |
| beans | potato, cucumber, tomato, strawberry, eggplant |
| cucumber | radishes, peppers, peas, cabbage, beans |
| carrot | lettuce, onion, sage, tomato, peas |
| lettuce | strawberry, cucumber, carrot, radish |
| pepper | lettuce, cucumber, beans |
| tomato | calendula, basil, beans, nasturtium, parsley |
The following pairs of plants are characterized by poor compatibility of planting vegetables in the garden:
- cabbage and strawberry;
- onions and beans;
- carrots and celery, dill, parsley;
- cucumbers and potatoes.

Even in a small area, you can get a high yield by using the plant-neighbor correspondence table when planting
Useful advice! In addition to the main crops, it is recommended to plant spicy and ornamental herbs pointwise in the garden. Thus, the garden will be not only beautiful, but also useful.
Examples of mixed planting vegetables in the garden: popular schemes
A good example of the compatibility of vegetables in the garden is the combination of onions and carrots. As an independent crop, onions are able to produce about 2.5 kg of yield from 1 m² of beds. Carrots on the same area gives about 6 kg of crop. With the joint cultivation of these crops with 1 m², you can get 9kg of vegetables. These plants create protective barriers for each other against pests, so the efficiency of the used area increases.
Onions and carrots are excellent neighbors, so they are usually planted side by side.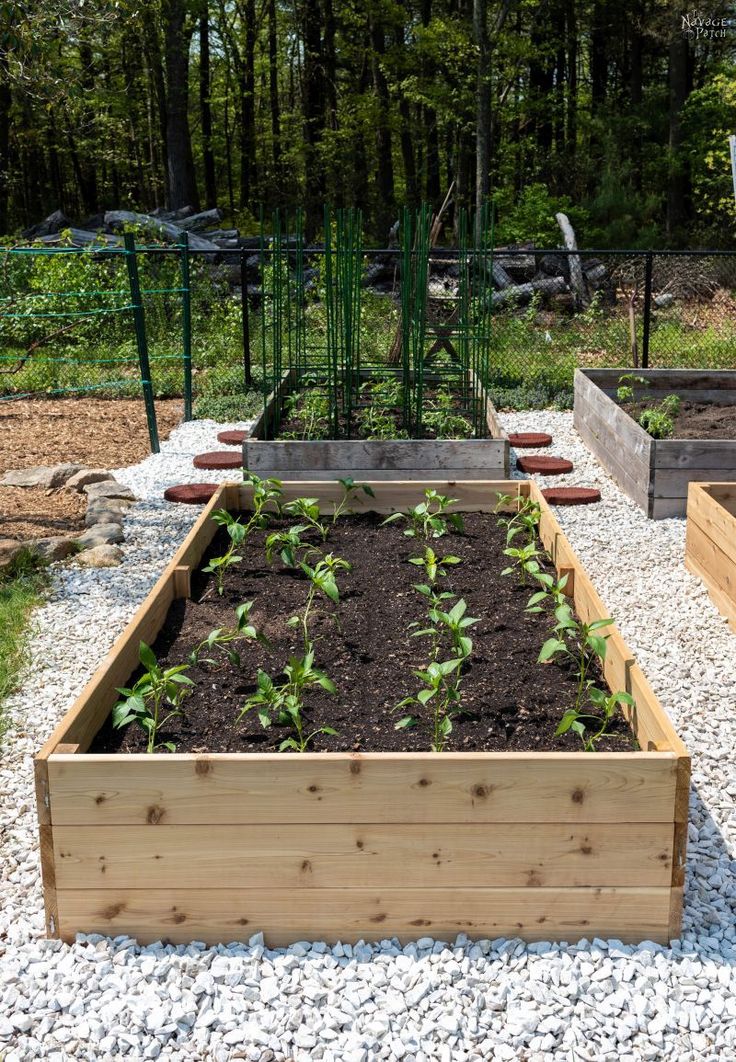
Of course, when planning a joint cultivation of crops in a garden, you need to group the plants according to their height so that none of them blocks the light for the other. This is necessary because vegetables can not only have different heights, but also grow at different rates. It is desirable that compactors that are planted additionally be lower in height than the main vegetables. The principle of a multi-tiered neighborhood of vegetables in the beds allows you to create favorable conditions for the root system of crops, and also contributes to the rational use of solar energy. nine0005
High yields are gathered from the beds where beets and late cabbage are planted. To do this, beets (9 plants) and cabbage (4 bushes) should be planted on an area of \u200b\u200b0.8x0.8 m, while not forgetting to fertilize the holes with a glass of compost and a handful of eggshells (pre-grind).
By planting marigolds near the beds, you can avoid some pests in the garden
To get an excellent result when planting beans and tomatoes, it is recommended to place the plants in a row with a step of 0.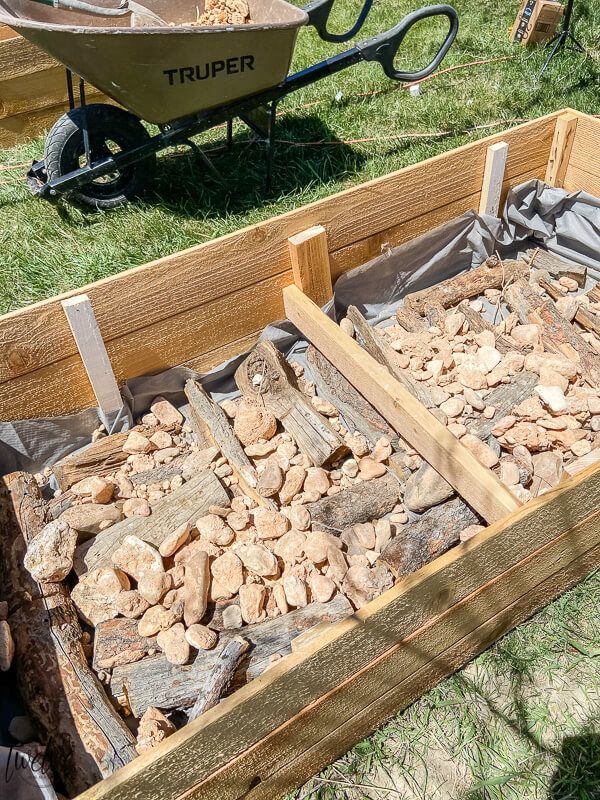 3 m. A drip irrigation system is installed along the row with bush beans so that each plant was on the drip. Tomatoes are planted in the central part of the garden. As a result, bean and tomato bushes should be staggered. nine0005
3 m. A drip irrigation system is installed along the row with bush beans so that each plant was on the drip. Tomatoes are planted in the central part of the garden. As a result, bean and tomato bushes should be staggered. nine0005
Good advice! Tomato stalks are best cut for the winter, and as low as possible. And the beans, on the contrary, are recommended to be left untouched.
Proper planting of vegetable crops is the key to a rich harvest
Table of vegetable rotation in beds by crop groups
Plant rotation can also affect the yield of beds. If the annual change of crops grown in the same garden is carried out in the correct order, the garden will produce good yields. nine0005
Benefits of proper crop rotation:
- eliminates the possibility of soil fatigue on the site, since the same vegetable every year absorbs the same set of nutrients from the soil and does it from the same depth;
- the spread of diseases and pests that infect plants of the same family is prevented;
- it becomes possible to rationally use fertilizers.

Green manure and crop rotation should be used to increase yields and restore the soil
The most primitive way of organizing crop rotation in the garden involves planting plants from different families on the same area every year. The easiest way is to break the crops into four groups:
- Leaf crops - these include various types of cabbage, green onions, leafy lettuces, and spinach.
- Fruit vegetables - cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, pumpkins.
- Legumes - beans, chickpeas, peas.
- Root crops - potatoes, beets, radishes, carrots. nine0010
Table of the simplest crop rotation in the garden:
| Planting sequence by years | Recommended crops for planting | |||
| 1st bed | 2nd bed | 3rd bed | 4th bed | |
| 1 year | fruit | roots | legumes | sheet |
| 2 year | roots | legumes | sheet | fruit |
| 3 year | legumes | sheet | fruit | roots |
Cucumber beds in the open field: photos and recommendations
For growing cucumbers in the open field, the beds are usually prepared in the fall. This should be done before the onset of rain and temperature drops. The planting area must be carefully dug up and saturated with organic fertilizers. Cucumbers like fertile, light soil that has a good level of air and water permeability. If the soil in the area is heavy, sawdust, peat or sand can be added to the ground to facilitate loosening. nine0005
This should be done before the onset of rain and temperature drops. The planting area must be carefully dug up and saturated with organic fertilizers. Cucumbers like fertile, light soil that has a good level of air and water permeability. If the soil in the area is heavy, sawdust, peat or sand can be added to the ground to facilitate loosening. nine0005
To get a rich harvest of cucumbers, the soil for the beds must be prepared in autumn
Useful advice! To get a rich harvest, it is recommended to add a tablespoon of superphosphate and a glass of ash per 1 m² of area. Instead of ash, you can use dolomite flour.
The process of preparing a bed for cucumbers in the spring includes a soil disinfection procedure. For this, the place of the future garden is spilled with potassium permanganate. The solution should be hot and strong. In addition, soil fertility can be increased by introducing chicken manure or manure. This procedure is carried out locally, that is, the fertilizer is placed directly in the trench or hole. After that, the bed is covered with a small layer of soil, where the seeds are then planted. nine0005
This procedure is carried out locally, that is, the fertilizer is placed directly in the trench or hole. After that, the bed is covered with a small layer of soil, where the seeds are then planted. nine0005
How to make a cucumber bed: agrotechnical secrets
To get a rich crop of cucumbers from the garden, you must follow the basic rules:
- Near the beds should not be irrigation canals, streams and flowing reservoirs.
- If the planting area is not protected, the vegetable garden is best placed in a quiet place where there are no drafts.
- Procedures such as watering and loosening the soil should be carried out on a regular basis. Otherwise, a hard crust will form on the surface, and the bed will dry out a lot. nine0010
- Cucumbers grown in the open field need to be fed much more often than plantings growing in closed beds.
- During harvest, it is not recommended to change the position of the vines of the plant or turn them over.

- Plants in open beds should be weeded more frequently than indoors.
- It is recommended to cover the entire surface of the bed with black film.
In order to collect clean cucumbers without soil, you need to think about what you can tie long shoots to
Cucumbers need a rich biological composition of the soil. Therefore, it is recommended to fertilize the land with organic matter, for example, grass, humus, branches, rotted manure, food waste. In the process of their decomposition, not only the fertility of the soil increases, but also heat is released, warming the soil. So that the high temperature does not damage the root system of cucumbers, experienced gardeners advise to carry out abundant watering.
Interesting fact! Sometimes the decomposition of organic fertilizers is so active that the soil in the garden warms up to 80 ° C. Under the influence of such a high temperature, many pests, viruses and pathogenic fungi contained in the soil die.
The result is a natural sterilization of the soil. nine0110
The soil where cucumbers are grown must be fertilized after harvest
There are several ways to grow cucumbers outdoors. For these purposes, you can form a long ridge bed, a hole, dig a ditch, or build a high structure.
How to make a garden bed for cucumbers with a bookmark
To form a bed with a bookmark, you will need to dig a trench. The depth of the ditch should be equal to two shovels. Then branches are laid out across and sawdust is poured. The next layer consists of straw and garden waste. You can add autumn leaves, cardboard or newspapers, compost. The thickness of the fertilizer layer should be within 5-7 cm. The bookmark is filled with warm water and covered with a mixture consisting of compost and earth. nine0005
A planted bed can last effectively for 5 years. In the second year of operation, it will not be necessary to add compost to the top layer, because during the decomposition of organic components, the bed itself will produce nutrients.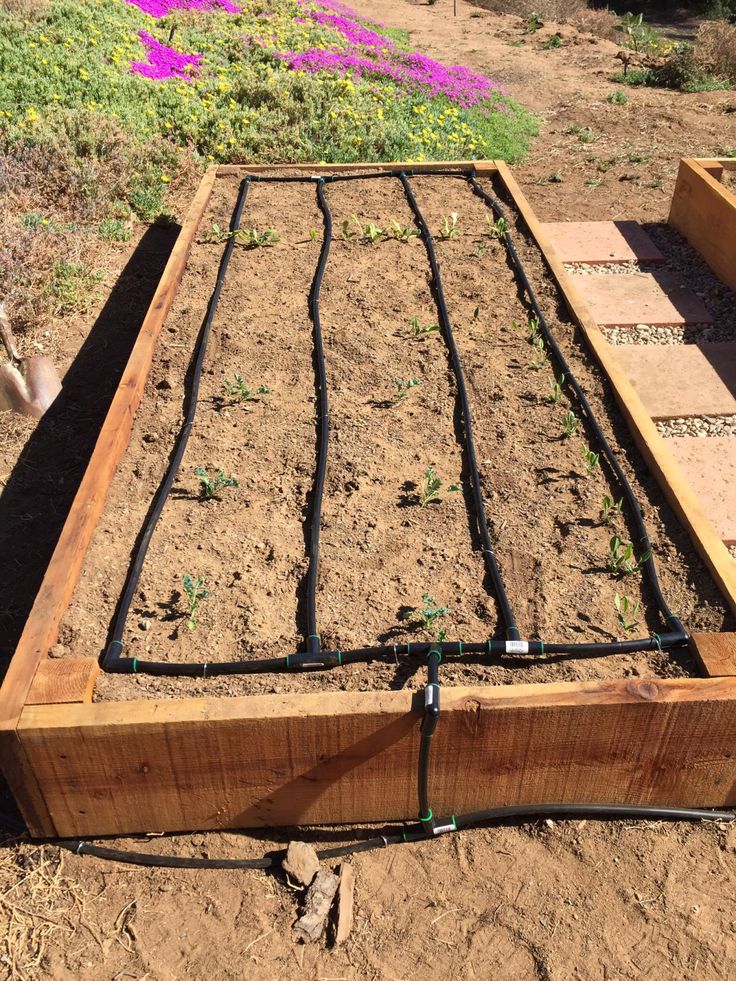
Planted cucumber bed
Benefits of planted cucumber bed:
- Convenient watering system;
- water stagnation is excluded;
- in the spring it is not necessary to dig up the soil, it is enough to loosen the soil. nine0010
Plants can be planted on this nutrient base much earlier than is customary to do in conventional beds. It is not recommended to use beds with a bookmark in low-lying areas and areas where water stagnates.
Cucumbers can only be watered from below, making sure that moisture does not stagnate at the roots
Warm surface beds for cucumbers in open ground
This type of warm beds for growing cucumbers is built on the surface of prepared soil. This technology will be the best option for areas that are located in the lowlands. In order to enhance the heating process, the bed is covered with a film. As a result, a greenhouse effect is formed, which has a positive effect on the growth of cucumbers and their yield. nine0005
nine0005
Surface beds also include structures in the form of boxes made of brick, slate or boards. The bottom of these containers is covered with sand, then with wood waste. Next comes a layer of organic waste and straw. After laying each component, the contents are carefully compacted and filled with liquid manure. Finally, the bed is covered with a mixture of compost and soil.
When making warm cucumber beds, you should follow clear instructions so as not to oversaturate the soil with fertilizers
Good advice! Vegetable and fruit skins, leaf litter, egg shells (powdered) may be used as organic waste.
Cucumbers are planted in two rows. Plants are placed along the edges of the bed-box, which ensures a sufficient level of illumination. If it is planned to plant cucumbers in early spring, the structures can be converted into greenhouses. To do this, you will need to install plastic arcs and stretch a plastic film over them. Thus, heating is enhanced and it becomes possible to get an early harvest. Moreover, the result is completely independent of weather conditions. nine0005
Thus, heating is enhanced and it becomes possible to get an early harvest. Moreover, the result is completely independent of weather conditions. nine0005
Insulated beds can be planted with cucumbers earlier than outdoors
Raised beds for cucumbers outdoors
Warm raised beds are used when the site is located in a region with a cold and humid climate. Due to this, there is a full warming up of the soil, which allows to achieve a harvest in the early stages. If groundwater comes too close to the garden, the bed rises high, due to which the plantings do not get wet on soil oversaturated with moisture. Stone trees, whose roots are severely affected by groundwater, are planted in a similar way. nine0005
Various materials are used as borders for these structures. The most popular of them are slate and wood. In rare cases, metal is used. This type of beds can be installed even in the middle of the lawn. If you make a frame in the form of paving stones or tiles, a raised garden with cucumbers will become a worthy decoration of your summer cottage.