How long do beets take to grow
Growing Beets - How to Grow Beets
More Articles
Find more garden information
Other Article Categories
Choose CategoryRecipesRaised Bed GardeningAnimal Pest ControlsGardening for the PlanetSoils & CompostSeed StartingGrowing Fruits & VegetablesPlanting Techniques & ToolsPest & Disease EncyclopediaHouseplant CareHome Beets
Beets are one of the easiest vegetables you can grow. They're almost never troubled by pests or disease. They don't need staking, pruning or fussing. Just sow the seeds and let the plants grow for about 6-8 weeks. You can harvest the roots at any time between midsummer and late fall.
Beets should be planted from seed, directly into the garden. Each beet seed is actually a hard little cluster of 2 to 4 seeds. It takes several days or even a week for the outer seed coat to soften and allow the seeds inside to germinate. It's important to keep the soil consistently moist during this period. Once the seeds have germinated, you will need to thin out (and eat!) some of the extra seedlings. Ideally you'll wind up with about 9 plants per square foot.
Like most vegetables, beets prefer growing in full sun and they like to get about 1" of water each week. Beets are cold tolerant, so they can be planted in early spring, several weeks before the last frost date. To keep the soil consistently moist during germination, cover the area with row cover until the seedlings break the soil surface.
Seedlings for red and gold beets. Photo: Ann Whitman
Beets can be harvested at any time. For baby beets, harvest when the root is no more than 1 or 2 inches in diameter. Cook the leaves as well as the roots — all parts of the plant are delicious. If you want the most food for the garden space, wait until the root has filled out to several inches in diameter. Depending on the variety, most beets will still be tender and flavorful, even when the root measures 4 or 5 inches across.
Early season crops such as lettuce and peas can be replaced by a midsummer planting of beets. A fall crop of beets will tolerate temperatures down to about 20 degrees. As temperatures continue to fall, you can cover the area with row cover fabric to prevent the roots from freezing. Beets can also be harvested and stored indoors for a month or more. Trim off the leaves, keeping a ½" tuft of stems at the top of the root. Gently brush off any soil, put the beets into a plastic bag (do not seal it up), and store them in your refrigerator crisper.
Beets can be boiled, baked, roasted or pickled. They're also delicious grated raw into salads. For variety, try planting both red and yellow beets. Choggia beets, which are spiraled with red and white, are another delicious option.
Last updated: 09/12/2022
Share this Article:
People who read this article often purchase
Related Articles
-
What to Plant
-
Grow Carrots in a Grow Bag
-
Success With Potatoes
Stay up to date on new articles and advice. Please fill out the information below.
Please fill out the information below.
Share this Article:
Related Articles
-
What to Plant
-
Grow Carrots in a Grow Bag
-
Success With Potatoes
Easy Gardening: Beets - Texas A&M Agrilife Extension Service
- Type
- Publication
- Date of Publication
- January 25, 2022
- Price
- See Agrilife Learn
Topics:
Overview
This publication explains all aspects of growing beets in a home garden. Beets can be grown all winter in many South Texas areas. Farther north they should be planted as soon as the soil can be worked in spring.
Beets can be grown all winter in many South Texas areas. Farther north they should be planted as soon as the soil can be worked in spring.
View on Agrilife Learn
Beets are a cool-season crop and grow well in the cool temperatures of spring and fall. They do poorly in hot weather. Beets are well suited to large or small home gardens since they require little room. They are grown for both the roots which usually are pickled and the young tops which are used as greens. About 10 feet of row per person will provide enough beets to use fresh or for canning. (4 pages)
Looking for solutions in your county? Contact your local extension experts
County Offices
Publication
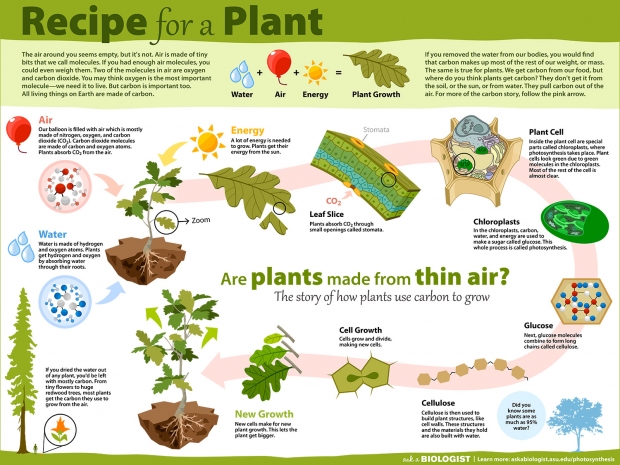
Crop Management Factors: What is Important?
Producers can use the information here to help with allocating scarce resources (time and money) among the five management areas discussed. Although management styles would influence the allocation, on average, the focus should be first on costs, then technology adoption, then yields, and finally prices.
 (4 pages).
(4 pages).Publication
2022 Texas Grape Pest and Weed Management Guide
Grapevine pests and diseases can cause significant damage and crop loss, and the signs and symptoms of these ailments can be hard to recognize. This publication describes several pests and diseases that plague grapevines as well as instructions to keep growers vigilant and prepared in administering treatment. (84 Pages)
Publication
Forage Quality and Quantity in Texas: Managing Nutrition in Range Beef Cattle
Nutritional management is complicated by changing forage quality and quantity. This publication discusses forage quality trends in various regions of Texas, tools to analyze the nutritional environment of cattle and differentiate between forage quality and availability problems, and nutritional management strategies. (8 pages).
Publication
Path to the Plate: Watermelons
In Texas, watermelons are a favorite summer treat.
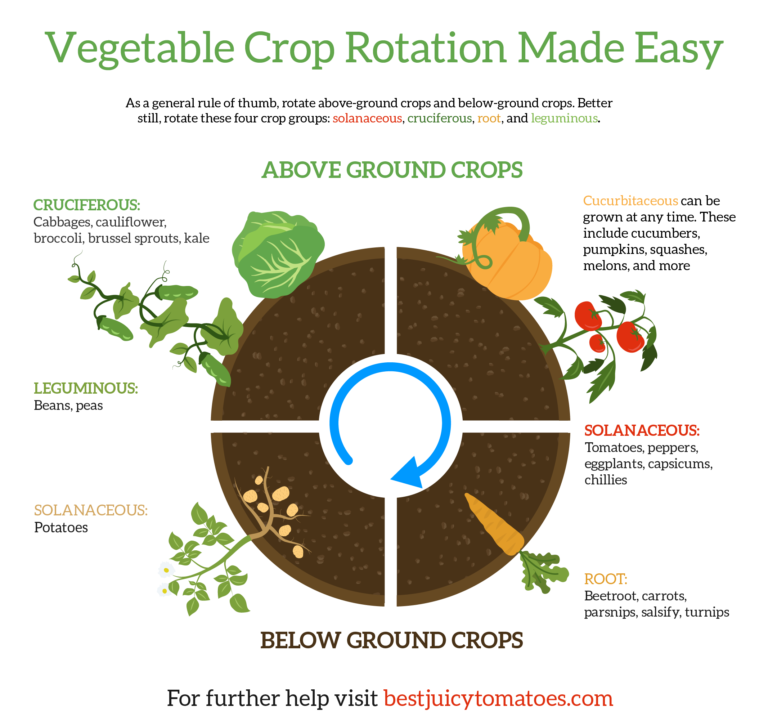 They are made up of about 90 percent water, making them the perfect way to quench thirst and satisfy a sweet tooth. Watermelons are a member of the cucurbit family, along with squash, cucumbers, and pumpkins. This factsheet instructs gardeners on the care of watermelon plants and […]
They are made up of about 90 percent water, making them the perfect way to quench thirst and satisfy a sweet tooth. Watermelons are a member of the cucurbit family, along with squash, cucumbers, and pumpkins. This factsheet instructs gardeners on the care of watermelon plants and […]Publication
Path to the Plate: Cantaloupes and Honeydew Melons
Cantaloupes and honeydew melons are vining crops that are grown during the warm season of Texas. This factsheet instructs gardeners on the care of cantaloupe and honeydew melon plants and provides two recipes that showcase the melons. (2 pages)
Publication
Irrigating Sorghum in South and South Central Texas
If irrigation for grain sorghum is managed well, the crop will produce high, profitable yields. This publication explains the water needs for sorghum at different growth stages, the calculations to use to estimate its water requirements, and adjustments to make for rainfall and soil moisture.
 (5 pages)
(5 pages)
See More Results
When to harvest beets from the beds and fields when the crop is ripe
The Bizon-Tech website is working in test mode.
Found a mistake? Write to
Our buffaloes are in a hurry to fill the website with useful information, as well as give you the opportunity to conveniently buy goods. Patience, friend, very soon all this will become a reality!
Market analysis
September 20, 2019
To avoid yield losses at the last stage of production, the correct time of maturity of the root crop should be determined. The period of the last phase of the growing season depends on many factors.
An important final step in the technology of beet production is its harvesting. This is a responsible and time-consuming process, which accounts for a quarter of the time spent on the total number of working hours spent on a complete production cycle. A clear organization of the harvesting campaign ensures the efficiency and timeliness of operations and the preservation of the maximum yield. nine0003
A clear organization of the harvesting campaign ensures the efficiency and timeliness of operations and the preservation of the maximum yield. nine0003
Why is it necessary to harvest beets on time? Therefore, it is not worth harvesting beets for storage in the early stages, the fruits can be small and will not last for a long time. However, there are exceptions, one of the reasons for harvesting beets early is a disease, root rot is common.
It is also not recommended to postpone the harvesting of beets, since frost is dangerous for the root crop. Its part, which is located on the surface, is easily affected by the first frost, so a significant amount may be unsuitable for storage and turn black inside. nine0003
Mid-season and late varieties
Mid-season varieties are the most popular among the other two classes. The main feature is the fruit ripening period, which is approximately 80-110 days. In addition, the quality indicators of the plant are characterized by high values compared to early ripe varieties. The harvesting campaign falls on the middle or end of August. If planted in the last days of May, you can collect in September. Popular mid-season varieties are such as Detroit, Borshcheva and Incomparable, and in addition, they are perfectly preserved in the winter. nine0021 Late-ripening beet varieties are planted in regions that have a temperate or warm climate. Such conditions are due to the long growing season of the culture - 135 days. These varieties can be grown over a consistently long heat period. Such root crops are optimally stored in winter, and they also contain a significant amount of valuable trace elements. The most famous varieties are Cylinder, Torpedo, Odnorostkovaya and Renova. You can buy sugar beet seeds on our website.
The harvesting campaign falls on the middle or end of August. If planted in the last days of May, you can collect in September. Popular mid-season varieties are such as Detroit, Borshcheva and Incomparable, and in addition, they are perfectly preserved in the winter. nine0021 Late-ripening beet varieties are planted in regions that have a temperate or warm climate. Such conditions are due to the long growing season of the culture - 135 days. These varieties can be grown over a consistently long heat period. Such root crops are optimally stored in winter, and they also contain a significant amount of valuable trace elements. The most famous varieties are Cylinder, Torpedo, Odnorostkovaya and Renova. You can buy sugar beet seeds on our website.
Beet maturity
The period for which the beets ripen is determined by the variety. Early ones ripen in 50-80 days, they are harvested in the last days of July or early August. Beets of medium ripeness become mature in 80-110 days. These root crops are harvested from the field in the middle or at the end of the last summer month. Late-ripening varieties ripen within 110-135 days. They persist until spring, and the time when beets are harvested is at the end of September or mid-October.
These root crops are harvested from the field in the middle or at the end of the last summer month. Late-ripening varieties ripen within 110-135 days. They persist until spring, and the time when beets are harvested is at the end of September or mid-October.
Sugar, fodder and table roots are harvested at about the same time. The harvesting time of sugar beets is calculated in accordance with the capabilities of the processing plant, since they lose quality during long-term storage. Harvesting fodder beet is also determined according to the demand of farms or the possibilities of laying. The term for harvesting red beets is usually set according to external signs. Its varieties differ from each other by the period of maturity. So, the early ones vegetate only 50 days, but they do not persist for a long time. Late varieties ripen in 100 or even more days. The general rule is to harvest the beets before the start of frost. nine0003
When is it worth harvesting
The maximum amount of important macro and microelements is found in beets in the last phase of development. Therefore, it is worth starting harvesting at an acceptable late ripening time, especially late-ripening varieties. However, if the autumn is warm, and the roots are in the soil for a long time, they can overripe, become fibrous, and light rings and voids form inside. If you collect unripe beets, which have a very thin outer shell, they will be stored for a long period. In both cases, the quality indicators are reduced. The worst option is early frosts, which can irreparably destroy the crop. Therefore, when determining the time when to harvest beets, it is important to choose the optimal period, taking into account natural and climatic features. The reference point is dry weather, the temperature is at a stable level of +5, but by the beginning of freezing of the soil. nine0021 There is no single date for harvesting beets in the fall; it is influenced by the crop variety, the growing area, and weather conditions. However, the period is defined - the harvesting campaign starts in September and ends in November.
Therefore, it is worth starting harvesting at an acceptable late ripening time, especially late-ripening varieties. However, if the autumn is warm, and the roots are in the soil for a long time, they can overripe, become fibrous, and light rings and voids form inside. If you collect unripe beets, which have a very thin outer shell, they will be stored for a long period. In both cases, the quality indicators are reduced. The worst option is early frosts, which can irreparably destroy the crop. Therefore, when determining the time when to harvest beets, it is important to choose the optimal period, taking into account natural and climatic features. The reference point is dry weather, the temperature is at a stable level of +5, but by the beginning of freezing of the soil. nine0021 There is no single date for harvesting beets in the fall; it is influenced by the crop variety, the growing area, and weather conditions. However, the period is defined - the harvesting campaign starts in September and ends in November.
So, if the root crop has reached the characteristic diameter for a certain variety, the corresponding growths have appeared on the surface, the lower shoots of the tops have become yellow and dry, and according to weather forecasts, there will be the first frosts - it's time to harvest. In addition, a risk factor for crop loss is a long rainy autumn, since excess moisture can provoke rotting of root crops. In this case, continue the time when it is worth digging the beets. In any case, the crop harvested in time from the field and placed in storage will be perfectly preserved for a long time without loss of quality characteristics. nine0003
How to determine the external signs of maturity of the root crop
First of all, the period when the beet harvest is set according to its varietal size, which is not difficult to determine, since the upper part is on the surface of the earth. In addition, maturity characterizes the diameter and weight of the root crop.
External signs of collection - yellowed and dry lower leaves, growths on the surface. In the last phases of the growing season, the main root becomes thinner, and in unripe beets there are several young fleshy roots. nine0003
In the last phases of the growing season, the main root becomes thinner, and in unripe beets there are several young fleshy roots. nine0003
What affects the ripening of the beet crop
An important element for the development of sugar beet, like other crops, is nitrogen. In the first phase of vegetation, nutrition with this element helps to quickly form a highly adaptive leaf apparatus of the plant. The best form of nitrogen fertilizer for beets (especially when grown on chernozems and podzolic soils) is sodium nitrate. Calcium, ammonium nitrate, urea and ammonium sulfate fertilize crops with less efficiency. It is better to choose the required amount of fertilizer after considering the presence of elements in the soil. Its analysis will help determine the optimal nutritional standards. However, excessive nitrogen content in the second half of the growing season inhibits beet growth and the accumulation of essential nutrients. This feature is due to the high competition between the active development of the leaves and the fruit. nine0021 In the initial phases of vegetation, when the root system is still poorly developed, beets also need phosphorus, which affects the increase in yield and quality characteristics. But if there is not enough nitrogen, plants stop the absorption of phosphorus, so these elements should be used in combination.
nine0021 In the initial phases of vegetation, when the root system is still poorly developed, beets also need phosphorus, which affects the increase in yield and quality characteristics. But if there is not enough nitrogen, plants stop the absorption of phosphorus, so these elements should be used in combination.
Feeding potash fertilizers is especially effective on sandy and peaty soils. It is advisable to add sodium under conditions of optimal supply of potassium to root crops, since sodium in the old leaf replaces potassium and carries out the outflow of the latter to the root. And vice versa: if there is not enough potassium in young leaves, the amount of sodium increases, and the botka begin to dry out in advance and, thus, the process of photosynthesis decreases. nine0021 Root crops grown in acidic soils require calcium. Another important element for beets is boron.
How to properly harvest beets
Harvesting beets with a combine involves performing technical operations so as not to damage the root crop. First of all, it is necessary to prepare the landing for digging - cut off the tops. This operation must be carried out carefully, because a cut of 1 cm of the neck of the fetus is a loss of up to 7% of the crop, and if you cut another 2 cm more, you can lose up to 27% of the total volume. A uniform cut of the tops can be ensured only on a leveled planting area, provided that the seeds are planted to the same depth and the fruit grows evenly in the row. nine0021 Deep root breaking is also not desirable, as it can lead to crop loss. If the tail is broken off by 3-5 cm, the loss of gross harvest can be 6-12%.
First of all, it is necessary to prepare the landing for digging - cut off the tops. This operation must be carried out carefully, because a cut of 1 cm of the neck of the fetus is a loss of up to 7% of the crop, and if you cut another 2 cm more, you can lose up to 27% of the total volume. A uniform cut of the tops can be ensured only on a leveled planting area, provided that the seeds are planted to the same depth and the fruit grows evenly in the row. nine0021 Deep root breaking is also not desirable, as it can lead to crop loss. If the tail is broken off by 3-5 cm, the loss of gross harvest can be 6-12%.
Therefore, beet harvesters must be adjusted so that the beet harvest can be carried out without root damage.
How to properly prepare beets for storage
According to the possibilities of the farm, after harvesting, either short-term storage is organized or transported to the premises for keeping for a long time. In the first case, the beets are placed in field piles. Before laying, the fruit is cleaned of plant residues, closely folded and treated with slaked lime (200 g per sq. M). In such conditions, only conditioned root crops are preserved. At the reception points, the crop is harvested in large piles, which are located on a specially designated area, on 1 hectare of which is placed from 50-240 thousand centners of beets. nine0021 Root crops for long-term storage are usually laid in mid-autumn. By the end of September, the air temperature in the growing regions is relatively high, which can lead to wilting, leaf growth, development of diseases and rotting in storage. However, a biologically mature root crop is already prepared for long-term storage even under unfavorable beet harvesting conditions.
Before laying, the fruit is cleaned of plant residues, closely folded and treated with slaked lime (200 g per sq. M). In such conditions, only conditioned root crops are preserved. At the reception points, the crop is harvested in large piles, which are located on a specially designated area, on 1 hectare of which is placed from 50-240 thousand centners of beets. nine0021 Root crops for long-term storage are usually laid in mid-autumn. By the end of September, the air temperature in the growing regions is relatively high, which can lead to wilting, leaf growth, development of diseases and rotting in storage. However, a biologically mature root crop is already prepared for long-term storage even under unfavorable beet harvesting conditions.
Preparing for planting is not enough to save the harvest. The conditions for harvesting and storing beets should be strictly observed. In storage, it is imperative to ensure optimal temperature conditions and control the level of humidity. nine0021 Thus, the key to successful storage is not only proper cultivation, but also harvesting beets for the winter.
So, in order to avoid yield losses at the last stage of production, it is necessary to determine the correct time of varietal maturity of the root crop. The period of the last phase of vegetation depends not only on the variety, but also on the region of cultivation, climatic features and the chosen technology. Timely implementation of a set of production measures will help to significantly reduce crop losses. nine0003
Other articles
Agronomic articles on the Bizon-Tech website
All articles
Top 5 best weed killers
Grain corn cultivation technology
Corn is one of the most valuable agricultural crops. Subject to all agrotechnical requirements, it can form a high yield.
Technology for growing winter wheat
In Ukraine, winter wheat is the leader in terms of sown area. And every year, despite bad seasons, hectares of grain continue to remain at a stable level. Such relative stability is ensured by the wheat growing technology.
Such relative stability is ensured by the wheat growing technology.
Fertilizers: types and features of the use of organic and mineral fertilizers
Soil depletion is a natural phenomenon in the cultivation of any crops. Plants draw nutrients from the fertile layer. Moreover, the more productive the variety, the more minerals and organic residues the crops will need. nine0003
Root rot: symptoms, methods of control and prevention
For both farmers and gardeners, fungal diseases are a big problem, they are highly resistant to many treatments and can spread quickly.
cultivation, planting, care in the open field
Growing beets
Among all root crops, beets are the most light-loving (1), so you need to choose a bright site for it - the sun should hit the beds all day. In the shade of trees, even a small one, there will be no good harvest. nine0003
Successful predecessors for beets are tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, onions and peas.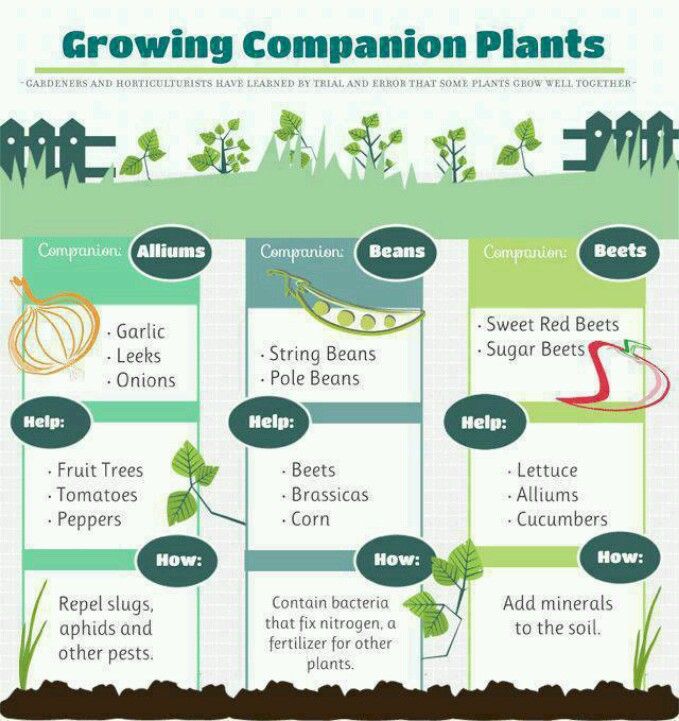 You can not plant it after the turnip, turnip, potato and cabbage.
You can not plant it after the turnip, turnip, potato and cabbage.
Prefers neutral soils, it grows very poorly on acidic soils, often gets sick, produces small, tasteless root crops that are poorly stored. To remedy the situation, before sowing, the site must be deoxidized - add 1 kg of dolomite flour per 1 sq. m. In neutral areas, it is not necessary to make dolomite flour!
It is advisable to fertilize poor soils before sowing: 1 bucket of humus, 1 tbsp. spoon of ammonium nitrate, 2 tbsp. spoons of double superphosphate and 2 teaspoons of potassium sulfate per 1 sq. m. Fertilizers should be evenly scattered over the site, and then embedded in the soil with a rake. nine0003
Do not use fresh manure for beets! Otherwise, root crops will not be stored.
Preparing seeds for sowing
Beet seeds germinate more easily than carrot seeds, but it is also useful to prepare them. There are many options, but the best way is soaking with hardening. This should be done 2 weeks before sowing.
Put the seeds in an enamel or glass dish, pour 1/4 cup of water at room temperature and leave for 1.5 days. Then drain the water and cover the container with a damp cloth so that it does not come into contact with the seeds. Leave for 3 days at a temperature of 15 - 20 ° C, stirring occasionally - during this time the seeds will swell. And then put them in the refrigerator for 7 - 10 days. nine0003
This method will allow you to get friendly, strong seedlings, and in the future - a big harvest.
Planting beets
Beets are not afraid of light spring frosts, but are very sensitive to soil temperature. Seeds germinate best when the beds at a depth of 10 cm have warmed up to 8-11 °C (2). In the middle lane, this is usually the beginning of May.
It is not worth sowing earlier - when the soil temperature is below 4 °C, the seeds can lie for a long time without germinating. But it is also undesirable to delay, because by mid-May the soil dries up, and beets need an abundance of moisture to sprout. Under optimal conditions, seedlings appear in about 10 days. nine0003
Seeds are sown in furrows to a depth of 2 - 3 cm. Row spacing - 8 - 10 cm. Between rows - 25 - 30 cm. but there are three important tasks to be done during the summer.
Thinning. Unlike other vegetable crops, beets do not have seeds, but seedlings. Therefore, 2 - 3 seedlings appear from each "glomerulus" (3). If you leave them all, they will prevent each other from growing - they will not have enough light, moisture, nutrition, and the roots will eventually turn out to be small. Therefore, it is important to thin them out in time - they do it 3 times per season:
- 5-10 days after germination - leave 2-3 cm between seedlings;
- in the phase of 4 - 5 true leaves - this time the distance between plants is increased to 4 - 6 cm;
- at the beginning of August - during this thinning, the largest root crops are removed, leaving 8 - 10 cm between the beets (4).

Best done after watering, on cloudy days.
Loosening. Beets do not like when a dense crust forms on the surface of the soil, so the next day after each rain or watering, the beds need to be loosened. nine0003
Watering. Beets need abundant watering during seed germination, seedling rooting and during the formation of root crops (5). The rest of the time, it is not worth watering it often, especially when the root crops increase in mass - this makes them watery, tasteless and poorly stored. Watering is needed only in drought and no more than 3 times during the summer. Consumption rate: 0.5 liters per plant.
Harvest of beets
Beets are harvested as the very first of the root crops, at the beginning of September. And sometimes at the end of August. It is important to follow the weather forecast here: root crops should not fall under frost, otherwise they will not be stored. But you shouldn't rush either. If September is dry and warm, leave the beets in the beds: scientists have found that most of the nutrients in it accumulate in the fall. nine0003
nine0003
Harvest signal - leaves start to turn yellow.
Cleaning is best on a warm sunny day. Varieties with rounded roots can be carefully pulled out by hand. It is better to dig up cylindrical beets with a pitchfork. If the soil is moist, the root crops must be dried, after which the dried dirt should be cleaned with your hands.
When harvesting, try to avoid damaging the beets as much as possible. You can not throw it on the ground and tap on each other.
Root crops with a diameter of 10-12 cm are best stored. Before laying in the cellar, they cut off the tops, leaving 1 cm long petioles. nine0003
Beet storage rules
Only whole root crops are stored for storage, without signs of rot, cuts and scratches on the skin.
Beets are best stored at 4°C and 90-95% humidity. That is, you can send it to the cellar and to the refrigerator.
Popular questions and answers
We talked about growing beets with agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova.
How to choose a beet variety?
First of all, pay attention to the yield - you can see it in the description of the variety in the State Register of Breeding Achievements (available on the Internet). Higher is better. By the way, cylindrical varieties have very high yields - we have more plants than a unit area, because root crops do not grow in breadth, but in depth. Well, look (ibid.), for which region the variety is intended. nine0003
Do all varieties of beets produce several sprouts?
No, not all. For example, there is an old beet variety, bred in 1970 - Odnorostkovaya. Its name speaks for itself - the seeds give only one sprout, so the crops can not be thinned out.
Is it possible to grow beets through seedlings?
There is a technique to get an earlier harvest. But you should remember 2 points. First, early harvested beets will not be stored. Secondly, growing beet seedlings is not an easy task. Under it, tall cups are needed so that the spine does not rest against the bottom and does not bend before disembarking.