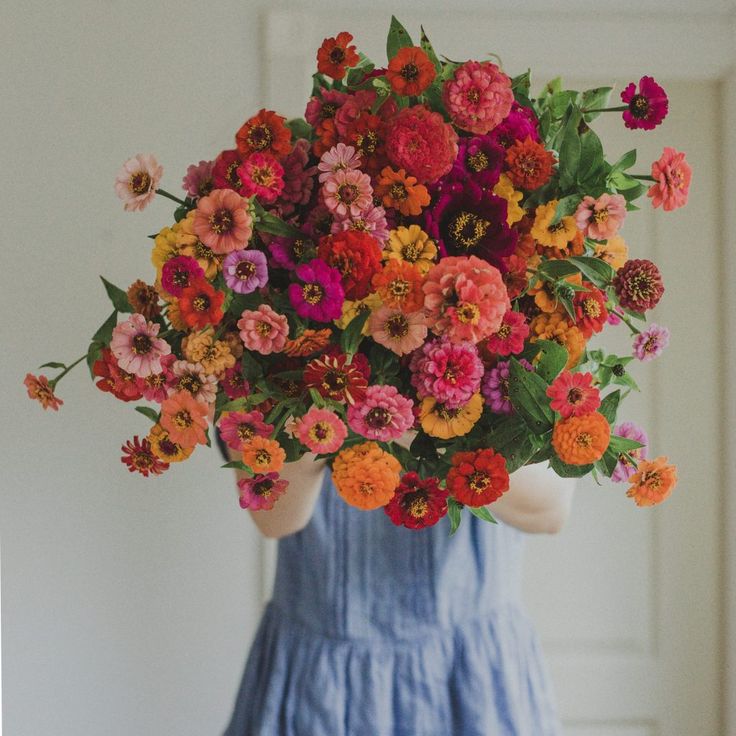
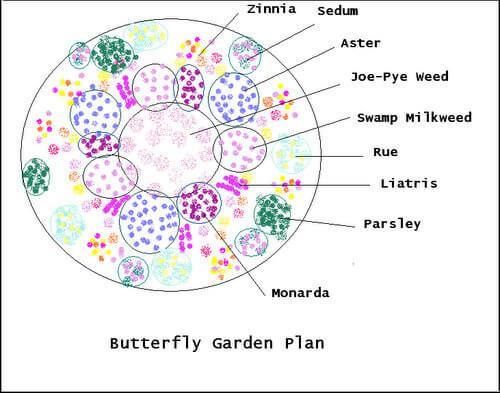
How close to plant zinnias
How Far Apart Should You Space Zinnias When Planting Them?
Flowers
If you are planting zinnias in your garden, you may be wondering how far you need to space them from one another, and how far the rows should be apart. In this article, gardening and flower expert Taylor Sievers walks through exactly how much distance these flowers need between each other, and between rows.
By Taylor Sievers Last updated: April 15, 2022 | 4 min read
If there’s one flower staple in the home garden I had to choose, then the zinnia would have to be it! These heat-loving Mexican natives are easy to start from seed, and are low maintenance. They also produce a jazzy pop of color all throughout the summer.
Zinnias can have versatile applications in landscaping and home gardens as long as you have a warm, sunny spot on your property. Plant a low-growing Zinnia angustifolia along a landscape border, a unique two-toned Zinnia haageana variety in a patio container, or a giant-flowered Zinnia elegans variety as a companion plant in your vegetable garden! None of these species will disappoint when it comes to cheeriness.
Okay–so now you’ve decided to add zinnias to your must-grow list. But zinnias don’t just come in one species or one height! And now you may be wondering, how far apart should I be planting my zinnias? Read on to learn more about zinnias and plant spacing specifics!
Contents
- 1 About Zinnias
- 2 Zinnia Planting Tips
- 3 Popular Varieties of Zinnias
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 5 Final Thoughts
How far apart should I space zinnias when planting?
Spacing depends on what variety you are planting and what your purpose is for your zinnias. Smaller zinnia varieties used as a border plant or in pots could be planted as close as 6 inches apart, while larger giant-flowered varieties may need up to 18 inches of space between each plant. If you live in a hot, humid climate, you may consider spacing your zinnias further apart to increase air circulation through the plants, and this will reduce disease incidence as well.
Smaller zinnia varieties used as a border plant or in pots could be planted as close as 6 inches apart, while larger giant-flowered varieties may need up to 18 inches of space between each plant. If you live in a hot, humid climate, you may consider spacing your zinnias further apart to increase air circulation through the plants, and this will reduce disease incidence as well.
About Zinnias
This beautiful flower can be grown in nearly any color.Plants of the Zinnia genus are considered herbaceous annuals. This means they produce non-woody growth (for the most part). They will flower and set seed within one year or season of growth. They prefer full sun (6 to 8+ hours of direct sunlight per day) and well-draining soil.
Zinnias produce bright, cheerful blooms in almost every color but blue. Flowers can be as small as an inch in diameter to 5 inches, depending on the variety. Some zinnia varieties are single-petaled (meaning they have one row of petals) and others will be double or multi-petaled.
Because they are members of the Asteraceae family, their flower is actually a composite flower. This means that what you see as the flower head is actually multiple small flowers. The “petals” are called ray flowers and the center portion of the flower is filled with disk flowers.
Zinnias can be prone to diseases like leaf spot diseases or powdery mildew. It’s important to make sure that any dew or moisture on the leaf surface can dry quickly. Spacing your zinnias further apart will help promote natural air circulation through the flower patch. You’ll notice dying zinnias usually turn brown before they are completely dead.
Watering at the base of the plant rather than overhead will help reduce moisture on the foliage. Planting in full sun will also help the foliage dry off faster in the morning from the dew that will collect on the leaves at night.
Zinnia Planting Tips
Different varieties of this swoon-worthy flower will require different spacing in your garden.
Zinnias should be planted after your last expected frost as they do not tolerate cold temperatures. Usually it is best to wait until the soil has reached at least 55⁰F before planting zinnias outside. They can be started indoors about 4 to 6 weeks before your last estimated frost date if you’d like to get a jumpstart.
Plant zinnias anywhere from 6 inches apart to 18 inches apart. Small bedding varieties that only reach about 8 inches in height can be planted between 6 to 10 inches apart. Larger varieties that reach up to 4 feet tall should be planted between 12 to 18 inches apart.
In my cut flower garden, I plant my large ‘Benary’s Giant’ zinnias in a grid that is 9 inches by 9 inches apart. This promotes longer, straighter stems, which is what I’m looking for as a cut flower grower. However, in the landscape I would normally plant these at least 12 inches apart, for reference. Zinnias can be planted indoors or outdoors. Outdoor planting can be beneficial, especially if you’ve saved a bunch of zinnia seeds from a prior harvest.
Direct Sowing Outdoors
Direct sowing of seeds is one of the more popular planting methods for these flowers.If you are direct sowing seeds outside, make sure to plant the seeds at least ¼ inch deep. You can plant them in a furrow and thin the seedlings to your desired spacing after they germinate. You may broadcast seeds, but you will need to rake them into the soil to promote seed to soil contact. Be aware that you may have reduced germination. You will likely need to thin out your seedlings if you are broadcasting seeds. Obviously, if you let your zinnia reseed itself, you’ll have a bit less control.
Thinning is the practice of uprooting and removing seedlings that have emerged. This ensures that your entire planting has correct spacing between plants. Gardeners will overseed sometimes when they are direct sowing into the garden.
This is because they know it’s likely some seedlings will not germinate for various reasons. Then they can thin out seedlings later that are not needed. It can be painful to thin your plants. But, if you leave your plants too close then you’ll have less vigorous plants that are competing for sunlight and moisture.
It can be painful to thin your plants. But, if you leave your plants too close then you’ll have less vigorous plants that are competing for sunlight and moisture.
Seed Starting Indoors
If you are starting seeds indoors, make sure to plant the seed at least ¼ inch deep in your cell tray or small pots. I like to poke holes in the cells using a pencil and drop the seeds in before covering and dusting the surface with vermiculite. Heat mats will definitely give you a jumpstart on germination.
Popular Varieties of Zinnias
This gorgeous ‘Uproar Rose’ variety is just one of many possible additions to your garden.Here are a few popular varieties along with recommended spacing for these varieties:
- ‘Benary’s Giant’ series zinnias will grow 3 to 4 feet tall with 4 to 5 inch blooms in 13 different colors. Plant this variety between 12 and 18 inches apart.
- ‘Uproar Rose’ is a stunning, large, rose-colored zinnia that is well-branching.
 Plant this variety between 12 and 18 inches apart.
Plant this variety between 12 and 18 inches apart.
- ‘Queen’ series zinnias have blooms in antique shades of rose, orange, and blush that fade into lime. These zinnias should be spaced between 10 and 12 inches apart.
- ‘Oklahoma’ series zinnias come in a range of colors, but the blooms are much smaller at about 2 inches in diameter. Space these plants between 10 to 12 inches apart.
- ‘Crystal’ series zinnias top out around 10 inches tall and is a single-petaled variety in colors of orange, white, and yellow. This zinnia could be planted between 6 to 10 inches apart.
- ‘Aztec Sunset’ zinnias can grow up to 2 feet tall with smaller 1 to 2 inch flowers in red, yellow, orange, and bicolor orange and maroon. Space this variety 10 to 12 inches apart.
- ‘Soleado’ has bright, cheerful blooms in orange or yellow with a mahogany ring around the center.
 Space this variety between 10 and 12 inches apart.
Space this variety between 10 and 12 inches apart.
Frequently Asked Questions
Shorter varieties of zinnias are excellent candidates for patio pots. Remember to think about the spread of the variety you are planting. Spread means how wide the plant will get at maturity. For the most part, the smaller varieties or dwarf varieties of zinnias will need to be planted at least 6 inches apart from a neighboring plant. If you’re planting in a very small pot (6 to 10 inches wide) you may consider only planting one zinnia plant per pot.
Zinnias are versatile plants in the garden or landscape. They can be planted in the vegetable garden, cut flower garden, landscape, or in a pot. They attract beneficial insects, especially pollinator insects that are important for certain fruit and vegetable plant pollination and fruit set.
Also, zinnia flowers come in very bright and attractive colors, providing a cheerful pop of color to a flower arrangement or in the landscape. The more you cut these flowers, the more they will bloom. Zinnias love full sun and well-drained soil, and they’ll thrive in the mid to late Summer heat.
The more you cut these flowers, the more they will bloom. Zinnias love full sun and well-drained soil, and they’ll thrive in the mid to late Summer heat.
Zinnias grow best in full sun (at least 6 to 8+ hours of direct sunlight per day). They prefer well-draining soils, but it’s not hard to grow them in other soils, like clay. The diseases that may plague zinnias, like powdery mildew and leaf spots, will have less of a chance of infection if the site where you’ve planted your zinnias has excellent air flow.
Excellent air circulation will reduce the amount of time that dew or rainwater rests on the plant leaves, which in turn will reduce the incidence of disease prevalence. Spacing zinnias adequately will help promote air circulation as well!
Final Thoughts
Zinnias are a wonderful plant to include on your garden list every season! There are many varieties and colors to choose from. So, there’s likely a zinnia for almost every spot in your garden or landscape (except full shade, remember?).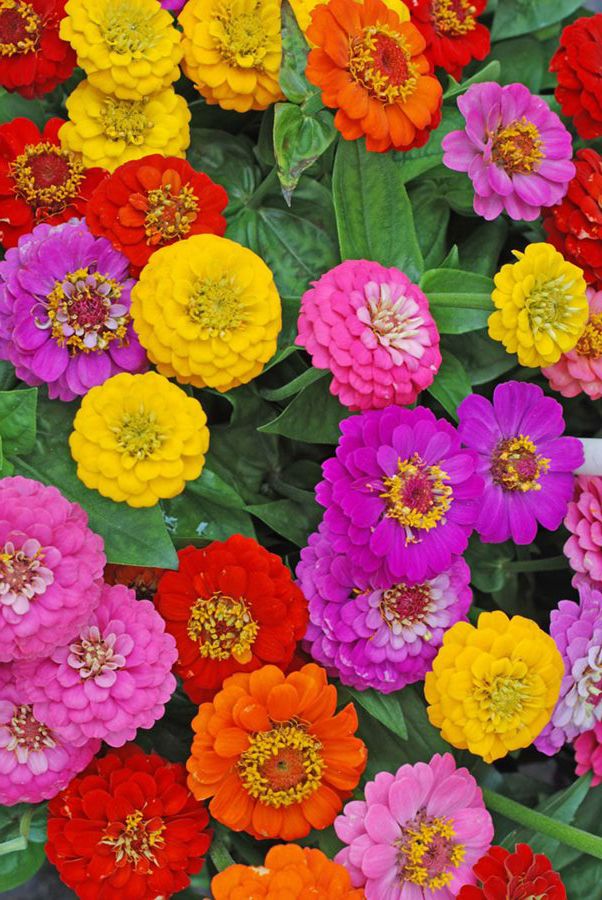
Spacing zinnias correctly is important for disease concerns and decreased competition between neighboring plants. It will also help make your garden aesthetically-pleasing. It’s important on know what variety you’re planting and where it’s going to be planted. After you have those basics, sit back and enjoy the beauty of zinnia blooms all Summer long!
SHARE THIS POST
Zinnias Love Summer but Need Their Space
By JULIE BAWDEN DAVIS
SPECIAL TO THE TIMES
Perhaps no other flower marks the coming of summer better than the zinnia. This heat-loving annual has striking, colorful round flowers that brighten up any garden.
Zinnias come in a variety of colors, including cream, yellow, red, gold, orange, pink, rose, lavender, purple, plum, scarlet, white and salmon. The flower also has many sizes, from several inches tall to 3 or 4 feet.
The flower also has many sizes, from several inches tall to 3 or 4 feet.
“May is a good month to plant zinnias,” said Gary Hayakawa, general manager of Three Star Nursery in Fountain Valley, a wholesale grower whose plants can be found in many Orange County nurseries.
“In May, zinnia roots have a chance to get established before the heat arrives,” he said. “Then once the weather warms up, they really take off. Zinnias do really well in hot areas.”
Many of the zinnias you’ll find in the nursery are medium-sized varieties, which grow 10 to 15 inches. Some common medium-sized varieties are the Peter Pan, Dreamland, Dasher and Pulcino.
You can also find dwarf zinnias, such as Thumbelina mix, that bloom at 3 inches. Tall varieties that grow 2 to 3 feet include State Fair and Dahlia-flowered.
Zinnias can also be grown from seed, and there are many seed types available.
To have success growing zinnias, keep the following tips in mind:
* Choose a full-sun location that does not get any overhead watering from sprinklers, as zinnias are prone to fungus.
* Amend the soil well before planting with homemade or bagged compost. Zinnias like a well-draining soil.
* Plant zinnias at the depth they are in containers, unless the plant is tall and unstable. In that case, plant it a little lower than the existing soil level.
* Give zinnias space, which promotes air circulation and prevents fungus and leaf spot problems. Large varieties should be spaced 12 inches apart and smaller varieties 6 inches apart.
* Plant zinnia seeds in small containers and then transplant or put the seeds directly in the ground.
To plant in containers, evenly space about six seeds in a 4-inch pot. Once they germinate, thin to four plants. Transplant in the garden when they are about 2 inches tall.
To direct seed, work the soil well and amend. Then make a small ditch with sides that are 3 or 4 inches high. This will hold the water in when you irrigate. Level the soil inside the ditch and place the seed exactly where you want the flowers to grow. Cover the seeds with a quarter-inch of potting soil and pat gently. Mist the bed twice daily until the seeds germinate.
Cover the seeds with a quarter-inch of potting soil and pat gently. Mist the bed twice daily until the seeds germinate.
* Water zinnias at ground level to prevent fungus. Once they are 3 to 4 inches high, water them deeply a couple of times a week, depending on weather. Zinnias aren’t drought tolerant, but they like their soil a little on the dry side. The soil should not be continuously wet.
* If we experience overcast June weather, cut down on watering. This will prevent fungus diseases. Once the hot days of July hit, fungus problems should disappear.
* Prolong bloom by removing faded blossoms.
* Fertilize regularly with an all-purpose fertilizer recommended for flowers.
care and planting in open ground, growing from seeds, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/en/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden Plants Substated: Last amendments:
Content
- Listen to Article
- Planting and Caring for Cynia
- Botanical description
- Cultivation of Qinia
- 9 900
- How to sow seeds
- Care for disorder
- Planting CNINIA in open soil
- them
- Diseases and their treatment
- Zinnia after flowering
- How and when to collect seeds
- Perennial zinnia in winter
The Aztecs have been cultivating zinnia since 1500, and it appeared in Europe in the 18th century, immediately becoming a favorite decoration of gardens and aristocratic receptions.
 By the twentieth century, zinnia was already cultivated on all continents, and from 1931 to 1957, the zinnia flower was even a symbol of the state of Indiana, USA.
By the twentieth century, zinnia was already cultivated on all continents, and from 1931 to 1957, the zinnia flower was even a symbol of the state of Indiana, USA. Today, about twenty species are known, many varieties and hybrids of this beautiful flower, which is distinguished by its beauty and undemanding to growing conditions.
Listen to article
Planting and caring for zinnia
- Planting: sowing seeds for seedlings - in late March or early April, transplanting seedlings into the ground - from mid to late May.
- Flowering: mid-June until frost.
- Lighting: bright sunlight.
- Soil: light, nutritious, well-drained, neutral.
- Watering: infrequent, but plentiful, under the root.
- Top dressing: during the seedling period - three times with mineral fertilizers with a low nitrogen content, after transplanting into the ground - at least twice: one month after planting and during the budding period.

- Reproduction: seed.
- Pests: May beetles and cockchafers, aphids, slugs and snails.
- Diseases: powdery mildew, Fusarium, bacterial spot, gray mold.
Read more about growing zinnia below
Botanical description
Depending on the species and variety, the height of zinnia can be from 20 to 100 cm or more. Zinnia leaves, entire, sessile, ovate, pointed to the top, pubescent with hard hairs, whorled or opposite. Inflorescences are apical single baskets with a diameter of three to fourteen centimeters, located on long peduncles. Reed flowers of zinnia, tiled in one or more rows, white, purple, orange, yellow, red - all possible colors except shades of blue; middle, tubular flowers - small, yellow or red-brown. The fruit is an achene with a tuft. Zinnia blooms from mid-June until frost, being resistant to heat and drought.
The zinnia plant is cultivated as a bright and unpretentious garden plant, which is excellent for cutting.
 Perennial zinnia grows only in regions with warm winters. In our climate, zinnia in the garden is exclusively an annual plant, since it is not able to survive even short and slight frosts. Summer residents call this flower major. Annual zinnias and marigolds, daisies and marigolds are staples for the rustic landscaping that is increasingly in vogue in Europe. Zinnia is also appropriate in a flower bed with so-called noble flowers, it is also grown in a garden among vegetables, using its remarkable ability to stretch upwards, almost without creating a shadow.
Perennial zinnia grows only in regions with warm winters. In our climate, zinnia in the garden is exclusively an annual plant, since it is not able to survive even short and slight frosts. Summer residents call this flower major. Annual zinnias and marigolds, daisies and marigolds are staples for the rustic landscaping that is increasingly in vogue in Europe. Zinnia is also appropriate in a flower bed with so-called noble flowers, it is also grown in a garden among vegetables, using its remarkable ability to stretch upwards, almost without creating a shadow. Growing zinnia from seeds
How to sow seeds
Perennial zinnia, like annuals, reproduces generatively. In places with a warm climate, where there are no frosts in May, planting zinnia directly into the ground is possible, but if night frosts are a common occurrence in your area, know that zinnia seeds sown in the ground will die already at a temperature of -1 ºC. That is why experienced flower growers believe that it is better to grow and harden this plant as seedlings, and then planting zinnia in the ground with subsequent rooting will be successful.

Before sowing, wrap the zinnia seeds in a cloth or gauze soaked in epin to determine which of them germinate and which do not. Fresh seeds hatch in a couple of days, and old seeds will take a week to sprout.
At the end of March or beginning of April, two or three viable seeds are sown spaciously to a depth of one centimeter in peat pots with a moist substrate, which will later avoid picking, which this culture does not like. Sowing is moistened and placed in a bright place. The optimum temperature for zinnia germination is 22-24 ºC. If you do everything right, sprouts will appear in a few days.
In the photo: How zinnia blooms
Seedling care
Young plants quickly form adventitious roots, and if the zinnia seedlings are stretched out, just add some soil to the pots. My zinnias didn’t stretch out very well, but a friend complained that she put the crops in partial shade, and the seedlings turned into painful translucent sprouts, so remember that zinnia seedlings require bright diffused light.
 With a sparse sowing of seeds, you do not have to dive seedlings, , especially since zinnia does not tolerate picking. At the end of May, in order for the planting of zinnia to be successful, the seedlings begin to harden, taking it out for a while in the fresh air during the day.
With a sparse sowing of seeds, you do not have to dive seedlings, , especially since zinnia does not tolerate picking. At the end of May, in order for the planting of zinnia to be successful, the seedlings begin to harden, taking it out for a while in the fresh air during the day. - Autumn planting of tulips - how to determine the timing of work, at what depth to plant?
Planting zinnias outdoors
When to plant zinnias
When to plant zinnias outdoors when can I plant zinnia seedlings? Planting of zinnia in the ground is carried out in the second half of May, towards the end of the month, when the danger of return frosts has passed. The plant prefers light areas, protected from the wind, with neutral, well-drained nutrient soil. Before planting zinnia, the intended area is cleared of weeds by digging the soil to a depth of 45 centimeters and adding to it when digging leafy humus, compost or rotted manure at the rate of 8-10 kg per m², and it is best to do this in the fall .

How to plant
Zinnia flowers are planted at a distance of 30-35 cm from one specimen to another by transshipment or together with a peat pot. You will see the flowering of zinnia in early July.
Caring for zinnia
Growing conditions
If the planting of zinnia was successful, we can talk about caring for it, which consists in regular loosening of the soil, weeding and infrequent but plentiful watering under the root so that water does not fall on the flowers. When zinnia begins to bloom, remove wilted flowers in time. Powerful stalks of zinnia do not need tying and props.
When to plant chrysanthemums to get lush blooms
Fertilizer
From the moment of germination until the time when zinnia is planted in the ground, seedlings are fed with mineral fertilizers with a low nitrogen content three times . A plant planted in the ground is fertilized with mineral fertilizers or liquid manure at least twice during the summer: the first time a month after planting, and the second - during the budding period.
 That's all the trouble. As you can see, planting and caring for zinnia is not burdensome at all.
That's all the trouble. As you can see, planting and caring for zinnia is not burdensome at all. How to pinch
Readers often ask if zinnia is pinched and, if so, how and when to do it. If you want the zinnia to bush, you need to pinch it over the third or fourth pair of leaves while still in seedlings, although you can do this when the zinnias in the open field have already taken root and take root. But if you want to grow elegant flowers for cutting on long peduncles, pinching zinnia is not needed.
In the photo: Variegated zinnia
Pests and pest control
The most common pests of zinnia are aphids, Maybugs, snails and slugs.
- Autumn planting of seedlings - why you should not rush and what are the optimal terms
Gastropods are usually lured to bowls of beer placed here and there on the plot, or pieces of slate or roofing material scattered between plants, under which mollusks like to crawl.
 You will have to collect them manually.
You will have to collect them manually. Maybugs will also have to be collected by hand and thrown into a bucket of soapy water. Aphids are destroyed by spraying zinnias with a solution of tar soap at the rate of 10 g per liter of water, and in case of severe infection, with a solution of Fufanon or Aktellik, prepared in accordance with the instructions.
Diseases and their treatment
Of the diseases, it is possible to infect zinnia with gray mold, fusarium, bacterial spot , but most often with powdery mildew. If at least one leaf of zinnia is disfigured by gray-brown spots of a round shape left on the plant by bacterial spotting, take immediate action: tear off the leaves that have traces of the disease, and in case of severe infection, destroy the entire plant - there is no cure for this disease.
Gray mold and fusarium are treated with fungicides (Topsin-M, Fundazol), as well as powdery mildew, which manifests itself as a white coating on the ground parts of zinnia - Topaz, Skor, Topsin are more suitable to get rid of this misfortune from fungicides.
I must say that diseases occur primarily due to violations of the rules for growing a plant, for example, due to too dense planting or excessive watering, so first diagnose the problem of zinnia, eliminate it if possible, and then do the work on the mistakes - re-read the rules for caring for the plant, find and analyze the discrepancy between them and how things really are. Only in this way can you avoid trouble in the future.
In the photo: Dense zinnia bushes
Zinnia after flowering
How and when to collect seeds
Zinnia seeds ripen about two months after the start of flowering, so mark a few of the buds that open first. First-order shoots have the best seeds, so all side shoots should be removed from the specimens you have chosen for seed ripening. When the ripened baskets turn brown, they are cut, dried, the seeds are peeled, the dry remains of the flowers are cleaned and stored in a dry place with a constant temperature.
 Zinnia seeds remain viable for 3-4 years.
Zinnia seeds remain viable for 3-4 years. In the photo:
Perennial zinnia in winter
As already mentioned, zinnia is grown as an annual plant in the garden. But if your zinnia does not grow outdoors, but in a container or pot, then bring the flower indoors with the onset of autumn and take care of it like a houseplant, turning it from an annual zinnia into a perennial.
- Evening: cultivation, care, types and varieties
Species and varieties
Of more than twenty species of zinnia, only four are grown in cultivation: elegant zinnia, narrow-leaved zinnia, aka Hage zinnia, fine-flowered zinnia and zinnia linearis. The first two species served as the basis for fruitful breeding work, and, thanks to its results, today we cultivate in gardens not only the main types of zinnia, but also many excellent varieties and hybrids of this plant.
Zinnia elegans
Herbaceous annual up to 1 meter high with simple white, orange and pink inflorescences.
 The stem is straight, for the most part not branched, rounded in cross section, densely pubescent with hard hairs, all shoots end in apical inflorescences-baskets. The leaves are sessile, entire, ovate, with a pointed apex, 5-7 cm long and 3-4.5 cm wide, the leaf surface is pubescent, like the stem. Inflorescences with a diameter of 5 to 16 cm, simple, semi-double and double, consist of reed flowers up to 4 cm long and up to 1.5 cm wide, painted in various colors, except for shades of blue, and median, tubular flowers of yellow or reddish-brown color .
The stem is straight, for the most part not branched, rounded in cross section, densely pubescent with hard hairs, all shoots end in apical inflorescences-baskets. The leaves are sessile, entire, ovate, with a pointed apex, 5-7 cm long and 3-4.5 cm wide, the leaf surface is pubescent, like the stem. Inflorescences with a diameter of 5 to 16 cm, simple, semi-double and double, consist of reed flowers up to 4 cm long and up to 1.5 cm wide, painted in various colors, except for shades of blue, and median, tubular flowers of yellow or reddish-brown color . Types and varieties of celosia - a flower of amazing beauty
Graceful zinnia blooms in June and can bloom until the very cold. In nature, it is most common in southern Mexico. In culture since 1796. Varieties and hybrids of elegant zinnia are classified according to several criteria: according to the structure of the inflorescences, according to their shape, according to the height of the stem and according to the timing of flowering.
On the photo: Zinnia elegans
Early-flowering, mid-flowering and late-flowering zinnias are distinguished by flowering time.
According to the structure of inflorescences, varieties are divided into simple, semi-double and double.
Depending on the height of the stem, there are:
- high zinnia (60-90 cm), grown for cutting, because it looks a little bulky in the flower bed;
- medium zinnia (35-50 cm) - suitable for both cutting and flower bed decoration;
- dwarf zinnia, or dwarf zinnia (15-30 cm) are usually well-branched shrubs grown both in flowerbeds and in balcony containers and simply in pots.
On the photo: Zinnia elegans
According to the shape of the inflorescences, zinnias are divided into seven categories. In our climate, the most commonly grown of them are:
- Zinnia dahlia – strong bushes, sprawling or compact, 60 to 90 cm high with shoots of the first order.
 The leaves are large - up to 12 cm long, inflorescences hemispherical, double, up to 14 cm in diameter. Varieties: Violet - terry zinnia 60-75 cm tall with dense inflorescences of different shades of purple, Orange kenig - on stems 60 to 70 cm high bright red-orange terry inflorescences up to 14 cm in diameter, Polar Bear - a compact plant up to 65 cm high cm with densely double white inflorescences with a greenish sheen;
The leaves are large - up to 12 cm long, inflorescences hemispherical, double, up to 14 cm in diameter. Varieties: Violet - terry zinnia 60-75 cm tall with dense inflorescences of different shades of purple, Orange kenig - on stems 60 to 70 cm high bright red-orange terry inflorescences up to 14 cm in diameter, Polar Bear - a compact plant up to 65 cm high cm with densely double white inflorescences with a greenish sheen; - zinnia midget, or zinnia pompom is a compact, branched shrub no higher than 55 cm with a large number of shoots of the second, third and fourth order, small leaves and small, only up to 5 cm in diameter, inflorescences resembling a pompom in shape. cap. Varieties: Little Red Riding Hood - a densely double variety up to 55 cm high with truncated-cone-shaped or rounded inflorescences of a bright red hue; Tom Thumb - a compact bush up to 45 cm in height with dense double red inflorescences in the form of a slightly flattened ball; Tambelina - a variety mixture of different shades with a bush height of up to 45 cm and an inflorescence diameter of 4 to 6 cm;
- fantasy zinnia almost spherical compact bushes 50-65 cm high with large leaves and loose curly inflorescences, in which narrow reed flowers are folded into tubules and bent in different directions, and at the ends some of them are bifurcated.
 Varieties: Fantasy - a bush up to 60 cm high with terry loose inflorescences up to 10 cm in diameter of different shades - purple, red, bright yellow, purple, red-orange, pink, white, salmon, etc .; The gift is bright red zinnia.
Varieties: Fantasy - a bush up to 60 cm high with terry loose inflorescences up to 10 cm in diameter of different shades - purple, red, bright yellow, purple, red-orange, pink, white, salmon, etc .; The gift is bright red zinnia.
In the photo: Zinnia elegans
Also popular in the culture of other countries:
- California giant zinnia - varieties of terry zinnias up to 16 cm in diameter with ligulate flowers and ligulate stems more. They differ in relatively late flowering;
- Giant cactus zinnia - cultivars from 75 to 90 cm high with double inflorescences up to 11 cm in diameter with reed flowers rolled into a tube, sometimes wavy with raised tips;
- Super cactus zinnia - varieties with inflorescences similar to giant cactus flowers, but not more than 60 cm high;
- zinnia scabiose-flowered (aka anemone-colored) - varieties with an inflorescence up to 8 cm in diameter, in which reed flowers are located in one row around the middle, consisting of tubular flowers overgrown with corollas, from which the middle looks like a hemisphere, painted to match the reed flowers.
Pictured: Zinnia elegans
Angustifolia zinnia (Zinnia angustifolia)
Or Haage zinnia (Zinnia haageana) also comes from Mexico. This is an annual upright plant that forms branched bushes. Leaves sessile, lanceolate or elongated, pointed. Inflorescences are small, simple or double, bright orange. Varieties:
- Glorienshine - strongly branched shrub up to 25 cm tall with double inflorescences, in which reed flowers are dark orange at the base, and red-brown at the ends;
- Series Persian Carpet Mixed With semi-double bicolor buds in red with lemon, white, orange and yellow, a large array of this zinnia really looks like an oriental carpet.
- The English variety mixtures Starbright and Classic also gained fame - plants with inflorescences of white, yellow and orange tones up to 30 cm in height with a thin and weak, but strongly branching creeping stem.
 These zinnias are mostly used as ground cover plants.
These zinnias are mostly used as ground cover plants. - Sombrero zinnias look pretty in the flowerbed - inflorescences of a red-brown shade with an orange border.
Pictured: Zinnia angustifolia (Zinnia angustifolia)
Fine-flowered zinnia (Zinnia tenuiflora)
Usually used for creating landscape flower beds and is a shrub about 60 cm high with articulated thin stems of a reddish hue. Inflorescences are small, up to 3 cm in diameter, reed flowers are narrow, bent, with twisted tips, purple hue. Varieties: Red Spider.
Zinnia linearis (Zinnia linearis)
It is sometimes confused with narrow-leaved zinnia because its leaves are thin and sharp, like the ends of nail scissors. This is the smallest of the cultivated species - branching, almost spherical bushes grow no higher than 35 cm. Linearis inflorescences are small, reed flowers of yellow color with an orange edge. Zinnia linearis is suitable for growing in pots, in balcony containers, on alpine slides and in small flower beds.
 Grades:
Grades: - Golden eye - white middle of tubular flowers, reed flowers of white color - the variety looks like an ordinary chamomile;
- Caramel - the color of the reed flowers is caramel yellow, the center is black;
- Yellow Star - variety with yellow inflorescences.
In the photo: Zinnia linearis
Many hybrids have been bred from the crossing of Haage zinnia and elegant zinnia, in particular, the Profusion series, which is very popular among flower growers - low bushes up to 35 cm, strewn with small multi-colored daisies. The Magellan series is also gaining popularity - bushes up to 35 cm tall with densely double dahlia-shaped inflorescences up to 10 cm in diameter of coral, cream, orange, pink, red, cherry, salmon and yellow colors. The Swizzle series has recently appeared in the gardens, consisting so far of two varieties - Cherry Ivory with cherry baskets with cream-tipped reed flowers and Scarlett Yellow with red buds and bright yellow tips.

Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Peculiarities and other plants of the family Asteraceae
- List of all species on The Plant List
- More information on World Flora Online
Cineraria: growing from seeds in the garden
How to treat and fertilize roses in August, whether to pruneSections: Garden plants Garden perennials Garden herbaceous plants Garden flowering plants Garden annuals Compositae (Asteraceae) Garden shrubs Plants on C
After this article is usually read
Add a comment
growing seeds for seedlings and planting in open ground
Zinnia is popularly called marjoram.
 Shrub perennial belongs to the Asteraceae family, South America is considered its homeland. The plant is very decorative, pleases with long flowering, and growing zinnia from seeds requires a minimum investment of time.
Shrub perennial belongs to the Asteraceae family, South America is considered its homeland. The plant is very decorative, pleases with long flowering, and growing zinnia from seeds requires a minimum investment of time. Description of the plant
Depending on the variety, the height of zinnia can range from 30 cm to one and a half meters. The flower has its own distinctive features, according to which its presence among other plants is always noticeable:
- Egg-shaped foliage. Along the edges with hard hairs.
- Quite large inflorescences are located on peduncles with single baskets.
- Varied color palette: red, magenta, yellow, white, orange.
- Fruits - a basket with a tuft.
Perennial plant blooms only in areas with warm winters. Flowers bloom in mid-July and do not wither until frost, retaining their shape and saturation of hue. Volumetric inflorescences on long stems set accents in flower beds with undersized crops, look great surrounded by tall flowers and among abundant green mass.

Requirements for soil and climatic conditions
Zinnia feels good and grows in almost all regions. The plant is grown at home and in gardens. The main thing is to provide comfortable conditions, plant them in a timely manner and do not forget about care.
Zinnias love sunshine and warmth. It is advisable to plant flowers away from tall trees and sprawling shrubs. The area should be well ventilated, but strong drafts can hurt as seriously as low temperatures. In cold weather, not only young, but also adult bushes can die.
Select areas with loose, well-drained, fertile soil for planting. Water stagnation on the territory is unacceptable. This can cause root rot and flower death. If the soil is very dense, sand or turf is added to it, this improves the drainage properties.
When to plant a perennial?
It all depends on the weather. If there are frosts at night, do not rush to sow seeds in open ground or transplant seedlings. The soil should warm up well, and the night temperature should not fall below 0 degrees.
 To plan your work, decide which growing method will be used. If you prefer seedlings, the best month for sowing is March. Planting zinnia seeds in open ground is carried out at the end of May.
To plan your work, decide which growing method will be used. If you prefer seedlings, the best month for sowing is March. Planting zinnia seeds in open ground is carried out at the end of May. Outdoor cultivation
Following a few simple rules will speed up the emergence of abundant, healthy seedlings. All work on the site is carried out sequentially:
- For 7-8 days, the seed material must be wrapped in a thin cloth moistened with a growth stimulator.
- Before planting seeds, the area is cleared, dug up, leveled.
- Make shallow grooves (no more than 5 cm) and place the hatched seeds in them (distance 30-35 cm). If planted too close, zinnias will grow small and weak. Landing pattern can be any. Most often, gardeners use curly, sowing seeds in a checkerboard pattern, in the form of a circle, rhombus, chamomile or heart.
Plants take a long time to sprout, so don't worry if sprouts don't appear for 2-3 weeks. As a rule, young bushes make their way to the light for a month, and seedlings are distinguished by rather thick leaves and legs.

Growing seedlings
Seeds for seedlings are soaked at the end of February or the first days of spring. Seedling containers can be used for sowing. The containers are filled with nutritious loose soil mixture, after which the seeds are distributed at a distance of 3 cm from each other. Sprinkle with soil on top and cover with a film.
Watch the seedlings. If the sprouts are intensively stretching upwards, most likely, she does not have enough light. Move the containers to a more lit place, but avoid direct sunlight.
Zinnia transplant is difficult to tolerate. Consider a possible delay in growth by about 1.5-2 weeks. Before planting, the plants are hardened, gradually accustoming them to outdoor living conditions.
Care of zinnia after planting
Zinnia is very hardy, but like all flower crops it needs care. In order for the plants to please with juicy green mass and luxurious flowering, you need:
- Water the flowers regularly and plentifully.
 Too frequent and superficial irrigation is unacceptable. Water the zinnia under the root. Water on leaves and branches can cause burns. In addition, moisture accumulating on the inflorescences deprives them of their attractiveness.
Too frequent and superficial irrigation is unacceptable. Water the zinnia under the root. Water on leaves and branches can cause burns. In addition, moisture accumulating on the inflorescences deprives them of their attractiveness. - Remove weeds. It is necessary to weed before flowering. For fragile seedlings, long-term proximity to weeds is undesirable. Zinnias will lack moisture and nutrients, leading to disease and stunted growth.
- Apply complex fertilizers. It is permissible to use universal compositions, mineral complexes with a minimum nitrogen content. Organics are used to enrich the soil, but it is not recommended to abuse organic mixtures, otherwise this will lead to the spread of powdery mildew.
- Loosen dry soil. After watering, the soil hardens. A crust forms, which prevents the penetration of air to the roots. This negatively affects the development of zinnias. Regular loosening of the earth provides normal air access.
- Pinch off top shoots.