Kidney beans growth
Tips On Caring And Harvesting Kidney Beans
Kidney beans are a healthy inclusion to the home garden. They have antioxidant properties, folic acid, vitamin B6, and magnesium, not to mention they are a rich source of cholesterol-lowering fiber. One cup (240 mL.) of kidney beans provides 45 percent of the recommended daily intake for fiber! High in protein, kidney beans, and other beans are a vegetarian’s mainstay. They are also a good choice for folks with diabetes, hypoglycemia, or insulin resistance because their rich fiber content keeps sugar levels from rising too rapidly. With all that goodness, the only question is how to grow kidney beans.
How to Grow Kidney Beans
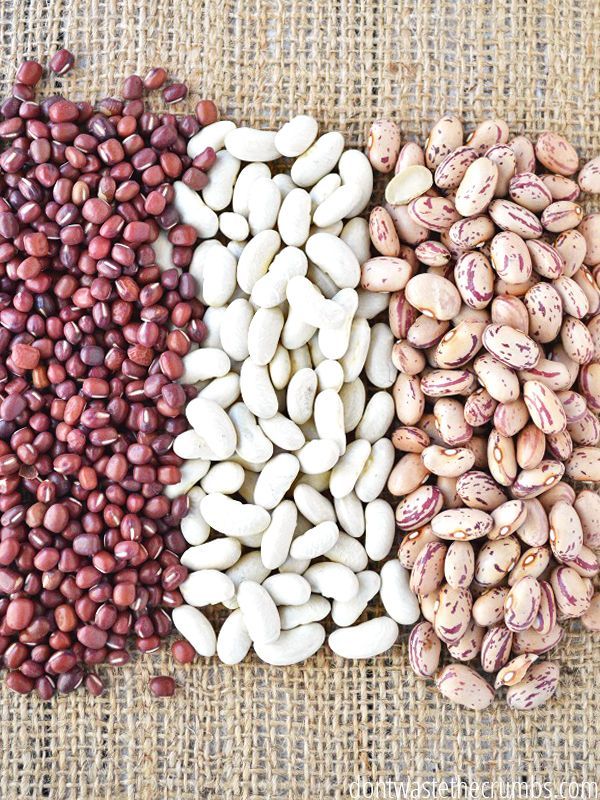
There are a number of kidney bean varieties to choose from. Some of them, like Charlevoix, are more prone to viruses and bacteria, so do your research. They come in both bush and vine varieties.
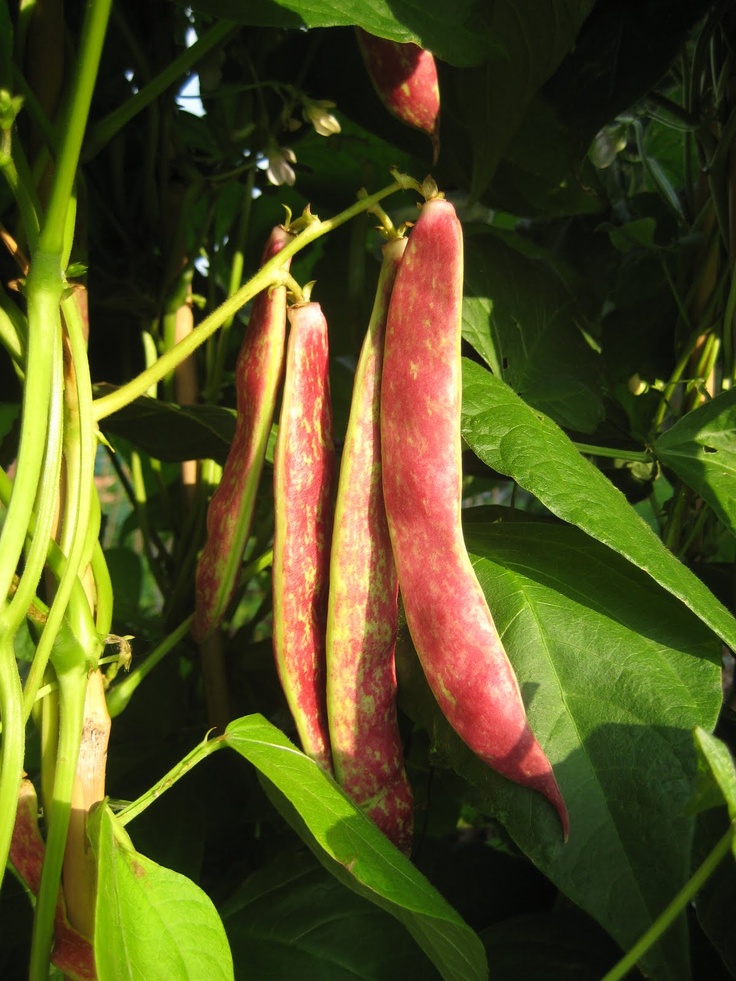
In the same family as black beans, pinto, and navy beans, these big red beans are a staple in most chili recipes. They are only used dried and then cooked, as the raw beans are toxic. A few minutes of cooking time, however, neutralizes the toxins.
Kidney beans do best in USDA growing zones 4 and warmer with temps between 65-80 F. (18-26 C.) for most of their growing season. They don’t do well transplanted, so it’s best to direct sow them in the spring after the last frost date for your area. Don’t plant them too early or the seeds will rot. You may want to lay down some black plastic to warm the soil.
Plant them in full sun exposure in well-draining soil. Beans don’t like to get their “feet” wet. When growing kidney beans, space the seed 4 inches (10 cm.) apart for vining beans and 8 inches (20.5 cm.) apart for bush varieties, one inch to 1 ½ inch (2.5 to 4 cm.) below the soil surface. The growing kidney bean seedlings should emerge between 10-14 days from planting. Keep in mind that the vining types will need some sort of support or trellis to grow on.
Beans shouldn’t be grown in the same area more than once every four years.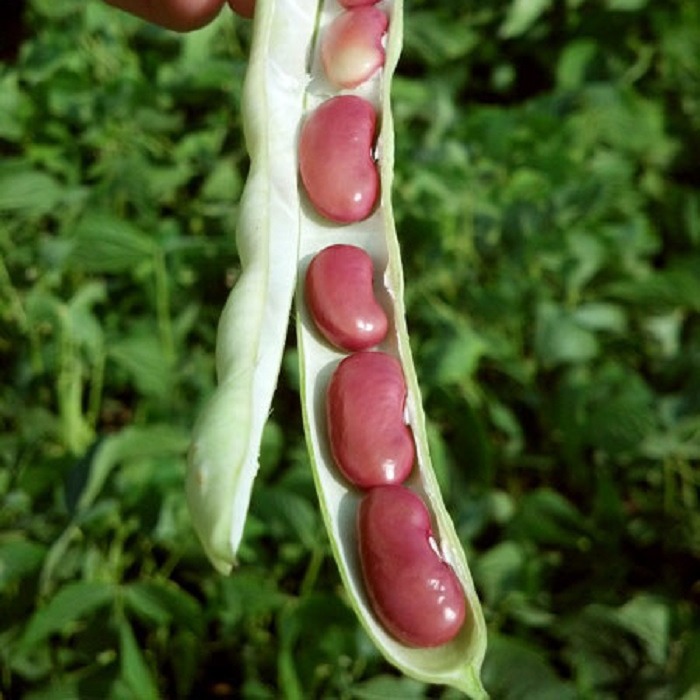 Plants such as corn, squash, strawberries, and cucumber benefit from companion planting with beans.
Plants such as corn, squash, strawberries, and cucumber benefit from companion planting with beans.
Kidney beans can be container grown, but it is best to use a bush variety. For each plant, use a 12-inch (30.5 cm.) pot. Keep in mind that it takes 6-10 bean plants to supply enough for one person’s use so container growing, while possible, may be impractical.
Care of Kidney Beans
The care of kidney beans is minimal. Beans produce their own nitrogen, so it usually isn’t necessary to fertilize the plants. If you feel compelled, however, be sure not to use a food that is high in nitrogen. This will only stimulate lush foliage, not bean production.
Keep the area around the beans free from weeds and keep them lightly moist, not wet. A good layer of mulch will aid in retarding weeds and maintaining moist soil conditions.
Harvesting Kidney Beans
Within 100-140 days, depending upon the variety and your region, the harvesting of kidney beans should be near. As the pods start to dry out and yellow, quit watering the plant. If it is not too humid and you have left plenty of space between plants, the beans may well dry on the plant. They will be hard as rocks and desiccated.
As the pods start to dry out and yellow, quit watering the plant. If it is not too humid and you have left plenty of space between plants, the beans may well dry on the plant. They will be hard as rocks and desiccated.
Otherwise, when the pods are the color of straw and it’s time to harvest, remove the entire plant from the soil and hang it upside down inside in a dry place to allow the beans to continue to dry out. Once the beans have completely cured, you can keep them in a tightly sealed container for about a year.
How to grow kidney beans – a healthy inclusion to the home garden
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Learn how to grow kidney beans for a versatile ingredient that’s packed with flavor and goodness.
Kidney beans are a fantastic source of protein and dietary fiber, and are rich in nutrients including iron, vitamin B6 and folic acid. Eating them regularly can help to control blood sugar levels as they are low on the glycemic index, and they can even reduce cholesterol when eaten in place of meat.
So much more than a staple of hearty chilis, kidney beans can be enjoyed in salads, stews and soups. They can also be dried and stored for year-round use, making them a fantastic addition to your kitchen garden ideas.
Kidney beans are easy to grow, but you do need to consider whether your local climate is suitable. 'They grow well in temperate climates, and love a temperature range of around 59-77°F (15-25°C),’ says Aditya Abhishek, a horticultural expert for Agriculture Review .
Bear in mind that kidney beans must be properly cooked before eating, as they contain lectin, which can cause sickness if not diminished through boiling.
(Image credit: Digihelion / Alamy Stock Photo)
How to grow kidney beans – step-by-step guide
Ideally you should sow your kidney beans in the spring. ‘Generally you can sow seeds from February to March for a good germination rate,’ says Abhishek. ‘However, this can vary according to local climate. In hot tropical areas, you can start sowing seeds from mid October to November. ’
’
The key issue when deciding when to plant kidney beans, is whether the soil feels warm enough. ‘Kidney beans love warm soil, so they should be planted only after the last frosts – otherwise, they will rot,’ says Emilly Barbosa Fernandes, small space gardener at HouseGrail .
- First, choose a good site to sow your kidney beans. ‘Select a spot that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. This will help in good vegetative growth and reduce the risk of pests and diseases,’ says Abhishek. ‘You need well-drained, loose soil that is rich in organic matter – soil pH in the range of 6.0 to 7.0 is ideal.’
- It’s important to space the plants to give them enough room to grow, as kidney beans do not like to be transported. ‘Grow pole beans at least 4 inches apart and increase that to 8 inches apart for bush kidney beans,’ explains Jason White, CEO of All About Gardening .
- To maximize chances of success, plant two seeds close to each other, and remove the weaker seedlings as they grow.
 ‘Sow the seeds 1-2 inches deep to guarantee that the plant will stay firmly in the ground,’ says Barbosa Fernandes. ‘Otherwise, wind or rain will easily break shallowly planted plants.’
‘Sow the seeds 1-2 inches deep to guarantee that the plant will stay firmly in the ground,’ says Barbosa Fernandes. ‘Otherwise, wind or rain will easily break shallowly planted plants.’ - Cover the kidney beans with soil, firm the ground and water them lightly.
- The seeds should germinate within two weeks, but it will take a little time before your beans are ready to harvest. ‘It will take around 100-140 days for the plant to mature, and to produce kidney beans,’ says Abhishek.
- Keep the plants moist, but do not over water them. ‘Kidney beans only need minimal care, so avoid watering them constantly,' says White. ‘Add a layer of mulch to help in retarding weeds and to maintain moisture in the soil.’
It is better to grow kidney beans in the ground, but if you choose a pot of at least 12-inch diameter, they can make a good vegetable garden container idea. Plant one seed per pot.
(Image credit: Digihelion / Alamy Stock Photo)
Do kidney bean plants need support?
Pole varieties of kidney beans will require support as they grow, so investigate one of the many vegetable garden trellis ideas.
The most simple solution is to add a cane close to the planting hole, when sowing the seeds. You can then tie in the vines as they grow.
If you are growing a bush variety of kidney bean, then the plants won’t require much support, but do keep an eye on them in bad weather.
Which variety of kidney bean?
When investigating how to grow kidney beans, there are a number of varieties to choose from, but bear in mind that some are more susceptible to viruses than others.
‘By picking the right varieties you will have better chances to have a good, healthy harvest,’ says Barbosa Fernandes. ‘I advise beginners to pick the kidney bean varieties that are less prone to mosaic viruses such as NY-15 and BY-1.
‘If you want to plant dark red kidney beans, Montcalm is a good variety that is resistant to viruses. Redkloud, Ruddy, and Redkote are good varieties of light red kidney beans that are resistant to major kidney beans viruses.’
(Image credit: Mongkol Nitirojsakul / EyeEm / Getty Images)
How to harvest kidney beans
You can harvest kidney beans when the pods are plump with well-formed beans – at this stage the pods will have yellowed and the beans will feel quite hard.
One of the benefits of growing kidney beans is that they can be dried and stored away for future use. To do this, remove the plants from the ground and hang them upside down in a dark, dry area.
It will take anything from a few days to a couple of weeks to cure the beans, at which stage you can remove them from the pods and store in an airtight container.
To rehydrate dried kidney beans, soak them in water for at least 8 hours, followed by a good rinse. Then, before eating them you must cook them to destroy the lectin – this requires a minimum boiling time of 10 minutes.
How long does it take to grow a kidney bean?
It takes anywhere from 3-5 months to grow kidney beans from seed to harvest, but germination will happen in as little as a few days.
‘Sprouting typically takes at least five days, but the length of time varies with temperature. Generally speaking, warmer temperatures make beans grow faster,’ says Pascal Harting from Gardening Lord .
Are kidney beans easy to grow?
Kidney beans are easy to grow if you live in a mild climate and have fairly neutral soil.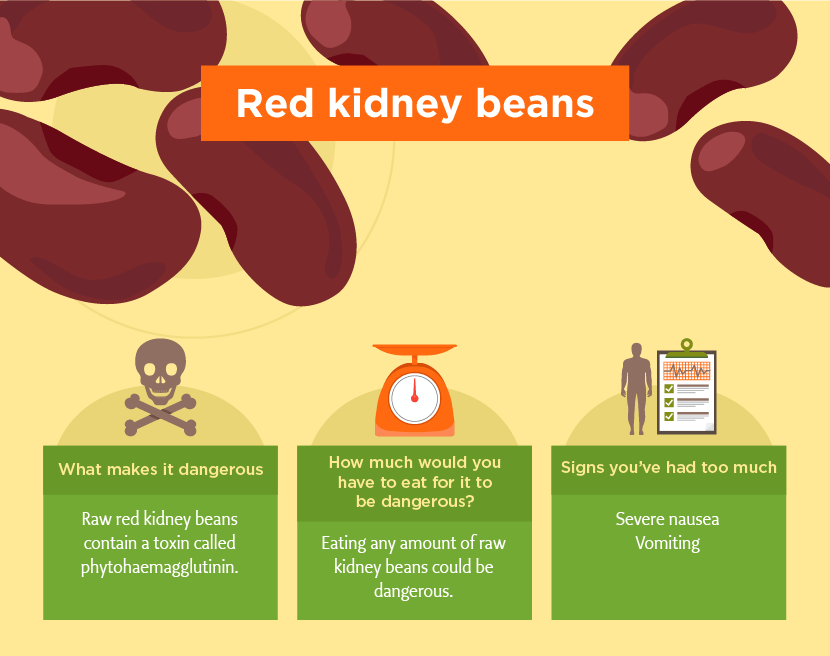 They are low-maintenance plants, and do not like being over-watered.
They are low-maintenance plants, and do not like being over-watered.
Kidney bean issues
Keep an eye out for pests when growing kidney bean plants. ‘Leafhoppers, slugs, aphids, and beetles are all attracted to kidney bean leaves,’ says Barbosa Fernandes. ‘Handpicking and organic pesticides are the ideal methods to get rid of these pests.’
If aphids are present, you can easily make your own treatment spray using a very weak concentration of dish soap.
'While watering kidney bean plants, avoid wetting of leaves as it can promote fungal infection in the plant,' adds Abhishek.
As editor of Period Living, Britain's best-selling period homes magazine, Melanie loves the charm of older properties. I live in a rural village just outside the Cotswolds in England, so am lucky to be surrounded by beautiful homes and countryside, where I enjoy exploring. Having worked in the industry for almost two decades, Melanie is interested in all aspects of homes and gardens. Her previous roles include working on Real Homes and Homebuilding & Renovating, and she has also contributed to Gardening Etc. She has an English degree and has also studied interior design. Melanie frequently writes for Homes & Gardens about property restoration and gardening.
She has an English degree and has also studied interior design. Melanie frequently writes for Homes & Gardens about property restoration and gardening.
from seed to adult plant, life cycle
Beans are considered a popular member of the legume family. It is a thermophilic and sensitive plant. However, most gardeners can grow crops in the middle lane. Beans are characterized by a different structure. Its fruits differ in taste, color, features of use. For successful cultivation of crops in the garden or at home, it is important to study the features of the formation and stages of germination of beans.
Content
- Growth of legumes
- Stage of bean seed germination
- Stage of BOB growth
- Reproductive stage of Bob
- Stage Pollination
- Stage of Green beans
Growth of bobic seeds
1 9000 plants have a number of characteristics. The optimal temperature regime for seed germination is +15…+26 degrees. In more severe conditions, seed germination deteriorates and the development of pods is disrupted.
In more severe conditions, seed germination deteriorates and the development of pods is disrupted.
It is important to choose the right timing for planting this crop. This is best done a week after the threat of frost has passed. Beans are recommended to be planted at intervals of 5-7 cm. This helps to provide them with optimal nutrition and enough space.
Important! It takes an average of 2-3 months for the beans to reach full maturity. In this case, the specific period is determined by the variety, climatic conditions, soil conditions.
Beans need moist soil that has good drainage. At the same time, the pH parameters should be 6-7.2. Untreated soil or high humidity can cause beans to rot.
It is important to ensure that the soil does not have a high moisture retention capacity. Excess water can cause rotting of grains or sprouts. Don't use too much fertilizer. This plant does not need a lot of feeding. It develops well in normal soil. However, to improve its quality characteristics, organic is suitable.
However, to improve its quality characteristics, organic is suitable.
Nutrient soil is required for good seed germination
Germination stage of leguminous seeds
Favorable conditions are required for the development of beans. The bean germination phase begins at a temperature of +15…+26 degrees. In this case, they begin to sprout after 2-3 days.
Observation of the germination of bean seeds shows that the beans include 2 cotyledons and a root, which subsequently transforms into a complete root system. Also at this stage of germination, a plume appears, forming a shoot, and a hypocotyl, which subsequently develops as a stem. All these fragments are in the seed coat.
The germination process begins at the stage of swelling of the beans. This happens under the influence of moisture. As a result, a rupture of the seed coat is observed and a root appears.
Important! This stage of bean growth is important. Sprouting seeds helps to get strong sprouts that help to endure lower temperatures and develop into a vigorous plant.
Before starting the process, it is necessary to select the highest quality seeds. In this case, damaged, moldy or shriveled grains must be removed. There are several sprouting methods. However, they all come down to providing the bushes with enough moisture and light. This helps to soften the tough skin and speed up the swelling of the seeds.
The process of seed germination depends on a number of factors. These include the following:
- Water - helps to activate growth processes and promotes the decomposition of complex spare elements.
- Heat - stimulates chemical reactions, including those that occur in grains.
- Air - all living cells need oxygen for proper respiration.
- Light - Sufficient light is required to initiate growth processes.
- Nutrients - saturate the embryo before the start of the photosynthesis process.
- Planting depth - the larger the seed, the deeper they can be planted.
Popular options for sprouting beans include:
- Wrap the beans in 2 layers of damp gauze.
 At the same time, it is important to ensure that the fabric is not very wet, otherwise there is a risk of mold. To prevent the appearance of plaque, gauze needs to be washed and squeezed out several times a day. If you want to plant beans in the ground as soon as possible, you can mix water with growth stimulants. Thanks to this, sprouts will appear the next day.
At the same time, it is important to ensure that the fabric is not very wet, otherwise there is a risk of mold. To prevent the appearance of plaque, gauze needs to be washed and squeezed out several times a day. If you want to plant beans in the ground as soon as possible, you can mix water with growth stimulants. Thanks to this, sprouts will appear the next day. - Place the seeds in a glass container and cover it with damp gauze. This means that the material must not come into contact with the grains. Thanks to the use of this method, it is possible to protect the beans from rotting. However, germination will take 2-3 days. The container must be constantly warm.
- Take cotton wool and make balls out of it. Moisten them a little with water. Put 1 grain on top and move them into a glass dish. Place the container in a bright and warm place. The first changes will be noticeable in a few hours. In this case, the sprouts will appear the next day.
Please note! Sprouted beans can not only be planted in the ground, but also eaten.
It saturates the body with useful substances and improves its functioning.
Bean seeds require a damp cloth to germinate. This element connects the spine to the drain. The direction of growth of this part of the bean depends on the sunlight.
Under its influence, it begins to grow upwards and straightens up. This results in a change in orientation. Thus, the sprout rushes to the top and develops into leaves. Cotyledons gradually degenerate and fall off. At the same time, after 6 weeks, the beans become a mature plant. This completes all stages of germination of bean seeds.
The bean growth stage has a number of characteristics
The bean reproductive stage
Legumes have male and female reproductive organs. The stamens, which include filaments with anthers, form the male reproductive organs. Carpel contains the brand, style and ovary, and therefore refers to the female reproductive organs.
Male gametes are formed in special sacs in the anther structure. They are called pollen grains. In this case, female gametes appear in the ovary.
They are called pollen grains. In this case, female gametes appear in the ovary.
Pollination and fertilization stage
After the formation of male and female gametes, the stage of pollination begins. Pollen grains fall on the stigma of the flower, which entails a number of processes.
After the pollen grains are attached to the stigma, they germinate and form a pollen tube. It passes into the ovary and provides a pathway for the movement of sperm. As a result, they penetrate the ovary. There, the fertilization process takes place, which contributes to the formation of the endosperm and zygote.
Green bean stage
Nutrients from the endosperm promote the development of the zygote in the ovary structure. Subsequently, they transform into beans, and the ovary enters the pod. At this stage, the bean pods are green in color and have a delicate texture.
Young pods and grains gradually lose moisture as they mature. This entails scattering the beans in the pod. Such grains are fully prepared for the start of a new cycle. They can be used to get the next bean bush.
Such grains are fully prepared for the start of a new cycle. They can be used to get the next bean bush.
Please note! Beans are an annual crop that completes its life cycle in 1 growing season.
At the green bean stage, the pods have a delicate texture
For self-cultivation, you need to know the development of the bean seed by day, which is shown in the table:

Watching beans germinate every day is considered quite an exciting process. Before planting the plant, it is advisable to germinate the seeds. This will significantly speed up the emergence of sprouts and help shorten the life cycle of the plant.
Influence of external environmental factors on seed growth (by the example of beans)
- Authors
- Executives
- Job files
- Award documents
Konovalova S.M. 1
1MBOU gymnasium No. 2 of the city of Krasnogorsk
Pastukhova N.V. 1
1MBOU Gymnasium No. 2 of the city of Krasnogorsk
The author of the work was awarded a diploma of the winner of the III degree
Diploma of a student Certificate of the head
The text of the work is placed without images and formulas.
The full version of the work is available in the "Files of the work" tab in PDF format
Introduction
Actuality: The world of wildlife is diverse and wonderful, necessary for the life of every living creature on our planet, which appeared long before man appeared. But at the same time, every time we can discover something new and amazing in it.
The choice of this topic of the project was interesting for us because we need to investigate what conditions are most favorable for plants, using the example of bean seed. It is necessary to preserve the conditions of the habitat so that life on our planet can continue.
A plant begins its life from a seed. A tiny seed falls into the ground, begins to grow, a root appears, then leaves, flowers and fruits. But for this it is important that there are optimal conditions for seed germination.
This was the basis for the study of the creation of our project. Among the variety of plants, there are those that are not very whimsical to environmental conditions. Since beans are grown all over the world, it can be assumed that beans do not require special environmental conditions.
Among the variety of plants, there are those that are not very whimsical to environmental conditions. Since beans are grown all over the world, it can be assumed that beans do not require special environmental conditions.
In the conditions of significant human influence on the world of wildlife and changing climatic conditions on our planet, it is very important to study plants that do not require special conditions for their growth.
Purpose: Investigate the influence of environmental factors and identify the most favorable conditions for the germination of the bean seed.
Tasks:
1. Review the literature on growing conditions for plants.
2. Study the conditions necessary for the germination and growth of seeds at home.
3. Experiment with the germination and growth of beans at home.
4. Summarize the results obtained and draw conclusions.
Summarize the results obtained and draw conclusions.
Object of study: germination and growth of a plant of the legume family.
Subject of research: germination conditions of bean seed.
Research Hypothesis: It is assumed that optimal environmental factors have a positive effect on plant germination and growth.
Research methods:
Literature review;
Surveillance;
Conducting an experiment.
What do I know about beans
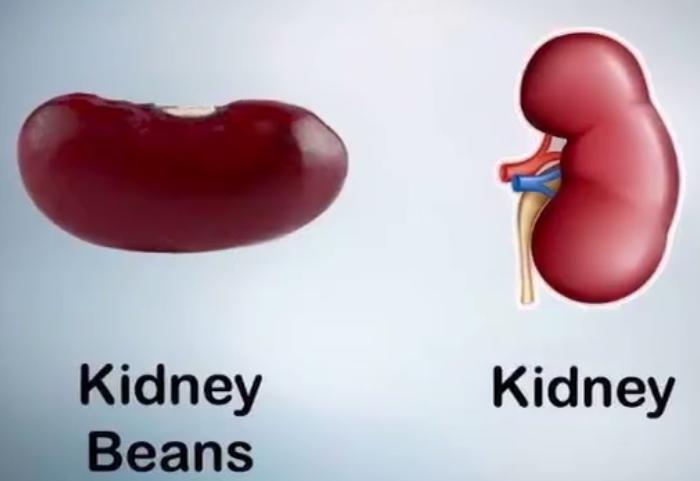
| Common beans (lat. Phaséolus vulgaris) - species of plants from the genus Beans of the leguminous family. | Beans are one of the oldest crops in the world. The place of origin is considered to be South and Central America. In Russia, beans appeared around the 17th century, first as a decorative flower crop, and since the 18th century they have firmly taken their place in the kitchen. Beans are among the top ten most useful vegetables in terms of nutritional value. In terms of protein content, beans are second only to meat. |
Beans come in many varieties and varieties. Varieties differ from each other in the shape and color of leaves, flowers and fruits. Both seeds and beans (pods) are used for food.
-
"There are many types of beans
And it grows on the field
Or weaves along the top
Where it is necessary, as it is necessary.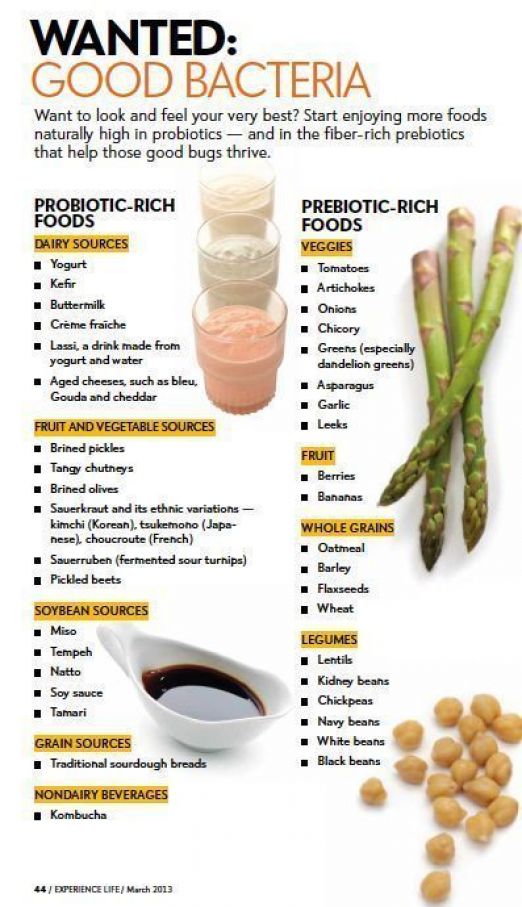
It's good when in the garden
She will be delicious sweet
In vinaigrettes and salads
Rich in vitamins.
2.1 Structure of beans
The bean fruit is a bivalve bean (not a pod), straight or curved. The bean contains, as a rule, from 4 to 10 seeds, the longer the pod, the more oblong the fruits have. In short beans, the seeds are usually rounded, while in flat beans, they are flattened.
All flowering plants propagate by seeds. The seed contains everything needed for the growth of a new plant.
The main part of the seed is the embryo , which is the germ of a new plant. In order for the embryo to develop, the seed contains a supply of nutrients. The seed is covered on the outside by a seed coat, which performs a protective function.
The embryo is the germ of the future plant.
It consists of germinal root, germinal stalk, germinal bud and cotyledons.
Embryonic root - the beginning of a new root. When a seed germinates, it develops first, breaks the seed rind and fixes itself in the soil.
Germinal stalk - the beginning of a new stem. It is located between the germinal bud and the germinal root.
Leaves, branches, flowers of the plant develop from germinal buds .
Cotyledons are the first leaves of the embryo. The number of cotyledons in a plant seed is an important feature. It is used when dividing all flowering plants into two large groups: monocots (the seeds of which contain one cotyledon (rye, wheat, oats, corn, onions, etc.) and dicots (the seeds of which contain two cotyledons (cucumbers, pumpkins, peas, beans) , apple, daisies and etc.)
Germination of seeds, the process of transition of seeds from a state of dormancy to intensive life activity, as a result of which the embryo starts to grow and a seedling is formed, from which a young plant develops. Germination of seeds occurs only when they are sufficiently provided with moisture, oxygen, at a certain temperature, and sometimes even light conditions. With a lack of oxygen, for example, when the seeds are immersed in water for a long time, substances harmful to the embryo (ethyl alcohol, lactic acid, ammonia, etc.) accumulate in them. The effect of temperature on seed germination is associated not only with the entry of moisture into the seeds and the activation of metabolism, but also with a change in the ratio of various growth regulators in them.
Germination of seeds occurs only when they are sufficiently provided with moisture, oxygen, at a certain temperature, and sometimes even light conditions. With a lack of oxygen, for example, when the seeds are immersed in water for a long time, substances harmful to the embryo (ethyl alcohol, lactic acid, ammonia, etc.) accumulate in them. The effect of temperature on seed germination is associated not only with the entry of moisture into the seeds and the activation of metabolism, but also with a change in the ratio of various growth regulators in them.
An interesting fact is that the germination of bean seeds lasts for 700 years.
2.2 Beans
String beans can be both bush and climbing , it has excellent decorative qualities, therefore it is loved by gardeners.
Curly legumes:
| Curly bean lashes can be up to 5 meters long, so it is most often grown near fences, walls of houses or other buildings. |
The vegetative period of varieties of curly beans is longer than that of bush forms.
Bush
| Bush bean is a low plant with a bush height of no more than 60 cm. Since it does not require support, it is grown in farms and for industrial purposes. Most varieties of this subspecies are characterized by early maturity, unpretentiousness, cold resistance and high yields. |
Vegetable and grain beans
Beans can be classified according to the way they are eaten:
- grain
- and vegetable, that is, ripe beans or shoulder blades are used for food along with unripe grains.
Grain beans.
In the grain variety, only the seeds are edible. Before use, the beans are shelled, hence another name for this variety - shelled beans. Beans (pods) of such beans have a hard wax coating, they are tough and tasteless. But the beans themselves are excellent in taste, have a varied appearance and special nutritional value.
Vegetable beans.
It differs from the grain one in that not only the grains, but also the pods themselves are edible. For this reason, vegetable beans are often referred to as green beans, asparagus, or sugar beans.
2.3 Health benefits of beans
It has been established that the plant reduces blood sugar levels, therefore, in folk medicine, a decoction of dry bean leaves is used for mild forms of diabetes, as well as for chronic pancreatitis. Bean seeds increase the secretion of gastric juice.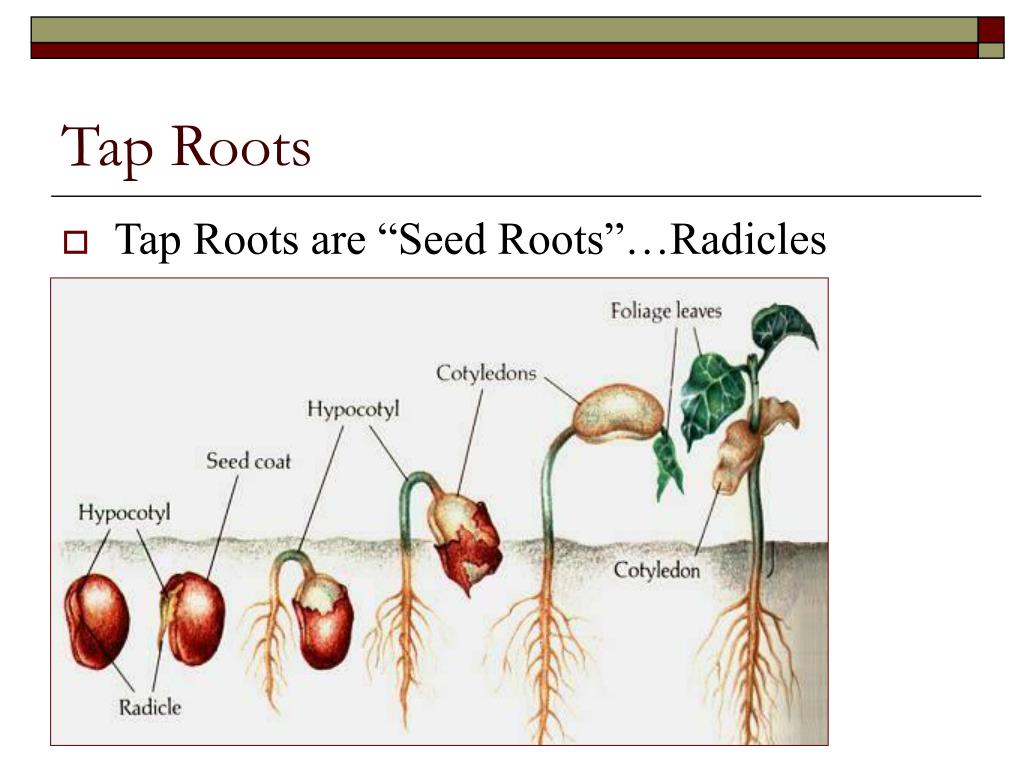 Due to the high content of potassium, beans are used for gastritis with reduced secretion of the gastric glands, for kidney disease and gout. Bean sashes are used mainly in the form of decoctions and infusions.
Due to the high content of potassium, beans are used for gastritis with reduced secretion of the gastric glands, for kidney disease and gout. Bean sashes are used mainly in the form of decoctions and infusions.
2.4 Use of beans in cooking
Bean dishes are very popular, in almost all countries of the world, where it is grown. Beans are cooked from soups to desserts.
-
Chili con carne with beans and tomatoes popular in Latin American cuisines
Pilaki
National dish in Turkey
Red bean lobio with eggs, meat, mushrooms, tomatoes, chopped nuts, pomegranate seeds and celery - a traditional Georgian dish
Chocolate Diet Black Bean Cake
Results of a study on sprouting beans
Preliminarily took one glass of bean seeds of one variety. Before sowing, bean seeds were soaked in warm water for one night (Fig. 1). Later, before germination, they were placed in a damp cloth, which was constantly moistened, but not so much that the beans floated in water (Fig. 2). On the fifth day, when the bean seeds germinated, 6 samples of germinated bean seeds were selected, approximately the same in shape and size of the seedling (Fig. 3). And on the same day, the samples were planted in the ground in cups (Fig. 4).
Before sowing, bean seeds were soaked in warm water for one night (Fig. 1). Later, before germination, they were placed in a damp cloth, which was constantly moistened, but not so much that the beans floated in water (Fig. 2). On the fifth day, when the bean seeds germinated, 6 samples of germinated bean seeds were selected, approximately the same in shape and size of the seedling (Fig. 3). And on the same day, the samples were planted in the ground in cups (Fig. 4).
-
Fig. 1. Soaking seeds.
Fig.2. Soaked seeds in a damp cloth.
Fig.
 3. Sampling.
3. Sampling.
Fig.4. Planting samples in the ground.
As mentioned above, 6 samples were selected for the experiment, 2 for each temperature and light conditions.
All specimens planted on October 28, 2019. By conducting the experiment, we will find out what conditions are best for the germination of beans.
-
Samples 1 - grew in the light and in heat. Moreover, one of them will be placed in a loosely closed, transparent jar.
Samples 2 - grew on a balcony (loggia) in the light at a temperature of +8 to -2 (depending on the weather in the autumn).
Samples 3 - grew on a balcony (loggia) in a dark place (in a turned off refrigerator) at a temperature of +8 to -2 (depending on the weather in the autumn).

The following photo (dated October 29, 2019) shows that the growth rate of plants is different, which was noted in the growth dynamics and was observed during the entire experiment.
-
10/29/2019
Fig.5
The seed on the window sill in the bank from all the samples gave the first shoots.
-
10/29/2019
Fig.6
Seed on the windowsill
10/29/2019
Fig.
 7
7 Semen on the balcony (loggia)
10/29/2019
Fig.8
Seed on the loggia in the dark (refrigerator)
-
10/30/2019
Fig.9
Seed on the windowsill in a jar
10/30/2019
Fig.10
Seed on the windowsill
10/30/2019
Fig.11
Semen on the balcony (loggia)
10/30/2019
Fig.
 12
12 Seed on the loggia in the dark (refrigerator)
-
10/31/2019
Fig.13
Semen in a cup on the windowsill and a seed in a jar almost the same height
10/31/2019
Fig.14
Semen in a cup on the windowsill and a seed in a jar almost the same height
10/31/2019
Fig.15
Seed on the balcony (loggia). Didn't germinate at all.
10/31/2019
Fig.
 16
16 Seed on the loggia in the dark (refrigerator). Didn't germinate at all.
Fig.17. The seed in the cup on the windowsill and the seed in the jar became even, and after opening the lid, parallel growth of both plants was noted.
We have found that the process of germinating a bean seed can be divided into several stages:
stage - absorption of water;
stage - swelling of seeds;
stage - increase in the size of cell division;
stage - the appearance of the spine;
stage - the appearance of the embryonic shoot.
At the same time, we determined the optimal conditions for seed germination. So the combination of light, humidity and temperature conditions favorably had a favorable effect on seed germination. Whereas low temperatures, lack of light had a delay in seed germination.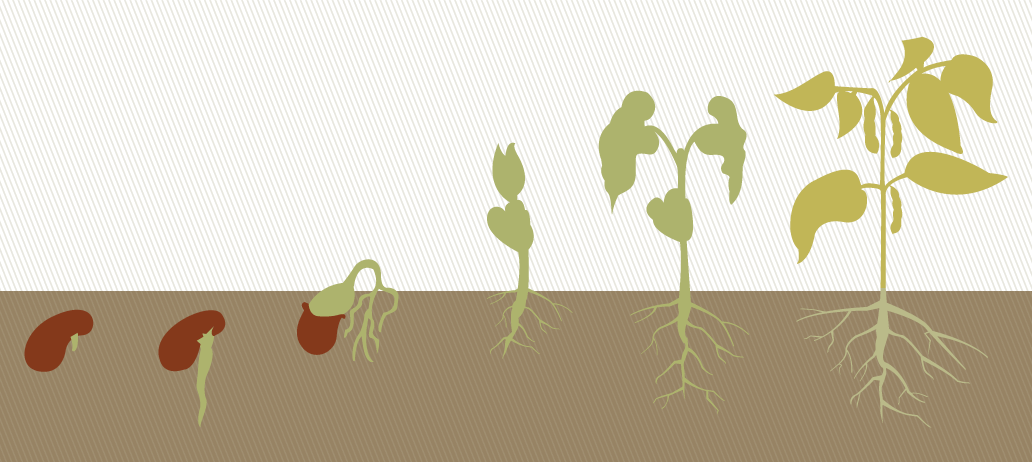 An interesting fact was revealed that the seed planted in a loosely closed transparent jar grew faster than all other samples. This allows us to conclude that in this case we created greenhouse conditions that are the best for seed germination, but when the lid of the jar was opened completely, growth slowed down, and then the same growth of plants was noted (Fig. 17).
An interesting fact was revealed that the seed planted in a loosely closed transparent jar grew faster than all other samples. This allows us to conclude that in this case we created greenhouse conditions that are the best for seed germination, but when the lid of the jar was opened completely, growth slowed down, and then the same growth of plants was noted (Fig. 17).
Thus, the conducted experiment on the germination of beans for 10 days allows us to conclude that the optimal environmental factors have a positive effect on the germination and growth of plants.
Conclusion
By placing bean seeds, initially at approximately the same stage of development, under different conditions, we traced the mechanism of bean seed germination and established what factors influence this process. Investigating the influence of external conditions on seed germination, we carried out a series of experimental work, as a result of which we were convinced in practice that bean seeds need water. Seed germination is impossible without light. Heat affects the rate of germination. Conducting a study on seed germination, we fulfilled all the tasks and goals set, namely, in practice, the role of the seed in the individual development of plants was considered using the example of germination of bean seeds.
Seed germination is impossible without light. Heat affects the rate of germination. Conducting a study on seed germination, we fulfilled all the tasks and goals set, namely, in practice, the role of the seed in the individual development of plants was considered using the example of germination of bean seeds.
Thus, it can be concluded that for plant growth it is very important that there is enough sunlight, heat and moisture. When all three environmental factors are observed, then the sprout very quickly becomes stronger in the soil and opens its leaves in a matter of hours. From this point on, the plant can independently absorb nutrients along with water through the root system and receive energy through photosynthesis in the leaves, which ensures the growth and development of the plant.
References:
Biology. Bacteria, fungi, plants. Grade 6: textbook. for general education institutions / V.V. Beekeeper. - 14th ed., stereotype.
 When grown in an open garden, climbing vines require support at least 2 meters high. The advantage of the variety is a significant saving of space on the site - from one square meter it gives a bountiful harvest.
When grown in an open garden, climbing vines require support at least 2 meters high. The advantage of the variety is a significant saving of space on the site - from one square meter it gives a bountiful harvest. 









