Growing fresh garlic
How to Grow Garlic | Gardener's Supply
More Articles
Find more garden information
Other Article Categories
Choose CategoryRecipesRaised Bed GardeningAnimal Pest ControlsGardening for the PlanetSoils & CompostSeed StartingGrowing Fruits & VegetablesPlanting Techniques & ToolsPest & Disease EncyclopediaHouseplant CareHome Garlic
Garlic is one of the easiest crops you can grow. In most regions of the country, garlic is planted in the fall, about 4-6 weeks before the ground freezes. By that time, many summer crops have already been harvested, leaving some free garden space. Just remember that the garlic bed won't be available for another type of crop until late next summer, when it's time to harvest the garlic you planted the previous fall.
Pick a Variety (or two.
If you're replanting garlic from your own stock, choose the biggest and best heads from the summer's harvest. Simply put, the larger the planted clove, the larger the harvested head. If purchasing, look for garlic sold specifically for planting. Garlic from the produce section at the supermarket may have been treated with a sprout inhibitor to prevent it from growing.
There are several types of garlic.
Hardneck garlic varieties produce a stiff stem that grows up through the center of the bulb. Compared to softneck varieties, then tend to have a sharper flavor, with more variation in flavor among the varieties. They're hardier, too, making them a good choice for regions with very cold winters. Once harvested, the bulbs have a somewhat shorter shelf life than softneck varieties.
Popular hardneck varieties: "Music", "German Red", "Chesnok Red"
Softneck garlic varieties don't produce a stiff central stem. This list the type of garlic you'll find at most supermarkets. It has a relatively mild flavor. Softneck garlic is the best choice for regions with mild winters, and it's the type to grow if you want to make garlic braids.
It has a relatively mild flavor. Softneck garlic is the best choice for regions with mild winters, and it's the type to grow if you want to make garlic braids.
Popular softneck varieties: "Inchelium Red", "California Whiite Early"
Elephant garlic resembles a giant head of garlic and, indeed, it does belong to the same genus, Allium. However, it isn't a "true" garlic but rather is more closely related to the leek.
Planting Garlic
- Plan to plant garlic in fall about four to six weeks before the ground freezes.
- Prepare the soil by loosening it to a depth of at least 8" and mix in some slow-release, granular organic fertilizer.
- Just prior to planting, break up the garlic heads into individual cloves, leaving as much of the papery covering on each clove intact as possible.
- Plant cloves 3" to 4" deep, orienting them so the pointy ends face up.
- Water gently to settle the soil, and then cover the bed with a 4" to 6" layer of straw.
 Even as air temperatures drop, the soil will stay warm enough for the newly planted cloves to establish roots before the ground freezes. Sometimes you'll see some green shoots form in fall; that's fine and won't harm plants. They'll begin growing in earnest in spring.
Even as air temperatures drop, the soil will stay warm enough for the newly planted cloves to establish roots before the ground freezes. Sometimes you'll see some green shoots form in fall; that's fine and won't harm plants. They'll begin growing in earnest in spring.
Here in Vermont it's easy to tell when the garlic should be planted. Look up at the hillsides. If they're a blaze of red, orange and yellow, it's time.
If you planted hardneck varieties, they'll probably form curly scapes. It's best to cut these off so the plants will direct their energy to producing large underground bulbs. The tender stalks can be used in stir-fries or sauteed with vegetables.
Last updated: 10/18/2022
Share this Article:
People who read this article often purchase
Related Articles
-
How To Grow and Harvest Garlic
-
Minty Pea Soup with Green Garlic & Cashew Cream
-
How to Grow Herbs
Get the Dirt
Stay up to date on new articles and advice. Please fill out the information below.
Please fill out the information below.
Share this Article:
Related Articles
-
How To Grow and Harvest Garlic
-
Minty Pea Soup with Green Garlic & Cashew Cream
-
How to Grow Herbs
How To Grow Garlic | BBC Gardeners World Magazine
- March: sow varieties suitable for spring sowing
- April to June: water
- July or August: harvest garlic
- November or December: sow most varieties of garlic
It’s easy to think of garlic as a Mediterranean plant and therefore a tender crop that needs lots of warmth to grow well. However, if you choose a good variety and give it the right conditions, you can produce a decent crop no matter where you live in the UK.
However, if you choose a good variety and give it the right conditions, you can produce a decent crop no matter where you live in the UK.
Garlic needs a long growing season to do well, and autumn through to early winter is the perfect time to sow so that plants develop roots and shoots before the heavy frosts. Some varieties can be sown in spring.
Home-grown garlic takes up little space and requires hardly any effort to get a good crop. It's an easy crop to grow – it's sown from garlic cloves as opposed to seeds. The certified garlic bulbs are sold at garden centres or online.
There are two types of garlic to grow: softneck garlic and hardneck garlic.
Softneck varieties
The most common type in supermarkets. It produces the greatest number of cloves per bulb – up to 18. It has a white, papery skin, stores well and rarely produces a flower stalk. Softneck garlic is less tolerant of prolonged cold temperatures and is therefore best suited to growing in mild southern counties, though it can be grown elsewhere with protection in the winter.
Hardneck varieties
Hardneck garlic has fewer cloves per bulb – usually 10 or less. They are generally hardier than softneck types and can be grown throughout the UK. Hardneck types will often produce a curling flower stalk or ‘scape’. This straightens out as it matures, to carry a head of tiny clove-like bulbils. It is best to remove the scape as soon as it appears (use it in stir fries) so that the plant will divert its energies into producing a larger bulb. If left to develop on the plants, you can harvest and plant the bulbils, but it may take 2-3 years to form a decent bulb.
There's also elephant garlic, which bears giant, mild-flavoured bulbs, which you can grow for a lighter garlic taste.
Growing garlic
Grow garlic in a warm, sunny spot, in fertile, well-drained soil that doesn't get too wet in winter. Garlic is usually planted in late autumn or early winter (although some cultivars can be planted in early spring). It can be sown directly in the ground, or started off in small pots if you have heavy soil.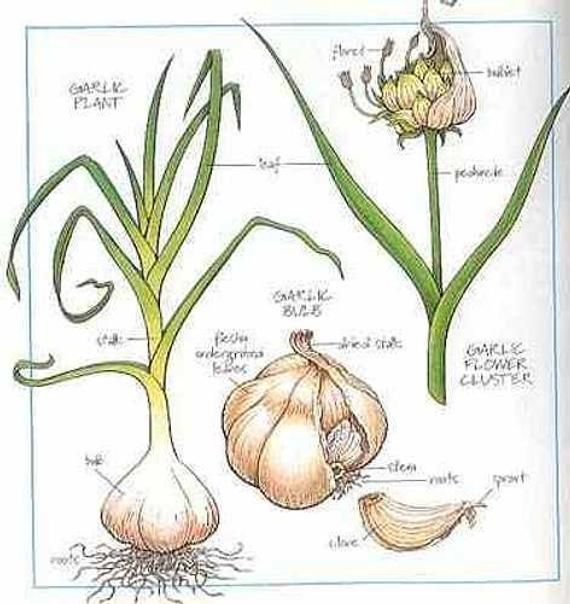 It can also be grown in a large container.
It can also be grown in a large container.
More like this
Whichever way you decide to grow garlic, always buy bulbs at the garden centre or order from a seed supplier – don't use bulbs from the supermarket. Break up the bulbs into separate cloves and plant the large ones with the fat end downwards and the pointy end 2.5cm below the soil surface. Harvest from July onwards, once the top growth has begun to die back. Leave the bulbs to dry in the sun for a few days before storing.
Growing garlic: jump links
- Planting garlic
- Caring for garlic
- Growing garlic: problem-solving
- Harvesting garlic
- Buying garlic
- Garlic varieties to grow
How to plant garlic
How to grow garlic - planting garlic cloves
Most varieties of garlic are best planted in late autumn or early winter, as the cloves need a period of cold weather to develop into bulbs.
Make sure your soil is cleared of weeds and the remains of summer crops. Before planting, dig in some home-made compost or well-rotted manure and rake over well. Push cloves in, or use a dibber to make holes 15cm apart, leaving 30cm between rows. Birds have a penchant for the bulbs and will pull them out of the soil, so lay bird netting or horticultural fleece over new plants until the shoots are 5cm tall. In cold areas, you may need to cover plants with cloches over winter. This extra protection will encourage root growth, so plants are ready to grow next spring.
Before planting, dig in some home-made compost or well-rotted manure and rake over well. Push cloves in, or use a dibber to make holes 15cm apart, leaving 30cm between rows. Birds have a penchant for the bulbs and will pull them out of the soil, so lay bird netting or horticultural fleece over new plants until the shoots are 5cm tall. In cold areas, you may need to cover plants with cloches over winter. This extra protection will encourage root growth, so plants are ready to grow next spring.
Here, Monty Don demonstrates how to plant garlic, with advice on planting depth and varieties to grow:
If you have heavy clay soil, you can start garlic off by planting cloves singly in module trays in autumn and growing them on in a cold frame. This prevents the bulbs rotting off in very wet soil during winter. You can then plant these out in spring, when the soil has dried out a little. You could also try growing garlic in mounds 15cm tall and 20cm wide at the base. Plant the garlic cloves into these mounds, 15-20cm apart and 7-10cm deep. Because the soil is slightly raised, it doesn't get as wet, so the garlic is less likely to rot.
Because the soil is slightly raised, it doesn't get as wet, so the garlic is less likely to rot.
How to grow garlic – starting garlic off in pots
How to grow garlic in a container
If you have no space, or your plot has been affected by onion white rot in the past, then growing in containers is for you. Use any pot that's at least 15cm wide and deep, filled with multipurpose compost. Sow three cloves in a 15cm wide pot, six in a 30cm one. Feed from April when you see strong spring growth, using a high nitrogen feed such as dried chicken manure pellets, or fill the container to the top with more compost. Stop feeding in mid May.
Watch Monty plant garlic in a container, with advice on drainage and feeding:
Where to buy garlic online
- Dobies
- Thompson & Morgan
- Van Meuwen
- Suttons
- You Garden
How to care for garlic
Garlic needs little care. Water regularly in spring and early summer, but reduce once you see the foliage turning yellow – this is a sign that the bulbs are reaching maturity. Weed between the plants to reduce the competition for water and nutrients. This is best done by hand, as hoeing could damage the developing bulbs. Remove any flowers, or 'scapes' the plants produce – you can eat these in stir-fries.
Weed between the plants to reduce the competition for water and nutrients. This is best done by hand, as hoeing could damage the developing bulbs. Remove any flowers, or 'scapes' the plants produce – you can eat these in stir-fries.
Growing garlic: problem solving
Garlic is generally pest free and is only affected by a few problems.
Birds
Birds, especially pigeons, will take freshly sown garlic cloves from the ground and will also eat recently germinated plants. Cover the area with netting or horticultural fleece immediately after sowing and don't remove until the young plants are at least 5cm tall.
Onion white rot
Onion white rot is hard to detect until it's too late – the first sign that anything is wrong is usually yellowing, wilting foliage but this is usually around harvest time, when you'd expect the leaves to be dying back anyway. When you dig up the plant, you'll notice a white fluffy fungus on the base of the bulb, along with tiny black growths. In severe cases, the bulb will be black and rotten.
In severe cases, the bulb will be black and rotten.
Onion white rot is a soil-borne disease, so there is no control and the problem can persist for years. Avoid spreading the problem around the garden on boots and tools, as the disease can affect the whole allium family, including onions and leeks. Dig up all of the affected plants and bin or burn them – do not add them to the compost heap. You may be able to salvage some of your crop to eat, but it won't store well. In future, grow garlic in containers, in fresh soil that does not come from the garden.
Leek rust
Garlic can be affected by leek rust, a fungal infection that is more common in wet weather. There is no cure. Orange pustules appear on the leaves in summer, which then begin to die back. The bulbs are perfectly safe to eat but it's a good idea to harvest affected plants immediately, to prevent the disease spreading, and to eat them straightaway. Dispose of the rest of the plant material (bin or burn it, don't add to the compost heap) and avoid growing garlic, leeks and onions in the same place for three years. Choose a variety that has some resistance to rust, and space plants out to reduce humidity.
Choose a variety that has some resistance to rust, and space plants out to reduce humidity.
Watch Monty Don's video guide to dealing with rust on garlic:
How to harvest garlic
How to grow garlic - harvesting garlic
Harvest garlic in summer when the leaves turn yellow. Gently lift out bulbs with a fork or trowel, taking care not to damage the bulbs. Leave the garlic to dry out for a couple of days, by laying it out on a table or tray, in full sun.
Watch Monty Don's video guide to harvesting garlic:
How to store garlic
How to grow garlic - plaiting garlic
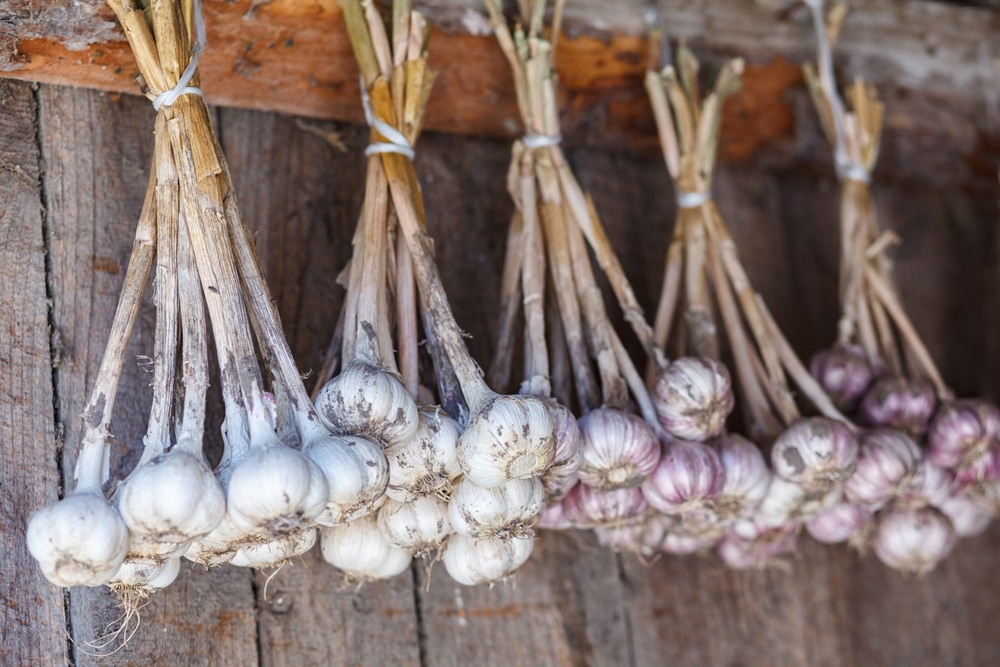
Once the bulbs are dry and feel papery to touch, you can either store them loose or plait their foliage to make a traditional string of bulbs. Store in a cool, dry place. Take care not to bruise the bulbs, as any damage can make them deteriorate in storage. Bear in mind that Softneck garlic varieties store better than hardneck garlic and should keep for several months, so eat the hardneck varieties first.
How to prepare and use garlic
Crush, slice or finely chop, or roast cloves whole, to add flavour to many dishes. Hardneck varieties tend to have more flavour than softnecks, so work well when roasted whole.
- Try BBC Good Food's recipe for garlic butter
Watch this 20-second video demonstration from our friends at olive magazine on how to chop and crush garlic.
Can you plant supermarket garlic?
It is possible to grow garlic from supermarket bulbs, but it's not recommended as there's a risk of virus infection. If you buy from proper planting stock, it should be virus free. And you can also choose a variety that has been bred especially for our climate.Advice on buying garlic
Here’s our guide to buying garlic, including where to buy garlic.
- Always buy from a garden centre or online seed supplier – do not use bulbs from the supermarket
- Choose from softneck or hardneck garlic.
 Softneck varieties tend to be hardier and last longer, but hardnecks are said to have more depth of flavour
Softneck varieties tend to be hardier and last longer, but hardnecks are said to have more depth of flavour - Check the garlic bulbs to make sure they have no signs of mould, and are firm to touch
Where to buy garlic online
- Dobies
- Thompson & Morgan
- Van Meuwen
- Suttons
- You Garden
Great garlic varieties to grow
1
Garlic 'Albigensian Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Albigensian Wight'
A heavy cropping, softneck variety from south west France. It has large bulbs and is a heavy cropper.
- Buy garlic 'Albegisian Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
2
Garlic 'Chesnok Red'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Chesnok Red'
This hardneck variety hails from the Ukraine and has attractive purple stripes. It’s said to be the best variety for garlic bread.
- Buy garlic 'Chesnok Red' from Thompson & Morgan
3
Garlic 'Early Purple Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Early Purple Wight'
This softneck variety produces mild, purple-tinged bulbs. As its name suggests, it crops very early, from mid May. It doesn’t store well, so use within three months.
As its name suggests, it crops very early, from mid May. It doesn’t store well, so use within three months.
- Buy garlic 'Early Purple Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
4
Garlic 'Iberian Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Iberian Wight'
This softneck variety from Spain has large bulbs with plump cloves. Good for plaiting, it stores well.
- Buy garlic 'Iberian Wight' from Thompson & Morgan
5
Garlic 'Solent Wight'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Solent Wight'
This softneck variety was bred on the Isle of Wight, so is well suited to the UK climate. It has small bulbs with a strong flavour and keeps well.
- Buy garlic 'Solent Wight' from Crocus
6
Garlic 'Christo'
How to grow garlic – Garlic 'Wight Christo'
This softneck variety is reliable and easy to grow and produces large bulbs. It can be planted in autumn or spring stores well.
- Buy garlic 'Christo' from You Garden
cultivation, planting, care in the open field
There are 2 varieties of garlic: winter and spring (1). You can tell them apart by the bulbs.
You can tell them apart by the bulbs.
Winter garlic. It has an even number of cloves in the head - from 4 to 10. They are large and arranged in a circle. And in the center there is always a stem - the rest of the stem. The problem with winter garlic is that it does not store well.
Spring garlic. His teeth are arranged in a spiral, and they are of different sizes - larger on the outside, closer to the center - smaller. And there are many more - up to 30 pieces. And there is no stem in the center. This variety of garlic is perfectly stored - it can easily lie for a whole year until the next harvest. nine0003
Winter garlic is planted before winter, spring - in the spring, respectively, their care has differences.
Cultivation of garlic
Garlic is a rather unpretentious crop; in many gardeners it grows almost without care and gives good yields. But still, he has one requirement - the soil must be pedigree. Therefore, before planting on the site, fertilizers must be applied (calculation per 1 sq. M):
M):
- humus - 1/2 bucket;
- rotted sawdust of deciduous trees - 1/2 bucket; nine0020
- ash - 5 glasses;
- fluffy lime - 5 cups.
Fertilizers should be mixed, spread evenly over the area and dug up by 10 cm. And he does not like urea and potassium chloride.
Place for garlic should be sunny - this is a light-loving crop.
Planting garlic
The timing of planting garlic depends on its variety. nine0003
Winter garlic. It is traditionally planted 2 - 3 weeks before the onset of hard frosts, in late September - early October (2), when the soil temperature drops below 15 °C.
Planting pattern is as follows:
- row spacing - 25 cm;
- in a row - 10 - 15 cm;
- planting depth - 8 - 10 cm.

Spring garlic. It is planted in the spring, no later than the end of April (3). He is not afraid of frosts, therefore, the earlier you plant, the more likely it is that the crop will have time to ripen - this is especially true in regions with a short summer. The optimum soil temperature is 5-6 °C. nine0003
Planting pattern:
- row spacing - 25 - 30 cm;
- in a row - 8 - 10 cm;
- planting depth - 2 cm.
The cloves are planted at a depth of 3 - 4 cm, and when they begin to take root, they themselves go deep into the soil by 6 - 8 cm (4).
Outdoor garlic care
Watering. It should be regular, but up to a certain point:
- in April-May - once a week: 10 liters per 1 sq. m
- in June-July - 1 time in 2 weeks: 10 liters per 1 sq. m; nine0020
- from August it is not possible to water.
In rainy summers, garlic does not need watering.
Top dressing. As a rule, in fertile areas of this crop, it is enough that they were applied to the soil before planting. On poor soils, it is useful to additionally feed it with phosphorus and potassium - fertilizers must be applied between the rows 2 weeks after planting the cloves:
As a rule, in fertile areas of this crop, it is enough that they were applied to the soil before planting. On poor soils, it is useful to additionally feed it with phosphorus and potassium - fertilizers must be applied between the rows 2 weeks after planting the cloves:
- double superphosphate - 30 g (2 tablespoons) per 1 sq. m;
- potassium sulfate - 20 g (1 tablespoon) per 1 sq. m.
- Winter garlic is important to cover in the winter - mulch with humus, compost or peat with a layer of about 5 cm, - advises agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova. - This should be done in late autumn, at the end of November. The mulch will help keep the bulbs from freezing if the winter turns out to be snowless and the frosts are severe. In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, the mulch must be removed so that the cloves in the soil do not get wet.
“Caring for spring garlic also has its tricks,” continues Svetlana Mikhailova. - It happens that in the cold summer, the ripening of the bulbs slows down, and they may not have time to ripen before the autumn frosts. In this case, in mid-August, you can collect the leaves in a bunch and tie them in a knot - then they will stop growing, the plants will direct all their forces to the ripening of the bulb. nine0003
- It happens that in the cold summer, the ripening of the bulbs slows down, and they may not have time to ripen before the autumn frosts. In this case, in mid-August, you can collect the leaves in a bunch and tie them in a knot - then they will stop growing, the plants will direct all their forces to the ripening of the bulb. nine0003
Garlic harvesting
Garlic harvesting time also depends on the variety.
Winter garlic. It is usually harvested at the end of July. There are three signs that it is already ripe:
- the covering skin begins to crack on the inflorescences, and the bulbs are exposed, but this only applies to arrow varieties - yes, garlic arrows usually break out (5), but you can always leave a couple of plants with inflorescences to use as beacons;
- lower leaves turn yellow; nine0020
- The outer, covering scales of the bulb become dry - this can be seen if you dig up one plant.
Spring garlic. It is removed later - around the end of August. Most varieties of this group do not form arrows, so yellowing of the leaves and lodging of the tops can serve as a visual signal for harvesting.
It is removed later - around the end of August. Most varieties of this group do not form arrows, so yellowing of the leaves and lodging of the tops can serve as a visual signal for harvesting.
– It is better to dig up garlic with a pitchfork – this way there is less chance of damaging the bulb, recommends agronomist Svetlana Mikhailova. - You need to dig in dry weather. After harvesting, the garlic, together with the tops, is removed to dry - for about a week it should lie under a canopy. nine0003
After drying, cut off the roots and stems of the bulbs, leaving a stump of about 10 cm (if the garlic is to be stored in braids, the stems are not cut).
Garlic storage rules
There are many ways to store garlic, but practice shows that almost all of them are unreliable. The best way is to braid the plants in the same way as you do with onions.
But there are some nuances:
- garlic stalks are hard and brittle, it is difficult to braid them, so you need to weave straw or twine there; nine0020
- Braids should be stored at a temperature of 1 - 2 °C - onions are stored at room temperature, and garlic dries quickly in heat.

Large heads are stored longer, so the small ones should be eaten first.
Popular questions and answers
agronomist Svetlana Mikhailova answered our questions about growing garlic.
Should garlic cloves be peeled before planting?
No way! Covering scales - reliable protection of teeth from mechanical damage, diseases and pests. Peeled cloves will rot rather than germinate. nine0003
Should winter garlic be watered after planting?
No. It will be enough for him to take root in the autumn rains. Over watering can cause tooth decay.
Can winter garlic be planted in spring?
It makes no sense. For winter varieties, it is important that there are low temperatures after planting. And the spring is too warm. If planted in April, the bulbs will grow inferior and will not be stored. And besides, underdeveloped teeth cannot be used for planting - they form roots very slowly and freeze out in winter. nine0003
nine0003
Is it possible to plant spring garlic before winter?
It is possible, but spring varieties, when planted in autumn, take root worse and often freeze, therefore, they will give a crop much less than winter varieties.
Why does winter garlic turn yellow in spring?
There may be 4 reasons:
- cold spring - in such a situation, the leaves begin to grow, and the roots cannot yet extract nutrients from the soil;
- lack or excess of moisture in the soil;
- acidic soil;
- Fusarium disease. nine0003
Sources
- Fisenko A.N., Serpukhovitina K.A., Stolyarov A.I. Garden. Handbook // Rostov-on-Don, Rostov University Press, 1994 - 416 p.
- Pantielev Ya.Kh. ABC vegetable grower // M .: Kolos, 1992 - 383 p.
- Group of authors ed. Polyanskoy A.M. and Chulkova E.I. Tips for gardeners // Minsk, Harvest, 1970 - 208 p.
- Shuin K.A., Zakraevskaya N.K.
 , Ippolitova N.Ya. Garden from spring to autumn // Minsk, Uradzhay, 1990 - 256 p. nine0020
, Ippolitova N.Ya. Garden from spring to autumn // Minsk, Uradzhay, 1990 - 256 p. nine0020 - Yakubovskaya L.D., Yakubovsky V.N., Rozhkova L.N. ABC of a summer resident // Minsk, OOO "Orakul", OOO Lazurak, IPKA "Publicity", 1994 - 415 p.
How to grow a good crop of garlic? All about growing and caring for garlic. Photo — Botanichka
It is difficult to imagine a country garden without a garden of garlic. Garlic is deservedly called a natural antibiotic, antifungal agent, folk healer. And caring for garlic does not take a lot of strength and golden summer time from gardeners. nine0003 Common garlic (Allium sativum)
Garlic belongs to the group of perennial plants of the Amaryllis family. The scientific type name of garlic sounds like "Sowing onion", "Sowing garlic" ( Allium sativum ), much less often - "onion-garlic". In everyday life, this vegetable crop is simply called garlic.
The cultivation of garlic began more than 5000 years ago, according to various references, in Egypt, where the culture was first used for treatment.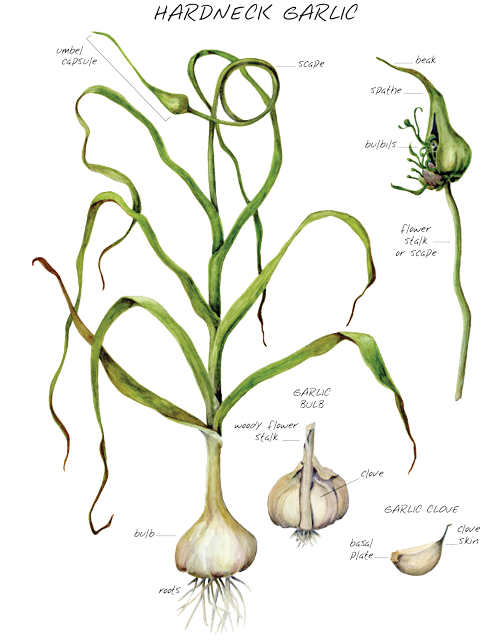 Garlic was part of the daily diet of the workers who built the Egyptian pyramids. For Greek athletes, participants in the early Olympic Games, garlic served as a kind of steroid, and for Greek soldiers as a stimulant of courage. Pasteur's early work identified 23 types of bacteria, including staphylococcus, salmonella, the ruthless killer of which was garlic. nine0003
Garlic was part of the daily diet of the workers who built the Egyptian pyramids. For Greek athletes, participants in the early Olympic Games, garlic served as a kind of steroid, and for Greek soldiers as a stimulant of courage. Pasteur's early work identified 23 types of bacteria, including staphylococcus, salmonella, the ruthless killer of which was garlic. nine0003
Mankind, having first learned the secret of curing many diseases with garlic preparations, never parted with this culture.
Biological characteristics of garlic
The root system of garlic is fibrous, but individual roots can reach a meter deep. The high stem is false, formed by leaf sheaths of leaf blades. As the plant develops, the lower part of the leaf thickens and forms into fleshy scales. Some of the outer scales, drying out, turn into the integumentary scales of the bulb. A real stalk of garlic, due to very short internodes, is flattened to a thin bottom. On it are fleshy scales-teeth, closed on top with integumentary scales. Inside the clove there is a kidney with one or two growth points and rudimentary leaves. After resting, the teeth germinate into a new plant. Garlic cloves are used for food and as material for vegetative propagation. nine0003
Inside the clove there is a kidney with one or two growth points and rudimentary leaves. After resting, the teeth germinate into a new plant. Garlic cloves are used for food and as material for vegetative propagation. nine0003
Garlic inflorescence is a simple umbel, located on a flower-bearing shoot 0.5 to 1.5 m high, which is called an arrowhead. Sterile flowers and air bulbs (bulbs) develop in the inflorescence, the number of which, depending on the variety, ranges from 10 to 500 pieces. The entire inflorescence of garlic before flowering is covered with a dense cover. Garlic inflorescences form seeds only under strong ultraviolet light. Under normal conditions, air bulbs are formed. Ripe garlic bulbs crumble and sprout with single-tooth bulbs (single-toothed). Sowing one-tooth gives the usual multi-tooth garlic bulb. When propagated by bulbs, the culture is considered two-year-old, that is, in the first year they receive single-toothed, and their sowing the next year forms an ordinary multi-toothed garlic bulb. nine0003
nine0003
Types of above-ground mass of garlic
Garlic forms two types of above-ground mass.
- Flower-bearing or shooters. They form a shoot with an inflorescence (arrow).
- Non-flowering or non-shooting. This type during the growing season forms only leaf mass.
Shooting garlic does not lodge. Straight peduncle (arrow) and leaves turn yellow by the end of the growing season. On the arrow, the common cover of the inflorescence is opened and the bulbs fall to the ground.
In non-shooting garlic, the leaves lose their turgor as they ripen, turn yellow, lie down on the soil and dry out.
Types of garlic
Garlic is divided into 2 types, which differ in planting time and the size of the formed bulb. In autumn, winter garlic cloves are planted. In spring - spring garlic cloves. Winter garlic has both forms: arrow and non-shoot, and spring - only non-shoot.
In the country, it is better to grow both forms. Winter crop forms the crop earlier, the heads are larger, the yield is higher. But it is characterized by low keeping quality. Already by January-February, winter garlic cloves dry out and need additional measures to preserve the seed. It is also better to grow arrow varieties of winter garlic. nine0003
But it is characterized by low keeping quality. Already by January-February, winter garlic cloves dry out and need additional measures to preserve the seed. It is also better to grow arrow varieties of winter garlic. nine0003
Differences between winter and spring garlic
Winter garlic forms cloves around a stem located in the center of the bulb. When separating the teeth, the stem remains bare.
Spring garlic does not have such a stem. The cloves are more curved due to the snug fit in the garlic bulb. The largest teeth are located in the outer rows, smaller in the middle.
For human consumption, both types of garlic are absolutely identical. According to biological characteristics, they differ in terms of planting. Spring forms a crop only during spring planting. Winter garlic produces the largest and healthiest crops, ripening by July, during autumn planting. When planting cloves in the spring, even if it forms a crop, it is not of high quality and not long-lived. nine0003 Common garlic (Allium sativum). © Jill Anderson
nine0003 Common garlic (Allium sativum). © Jill Anderson
Winter Garlic Growing Technology
Winter Garlic Planting Time
Winter garlic is planted in autumn. In the south, with a warm long autumn, planting can be pushed back to the end of October, and even November-December. In 2016, I sowed winter garlic in the first decade of December (more precisely, on December 3). The teeth are rooted, the tops of future leaves are slightly green. This development is a great transition to winter holidays. If sown early, when warm weather often returns to +10 .. + 12 ° С in the south, garlic manages to form leaves up to 5-6 cm, which freeze with the onset of cold weather and the plants are greeted with damaged spring, which subsequently leads to chopping heads . nine0003
Frequent temperature fluctuations in the autumn required a revision of the planting dates for winter garlic cloves in the middle zone of the Russian Federation and the CIS countries. In medium-sized regions, the period from the second half of September to mid-October was considered the optimal period. Currently, the optimal time for autumn planting has moved to mid-October. It is better to start planting when the air temperature at night approaches +8..+10 °С. Garlic will have time to form a developed root system without green above-ground shoots. Thus, a very important point is to most clearly determine the time for planting cloves and sowing bulbs for reproduction. If the teeth and bulbils form leaves in the fall, they may die in the spring during return frosts or be constantly ill throughout the growing season. nine0003
Currently, the optimal time for autumn planting has moved to mid-October. It is better to start planting when the air temperature at night approaches +8..+10 °С. Garlic will have time to form a developed root system without green above-ground shoots. Thus, a very important point is to most clearly determine the time for planting cloves and sowing bulbs for reproduction. If the teeth and bulbils form leaves in the fall, they may die in the spring during return frosts or be constantly ill throughout the growing season. nine0003
Lighting for garlic
The next condition for a good harvest is the intensity of the light. If the garlic beds are shaded by taller crops, the heads will be crushed. Large heads are not formed when growing garlic in partial shade.
Predecessors
So that garlic does not become infected with infectious diseases, the culture is returned to its former place of cultivation after 4-5 years. An equally important condition is the previous cultures. The best predecessors are cultures of the nightshade family (tomatoes, peppers, eggplant), pumpkin (pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini), cruciferous (cabbage, salads). nine0003
The best predecessors are cultures of the nightshade family (tomatoes, peppers, eggplant), pumpkin (pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini), cruciferous (cabbage, salads). nine0003
Winter garlic is a good neighbor for a number of fruit bushes: black currant, raspberry, gooseberry, strawberry and strawberry. It has a good effect on the growth and development of cucumbers, potatoes. Protects them, like roses, gladioli, tulips from slugs, drillers, caterpillars. The smell of garlic is unbearable for moles. Garlic planted next to a rose reduces the possibility of black spot damage to the crop.
Soil disinfection
The level of infectious background is very important for garlic. The higher it is, the less hope for the formation of healthy garlic heads. Therefore, it is always necessary to carry out disinfection measures before planting garlic. nine0003
The main one is the sowing of green manure phacelia. Phacelia is an excellent green fertilizer. It heals the soil from almost all types of fungal diseases (late blight, root rot), destroys pests (wireworm, nematode, locust). Phacelia successfully deoxidizes the soil. Suppresses the growth of weeds (woodlice, etc.).
Phacelia successfully deoxidizes the soil. Suppresses the growth of weeds (woodlice, etc.).
Well removes the wireworm from the site the introduction of ammonium forms of mineral fertilizers, including ammonia water, ammonium sulfate, potassium sulfate. nine0003
If the garlic bed occupies a small area, you can shed the area with a solution of potassium permanganate.
Preparing the soil for planting garlic
Garlic prefers light soils with neutral acidity. If the soil is acidified, add 1 glass of lime or dolomite flour per 1 sq. m. Garlic does not tolerate flooding and fresh organics. When fresh organics are introduced directly under the planting of garlic, there is a strong defeat by fungal diseases, and the quality of garlic bulbs decreases. Therefore, if necessary, loosen heavy soil, it is better to apply humus and manure under the previous crop, and under garlic - high-moor peat, sand, sawdust of deciduous trees (conifers acidify the soil). nine0003
For autumn digging (25-30 cm) use a complex mineral fertilizer - 35-50 g / m² or a mixture of a glass of ash and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers - 30 and 20 g / m², respectively. The soil is carefully leveled. Planting begins after 1-2 weeks, so that the soil fluffed up by digging settles. Literally 1-2 days before planting, 15 g / m² of ammonium nitrate is applied or grooves are shed with root solution. This procedure is especially desirable when planting late, in order to speed up the formation of the root system. nine0003
The soil is carefully leveled. Planting begins after 1-2 weeks, so that the soil fluffed up by digging settles. Literally 1-2 days before planting, 15 g / m² of ammonium nitrate is applied or grooves are shed with root solution. This procedure is especially desirable when planting late, in order to speed up the formation of the root system. nine0003
Preparation of planting material
Planting material can be purchased from specialized outlets, but it is better to use a sample of the crop grown in the current year. For planting, the largest heads are selected and, on the day of planting, they are cut into separate one-sized teeth. If the teeth are prepared in advance, then the bottom of the clove dries up and, accordingly, the germination energy decreases. With long-term storage of separated cloves, they may not sprout.
The teeth are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate (30-40 minutes) and planted. Disinfection of teeth can be carried out in a 1% solution of copper sulphate. The teeth are kept in the solution for no more than 1 minute. Some experienced gardeners recommend first rinsing the teeth for 1-2 minutes in a salt solution (40-50 g / 5 l of water). Then immediately lower into a 1% solution of copper sulfate for 1 minute and, without washing, start planting the planting material. nine0003
The teeth are kept in the solution for no more than 1 minute. Some experienced gardeners recommend first rinsing the teeth for 1-2 minutes in a salt solution (40-50 g / 5 l of water). Then immediately lower into a 1% solution of copper sulfate for 1 minute and, without washing, start planting the planting material. nine0003
If these materials are not available, decontamination of planting material can be carried out with an alkaline solution. 400 g of ash is poured into 2 liters of water, boiled for 0.5 hours, cooled. The cold solution is filtered and the teeth are kept in the prepared concentrate for 1.5-2.0 hours. Washed with boiled cold water and planted.
Planting winter garlic
The optimal scheme for planting garlic is row or two-row (two-line). Width between lines 10-12 cm, between rows 25 cm or the width of the chopper blade. Distance in a row 8-10 cm or the length of a standard matchbox. When the plantings thicken, the teeth and bulbs become smaller. The embedment depth is 2 clove heights or at least 5-7 cm. In case of shallow planting, the rapid heating of the upper layers of the soil in spring will lead to the grinding of heads and cloves. If the soil is dry, pre-water the bottom of the furrow with a watering can. Close and level the ground. Despite the sufficient frost resistance of winter garlic (-18 ..-25 ° C), the plantings must be mulched with any small mulch. From crows, you can cover the bed with spruce branches or dry branches. nine0003 Planting garlic cloves. © Amanda Eastvold
In case of shallow planting, the rapid heating of the upper layers of the soil in spring will lead to the grinding of heads and cloves. If the soil is dry, pre-water the bottom of the furrow with a watering can. Close and level the ground. Despite the sufficient frost resistance of winter garlic (-18 ..-25 ° C), the plantings must be mulched with any small mulch. From crows, you can cover the bed with spruce branches or dry branches. nine0003 Planting garlic cloves. © Amanda Eastvold
Caring for garlic
Loosening the soil
In the spring, after the snow melts, garlic plants should be loosened. Loosening will remove the soil crust, remove the beginnings of weeds, and increase the access of oxygen to the roots of plants. The presence of a soil crust delays the development of the garlic bulb. They are stunted and form shredded heads.
Watering
Active growth of above-ground mass of garlic takes place in May, June and the first half of July. Watering is carried out 3 times a month in normal weather. In hot summers, watering is increased up to 5-6 times a month. If the summer is humid, do not water the garlic. Plants in the period of active growth need high humidity, but the coincidence of rain and abundant watering leads to fungal and bacterial diseases, root rot, leaf rust. To reduce the number of waterings and keep the soil moist for a longer time, it is necessary to loosen and mulch the soil after each watering. In hot summers, when the soil dries out quickly, large heads of garlic cannot be obtained without mulching. nine0003
In hot summers, watering is increased up to 5-6 times a month. If the summer is humid, do not water the garlic. Plants in the period of active growth need high humidity, but the coincidence of rain and abundant watering leads to fungal and bacterial diseases, root rot, leaf rust. To reduce the number of waterings and keep the soil moist for a longer time, it is necessary to loosen and mulch the soil after each watering. In hot summers, when the soil dries out quickly, large heads of garlic cannot be obtained without mulching. nine0003
Approximately from the first decade of July, when the pre-harvest ripening of garlic heads begins, they switch to maintaining soil moisture or cancel irrigation. They do not allow drying out so that dry soil does not take away moisture from ripening teeth.
Garlic top dressing
To make top dressing more effective, they are combined with watering. Garlic heads are capable of accumulating nitrogen, so the additional supply of nutrients to the culture must be carefully considered. During the growing season, garlic is fed 2-3 times, no more. nine0003
During the growing season, garlic is fed 2-3 times, no more. nine0003
The first dressing of winter garlic is carried out on moist soil in the phase of 3-4 leaves with a solution of urea (20-25 g / 10 l of water) with a consumption rate of 3 l of solution per 1 sq. m area.
The second dressing of garlic is carried out after 2 weeks with nitrophosphate, nitroammophos or other fertilizer at the rate of 2 tablespoons per 1 m². Top dressing can be applied dry or in solution (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water, per 2 m²).
The third top dressing on fertile soils can be omitted. On sandy and light soils, they are fed in the phase of formation and growth of heads (second decade of June) with superphosphate - 30-40 g / m². nine0003
If it is noticed that the plants are slowly increasing the above-ground mass, additional foliar top dressing can be carried out with infusion of ash or bird droppings, water-soluble fertilizers with a set of trace elements.
Prepare solutions of the following concentration:
- dilute 1 glass of ash or bird droppings per 10 liters of water, filter and spray the plants,
- , you can use a spoonful of crystallin with a microelement kit (buy in a store) for 8-10 liters of water.
 nine0027
nine0027 - Alcor - for the conditions of Western Siberia,
- Podmoskovny (non-shooting) - for the Moscow region and areas close to them,
- Lyubasha - for Ukraine and middle regions of Russia, nine0019 Nazus is intended for the Urals and nearby regions,
- Komsomolets - for the northern regions.
- Artisan kitchenaid reviews

- Best food for an air fryer

- Glass interior wall

- Black garden fencing

- Plant kiwi seeds

- Outdoor summer decorating ideas

- Sun hanging baskets

- Room placement ideas
- Paint colors for small kitchens ideas

- Dark gray furniture what color walls

- Trees that grow fast in clay soil

Garlic foliar can be used in any combination, but at a low concentration, as it complements rather than replaces the main food. If you overfeed the plants, the taste and quality of the bulbs deteriorate noticeably.
Garlic is degenerate. It is no longer possible to obtain large heads from long-term selection over time. Therefore, the material must be updated after 3-4 years. To do this, ripened inflorescences are removed, large bulbs are selected and they are sown around September - early October. One-toothed cloves are obtained the next year, which, when sown in the autumn, form full-fledged healthy large heads of winter arching garlic. nine0003
See also our material: Growing garlic from bulbs.
Large heads are formed by winter garlic, if the arrows are removed in a timely manner as they appear. The arrows are removed at 10 cm in height. They are broken off or cut off, leaving a 2-3 cm column.
Protection of garlic from diseases and pests
Diseases of garlic
Like all vegetable crops, winter garlic is susceptible to infection by fungal, microbial and viral diseases.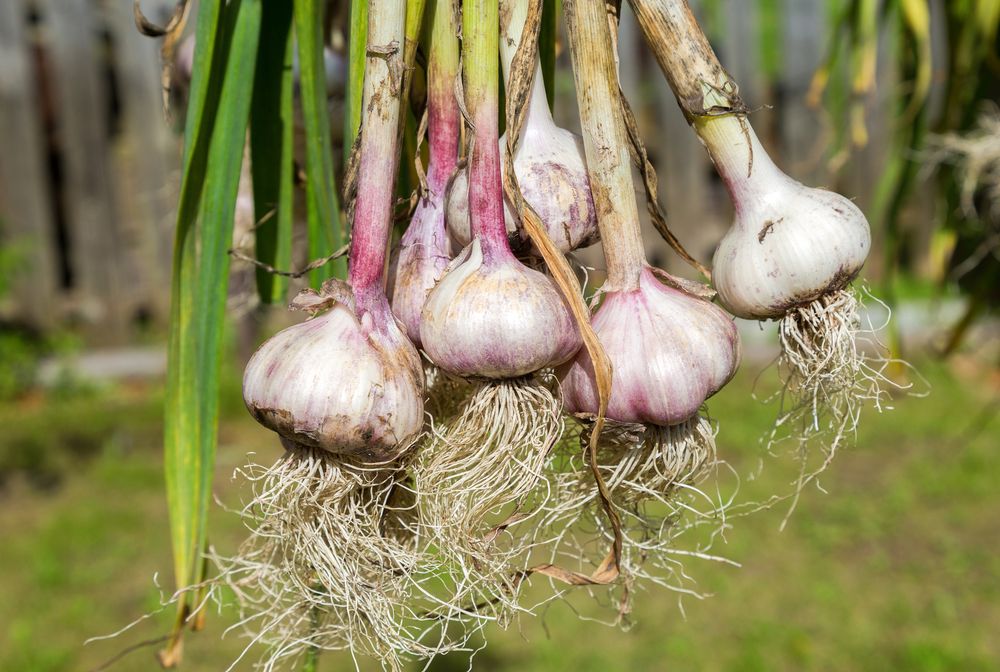 Chemical preparations for protection against diseases and pests on garlic are not recommended for use. The most practical and without a threat to the health of the owners of the cottage, children, animals, it is better to use biofungicides. They can process plants from the first days of their life until harvest, which will allow you to get healthy products. nine0003
Chemical preparations for protection against diseases and pests on garlic are not recommended for use. The most practical and without a threat to the health of the owners of the cottage, children, animals, it is better to use biofungicides. They can process plants from the first days of their life until harvest, which will allow you to get healthy products. nine0003
If, with the timely fulfillment of all agrotechnical requirements, winter garlic changed color, spots, dots, arrows appeared on the leaves, growth stopped, then the plant is infected. The most common diseases are leaf rust, root rot, fusarium, powdery mildew, white rot of the donuts, etc. It is necessary to immediately start treating plants and soil with alirin, hamair, phytosporin, gliocladin, planriz. The preparation of working solutions and their use are given in the recommendations, it is impossible to deviate from their requirements. An independent increase in concentration, spraying at low temperatures will not have the expected positive effect on plants. nine0003
nine0003
Pests of garlic
Of the pests, the most harmful are: the onion fly, whose larvae eat the pulp of cloves, stem nematode, onion hoverflies, thrips, mites, secretive proboscis and others.
The main methods of control include mandatory dressing of planting material and treatment of plants and soil with bioinsecticides. Due to the natural biological basis, bioinsecticides do not have a negative impact on human health and are not addictive to pests.
These include the most commonly used actofit, avertin-N, mycoafidin, lepidocide, bitoxibacillin, nemabact, bicol, pecilomycin (from nematodes) and others.
Effective as a preventive measure, planting calendula and marigolds along the edge of the bed and between wide spacings of garlic. Nematode larvae, crawling to the smell of flower crops, use the juice of their roots for nutrition, which is poisonous for nematodes and leads to the death of pests.
Harvesting
Harvesting starts in late July - early August. The dug out plants are dried in the shade for 3-5 days. Then the aerial part is cut off, leaving 5-6 cm of the column. It should be noted that almost all varieties of winter garlic are distinguished by large bulbs. Thus, the Komsomolets variety forms heads weighing up to 80-110 g, Sofievsky - 90-110 g, Otradnensky - up to 100 g.
The dug out plants are dried in the shade for 3-5 days. Then the aerial part is cut off, leaving 5-6 cm of the column. It should be noted that almost all varieties of winter garlic are distinguished by large bulbs. Thus, the Komsomolets variety forms heads weighing up to 80-110 g, Sofievsky - 90-110 g, Otradnensky - up to 100 g.
Varieties of winter garlic for growing in the country
Early ripe varieties : Bashkir (non-shooting), Broad-leaved -220 (non-shooting).
Mid-season varieties:
Other mid-season varieties of garlic can be recommended for cultivation in the middle zone and cold regions: Nadezhny, German, Dubkovsky, Antonik, Gribovsky jubilee, Gribovsky-60, Novosibirsk (non-shooting), Zubrenok, Losevsky, Sofievsky, Skif, Danilovsky and others. All varieties can grow in the southern regions, forming high quality crops.
All varieties can grow in the southern regions, forming high quality crops.
How to grow spring garlic
Unlike winter garlic, spring garlic is sown in spring, when the soil warms up in the upper 15 cm layer to +5…+8 °C. Spring garlic is distinguished by the formation of small heads. To get bigger heads, it is sown as early as possible. The culture is quite frost-resistant and develops better at low temperatures. Therefore, if it is not possible to measure the temperature of the soil, then usually gardeners, focusing on the period from the melting of snow, and also depending on the region and climate, start sowing in early - mid-April. nine0003
Shoots of spring garlic are not afraid of return spring frosts and appear at an air temperature of +3…+4 °С.
The soil for spring garlic is prepared in the fall, so that in the spring one does not mess around in the cold, half-frozen ground.
Agrotechnical requirements for environmental conditions, soil preparation and planting material do not differ from winter garlic.
Spring garlic temperature requirements
Spring garlic temperature requirements change during the growing season. You can adjust it by the depth of planting teeth. In order for the temperature to be optimal in the zone of development of the root system (+5 ... + 10 ° С), the teeth are planted to a depth of 5-6 cm and the sowing is mulched so that the soil in this layer warms up more slowly. At a low soil temperature, the teeth start growing more actively, the development of the root system proceeds faster. A month later (from the phase of laying garlic bulbs) the best air temperature is +15…+20 °C, and later, when the bulbs ripen, +20…+25 °C. nine0003
Air and soil temperature can be controlled (relatively of course) by mulching and light fogging. In cold weather, dark-colored mulch (high-moor peat) is used, in hot weather - light mulch (sawdust, shavings). You can mulch with mowed dried grass. The loose layer passes air well and prevents the soil from heating. A layer of mulch is recommended not lower than 4-5 cm. This technique can reduce the temperature on the soil from 1 to 3 ° C and even more.
This technique can reduce the temperature on the soil from 1 to 3 ° C and even more.
Spring garlic dressing
Spring garlic is fed 2 times during the growing season. It is impossible (like winter) to overfeed the crop. When overfeeding, the nitrite form of nitrogen compounds accumulates in the teeth (poisonous for humans), the quality of the teeth decreases sharply. To feed spring garlic, if the soil is well seasoned with fertilizers during the main preparation, you can use nitrophoska or an infusion of 1 cup of fresh mullein or bird droppings with 2 cups of ash per 10-12 liters of water. Stir the solution well, strain and bring into the aisles for irrigation, followed by mulching. nine0003
Care of spring garlic
Care of spring garlic (loosening, watering, protection against diseases and pests) does not differ from winter garlic.
Harvest
By August the leaves turn yellow and fall, the crop is ready for harvest. Garlic is dug up, shaken off the ground and, after drying, twisted into braids.