Grow your own spinach
Spinach Planting & Spinach Growing
Spinach is a fast-growing plant, yielding many leaves in a short time in the mild weather of spring and fall. Get expert tips for growing spinach.
Spinach is a cool-weather vegetable related to beets and Swiss chard. A fast-growing plant, it yields many leaves in a short time in the mild weather of spring and fall. When growing spinach, the trick lies in making it last as long as possible, especially in the spring, when lengthening days shorten its life. One great way to do that is to start with vigorous young Bonnie Plants® spinach plants, which are already well on their way to maturity when you put them in your garden. Although it prefers full sun, spinach will still produce a respectable harvest in partial shade.
Quick Guide to Growing Spinach
- Plant spinach during the cool weather of spring and fall.
- Space spinach plants 12 inches apart in fertile, well-drained soil with a pH of 6.5 to 7.0.
- Start off the growing season right by mixing in several inches of aged compost or other rich organic matter into your native soil.
- Check soil moisture often or consider using a soaker hose to keep moisture levels consistent.
- For tender and rapid leaf production, feed regularly with a water-soluble plant food.
- Harvest spinach starting with the outermost leaves once leaves are large enough to eat.
Soil, Planting, and Care
Spinach grows most quickly in well-drained soil rich in organic matter such as compost or composted manure and with a pH of 6.5 to 7. A simple way to improve your existing soil is to mix 3 inches of aged compost-enriched Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® All Purpose In-Ground Soil with the top 6 inches of existing soil. In order to grow spinach twice a year, plant it about 4 to 6 weeks before the last frost in the spring, and again 6 to 8 weeks before the first frost in the fall. Space plants 12 inches apart; this gives leaves room to reach full size. Perhaps the easiest growing option is to plant spinach in pots filled with premium quality potting mix, such as Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® All Purpose Container Mix which will provide roots with just the right environment for strong growth.
For the most tender leaves, encourage spinach to grow fast and without interruption by fertilizing regularly with a water-soluble fertilizer like Miracle-Gro® Performance Organics® Edibles Plant Nutrition that feeds the soil along with the plants for better growth. (Be sure to follow directions.) This plant food works in tandem with great soil to help you achieve the best possible spinach harvest.
In the spring, plants will grow tall and bloom (called bolting) as soon as the days are longer than 14 hours. Heat also speeds up bolting, since spinach prefers temperatures between 35 and 75 degrees. Our variety is slow to bolt, which is a real bonus for gardeners who don't have the luxury of long stretches of mild weather.
Because it bolts in the lengthening days of spring, spinach is an especially popular crop for fall, when days are short and cool. Plants are very cold-hardy, tolerating temperatures as cold as the teens to low 20s once they are well established. This quality makes them great for overwintering over in zones 8 and southward.
In cold climates, some gardeners plant spinach in a cold frame or cover plants with hay and leave them all winter; they'll be first to produce a very early spring harvest.
Troubleshooting
Heat and long days will end your crop, so plant as mentioned above. Pests that enjoy spinach include flea beetles, spider mites, and aphids, which feed on the leaves. Diseases that attack plants are downy mildew (a mildew that may appear during cool, moist weather) and white rust (which causes white spots on the leaves). For instructions on how to fight back against these pests and diseases, contact your local Extension agency.
Harvest and Storage
Spinach leaves are ready to harvest as soon as they are big enough to eat. Harvest by removing only the outer leaves and allowing the center leaves to grow larger; this will allow the plant to keep producing. Picking the outer leaves also gives the advantage of briefly delaying bolting. In spring, when plants are about to bolt, pull the entire plant at once to enjoy the leaves before they become bitter.
FAQs
When is the best time to plant spinach?
In late winter or early spring for a fast crop and again in late summer or early fall, after the hottest temperatures have passed. Spinach is a cool-weather vegetable.
How can I know when my spinach is ready for harvest? What is the method of harvesting?
When the outer leaves are about 6 inches long, they're ready to be harvested. Or, if it is spring and plants are near the end of the season where they will soon bolt (bloom), you can pull up or cut the entire plant.
My spinach bolted, and I cut the plants just above the soil line.
 Will I get another crop from them?
Will I get another crop from them? No, they are finished. It is time to pull them up and replace them with a warm-weather crop. You can plant spinach again in late summer for a fall harvest.
Container Gardening Cool Season Gardening Fall Gardening Frost Growing Techniques Spinach Vegetables
How to grow spinach: indoors or outdoors for healthy leaves
(Image credit: Poungpeth EyeEm/GettyImages)
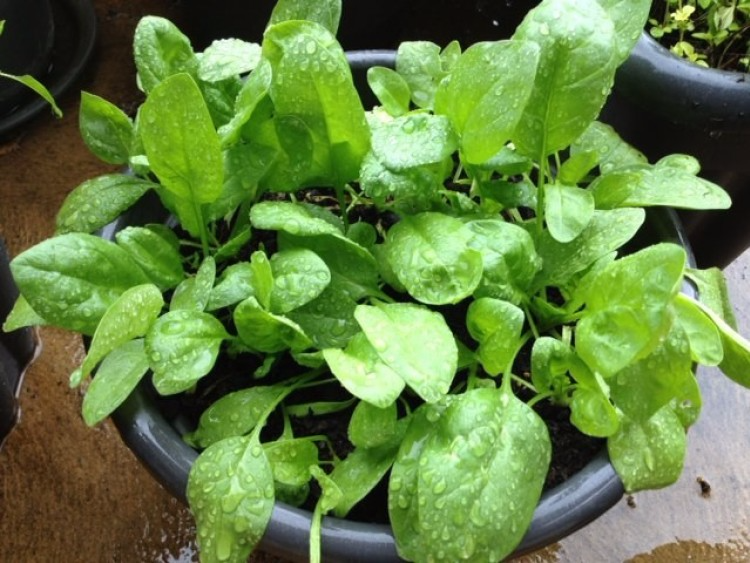
It is easy to learn how to grow spinach and the tasty homegrown leaves are packed with nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, iron and calcium and 13 compounds that function as antioxidants and cancer fighting agents – making it an excellent choice to add to your vegetable garden ideas.
Quick and easy to grow, you could be enjoying spinach leaves within six to eight weeks of planting. With many different varieties to choose from, if you plan carefully, and sow different types successionally, you could enjoy the green nutritious leaves year round.
An ideal crop for vegetable garden container ideas, spinach can be grown as cut-and-come-again baby leaves to enjoy in salads or sandwiches, or leave the leaves to grow larger and mature to use in cooking, such as to add to pasta dishes or use as a side vegetable. It is a productive and highly versatile crop, making growing spinach a popular choice for small vegetable garden ideas, where every inch of space needs to be used to the best advantage.
How to grow spinach
(Image credit: Sigmund/Unsplash)
There are a number of options for how to grow spinach. You could grow it indoors or outdoors, in pots on a terrace or courtyard along with other salad leaves such as lettuce, among other crops as part of your kitchen garden ideas, or in raised garden beds.
'Select from one of three types of spinach. The curly leafed savoy, flat leafed or the slightly curly semi-savoy. The flat leafed types generally have the mildest flavor and their smallest leaves are sold as baby spinach,' explains gardening expert Melinda Myers .
When is the best month to plant spinach?
The best month for growing spinach will depend to a certain extent on the hardiness zone where you live. However, you want to be growing spinach during the cool weather of spring and fall, as it is a cool weather crop.
Summer spinach cultivars: Plant summer varieties of spinach every few weeks from early until late spring.
Winter spinach cultivars: Sow hardy winter cultivars from mid summer to early fall.
The experts at Bonnie Plants provide the following advice for growing spinach twice a year: plant it about four to six weeks before the last frost in the spring, and again six to eight weeks before the first frost in the fall.
By sowing spinach seeds every three to four weeks as part of your planning of when to plant vegetables, you can enjoy a constant supply through the growing season.
How to grow spinach from seed
(Image credit: Getty Images)
First decide on where you want to grow your spinach crops, as some of the smaller varieties are particularly well suited to containers, for instance.
For success in growing spinach, before sowing the seeds enrich the soil, such as by digging in homemade garden compost and a general fertilizer. This will both help the spinach to grow well, and also prevent the leaves tasting bitter.
'There is no such thing as putting too much compost in garden soil. Mix at least 2-4 inches of compost in the row before planting,' advises Simon Crawford, breeder at Burpee Europe .
'The key to success begins with getting the plants off to a good start. Plant the right varieties in a rich, organic soil. Supply lots of moisture, and don't be shy about fertilizing. Vigorous spinach is tasty spinach,' adds Simon.
Vigorous spinach is tasty spinach,' adds Simon.
Follow these steps for how to grow spinach from seed:
- Grow spinach in moist but well-drained soil or compost.
- Winter spinach cultivars need a sunny position; summer spinach varieties are better in partial shade so are among the easiest vegetables to grow in shade
- Sow seeds thinly in a shallow drill – about 1inch deep.
- If sowing more than one row then space each row about 14 inches apart.
- Cover seeds lightly with soil.
- After the seeds germinate thin them to 3-5 inches apart. 'Thinning is very important and you must be ruthless,' says Simon Crawford.
- Fertilize plants regularly with a water-soluble plant food.
- Sow seeds every three to four weeks for a regular supply through the growing season.
- Keep spinach crops well watered – watering at the base of the plant.
‘Spinach can be cut again and again and last for months and months. I sow seeds deliberately quite thickly as a cut and come again salad crop. It’s important to keep them well watered and that way you will get delicious growth,' advises Monty Don in a video for Gardeners' World .
I sow seeds deliberately quite thickly as a cut and come again salad crop. It’s important to keep them well watered and that way you will get delicious growth,' advises Monty Don in a video for Gardeners' World .
Growing spinach in raised beds
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Choosing raised beds for growing spinach can get round the problem of your garden having poor soil or the wrong soil type for crops to grow successfully – as spinach prefers a neutral to alkaline soil.
Raised beds offer good drainage and are also easily manageable as a low maintenance garden border idea. You can fill them with rich, organic soil, working in 2-4 inches of compost prior to planting spinach seeds.
As above, sow spinach seeds in a shallow drill about 1 inch deep, each row about 14 inches apart. When seedlings are large enough to handle, thin them out to about 3 inches apart. Water and fertilize the plants regularly.
How to grow spinach in pots
(Image credit: Getty Images)
For how to grow spinach in pots, choose a wide pot or trough so that you can space out the spinach plants, and one that is about 6-8 inches deep. Spinach works well growing in pots alongside herb planter ideas.
Spinach works well growing in pots alongside herb planter ideas.
- Use quality potting mix rich in organic matter.
- Well-draining soil is important for spinach to grow well in pots.
- Sow seeds 1/2 inch deep in containers.
- Seedlings should germinate in five to 14 days depending on the variety and growing conditions.
- Space each spinach plant at least 3 inches apart - or slightly further apart if you want to harvest larger leaves.
- Keep the pot in a sunny spot when growing spinach in the fall.
- When growing spinach in spring and summer keep the containers in semi shade.
- Do not let the spinach plants sit in wet soil – keep the soil moist but not wet – so make sure the pot has good drainage.
- Fertilize the soil regularly.
'One of the great advantages of container growing is that it is easy to extend the growing season. Many plants will benefit from the additional warmth found close to the house,' says Aaron Bertelsen, gardener and cook at Great Dixter and author of Grow Fruit & Vegetables in Pots: Planting advice and recipes from Great Dixter .
How to grow spinach indoors
(Image credit: Angèle Kamp/ Unsplash)
It is easy to grow spinach indoors on a windowsill. If you are growing herbs indoors then place your spinach crops by these so you can tend to them all at the same time.
If planting in fall, place the pots on a sunnier windowsill as there are fewer hours of sunlight. Do not allow the plants to get too cold or too hot – so do not place directly above a radiator, for instance.
If planting spinach in spring, then position the pot where it will get some shade.
Sow spinach seeds in a pot at least 6 inches deep, and plant seeds at a depth of 1/2 inch, with each plant spaced about 3 inches apart. Keep the spinach plants well watered, although do not allow the soil to get waterlogged.
(Image credit: Getty Images)
How often should you water spinach?
You should water and fertilize spinach plants regularly, but try to avoid getting the leaves wet. The is to keep the soil moist but not soggy. Regular watering is especially important in periods of warm weather to prevent the plants from 'bolting' or producing flowers – if they do so the leaves will taste bitter.
Regular watering is especially important in periods of warm weather to prevent the plants from 'bolting' or producing flowers – if they do so the leaves will taste bitter.
Other ways to care for spinach include:
- Protect spinach seedlings sown in the fall from the cold by covering with fleece or a cloche.
- Shade spinach crops in hot weather to stop the soil drying out and the spinach plants bolting. You can do this through companion planting them next to pole – or runner – beans which as they grow will provide shade to protect the tender spinach plants from the heat of the sun.
- Protect young spinach seedlings from slugs, snails and birds.
Harvesting spinach
(Image credit: Getty Images)
You can harvest spinach between 6 to 10 weeks after sowing. If you sow successionally in spring and fall, you can have spinach to harvest throughout the year.
Summer spinach cultivars – you can generally pick summer varieties of spinach from May to October, depending on the climate in the area where you live.
Winter spinach cultivars – these can be harvested between October and April.
'Harvest a few leaves at a time from each plant. This will allow the plants to continue producing all season,' advises Simon Crawford.
This makes spinach a great crop to grow when gardening with children as they can continue to enjoy the fruits of their labors. This is the same as for other cut-and-come-again salad leaves, or if you're growing basil, or other leafy herbs.
Others gardening experts advise to harvest every alternate plant for use in the kitchen, giving the rest more room to grow.
Keep an eye on spinach crops as the plants usually grow quicker in warmer weather.
There are options for how to pick the leaves for a later harvest, much in the same way as when harvesting swiss chard. 'You can cut individual outer leaves when the plants are 3 inches tall and allow the inner leaves to continue to grow for later harvests. Or cut the whole head when the plant is 6 inches tall and wait several weeks for regrowth and a second harvest,' advises Melinda Myers,
Baby spinach leaves are great for use in salads, whereas mature leaves can be wilted into soups, stews, pasta or risotto dishes, to name but a few.
Leaves are ideally used directly after harvesting for the best flavor, and any extras can be stored in the fridge for up to 14 days.
Is spinach easy to grow?
If you've ever wondered if spinach is easy to grow, the simple answer is, yes. Like beets, it is a cool weather crop and requires minimal fuss.
It can be grown all year round if you choose the right spinach varieties and works well in containers, too. While the most cost effective method is to grow spinach from seed, you can buy transplants often at local nurseries, or online, too, in the main growing seasons. 'These young plants will already be well on their way to maturity when you put them in your garden,' explains the experts at Bonnie Plants .
How long does it take to grow spinach?
Spinach takes about six weeks to grow from being sown to harvesting.
There are both winter cultivars and summer cultivars of spinach, which are sown and harvested at different times. Choose a variety of each to sow and you can enjoy the leaves all through the year.
'A fast-growing plant, spinach yields many leaves in a short time in the mild weather of spring and fall. The main trick in how to grow spinach lies in making it last as long as possible, especially in the spring, when lengthening days shorten its life,' explain the Bonnie Plants experts.
Does spinach like full sun?
If you are growing winter cultivars of spinach in fall then these prefer full sun to grow well. Summer varieties prefer partial shade as otherwise the leaves can get scorched by hot sun in summer.
Will spinach regrow after cutting?
Spinach will regrow after cutting and if you keep harvesting the leaves, a few at a time, it will continue producing leaves through the season.
Rachel is senior content editor, and writes and commissions gardening content for homesandgardens.com, Homes & Gardens magazine, and its sister titles Period Living Magazine and Country Homes & Interiors. She has written for lifestyle magazines for many years, with a particular focus on gardening, historic houses and arts and crafts, but started out her journalism career in BBC radio, where she enjoyed reporting on and writing programme scripts for all manner of stories. Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
How to grow spinach in your garden
- Details
- Anatoly Vorontsov
Spinach is a leafy green that grows best in cool climates. Spinach, rich in iron, is also rich in vitamins A and C, potassium, thiamine and folic acid, among other nutrients.
Spinach contains carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, which are abundant in most dark green leafy vegetables.
Spinach is delicious both raw and cooked.
When to plant spinach
Spinach grows in the same way as lettuce in terms of conditions and requirements, but it is more nutritious and can be eaten raw or cooked.
It has more iron, calcium and vitamins than most plants and is a good source of vitamins A, B and C.
- Spring planting can begin as soon as the soil is tilled. It is very important to plant spinach as soon as possible to give it the six weeks of cool weather it needs between planting and harvest.
- Soil temperature should not exceed 21°C for optimum germination.
- During early spring, planting should be done every two weeks.
- Northern growers can harvest spinach in early spring by planting just before the fall frost. In winter, cover young plants with a thick mulch, and then remove the protection when the soil temperature in the area reaches 5°C.
- Spinach cannot grow in the middle of summer. Consider New Zealand spinach or Malabar spinach, two comparable leafy vegetables with higher heat tolerance for a summer harvest.

- If you live in a mild climate, spinach can also be planted in autumn.
- Planting should be suspended until the soil temperature has cooled.
Where to plant spinach
There are many possibilities when it comes to growing spinach. You can grow spinach indoors or outdoors, in pots on a patio or yard, in a vegetable garden alongside other crops, or in raised beds.
Prerequisites:
1. In warm climates, grow spinach in partial shade.
2. Plant spinach in well-drained, loamy soil with a high organic content. Before planting, add old compost or organic planting mix to the beds and plow the soil to a depth of 30 cm.
- Spinach grows best in soils with a pH of 6.0 to 6.8.
- Spinach is a hardy plant that grows well in cool weather - the ideal temperature range is 10-21°C.
How to plant spinach
Spinach is a nutritious and delicious vegetable that can be eaten straight from the garden or used in a variety of recipes. Spinach is known as a "superfood" rich in calcium, iron and vitamins like A and C.
Spinach is known as a "superfood" rich in calcium, iron and vitamins like A and C.
Learn how to grow spinach and add this cool season nutrient to your garden by following these simple instructions:
1. Sow the seeds at a distance of 1 cm from each other.
When planting in rows, make sure the rows are at least 20 cm apart. This allows the seeds to mature without competing for space. Make sure you get new seeds to plant each year as they don't stay viable for long periods.
2. Cover the seeds with soil.
Do not press the soil over the seeds; rather, it should be light and fluffy. Make sure the seeds are completely covered with soil and not exposed to air.
3. Spread the mulch evenly over the entire planting area.
Mulch the planting area with hay, straw, leaves, or grass to prevent weeds from sprouting. Removing unwanted weeds can damage spinach roots, making mulching a useful weed control method.
4. Thoroughly water the planting area.
Water the area with a hose or can using a gentle shower. A powerful environment can disrupt or even wash away newly sown seeds.
5. Adapt to the heat.
Consider using cold frames or thick row covers to keep the soil cool during hot summers in hot weather. If you are growing in hot weather, sow additional seeds and water them twice a day.
Spinach Pest and Disease Prevention Tips
If you are looking for a pest or disease resistant crop, spinach is a gardener's dream because it rarely succumbs to any major problems. These few tips will help you avoid pests and diseases:
- Aphids, flea beetles, slugs and spider mites, among other pests, are attracted to spinach leaves, making them vulnerable to attack. You can remove aphids from plants by spraying them with a strong jet of water. Pinch off any foliage that has been badly damaged by the pest.
- Using diatomaceous earth to form a barrier around plants will prevent slugs and snails from eating spinach.

- Spinach is prone to various diseases including mold, rust and mosaic virus. In the first place, preference should be given to growing varieties resistant to rust and disease.
- Yeasts such as mold and rust, which can cause disease, are plant fungi. You should sprinkle compost tea on the leaves after they have been harvested to prevent fungal diseases.
- Plants infected with mosaic virus should also be removed from the garden. Leaf spotting or streaks of white or yellow are caused by the mosaic virus, which can be caused by several different strains.
- It would be nice if you took out the garbage in the garden. Diseased plants should be removed and destroyed.
Spinach varieties
There are many varieties of spinach. When it comes to growing them, each has its own set of subtleties and nuances. Spinach leaves can also be eaten raw or cooked in a variety of ways. Let's learn about spinach varieties!
1. Red Cardinal
'Red Cardinal' leaves are veined red and stems are dark red. However, this variety should be harvested when the leaves are still young and tender, as it grows faster than any other green leafed spinach variety.
However, this variety should be harvested when the leaves are still young and tender, as it grows faster than any other green leafed spinach variety.
2. New Zealand spinach
The leaves of this plant are crunchy and juicy, it comes from New Zealand. The leaves practically melt in your mouth and can be eaten raw or cooked.
3. Malabar spinach
This variety of spinach needs many years of warmth and a trellis to climb on to reach its maximum growth potential.
4. Catalina
This plant has thick, succulent, spear-shaped leaves with a succulent texture. The structure of the foliage makes it the most suitable for cooking in the kitchen.
5. Indian Summer
This is an excellent and productive three-season spinach that can be harvested in spring, summer and autumn. The leaves of the plant are smooth, flattened.
Watering and feeding spinach
Each plant requires care when growing.
When watering and feeding spinach, you should keep the following points in mind:
- Keep the soil evenly moist throughout the growing season if you want to see rapid growth of spinach.
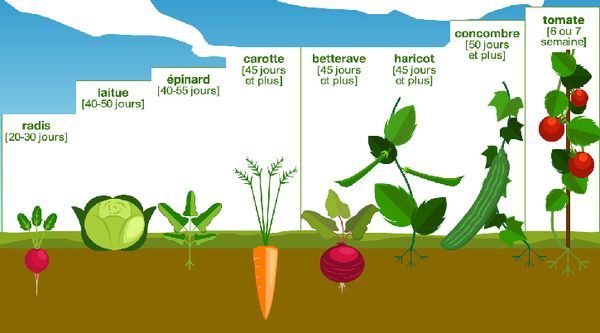
- It is better not to water the leaves with dirty water; instead, mulch surrounding plants with straw or shredded leaves to prevent soil from getting on the leaves.
- Use fertilizer only if necessary due to stunted growth, or as an additive if your soil pH is low.
- Apart from thinning, the need for cultivation is low. Fine roots are easily damaged because they are so small.
- During the growing season, water your plants with compost tea or dilute emulsion solution every two weeks to keep them looking their best.
- Mid-season is a good time to compost your spinach.
More tips for growing spinach
Growing spinach requires persistence and care.
Keep these tips in mind if you want to grow spinach:
- Plant spinach at the right time of the year: Spinach can be grown in almost any climate if the right conditions are met. Plant spinach as soon as the soil reaches a temperature suitable for growing in cold winter locations.
 Spinach needs about six weeks of cool weather from seed to harvest and can tolerate a bit of frost.
Spinach needs about six weeks of cool weather from seed to harvest and can tolerate a bit of frost. - Choose the perfect place to plant your spinach: spinach thrives in conditions ranging from full sun to light shade. • Spinach prefers rich, moist soil that is neutral or alkaline in ph (pH 7.0 or higher). Enrich the soil before planting.
- Grow spinach carefully: plant spinach at the right time for your climate. Spinach prefers moist soil and regular feeding.
- Use row covers to keep out pests. Remove damaged leaves over time.
- Choose young spinach for the best taste: harvest the leaves when they have reached the desired size. Larger leaves may become bitter; therefore, harvest quickly. Harvest the outer leaves, reserving the inner leaves for late harvest, or cut the plant at the root.
When to harvest spinach
How long does it take for spinach to grow? Spinach can be harvested at any time. Pruning promotes fresh growth and new leaves, making all gardeners happy!
- Spinach leaves can be harvested once they have reached a size suitable for consumption.
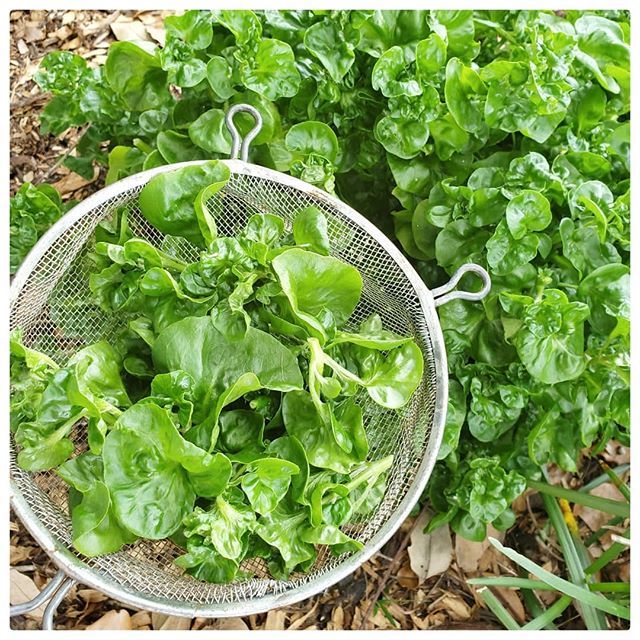

- Large and old leaves may be bitter; thus, harvest the leaves as soon as possible rather than postponing.
- Diseases, flowering and seeding in spinach are caused by long days (days longer than 14 hours) and warm weather (temperatures above 24°C).
How to Store and Preserve Spinach
Once the leaves have been successfully harvested, you need to store them properly so that they do not wilt or spoil.
To store spinach, proceed as follows:
- Rinse the spinach well to remove any grains of sand that may have stuck to shriveled leaves.
- Spinach can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week.
- You can also store spinach in a variety of ways, including freezing, canning, or drying.
Spinach is one of the easiest plants to grow in your garden. It has a long growing season, is stable and requires little maintenance.
To get started, just choose a suitable spot in your garden with adequate drainage.
Getting started with spinach is simple after a little soil preparation and choosing the variety you want to grow. You will have a lot of greens for salads and various ready meals.
Share with friends:
rules for planting and caring for outdoors
All spinach lovers and those who want to try growing it with their own hands will find this article useful. In it you will find a lot of useful information about growing spinach at home.
By following the tips from the article, you can forget about buying greens in the store forever: you will always have fresh spinach grown by yourself on your table. Read the step-by-step instructions for growing it in the open field and on the windowsill only with us.
Contents:
- Features of spinach: cultivation and care in the open field
- What you need to grow spinach at home
- Features
- Care instructions
- Conditions
- Growing technology
- Spinach soil
- What should be
- Soil care
- Spinach Fertilizer
- Methods
- The better
- Strawberry spinach: planting and care
- Growing from seed
- Outdoor planting and care
- How to grow spinach on a windowsill
- Features
- How to grow spinach in a vegetable garden
- Spinach: benefits and harms, growing
Features of spinach: cultivation and care in the open field
Spinach is mainly an annual, early ripening cold-resistant plant, which ranks first among vegetables in terms of iron content, and second only to legumes in terms of protein content.
Note: Almost all B vitamins are isolated in this plant, and the content of vitamin K in 100 g of leaves is 4 times higher than the daily norm.
It is also rich in such elements as manganese, potassium, magnesium, and about a hundred other components that are no less useful for the human body are contained in this plant.
And yet, having such wonderful properties, it is still an infrequent guest on our table. This article will tell you more about growing and caring for spinach in the open field.
What you need to grow spinach at home
How to grow spinach at home? Firstly, this plant is quite demanding on soil fertility. Therefore, the first necessary condition for its cultivation should be a cultivated, well-fertilized area.
Note: When choosing a site, it should be taken into account that vegetable crops are the best predecessors for it, since organic fertilizers have already been applied under them.
Secondly, you need to know that for continuous harvest throughout the spring and summer, it is recommended to plant at several times.
Thirdly, it is important to observe the care conditions, which consist of weeding and regular watering, loosening the soil and top dressing. Let's consider in more detail all the listed conditions.
Features
Growing spinach along with other greens is something anyone can do. This can be done both in the greenhouse and in the open field, depending on your desires and capabilities. Growing options are shown in Figure 1.
This crop is cold-resistant and unpretentious, almost unaffected by pests and diseases, has early maturity. Tolerates small (-6-8 degrees) short frosts. Therefore, crops planted before winter can safely winter under snow. It goes well with all garden crops.
See also: Independent cultivation of thyme
The plant is photophilous, therefore, for example, in the Moscow region, spring sowings in protected ground begin only at the end of February. It is in greenhouses in early spring that you can create conditions for a good harvest of greens.
It is in greenhouses in early spring that you can create conditions for a good harvest of greens.
After the snow has completely melted (which is usually mid-April), you can start sowing in open ground. For continuous production of greenery, such crops are carried out in a conveyor way, that is, with an interval of 20-30 days. The sown areas are covered with matting or special materials to accelerate the appearance of the first shoots.
In summer, sowing should be preceded by a thorough moistening of the soil. Plantings in June and July will provide you with greenery throughout the fall, while plantings in August become a winter crop.
Care Rules
Regardless of how and where you grow spinach, there are certain rules for caring for the plant (Figure 2):
- After the first shoots appear, weeding and watering should become regular.
- Controlling crop density has a direct impact on product quality.
 Therefore, for the first time this procedure can be carried out at the stage when the plant has 2-3 true leaves. At the same time, torn sockets can quite safely take root in another garden bed.
Therefore, for the first time this procedure can be carried out at the stage when the plant has 2-3 true leaves. At the same time, torn sockets can quite safely take root in another garden bed. - It is mandatory to water after transplanting and thinning, in order to maximize the roots in the soil.
Since the daylight hours are quite long in summer, it becomes necessary to reduce them specifically for this crop. To this end, the plants are covered in the morning and evening, protecting from light, because its excess leads to the shooting of the plant, which affects the growth of leaves and their taste.
Conditions
Planting and caring for spinach in the open field requires certain conditions to be met (picture 3):
- The soil must be well saturated with organic and mineral substances;
- When sowing, the soil must be moist. The optimal level of soil moisture is maintained during the entire growing season;
- Daylight hours must be of optimal length for the formation of lush green mass;
- The density of crops is constantly monitored by removing excess plants;
- Weed and loosen regularly.

Additional top dressing is also an important condition. But it will be required only if the soil itself does not have sufficient fertility or has not been fertilized with organic matter.
Growing technology
It should be known that in the crop rotation spinach acts as a precursor of heat-loving crops and a re-crop after green crops. At the same time, it is important to wait a certain period of time when growing crop by crop in order to avoid plant diseases.
Note: It is known that the yield of greenery is much larger and better in well-lit areas, especially in spring and autumn, when there is not enough daylight.
Even if the land in the allotted area is quite fertile, it will still not be superfluous to slightly feed it. To do this, it will be enough to add a little organic (half a bucket per 1 square meter) and complex mineral fertilizer. Acidic soil additionally needs liming.
Acidic soil additionally needs liming.
All preparatory work should be carried out in advance, that is, the soil should be prepared for sowing in the fall. This is due to the fact that the introduction of organic matter directly under the culture negatively affects its taste. In addition, in early spring, urea is applied under a rake to the prepared area in the amount of 20 g per 1 sq. m.
Note: For continuous greenery, it can be sown from the end of April to the beginning of August with some time periods.
Before sowing, it is advisable to soak the seeds for 1-2 days in warm water. The swollen planting material is dried and sown in rows to a depth of 3 cm. The distance between rows should be 30 cm. The sown area should be compacted.
Further care consists of thinning after the appearance of the first true leaves, regular watering, loosening and weeding.
Particular attention should be paid to watering, because spinach is especially sensitive to lack of moisture. This is especially pronounced during seed germination and after the appearance of a large number of leaves. However, if the weather is too wet, powdery mildew can damage the plants, and if the weather is too dry, leaf aphids can occur.
This is especially pronounced during seed germination and after the appearance of a large number of leaves. However, if the weather is too wet, powdery mildew can damage the plants, and if the weather is too dry, leaf aphids can occur.
Harvest begins in the phase of rosette formation of 5-8 full leaves. It is best to cut them in the early morning, while removing yellow and damaged leaves.
Soil for spinach
Spinach prefers fertile or well-drained soil. The plant is sensitive to both waterlogging and lack of moisture, as well as to the acidic reaction of the soil. Under adverse conditions, plant growth slows down, it turns yellow and dies.
What should be
So, what kind of soil to choose? The best option would be loamy soil. Sandy requires frequent watering. Acidic soil must first be limed, but even after that it will not be good enough due to the low content of the required amount of iron. And yet, no matter what the soil was originally, it needs some care.
Soil care
Soil care begins with site selection. It should be exposed to the sun and well drained. In case of stagnant water in the soil, you will have to make a raised bed.
Figure 3. Outdoor Growing ProcedureFor this type of bed, it is best to choose a material that will not rot when exposed to water (such as cedar planks). Do not forget to ask about the acidity of the soil, because the culture prefers slightly acidic soils.
In case of increased acidity, it is necessary to carry out liming of the soil in advance (2-3 months before planting) by adding limestone to it.
See also: How to grow sorrel from seeds in the open field and on the windowsill
To ensure sufficient saturation of the soil with nutrients, do not forget to add organic fertilizer to it (rotted manure, alfalfa and soy flour).
Note: Before fertilizing, make sure that the area is clear of cobbles and hard clods of earth, as well as weeds.
Planted soil is mulched with leaves, hay or grass to stop the development of weeds, because spinach sprouts are too fragile and pulling weeds can damage seedlings.
Be sure to water the planted area. However, remember that a strong jet of water can disturb the order of the sown seeds or wash them out of the ground. Therefore, use a watering can, or a sprinkler nozzle on the hose.
Spinach Fertilizer
Most often, fertilizer is applied in the autumn period, when the plot is being prepared for sowing. In the spring, just before sowing, fertilizer is carried out with mineral substances (for soils with low fertility).
During the growth period, top dressing is carried out when absolutely necessary.
Methods
Naturally, the dosage of applied fertilizers must be combined with the level of soil fertility.
Thus, potash and phosphorus fertilizers are applied to fertile soil in autumn. Then the soil is fertilized with humus or rotted manure. In this case, fertilizers are applied during digging the soil.
In this case, fertilizers are applied during digging the soil.
On less fertile soils, it is advisable to apply mineral fertilizers (potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen) just before sowing.
But with spring top dressing, you should be careful, because the leaves accumulate chemical compounds introduced under the plant (for example, nitrates).
The better
Experienced gardeners prefer autumn soil fertilization. Indeed, during the winter period, she manages to assimilate the nutrients introduced as part of organic top dressing. With the advent of spring, such soil is ready for cultivation.
Note: Since spinach is a fast-growing crop, the introduction of fresh organic matter directly under it is not recommended, because this is reflected in its taste.
During the growth period, it is also not recommended to carry out top dressing with phosphorus and potash fertilizers, which stimulate the shooting of the plant. And this is extremely undesirable for obtaining a quality crop.
And this is extremely undesirable for obtaining a quality crop.
Sometimes it is necessary to fertilize with nitrogenous fertilizers. In this case, it is carried out along with watering. And yet, for such top dressing there should be quite good reasons, since all substances absorbed from the soil are collected in the leaves of the culture, and it is they who are eaten.
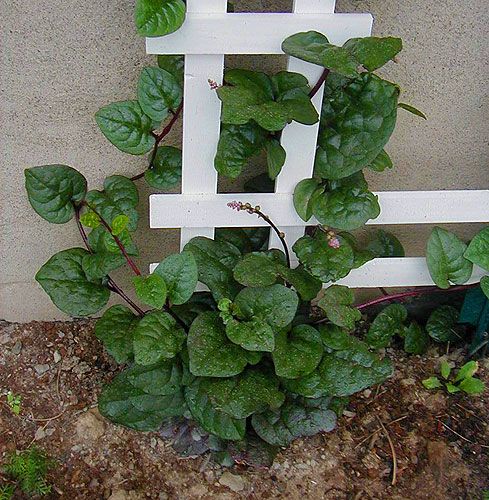
Strawberry spinach: planting and care
Strawberry spinach (spinach-raspberry) is both annual and perennial herbaceous plant. Its peculiarity is bright red flowers twisted into spherical balls. They are often mistaken for berries (Figure 4). The plant blooms from mid to late summer, and bears fruit from August to September.
The fruits are indeed shaped like strawberries (strawberries), but, unlike berries, they are completely tasteless. Then why is he so good? The leaves have a special juiciness, and the plant itself is unpretentious and cold-resistant. It also tolerates drought and hot weather well.
Note: You can meet this plant near fences and along roads, in garbage dumps and heaps of rubble. However, in recent years, it has begun to be grown as a vegetable salad crop.
It has an average ripening time and, with the seedling method of growing, seedlings ripen already in July. In addition, the culture is practically not susceptible to diseases and pests, with the exception of aphids.
As usual, the strawberry variety is grown from seeds or seedlings. To get an earlier harvest, they practice growing seedlings in a pot. At the same time, seeds begin to be sown in a special substrate in mid-March. The grown seedlings at the age of 30 days are planted in the ground. The landing order is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4. Appearance of strawberry spinach It is possible to sow directly into the prepared soil only after the snow cover has completely melted. To do this, 4-5 pre-prepared seeds are lowered into the prepared wells.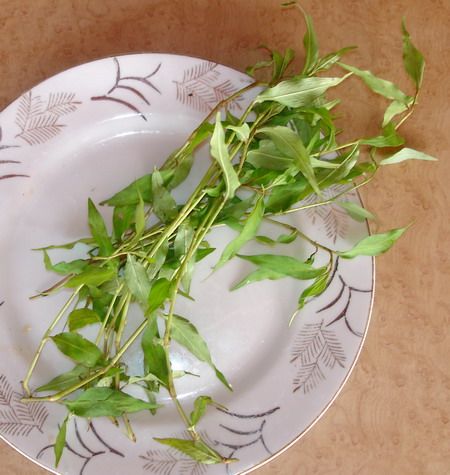 The sown area is mulched.
The sown area is mulched.
When two true leaves appear on seedlings, the crops should be thinned out, removing weaker plants. Further care involves weeding, loosening, watering, feeding and tying branches.
Fertilize twice a season with organic manure, such as wood ash, which is embedded in moist soil.
Figure 5. Preparing seeds and planting in open groundWith good care, the bush grows so much that it "clogs" other plants, and its branches are literally strewn with berries. Heavy whips must be tied to pre-prepared supports.
Ripe and crumbling berries are perfectly preserved under the snow, and in the spring they sprout together. Therefore, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of self-seeding of the plant and take care of the control of growth.
Berries can be juiced, made into jam, used for decoration. Young green leaves are added to salads and soups, used as a side dish. In addition, the greens of strawberry spinach lend themselves perfectly to various types of harvesting for the winter.
Growing from seed
Growing from seed properly will allow a good harvest of this deciduous crop. The principles of cultivation are quite simple and accessible (picture 6):
- When choosing a variety, you should know that there are two types of spinach - summer and winter. Summer varieties are grown for their delicate, juicy taste and are harvested from late May to late September. Winter varieties are distinguished by their prickly fruits, and they are harvested from October to April.
- Depending on the selected variety, planting in open ground is carried out. So, summer varieties are sown every few weeks from mid-March to the end of May. Winter sown in August, and the second time - in September.
- Prefer fertile soil with good drainage. The ideal place for the summer will be the aisle of vegetable crops, and for the winter - a plot well-lit by the sun.
- If necessary, apply organic fertilizer while digging the site before winter.
 Complex fertilizers should be applied just before sowing with the arrival of spring.
Complex fertilizers should be applied just before sowing with the arrival of spring. - Sow 2-3 seeds. in well-moistened soil, planting them to a depth of about 3 cm at a distance of 60 cm from each other. Shoots that appear soon must be thinned out, leaving stronger sprouts.
When caring for spinach, keep the soil well moist and loose, and take care to thin out the seedlings. Starting in October, winter varieties will have to be covered.
Figure 6. Preplant Seed TreatmentStart harvesting when the leaves are large enough and the flesh is tender. Remove leaves gradually, thereby stimulating the emergence of new ones. Remember that in summer varieties you can simultaneously remove up to half of the leaves, in winter - less than half.
Planting and care in the open field
Most often, spinach is not allocated a separate area, but sown in the spring as a precursor of heat-loving vegetable crops, or in the summer after harvesting early vegetables. Sometimes the culture is grown as a compactor or as a beacon plant. And yet, it is better to give preference to the beds where cucumbers, tomatoes and greens were previously grown, because they are the best predecessors.
Sometimes the culture is grown as a compactor or as a beacon plant. And yet, it is better to give preference to the beds where cucumbers, tomatoes and greens were previously grown, because they are the best predecessors.
Although spinach is not a particularly demanding plant, take care of the fertility of the soil: when digging, add humus (5 kg per 1 sq.m.) or ash (200 g per 1 sq.m.) to it. It would be best to carry out such top dressing in the fall. If the soil has not been fed, you can add mineral fertilizers to it 2 weeks before sowing.
Note: In order to continuously obtain green produce, the crop is sown at intervals of two weeks from mid-April to the end of August.
For autumn consumption, the crop is sown in June-July. Harvest from August crops is harvested in early spring as a winter crop. In regions where the air temperature in winter does not fall below -12 degrees, the spinach crop sown in autumn is harvested during the winter.
For early germination, the seeds are pre-soaked for 1-2 days until they swell. Swollen seeds are sown in rows in prepared and moistened soil.
So, on light soils, spinach is sown with multi-line tapes, and on heavy soils - in a two-line method or across the beds. At the same time, the seeds are planted to a depth of up to 4 cm (for loose soil), 2-3 cm (for heavy soil).
Seedling care consists of thinning, regular row spacing, weeding and watering. After the appearance of two true leaves, the sprouts are thinned at intervals of 10 cm 3-4 days after thinning, the crops can be fed with a solution of urea (5-10 g per bucket of water).
Harvested selectively, best in the morning. With continuous crops, greens are mowed in the phase of 4-5 true leaves. How to grow spinach on a windowsill? In this case, there is no better crop than spinach. After all, it can be grown in pots on the windowsill.
Since this is a cold-resistant plant, it can withstand temperatures down to + 8 degrees, and grows well behind glass until late autumn.
Features
You should know that the bush on the windowsill brings green foliage for 2 months from the moment the first leaves suitable for food appear. Therefore, after several harvests, the shooting process begins, and the leaves are no longer suitable for consumption. In this regard, it is recommended to update the planting every 2-3 months.
See also: Leaf beet Chard: planting, care and propagation humidity. If the seeds are sown in autumn, when there is not enough daylight, it is worth taking care of artificial lighting. It can be arranged using fluorescent lamps, both during the day, in gloomy weather, and after sunset. As a substrate for the plant, it is recommended to choose biohumus in combination with coconut fiber (1:2), which retains moisture well, preventing it from drying out or stagnating in the soil. You can also use universal soil for seedlings. When purchasing it, pay attention to the level of acidity, because spinach does not tolerate acidic soils. Early varieties are best suited for indoor growing conditions (picture 7). It is advisable to pre-soak them for a while to swell. Then dry and plant in a special planting pot to a depth of 1.5 cm. Then the pot is covered with cellophane until the first shoots appear and are no longer used. In another month, the greens will be ready for use, but remember that after 1-2 months, the process of shooting will begin, and the plant will become unsuitable for cutting leaves. To delay this process, do not forget to water the plants often and abundantly, especially in dry and hot weather. However, pay attention to the fact that there is no stagnation of water in the pot. Daily spraying is also acceptable, especially in winter, when heating devices are on and the air is too dry. Since spinach is one of the earliest vegetable crops and has sufficient cold resistance, it can be sown quite early (mid-April), as well as sown for the winter. The culture develops well on fertile loose soils, well fertilized earlier when growing predecessors, with a neutral reaction. The application of fresh organic fertilizer directly under the bushes has a negative effect on the taste of greens. Growing and caring for outdoors includes some important rules : Watering can be combined with top dressing with complex fertilizers. However, care must be taken with nitrogen, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Nitrogenous can contribute to the accumulation of nitrates in the leaves, and phosphorus and potassium can accelerate the process of bolting. Spinach is the richest source of vitamins and minerals, so its beneficial properties are undeniable. It saturates the body with nutrients and increases hemoglobin, has a positive effect on metabolism and helps to cleanse the body of toxins. It is clear that with such useful properties, this herb is used not only as a food product, but also as a medicine. For example, it is prescribed as an additional diet for patients suffering from radiation sickness. If you are often stressed, spinach is your vegetable. It will restore efficiency and put the nervous system in order. Are you suffering from constipation? Spinach contains a fairly large amount of fiber and chlorophyll, which stimulate the action of the intestines. Do you spend a lot of time at the computer? And here spinach will help you, because the lutein contained in it improves visual acuity and reduces eye fatigue. Useful properties are possessed not only by the leaves in green form, but also by the juice from them. It is used for both external and internal use. Therefore, the composition of the substrate should not contain peat, which contributes to its oxidation. Don't forget about drainage. Thus, it is necessary to put expanded clay (drainage) at the bottom of the pot with a layer of 2-3 cm, then fill it with a wet substrate.
Therefore, the composition of the substrate should not contain peat, which contributes to its oxidation. Don't forget about drainage. Thus, it is necessary to put expanded clay (drainage) at the bottom of the pot with a layer of 2-3 cm, then fill it with a wet substrate. Note: Wait until one or two pairs of true leaves are formed and dive seedlings into permanent containers. Moisten the soil abundantly before removing the seedlings from the planting container. So the root system of plants will more easily tolerate the transplant.

How to grow spinach in the garden
Note: Seeds begin to germinate at a temperature of +3-4 degrees, but still, +15-18 degrees will be optimal for growth. Mature plants can tolerate slight frosts, in contrast to the heat, when at +20 it starts throwing arrows.


Spinach: benefits and harms, growing
 In addition, the use of the plant helps to strengthen teeth and gums, prevents anemia and weakening of blood vessels, stimulates the pancreas and normalizes bowel function.
In addition, the use of the plant helps to strengthen teeth and gums, prevents anemia and weakening of blood vessels, stimulates the pancreas and normalizes bowel function. Note: Unlike rhubarb, spinach can be beneficially consumed by pregnant women and young children. This plant is perfectly digestible, has a tonic and anti-inflammatory effect, a slight diuretic and laxative effect.











