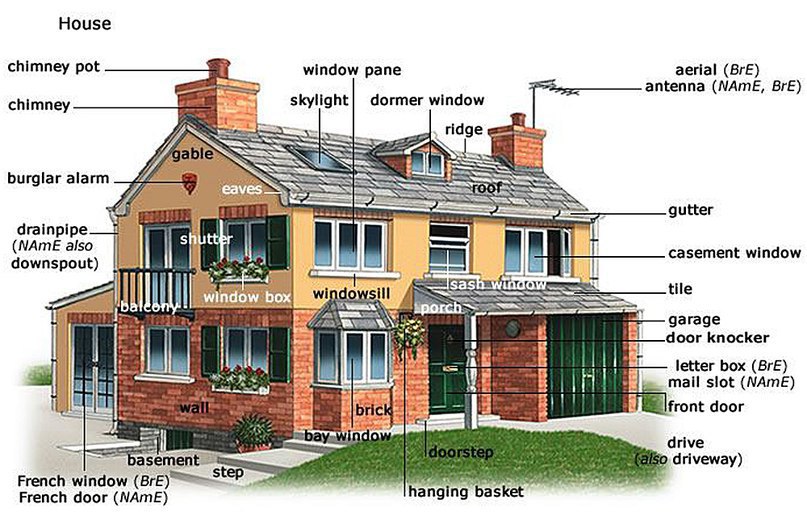
Cost to turn crawl space into basement
Basement conversion costs: an expert guide
If you need extra living space in your home, you might be asking how much a basement conversion costs? The beauty of a basement extension is that it could add to total square footage but, unlike an addition, won’t make your yard smaller.
And a basement extension has plenty of potential. It could be used as an additional living room or a home movie theater, create space for guests, add a playroom for kids, or a games room for all ages, a home office, a crafts room, and more.
But crucial to whether it’s the right project for your home is the cost of a basement conversion cost – we’ve called on an expert to provide the lowdown so that your basement ideas can become reality.
How much does a basement conversion cost?
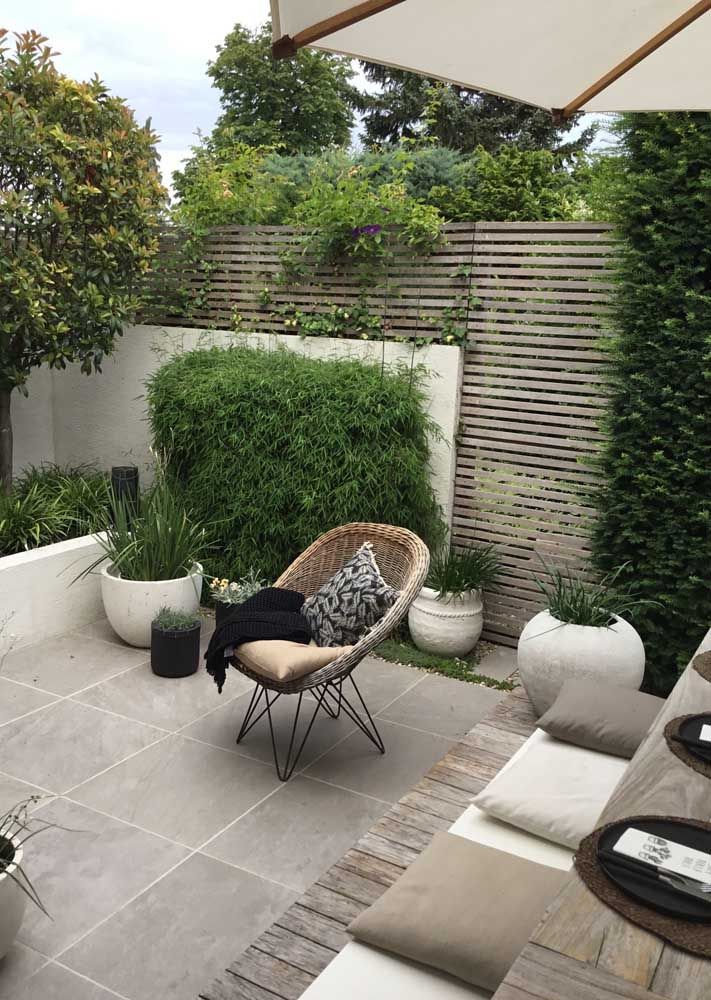
(Image credit: Future Publishing Ltd Photograph: Jonathan Gooch)
The cost of a basement conversion will depend on what the project consists of. You might already have a basement but plan to remodel it to create living space. Alternatively, a crawl space could be converted into a basement, or it might be a question of planning a basement conversion by digging where the house didn’t have one before.
How much does it cost to remodel a basement?
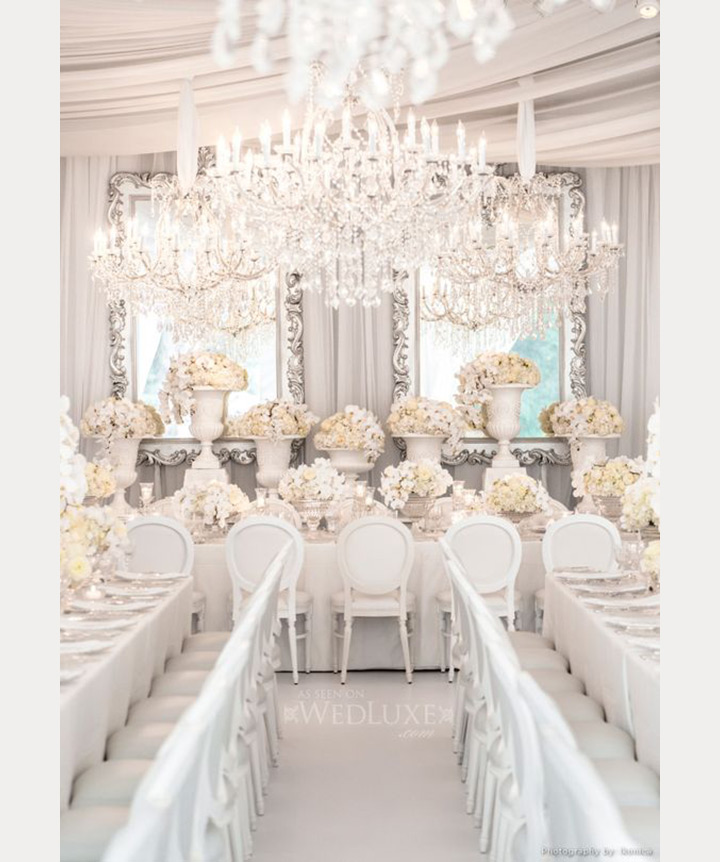
(Image credit: Future Publishing Ltd Photograph: Mark Bolton Photography)
If the house already has a basement, adding a basement extension could just be a case of remodeling. How much does a basement conversion cost in these circumstances?
‘Remodeling an existing basement into a living space can range in cost from $12,000 to $70,000 (£9,000 to £52,000) but tends to average around $21,500 (£16,000),’ says Bailey Carson, home care expert at Angi .
Be aware that what you plan to use the basement for will influence costs. ‘Adding a basement bedroom may cost between $3,000 and $10,000 (£2,250 and £7,500), while an additional bathroom will cost more along the lines of $6,500 to $16,500 (£4,900 to £12,300),’ says Bailey. ‘A home theater averages around $12,000 (£9,000), basement bar ideas around $8,000 (£6,000) and a home gym can range from $300 to $15,000 (£225 to £11,200), depending on equipment and other components.
‘Finally, an office may range from $500 to $3,000 (£375 to £2,250), depending on lighting, framing, flooring, doors, furniture and more.’
And if you have included any of these, you might want to factor in basement bathroom ideas, too.
Other factors that should be kept in mind? ‘The cost of a basement remodel will depend on factors including size, location, design, labor, materials, permits and inspections,’ says Bailey.
‘It will also depend on the status of your basement pre-remodel. For example, finishing an unfinished basement will cost more than a finished basement refresh. Adding or moving plumbing, walls or electricity, as well as installing egress windows or separate entrances, will also impact cost.’
This type of basement conversion can prove a worthwhile undertaking. ‘Remodeling a basement can turn an under-utilized space into more liveable space for you and your family,’ Bailey says. ‘The basement could be used as a gym, office, playroom, entertainment area, guest suite or even an ADU (accessory dwelling unit) you can rent out for additional income.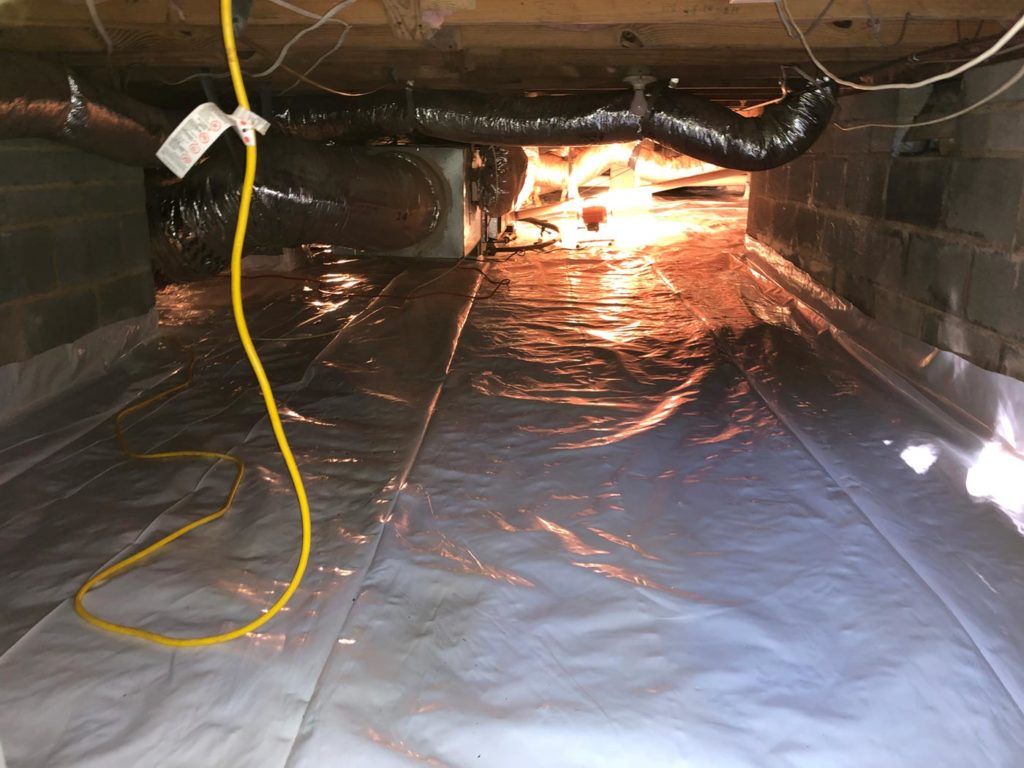 Remodeling a basement can have a great return on investment while also adding liveable space while you’re still in your home.’
Remodeling a basement can have a great return on investment while also adding liveable space while you’re still in your home.’
Basement stair ideas also need factoring into your final tally – and these will vary widely, depending on the materials used and whether they are made-to-order or off-the-shelf. And if you are thinking of renting out your basement, you will definitely want to consider basement kitchen ideas.
How much does it cost to covert a crawl space into a basement?
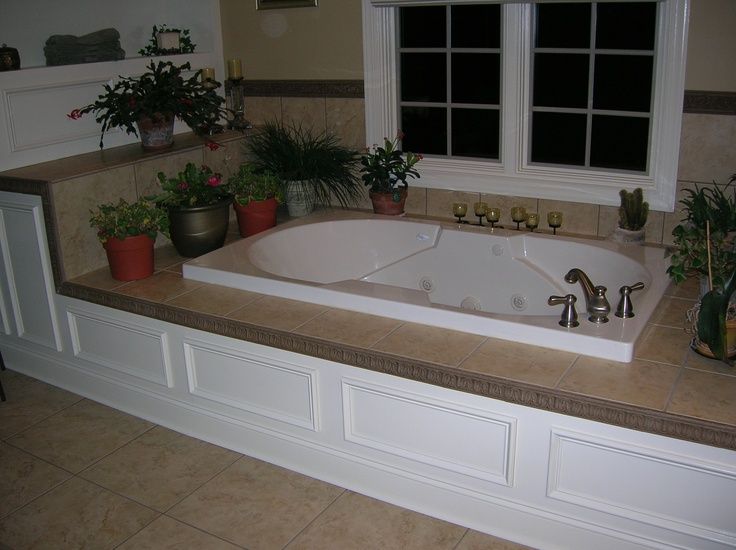
(Image credit: Future/ James Merrell)
Converting a crawl space into a basement is a much bigger investment. So how much does a basement addition cost in this scenario?
‘The average cost to convert a crawl space to a basement is around $50 per square foot (£540 per square metre), ranging from $50,000 to $150,000 (£37,300 to £112,000) for 2,000 square feet,’ says Bailey. ‘This includes digging out the crawl space, raising and bracing your home, installing drainage and plumbing, pouring foundation and more.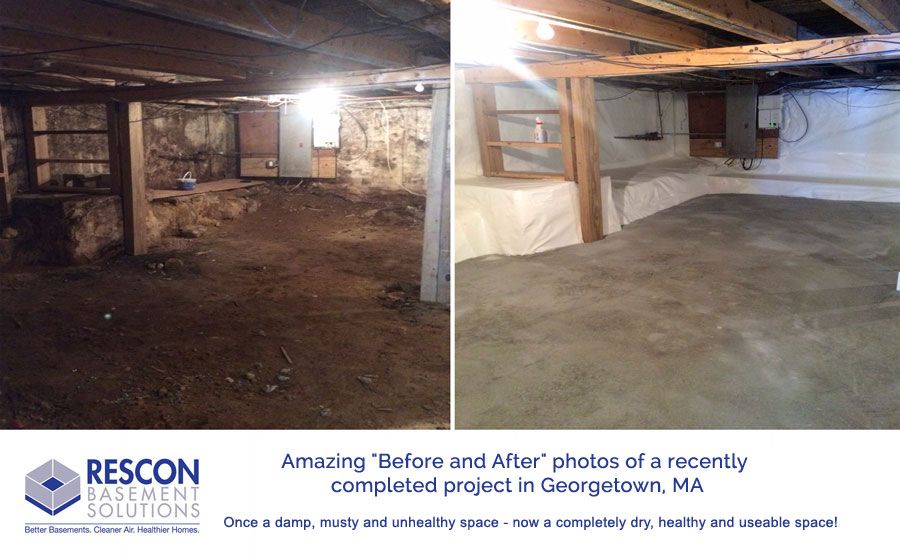
‘The additional cost to finish the space will then add anywhere from $10,000 to $70,000 (£7,500 to £52,250), depending on how you want to use the finished basement.’
Bear in mind the factors that will impact the final bill. ‘How much it costs to convert a crawl space will depend on the size and layout of your home, how deep you want to dig, and how you want to design the finished space,’ says Bailey.
‘The type of foundation you need as well as any landscaping or repairs to your home after it has re-settled may also increase the cost of converting a crawl space into a finished basement.’
As for whether it’s a project you should contemplate, Bailey says: ‘Digging out a crawl space is risky and expensive, so we generally don’t recommend it. If possible, consider building an addition with or without a basement, or building up instead of down. If you have an attic, you can also look at redoing that – instead of the crawl space – to add to your home.’
How much does it cost to dig out a new basement?
(Image credit: Bisca)
If you live in a home without a basement in a region where digging one of these out is a viable project, how much does a basement extension cost?
‘The average cost to build a full basement of around 2,000 square feet is around $110,000 (£82,100) if you’re starting from scratch,’ says Bailey. ‘If you need to lift your home to add a basement, you could be looking at a cost of up to $175,000 (£130,600).
‘If you need to lift your home to add a basement, you could be looking at a cost of up to $175,000 (£130,600).
‘However, these estimates do not include the cost of finishing the space and making it livable, which could add up to $35,000 (£26,100) in additional expenses for up to 1,500 square feet.
‘It’s important to note here that location plays a major role in the cost of adding and finishing a new basement. While the national average for finishing a basement is around $18,500 (£13,800), the cost in major cities like New York or Denver may be much higher.’
There are variables you should be aware of that can affect the final total. ‘How much it costs to add a basement will depend on a variety of factors, starting with size, layout, location, permits and design,’ says Bailey. ‘Costs will also increase if it needs waterproofing, plumbing and electricity. You also need to factor in the cost of raising your home to add the basement, if necessary.’
This type of basement conversion could be worth the spend.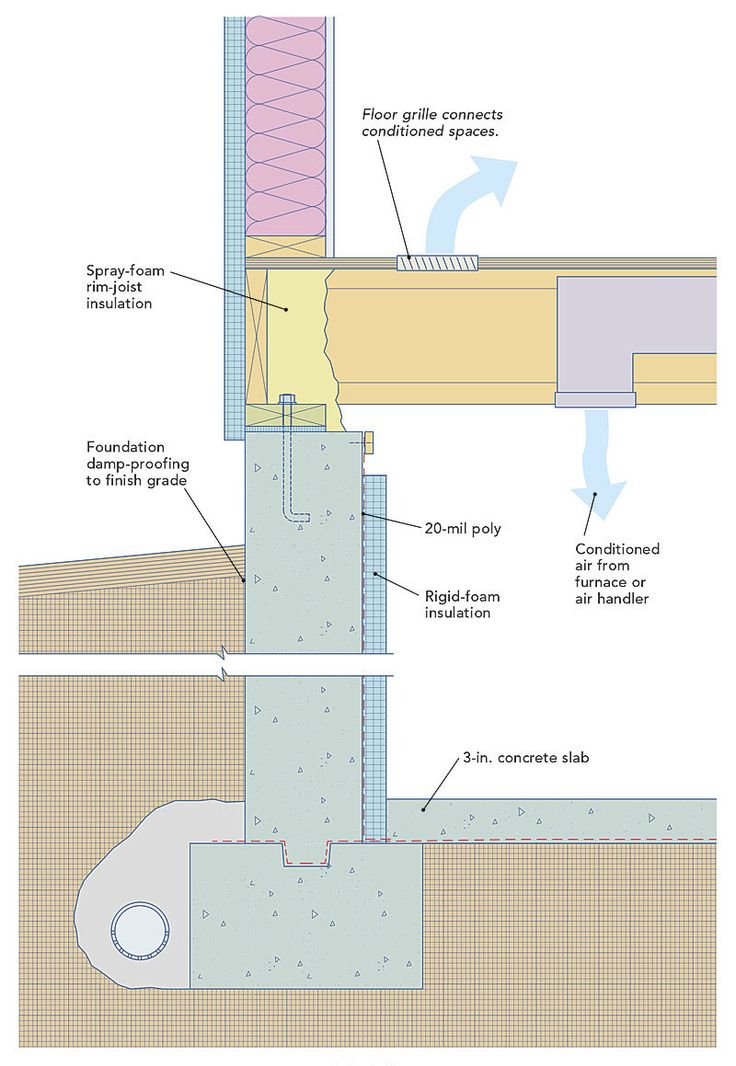 ‘Adding a basement can add storage space or living space to your home without taking up your yard space or raising your roof,’ says Bailey.
‘Adding a basement can add storage space or living space to your home without taking up your yard space or raising your roof,’ says Bailey.
‘It is also likely to increase the value of your home since you’re creating additional square footage. It may be a worthwhile investment if you’re planning to stay in your home for a while and need more liveable or storage space. However, it’s an expensive investment and if you live in warmer regions, like Florida or Georgia, a basement may not be an option.’
Can a basement extend past the house?
A basement can extend past the house in theory. However, be aware that there may be restrictions on what you are permitted to do in your area, so check whether you can consider it as an option first. The soil also needs to be suitable and you will need a professional to survey the yard.
Extending the basement past the house will, of course, have an impact on the size of the backyard, and if doing so will make the property less desirable when you come to sell as well as affecting your enjoyment of it in the mean time, then it’s an option you’ll want to avoid.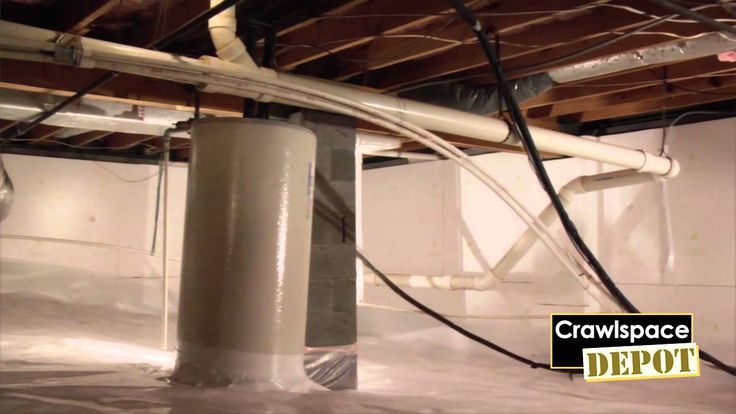
Is it worth digging out a basement?
It can be worth digging out a basement, but if you’re also concerned by the question how much does a basement extension cost, be mindful that is is not a low budget approach to increasing the square footage of a home. Other ways to add to a home’s square footage – such as building an addition – could prove a less costly strategy if circumstances allow.
If it is an option you’re considering, be mindful that it is a major project, and costs can increase if access to the site is difficult and neighbors’ homes are close to yours. Take expert advice before deciding if it is the right approach for your home.
2023 Cost to Convert a Crawl Space to Basement
Typical Range:
$60,000 - $150,000
Cost data is based on research by HomeAdvisor.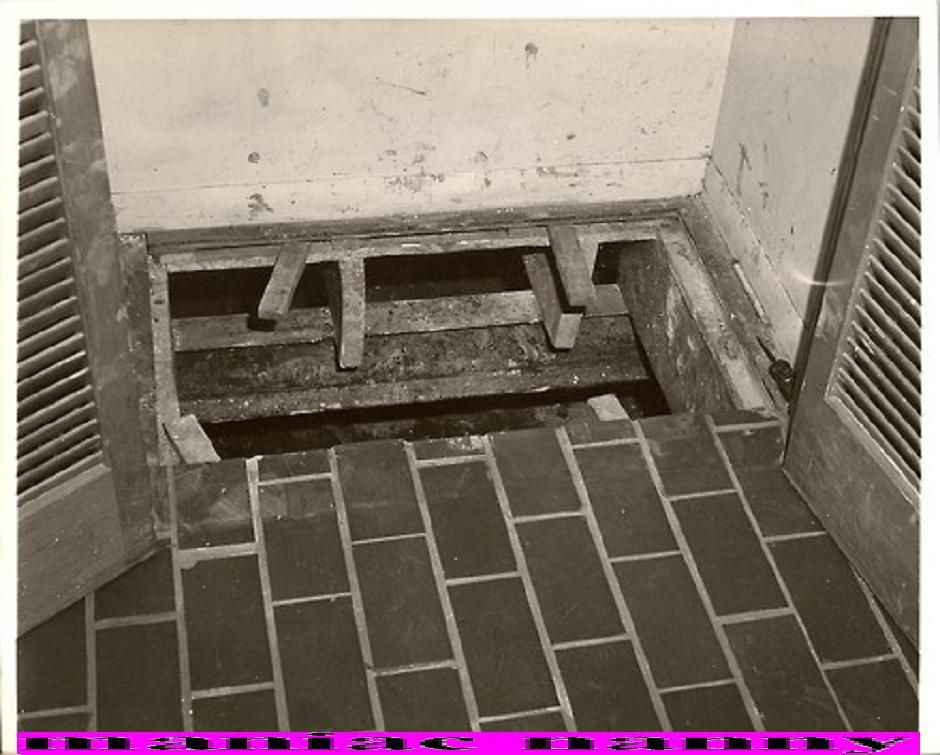
Updated July 7, 2022
Written by HomeAdvisor.
Convert Crawl Space to Basement Cost
Converting a crawlspace to a completely finished basement costs $50 per square foot on average with a typical range of $30 to $75 per square foot. Adding 2,000 square feet under your home runs $60,000 to $150,000. Expanding an existing partial basement into a full one might run $20,000 to $70,000.
It’s almost always cheaper to build an addition. But if you don’t have the room to add on, you’ll need to know what it takes to add a basement.
In this article
- Average Cost to Convert a Crawl Space Per Square Foot
- Cost to Dig Out Crawl Space
- Cost to Convert Into Full Basement
- Is Digging Out a Crawl Space a Good Idea?
- DIY vs.
 Hire a Professional
Hire a Professional - FAQs
Average Cost to Convert a Crawl Space Per Square Foot
| Average Cost | High Cost | Low Cost |
|---|---|---|
| $50 | $75 | $30 |
Cost to Dig Out Crawl Space
The cost of digging a basement under a crawl space will range between $10,000 and $30,000 in most cases. This includes raising or bracing the home and digging out the actual dirt and rock. You’ll do this in two steps:
Raise or brace your home
Dig out the dirt and rock
Remember that this area usually has an unfinished floor, meaning there’s no slab or concrete to go through, so the digging is fairly easy, the real problem comes down to access. Although uncommon, it’s possible you might have poured concrete under your home, which might adds a little time and maybe $500 to $1,500 to remove.
Cost to Raise or Brace a Home
You’ll spend somewhere between $3,100 to $20,000 or more to raise or brace the home. Some contractors opt to jack it up while others prefer to simply dig and brace each footing individually as part of the process.
Raising a home costs $3,100-$9,400. Your general contractor will hire a specialized professional for this.
Bracing the foundation footings come as part of the digging process but adds up to $20,000 to the cost. This simply adds more labor time to the project. While it adds more to the bill, it keeps your home from moving, meaning less damage to interior walls, ceilings and floors.
Crawl Space Excavation Costs for a Basement
For a 1,000 square foot crawlspace, you’re looking at $30,000 to $45,000 just to excavate space for a basement. It’ll cost $75 to $150 per cubic yard to excavate under your home.
Every 1,000 square feet of home has approximately 300 cubic yards of dirt to remove. It’s a slow process since most of the work gets done manually, without large machinery.
It’s a slow process since most of the work gets done manually, without large machinery.
Get Quotes From Basement Contractors
ZIP Code
Talk to ProsCost to Convert Crawl Space Into Full Basement
Converting a crawl space into a full basement costs $50,000 to $150,000. Done right, it’s quick, but still takes a few distinct steps. For an unfinished basement, you’ll need to first dig out the crawlspace, discussed above. Once that’s done, you’ll need to:
Install drainage and plumbing.
Place the forms and pour the foundation.
You can then opt to finish the space for living or leave it unfinished for storage and utility use.
Installing Drainage and Plumbing
Installing drainage, plumbing and sewer lines under a new foundation runs $3,000 to $9,000. But it’s broken up between the two. Look for the following rates as line items on your bill:
Installing plumbing costs: $1,000-$3,000
Drainage installation prices: $2,000-$6,000
Cost to Pour a Foundation
Pouring a foundation costs $10,000 to $30,000 on average. This includes the footings, floor and walls. Once the space is empty with drainage and plumbing placed, it’s a simple process. Your pros will set up forms and pour the foundation like any other.
This includes the footings, floor and walls. Once the space is empty with drainage and plumbing placed, it’s a simple process. Your pros will set up forms and pour the foundation like any other.
Adding a Finished Basement
Once dug out, you can turn the area into a fully functioning basement. A full basement remodel costs another $12,250 to $33,250 depending on the size of the project and your desired finishings.
Finishing a basement costs $7 to $23 per square foot. Individual costs vary for the following parts of a completed space:
Wall framing costs: $1,000-$3,000+
Electrical wiring costs: $3,500-$8,000
Drywall costs: $1.50-$3 per square foot
Flooring prices: $1,500-$4,600
Painting fees: $1,000-$3,000
Is Digging Out a Crawl Space a Good Idea?
Generally, digging out a crawl space isn’t a great idea. It’s risky and costly with other easier and cheaper options available. Ask yourself a couple questions:
Ask yourself a couple questions:
What’s the ROI? Contact a local Realtor or appraiser to find out if it makes sense for your neighborhood and the costs involved.
Do you want to pay for damages and landscaping? Jacking it up causes drywall to crack and might cause other issues with plumbing and electrical. Plus, you’ll probably need to worry about landscaping after its all done.
Addition vs. Digging. Do you have room to add an addition rather than dig out under your home? It’s almost universally cheaper to add on.
Basement vs. Addition Costs
If you have the room, it’s more cost effective to build an addition with a basement under it. Consider the prices:
Adding an addition costs: $21,000-$73,000
Adding a basement: $60,000-$150,000
DIY vs. Hire a Professional
Never try to do this DIY. It’s a complicated process that can cause catastrophic damage to your home when done improperly. Whether you choose to shore up the footings while digging or jack the home up, any mistake might mean irreparable damage.
Whether you choose to shore up the footings while digging or jack the home up, any mistake might mean irreparable damage.
Call a foundation installation professional near you to get quotes and answer specific questions about your project.
FAQs
How much does it cost to finish a crawl space?
Encapsulating a crawl space costs $1,500 to $15,000 depending on both the size and type of process used.
Can you make a basement deeper?
You can make a basement deeper. Excavating out a basement runs $50,000 to $90,000 on average, a bit cheaper than digging out a crawlspace, but not by much. The process is almost identical.
Can you add a basement to an existing house?
You can add a basement to an existing house for $20,000 to $150,000. A typical scenario you’ll run into is a home with a partial basement and a small crawlspace. You can expect to spend around $50,000 for partial installs.
Hire a Pro for Your Basement Project
ZIP Code
Get Estimates NowRelated Projects Costs
- Repair or Clean a Crawl Space
- Remodel a Basement
- Repair Basement Drainage
- Seal a Basement or Foundation
- Excavate Land
- Raise a Foundation
- Repair a Foundation
- Build Stairs or Railings
- Install New Plumbing Pipes
- Build an Addition
Find Pros Nearby
- Basement Leak Repair Near You
- Basement Remodelers in Your Area
- Basement Waterproofing Nearby
- Concrete Foundation Contractors in Your City
- Foundation Installation in Your Area
- Foundation Repair Nearby
- Local Water Damage Restoration Services
- Remodeling Contractors Near You
Popular Categories
- Additions & Remodels
- Bathrooms
- Heating & Cooling
- Kitchens
- Landscape
- All Categories
Popular Projects
- Hire a Handyman
- Hire a Maid Service
- Install Landscaping
- Remodel a Bathroom
- Remodel a Kitchen
Featured Articles
- How Much Does it Cost to Install or Replace Kitchen Cabinets?
- How Much Does a Home Addition Cost?
- Install Countertops
- How Much Does it Cost to Install a Window?
- How Much Does It Cost to Clean Gutters?
Find Addition Contractors Near You
- Atlanta, GA
- Austin, TX
- Charlotte, NC
- Chicago, IL
- Cincinnati, OH
- Colorado Springs, CO
- Columbus, OH
- Dallas, TX
- Denver, CO
- El Paso, TX
- Fort Lauderdale, FL
- Fort Worth, TX
- Houston, TX
- Indianapolis, IN
- Jacksonville, FL
- Kansas City, MO
- Las Vegas, NV
- Los Angeles, CA
- Louisville, KY
- Miami, FL
- Minneapolis, MN
- Nashville, TN
- Orlando, FL
- Philadelphia, PA
- Phoenix, AZ
- Pittsburgh, PA
- Portland, OR
- Riverside, CA
- Sacramento, CA
- Saint Louis, MO
- Saint Paul, MN
- Saint Petersburg, FL
- Salt Lake City, UT
- San Antonio, TX
- San Diego, CA
- San Jose, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Tampa, FL
- Tucson, AZ
- Washington, DC
Don't see your city?
| Home \ Articles of companies Often the culprit of legal battles with housing and communal services - the basement - can be an excellent platform for business development. True, not everyone and not always. Investors are attracted by the quick payback and low rate per square meter. meter. It's nice that developers, when designing new houses, as a rule, already consider the possibility of placing commercial premises in the basement and on the first floors of houses. In the classic case, the basement can be converted into an office or cafe by buying or renting non-residential premises. About how to do it legally, our material. Basement basement strife In the view of the layman, the basement is a dark, damp room, the realm of pipes, risers and ventilation ducts. Sometimes the basement is used as a warehouse for unnecessary things, or worse, as a place of residence for individuals of strange appearance. Maria Pogodina specially for www.theproperty.ru Catherine March 25, 2013
Comments: |
Basement construction
The basement is a type of buried foundation. A basement floor is considered to be a floor in which the floor level of the premises is lower than the level of the planning mark of the ground by more than half of their height. The height of the basement is taken equal to 1.9...2.2 m. This is enough to accommodate storage facilities or to install heat generators. If it is planned to arrange a gym or a games room in the basement, then its height is assigned not less than in the living rooms.
In the basement it is convenient to store products, to make preparations. This is due to the property of the soil to maintain an almost constant temperature. At a depth of 1.5 ... 2 m from the surface of the earth, it keeps at a level of 5 ° C - in winter and 10 ° C - in summer.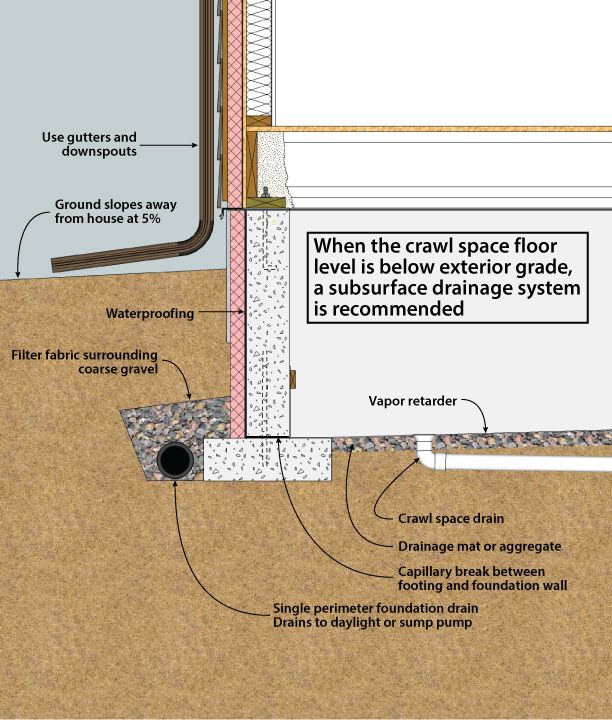
The basement (semi-basement) floor is buried in the ground no more than half the height of the floor. Quite often, the basement is arranged during construction on difficult terrain. The height of the basement is equated to the height of the living quarters.
Having a basement is a wish of any builder. This is understandable. Useful areas increase without increasing the dimensions of the house. The cost level of housing, if it is supposed to be sold someday, is also rising.
It should be taken into account that the cost of creating a basement is almost 1.5 - 2 times higher than the above-ground floor, if reliable waterproofing from groundwater is required.
At the same time, when the house is located on dry soils, the presence of a basement or basement floor in it is justified and desirable, since the costs for it are 2-4 times less than those required to create an ordinary floor with the same usable area.
Attention!
If you intend to use imported liquefied gas (propane) instead of mains gas as fuel for cooking or heating, it is better to refuse from the basement or basement. This gas is heavier than air. If accidentally leaked, it can accumulate in the lower unventilated cavities of the house and cause an explosion of (Fig. 1).
This gas is heavier than air. If accidentally leaked, it can accumulate in the lower unventilated cavities of the house and cause an explosion of (Fig. 1).
1
The design of the basement and the foundation under it is determined by the level of groundwater, the degree of heaving of the soil, the type of ceiling and the basement waterproofing scheme.
From the standpoint of the foundation under the house, the basement is made according to two schemes: supported on a slab (Fig. 2, a) and supported on a tape (Fig. 2, b) . Each of them has its applicability and its cost.
Fig. 2
Building a house with a basement with a high groundwater level should be done on a slab. Reinforcement of the slab and its concreting will require a lot of money, but it is much easier to ensure the tightness of the connection between the slab and the basement walls. The thickness of the slab (15 ... 25 cm) depends on the dimensions of the house and the location of the internal load-bearing walls of the basement. The slab reinforcement is a rigid spatial frame laid over its entire area. Reinforcement diameter - 12... 15 mm.
The thickness of the slab (15 ... 25 cm) depends on the dimensions of the house and the location of the internal load-bearing walls of the basement. The slab reinforcement is a rigid spatial frame laid over its entire area. Reinforcement diameter - 12... 15 mm.
With a high level of groundwater, for those who want to build a house with a basement, you can use a well-known technique. The depth of the pit under the basement is made small, to the level of groundwater. After the construction of the basement, the excavated soil is poured around the future house, which will be on some elevation. The visual image of the house will be more advantageous, and groundwater will not bother you much.
If the groundwater level is low and the builder does not face the problem of ensuring the tightness of the basement, then the basement walls can be supported on the tape. With this design, the basement floor is not power. It does not connect with the foundation tape and with the walls. Tape thickness - 20 .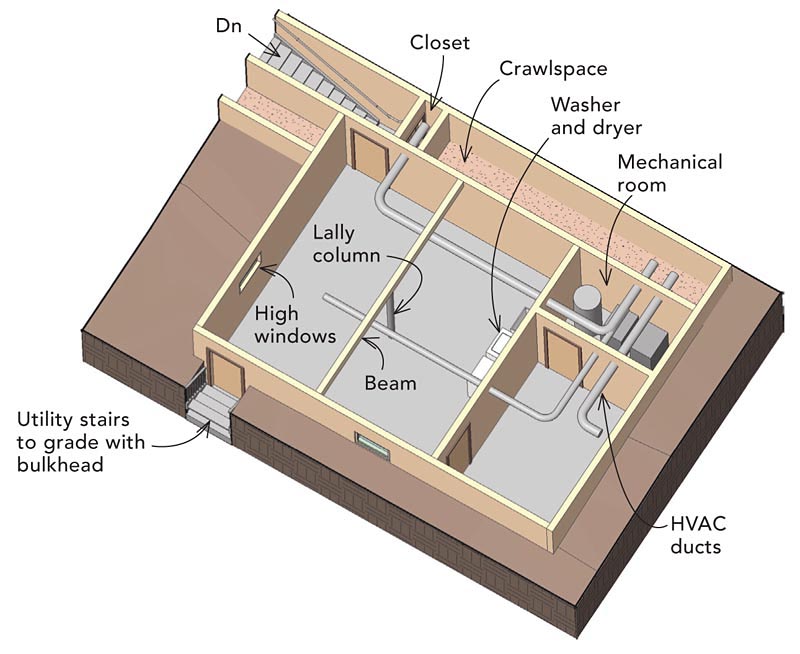 .. 30 cm, width - more than the wall thickness by 4 ... 5 cm.
.. 30 cm, width - more than the wall thickness by 4 ... 5 cm.
As for the thickness of the basement walls, it is determined by the building material itself, the heaving of the soil, the depth of the basement into the ground, the length of the walls and the type of floors (Fig. 3) . If the walls are buried in non-rocky soil by more than 1 m, then their thickness is determined taking into account the lateral pressure of the soil (Table 1).
3
Table 1. Minimum basement wall thickness in non-rocky soils
| Basement wall material | Basement depth from floor to blind area (m) | Basement wall thickness at their length clear (cm) | ||
| up to 2 m | 2 -Zm | 3-4m | ||
| Reinforced concrete | 1. 1.5 - 2.0 | 10 15 | 15 20 | 20 25 |
| In-situ concrete | 1.0 - 2.0 2.0 - 2.5 | 20 25 | 25 30 | 30 40 |
| Concrete blocks | 1.0- 1.5 1.5 - 2.0 | 25 30 | 30 40 | 40 50 |
| Reinforced concrete | 1. 1.5 - 2.0 | 30 35 | 35 40 | 40 50 |
| Brickwork | 1.0-1.5 1.5 - 2.0 | 25 38 | 38 51 | 51 64 |
| Rubble masonry | 1.0- 1.5 1.5 - 2.0 | 40 50 | 50 60 | 60 70 |
With such wall thicknesses on non-rocky soils, the basement floors do not have to be concrete.
The main task of the builder, who decided to build a basement, is to exclude its moisture from groundwater or flood waters. Capillary moisture should not cause an increase in humidity in the room or dampening the structure of the house itself.
For basement sealing, three layouts of the sealing layer are used:
- external anti-pressure;
- internal anti-pressure;
- waterproofing to protect against capillary moisture.
When performing external anti-pressure waterproofing , it should be taken into account that its upper edge must be at least 0.5 m above the expected groundwater level (Fig. 4, a) . The pressure from the waterproofing layer is transferred to the load-bearing enclosing elements of the floor and walls, which makes it more preferable.
4
A horizontal section of waterproofing is applied over leveled and smooth concrete preparation up to the basement floor. Such a screed with a thickness of 4 ... 5 cm is made from a mixture of sand and cement 6: 1, which is desirable to be reinforced with a mesh. A layer of primer is applied to the prepared surface of the slab, and bituminous mastic is applied to it. After that, sheets of roofing material are laid with an overlap of at least 10 cm. The roofing material should protrude 15 cm beyond the basement walls. In wet soils, insulation is made of two layers of roofing felt or roofing material is used. To protect the insulation from damage, it is covered from the outside with a layer of cement mortar. If roofing is used as a roll material, then tar impregnation is applied to the concrete.
Such a screed with a thickness of 4 ... 5 cm is made from a mixture of sand and cement 6: 1, which is desirable to be reinforced with a mesh. A layer of primer is applied to the prepared surface of the slab, and bituminous mastic is applied to it. After that, sheets of roofing material are laid with an overlap of at least 10 cm. The roofing material should protrude 15 cm beyond the basement walls. In wet soils, insulation is made of two layers of roofing felt or roofing material is used. To protect the insulation from damage, it is covered from the outside with a layer of cement mortar. If roofing is used as a roll material, then tar impregnation is applied to the concrete.
Vertical sections of rolled waterproofing are applied to the walls and protected from the outside with half-brick masonry, concrete slabs or a layer of sprayed concrete. The overlap of the horizontal and vertical sections of the waterproofing is carried out by bending the horizontal waterproofing by at least 15 cm. The vertical waterproofing is removed at least 15 cm above the ground surface.
The vertical waterproofing is removed at least 15 cm above the ground surface.
If the ground waters lie below the basement floor and the soils there are low-moisture, then it is enough to confine oneself to coating waterproofing with the application of hot bituminous mastic in two layers up to 2 mm thick. Before applying the mastic, the walls should be coated with a primer.
The space between the basement walls and the ground is filled with greasy clay, making a clay castle.
Internal anti-pressure waterproofing is arranged, as a rule, in already existing buildings or during repair work related to the elimination of leakage of basement enclosing structures (Fig. 4, b). Since the pressure on individual sections of the walls of the inner caisson can be significant, structural reinforcements are required to perceive it.
Basement waterproofing against capillary moisture does not require high quality work, as was required when creating anti-pressure waterproofing. Of course, this waterproofing scheme is not suitable for protection against pressure water (Fig. 4, c).
Of course, this waterproofing scheme is not suitable for protection against pressure water (Fig. 4, c).
Internal anti-pressure waterproofing on plaster mortar has been used relatively recently, with the advent of plaster mortars with a high degree of adhesion and fast setting. With heads up to 2 - 3 meters, which is typical for the basements of residential buildings, the use of such waterproofing plaster compositions and mastics allows you to perform internal waterproofing without creating a caisson, with the transfer of water load to the plaster mortar (Fig. 4, d). As a rule, such a waterproofing option is used during repair and restoration work as an addition to the existing option.
If the sealing layer did not withstand and a leak occurred, then eliminating this shortcoming, even by filling the basement with soil, will not lead to anything good, because it is very difficult for moisture to leave the sealed basement. Therefore, constant dampness in the underground is inevitable, even when the groundwater goes far down. True, one can hope for modern waterproofing coatings, putties. But if floors have already been laid in the basement, finishing work has been completed, then it will not be easy to eliminate such leaks.
Therefore, constant dampness in the underground is inevitable, even when the groundwater goes far down. True, one can hope for modern waterproofing coatings, putties. But if floors have already been laid in the basement, finishing work has been completed, then it will not be easy to eliminate such leaks.
Many developers who are just starting their construction path do not take into account the hydrostatic pressure of groundwater. This can lead to the emergence of basements and cellars, inspection pits of garages and sewer cesspools, unfilled pools. All of the above are quite frequent phenomena if the level of groundwater or flood waters is high, and the weight of the structure is small.
From the practice of the river fleet
For a long time, floating landing stages have been used as piers on rivers and lakes - piers, the lower, which is the main part of which is a sealed reinforced concrete hull. On top of it, a light two-story wooden structure of the pier itself is being built .
This is how a house with a basement or cellar should be presented to those who may have ground or flood water levels rising above their floor level.
The tightness of the basement is ensured by the watertightness of the walls and the slab of the house on which it is built.
Fig. 5
From the practice of an individual developer
With a sufficiently high level of flood waters, the developer nevertheless decided to build a basement. The house is small, 6x8 m, you can try. Everything was done almost according to science.
They dug a pit 1.8 m deep, made a backfill of coarse-grained sand, laid waterproofing, and cast a 10 cm thick concrete base on it with reinforcement with mesh (you can’t call such a thin reinforced concrete creation a slab). After that, exactly along the perimeter, the developer laid three rows of FBS foundation blocks and blocked the basement with slabs.
Spring has come. Guard!!! The floor of the basement was strongly raised, water went through the cracks formed (Fig. 5).
What happened?
The hydrostatic pressure acting on the floor from below turned out to be supercritical. When the water level in the soil is 1 m above the basement floor, a pressure of 1 ton acts per unit area of the floor. That is, a force of 48 tons acts from below on the entire area of \u200b\u200bthis basement of 48 m 2 . This is the weight of a very heavy tank or a whole wagon. The thin floor couldn't handle it.
How it should have been done. The floor slab must be at least 20 cm thick, and its reinforcement must be correctly performed. Significant strengthening of the basement floor could be provided by the construction of one transverse wall.
If you take a closer look at such a foundation, you will notice that the wall is too close to the edge of the slab on which it rests. Our builder laid the foundation blocks close to the perimeter of the concrete floor. Apparently, he decided to save on the volume of earthworks and concreting. With this design of this unit, the basement floor from the pressure of the soil immediately from the edge begins to be intensively loaded with a bending moment (Fig. 6, a) .
Our builder laid the foundation blocks close to the perimeter of the concrete floor. Apparently, he decided to save on the volume of earthworks and concreting. With this design of this unit, the basement floor from the pressure of the soil immediately from the edge begins to be intensively loaded with a bending moment (Fig. 6, a) .
Large bending loads are both significant deformations and breaking stresses in the basement slab. With weak soil compaction under the slab, this manifests itself to a greater extent.
In the variant when the floor slab extends beyond the wall contour by 30 - 40 cm (Fig. 6, b) , the maximum value of the bending moment becomes much lower. The plate could be made thinner without fear of deformation and destruction.
Fig. 6
A similar failure of the floor slab can occur with an unburied slab. A heavy garage can severely deform the slab, especially if its integrity is compromised by an elongated opening for a viewing hole (Fig. 7).
7).
7
When constructing a basement, concrete floors are laid on its walls. This is due to the fact that the lateral pressure of the soil on the walls must be transferred to something. Especially large lateral loading of the walls arises from heaving of the soil, since it tends to expand when it freezes in all directions. Rigid ceilings allow you to close on yourself the loads that fall on the walls of the basement from all sides. This calculation model considers the basement wall as a set of vertically located beams that transfer the load from the soil to the concrete floor and to the concrete floor (Fig. 8).
8
That is why basement walls during construction are loaded with concrete slabs in the same season, without waiting for the heaving soil to tilt the walls inside the basement with its expansion.
This scheme was adopted during the construction of the basement using the TISE technology. Such vertical beams are created in every fourth vertical channel of the wall after they are filled with reinforcement and concrete. This scheme works well regardless of the dimensions of the basement and the breakdown of its internal walls.
Such vertical beams are created in every fourth vertical channel of the wall after they are filled with reinforcement and concrete. This scheme works well regardless of the dimensions of the basement and the breakdown of its internal walls.
This is interesting
With a power scheme representing a wall as a set of vertical beams, the basement walls can be made thinner, the heavier the house is from above (from the conditions of the stress state of the wall, loaded with weight and lateral pressure). Under these conditions, there are no tensile stresses in the concrete mass, from which it could collapse.
When constructing basement walls from ready-made concrete blocks, horizontal reinforcement is performed. In this case, the wall works according to a different design scheme, in which it is considered as a set of horizontal beams that transfer the lateral load from the soil to the external and internal walls of the basement.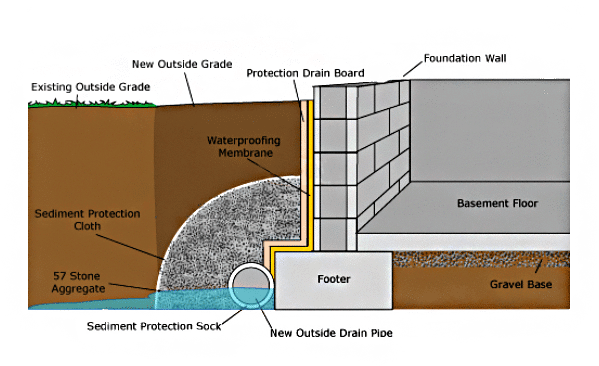 Due to the large span of such a horizontal beam, the basement wall must have a large thickness or effective horizontal reinforcement (Fig. 9).
Due to the large span of such a horizontal beam, the basement wall must have a large thickness or effective horizontal reinforcement (Fig. 9).
9
In reality, the basement wall should be considered as a set of simultaneously working vertical and horizontal beams. Moreover, the heavier the house itself, the more weight the basement walls are loaded with, the closer the design scheme is to the wall with vertically arranged beams.
From construction practice
Basement walls are often erected using large-sized ready-made foundation blocks FBS (Fig. 10). As a rule, when performing corner bonding with these blocks, the overlap of the blocks along the entire length of the wall is the most minimal.
With weak horizontal reinforcement, the narrow area of the vertical joints of the FBS turns into a hinged joint. In the absence of a basement floor and a sufficiently large soil pressure subject to heaving phenomena, part of the wall may go inward.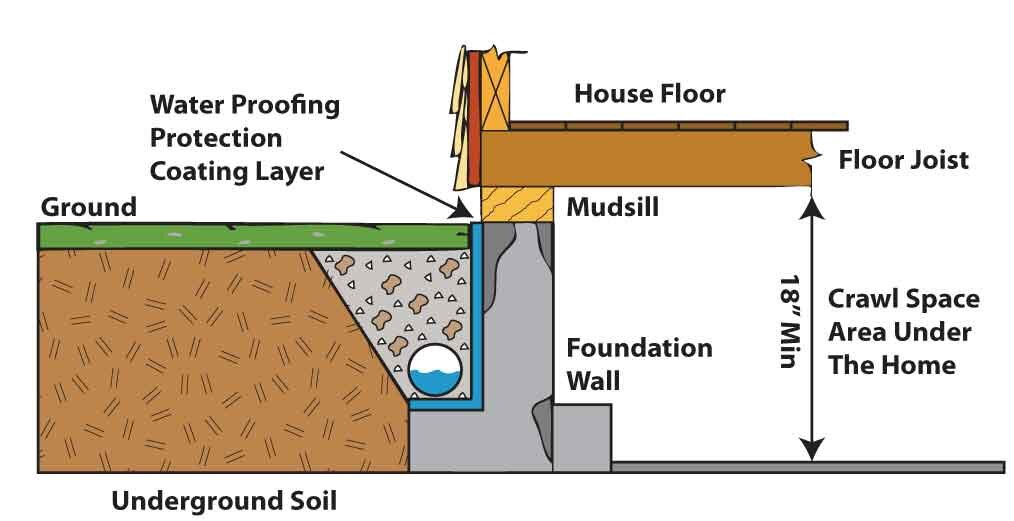
10
Correcting the situation and stopping the process of destruction of the basement walls is possible only with the erection of reinforcing walls in the basement. This is quite an expensive pleasure, and the basement will lose all its attractiveness.
The basement wall can collapse from the pressure of the soil even without heaving phenomena, during the installation of floor slabs. The truck crane supports, installed in close proximity to the basement walls, create a sufficiently high level of stress in the soil. The load on the retractable support and the lateral soil pressure on the basement walls are especially high when the installation of distant slabs, the furthest from the truck crane, is in progress (Fig. 11).
11
To prevent such destruction, the distance from the wall to the edge of the truck crane support platform must be at least 0. 8 m.
8 m.
Construction of a basement begins with digging a foundation pit. When planning this stage of work, the developer should not forget that in winter the freezing boundary in the pit area will drop. A soil with a dense structure, when saturated with water and freezing, can reduce its density and rise by 10 ... 15 cm (Fig. 12, a). If the developer managed to build a basement, but did not provide for its insulation, then heaving phenomena can raise the basement by 10 ... 15 cm, causing destruction or unacceptable displacements. To prevent this from happening, the basement should be insulated according to one of two schemes that provide for insulation along the floor or along the basement floor (Fig. 12, b, c). The last option is more successful, since in the absence of overlapping, the walls of the basement can lean inward from the pressure of heaving soil. Snow cover here can be considered basement insulation.
12
When planning the insulation and waterproofing of basement walls from the outside, we pay attention to the quality of their installation.
 Terra Incognita
Terra Incognita  Not everyone can give a clear answer who owns the basement: the residents of the house, the city or the developer company. The possibility of renting or buying non-residential premises in the basement of the house largely depends on the type of basement. Among them are independent real estate objects, technical premises, as well as basements that are in common ownership, but which, by decision of the tenants, can be rented out or alienated. Compared to ground floor properties, basements as commercial space have a number of advantages. First, it is a low cost. So, the average price per sq. m. of the basement is 500 dollars per meter, while the cost of a square meter on the ground floor is 5-10 thousand dollars. The same is true for rent. You can rent a room in the dungeon for 30-50% cheaper than on the ground floor of a residential building. Secondly, basements pay off very quickly. According to analysts, investments in business premises on the ground floor will begin to bring dividends in an average of 8-9years, while the basement will "return" the money after 3 years.
Not everyone can give a clear answer who owns the basement: the residents of the house, the city or the developer company. The possibility of renting or buying non-residential premises in the basement of the house largely depends on the type of basement. Among them are independent real estate objects, technical premises, as well as basements that are in common ownership, but which, by decision of the tenants, can be rented out or alienated. Compared to ground floor properties, basements as commercial space have a number of advantages. First, it is a low cost. So, the average price per sq. m. of the basement is 500 dollars per meter, while the cost of a square meter on the ground floor is 5-10 thousand dollars. The same is true for rent. You can rent a room in the dungeon for 30-50% cheaper than on the ground floor of a residential building. Secondly, basements pay off very quickly. According to analysts, investments in business premises on the ground floor will begin to bring dividends in an average of 8-9years, while the basement will "return" the money after 3 years. Who is the owner? However, in practice, there is a real obstacle course behind the low price and quick payback of the basement. Often dreams of owning a business in the basement of a residential building are destroyed by the strong armor of the merciless machine of bureaucracy. The basement is turning into a bone of contention for municipal authorities, apartment residents and potential owners. On the one hand, in the Federal Law "On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it" in Art. 1 non-residential premises is directly named among independent real estate objects. On the other hand, Art. 288 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in addition to indicating that residential premises can be transferred to the category of non-residential premises in the prescribed manner, the basement is not mentioned at all as a piece of real estate. Meanwhile, according to Art. 290 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, owners of housing in an apartment building on the right of common shared ownership own the common premises that support the structures of the house, mechanical, electrical, sanitary and other equipment outside and inside the apartment, serving more than one apartment.
Who is the owner? However, in practice, there is a real obstacle course behind the low price and quick payback of the basement. Often dreams of owning a business in the basement of a residential building are destroyed by the strong armor of the merciless machine of bureaucracy. The basement is turning into a bone of contention for municipal authorities, apartment residents and potential owners. On the one hand, in the Federal Law "On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it" in Art. 1 non-residential premises is directly named among independent real estate objects. On the other hand, Art. 288 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in addition to indicating that residential premises can be transferred to the category of non-residential premises in the prescribed manner, the basement is not mentioned at all as a piece of real estate. Meanwhile, according to Art. 290 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, owners of housing in an apartment building on the right of common shared ownership own the common premises that support the structures of the house, mechanical, electrical, sanitary and other equipment outside and inside the apartment, serving more than one apartment. We are talking about technical basements in which water supply or sewer pipes pass, risers, metering devices and other common house equipment are located. These basements cannot be sold or rented out. The same is said in Art. 36 p. 1 of the LC RF. Accordingly, these premises cannot be transferred separately from the right to an apartment and are not intended for independent use. However, in practice, municipalities, guided by 131-FZ, often enter the basement in the state register as their own property, regardless of the opinions of the residents of the house. Often, such actions lead interested parties to court. The lack of a proper legal regime for basement areas gives rise to various interpretations. Is the non-residential premises only a technical part of the building, or is it an independent property. More often, objects that are controversial in terms of technical function are classified as independent non-residential premises that are not intended to serve the owners' premises in an apartment building, which means that they can be bought or rented.
We are talking about technical basements in which water supply or sewer pipes pass, risers, metering devices and other common house equipment are located. These basements cannot be sold or rented out. The same is said in Art. 36 p. 1 of the LC RF. Accordingly, these premises cannot be transferred separately from the right to an apartment and are not intended for independent use. However, in practice, municipalities, guided by 131-FZ, often enter the basement in the state register as their own property, regardless of the opinions of the residents of the house. Often, such actions lead interested parties to court. The lack of a proper legal regime for basement areas gives rise to various interpretations. Is the non-residential premises only a technical part of the building, or is it an independent property. More often, objects that are controversial in terms of technical function are classified as independent non-residential premises that are not intended to serve the owners' premises in an apartment building, which means that they can be bought or rented.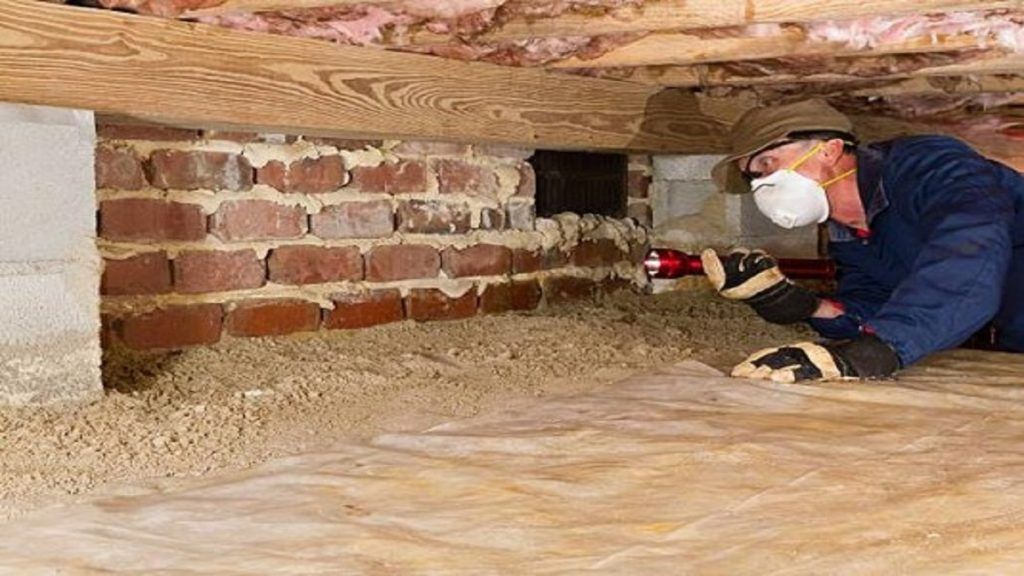 Basement case For commercial purposes, only basements with the status of independent real estate objects are suitable. Most often, basement areas are designed for offices, banks, shops, fitness centers or warehouses. According to the legislation, catering establishments cannot be arranged in the basement of a residential building. However, this does not stop enterprising owners: they expand the hood of the house in such a way that the smells from the kitchen do not embarrass residents. For example, this is what the owners of the cafe on the street did. M. Sadovaya, 1/25, who converted the basement into a catering enterprise. Moreover, establishments such as restaurants and clubs a priori cannot appear on the first floors of a residential building. Otherwise, it will be a violation of the rights of tenants. But in the basements - they have a right to exist. What you should not start in the basement under any circumstances is to arrange production, whether it be a furniture workshop or a recording studio.
Basement case For commercial purposes, only basements with the status of independent real estate objects are suitable. Most often, basement areas are designed for offices, banks, shops, fitness centers or warehouses. According to the legislation, catering establishments cannot be arranged in the basement of a residential building. However, this does not stop enterprising owners: they expand the hood of the house in such a way that the smells from the kitchen do not embarrass residents. For example, this is what the owners of the cafe on the street did. M. Sadovaya, 1/25, who converted the basement into a catering enterprise. Moreover, establishments such as restaurants and clubs a priori cannot appear on the first floors of a residential building. Otherwise, it will be a violation of the rights of tenants. But in the basements - they have a right to exist. What you should not start in the basement under any circumstances is to arrange production, whether it be a furniture workshop or a recording studio. Before planning commercial activity in the basement, you need to find out the status of non-residential premises. Yes, not every dungeon can be equipped. So, you can not touch the basements that are bomb shelters, as well as, as mentioned above, the premises in which the main communications of the house pass. Basements in houses under demolition and in need of reconstruction are among the basements unsuitable for use. Main obstacle - residents In the event that the basement is a common property, the first thing to do is to obtain the consent of all residents to re-profiling the premises. If the house is municipal, then all owners of apartments must be present at the meeting. The HOA or the housing cooperative is also required to convene a general collection of signatures. This is not so easy to do, especially if the house is an apartment building. The investor is obliged to consider all complaints of tenants and compensate them at his own expense. Often, in order to "buy out" the basement, the investor glazes the loggias, carries out work on the improvement of the territory - everything that the intractable residents wish.
Before planning commercial activity in the basement, you need to find out the status of non-residential premises. Yes, not every dungeon can be equipped. So, you can not touch the basements that are bomb shelters, as well as, as mentioned above, the premises in which the main communications of the house pass. Basements in houses under demolition and in need of reconstruction are among the basements unsuitable for use. Main obstacle - residents In the event that the basement is a common property, the first thing to do is to obtain the consent of all residents to re-profiling the premises. If the house is municipal, then all owners of apartments must be present at the meeting. The HOA or the housing cooperative is also required to convene a general collection of signatures. This is not so easy to do, especially if the house is an apartment building. The investor is obliged to consider all complaints of tenants and compensate them at his own expense. Often, in order to "buy out" the basement, the investor glazes the loggias, carries out work on the improvement of the territory - everything that the intractable residents wish. After the consent of the tenants is obtained, the procedure for agreeing on the reconstruction of the basement follows, which is not much different from obtaining permission to redevelop the apartment. Theoretically, municipal DEZs and REUs or HOAs in commercial buildings are responsible for the basements - they will also need to agree on the reconstruction of the premises. When all the necessary signatures have been collected, you can order a redevelopment project for the reconstruction of the premises. Note that this document lays down the work necessary for reprofiling the basement - drainage, replacement of communications, sealing of floors. As needed, owners or tenants design a separate entrance from the street. Coordination can be obtained in two ways: traditional, by going through all instances, and through the court. The latter, as experts say, is much faster and less expensive. The claim for recognition of the ownership of the basement is satisfied in most cases. However, for this, a construction expertise should be carried out, it is necessary to identify violations of SNIPs and construction errors.
After the consent of the tenants is obtained, the procedure for agreeing on the reconstruction of the basement follows, which is not much different from obtaining permission to redevelop the apartment. Theoretically, municipal DEZs and REUs or HOAs in commercial buildings are responsible for the basements - they will also need to agree on the reconstruction of the premises. When all the necessary signatures have been collected, you can order a redevelopment project for the reconstruction of the premises. Note that this document lays down the work necessary for reprofiling the basement - drainage, replacement of communications, sealing of floors. As needed, owners or tenants design a separate entrance from the street. Coordination can be obtained in two ways: traditional, by going through all instances, and through the court. The latter, as experts say, is much faster and less expensive. The claim for recognition of the ownership of the basement is satisfied in most cases. However, for this, a construction expertise should be carried out, it is necessary to identify violations of SNIPs and construction errors.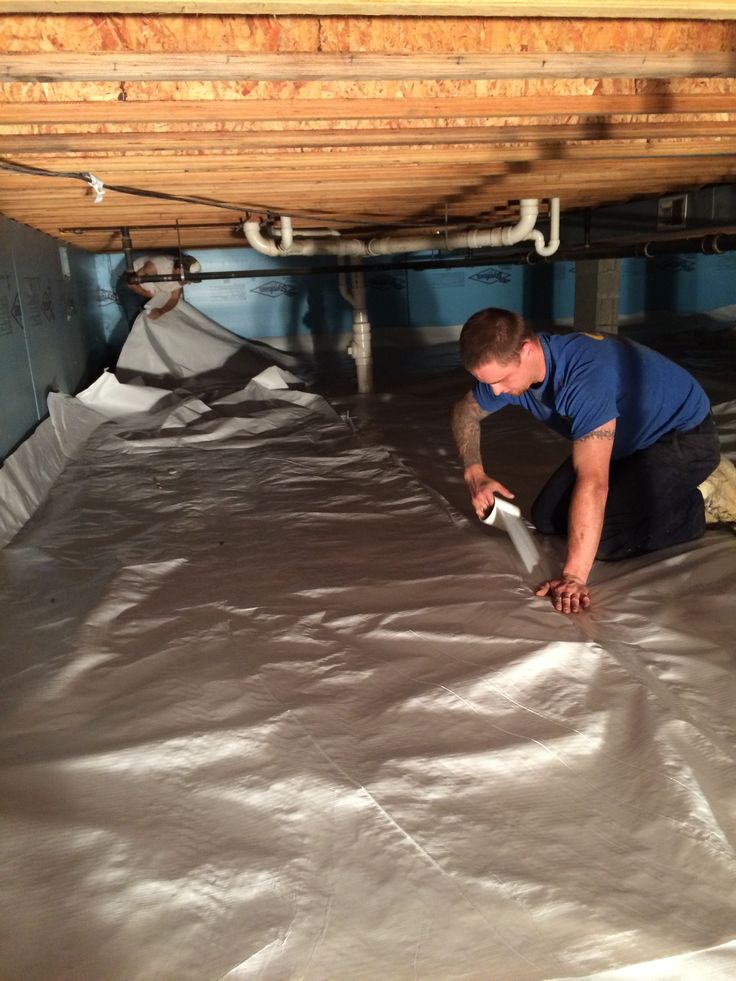 If all the rules are met and the consent of all residents of the house is obtained, then most likely the judge will make a positive decision. Next, you should request a cadastral passport at the BTI, and then register the non-residential premises as a property. There is another scenario for the development of actions. The investor can buy the basement from the previous owner of the entire building, for example, from the developer. In a number of rare cases, the basement is owned by the Russian Federation, and the only way to get it into ownership is to wait until the Federal Property Management Agency puts the non-residential premises up for sale on the basis of a tender. Basements are often referred to as free-use premises. In other words, their status is not fixed, so they can be converted into offices, warehouses, shops or catering establishments. Thus, the basement becomes multifunctional, and its cost determines in many respects an advantageous location. For example, cellars in the house at 9 Torez Ave.
If all the rules are met and the consent of all residents of the house is obtained, then most likely the judge will make a positive decision. Next, you should request a cadastral passport at the BTI, and then register the non-residential premises as a property. There is another scenario for the development of actions. The investor can buy the basement from the previous owner of the entire building, for example, from the developer. In a number of rare cases, the basement is owned by the Russian Federation, and the only way to get it into ownership is to wait until the Federal Property Management Agency puts the non-residential premises up for sale on the basis of a tender. Basements are often referred to as free-use premises. In other words, their status is not fixed, so they can be converted into offices, warehouses, shops or catering establishments. Thus, the basement becomes multifunctional, and its cost determines in many respects an advantageous location. For example, cellars in the house at 9 Torez Ave. are located three minutes walk from the station. m. "Ploshad Muzhestva", in the center of the densely populated Vyborg district. High traffic is provided by the location of the house on the first line of the highway. Quite often, such premises already have separate entrances from the street, which is an additional advantage for the investor. From this graining point, the commercial premises at 9 Torez Ave., letter A are very attractive. Two basements with an area of 761.2 sq. m. are offered for sale in this house. m. and 642.3 sq. m. Interest in basements is fueled by the fact that there are practically no free areas in the city, and the cost per square meter is an order of magnitude lower than the areas on the first floors. Residents of residential areas still need infrastructure facilities, while the construction of new shops and cafes is almost not carried out. Not to mention the central regions, in which it is almost impossible to organize your own business due to high rates and an extremely small number of offers.
are located three minutes walk from the station. m. "Ploshad Muzhestva", in the center of the densely populated Vyborg district. High traffic is provided by the location of the house on the first line of the highway. Quite often, such premises already have separate entrances from the street, which is an additional advantage for the investor. From this graining point, the commercial premises at 9 Torez Ave., letter A are very attractive. Two basements with an area of 761.2 sq. m. are offered for sale in this house. m. and 642.3 sq. m. Interest in basements is fueled by the fact that there are practically no free areas in the city, and the cost per square meter is an order of magnitude lower than the areas on the first floors. Residents of residential areas still need infrastructure facilities, while the construction of new shops and cafes is almost not carried out. Not to mention the central regions, in which it is almost impossible to organize your own business due to high rates and an extremely small number of offers. There, the conversion of basements is even more relevant. Yes, there are already good examples. For example, a cafe in the basement on the street. Malaya Sadovaya, 1/25. Intense pedestrian traffic, proximity to the metro and the historical center, as well as an attractive price for non-residential space will ensure a quick return on investment. What makes this type of commercial real estate interesting for investors and businessmen.
There, the conversion of basements is even more relevant. Yes, there are already good examples. For example, a cafe in the basement on the street. Malaya Sadovaya, 1/25. Intense pedestrian traffic, proximity to the metro and the historical center, as well as an attractive price for non-residential space will ensure a quick return on investment. What makes this type of commercial real estate interesting for investors and businessmen. 
 0-1.5
0-1.5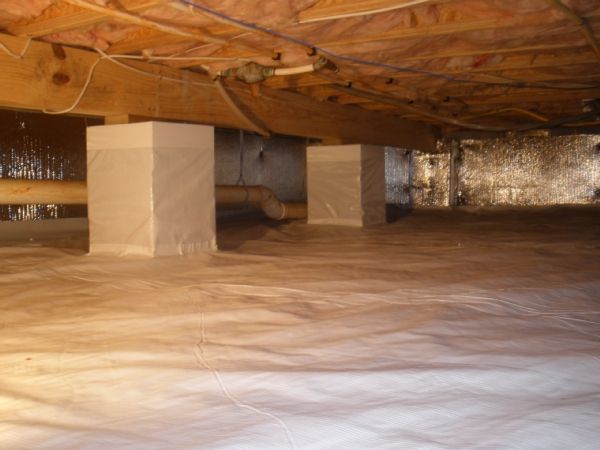  0 - 1.5
0 - 1.5