Best soil for rose cuttings
Grow Roses from Cuttings: 2 Best Ways to Propagate!
How to grow roses from cuttings easily! Compare the BEST & worst ways to propagate in water or soil, using potatoes, & root by air layering.
Maybe it’s a beautiful rose plant in the garden that you want to multiply, or a Valentines rose bouquet that you want to grow into more roses, it’s easy to want more colorful and gorgeous rose bushes and vines in our homes and gardens.
Many plant lovers have tried to grow roses from cuttings. There are many rose propagation methods such as rooting in soil or water, air layering, and some even try to grow rose cuttings in potatoes! Some of these methods are great, some actually don’t work very well.
Today we are going to compare which ways are the best and easiest to propagate roses from either a plant, cut flowers or even a bouquet. Wouldn’t it be nice to have more roses in our gardens or as gifts to share with friends? 🙂
Can you propagate patented roses?
* Some resources in article are affiliate links. Full disclosure here .
A plant patent lasts for 20 years, after which the plant is allowed to be propagated.
If the roses are patented within the last 20 years, it is illegal to propagate the rose without the consent of the patent holder. ( Source )
However, there are endless varieties of roses you CAN propagate. For example, the famous “New Dawn” and “Charlotte Armstrong” roses were patented over 50 years ago, and old-fashioned heirloom roses often root easier than modern hybrids.
Now you know which roses not to propagate, let’s look at the best and easiest methods to root rose cuttings! ( Source )
Best time to grow roses from cuttings
The best time to grow roses from cuttings is from spring through summer, when flexible new stems (current year’s growth) are actively growing. They are called softwood cuttings, who are the fastest and easiest to root when you select healthy stems.
Look at all the beautiful rooted rose cuttings by Vuon & Nha on YouTube! Video tutorial below:
The next best are semi-hardwood cuttings, taken in late summer and early fall, when new stems have partially matured.
Hardwood cuttings are most difficult type of cutting to root. They are taken in late fall or early winter, when the rose stems have matured and entered dormancy.
Grow roses from cuttings by air layering
Air layering is a fascinating propagation method being used for thousands of years! Nowadays there are easy products like these reusable air layering pods you can get, or make your own with simple materials such as small water bottles or plastic bags.
Air layering is the BEST way to propagate roses (and many woody plants) if the rose bush or vine that you want to multiply is already growing in your garden or in a friend’s garden.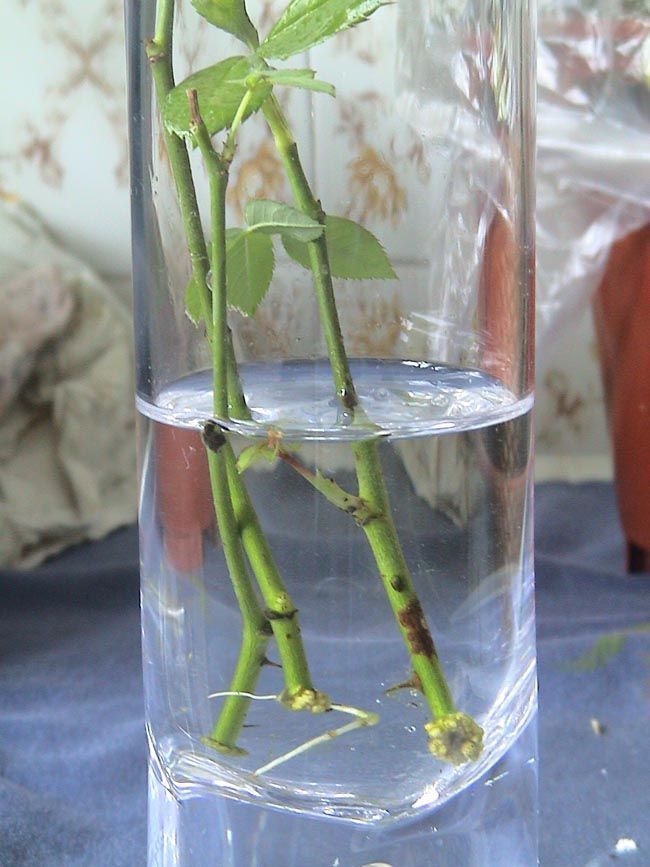 You don’t even have to use rooting powder with this method.
You don’t even have to use rooting powder with this method.
The best time for air layering roses is in late spring or summer when the weather is warm and the rose bushes are actively growing. ( Air layering rose video tutorial below. )
Select a stem that is about the thickness of a pencil and longer than a foot. Take a clean sharp knife, find a spot at about 1 foot for the top tip of the stem, remove leaves and thorns around this area, peel off about a 1 inch section of the green bark tissue to get to white wood.
You can also make a 2” long cut along the middle of the stem, and insert a little piece of plastic straw to prop the cut open, like shown in the above video tutorial by Vuon & Nha.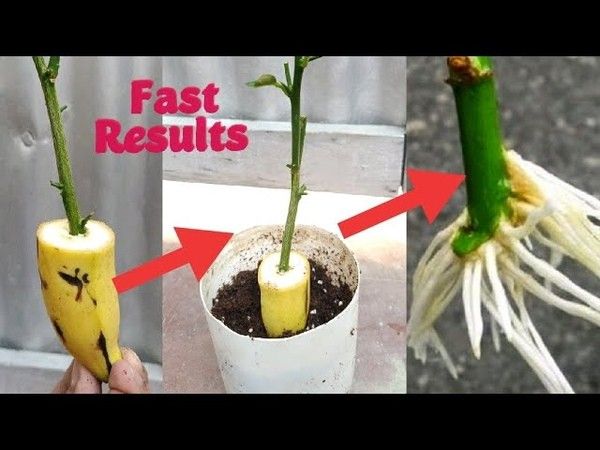
Don’t cut too deeply into the stem or it could break.
Dust the cut area with rooting hormone. You can skip this, but rooting hormone does help speeding up the process.
Next, make a 3” to 4” size pouch using either plastic wrap or a small plastic bottle filled with moist peat moss, coir, or potting soil. Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
The cut area should be completely covered with enough room for roots to develop. Video tutorial below by Vuon & Nha.
Secure top and bottom with strings or twist-tie (Not too tight so the plant can grow and expand). You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
Because the stem is still attached to the mother plant, it is receiving water and nutrients as the new roots are growing from the cut area. This greatly increases the propagation success rate to nearly 100%!
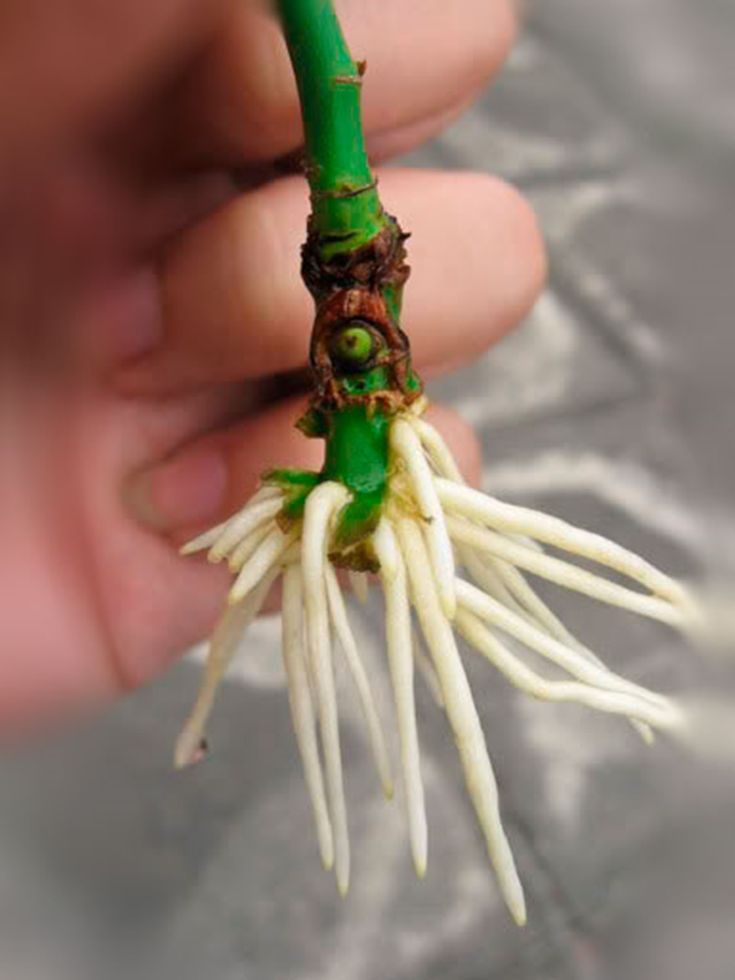
Most rose plants show their white roots in 3 – 5 weeks. When you see good root system develops with lots of healthy roots, clip the stem off below the layer.
Gently remove ties and covers. Carefully plant your new rose plants and keep them well watered and protected from direct sunlight for a couple of weeks so it can adapt.
Grow roses from cuttings in soil or medium
Fill some clean pots or containers rooting mix and water well so it’s moist and fully hydrated. You can use clean potting soil or a soil-less mix such as clean sand, peat moss, perlite, or Coco coir. ( Photo by Hedgerow Rose)
IMPORTANT: The containers should have drainage holes and never sit in water for too long. ( Photo by Grownups )
( Photo by Grownups )
Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
Take rose cuttings only from healthy plants that are well watered. Choose fresh healthy rose stems newly grown from the woody base, with at least 3-5 leaf nodes on the stem. Cut near the base at a 45-degree angle. Put cut stems in water immediately.
Video tutorial by Vuon & Nha on YouTube. How to propagate rose cuttings in coco coir!Cut longer stem into 6 inch to 8 inch long, and make sure each cutting have at least 3 nodes – where leaf meets stem. Remove all flower buds and leaves except for one set of leaves at the top of each cutting.
Dip the cutting’s bottom half in the rooting hormone powder or gel. Use a pencil to make a planting hole 3 to 4 inches deep in your rooting mix. Plant the rose cutting into the hole so at least two nodes are covered.
Keep the cuttings in a warm and bright place away from direct sun. Water when the rooting mix start to feel dry on the top inch. Pamela at Flower Patch farm used recycled coffee cups (above) and large jars (below ) as humidity tent. Such great ideas!
You can also use a propped- up plastic bag or a mini greenhouse. Here are 45 best DIY greenhouses you can make from tiny to big!
If you live in a warm humid climate with a shaded outdoor area, you can skip the humidity cover. ( Photo below by Hartwood Roses )
Most softwood rose cuttings will root within 2 to 6 weeks. If you see healthy leaves growing, and feel some resistance when you very gently tug on the cuttings (don’t do this too soon!) , it’s likely they have rooted.
Here’s a YouTube tutorial by Mike on how to use a humidity cover made from plastic bottles.
Now you can remove the humidity tent and let them grow for a couple more weeks before transplanting the cuttings. Below is another propagation example by Lilisim.
Can you root rose cuttings in water?
Rose cuttings do not propagate well in just water. Some cuttings will root, but the success rate is usually about 20%, while you can get 80% success by propagating rose cuttings in soil medium or by layering.
The rose cuttings tend to take a long time to root in water, and is prone to rotting.
However, some favorite plants can root very easily in water! Here are a couple of tutorials on how to propagate Fiddle Leaf Fig or Hydrangea cuttings in soil or water with almost 100% success!
Hydrangeas are some of the easiest flowers to propagate! Tutorial here!Can you grow rose cuttings using potatoes?
There are many viral images of rose cuttings in potatoes, but I have not seen any scientific or real life evidence of potatoes or dipping in honey making rose cuttings grow more quickly or successfully.
On the contrary, there are many reports of failures from gardeners who actually tried to grow rose cuttings in potatoes.
The potatoes may grow roots, which will not magically become rose roots. The rose cuttings need a medium that holds moisture and air, which isn’t really what a potato does.
That’s it! Use the first 2 methods, and happy gardening! 🙂
Rooting Roses: Growing Roses From Cuttings
Roses
By: Stan V. Griep, American Rose Society Consulting Master Rosarian, Rocky Mountain District
One way to propagate roses is from rose cuttings taken from the rose bush one desires to have more of. Keep in mind that some rose bushes may still be protected under patent rights and thus, are not to be propagated by anyone other than the patent holder. Keep reading to learn more about how to root roses.
The best time to take rose cuttings and rooting roses is in the cooler months, perhaps starting in September, as the success rate is higher for home gardeners at this time. The rose cuttings that one is going to try to root are best taken from the stems of the rose bush that have just flowered and are about to be deadheaded.
The rose cuttings that one is going to try to root are best taken from the stems of the rose bush that have just flowered and are about to be deadheaded.
The rose cutting should be 6 to 8 inches (15-20.5 cm.) in length, measuring down the stem from the base of the bloom. I recommend keeping a jar or can of water handy so that the fresh cuttings may be placed directly into the water after making the cutting. Always use sharp, clean pruners to take the cuttings.
The planting site for growing roses from cuttings should be one where they will get good exposure from the morning sun yet be shielded from the hot afternoon sun. The soil in the planting site should be well-tilled, loose soil, with good drainage.
To start rose bushes from cuttings, once the rose cuttings have been taken and brought to the planting site, take out a single cutting and remove the lower leaves only. Make a small slit with a sharp knife on one or two sides of the lower portion of the cutting, not a deep cut but just enough to penetrate the outer layer of the cutting. Dip the lower portion of the cutting into a rooting hormone powder.
Dip the lower portion of the cutting into a rooting hormone powder.
The next step when you grow roses from cuttings is to use a pencil or metal probe and push down into the planting site soil to make a hole that is deep enough to plant the cutting up to about 50 percent of its overall length. Place the cutting that has been dipped into the rooting hormone into this hole. Lightly push the soil in around the cutting to finish the planting. Do the same thing for each cutting keeping them at least 8 inches (20.5 cm.) apart. Label each row of rose cuttings with the name of the mother rose bush it was taken from.
Place a jar over each cutting to form a sort of miniature greenhouse for each cutting. It is extremely important that the soil moisture for the cuttings does not dry out at this rooting time. The jar will help to hold humidity in but can be a problem if it is subjected to a lot of hot afternoon sun, as it will overheat the cutting and kill it, thus the need for shielding against the exposure to the hot afternoon sun when you root roses.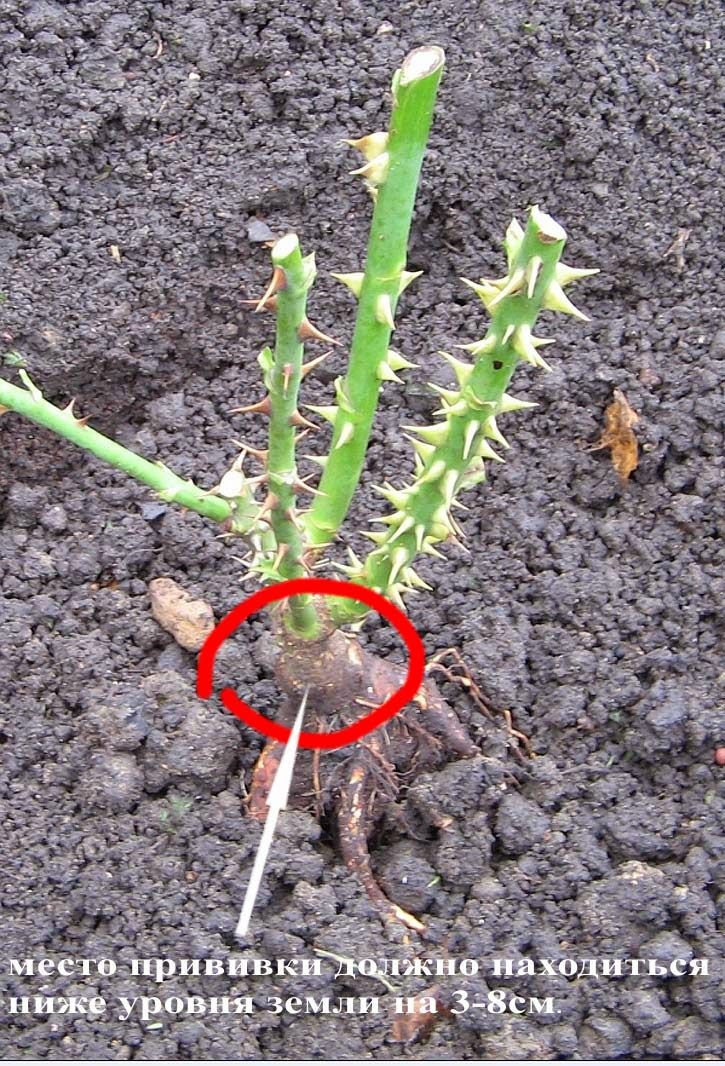 Watering of the planting site every other day may be required to keep the soil moist but do not create a standing water or muddy soil situation.
Watering of the planting site every other day may be required to keep the soil moist but do not create a standing water or muddy soil situation.
Once the new roses have taken root well and have begun to grow, they may be moved to their permanent locations in your rose beds or gardens. The new rose bushes will be small but usually grow fairly quickly. The new rose bushes must be well protected against the hard winter freezes in their first year as well as extreme heat stress conditions.
Please keep in mind that many rose bushes are grafted rose bushes. This means that the bottom part is a hardier rootstock that will withstand cold and heat better than the top and more desired part of the rose bush. Starting a rose bush from cuttings places the new rose bush on its own roots, so it may not be as hardy in cold climates or in extreme heat conditions climates. Being on its own root system can cause the new rose bush to be far less hardy than its mother rose bush.
This article was last updated on
Read more about Roses
Did you find this helpful? Share it with your friends!
90,000 diamond requires a decent cut! care tips and tricks for gardenersDenBen 31 December 2015
There are three main conditions for the successful planting of the queen of flowers.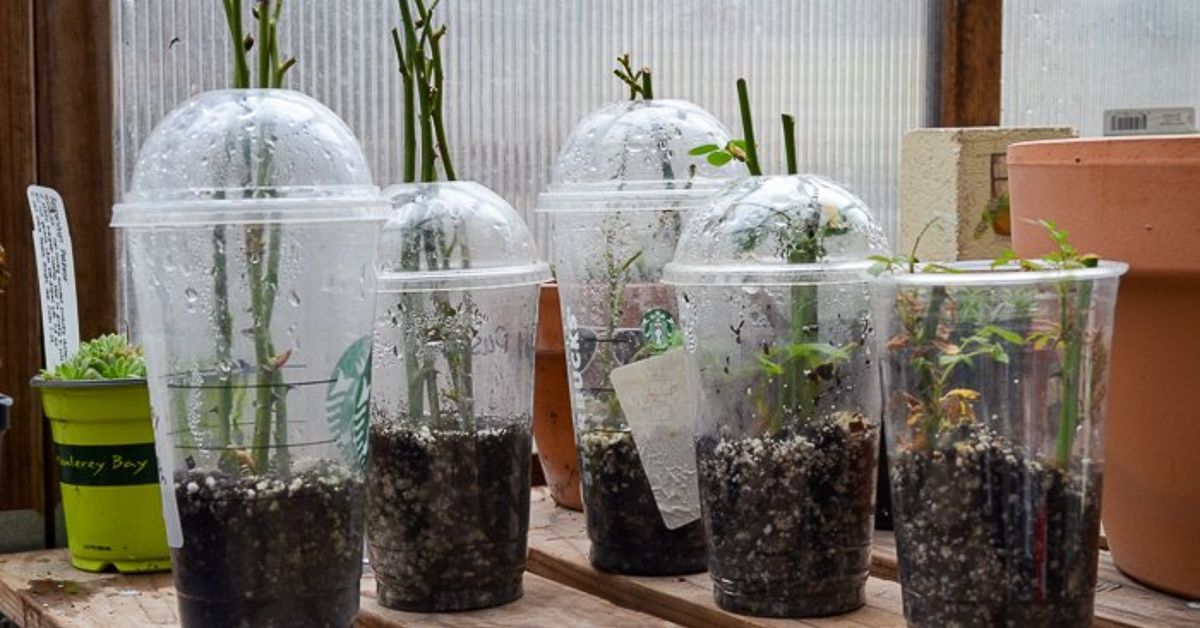 In the soil for roses, the presence of peat, sand and compost is mandatory. Please note that after planting, the fate of a rose is entirely determined by the quality of the soil in which it was planted.
In the soil for roses, the presence of peat, sand and compost is mandatory. Please note that after planting, the fate of a rose is entirely determined by the quality of the soil in which it was planted.
Never plant young rose seedlings in an old place, because the soil, in addition to the general depleted state, may also be infected with some kind of disease or pests. As a rule, planting a young rose bush on such a site ends with its constant illnesses, weak resistance to even the slightest environmental influences. Often, everything ends with the early and inglorious death of the plant. If you have no other place to plant roses, remove at least a 50-70 cm layer of soil from the surface of the site, replacing it with fresh soil - this way you minimize the risks.
Primer for garden roses Robin Green pressed 25 l
Liquid fertilizer Ogorodnik Barrel and four buckets organic-mineral potassium humate 0.6l
Naturally, the soil for planting roses should be enriched with fertilizers - manure and mineral elements.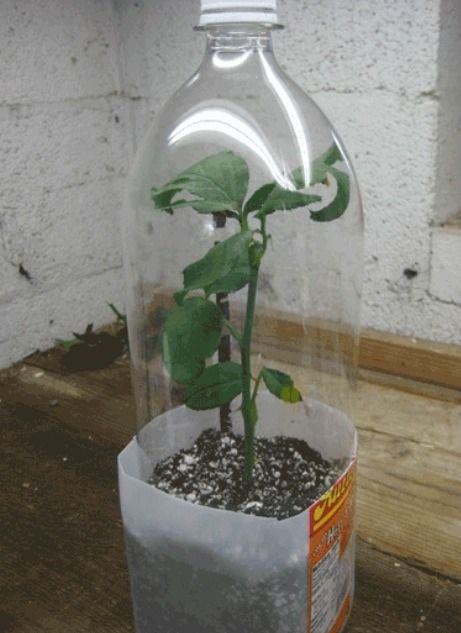 When it comes to planting grafted roses, the thickness of the nutrient soil layer should be at least 0.7 m, and 0.5 m is enough for the rest of the roses. The width of the planting pits should be 0.5 m. The bottom of the planting pits is lined with rotted manure, compost or peat. A layer of garden soil is laid on top, cleared of plant residues and weeds, and then these 2 layers are mixed. It is recommended to fill up the planting pits with a mixture of garden soil, peat, compost, rotted manure and mineral fertilizers. Or you can prepare a mixture to fill the planting pits as follows: rotten manure - 1 bucket, peat - 1 bucket, sand - 2 buckets (added to clay soils), clay soil - 2 buckets (added to sandy soils) dolomite flour - 2 cups, bone meal - 2 cups, superphosphate - 2 pinches. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed, after which the soil for roses is ready for use.
When it comes to planting grafted roses, the thickness of the nutrient soil layer should be at least 0.7 m, and 0.5 m is enough for the rest of the roses. The width of the planting pits should be 0.5 m. The bottom of the planting pits is lined with rotted manure, compost or peat. A layer of garden soil is laid on top, cleared of plant residues and weeds, and then these 2 layers are mixed. It is recommended to fill up the planting pits with a mixture of garden soil, peat, compost, rotted manure and mineral fertilizers. Or you can prepare a mixture to fill the planting pits as follows: rotten manure - 1 bucket, peat - 1 bucket, sand - 2 buckets (added to clay soils), clay soil - 2 buckets (added to sandy soils) dolomite flour - 2 cups, bone meal - 2 cups, superphosphate - 2 pinches. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed, after which the soil for roses is ready for use.
If the soil on the site is initially fertile, it is dug up twice - this adds air permeability to the soil surface. If you plant single seedlings, separate planting pits are prepared, and when planting in groups, flower beds should be prepared.
If you plant single seedlings, separate planting pits are prepared, and when planting in groups, flower beds should be prepared.
- Rose Fertilizer: Gourmet for the Flower Queen
- Rust on roses: treatment of diseased bushes
- How to grow a rose from a gift flower
It is advisable to start soil preparation in the fall if you plan to plant in the spring.
Soil for planting roses: acidity
The acidity of the soil for planting roses must be under vigilant control. If you do not have the opportunity to check the acidity with litmus, you can understand its state from plants. For example, horsetail growing on your site, narrow-leaved tenacity, oxalis and sorrel signal that the soil is acidic. Alkaline soil is a fertile paradise for clover, horseradish and similar plants. Alkaline soil is necessarily slightly acidified - it will not be possible to increase its acidity in other ways. For acidification, the introduction of acidic peat, leaf or coniferous humus, as well as superphosphate works great. With an acidic soil reaction for roses, on the contrary, it should be limed. Best of all, such procedures are carried out with crushed limestone, dolomite flour, ash or bone meal. And be careful with lime - its introduction in large quantities contributes to the inhibition of plant development processes.
With an acidic soil reaction for roses, on the contrary, it should be limed. Best of all, such procedures are carried out with crushed limestone, dolomite flour, ash or bone meal. And be careful with lime - its introduction in large quantities contributes to the inhibition of plant development processes.
Soil for rose cuttings
What kind of soil do roses and their cuttings like? The soil for cuttings of roses, more precisely, for their rooting, you can use purchased - it can be found in the online store or garden center. Specialized substrates from the Fasco trading company have proven themselves to be excellent.
If you make up the soil yourself, the ingredients and proportions will vary depending on what type of soil you later plant these cuttings in. In principle, the rose does not take root only on marshy and saline soil. Other types of soil are quite acceptable for her, although loam is still considered the best option.
- If planting is planned on sandy soil, the cuttings are rooted in a mixture of the actual soil from the planting site, 1 part soddy soil, 1 part humus, 1 part compost, 2 parts clay powder
- To loamy soil for cuttings of roses, add sand - 3 parts, humus - 1 part, compost - 1 part, soddy soil - 1 part.

- To clay soil add coarse sand - 6 parts, humus - 1 part, compost - 1 part, soddy soil - 1 part, sheet soil - 1 part.
Retail catalog
Wholesale catalog
Note: to enhance the effect in all the above mixtures, replace humus, compost and sod soil with biohumus.
What soil do roses like
Are you still wondering what soil roses like? Roses love fertile soil, so fertility must be attributed with special attention. And roses also love excellent drainage, so the bottom of the planting hole, the optimal size of which when planting a bush is 60 * 60 * 70 cm, is necessarily lined with pebbles, gravel or broken bricks. Only with such a drainage layer is the rose bush not doomed to death from overflow. When landing, it will not be superfluous to use natural biostimulants. Moreover, it does not have to be purchased drugs. Do not forget about the amazing properties of the good old clay talker - a mixture of clay and manure in equal proportions.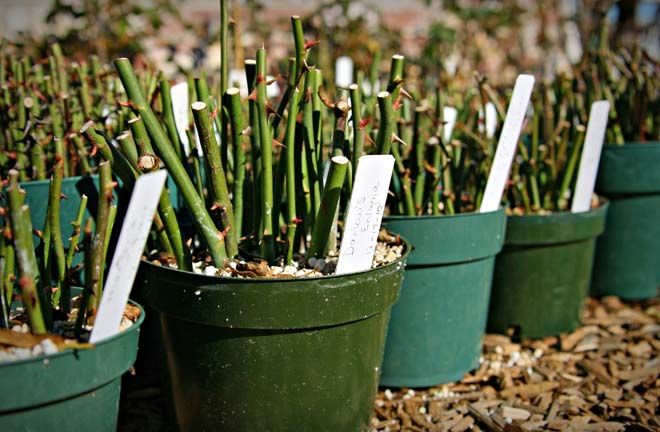 The finished mash has a creamy consistency. If you purchased open-rooted rose seedlings, dip them in this mixture for 10 minutes, then plant immediately.
The finished mash has a creamy consistency. If you purchased open-rooted rose seedlings, dip them in this mixture for 10 minutes, then plant immediately.
The right substrate for cuttings of roses
To understand what substrate the cutting needs for better rooting, let's think about the conditions under which roots will germinate comfortably. There are only four of them:
- Sterility.
- Air.
- Water.
- Essential nutrients.
Coarse river sand . For sterility, it can be fried, washed with boiling water. It passes air and water well. But the catch is that it does not contain food for the future plant. And when the roots appear, a transplant is necessary. Plus, it dries out quickly.
Sand mix. All the pluses of sand will be supplemented with a nutritional supplement, which can be peat, turf, leafy soil. But there's a catch here too. Lost sterility. And if we fry the earth or peat, then all organic matter will simply burn out.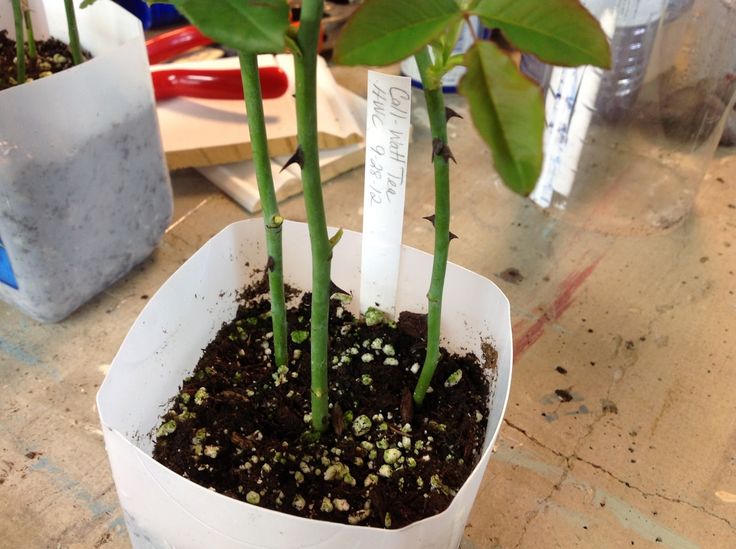 You can, of course, disinfect the soil by spilling it with a solution of manganese, but you can’t get it on young roots, which can cause them to burn.
You can, of course, disinfect the soil by spilling it with a solution of manganese, but you can’t get it on young roots, which can cause them to burn.
Vermiculite. In flower shops you will find vermiculite in small and large bags. These are lamellar crystals of natural origin, yellowish-gray, silvery, brown or greenish in color, perfectly retaining moisture. Vermiculite is literally crammed with microelements useful for plants and is inert to acids and alkalis. Its high porosity allows it to absorb 4 times more moisture than its own weight. So for example, 200 g of vermiculite hold 800 ml of water.
A mixture of sand and vermiculite is the best choice
In botanical gardens, a mixture of river sand and vermiculite is successfully used to propagate roses in unheated film greenhouses. For 1 part of vermiculite, 2 parts of sand are taken. At home, you can root cuttings of roses in such a mixture on cold verandas or glazed balconies and loggias at the beginning and end of summer.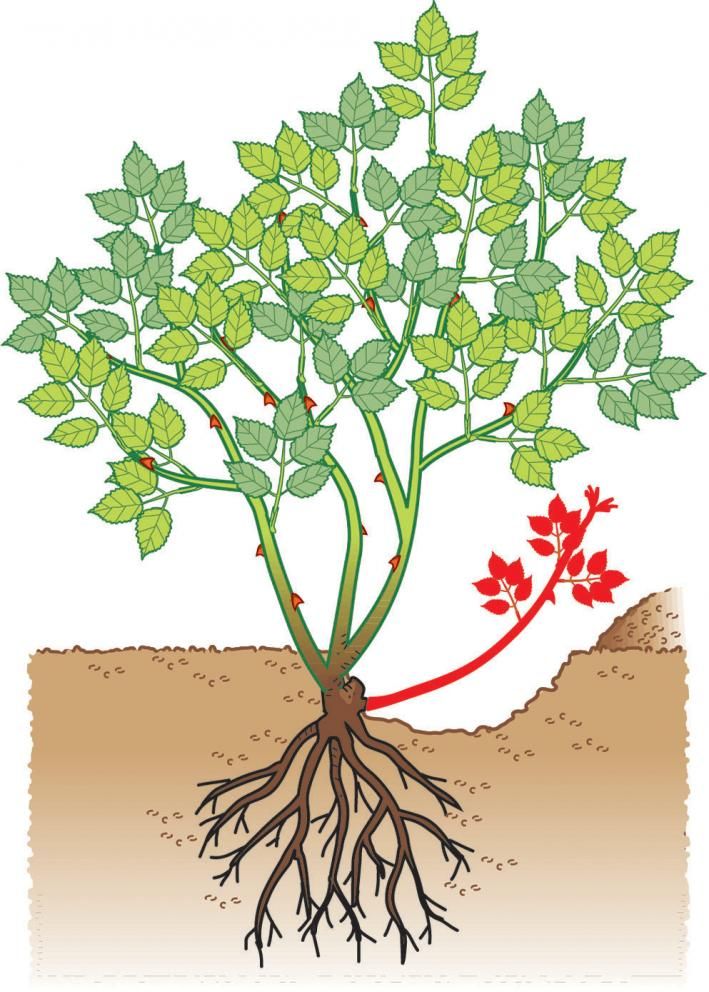 It is in such a substrate that it is easy to maintain breathability, thanks to sand, constant moderate humidity, thanks to vermiculite.
It is in such a substrate that it is easy to maintain breathability, thanks to sand, constant moderate humidity, thanks to vermiculite.
Cuttings planting depth - 2-2.5 cm. Cuttings are planted obliquely, parallel to the lower oblique cut.
Cuttings at home
At home, to ensure constant air humidity, it is best to cover the cuttings planted in pots with a glass jar, a plastic transparent bag or a transparent cut plastic bottle.
25 days is the rooting time for most rose cuttings. All this time they need: light (25% of open ground illumination), constant ground temperature of 20-25 degrees Celsius, high air humidity 90-100%, moderate soil moisture, regular ventilation.
When sprouts emerge from the leaf axils, this is a signal that the cuttings are rooted. Now they need to be fed with a complete mineral complex (A, P, K + microelements), abundant watering, reducing air humidity and increasing illumination.
Read also an interesting article about rose cuttings Burrito is a simple and effective method of propagating roses.










