Architectural styles throughout history
Architectural Styles Through the Ages!
Architecture has seen rapid changes over time, ranging from the old age to that of the modern era, thereby witnessing evolution at every step. The one question that remains prominent among today’s generation is regarding the beginning of Architecture, either Western, Eastern or Indian. Even before the Greeks and the Romans came in, humans were actively involved in designing and constructing. This era was known as the Classical era. It was during the classical era that ideas and construction techniques came into the forefront. The classification of most of the architectural styles is according to the respective periodical styles, marked with the reflecting and unique characteristics that often keep on changing over time.
Each age has seen a specific and new type of architectural growth in the building construction. One important thing to note is the connection between those periods and related construction style. Each period or era flaunts its specific style. Sometimes, a particular period reflects the overflow of new ideas, and sometimes the merging of two contradictory ideas makes way for innovative architectural movements. Architecture is a fluid art that has evolved through the years, and we can say it as a constant movement, one of the essential things to take into consideration.
An architectural style is a representation of an art form in a building making its features and structures historically identifiable. Based on the architectural style, there are different features and genres. The style talks about the various aspects such as materials, regional character, form, method of making, and so on. There’s a complete chronology for the buildings and styles that keep on changing over the time period. It is usually because of the changes in belief, religion, fashion, and of course the technology and innovation in new materials and tools for construction, that the architecture always keeps on exploring new horizons.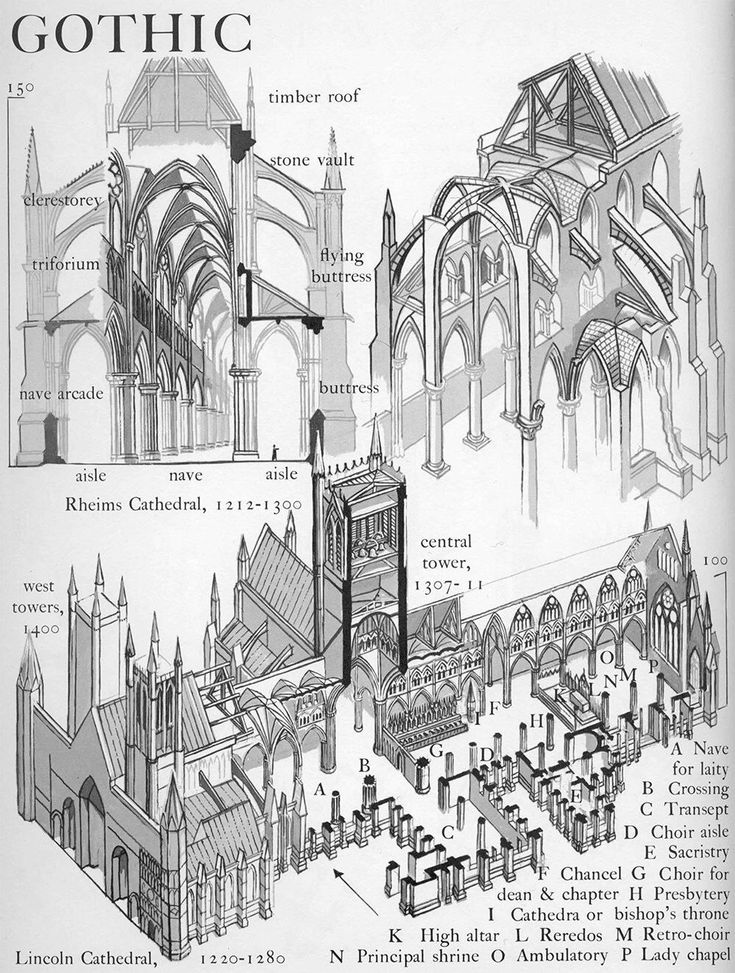
Timeline of Architectural Style
The styles of the different chronological era are listed under architectural history. Based on the fashion of the period, the architects have contributed to adapting newer ideas. These architectural styles have, however, seen gradual development over time with different twists based on the area it spreads. The revival of a new or old genre in architecture is pretty common. For instance, neoclassicism eventually brought back classicism.
Vernacular architecture has also found its way in modern architecture and is often considered as a different part. The vernacular architecture, however, varies from one state, country to another. It, however, gives birth to the national and international styles as well. Vernacular architecture is very much prominent in India as well as in western society.
Architecture
Vernacular Architecture… Accommodating Local Culture
Prominent Architectural StylesFrom the prehistoric to modern and post-modern, art and architecture seem to flourish all the way. From Western to Eastern countries, each of it flourished by the prominence of architecture. Some of the popular types of architectural styles through the age of history include:
From Western to Eastern countries, each of it flourished by the prominence of architecture. Some of the popular types of architectural styles through the age of history include:
Ranging from 11,600 B.C. to 3,500 B.C., archaeologists have dug into prehistory to bring about the changes. It is considered to be one of the oldest architectural styles. Prehistory covers the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic), Middle Stone Age (Mesolithic), and New Stone Age (Neolithic) periods. Additionally, it also includes the portions of the Bronze Age and Iron Age. One of the essential characteristics of prehistoric builders was the creation of structures in the geometric patterns. One of the most excellent examples of prehistoric architecture is Göbekli Tepe in the present day. The prehistoric architecture usually deals with different monumental structures include cliff dwellings, Stonehenge, cliff dwellings, mud structures, thatch, and many more.
Examples of Prehistoric architecture: Stonehenge, Göbekli Tepe
Southern Britain has some of the most excellent examples of prehistoric architecture, which are named as prominent UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Stonehenge in Amesbury is another excellent example of prehistoric structures. Often, the Prehistoric structures are considered as the birth of architecture because of these paved ways for the architectural roadmap later on.
Stonehenge in Amesbury is another excellent example of prehistoric structures. Often, the Prehistoric structures are considered as the birth of architecture because of these paved ways for the architectural roadmap later on.
This architectural style ranges from 3,050 B.C. to 900 B.C. It depicts the prominent period of Egyptian architecture. The Egyptians created the most impressive structures of the ancient world. The period saw the construction of some of the prominent pyramids with several noticeable architectural characteristics. Scholars over the time often have considered this period of history in ancient Egypt as an entirely unique one.
The Pyramids of Egypt
The pyramids of Egypt are some of the finest examples of engineering. The excellence of Egyptians in engineering gave them the ability to build bigger tombs for their kings. It involved a higher degree of the architectural knowledge to develop such structures..jpg) The Egyptian pyramids, tombs and palaces still stand as monuments to mankind’s creativity and genius in spite of thousands of years of invading armies, earthquakes, and other forces of natural calamities.
The Egyptian pyramids, tombs and palaces still stand as monuments to mankind’s creativity and genius in spite of thousands of years of invading armies, earthquakes, and other forces of natural calamities.
Architecture
Top 6 Famous Historical Monuments in India!
03. Classical PeriodEglise de la Madeleine – Roman Catholic Church
The classical period lies between 850 B.C. to 476 A.D., derived the designs and styles from ancient Greek and Rome. The period between the rise of the Greek Empire and the fall of the Roman Empire has eventually seen the construction of several buildings. The most important architectural feature which highlights this style is the column placed on the façade. The identifiable features of classical aesthetic include symmetry, proportion, rational order, the relationship of individual parts to the whole and calm logic.
The Roman architect Marcus Vitruvius, from the first century B.C., suggested the idea of using mathematical formulas to propound the construction of buildings. Vitruvius was the one to introduce the three different Classical orders Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. In his book De Architectura (first published in Italian language) or Ten Books on Architecture (English), he has introduced the importance of symmetry and proportion for building construction. It helped in constructing and planning out symmetrically advanced and reliable structures later on.
Vitruvius was the one to introduce the three different Classical orders Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. In his book De Architectura (first published in Italian language) or Ten Books on Architecture (English), he has introduced the importance of symmetry and proportion for building construction. It helped in constructing and planning out symmetrically advanced and reliable structures later on.
Architecture
The Symmetry in Architecture: All you Need to Know!
04. ByzantineHagia Sophia – Museum in Istanbul
Ranging from 527 to 565, the Byzantine empire took place after the capital of Constantine shifted to the Byzantium. The empire brought into prominence the classical forms, domed roofs, and mosaics. Basilicas, apse, mosaic and clerestory are the most common structures found in this architectural style. The basilica is a large famous church. The Byzantine architecture had seen a thorough combination of the Eastern and Western traditions. One characteristic feature of these buildings was a central dome. This design further spread to other parts of the Middle East as well. Undoubtedly, the architecture during this period was not only transformational but transitional as well. Hagia Sophia is one of the examples of Byzantine Architecture.
One characteristic feature of these buildings was a central dome. This design further spread to other parts of the Middle East as well. Undoubtedly, the architecture during this period was not only transformational but transitional as well. Hagia Sophia is one of the examples of Byzantine Architecture.
Basilica of St. Sernin in Toulouse, France
The influence of Rome on Europe also brought into effect the Romanesque architecture. It was prevalent during the 11th and 12th centuries. According to ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Architectural styles of building erected in Romanized Western Europe having characteristics notably the semicircular-headed arch, the use of the basilican form for churches, and the survival of design elements such as the Classical capital.” The characteristic features of such an architecture were round arches, barrel vaults, thick walls, large towers, sturdy pillars, supporting vaults, and decorative arcading. Every building has defined forms, symmetrical plans, and the overall appearance is one of the simplicities when compared to other complex architectural styles. One of the finest examples of Roman architecture in Europe is the Basilica of St. Sernin in Toulouse, France. It also brings into prominence the Latin influence as well.
Every building has defined forms, symmetrical plans, and the overall appearance is one of the simplicities when compared to other complex architectural styles. One of the finest examples of Roman architecture in Europe is the Basilica of St. Sernin in Toulouse, France. It also brings into prominence the Latin influence as well.
Notre Dame Cathedral in Paris, France
The influence of Gothic culture came around the 12th century in the Western World. It not only supported the graceful structure but far taller ones. The innovation was at a peak during the time. Some of the characteristic features of the buildings during this age were flying buttresses, pointed arches, and ribbed vaulting. According to ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Gothic is one of the architectural styles evolved in Europe from the late 12th century until 16th century. It is the architecture of the pointed arch, pointed ribbed vaults, piers with clusters of shafts, deep buttresses, window tracery, pinnacles, spires, battlements, and a soaring verticality. ” The buildings also saw the introduction of elaborate stained glasses and clerestory windows. The prominent decoration materials used were Gargoyles.
” The buildings also saw the introduction of elaborate stained glasses and clerestory windows. The prominent decoration materials used were Gargoyles.
Some of the famous examples of Gothic buildings in today’s world include Chartres Cathedral and Paris’ Notre Dame Cathedral in France. Another well-known example includes Adare Friary in Ireland.
07. RenaissanceSt. Peter’s Basilica in Rome
The Renaissance period had brought into prominence, a significant development in the buildings. The architects during the Renaissance era were majorly inspired by the architects and builders from Greece and Rome. The Renaissance is often called as the Italian Renaissance. It is the period of cultural rebirth. It brought the invention of perspective, bringing the sense of infinity in the Renaissance paintings, thus helping the humans to shape the new humanist thought. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Renaissance is an architectural style developed in the early 15th century which was based on the architecture of Roman Antiquity. ”
”
St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome is one of the examples of the Renaissance period. Andrea Palladio contributed towards symmetrical villas like Villa Rotunda near Venice, Italy. Palladio followed the ideas of Vitruvius. He even published the new technology in I Quattro Libri dell’ Architectura (first published in Italian language) or The Four Books of Architecture (English).
His ideas did not bring back the Classical order of literature, but it reflected the ancient designs to a lot of extent. They, however, are also referred to as neoclassical in the US.
08. Indian ArchitectureIndia is the most ancient civilization. It has been a knowledge civilization since centuries ago. It had a share of 25% to 35% in the world GDP till 1800 to 1850 A.D. It is also the land where ‘zero’ was discovered and from where the knowledge of Astronomy has prevailed, for 5000 years.
The evolution of architecture in India has flourished in various ages in different parts and regions of the country. The earliest evidence of Indian Architecture is found in the urban planning of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappan Civilizations. The development of cave architecture marks a crucial phase in the history of Indian Architecture. In the post-Harappan period, the classification of architectural styles was done into Hindu, Buddhist and Jain Architectures.
The earliest evidence of Indian Architecture is found in the urban planning of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappan Civilizations. The development of cave architecture marks a crucial phase in the history of Indian Architecture. In the post-Harappan period, the classification of architectural styles was done into Hindu, Buddhist and Jain Architectures.
The excavation of caves took place around the 2nd century B.C. to 10th century B.C., out of which the famous ones include Ajanta and Ellora Caves where huge temples have been carved in the form of a single hill or rock. The ancient forts on the top of the hills as well as the Sun temple at Konark, Orissa and Modhera, Gujarat are the classic combination of Indian architecture and astronomy. The roots of Indian architecture can be traced to classical ancient text in Sanskrit on Vastu shastra i.e. architecture like Mayamtam, Mansara-architecture, etc. These are also the texts which describe the construction technology of those days.
The emergence of Jainism and Buddhism has helped in developing early architectural styles in building stupas, viharas and chaityas.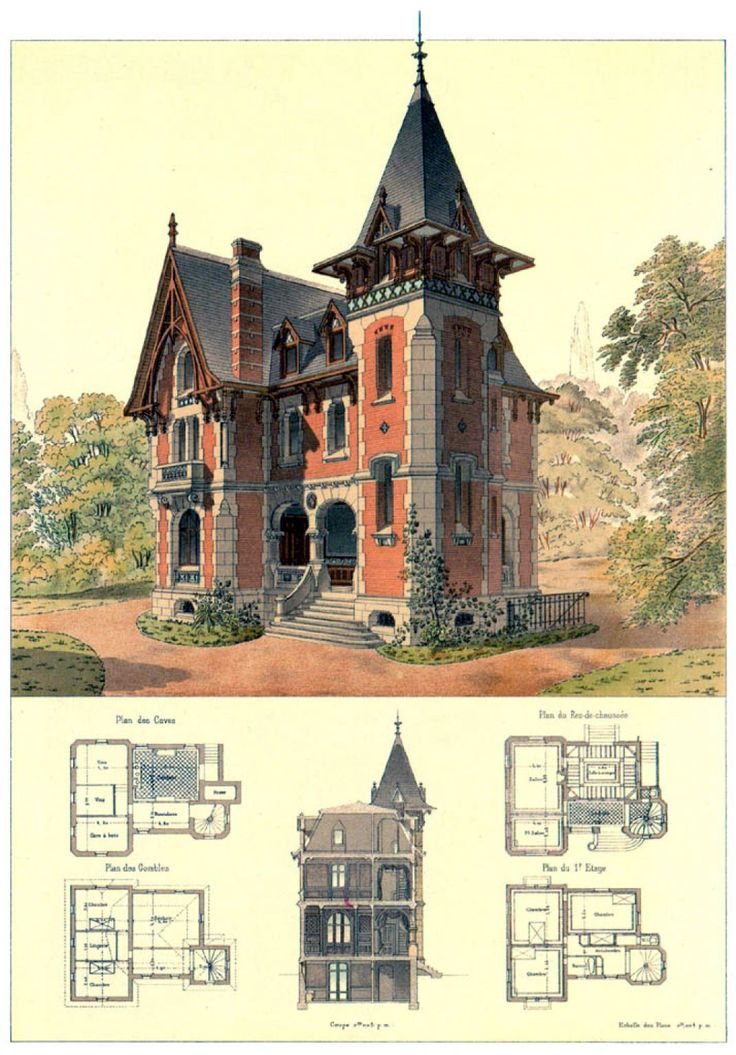 The Buddhist Stupas made of huge mounds of mud, enclosed in burnt small standard bricks. The Sanchi Stupa is a symbol of Mauryan architecture. The ancient temples built in India 1000 or more years ago are the classic examples of Indian Architecture. Many ancient temples had been destroyed by Barbaric invaders in the past. Temple Architecture flourished in the 6th to 10th century. Khajuraho temple located in Madhya Pradesh is one of the examples of temple architecture which simultaneously narrates knowledge from various disciplines.
The Buddhist Stupas made of huge mounds of mud, enclosed in burnt small standard bricks. The Sanchi Stupa is a symbol of Mauryan architecture. The ancient temples built in India 1000 or more years ago are the classic examples of Indian Architecture. Many ancient temples had been destroyed by Barbaric invaders in the past. Temple Architecture flourished in the 6th to 10th century. Khajuraho temple located in Madhya Pradesh is one of the examples of temple architecture which simultaneously narrates knowledge from various disciplines.
Khajuraho Temple, Madhya Pradesh
Indian architecture has observed rapid growth and transformation along with the history of India. However, its development in architecture can be traced through the development of the ages. Modern day India has a diverse culture which is well represented in its architecture, such as the diversity from Hindu temple architecture to Islamic mosque architecture. These diverse cultures help us to understand the rich traditions prevalent at all times in the land called India. UNESCO has listed 830 Heritage Sites in the world out of which 26 are Indian. It is a combination of indigenous styles and external influences, giving it a unique characteristic of its very own.
UNESCO has listed 830 Heritage Sites in the world out of which 26 are Indian. It is a combination of indigenous styles and external influences, giving it a unique characteristic of its very own.
In the medieval period, there was a combination of Persian Architecture. Indo-Persian style of architecture prevailed at that very time. After that, the colonial period brought the influences of western architectural forms to the India. It is majorly seen in office buildings. The Parliament House and Connaught Palace in Delhi are examples of colonial architecture.
Architecture
Importance of Hierarchy in Architecture
09. Buddhist Architecture (i) Indonesian ArchitecturePagaruyung Palace in Indonesia
Indonesian Architecture not only reflects cultural diversity but historical inheritance as well. The geographic location of Indonesia itself reflects the variation between Hindu-Buddhism architecture and Oceania. The arrival of European, the spread of Islam also contributed towards the popularity of Indonesian Architecture and influenced it a lot. However, with the following years, modern art was as well developed in the culture of Indonesian architecture. It is characterized by wooden pile dwellings, high pitched roofs and extended roof ridges. Pagaruyung Palace in Indonesia is an example of exclusive Indonesian Architecture.
The arrival of European, the spread of Islam also contributed towards the popularity of Indonesian Architecture and influenced it a lot. However, with the following years, modern art was as well developed in the culture of Indonesian architecture. It is characterized by wooden pile dwellings, high pitched roofs and extended roof ridges. Pagaruyung Palace in Indonesia is an example of exclusive Indonesian Architecture.
The Forbidden City, Beijing
Chinese Architecture is very much intermingling of the different architectural styles that once existed in different parts of Vietnam, Korea, Japan, and Ryukyu. The modern times have observed a shift in the decorative style, but the significant portion remains still unchanged. Most of the knowledge regarding the Chinese Architecture was passed on generation by generation from one tradespeople to the other. The key architectural features are standing on a platform, grand palace and three-layered platform. The ancient Chinese Architecture is mainly made of timberwork. The buildings are usually built in square, round, hexagon and octagon and their architecture are always graceful in appearance. The Forbidden City, Beijing is an example of Chinese Architecture.
The ancient Chinese Architecture is mainly made of timberwork. The buildings are usually built in square, round, hexagon and octagon and their architecture are always graceful in appearance. The Forbidden City, Beijing is an example of Chinese Architecture.
Korean Bell of Friendship, in San Pedro
Korean Architecture is almost similar to the Eastern Asian building system. Most of the Korean Architecture buildings are available in the vertical and horizontal style. The buildings are built according to the kan unit; the distance usually is measured between the two posts with about 3.7 meters. The kan unit is the traditional unit in Korean architecture still used to describe palaces, shrines and Buddhist temples. Such an architecture is characterized by the difference of transitional space between inside and outside. The curved line of the roof, eaves and their overlapped composition is the characteristic feature of Korean architecture. Simplicity is the strength of this architecture. Korean Bell of Friendship, in San Pedro is an example of Korean Architecture.
Simplicity is the strength of this architecture. Korean Bell of Friendship, in San Pedro is an example of Korean Architecture.
Byodo-in, Kyoto
The Japanese culture had a significant influence on the Japanese Architecture. The features and characteristics make it widely different from other forms. It is characterized by wooden structures, elevated from the ground, with tiled or thatched roof. Moreover, the development of two new forms contributed to the militaristic climate. The castle is made as to the defensive structure. After World War II, Japan saw a rise in the modern architecture. Thus, from the 1950s, modernism became an essential part of the Japanese Architecture. Byodo-in, Kyoto is the beauty of Japanese Architecture.
13. Islamic ArchitectureThe Taj Mahal, Agra
Secular and religious architectural styles very much influenced the Islamic architecture. It took inspiration from Islamic culture, and the roots of Islamic architecture are found even today. Islamic architecture is characterized by its wide range of distinctive features such as mosques, tombs, palaces, and forts. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Islamic architecture has several characteristic features including pointed, multifoil, low, wide, four-centered, and horseshoe arch, cladding of coloured glazed earthenware and patterned tilework and serene geometry.” The widespread of Islamic architecture gave further birth to Afro-Islamic, Ottoman, Moorish, and Tirmud architecture. The Taj Mahal is one of the examples of Islamic Architecture.
It took inspiration from Islamic culture, and the roots of Islamic architecture are found even today. Islamic architecture is characterized by its wide range of distinctive features such as mosques, tombs, palaces, and forts. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Islamic architecture has several characteristic features including pointed, multifoil, low, wide, four-centered, and horseshoe arch, cladding of coloured glazed earthenware and patterned tilework and serene geometry.” The widespread of Islamic architecture gave further birth to Afro-Islamic, Ottoman, Moorish, and Tirmud architecture. The Taj Mahal is one of the examples of Islamic Architecture.
Agha Bozorg mosque in Kashan, Iran
Although the roots are in Persia, the prominence of Persian architecture is found in every corner of the world. Although it had met its destruction under Alexander, the ruins of the structures are enough to talk about the exquisite architecture.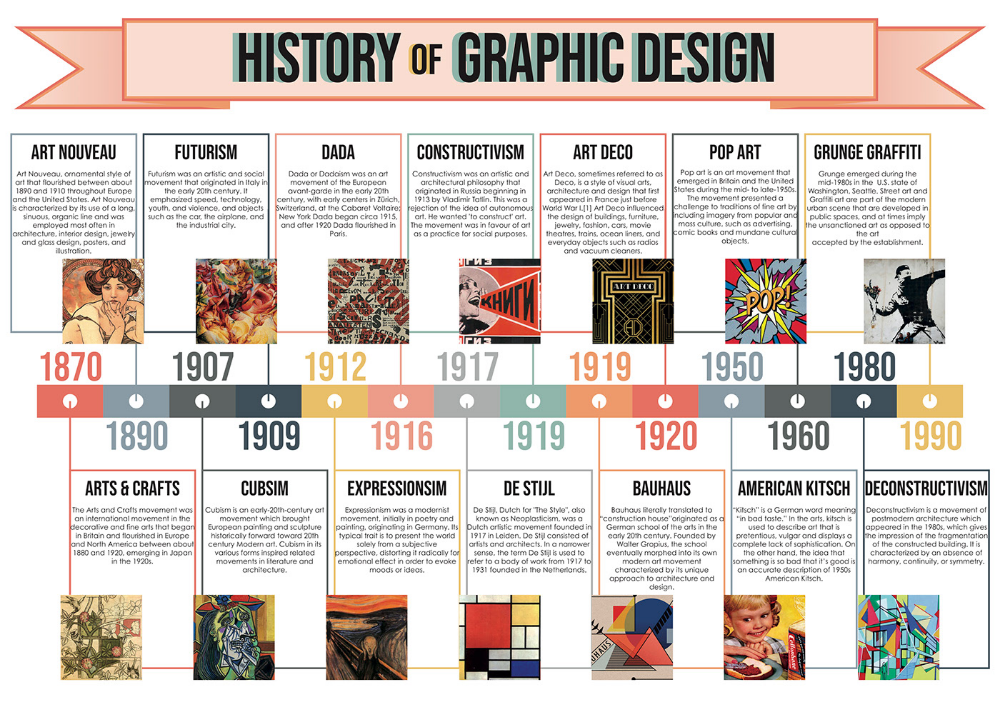 Moreover, the coming in of Parthians and Sassanids led to the development of new architectural design forms under the Persian architecture. Semi-circular and oval-shaped vaults characterize Persian architecture. The architectural features representing this style are geometrical and repetitive forms, richly decorated with glazed tiles, carved stucco, patterned brickwork, floral motifs and calligraphy. Agha Bozorg mosque in Kashan, Iran is an example of Persian Architecture.
Moreover, the coming in of Parthians and Sassanids led to the development of new architectural design forms under the Persian architecture. Semi-circular and oval-shaped vaults characterize Persian architecture. The architectural features representing this style are geometrical and repetitive forms, richly decorated with glazed tiles, carved stucco, patterned brickwork, floral motifs and calligraphy. Agha Bozorg mosque in Kashan, Iran is an example of Persian Architecture.
Mapungubwe Interpretation Centre, South Africa
The Ethiopian architecture saw a massive growth from the Aksumite style to other parts of the world. The most characteristic feature of such form of architecture was the use of wood and round structures. The influence of the Aksumite style is still found in the Late Aksumite and Zagwe period. The dominance of the African Architecture can be well found around the Great Zimbabwe. Mapungubwe Interpretation Centre in South Africa is an example of African Architecture.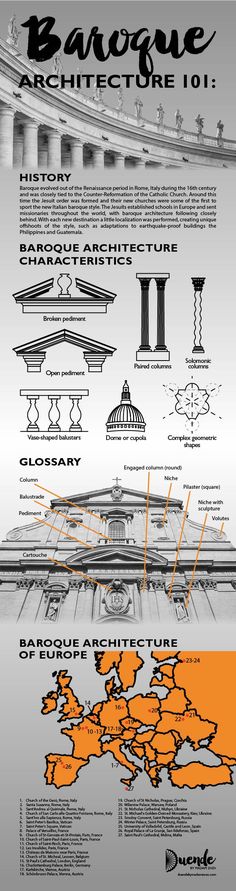
The Central Plaza of The Mayan City of Palenque
The Mesoamerican Architecture is a combination of Columbian architecture and Mesoamerica (Maya, Aztec, Olmec). The interrelation of the different regional and historical styles has contributed to the growth of Mesoamerican architecture. One of the distinctive examples of Mesoamerican architecture is pyramids. The development of the architecture resulted in the intensive cultural exchange. The central plaza of the Mayan city of Palenque (Chiapas, Mexico) is a fine example of Classic period Mesoamerican architecture.
17. Incan ArchitectureMayan temple of El Castillo
Incan developed certain distinctive features of their architecture. Incan Architecture is strongly characterized by the ability to merge their architecture with their surroundings. It is known for its fine masonry which features precisely cut shaped stones closely fitted without mortar. They were the ones to introduce the road system. The first rope suspension bridge of the world were Incan rope bridges. The Mayan temple of El Castillo is one of the most excellent examples of Incan architecture. Machu Picchu is also another excellent example of Incan Architecture.
It is known for its fine masonry which features precisely cut shaped stones closely fitted without mortar. They were the ones to introduce the road system. The first rope suspension bridge of the world were Incan rope bridges. The Mayan temple of El Castillo is one of the most excellent examples of Incan architecture. Machu Picchu is also another excellent example of Incan Architecture.
The Cliff Palace of Mesa Verde from Colorado, United States
The public architecture of the United States and Mississippians is brought about by the prominence of culture. The Mississippian culture is brought about by the mound-building people for the large earthen platforms. The Cliff Palace of Mesa Verde from Colorado, United States is one of the most excellent examples created by the Ancient Pueblo People.
19. Baroque ArchitectureTrevi Fountain, in Rome, Italy
The period between Mannerism and Baroque marked the increase in anxiety and representation in artwork. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Baroque is a European architectural style of 17th and 18th century derived from Mannerism and evolving into Rococo before Neo-Classicism eclipsed it.” The Baroque architecture noticed a significant influence of science and philosophy apart from the mathematical representation and cultural influence. There were new variations in this type of architecture for everyone. The decorative tastes of Rocco gave a boost to the development of Baroque architecture. Baroque architecture is highly decorative and theatrical style. In churches is highly characterized by broad naves (the central part of the church where services are held) with oval forms. It is deliberately left unfinished to give a unique feature to the design. The ceiling frescoes are on large scale. The use of ornaments, plaster or marble gives it a decorative look.
As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Baroque is a European architectural style of 17th and 18th century derived from Mannerism and evolving into Rococo before Neo-Classicism eclipsed it.” The Baroque architecture noticed a significant influence of science and philosophy apart from the mathematical representation and cultural influence. There were new variations in this type of architecture for everyone. The decorative tastes of Rocco gave a boost to the development of Baroque architecture. Baroque architecture is highly decorative and theatrical style. In churches is highly characterized by broad naves (the central part of the church where services are held) with oval forms. It is deliberately left unfinished to give a unique feature to the design. The ceiling frescoes are on large scale. The use of ornaments, plaster or marble gives it a decorative look.
Palais Garnier in Paris, France
The Beaux-Art architecture promotes the academic classic architectural style. Ecole des Beaux-Arts taught such architectural styles in Paris. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Beaux-Arts is a florid classical style evolved in France. It evolved in the second half of the 19th century, especially in Paris.” It was a coming together of two and a half centuries of instructions and authority — the style followed by the Beaux-Arts architecture without any developments till 1968. Palais Garnier is a corner piece of Beaux-Arts architecture.
Ecole des Beaux-Arts taught such architectural styles in Paris. As said by ‘James Stevens Curl and Susan Wilson’, (Authors of The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture), “Beaux-Arts is a florid classical style evolved in France. It evolved in the second half of the 19th century, especially in Paris.” It was a coming together of two and a half centuries of instructions and authority — the style followed by the Beaux-Arts architecture without any developments till 1968. Palais Garnier is a corner piece of Beaux-Arts architecture.
Einstein Tower in Postdam, Germany
The early Modern architecture began with the coming in of similar characteristics, simplified form, and more ornamentation by 1900. However, by 1940, this architectural style had already spread across the world, primarily identified as a prominent International Style. The key features of this style include building styles with similar characteristics, primarily the simplification of form and the elimination of ornaments. Einstein Tower is an example of early Modern architecture.
Einstein Tower is an example of early Modern architecture.
Villa Savoye, Paris
International Architecture was one of the key architectural trends during 1920-30. These were the buildings before World War II. The International Architecture was very much similar to that of modernism. The characteristic feature includes rectilinear form, open interior spaces and a weightless quality generated by the use of cantilever construction. Villa Savoye, Paris by Architect ‘Le Corbusier’ is an example of international architecture.
23. ModernismFrank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater, Pennsylvania
Modern Architecture focuses on simple forms and ornament creation through structures and themes of the building. The influence of modern architecture can be well observed in the 21st-century corporate buildings. Different movements have contributed to the standing out of modern architecture. Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater is one of the unique examples of the Modern Architecture. The modern architecture has become possible due to modern construction technology with sophisticated plant, machinery, tools, and equipment along with new age complex but strong materials.
Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater is one of the unique examples of the Modern Architecture. The modern architecture has become possible due to modern construction technology with sophisticated plant, machinery, tools, and equipment along with new age complex but strong materials.
Architecture
Modern Architecture | Glimpse of its Advantages and Features!!!
24. PostmodernSony Building of New York
Postmodern architecture is one of the architectural styles which continues to influence present-day architecture. It was the one that came in after the 1950s. The postmodern architecture observed the return of “wit, ornament and reference” trend. Some of the prominent examples of postmodern architecture are Portland Building of Portland, Sony Building of New York and the Las Vegas strip.
Summing up, the architectural styles have only seen a gradual rise over the years. Several old and new building designs act as reminisce of the specific eras. The eras gave birth to several architectures, which are relevant even today. The evolution of architecture has come across many varied cultures and landscapes. It marks the changes in architecture through various traditions, regions and stylistic trends.
The eras gave birth to several architectures, which are relevant even today. The evolution of architecture has come across many varied cultures and landscapes. It marks the changes in architecture through various traditions, regions and stylistic trends.
Features of Contemporary Architecture | All you Must Know!
History of Bay Window
Heritage Homes & Sites of India | All You Need to Know
Image Courtesy – Image 7, Image 16, Image 17, Image 18
The Characteristics of 12 Architectural Styles From Antiquity to the Present Day
The Characteristics of 12 Architectural Styles From Antiquity to the Present Day
© ArchDaily- Written by Julia Daudén | Translated by Fernanda Cavallaro
History has often been taught in a linear way. This way of teaching has often left out grand historical narratives, and focused primarily on the occidental world.
However, it is also known that to understand how one phenomenon leads to another, it can help to create a broad overview of what humanity has produced over the years. In the history of architecture, it is interesting to understand the central movements and consecrated styles that emerged over time as reactions, that is, continuities or ruptures, in relation to what had been produced so far. Therefore, we present some of the most influential architectural styles and movements in history, its features, and singularities.
ClassicThe Parthenon ruins, Acropolis of Athens, Greece. © Kristoffer Trolle via VisualHunt.com / CC BYClassical architecture was constructed in Ancient Greece between the 7th and 4th century BC. It is best known for its large religious temples built in stone, designed from principles of order, symmetry, geometry, and perspective. A notable characteristic of its expressiveness are the principles of the “architectural orders”: Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. The greatest work of Classical architecture is the Parthenon. Built in the Acropolis of Athens in the 5th century BC, the Parthenon exhibits striking characteristics: a volume built upon a foundation that supports the sequence of columns and its capitals, which, in turn, support a pediment.
The greatest work of Classical architecture is the Parthenon. Built in the Acropolis of Athens in the 5th century BC, the Parthenon exhibits striking characteristics: a volume built upon a foundation that supports the sequence of columns and its capitals, which, in turn, support a pediment.
Developed in Europe between the 6th and 9th centuries, this architectural style has a great relation to its historical context. In a period when European countries were at war and worried about protecting against invasions, the buildings, inspired by the Republic of Ancient Rome, were characterized by heavy and resistant walls and minimal openings in semicircular arches. Its main exemplars were the churches built during this period, and one of its most important works is the Santiago de Compostela Cathedral in Spain. It was built during the Crusades, and it is the greatest product of this style.
What we now know as Gothic architecture was originally named Opus Francigenum, or “French work,” as it originated in the Late Middle Ages in France, between the years 900 and 1300. It was only during the Enlightenment that the name “Gothic” came about to refer to the vertical and majestic architecture produced in that period. The main Gothic works are related to ecclesiastical buildings -- churches and cathedrals with ogival arches and rib vaults. Most Gothic buildings are considered UNESCO World Heritage sites, such as the Notre Dame Cathedral and Reims Cathedral.
BaroqueChurch of Gesù, Rome. © Alessio Damato, via Wikimedia. License CC BY-SA 3.0Beginning in the 16th century under a Monarchist regime in Europe, Baroque architecture can also be seen in religious buildings. Making use of ornaments and elements that sought to establish a dramatic sense -- especially by contrasting light and dark -- Baroque architecture viewed structural elements as platforms for decoration. One of the early exemplars of this style is the Church of Gesù in Rome, which boasts the first truly Baroque façade.
One of the early exemplars of this style is the Church of Gesù in Rome, which boasts the first truly Baroque façade.
From the 18th century onwards, Neoclassical architecture sought to revive Classical Greek and Roman buildings. Its expression is strongly related to its social and economic context, the Industrial Revolution in Europe, and a period in which upper-middle-class students began the Grand Tour tradition -- traveling around the world and coming into contact with ancient works. The revival of European cultural production brought an architecture oriented toward rational symmetry as a response to Baroque architecture. This movement continued until the 19th century and was manifested in various countries.
Beaux-ArtsGrand Central Terminal, New York. © Eric Baetscher, via Wikimedia. License CC BY-SA 3.0This academic style originated in the Fine Arts School in Paris in the mid-1830s. It established a language that referred to other periods, such as French Neoclassicism, Gothic architecture, and the Renaissance, however, it also employed contemporary materials such as glass and iron. Although it emerged in France, this style influenced American architecture and served as a reference to architects such as Louis Sullivan, “the father of the skyscraper." The buildings from this movement exhibit sculptural ornamentation blended with modern lines. In Europe, an important example is the Grand Palais in Paris, and, in the United States, the Grand Central Terminal in New York.
It established a language that referred to other periods, such as French Neoclassicism, Gothic architecture, and the Renaissance, however, it also employed contemporary materials such as glass and iron. Although it emerged in France, this style influenced American architecture and served as a reference to architects such as Louis Sullivan, “the father of the skyscraper." The buildings from this movement exhibit sculptural ornamentation blended with modern lines. In Europe, an important example is the Grand Palais in Paris, and, in the United States, the Grand Central Terminal in New York.
Art Nouveau originally served as a guide to several disciplines from architecture to painting, and furniture design to typography. As a reaction to the eclectic styles that dominated Europe, Art Nouveau manifested itself in architecture in decorative elements: the buildings, full of curved and sinuous lines, received ornaments inspired by organic shapes such as plants, flowers, and animals, both in terms of design and the use of color. Its first buildings were designed by Belgian architect Victor Horta, however, the most emblematic exemplars were authored by the Frenchman Hector Guimard.
Its first buildings were designed by Belgian architect Victor Horta, however, the most emblematic exemplars were authored by the Frenchman Hector Guimard.
Art Deco emerged in France right before World World I, and, just like Art Nouveau, influenced several areas of art and design. Blending modern design, handcrafted elements, and luxurious materials, the movement represented a moment of great belief in social and technological progress in the continent. Auguste Perret, a French architect and pioneer in the use of reinforced concrete, was responsible for designing one of the first Art Deco structures. Perret's Champs-Elysées Theater (1913) combined the movement’s characteristics and marked a departure from the previously proposed language of Art Nouveau.
BauhausBauhaus Dessau. © Thomas LewandovskiBauhaus was born at the first design school in the world at the beginning of the 20th century. It was embedded in a discourse that spanned from furniture design to plastic arts and the avant-garde posture in Germany. The relationship between industrial production and product design was critical to the school’s architectural proposals, adopting a highly rationalized stance on the design process. One of its founders, Walter Gropius, implemented revolutionary teaching methods and applied these principles in his modern and functional works.
It was embedded in a discourse that spanned from furniture design to plastic arts and the avant-garde posture in Germany. The relationship between industrial production and product design was critical to the school’s architectural proposals, adopting a highly rationalized stance on the design process. One of its founders, Walter Gropius, implemented revolutionary teaching methods and applied these principles in his modern and functional works.
Modernism was born in the first half of the 20th century. It can be said it began in Germany with Bauhaus, or France with Le Corbusier, or the U.S. with Frank Lloyd Wright. However, Le Corbusier’s contribution to the understanding of Modern architecture is most notable, particularly for his ability to synthesize the precepts he adopted in his works, design, and discourse. An example is his 1926 manifesto “The Five Points of New Architecture,” also known as the Five Points of Modern Architecture.
From 1929 onwards, with the onset of the Great Depression, a chain of criticism of Modern architecture begins and continues until the late 1970s. Postmodern architecture examines some of Modernism’s central principles from a new historical and compositional perspective, both in discourse and built works. For this, different strategies for questioning were adopted, sometimes by the use of irony, others by an intense interest in popular culture. The book “Learning from Las Vegas” is one of the seminal works of Postmodern thought.
DeconstructivismParc de la Villette, designed by Bernard Tschumi. © victortsu on Visual Hunt / CC BY-NCDeconstructivism originated in the 1980s and questions the precepts and process of design and incorporates nonlinear dynamics to the field’s reasoning. Deconstructivism relates to two main concepts: deconstruction, a literary and philosophical analysis that rethinks and dismantles traditional modes of thinking; and constructivism, the artistic and architectonical Russian movement from the early 20th century. A landmark event for Deconstructivism was the 1988 MoMA exhibition curated by Phillip Johnson. It brought together the works of Peter Eisenman, Frank Gehry, Zaha Hadid, Rem Koolhaas, Daniel Libeskind, Bernard Tschumi and Wolf Prix.
Cite: Daudén, Julia . "The Characteristics of 12 Architectural Styles From Antiquity to the Present Day" [Características e diferenças de 12 estilos arquitetônicos] 13 Aug 2018. ArchDaily. (Trans. Cavallaro, Fernanda) Accessed . <https://www.archdaily.com/900027/the-characteristics-of-12-architectural-styles-from-antiquity-to-the-present-day> ISSN 0719-8884
7 architectural styles that predetermined the development of Western culture
Throughout the history of mankind, architecture has been a functional creative tool that best characterizes the cultural depth of society's achievements. As a rule, architectural styles, closely intertwined, gave impetus to the development of the next direction in culture and the emergence of new styles and fashion trends, and not necessarily architectural structures. nine0006
Architecture best characterizes the cultural depth of a society's achievements.
Architectural styles are a kind of time machine that can tell about turning points in the history of mankind. The authors of Novate.Ru have selected 11 main architectural trends, the first of which have been considered the standard of fine art for thousands of years, leaving an unforgettable mark and becoming the basis for the emergence of new styles and trends that never cease to amaze. nine0006
1. Architecture of Ancient Egypt (3050 BC - 900 BC)
Giza Pyramid Complex (Egypt). | Photo: lifeglobe.net.
Egypt, being one of the most powerful civilizations in the history of mankind, left a considerable cultural heritage, which is rightfully considered a cult, becoming an ideal basis for the further development of all types of fine arts without exception.
The temples of Abu Simbel, dedicated to Pharaoh Ramses II and Queen Nefertari, were carved from stone around 1260 BC. (Egypt). | Photo: lifeglobe.net. nine0006
And although many people think that the majestic pyramids were the top of the achievements in the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, they are very mistaken. No less impressive are the temple complexes, which perfectly combine engineering skills with rich symbolism, unique aesthetics and functionality.
Majestic temples of Ancient Egypt. | Photo: tripegypt.su.
It is from here that the origins of the classical canons of architecture come, expressed in the main directions: monumentality, geometricity, conciseness of forms, decor, symmetry and synthesis of arts. All these features were picked up by the ancient Greeks and Romans, who contributed to the further development of fine arts. nine0006
2.
Parthenon Temple in Athens. | Photo: sc.adm-edu.spb.ru.
The temple of Poseidon in Attica and the theater of Epidaurus, created by the ancient Greeks. | Photo: holidaygreece.ru.
As a rule, the achievements of the ancient Greek and Roman cultural heritage are not separated, because they created the basis for classical architecture, strengthening the idea of building structures according to a given pattern. The Greek order of column placement (Doric, Ionic and Corinthian) is still used in construction, because the rules of proportion that they preached lead to complete harmony. A striking example of greatness and originality was the Acropolis in Athens, the Colosseum and the Pantheon in Rome. nine0006
The triumphal arch of Constantine and the Roman Pantheon are among the most significant achievements of the architecture of Ancient Rome. | Photo: architan.ru.
Colosseum and ancient Roman aqueduct. | Photo: dom-sweet-dom.ru.
This time was famous for its masters of engineering and great scientists: the Romans built incredible systems of highways and aqueducts to deliver a variety of goods from their vast possessions. The Greeks, on the other hand, reached unprecedented heights in the creation of various mechanisms that facilitated not only construction, but also played an important role in the everyday life of people. It is difficult to overestimate the contribution of the ancient Greeks to the development of sciences, it was here that mathematics, biology, astronomy, medicine, geography, etc. were born.
3. Mesoamerican architecture (2000 BC - 1519 AD)
The Temple of Kukulkan (El Castillo Pyramid) is a multi-stage pyramid in the Mayan city of Chichen Itza. | Photo: mymodernmet.com.
Mesoamerican or pre-Columbian architecture is directly related to the structures that were created by the indigenous people of Central America - from central Mexico to northern Costa Rica. The period is identified with Maya architecture and the great step pyramids created by this civilization. During this period, urban planning was guided by religious and mythological beliefs, as the local peoples believed that architecture was a tangible form of their faith. nine0006
Mesoamerican architecture and culture is completely dominated by religious and mythological beliefs. | Photo: en.wikipedia.org.
Mesoamerican buildings are known for their rough stonework and primitive tools, so huge labor resources were used to create the objects. The El Castillo Pyramid in the legendary Mayan city of Chichen Itza is an example of what is called pre-Columbian architecture. Later volumetric architecture would influence Frank Lloyd Wright, who at 19The 20s and 1930s worked in the Mayan Revival style.
4. Byzantine architecture (527–1453 AD)
Starting from the 6th century, a unique style of temple construction began to take shape in Byzantium. | Photo: novaiagazeta.org.ru.
The stage of formation of Byzantine architecture begins after the capital of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople (now Istanbul). Having become the successor of a great culture, Byzantium improved construction work and introduced new methods in decorating buildings. During the heyday of civilization, mosaic decoration came into fashion, which later became a hallmark of the style. nine0006
The minarets around the Hagia Sophia were not created by Byzantine masters, but appeared much later. | Photo: travelermap.ru.
The most iconic example of Byzantine architecture is the Hagia Sophia, which demonstrates the engineering prowess of the Byzantine architects who created the first domes. The artistic system of images created by the Byzantines is a harmonious fusion of deep religiosity and the desire for magnificent entertainment, while the refined decorativeness of the elements is especially surprising. nine0006
Note: The minarets were an Ottoman addition and are therefore not considered part of the original design.
5. Gothic architecture (1150-1530)
The first cathedrals built in Western Europe in the Gothic style. (St. Stephen's Cathedral in Vienna and Reims Cathedral in France). | Photo: most-beauty.ru.
Gothic originated in the 12th century. in France and replaced the Romanesque style. Most people associate the term "Gothic style" with architectural structures, but this concept includes painting, sculpture, book miniature, fashion design, ornaments, etc. nine0006
The combination of pointed arch and ribbed vault created exceptional verticality in Gothic architecture. | Photo: mymodernmet.com.
Note: The word "Gothic" comes from the Italian "gotico" - unusual, barbaric. Initially, it was used as a swear word.
The vaulted ceilings of Gothic cathedrals have always amazed with their grandeur and beauty. | Photo: ukrsmeta.ua.
Given that the architectural style of any era grows out of beliefs and lifestyles, it is not at all surprising that during this period religious buildings became leading objects and even trendsetters, because religion, more than ever, had a huge impact on political and social life, the economy, science, education and art. The main buildings in the Gothic style were majestic cathedrals, which were a kind of synthesis of architecture, sculpture, painting and stained glass art. nine0006
Magnificent stained-glass windows adorn Gothic cathedrals. | Photo: most-beauty.ru.
Such a refined and majestic architecture of Gothic cathedrals arose thanks to the main invention of that era - the frame structure, which made it possible to build a rib vault with an openwork structure. The creation of spectacular textures and the decoration of structural elements have evolved along with the solution of construction and technological problems, reaching a perfection that makes Gothic structures easily recognizable among similar structures. nine0006
6. Art Nouveau architecture (1890–1914)
Art Nouveau in architecture was characterized by vivid expressiveness and decorativeness (the Singer House in St. Petersburg, the Stauder House in Austria). | Photo: architan.ru.
Extending to architecture and applied arts, Art Nouveau became an international movement, born on the wave of artistic protest against the established canons of architecture, actively imitating the style of eclecticism.
Modern style in interior design. | Photo: ispaniainfo.ru.
Curved natural lines (the style does not accept straight lines and angles) were fully used not only in the aesthetics of the forms of the building itself, but also in the creation of interiors and furniture design. This was facilitated by innovative developments in the field of technology, which experienced an unprecedented rise during this period. Such a breakthrough in the industry helped to organize the production of not only artsy iron elements, which became the main feature for the Art Nouveau style. nine0006
The great creations of the Spanish architect Gaudi are created in the Art Nouveau style. | Photo: worlds-interior.ru.
With the invention of such a material as reinforced concrete, it became possible to create curvilinear facades and complex configurations of cornices, as well as unusual window and door openings.
7. Neo-futuristic architecture (since 2007)
Neo-futuristic creations by Zaha Hadid. | Photo: 7sisters.ru.
Already in the third millennium, on the basis of the best architectural traditions, a new style was born, about which the designer Vito Di Bari, who is one of its founders, said: "Cross-fertilization of art, advanced technology and ethical values combined to create a higher quality of life everywhere" .
Neo-futurism is defined as "author's architecture". | Photo: en.wikipedia.org.
Since the end of the 20th century, neo-futurist architects have not only dreamed of fully integrating new technologies into the building industry, they have completely rethought aesthetics and functionality. During this period, they begin to use high-tech systems and structures, giving preference to environmentally friendly materials. They sincerely believe that this trend will improve the quality of life of residents of megacities and improve their aesthetic appearance. nine0006
The construction of unusual structures has always aroused great interest among contemporaries and, despite the fact that the first skyscrapers appeared at the end of the 19th century , their amazing shapes and sky-high height never cease to amaze.
History and styles of architecture. Presentation.
"CONVERSATIONS ABOUT ART" cycle
Center for aesthetic education of children "Nuts" Theater department subject “Conversations about art” Topic No. 4 “The emergence of architecture. Relationship of architectural styles» Author: artistic director of the children’s theater
From the history of architecture
It is assumed that the beginnings of architecture as an art arose during the period of primitive society. It was during the Neolithic era that man began to build the first dwellings using natural materials.
In the Neolithic era, megalithic and piled buildings appear. Megalith - the Greek word, consists of two parts: mega - large, and lithos - stone.
Dolmen
Dolmens - ancient megalithic (that is, made of large stones or stone slabs) man-made structures of a certain shape 90.961
Grandiose, simple in form, stone structures were erected by the labor of the entire primitive community, they were an expression of the unity of the clan, its power. (cromlechs).
Cromlech - an ancient structure representing several processed or unprocessed elongated stones placed vertically in the ground ( menhirs ). dolmen
Cairn, houri, tour - an artificial structure in the form of a pile of stones, often conical
Menhir - the simplest megalith in the form of a roughly processed or wild stone installed by a person, in which the vertical dimensions noticeably exceed the horizontal ones.
Menhir - a megalithic monument, not associated with a funeral ritual, which is a single stone, vertically fixed in the ground; its specific purpose has not yet been clarified, although it is often associated with religious practices, for example, with the cult of the Sun. Sometimes menhirs form parallel rows or circles, the so-called cromlechs. nine0097
As a field of art, architecture takes shape in the cultures of Mesopotamia…
and Egypt
The naive Egyptians believed that if the body of the deceased is mummified, endowed posthumously with everything acquired and placed in a "pyramid",
then the spirit of the body Ka, returning from the land of the dead, will recognize himself" and enter his body.
Therefore, the monuments that have come down to us are temples, palaces and tombs, i.e. monumental structures designed to personify eternity. Although the style has endured for 4,000 years, the decorating tradition has hardly changed.
Walls, pylons, columns, as a rule, were covered with hieroglyphic inscriptions and scenes of funeral rituals,
where the figures of people were depicted in a characteristic "Egyptian" pose - the head and lower part of the body - in profile, and the body and arms - in front. nine0097
There are 3 types of columns in buildings:
lotus (lotus flower or bud capital),
papyrus-shaped (papyrus-shaped capital)
gatoric (capital with the image of the head of the goddess Gator - a woman with a dog's head).
Capital
As an author's art, it develops by the 5th century. BC. in ancient Greece.
Antiquity
- Antiquity refers to the architecture of ancient Greece and Rome.
The ancient Greek architecture that arose on the islands of the Aegean Sea was so harmonious and holistic that it was subsequently perceived by later styles (Renaissance, Classicism, Neoclassicism) as a primary source, as a kind of standard to follow.
The Greeks were talented, cheerful and cheerful people. They, of course, had gods, but they were so "humanized" that they had all the vices inherent in man - stupidity, greed, gluttony, and so on. nine0097
Based on mythology, naively personifying the forces of nature, Greek art was essentially quite realistic.
It is impossible not to mention the emergence of geometry as a science, which made it possible to realize proportions as a measure of harmony .
The ancient Romans, being good students of the Greeks, not only fully accepted their heritage, but also developed it, supplementing the system with their architectural elements. nine0097
The real achievement of the Romans is that they "invented" the triumphal arch.
The Romans also experimented with such a stunningly beautiful shape, as a dome.
Byzantium
The Byzantines created an artistic system in which strict norms and canons dominate, and the beauty of the material world is regarded only as a reflection of unearthly, divine beauty. These features were clearly manifested both in architecture and in the visual arts. nine0097
- Now the temple began to serve not as a place to store a statue of a deity, as it was in ancient times, but as a meeting place for believers to participate in the sacrament of communion with a deity and listen to the “word of God”.
Therefore, the main attention was paid to the organization of the internal space.
Outside buildings, palace and cult, always received a very simple treatment: the facades, as a rule, were not plastered, but were decorated with brick, alternating with layers of pink cement mortar, and sometimes (in later periods) with darkish limestone. nine0097
The patterned brickwork used gave the buildings a special texture. Brick, sometimes in combination with stone, was the main building material that determined the appearance of many Byzantine structures.
A characteristic architectural element was narrowed arched windows, which were often brought together in groups of two or three windows, often separated by columns and united by an outer arch above them.
A popular theme of Byzantine architecture is arcades on tall columns with basket-shaped capitals. Such arcades often covered the facade along its entire length.
arcade - (from the French Arcade) a series of arches of the same shape and size, based on columns or pillars. Most often used in the construction of open galleries.
architecture
Until the middle of the 12th century, being in synthesis with painting, sculpture, decorative art and occupying a dominant position among them, architecture determined the style of . nine0167
Painting and sculpture
Decorative arts
Subjugates science, worldview, philosophy, everyday life and much more
Occupies a dominant position
romanesque
romanesque
Great styles - romanesque, gothic, renaissance, baroque, classicism, empire / variant of late classicism / - equally valid. nine0097
In fact, the great styles cover either a larger or a smaller area of culture,
At the same time, none of the great styles completely determined the cultural face of an era and a country.
Gothic
Gothic
Renaissance
Renaissance
Baroge
Baroque
Classicism
9000Romanesque style
is replaced by more than 100 years
Gothic style
Romanesque and Gothic styles are closely interconnected in their development 9000 9000 9000
Within gothic then maturing renaissance .
Gothic
Gothic
Renaissance
Renaissance
Baroque
Baroque
passes in some arts (architecture, painting, applied arts, literature) into
Rococo
Rococo
Then the Baroque is replaced by
9000 Classicism 9000
Classicism
Secondary style is born as a result
Fixing material.