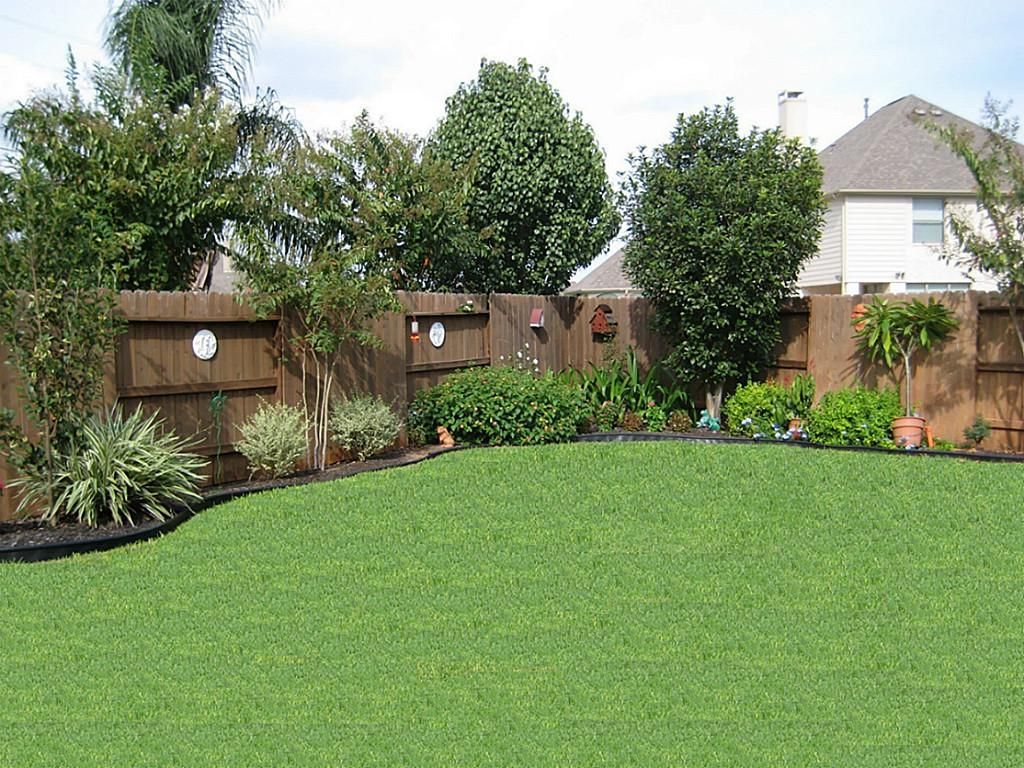
What does birch trees look like
11 Common Species of Birch Trees
Identified by their unique bark, birch trees look lovely in the landscape.
By
Vanessa Richins Myers
Vanessa Richins Myers
Vanessa Richins Myers is a seasoned horticulturist, writer, and educator with over 10 years of training and experience as a professional horticulturist and gardener. She has a Bachelor of Science degree in horticulture, with an emphasis in landscape design and urban horticulture. She volunteers as a community garden specialist.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
Updated on 07/29/22
Reviewed by
Andrew Hughes
Reviewed by Andrew Hughes
Andrew Hughes is a certified arborist and member of the International Society of Arborists specializing in tree heal care. He founded and runs Urban Loggers, LLC, a company offering residential tree services in the Midwest and Connecticut.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
The Spruce / Letícia Almeida
Birch trees belong to the genus Betula and are classified as part of the Betulaceae family of plants. They are typically small to medium-sized trees and shrubs found in temperate zones across the Northern Hemisphere. Some varieties grow in shrubby clusters. Others are trees that clump with multiple trunks, and still more grow as classic single-trunk trees. Ask anyone what's special about a birch tree and its beautiful bark immediately comes to mind. Birches are a common choice in landscaping, but they are relatively short-lived trees when compared to other hardwoods, and many become damaged by insects and diseases.
Tip
Most birches are characterized by varicolored or white bark with papery plates, distinctive horizontal markings, and peeling layers; the appearance of the bark often is the feature that gives the species its common name.
Click Play to Learn About Common Species of Birch Trees
Most birch trees grow best in moist soil and they love full sun. However, the roots might head for your plumbing pipes if a large tree is planted too close to your house. Do not let this deter you though; these are magnificent trees that are not hard to grow and should be a choice for your landscape. Birches are fast-growing trees that can quickly provide benefits to your yard.
However, the roots might head for your plumbing pipes if a large tree is planted too close to your house. Do not let this deter you though; these are magnificent trees that are not hard to grow and should be a choice for your landscape. Birches are fast-growing trees that can quickly provide benefits to your yard.
Insect pests are most likely to strike a birch tree in areas where it is wounded or diseased. By keeping your trees well pruned and free of damaged branches, you can greatly reduce the likelihood of infestation by bronze birch borer or other insects.
Here are 11 common types of birch trees to consider for your landscape and areas where they are typically grown in the United States and around the world.
-
01 of 11
Bog Birch (Betula pumila)
Western Arctic National Parklands/Flickr/CC 2. 0
0 Bog birch is a medium-sized, short-lived, clump-forming shrub that thrives in wet sites. The plant tolerates occasional flooding, alkaline soil, clay soil, and road salt. When planted in residential landscapes, it grows well around bodies of water or in boggy areas. Bog birch is a good choice for rain gardens.
Other common names include swamp birch, glandular birch, dwarf birch, and resin birch.
- Native Area: North America
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 2 to 9
- Height: 5 to 10 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun
-
02 of 11
F. D. Richards / Flickr/ CC By 2.0River birch is an increasingly popular, fast-growing tree for the home landscape. It may grow either as a single-trunk tree or a multi-trunk clumping tree. It has distinctive salmon-pink to reddish-brown bark that exfoliates to reveal lighter inner bark providing year-round interest in the landscape. Dark green foliage turns a beautiful buttery yellow in the fall.
 River birch has good resistance to the bronze birch borer. It is one of the only truly heat-tolerant birches.
River birch has good resistance to the bronze birch borer. It is one of the only truly heat-tolerant birches. River birch may also be known as red birch, black birch, or water birch.
- Native Area: Eastern U.S.
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 4 to 9
- Height: 40 to 70 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to part shade
-
03 of 11
Cherry Birch (Betula lenta)
Stephen Robson / Getty Images
Cherry birch is a large tree that grows from a single main trunk. Shiny, red-brown bark and yellow foliage make this an attractive tree for lawns and naturalized areas. The bark on mature trees develops vertical cracks that form irregular scaly plates, closely resembling the bark of cherry trees. Flowering in April and May, the tree produces fruiting catkins from August through October and serves as a food source for deer, moose, rabbits, and various birds. This tree also attracts beautiful butterflies to the landscape and is resistant to the bronze birch borer which can devastate other species of birch.
 Its broken twigs emit a spicy wintergreen fragrance and fermented sap is an ingredient used in birch beer.
Its broken twigs emit a spicy wintergreen fragrance and fermented sap is an ingredient used in birch beer. Regionally, the cherry birch may be called by other common names, including black birch, sweet birch, mahogany birch, Virginia roundleaf birch, or spice birch.
- Native Area: Eastern U.S., from Maine to northern Georgia
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 3 to 8
- Height: 40 to 70 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to part shade
-
04 of 11
MAKY_OREL / Pixabay / CC By 0Betula nana is a small dwarf shrub, native to arctic and cool temperate regions, especially tundra landscapes. It will grow in a variety of conditions, though it favors wet but well-drained sites with a rocky, nutrient-poor, acidic soil. It does not tolerate shade well. The dwarf birch is rarely planted in landscapes, but it is important to cover vegetation in cold northern territories.
Other names for this tree include bog birch and arctic birch.

- Native Areas: Greenland, Iceland, northern Europe, northern Asia, and northern North America
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 1 to 8
- Height: 6 inches to 3 feet tall
- Sun Exposure: Full sun
-
05 of 11
Eerik / Getty Images
The silver birch has an attractive pendulous habit and distinctive white bark that peels away in papery strips. It grows as a single-trunk tree that gradually transforms from pyramidal in shape to a more rounded, oval crown. Also known as weeping birch or European white birch, the silver birch was once used extensively in landscapes, but its high susceptibility to the bronze birch borer has limited its use in more recent years.
- Native Area: Europe, Asia
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 2 to 7; can be grown in 8 and 9 but will have a shorter life
- Height: 40 to 80 feet, depending on cultivar
- Sun Exposure: Full sun
-
06 of 11
John Lord / Flickr / CC By 2. 0
0 The ornamental interest of Himalayan birch includes pretty spring flowers, rich yellow fall color, and bright white papery bark. It is a medium-sized tree with a single trunk that quickly branches out into a pyramid shape. This birch species is very vulnerable to damage by the bronze birch borer and usually requires removal and/or replacement, especially in warmer zones. It is a heartier and longer-lived tree in cooler climates.
This tree has other common names, including white-barked Himalayan birch and jacquemonti birch.
- Native Area: West Himalayas, Nepal
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 4 to 7
- Height: 30 to 50 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun; can take some light shade
-
07 of 11
Japanese White Birch (Betula platyphylla 'Japanica')
View Photos/a.collectionRF / Getty ImagesThis species, also known as Asian white birch, is a medium to large tree with white bark and thin spreading branches that terminate in drooping branchlets.
 This tree grows best in medium to wet, well-drained, sandy, or rocky loam. Although it prefers full sun, the Japanese white birch thrives in northern and eastern exposures that receive some afternoon shade. The main requirement is a consistently moist soil. Like several other members of the birch family, this birch performs best in cooler climates; with warmer zones causing increased susceptibility to birch borer insects.
This tree grows best in medium to wet, well-drained, sandy, or rocky loam. Although it prefers full sun, the Japanese white birch thrives in northern and eastern exposures that receive some afternoon shade. The main requirement is a consistently moist soil. Like several other members of the birch family, this birch performs best in cooler climates; with warmer zones causing increased susceptibility to birch borer insects. - Native Area: Manchuria, Korea, Japan
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 3 to 8
- Height: 40 to 50 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to part shade
-
08 of 11
Plant Image Library / Flickr / CC By 2.0Primarily native to Alaska, Canada, and northern U.S. states, this tree has lovely white bark and yellow fall color. It can grow either as a single-trunk tree or in small clumps with multiple trunks. Paper bark birch is so-named due to the thin white bark which often peels in paper-like layers from the trunk.
 It also is known as the canoe birch or white birch. This is the classic birch tree historically used to make many useful products from footwear to birch-bark canoes. Buds, catkins, and leaves along with twigs and bark are a source of food for birds and other wildlife. The paper bark birch demonstrates some resistance to the bronze birch borer.
It also is known as the canoe birch or white birch. This is the classic birch tree historically used to make many useful products from footwear to birch-bark canoes. Buds, catkins, and leaves along with twigs and bark are a source of food for birds and other wildlife. The paper bark birch demonstrates some resistance to the bronze birch borer. - Native Area: Northern North America
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 2 to 7
- Height: 45 to 100 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to light shade
-
09 of 11
Weeping Birches (Betula pendula var.)
Ron Evans / Getty Images
Trees known as weeping birches generally are different naturally-occurring or cultivated varieties of silver birch (Betula pendula), described above. Exact details such as growing zones and height will depend on the particular variety.
Common varieties include:
- Curly birch (B.
 pendula 'Carelica')
pendula 'Carelica') - Cutleaf weeping European birch (B. pendula 'Gracilis')
- Golden cloud weeping birch (B. pendula 'Golden Cloud')
- Purple weeping birch (B. pendula 'Purpurea')
- Swedish birch (B. pendula 'Dalecarlica' or 'Laciniata')
- Tristis weeping birch (B. pendula 'Tristis')
- Young's weeping birch (B. pendula 'Youngii') (pictured)
- Curly birch (B.
-
10 of 11
Water Birch (Betula occidentalis or Betula fontinalis)
Thayne Tuason / Wikimedia Commons / CC By 4.0
Water birch typically occurs along streams in mountainous regions, where it grows in dense thickets. The bark is dark red-brown to blackish, and smooth. Unlike other birch trees, its bark does not peel. This tree is a source of food and lodge material for the common North American beaver.
Other common names for this tree include western birch, red birch, river birch, black birch, and western red birch.
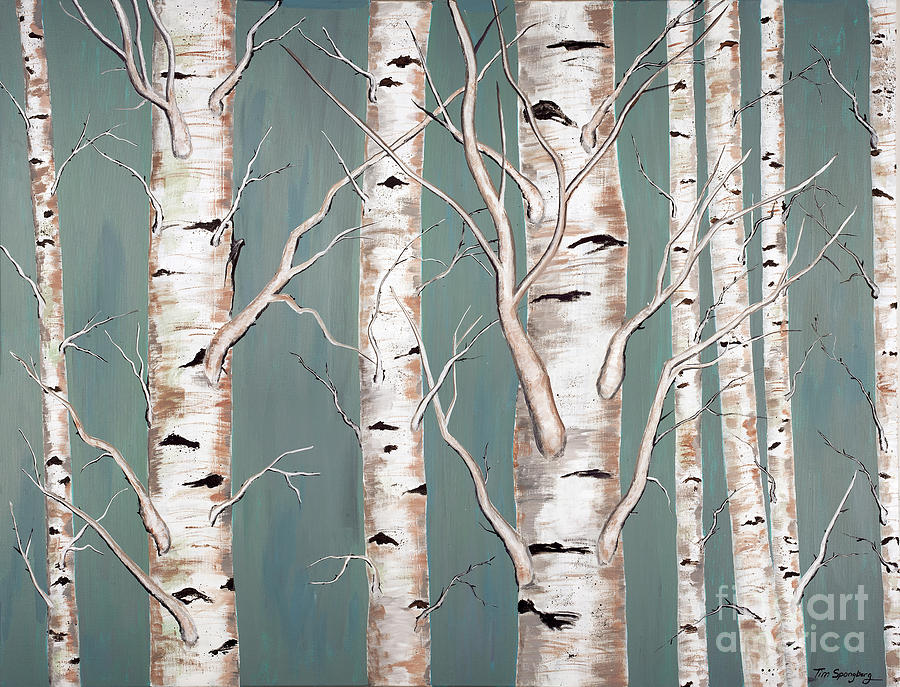

- Native Area: Western North America, mountainous regions
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 3 to 7
- Height: Shrubby form can grow 25 feet tall; as a tree, to 40 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to part shade
-
11 of 11
Cora Niele / Getty ImagesYellow birch, named for the color of its bark, is a relatively long-lived birch that typically grows for 150 years and may even age to 300 years in old-growth forests. It is a single-stemmed tree with yellow-bronze bark that peels in narrow horizontal strips. This is an important species to the North American lumber industry and a major woodland food source for birds and wildlife.
Yellow birch may be known regionally as swamp birch, curly birch, gold birch, or hard birch.
- Native Area: Northeastern North America
- USDA Hardiness Zones: 3 to 7
- Height: 50 to 80 feet
- Sun Exposure: Full sun to part shade
The various species of birch trees in the Betula genus include at least these 11 that are important landscape trees. Birch trees offer interesting bark color and texture and attractive foliage, but they are relatively short-lived and they are prone to suffer from diseases and insects, especially the bronze birch borer. But birches still make excellent, fast-growing landscape specimens, provided you have realistic expectations.
Birch trees offer interesting bark color and texture and attractive foliage, but they are relatively short-lived and they are prone to suffer from diseases and insects, especially the bronze birch borer. But birches still make excellent, fast-growing landscape specimens, provided you have realistic expectations.
6 Birch Trees with Gorgeous Fall Foliage
Article Sources
The Spruce uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
Bog Birch. The Morton Arboretum.
The Bronze Birch Borer and Its Management. University of Minnesota Extension Service.
Birch Trees: Types, Leaves, Bark
Birch trees (genus Betula) are flowering medium-sized deciduous trees with thin papery bark and egg-shaped pointed leaves. Birch trees have spectacular fall colors that can be golden yellow, vibrant orange, or fiery red. Common birch trees get their names from the bark’s distinctive colors, which can be white, silver, black, gray, or yellow.
Common birch trees get their names from the bark’s distinctive colors, which can be white, silver, black, gray, or yellow.
Common species of birch include the white birch, silver birch, and paper birch. Typically, you can identify birch trees by their bark, leaves, and flowers. For example, some birches have thin peeling bark that exfoliates in long strips, whereas some species don’t peel. Also, birch leaves can be egg-shaped, triangular, or diamond-shaped.
This article is a guide to identifying common birch trees. Pictures and descriptions of birches will help you choose the best type of ornamental tree for your garden landscape.
Birch Tree FactsBirch forest
Birch trees belong to the genus Betula in the beech-oak family Fagales. Birch trees typically grow between 40 and 70 ft. (12 – 21 m) tall with canopies 35 to 60 ft. (10 – 18 m) wide. Dwarf birch trees are small trees that don’t grow taller than 30 ft. (9 m), and some only grow 3 ft. (1 m) tall.
(1 m) tall.
There are between 30 and 60 birch (Betula) species, with 18 being native to North America. Birch is a short-lived tree that thrives in cold, northern climates where it grows in moist ground. Birch trees grow best in USDA zones 2 through 7.
Some species of birch have slender, single trunks with irregular-shaped canopies. The birch foliage tends to grow higher up the tree, revealing white-gray, red, or black bark. You’ll also find clumping birch trees with multiple trunks growing together from the ground.
White birch trees are also ornamental trees suitable for residential landscapes.
Birch wood is also prized for its density and strength. Wood from birch trees is used to make skateboards, plywood, and loudspeaker cabinets. Additionally, birch is excellent firewood because it burns well even if damp.
Birch Tree LeavesBirch tree leaves have pointed tips and serrated edges. On the right picture: autumn foliage
Birch tree leaves are triangular or egg-shaped with a rounded base, pointed tips, and serrated margins. Glossy green birch leaves grow between 2” and 3” (5 – 7.5 cm) long. The simple leaves are arranged alternately on branches. In fall, birch leaves turn spectacular shades of yellow, red, and orange.
Glossy green birch leaves grow between 2” and 3” (5 – 7.5 cm) long. The simple leaves are arranged alternately on branches. In fall, birch leaves turn spectacular shades of yellow, red, and orange.
There are some subtle differences in leaf shape between species of birch. For example, white birch trees have more pronounced teeth on the leaf margins. River birch leaves tend to have a diamond shape, whereas gray birch leaves are more triangular-shaped.
Birch BarkBirch tree bark
Birch tree bark is usually whitish-gray, silver, or sometimes red. The bark on most birch trees has horizontal dark streaks that look like scoring (called lenticels). Birch tree bark is also well-known for its paper-like texture and peeling nature. The peeling bark on birch trees gives them ornamental value in wintertime.
Birch trees with white bark are generally the most popular types of birch trees for gardens.
Birch FlowerBirch flower are called catkins
Birch tree flowers are small, insignificant clusters of flowering spikes called catkins. Birch trees bloom in spring at the same time leaves appear. Flowers on male birch trees are 1.2” (3 cm) long, and the flowers on female trees are 0.4” to 0.8” (1 – 2 cm) long.
Birch trees bloom in spring at the same time leaves appear. Flowers on male birch trees are 1.2” (3 cm) long, and the flowers on female trees are 0.4” to 0.8” (1 – 2 cm) long.
The bark and leaf shape are the best ways to identify species of birch trees. You can recognize birch trees by their peeling bark that can be white, gray, or yellow. You will also notice horizontal diamond-shaped raised marks on the light-colored bark. Look at the leaves—birch leaves are typically triangular with jagged-looking edges.
Birch Trees vs. Aspen Trees — How to Tell Them ApartAspen tree trunks (left) are very similar to birch trunks (right)
It’s easy to mistake birch trees for aspen trees. From a distance, birch trees and aspens look similar with their slender white or gray trunks. However, looking up close, you’ll see that birches have peeling bark, whereas aspen trees have rough, fissured bark.
Another way to tell birch trees apart from aspen trees is by their leaves.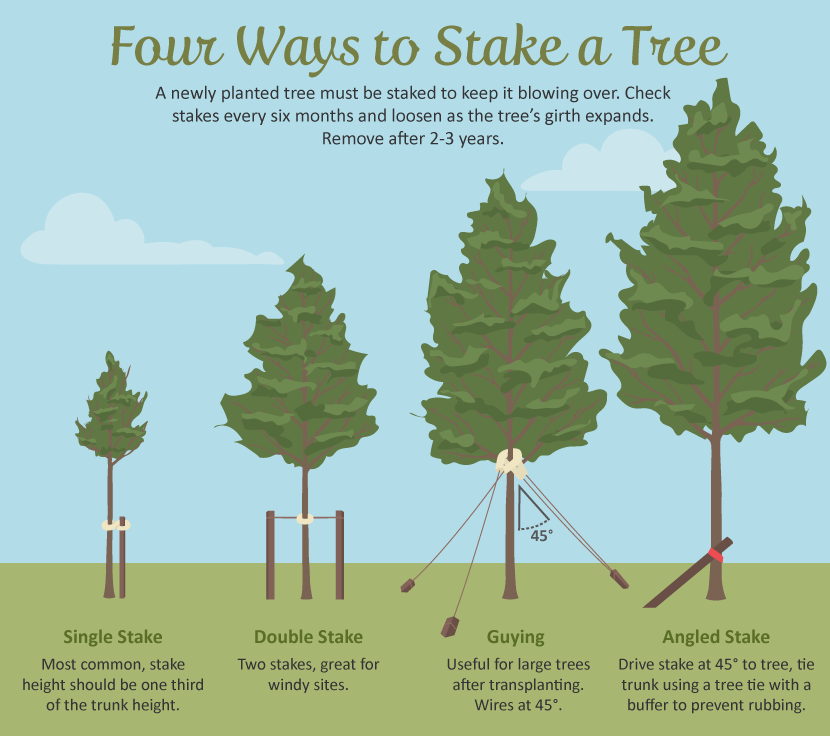 Birch leaves tend to be triangular or spear-shaped with noticeable serrated margins. Aspen tree leaves are more heart-shaped with finely toothed edges. Also, birch leaves have a “V” shape and are elongated rather than like the flat leaves of aspens.
Birch leaves tend to be triangular or spear-shaped with noticeable serrated margins. Aspen tree leaves are more heart-shaped with finely toothed edges. Also, birch leaves have a “V” shape and are elongated rather than like the flat leaves of aspens.
Aspen leaves (left) are usually rounder and shorter than birch leaves (right) and have less serrated edges
Birch Trees in the FallAutumn foliage of birch tree
Birch trees are deciduous trees that have stunning ornamental appeal in the fall. The leaves of birch trees turn from glossy green to magnificent shades of yellow in the fall. Birch tree fall colors can range from golden yellow to warm autumn hues of orange, bronze, and red. Some birch trees have bark that also turns golden like the leaves.
Types of Birch TreesLet’s look in more detail at the common types of birch trees growing in forests and residential parks and gardens.
White Birch Tree (Betula pubescens)White birch trees (Betula pubescens)
The white birch tree has ovate-shaped fuzzy leaves and white, thin, papery peeling bark.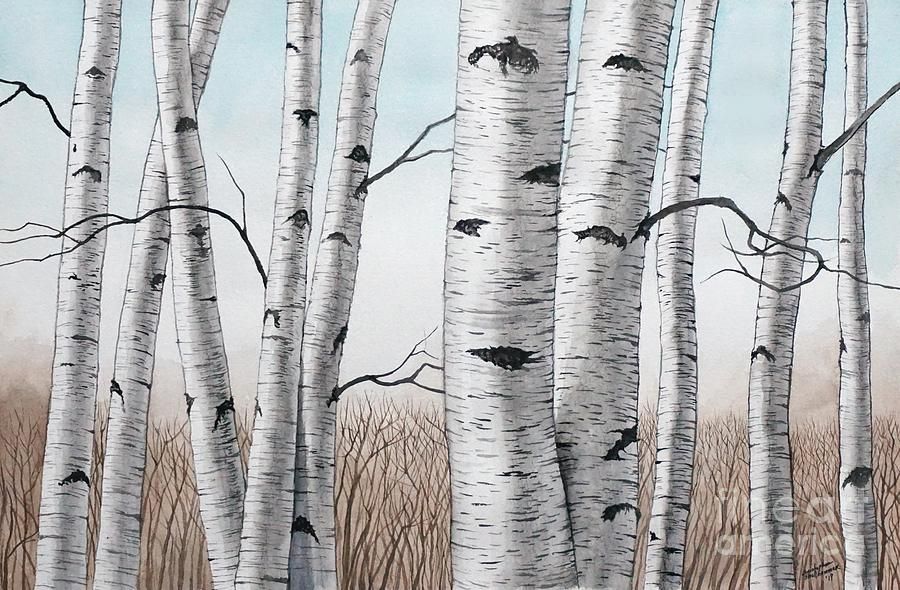 White birch trees grow between 30 and 65 ft. (10 – 20 m) tall. The slender white trunk has upright branches, giving the tree a columnar appearance. White birches have warm yellow fall colors.
White birch trees grow between 30 and 65 ft. (10 – 20 m) tall. The slender white trunk has upright branches, giving the tree a columnar appearance. White birches have warm yellow fall colors.
White birch (Betula pubescens) is a tree native to Europe. Other names for white birch tree include ‘downy birch,’ ‘hairy birch,’ and ‘moor birch.’ The white birch is sometimes confused with the silver birch (Betula pendula). However, it has smooth downy shoots.
Compared to other birch trees, the leaves of white birch have coarsely serrated margins.
The white birch tree is a cold-hardy broadleaf tree that grows in USDA zones 2 through 9. The tree thrives in full sun and moist, damp ground.
White birch tree leaves: Simple leaves are arranged alternately. The triangular leaves have a rounded base and tapered tip. Also, look for unevenly serrated margins. White birch leaves measure 1.2” to 2.4” (3 – 6 cm) long and up to 2” (5 cm) wide.
White birch leaves and male catkins
White birch tree bark: Dull white thin bark that exfoliates in papery strips.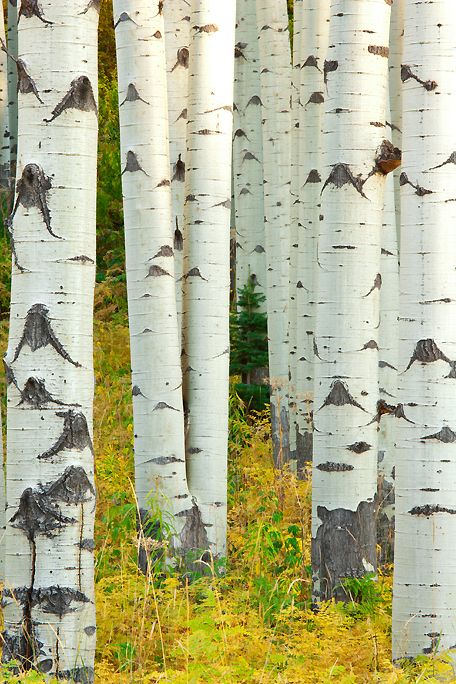
White birch tree bark
Weeping Silver Birch Tree (Betula pendula)Weeping Silver Birch Tree (Betula pendula)
The silver birch has pendulous branches, giving the tree a weeping appearance. The weeping silver birch has glossy green leaves that turn a warm yellow in the fall. Leaves are ovate-shaped with double-toothed margins. As its name suggests, the bark of Betula pendula is silvery-white and has contrasting horizontal black stripes.
Weeping silver birch trees grow best in large gardens as shade trees. The arching canopy, oval shape, and slender silvery trunk look stunning as a landscape tree.
Silver birch trees are suitable for growing in USDA zones 2 through 7. The deciduous trees prefer full to partial sun and growing in well-draining ground.
The weeping silver birch is also called the ‘lady of the woods,’ ‘weeping birch,’ European white birch,’ ‘warty birch,’ and ‘lady birch.’
Silver birch tree leaves: Shiny green leaves are 2. 5” (7 cm) long and have a distinct triangular shape with jaggy-looking edges. Silver birch fall colors are hues of warm yellows.
5” (7 cm) long and have a distinct triangular shape with jaggy-looking edges. Silver birch fall colors are hues of warm yellows.
Weeping silver birch leaves and male catkins
Silver birch tree bark: Bark is golden brown on young growth before turning silvery white with black patches.
Weeping silver birch bark
Paper Birch Tree (Betula papyrifera)Paper birch trees (Betula papyrifera)
Also called the white birch tree, the paper birch gets its name from its thin, white papery bark. The paper birch tree has ornamental value in garden landscapes due to its golden fall color and thin, exfoliating, smooth pure white bark. Leaves are egg-shaped with irregularly toothed margins.
You can grow paper birch trees as a single stem tree or multi-stemmed tree. Typically, paper birch trees grow between 50 and 70 ft. (15 – 21 m) tall and have a rounded crown. Multi-stemmed paper birch trees don’t grow as tall.
Paper birch trees grow best in USDA zones 2 through 7. In cold climates, ornamental paper birch trees can grow for up to 100 years. In warmer regions, they don’t live as long.
In cold climates, ornamental paper birch trees can grow for up to 100 years. In warmer regions, they don’t live as long.
The paper birch tree was used to make canoes. That’s why the Betula papyrifera tree is also called the canoe birch tree. Its brilliant white bark is the reason it’s called the white birch.
Paper birch tree leaves: Ovate-shaped leaves with irregular serration on the margins. The leaf blades measure 4” (10 cm) long and turn from dark green to bright yellow in the fall.
Paper birch leaves
Paper birch tree bark: Shiny white bark that peels in strips revealing orangey-brown bark underneath.
Paper birch bark
Yellow Birch Tree (Betula alleghaniensis)Yellow birch tree (Betula alleghaniensis)
The yellow birch tree is a medium-sized tree with elongated oval, glossy green leaves, finely serrated margins, and beautiful bright yellow colors in the fall. This slender deciduous tree has foliage growing in a conical shape. The tree’s bark starts as shiny bronze before turning shaggy and papery and a gray-brown color.
The tree’s bark starts as shiny bronze before turning shaggy and papery and a gray-brown color.
Yellow birch trees grow between 50 and 80 ft. (15 – 24 m) tall. Yellow birches have year-long seasonal interest thanks to the beautiful bark, large pointed leaves, and bright fall colors.
Other names for yellow birch tree include ‘swamp birch,’ ‘gray birch,’ ‘hard birch,’ and ‘silver birch.’
Yellow birch tree leaves: Lanceolate shaped with irregularly toothed margins. Dark green birch leaves turn bright yellow with hints of lime green in fall. The long birch leaves measure between 3” and 5” (7 – 12 cm) long.
Yellow birch leaves
Yellow birch tree bark: The bark is a polished brown color when young and turns a silvery-gray color as it matures. The bark has a yellow-bronze tinge that peels in narrow strips.
Yellow birch bark
River Birch Tree (Betula nigra)River birch trees (Betula nigra)
The river birch tree is a type of clumping birch tree with reddish-brown exfoliating bark, glossy green diamond-shaped leaves, and a pyramidal crown. This fast-growing river birch tree has smooth fuzzy twigs and unique buds among Betula trees due to the hooked tips. River birch fall color is golden yellow.
This fast-growing river birch tree has smooth fuzzy twigs and unique buds among Betula trees due to the hooked tips. River birch fall color is golden yellow.
Betula nigra grows between 80 and 100 ft. (25 – 30 m) and typically has multiple slender trunks. The clumping river birch grows best as decorative trees in garden landscapes where there’s wet soil.
The river birch is the best choice of birch trees for hotter areas. River birches are the most heat-tolerant of all the Betula species. You’ll find river birch thriving in northern states, as well as Florida and Texas. This birch species grows in USDA zones 4 through 9.
Other names for the river birch include ‘black birch,’ ‘water birch,’ or ‘clump river birch.’
River birch tree leaves: Diamond-shaped leaves with double-serrated margins. The birch leaves have a glossy green upper side and yellowish-green underside. In fall, all the foliage turns bright yellow.
River birch leaf
River birch tree bark: Flaky bark that peels and curls from the tree trunk. The bark starts pink, smooth, and shiny. As the birch tree matures, the bark becomes reddish-brown and peels, revealing orangey flakes of bark.
The bark starts pink, smooth, and shiny. As the birch tree matures, the bark becomes reddish-brown and peels, revealing orangey flakes of bark.
River birch bark
Gray Birch Tree (Betula populifolia)Gray birch tree (Betula populifolia)
The gray birch tree is a fast-growing, slender deciduous tree, often with multiple trunks. Gray birch leaves are triangular shaped with an elongated tip. The ovate leaves have a glossy green upper side and a pale underside. Gray birch bark is a light gray, almost white color with black patches on the bark.
Gray birch trees are medium-sized trees, growing between 20 and 30 ft. (6 – 10 m).
The scientific name for gray birch trees—Betula populifolia—comes from the leaves that look like leaves on poplar trees.
Gray birch trees can look like paper birch trees. However, to tell the trees apart, look at the bark and leaves. Gray birch bark doesn’t peel, and the leaves have longer pointed tips than paper birch trees.
Gray birch tree leaves: Triangular leaves that taper to a long tip. Look for double-toothed margins and shiny upper leaves to identify gray birch trees. Fall color is an undistinguished yellow.
Gray birch leaves
Gray birch tree bark: Chalky whitish-gray bark that doesn’t peel.
Gray birch bark
Sweet Birch Tree (Betula lenta)Sweet birch tree (Betula lenta)
The sweet birch tree is a deciduous tree with large, ovate-shaped leaves that have finely serrated margins. Leaves on sweet birch trees are some of the biggest in the Betula genus, measuring up to 6” (15 cm) long. Pendulous flowers emerge in spring before the leaves appear.
The sweet birch tree gets its name from the scent of wintergreen in the twigs, bark, and leaves. The other common names of Betula lenta refer to other features of the tree. For example, ‘black birch’ due to its dark bark color. ‘Cherry birch’ and ‘mahogany birch’ because of the way the bark looks on mature birch trees. And ‘spice birch’ due to the aromatic wintergreen scent it emits.
And ‘spice birch’ due to the aromatic wintergreen scent it emits.
Sweet birch trees grow up to 100 ft. (30 m) tall. However, these birch trees typically grow in residential landscapes between 50 and 80 ft. (15 – 24 m) tall.
Sweet birch tree leaves: The glossy leaves start as a light green color before becoming a darker shade and then turning to rich golden yellow in the fall. Leaves measure between 2” and 6” (5 – 15 cm). These birch leaves give off a sweet fragrance when crushed.
Sweet birch leaves
Sweet birch tree bark: Younger sweet birch trees have bark smooth grayish bark with slender horizontal lenticels. Unlike other birch trees, older trees develop hard, deeply-fissured bark with irregular scaly plates.
Sweet birch bark
Dwarf Birch Tree (Betula nana)Dwarf birch tree (Betula nana) and a close up picture of the leaves
The dwarf birch tree is more of a large shrub than a tree. This shrubby plant grows around 3 ft. (1 m) tall and has rounded leaves with bluntly-toothed edges. Leaves are light green and turn red in the fall. Dwarf birch trees are well-suited to arctic conditions and thrive in USDA zones 1 through 8.
(1 m) tall and has rounded leaves with bluntly-toothed edges. Leaves are light green and turn red in the fall. Dwarf birch trees are well-suited to arctic conditions and thrive in USDA zones 1 through 8.
Apart from dwarf birch tree, other names for Betula nana include ‘bog birch’ and ‘arctic birch.’
The American dwarf birch (Betula glandulosa) is similar to Betula nana. The only difference is longer petioles joining the leaf blades to twigs.
Betula glandulosa leaves have longer petioles
Himalayan Birch Tree (Betula utilis)Himalayan birch tree (Betula utilis) and leaves
The Himalayan birch tree has thin, papery bark, egg-shaped, slightly fuzzy leaves, and short conical flowers. Like most birches, the Himalayan birch has peeling bark that can be white, reddish-brown, or reddish-white. The bark peels in thin sheets, revealing pinkish bark underneath. The glossy green birch leaves measure between 2” and 4” (5 – 10 cm).
The Himalayan birch tree grows as a large shrub or tree up to 66 ft. (20 m) tall. The single trunk branches out low to the ground to create a vase-shaped crown of green foliage contrasting with white bark.
Himalayan birch tree bark
Japanese White Birch (Betula platyphylla)Japanese white birch (Betula platyphylla) trees and bark
Also called the ‘Asian white birch,’ the Betula platyphylla has grayish-white bark, spreading branches, and yellowish-green triangular leaves with tapered tips. The 3-inch (7.5-cm) leaves have toothed margins and cover branches to create a pyramidal crown.
The Japanese white birch thrives in zones 4 through 7. In colder climates, the decorative birch tree grows between 30 and 40 ft. (10 – 12 m) and is 15 to 25 ft. (4.5 – 7.6 m) wide.
Related articles:
- Aspen Trees: Types, Leaves, Flowers
- Types of Magnolia Trees and Shrubs
- Crape Myrtles: Trees, Dwarf Plants and Shrubs
Read Next
Types of Pine Cones: Large, Small, Giant, and More (with Pictures) - Identification Guide
Types of Pine Trees with Identification Guide, Chart and Pictures
Willow Oak: Leaves, Bark, Acorns (Pictures): Identification and Growing Guide
Fast Growing Trees (With Pictures) - Identification Guide
description, properties of Birch, application, interesting facts
image of Birch
Birch - bright beauty of Russian forests. Its trunks turn white in the forest, giving people joy, peace and hope. From time immemorial, people have come to her for advice and consolation. Birch is the pride and symbol of the Slavs. It is often called the tree of life.
Its trunks turn white in the forest, giving people joy, peace and hope. From time immemorial, people have come to her for advice and consolation. Birch is the pride and symbol of the Slavs. It is often called the tree of life.
Birch is not without reason considered a sacred tree, a spiritual symbol. Since ancient times, she has taken care of a person. Leaves - for health, branches - for brooms, bark for writing, crafts, tar and making fire, wood for warmth. nine0007
Birch in Rus' has always been associated with a young maiden with its purity, whiteness, and sophistication. Branches Birches bend over the traveler like a woman's hands to enclose him in their tender embrace.
The name Bereza
The Russian word Bereza comes from praslav. berza, from the root *bhereĝ- “shine, turn white”.
Where does Birch grow?
Birch is widespread throughout Russia and the Northern Hemisphere as a whole, even beyond the Arctic Circle. Birch is undemanding, tolerates both heat and cold. nine0023
Birch is undemanding, tolerates both heat and cold. nine0023
Dwarf Birch grows in the tundra of Europe and North America and the mountain tundra of Siberia. It does not even reach 1 m in height. In the glacial and post-glacial periods, this Birch was distributed much further south, now it is found there only in swamps as a relic.
What does Birch look like?
Birch is probably familiar to everyone. But still, let's write a few words.
Birch - tall light tree with spreading crown. It is always light in the Birch Forest, and not only because of the white trunks. Birch leaves are not large and the crown lets in a lot of light. nine0007
Birch height usually 15-30m. However, the age of Birch is not long. Actually, 1st century. Birch usually lives for about 100 years.
The bark of Birch is white in most species. The outer part of the bark - birch bark - usually easily peels off with ribbons. In old birches, the lower part of the trunk is covered with a dark crust with deep cracks.
In old birches, the lower part of the trunk is covered with a dark crust with deep cracks.
Birch leaves are small, toothed, pointed at the end, sticky in spring.
Birch Flowers - earrings. Birch's earrings are not all the same: there are men's, there are women's. nine0007
Men's earrings on Bereza appear in summer. At first they are erect and green in color, then gradually turn brown. Outside, the entire earring is covered with a resinous substance impervious to moisture. In this form, catkins hibernate.
In spring, in March-May, the shaft of the male catkin lengthens, as a result of which the scales surrounding the flower open, and yellow stamens become visible between them, abundantly secreting pollen.
Women's birch catkins always sit on the side of the branch. During flowering, they are always shorter and narrower than males, which immediately fall off after pollination.
When to collect birch leaves?
Birch Leaves must be collected in mid-May, as soon as the leaves are no longer sticky.
Birch leaves are harvested in May - June - birch leaves should be fragrant and sticky, young, not coarse. For drying, birch leaves are laid on wide paper sheets in a dark, cool place with good ventilation. nine0023
Medicinal properties of Birch
The main medicinal properties of Birch : antimicrobial, wound healing, good anti-inflammatory properties, resolving ability - this is not a complete list of the remarkable properties of these leaves.
Diuretic, and most importantly, choleretic properties are often used by herbalists in a variety of preparations.
Application Birch
Birch leaves have a rich composition - essential oils, phytoncides, vitamin C, carotene, vegetable glycosides, tannins, nicotinic acid and other elements. A decoction of birch leaves is used as a disinfectant and antiseptic, diuretic and choleretic drug. nine0007
Infusion from birch leaves is more saturated, so it is used for local treatment. Alcoholic and ethereal substances that contain birch leaves have antimycotic and antiviral effects. Tannins, which are rich in birch leaves, have bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties. Phytoncides and flavonoids are antioxidants that absorb free radicals, so Birch leaves can rejuvenate cells and tissues and restore them.
Alcoholic and ethereal substances that contain birch leaves have antimycotic and antiviral effects. Tannins, which are rich in birch leaves, have bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties. Phytoncides and flavonoids are antioxidants that absorb free radicals, so Birch leaves can rejuvenate cells and tissues and restore them.
Infusion from young birch leaves is used as a stimulant, prescribed for disorders of the nervous system, renal colic, jaundice, as an anti-inflammatory and vitamin remedy.
Birch buds are diaphoretic, diuretic and choleretic. In diseases of the kidneys and bladder, dropsy, an aqueous infusion or decoction is used in a ratio of 1:5. Infusions from the kidneys are prepared at the rate of 2 teaspoons per glass of boiling water. Take 2-3 tablespoons 3-4 times a day. A decoction is prepared from 30 g of kidneys per glass of water and is also taken as an infusion. nine0007
Birch leaves are used to make vitamin drink : young leaves are crushed and poured with hot boiled water, infused for 4 hours.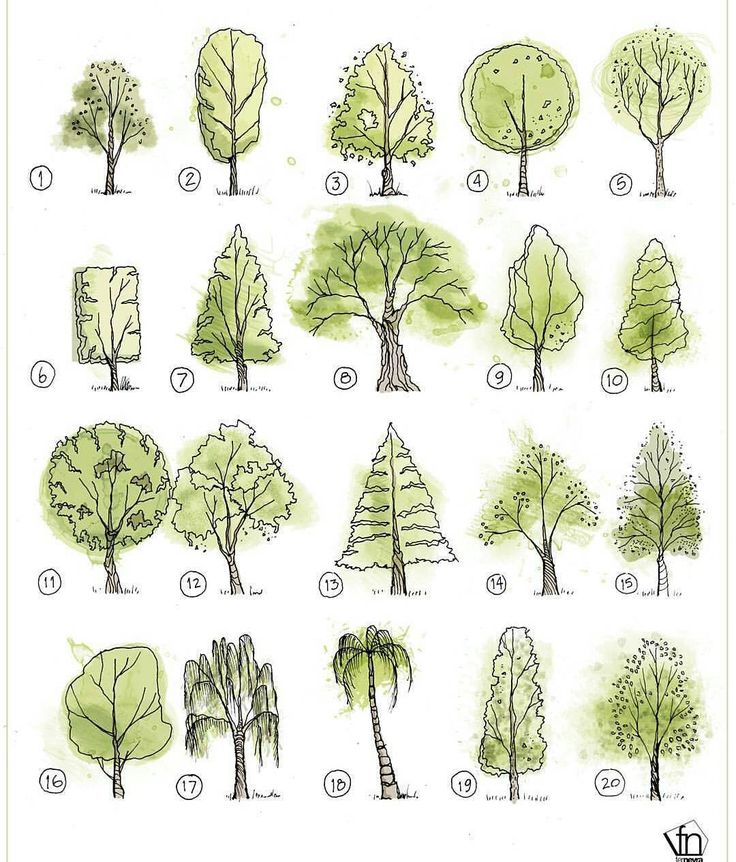
Birch sap . Birch sap is not only tasty but also healthy, has a good tonic effect, its ability to dissolve stones has been revealed, so the juice is used in complex therapy for urolithiasis.
The usefulness of birch sap is determined by its chemical composition, the presence of many valuable substances, in particular glucose and fructose, which are well absorbed by the body, nicotinic, glutamic, aminoacetic acids. nine0007
Birch broom in the bath promotes healing of wounds, abrasions, cleanses the skin from rashes and acne. It helps well after physical exertion, relieves pain and tension in the muscles. And its main advantage is that it helps to improve ventilation in the lungs.
It is believed that the smell of Birch cures melancholy and helps from the evil eye, and birch sap, collected on special days of March and April, cleanses the blood.
Birch bark is one of the best materials for making a fire in any weather. nine0007
nine0007
Birch. Interesting facts
Sometimes you can see outgrowths on the Birch - cap - in the section they have a peculiar complex and beautiful pattern. The processed burl has long been used for the manufacture of elegant handicrafts: caskets, snuff boxes, decorative details of furniture.
Birch is also characterized by specific species of fungi - dead wood destroyers (saprotrophic), which play an important role in the process of self-purification of forests from deadwood and windbreaks. nine0023
Why is Birch white? The cell cavities of the birch bark are filled with a white resinous substance - betulin, which gives the birch bark a white color.
Birch is important as a pollen carrier in beekeeping. After all, bees collect not only nectar, but also pollen - the main source of protein and vitamins.
People living near a birch grove are much less likely to get colds, as the volatile phytoncides released by the tree inhibit the growth and development of bacteria.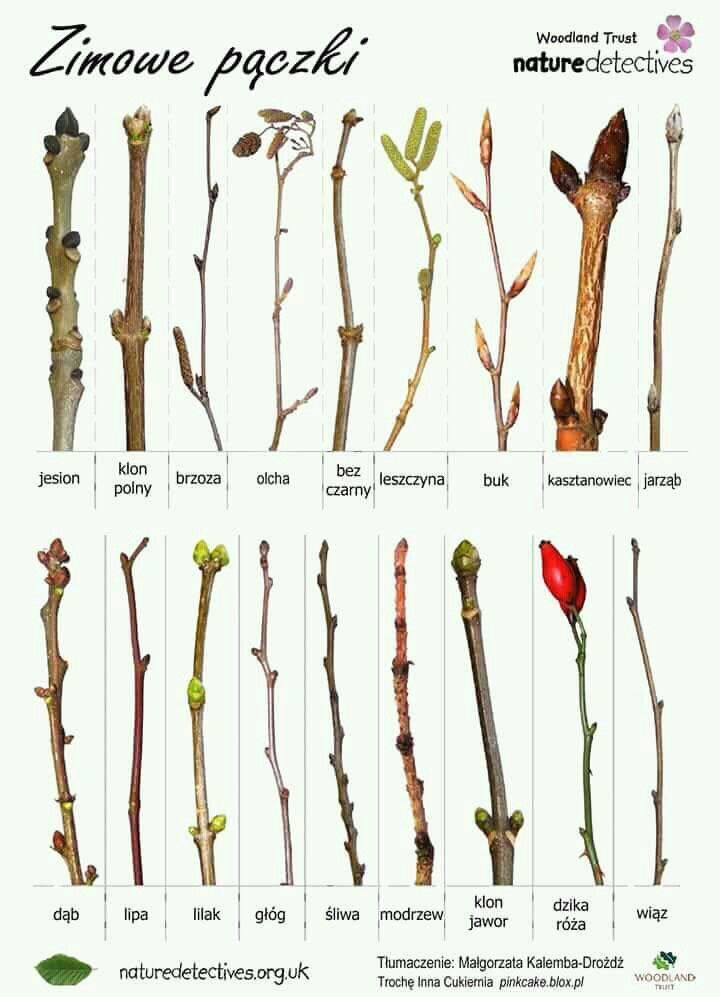 nine0023
nine0023
Birch's photo: *Galina*, ShepelevaV, karyuk.nina, Elena Shukhobova, Zosia
What does a birch fruit look like. Description of birch for children. Description of a birch leaf. Types of birches, names and photos
The common birch can be safely considered a symbol of Russia. This tree is extremely widespread throughout our country. It is hardly possible to find someone who does not know this plant. It is used in industry, medicine and ornamental horticulture. nine0007
Birch is a deciduous tree belonging to the Birch family. There are more than a hundred species of this plant in botany. Most of them are trees, their height can reach 30-35, and sometimes 45 m. Among this variety there are shrubs, which are quite large and very small, creeping. These plants usually live 200-250 years, but sometimes their age can exceed 300.
Description birch
The root system of birch is developed and very powerful. It is core and superficial. The seedling usually has a taproot, but it quickly stops growing and dies. Then lateral root shoots begin to develop, giving many branches. They are located obliquely at an angle of 30-40º and go shallow into the ground. This position of the adventitious roots allows the birch to have increased stability and strength. A lot in the structure of the roots depends on where exactly the plant grows. nine0007
It is core and superficial. The seedling usually has a taproot, but it quickly stops growing and dies. Then lateral root shoots begin to develop, giving many branches. They are located obliquely at an angle of 30-40º and go shallow into the ground. This position of the adventitious roots allows the birch to have increased stability and strength. A lot in the structure of the roots depends on where exactly the plant grows. nine0007
The birch grows very slowly for the first few years of its life. But when the main root dies and the peripheral part grows, the tree begins to grow much faster. Roots that are fairly close to the surface take all the moisture and nutrients from the ground. Where birch grows, it is extremely difficult for other plants to survive.
Mature tree usually has white, whitish-yellow, brown-reddish, sometimes brown, grayish and even almost black bark, depending on the variety. The white color is due to the presence in the cells of the tissue of the bark of begulin - a white coloring resinous substance. The outer layer is called birch bark and is usually easily removed in layers or strips. In fairly old birches, the lower sections of the trunk acquire a dark gray color and are furrowed with deep cracks. The girth of the trunk is up to 1.5 m.
The outer layer is called birch bark and is usually easily removed in layers or strips. In fairly old birches, the lower sections of the trunk acquire a dark gray color and are furrowed with deep cracks. The girth of the trunk is up to 1.5 m.
The leaves of the tree are smooth, with small serrations along the edges, rounded or triangular in shape with an elongated sharp tip, sitting alternately on a short petiole. On the leaf blade, pinnate veins are clearly visible, which end in denticles. Young fresh leaves are covered with sticky resin and have a pale green color. In autumn, before falling, the foliage turns yellow.
Birches are dicotyledonous, dioecious and wind pollinated. Male earrings appear in the summer, bloom in the spring and then immediately fall off. The female ones bloom together with the leaves and, after pollination, fruits ripen in them, which are a small flattened nut equipped with “wings”. Thanks to these membranes, birch fruits are able to be blown away by the wind over a distance of more than 100 m.
Varieties
The classification of birches is quite complicated, botanists cannot come to a consensus on this matter. Their description is confusing due to polymorphism. Usually the following 4 groups are distinguished:
Albae - this includes trees with bark of white, yellowish, pinkish and other light shades.
Costata - trees with dense wood having various shades (cherry, white, black, yellow). The trunk is ribbed, and the leaves have interesting voluminous veins. nine0007
Acuminatae - large trees with large leaves, growing in a subtropical climate.
Nanae - dwarf trees with small leaves.
Birch species
Consider some types of birch:
Ordinary (warty, drooping). Height up to 35 m, trunk thickness 0.7-0.8 m. The most common variety of birches with white bark, which in young plants (up to 10 years old) is brown, and then turns white. The branches are strewn with many resinous growths resembling warts, hence the name - warty. It grows throughout Europe, Asia and North Africa. The tree is unpretentious, tolerates severe frosts and droughts very well, but requires good sunlight. nine0007
It grows throughout Europe, Asia and North Africa. The tree is unpretentious, tolerates severe frosts and droughts very well, but requires good sunlight. nine0007
Fluffy (pubescent). Height - 25-30 m, diameter - up to 0.8 m. Young trees resemble alder because of the red-brown bark. But with age, the similarity disappears, as the trunk turns white. Branches directed almost vertically upwards form a wide spreading crown. It grows in Western Europe, the central regions of Russia, the Caucasus and Siberia. Very winter-hardy, shade-tolerant, loves wet and even swampy soils.
Erman (stone). Relatively low tree (up to 15 m) with a crooked trunk, but up to 0.9 in diameterm. It has a flaky bark of dark gray and brown colors, which eventually ulcerates with large cracks. A translucent, wide and luxurious crown is formed from upright branches. It tolerates cold, shade-tolerant and undemanding. It tolerates swampy and wet soils very poorly, preferring rocky areas. Often found on the islands of Japan, in the northern provinces of China, on the Korean Peninsula. On the territory of Russia, it grows in the Far East, in Transbaikalia, Buryatia, Yakutia and Kamchatka. nine0007
On the territory of Russia, it grows in the Far East, in Transbaikalia, Buryatia, Yakutia and Kamchatka. nine0007
Cherry . Height up to 25 m, thickness up to 0.6 m. This birch is distinguished by uneven, cracked, brownish-reddish, almost cherry-colored bark. Grows in moist, light, well-drained soils. In cold winters it can freeze. Distributed in North America, the Baltic countries, Belarus and in the central part of Russia.
Black (river). Height up to 30 m, girth more than 1 m. It grows in the southern states of the USA, as it is very thermophilic.
Karelian . Able to be a small bush, but it can also grow to a height of 6-8 m. The trunk is covered with all sorts of irregularities, thanks to which the wood has an extremely interesting marble pattern.
Dwarf . A typical inhabitant of the highlands and tundra. It looks like a shrub with fairly branched warty branches. Prefers to grow on highly moist, heavy soils.
Application
Birch is very widely used. First of all, use its wood. Various carpentry products, plywood, laminate are made from it. There is even a color - birch, which is used in furniture production. The Karelian variety is especially appreciated for the manufacture of various handicrafts and furniture. Birch firewood is considered one of the best. nine0007
First of all, use its wood. Various carpentry products, plywood, laminate are made from it. There is even a color - birch, which is used in furniture production. The Karelian variety is especially appreciated for the manufacture of various handicrafts and furniture. Birch firewood is considered one of the best. nine0007
Birch sap is used in the food industry to prepare various drinks.
Tar is obtained from birch bark by dry distillation, which is used in veterinary medicine and medicine, as well as in the cosmetic industry.
For medical purposes, birch leaves, bark and buds are used, which have bactericidal, choleretic, wound healing, expectorant, diuretic, antiseptic and antipyretic properties. Birch brooms have been used since ancient times for the prevention and treatment of various diseases. nine0007
These trees are widely used in plantations, landscaping and horticulture. Virtually maintenance-free and very decorative.
Birch is a very widespread tree in the northern hemisphere. Many peoples associated their beliefs and their gods with it, used it in everyday life and for treatment. What this symbol of the northern peoples represents, what it looks like, what species are more common and how birch is used in the economy and medicine - this will be discussed further. nine0007
Many peoples associated their beliefs and their gods with it, used it in everyday life and for treatment. What this symbol of the northern peoples represents, what it looks like, what species are more common and how birch is used in the economy and medicine - this will be discussed further. nine0007
What it looks like: biological description
White slender trunks with black spots, green sharp leaves, flexible branches - birch in northern latitudes is not difficult to find.
Bark
The color of the bark of most birch species is light - from yellowish to reddish-brown. There are trees with black and gray bark. The tree looks white because of betulin - a substance in the cork layer of the bark; it fills all the cavities in this layer. The uppermost layer of bark, called birch bark, is quite thin and easily detached from the trunk. nine0007
Leaves
Leaves entire, arranged alternately on the branches, rounded-triangular in shape, widened at the base and tapering towards the edge, serrated. In autumn they change color to yellow and fall off. Young leaves are covered with a sticky substance.
In autumn they change color to yellow and fall off. Young leaves are covered with a sticky substance.
Kidneys, male and female catkins
Kidneys alternate, covered with sticky spiral scales.
Flowers are divided into male and female. Male, formed into inflorescences, resembling earrings, grow on long shoots of two to four pieces. At first they are green, up to 4 cm long, then they begin to darken. nine0007
Earrings consist of flowers covered with scales; each flower has a perianth with stamens. Covered with resin that protects the stamens from moisture, the flowers hibernate and begin to open in spring.
In the spring, from March to May, the flowers release pollen that is carried by the wind, after which the catkins fall off.
Do you know? Birch trees are male - « birch » and birch for women. They can be distinguished by the direction of growth of the branches - for males, the branches are directed upwards, for females - to the sides. nine0193
nine0193
Female catkins appear at the ends of short branches that develop from last year's shoots, they are smaller than male ones. Both male and female flowers bloom at the same time.
After fertilization, the female earring increases, she may have a stem; gradually the earring turns into a small "bump". When the fruit is ripe, the earring will fall off.
Fruit
The fruit is a nut, flattened on both sides and surrounded by small membranes. nine0007
Seeds
Light birch seeds - up to 5000 seeds per gram. They are well carried by the wind. They fall in two stages - in autumn and winter. Winter seeds survive well under snow and begin to germinate in a new place in the spring.
Root system
The root system is strong and branched, usually going deep into the soil. Occasionally there are superficial roots. The roots going down branch out at a depth, overgrown with many thin uriculate roots. nine0007
Thanks to this root structure, in the third or fourth year of development, the tree begins to grow rapidly and actively.
Where birch grows
Species diversity determines the wide distribution of birches in the northern hemisphere. These trees coexist comfortably both beyond the Arctic Circle and in the tropics of Asia.
Their wide distribution is also caused by their unpretentiousness to the composition of the soil - they survive both in the permafrost beyond the Arctic Circle and in mountainous areas, and shrubs of the dwarf birch species actively grow in the tundra. nine0007
Main species
There is no exact and unanimous opinion on the number of species of these trees; most botanists agree that there are more than 100 species of the genus Birch in the world. All of them are conditionally divided into four groups:
The most common types:
Some features
There are some features that distinguish birch from many other trees and make it dominant in forests. So, it is this tree that becomes the first in an empty space, whether it is a felling, a conflagration or an outcrop. nine0007
nine0007
Average height, trunk girth
In most species, the height of the trunk reaches 30 m. Some specimens grow up to 40-45 meters. There are also dwarfs, whose height does not exceed 2-3 meters.
The most common are trees with a girth of the trunk up to 150 cm. But after three or four years the situation changes and growth becomes more active. Due to the high growth rate, young growth can compete with fast-growing grass. nine0007
Do you know? Birch occupies an important place in various ritual and religious folk rituals - the Celts buried the dead in birch-bark hats, and in Orthodoxy, birch branches decorate dwellings and churches on the feast of the Holy Trinity.
Life expectancy
The average life expectancy of a birch is 100-150 years. There are trees that live for 300-400 years.
Frost resistance
Many species tolerate moderate frosts very well. Some survive even in the Arctic, at high negative temperatures. There are also such as the stringy birch and the river birch, which do not tolerate cold well and prefer a temperate climate with mild winters. nine0007
There are also such as the stringy birch and the river birch, which do not tolerate cold well and prefer a temperate climate with mild winters. nine0007
Chemical composition
Different parts of the tree are rich in various chemical elements that determine their useful properties and appearance.
Bark
The bark of almost all varieties contains betulin, a white organic pigment that gives the bark its white color. The content of betulin ranges from 5 to 44%, depending on the type of tree.
Buds
Birch buds contain resins, alkaloids, vitamin C, flavonoids and fatty acids. There are also essential oils. nine0007
Leaves
Leaves are rich in essential oils, dammarane derivatives, coumarins, tannins and flavonoids.
How they are used
Birches have found their application in human activities, medical practice and design.
In landscape design
In landscape design, birch trees are widely used to design ponds, alleys and create group compositions with coniferous plants. Exotic species are also used as central plants of the site. nine0007
Exotic species are also used as central plants of the site. nine0007
Important! It should be remembered that birch has an overwhelming effect on most plants, as it grows and develops faster, drying up the soil around it. In addition, its rotten foliage oppresses many plant species.
In beekeeping
Bees do not collect birch pollen very willingly. But on the other hand, the sticky resin from the leaves and bark serves as a good source of a substance vital for the bee swarm.
In folk medicine
Healers and herbalists actively use birch in their potions. Means based on it heal wounds well, eliminate inflammation, relieve fever, and are an excellent diuretic. And everyone heard about the bath with birch brooms - this is how our ancestors treated colds, wounds and skin diseases, relieved fatigue.
Important! Birch-based products can be dangerous for people with kidney disease and should be used with caution.
Wood
Firewood from this tree give a lot of heat and burn for a long time - this is one of the best breeds for furnaces.
Not suitable as a building material - it starts to rot and decay very quickly, but it is a good material for furniture and various handicrafts. The Karelian birch is especially appreciated with its unusual wood texture.
Good and durable skis, gun stocks, toys are made from birch; it is also suitable as a raw material for the creation of plywood. nine0007
Cap - growth on the trunks - serves as a good material for creating snuff boxes, cigarette cases, various souvenirs.
Tar
This is a liquid obtained from the pyrolysis of wood. Birch tar contains paraffin, creosote, toluene, resins. It was mainly produced in the Russian Empire, exported and was known abroad as "Russian oil".
It was used as a preservative in the leather industry to protect against decay and in the dressing of yuft (soft leather), as a lubricant for wooden parts, including wheels, to protect against insects and pests in the garden.










