What are the architectural styles
15 Top Architectural Styles
The Spruce / Christopher Lee Foto
The built environment is a rich and varied architectural tapestry with overlapping styles and movements that have often traveled around the world, adapting themselves to different climates, landscapes and cultural needs. Here is a rundown of 15 popular architectural styles throughout history.
-
01 of 15
Westend61 / Getty Images
An umbrella term that refers to the building styles that originated in ancient Greece and Rome, classical architecture has influenced centuries of subsequent design movements throughout the world, including Neoclassical and Greek Revival architecture. Some of the most famous buildings in the modern world are based on ancient Greek and Roman designs.
Classical architecture focuses on symmetry and proportions; columns with Doric, Ionic, or Corinthian detailing; the use of materials such as marble, brick, and concrete; and classical design motifs such as interior molding, medium pitched roofs, boxed eaves, decorative door surrounds, and broken pediments over the entry door.
While classical architecture was largely replaced by modernism and contemporary architecture in the 20th century, classical architecture continues to be built in what has been rebranded as "new classical" style.
-
02 of 15
SeanPavonePhoto / Getty Images
Neoclassical architecture refers to a style of buildings constructed during the revival of Classical Greek and Roman architecture that began around 1750 and flourished in the 18th and 19th centuries. Whereas Greek Revival architecture utilizes classical elements, such as columns with Doric, Ionic, or Corinthian details, neoclassicism is characterized by a more whole-scale revival of entire and often grand-scale classical volumes.
Some of the most famous and easily recognizable institutional and government buildings in Europe and the United States are neoclassical in style, such as the White House and U.S. Capitol building.
-
03 of 15
tose / Getty Images
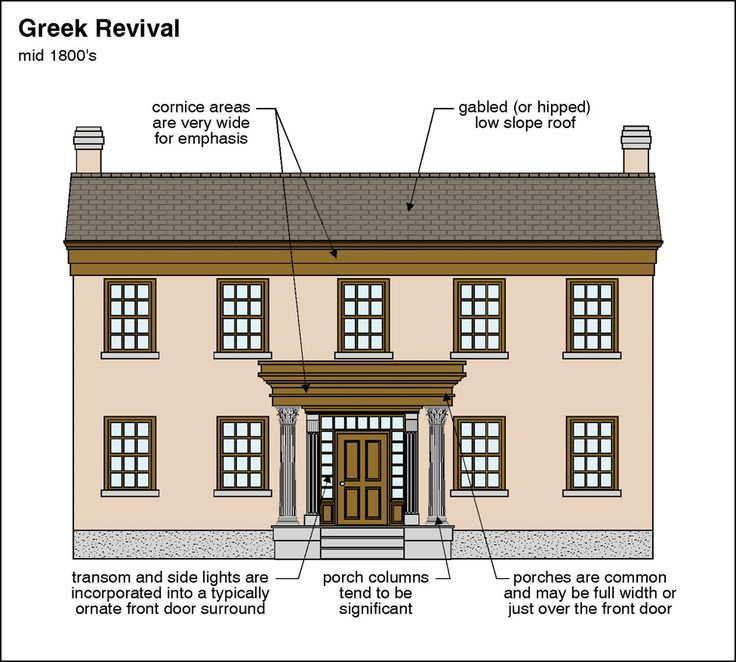
Greek Revival architecture is inspired by the symmetry, proportion, simplicity, and elegance of the ancient Greek temples of 5th century B.C. In the U.S., Greek Revival reached peak popularity from 1825 to 1860, and became the first dominant national style of architecture in the U.S. as it spread from the East Coast across the country to the West Coast, leaving state capitol buildings, banks, New England churches, urban row houses, galleried cottages, and southern plantation houses in its wake.
Inspired by the birthplace of democracy, Americans borrowed classical elements to design buildings for what was then a still new democracy, such as columns with Doric, Ionic, or Corinthian details, painted white to mimic the marble used in ancient Greece; gently sloping roofs with gable fronts; and elaborate door surrounds.
 Interiors featured simple, fairly open layouts; graceful proportions; tall parlor floor windows and doors; ornate plasterwork ceilings; plain plaster walls; wide plank floors; and ornate ceiling mantels.
Interiors featured simple, fairly open layouts; graceful proportions; tall parlor floor windows and doors; ornate plasterwork ceilings; plain plaster walls; wide plank floors; and ornate ceiling mantels. -
04 of 15
ethanfink / Getty Images
An umbrella term used to describe buildings constructed to facilitate the needs of industry, industrial architecture encompasses a range of building types and styles that mix functionality and design and can be found all over the industrialized world, such as factories, warehouses, foundries, steel mills, water towers, grain silos, distilleries, breweries, refineries, power plants, and other utilitarian structures. The first industrial buildings were constructed in the 1700s during the first Industrial Revolution that took place mainly in Britain from about 1760 to 1840.
But today when we reference industrial architecture, we are mostly referring to the buildings that emerged as a response to the widespread use of new materials such as metal and concrete as well as mass production methods brought on by the Second Industrial Revolution of the late 19th and early 20th century, and which formed the building blocks for Modern Architecture.
 Features of industrial architecture may include large, open floor plans; high ceilings; raw rough materials such as concrete, brick, and metal; lack of ornamentation on building façade; exposed brick, ductwork and piping; and large metal-grid windows.
Features of industrial architecture may include large, open floor plans; high ceilings; raw rough materials such as concrete, brick, and metal; lack of ornamentation on building façade; exposed brick, ductwork and piping; and large metal-grid windows. What Is Industrial Architecture?
-
05 of 15
Cethegus / Wikimedia Commons
Bauhaus architecture came out of the influential German school founded by Walter Gropius (1883-1969) in the early 20th century, which had a utopian aim to create a radically new form of architecture and design to help rebuild society after World War I. By synthesizing fine arts, crafts, design, architecture, and technology, the Bauhaus promoted rational, functional design that embraced a form follows function, less is more ethos.
Not all Bauhaus buildings look alike, but in general they eschew ornamentation to focus on simple, rational, functional design; use simple geometric forms such as the triangle, square, and circle; asymmetry; use of modern materials such as steel, glass, concrete; flat roofs; glass curtain walls; smooth façades.
 Bauhaus developed into the International Style when Gropius and other prominent members of the Bauhaus emigrated to the U.S. in the 1930s and later influenced the development of modernism in the 1950s and '60s. Bauhaus architecture and design principles still influence the shape and look of everyday objects.
Bauhaus developed into the International Style when Gropius and other prominent members of the Bauhaus emigrated to the U.S. in the 1930s and later influenced the development of modernism in the 1950s and '60s. Bauhaus architecture and design principles still influence the shape and look of everyday objects. -
06 of 15
LimeWave / Getty Images
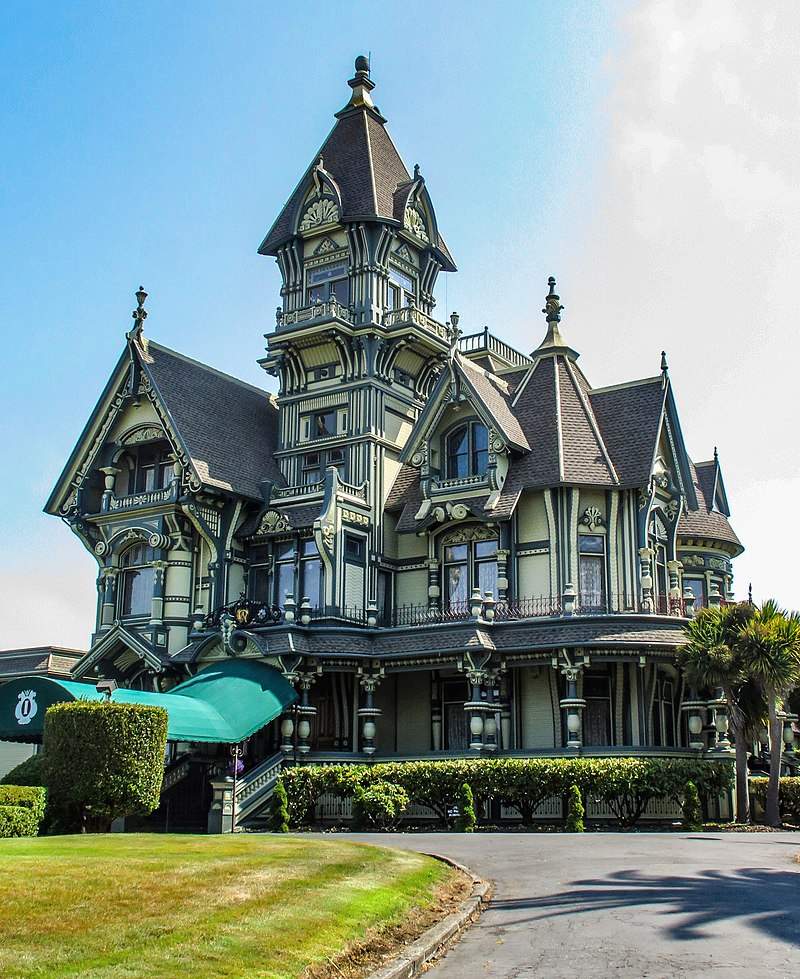
The term Victorian architecture refers not to a particular style but to an era—the reign of Queen Victoria from 1837 to 1901. The style originated in England and still largely defines the architecture of its cities and towns, but varying styles of Victorian era architecture spread to places like North America, Australia, and New Zealand. Victorian era architecture is marked by its unapologetic devotion to ornament and its ornate interior design. Some features that will help you spot a Victorian from the outside include: steeply pitched roofs; plain or colorfully painted brick; ornate gables; rooftop finials; sliding sash and bay windows; octagonal or round towers; and generous wraparound porches.
 Interiors often include grand staircases; complicated layouts; high ceilings; intricately carved wood paneling; and decorative fireplaces.
Interiors often include grand staircases; complicated layouts; high ceilings; intricately carved wood paneling; and decorative fireplaces. -
07 of 15
Douglas Keister / Getty Images
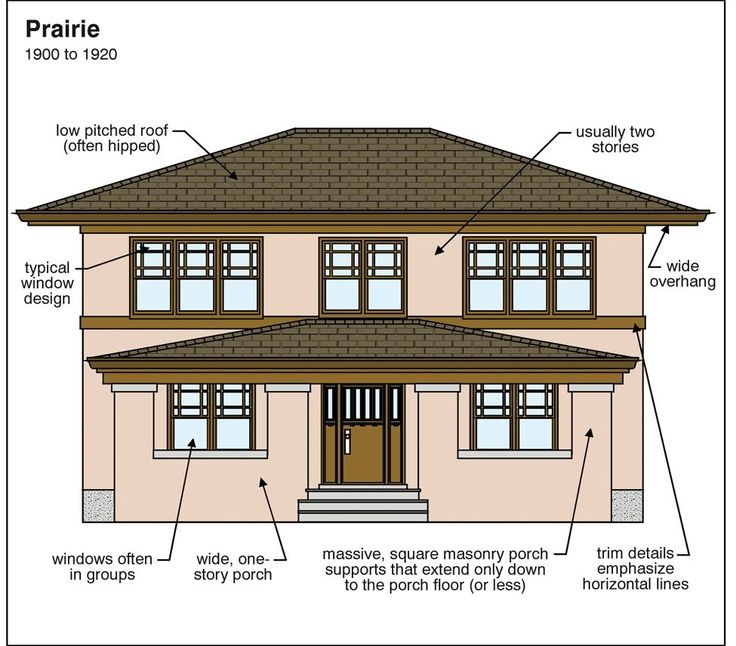
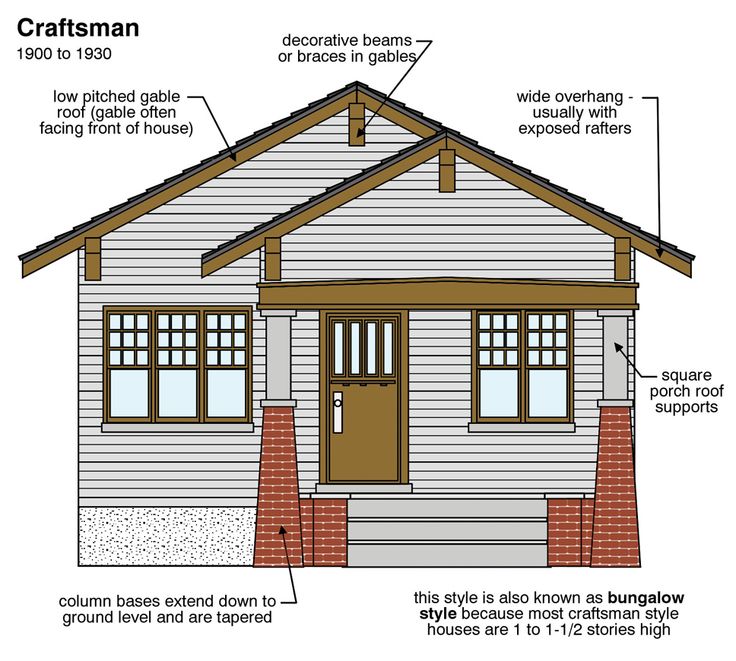
The Arts and Crafts movement was a reaction to the ornate and mass produced styles of Victorian architecture that embraced handcrafted design and the use of natural materials such as stone, brick, wood, and hammered copper and bronze metalwork detailing. Originating in Great Britain in the mid 19th-century, the Arts and Crafts movement migrated to the U.S. in the beginning of the 20th century, encompassing architecture, interior design, textiles, fine art and more. Many architectural styles came out of the Arts and Crafts movement, including the popular Craftsman and Bungalow-style homes, simple, thoughtfully made structures originally designed for working class families.
Arts and Crafts-style homes are symmetrical; low to the ground; designed for efficiency and minimal upkeep; often feature large fireplaces; low-pitched roofs with wide overhangs; exposed interior beams; built-in bookshelves, window seats and cabinets; and multiple windows with small panes; prominent porches; and open floor plans.

-
08 of 15
KenWiedemann / Getty Images
Cape Cod architecture is named after the Massachusetts coastal region where it is the signature style. Homey and effortlessly appealing, Cape Cod houses have simple, timeless clean-lined silhouettes, with elements such as oak and pine wood post and beam framing and wood flooring; brick fireplaces; and clapboard or cedar shake roof and side shingles.
English colonists in the 17th century first adapted English half-timber hall and parlor houses to suit the bitter New England climate, creating a boxier, lower slung silhouette to stand up to the elements. A second wave known as Cape Cod Revival in the 1920s to the 1950s helped popularize the style, which spread across the United States, and became an economical solution during both the Depression and the post-war housing boom of the 1940s and '50s. Even in super-sized 21st-century America, Cape Cod style homes retain a nostalgic popular appeal with new builds of all sizes today, from sprawling homes to tiny houses.
-
09 of 15
Blaine Harrington III / Getty Images
Originating in England during the Tudor period starting in 1485, Tudor architecture evokes storybook cottages and old-world charm. Tudor homes were built by craftsmen who combined Renaissance and Gothic design elements to create a transitional style that spread throughout England until it was supplanted by Elizabethan architecture in 1560. Tudor style was reborn in the United States in the 1890s and remained popular through the 1940s. Tudor homes feature signature half-timber detailing, long vertically placed decorative wood beams that create a two-toned exterior. However, Tudor Revival homes often eschewed this original Tudor look for red-toned brick with ornate detailing around windows, chimneys, and entryways.
-
10 of 15
QwazzMe Photo / Getty Images
Art Deco architecture is part of the Art Deco movement, an inventive design period in the U.S. and Europe in the 1920s and 30s that spanned the realms of fashion, art, homewares, and building styles throughout the Roaring Twenties and the Great Depression.
 The earliest examples of Art Deco architecture can be found in Paris, France, before the style spread to the United States in the 1930s, influencing the skyline of Manhattan forever with now iconic skyscrapers such as the Empire State Building, Rockefeller Center, and the Chrysler building.
The earliest examples of Art Deco architecture can be found in Paris, France, before the style spread to the United States in the 1930s, influencing the skyline of Manhattan forever with now iconic skyscrapers such as the Empire State Building, Rockefeller Center, and the Chrysler building. Art Deco buildings utilize materials like stucco, terracotta, decorative glass, chrome, steel, and aluminum. They feature ornate, geometric detailing such as chevrons, pyramids, stylized sunbursts or florals, zig-zags, and other geometric shapes. Many Art Deco buildings feature bright, opulent colors accented with contrasting black, white, gold or silver. And they often feature fragmented triangular shapes; decorative, geometric windows; parapets and spires.
-
11 of 15
Solidago / Getty Images
Modern architecture refers to the style of architecture that flourished in the early to mid 20th century. Rejecting the ornamental styles of the recent past, modern architecture favors clean lines; functional design; open floor plans; built-in storage; a focus on materials such as steel, concrete, iron, glass, wood, brick, and stone; and a focus on integrating architecture into the natural landscape while bringing the outdoors inside with the use of large windows to let in natural light and air.
Modern architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright redefined a new world of architecture with form follows function design, and a host of mid-century designers transformed the built landscape and the world of interior design with mid-century modern furniture that continues to be wildly popular today.
-
12 of 15
peterhowell / Getty Images
Brutalist architecture (1950s-1970s) is characterized by simple, block-like, hulking concrete structures (the term is a play on the French phrase for raw concrete, béton brut). With simple, graphic lines, a heavy appearance, a monochromatic palette, and a lack of ornamentation, Brutalism is a bold, in-your-face and eternally polarizing style. An offshoot of modernism, brutalist architecture became a popular if perennially controversial choice for institutional buildings around the world before fading out in the 1980s, giving way to the postmodernism and today’s contemporary styles. But the style's influence can be seen in contemporary product and interior design, furniture, objects, and web design.
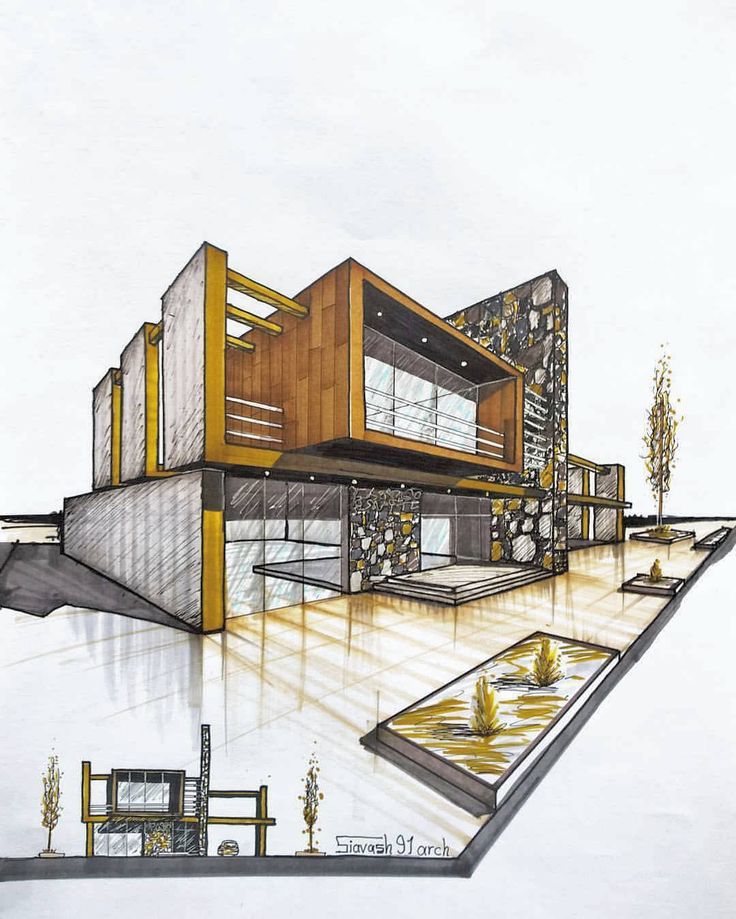

-
13 of 15
asbe / E+ / Getty Images
Contemporary architecture is a blanket phrase that comprises a range of present day building styles that often look radically different from one another and sometimes from anything that has come before. Contemporary architecture followed the modern period of the first half of the 20th century and the postmodern period through the 90s. Using innovative materials and building methods such as computer-generated curves, laser-cutting technology, and 3D printing, contemporary architects often embrace rounded forms, curved lines, unconventional volumes, asymmetry, and open floor plans. Sustainability is an important feature of contemporary architecture.
-
14 of 15
LIVINUS / Getty Images
Beaux-Arts architecture is a building style that emerged from Paris’ École des Beaux-Arts in the late 1800s and spread to the US during the Gilded Age. Beaux-Arts buildings are grandiose, theatrical, highly ornate buildings that are inspired by Roman and Greek classicism and inspired by French and Italian Renaissance and Baroque building styles, such as the Musée D'Orsay.

Notable American architects such as Richard Morris, HH Richardson and Charles McKim trained at the Beaux-Arts school in Paris, and Beaux-Arts style was embraced for major building projects in the US, such as the Library of Congress in Washington D.C. and prominent buildings such as Grand Central Terminal and the New York Public Library’s main branch in NYC. Beaux-Arts architecture faded around 1930 with the onset of the Depression rendering such over-the-top displays of opulence as out of touch and obsolete.
-
15 of 15
wiesdie / Getty Images
Italianate architecture refers to a particular 19th-century style of building that was inspired by 16th century Italian Renaissance architecture combined with picturesque influences that featured architectural elements from a romanticized past that broke some of the strict rules around formal classical architecture.
The Italianate style was born in 1802 when architect John Nash built the first Italianate villa in England, Cronkhill in Shropshire, and was promoted by the work of Sir Charles Barry in the 1830s.
 The style spread throughout Northern Europe, the British Empire and the US from the late 1840s to 1890. It was a hugely popular building choice used in both rural and urban settings in the US in the 1860s after the Civil War.
The style spread throughout Northern Europe, the British Empire and the US from the late 1840s to 1890. It was a hugely popular building choice used in both rural and urban settings in the US in the 1860s after the Civil War.
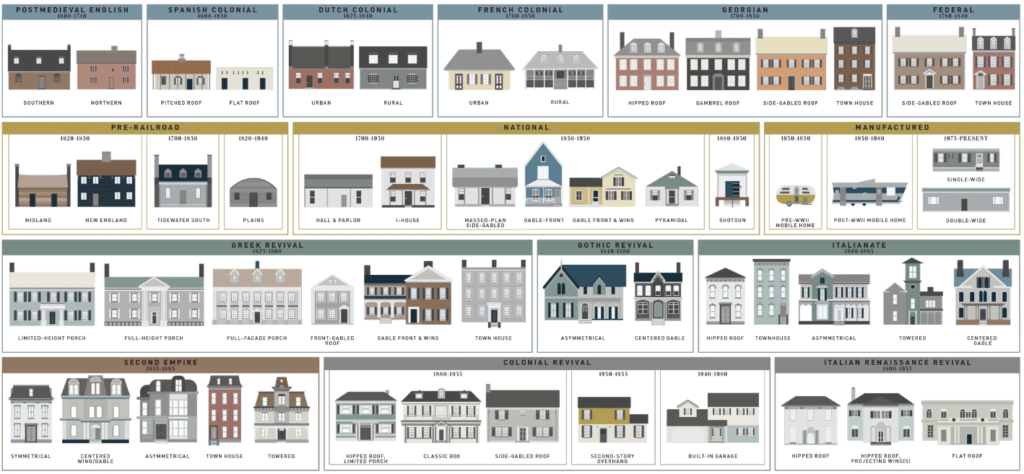
24 Popular Types of Architectural House Styles
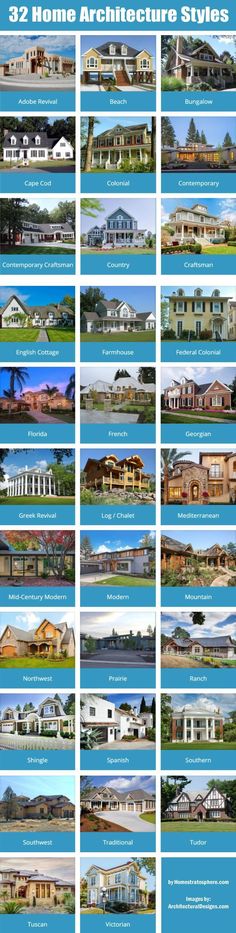
Most Recognised Architectural Styles - Barker Associates
The design of a building is one of the first things that will capture your attention. If a building is architecturally remarkable, it often becomes a landmark that defines a city and is visited by tourists from all over the world.
Memorable buildings often follow certain architectural styles that are immediately identifiable. Many of these design elements are still being utilised by architecture and design consultants adopting timeless principles of good design as an inspiration for their design projects.
Here are 8 of the most recognised architectural styles that have been applied in many popular structures around the globe.
Greek and Roman Classical Architecture
This type of architecture refers to the style that was prominently used in ancient Greece and Rome. This architectural style adhered to the concept of building structures utilising a set template. Classical architecture is often expressed by the temple, an oblong enclosure or surrounded by columns.
The Greek order of columns, Doric, Ionic and Corinthian, are some of the more identifiable elements of classical architecture. These guidelines were followed by Roman architects, with the Corinthian being the more favoured style used in many Roman buildings.
Some of the most popular examples of classical architecture are the Acropolis complex in Athens and the Colosseum in Rome.
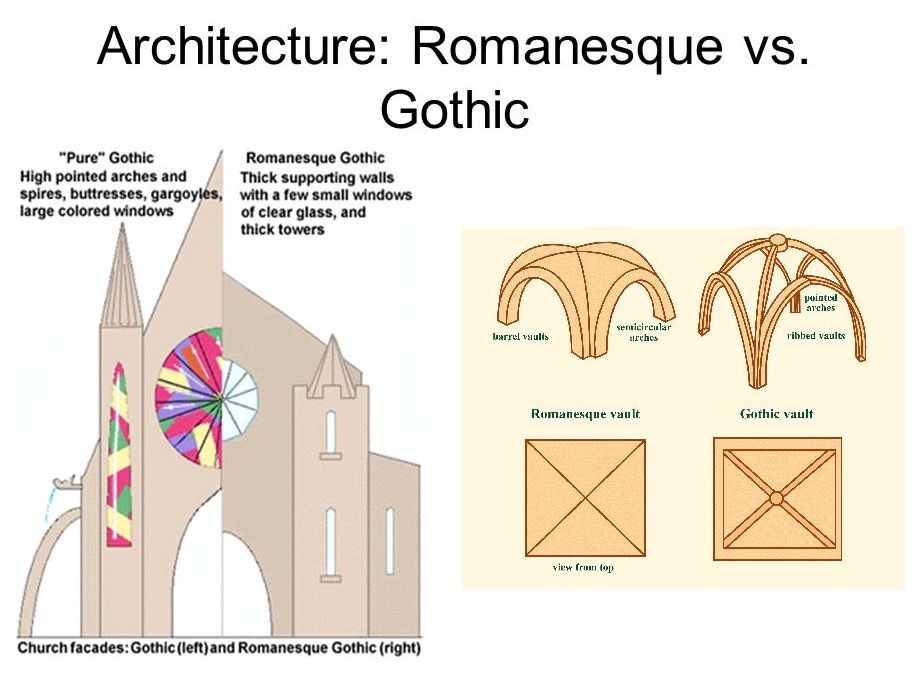
Gothic Architecture
Some of the most famous churches in Europe feature the Gothic style of architecture. This architectural type that dominated for hundreds of years began in France and was then adapted throughout the continent. This is a style of stonework/masonry building that is characterised by three main features: sharply pointed arch, ribbed and vaulted columns, and flying buttress.
This is a style of stonework/masonry building that is characterised by three main features: sharply pointed arch, ribbed and vaulted columns, and flying buttress.
One of the most famous examples of French Gothic architecture is the Notre-Dame in Paris, France. Other prominent examples of structures that used Gothic architecture are Canterbury Cathedral in England, Cologne Cathedral in Germany, Milan Cathedral in Italy, Basilica of St. Denis in Paris, and Salisbury Cathedral in England.
Baroque
This style of architecture originated in Italy and was said to be a more emotional and dramatic style designed to appeal to the senses. Baroque architecture usually includes curving forms such as ovals, as well as concave and convex forms that suggest motion. Distortion is also another key aspect in this style where you will see figures that are broken, elongated or manipulated to make them stand out.
Some of the examples of buildings with the Baroque style are the Palace of Versailles in France, St. Paul’s Cathedral in London, St. Peter’s Square in Vatican, and Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna.
Paul’s Cathedral in London, St. Peter’s Square in Vatican, and Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna.
Neoclassical Architecture
As the name suggests, Neoclassical architecture is the revival of Classical architecture. The style is very reminiscent of the Greek and Roman forms. This resulted in 18th-century buildings somewhat resembling Greek and Roman temples.
Neoclassical architecture is defined by clean, elegant lines, uncluttered appearance, free-standing columns and massive buildings. Some of the more popular examples are the Bank of England Building in Liverpool, the White House in the United States, and the General Post Office in Dublin.
This is not always necessarily true, and that’s why involving sustainability experts early in the design process is a critical decision. Working with a design team that understands the complexities, demands, and challenges of constructing a sustainable building will be able to better offer proven solutions that can deliver both the required environmental benefits and cost-efficiency.
For expert advice on sustainable architecture, contact Barker Associates to find out how they help your project.
Image Source: Brad Kahn on Flikr
Victorian Architecture
This style of architecture refers to buildings that were constructed during the reign of England’s Queen Victoria. Unlike other styles, Victorian architecture is not limited to a single particular design but is used as a broad term that saw the revival of Gothic, Romanesque, and Tudor elements.
The Victorian style was applied to residential house designs during the industrial revolution. Many homes in the UK, US, and Australia utilised this style. One characteristic that most Victorian homes share is the “dollhouse” look having elaborate trims, vivid colours, and asymmetrical designs.
Some of the more prominent Victorian buildings are the Palace of Westminster and Royal Albert Hall in London, Osborne House in the Isle of Wight, Balmoral Castle in Scotland, and Postcard Row in San Francisco, California.
Modern Architecture
This architectural style is an umbrella term that encompasses several different styles that became prominent during the first half of the 20th century. This is a minimalist style that was practised by many architects until after World War 2.
The modernist style prioritise simplicity of form, clean structure, lack of ornamentation, and function over form. This style also took advantage of the advances in steel, glass and concrete. Some of the best known architects of the 20th century flourished during this era including Frank Lloyd Wright and Le Corbusier.
It follows that some of the most iconic examples of Modern architecture include Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater house in the United States, Le Corbusier’s Villa Savoye in France, and Ludwig Mies van Der Rohe’s Neue Nationalgalerie in Berlin.
Image Source: trendir
Post-Modern Architecture
As a reaction to the austerity and rigidity promoted by Modern architecture, the Post-Modernist architects launched this design movement in the 1960s. The post-modern designs incorporated artistic ornamentation and decorative elements into the building’s façade as opposed to just the clean lines upheld by modernist styles.
The post-modern designs incorporated artistic ornamentation and decorative elements into the building’s façade as opposed to just the clean lines upheld by modernist styles.
The Post-modernist style refused to be boxed to just one type so designs often drew inspiration from a mix of architectural styles. For some buildings, this combination often resulted to a somewhat hybrid and whimsical design.
The Vanna Venturi House in Pennsylvania, USA designed by Robvert Venturi is one of the first prominent structures of the post-modern architecture movement. Two famous structures designed by architect Frank Gehry, the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain and the Dancing House in Prague are also notable examples. In the UK, the SIS Building and the No 1 Poulty in London are some examples.
Neofuturist Architecture
Neofuturism is an architectural style that is seen as a more idealistic approach to the future. The designs increasingly take advantage of new technologies to build seemingly impossible forms and innovative structures that have never been done before.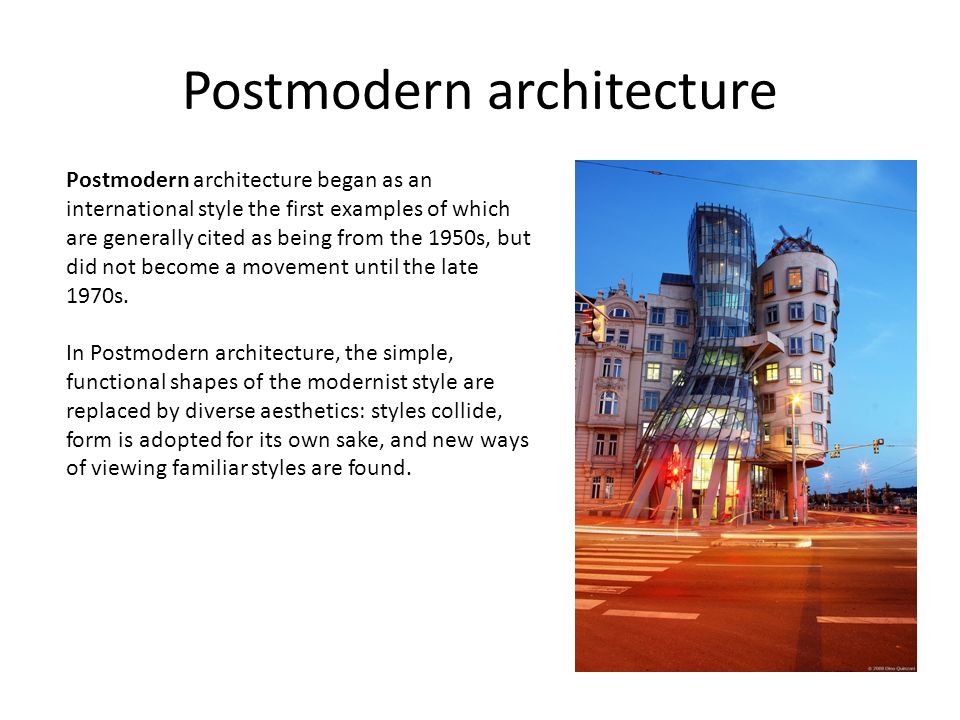 Neofuturist architecture is identified with structures that seem to defy natural physics which were only previously seen in sci-fi movies.
Neofuturist architecture is identified with structures that seem to defy natural physics which were only previously seen in sci-fi movies.
One of the best-known architects of Neofuturist architecture is ground-breaking Iraqi-British architect Zaha Hadid. In 2004, she was the first female architect to be awarded the Pritzker Prize in Architecture which was considered the Nobel Prize in the architecture world. She was also a two-time recipient of the Riba Stirling Prize- the UK’s most prestigious architecture award.
Hadid, who passed away in 2016 at the age of 65, was known for her distinctive projects including The New Riverside Museum in Glasgow, Serpentine Sackler Gallery in Hyde Park, the 2020 Tokyo Olympic Stadium in Japan, the 2022 FIFA World Cup Stadium in Qatar, and the Heydar Aliyev Cultural Centre in Azerbaijan.
Image source: Zara Hadid
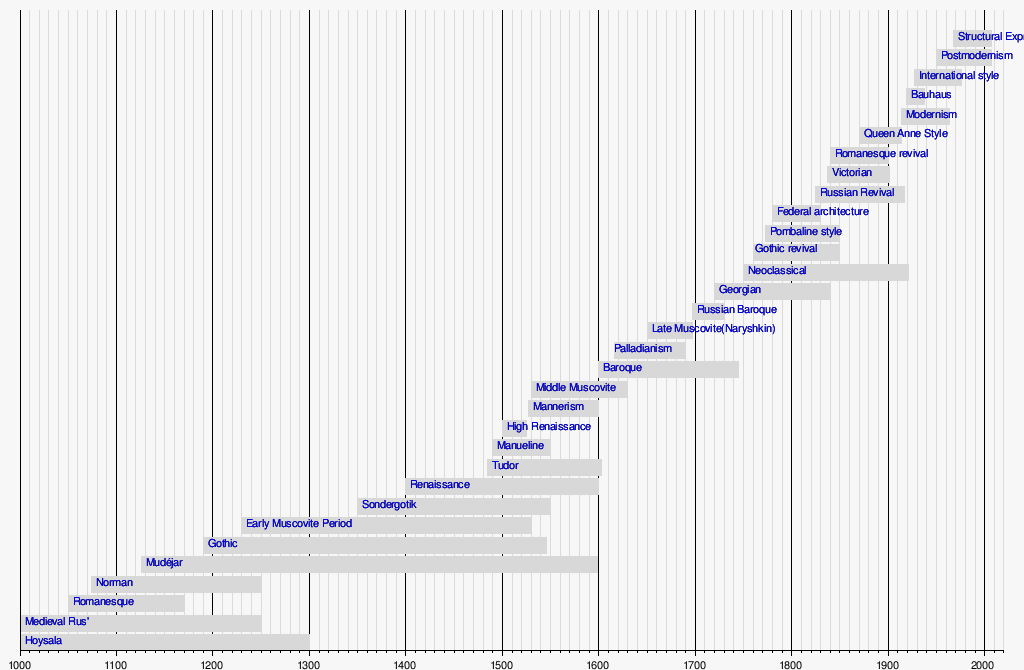
Architectural styles in chronological order
Architectural styles in chronological order, starting from the time of the Ancient World, have been sorted for you. We wrote a few words about each, added examples, photos, videos to make everything easy to understand. At the end of the article is a short list of architectural styles to make it easier to imagine the development of this area of art.
We wrote a few words about each, added examples, photos, videos to make everything easy to understand. At the end of the article is a short list of architectural styles to make it easier to imagine the development of this area of art.
Contents
Styles in architecture and their features
Architectural styles are formed features and properties of a historical period, region or country that are manifested in the distinctive features of buildings and compositions, such as:
- purpose of buildings (temples, palaces, castles),
- structures and materials used in construction,
- composite receptions,
- lines and facade design,
- plans,
- forms used.
Various styles arise in the specific conditions of the development of the economy and social structure. They are affected by:
- religious movements,
- statehood,
- ideological component,
- historical methods of architecture and
- national differences,
- climate,
- landscape and relief.
Technical progress, ideological changes or geopolitical relations have always led and continue to lead to the birth of a new style.
Architectural styles of the archaic period
Ancient Egyptian style
This style has given rise to a great variety of architectural structures and great monuments. The architecture of ancient Egypt, including the palaces, temples in Luxor and the pyramids on the Nile River, is evidence of the existence of one of the most outstanding civilizations in the world. The predominant building materials are sun-baked brick, limestone, sandstone, and granite.
Architecture of Ancient Egypt: Pyramids of GizaUnderstanding of the ancient Egyptian style by modern people is based on the preserved religious temples and massive, incomprehensible structures, with characteristic sloping walls with a small number of holes, surrounded by mystery. It is widely believed that these are tombs, but there are other theories. Learn more about architecture
- Ancient Egypt,
- Egyptian pyramids,
- temples.

Architectural styles of antiquity
Antiquity is Ancient Rome plus Ancient Greece.
Ancient Greek style
The Greeks built many temples for sacrifices to the gods. They laid the foundation for European architecture, which served as an example for the whole world. Their high-tech systems for proportion and style, using mathematics and geometry, created external harmony and beauty. Replacing wood with white marble and limestone back in the archaic era, the Greeks built noble and durable buildings. Can be divided into the following periods:
- Archaic,
- Classical,
- Hellenistic.
The periods of architecture of Ancient Greece are marked by the birth of three styles: Doric, Ionic and Corinthian.
- In the archaic - Doric and Ionic.
- Corinthian was added during classical times.

- Hellenism uses all three.
Read a brief overview of the architectural styles of Ancient Greece.
Ancient Roman style
Ancient Roman architecture is a form of Etruscan architecture. This style is characterized by greatness, power and strength. The Greeks had a strong influence on it. It is distinguished by monumentality, a lot of decorations and magnificent decoration of buildings, strict symmetry.
The Romans built most buildings for practical purposes, not temples, as in Greece. Read about the architecture of Ancient Rome briefly. The history, applied materials, technologies and urban planning are described. nine0003 Ancient Roman architectural style: Pantheon, Santa Maria in Via lata, Rome, Italy
Byzantine style
The capital of the Roman Empire was transferred by the Roman emperor Constantine I to the city of Byzantium (Constantinople) in 330 and became known as New Rome . Naturally, in the architecture of Byzantium, one can see a strong influence of the ancient Roman style. At the same time, in terms of elegance and luxury, she sought to surpass the old Rome.
At the same time, in terms of elegance and luxury, she sought to surpass the old Rome.
Byzantine style is a fusion Christian and ancient worldview with elements of the artistic culture of the East .
The empire expanded its territories at the expense of the former provinces of Rome in the west, where it erected monuments, palaces, temples, churches in order to show luxury and establish the status of the new imperial power.
- Buildings have become geometrically more complex.
- In addition to stone, brick and plaster were used to decorate the buildings. nine0014
- There is a looser attitude towards classical elements; carved decorations were replaced by mosaics.
- The simplicity and restraint of the exterior of the temples contrasted sharply with the magnificent precious mosaics sparkling with gold inside.
Read briefly about the development of Byzantine architecture with examples and photographs.
Pre-Romanesque architectural styles
Pre-Romanesque or Pre-Romanesque architecture covers 9 times0003
- Merovingian (5th - 8th centuries),
- Carolingian (8th - 9th centuries) and
- Ottonian (10th century) until the beginning of the 11th century, when the Romanesque style was born.
The main theme in this period is classical Mediterranean and early Christian forms in interaction with Germanic ones. They contributed to the emergence of new innovative designs. This, in turn, gave rise to the Romanesque architectural style.
Merovingian style
Merovingian architectural style: Cathedral of Saint-Leons, Fréjus, France The period of the distribution of this style falls on the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries, when the Frankish royal dynasty of the Merovingians ruled the lands belonging to modern France, Belgium and partly Germany. This is the time of the baptism of the barbarians. Combines the traditions of the late antique Roman style and barbarian traditions.
Carolingian architecture
Pre-Romanesque architecture: typical Carolingian church in northern France Nova CorbeiaThe Merovingian era was replaced by the Carolingian era (780-900).
After becoming emperor, the German king Charlemagne wanted his empire to be as great as Rome before him. He sponsored art and financed building projects, mainly cathedrals and monasteries. Many of these buildings also served as schools as Charlemagne sought to create a large literate base for his empire.
Trying to consciously imitate Roman architecture, the Carolingian style borrowed many elements from early Christian and Byzantine architecture. nine0003
Ottonian style
Ottonian Church of Saint Cyriacus (960 - 965), Germany The Ottonian period follows the Carolingian period and precedes the emergence of Romanesque architecture. Surviving examples of this style are found in Germany and Belgium. The Ottonian Renaissance (951-1024) originated in Germany during the reign of Otto the Great and drew inspiration from the Carolingian and Byzantine eras.
Respect for the mathematical sciences is expressed in the balance and harmony of the building elements. Most Ottonian churches make generous use of the round arch and have flat ceilings. The exterior of most basilicas resembles the Carolingian style, while the interior is early Christian. nine0003
Romanesque
Romanesque buildings were built in Europe from around 1000 until the arrival of the Gothic style in the 12th century.
This style contains many of the main features of Roman and Byzantine architecture.
It personifies the construction of fortified castle cities with powerful walls, narrow windows and defensive ditches around the fortifications, where bridges and city gates were guarded by guards, streets were blocked with chains at night.
The castle was usually built on a hill, which was of strategic importance for defense and surveillance. Shelter towers served as decoration of the composition. Their shape could be round, four- or hexagonal with a pointed roof. The rest of the buildings of unpretentious geometric shape were located around it. nine0003
The rest of the buildings of unpretentious geometric shape were located around it. nine0003
Romanesque style can be seen most vividly in temples connected to such towers, having semicircular doorways and windows. Galleries and outer walls of churches were decorated with decorative pillars connected by small arches.
Romanesque buildings look solid, solid and harmonious against the backdrop of the surrounding nature.
Romanesque Church of San Millan, Segovia, SpainGothic style
The Romanesque style evolved from the Gothic style with soaring spiers, pointed arches and religious carvings. This style originated in northern France in the 12th century. It has become widespread in Austrian, German, Czech, Spanish, English cities. nine0003
It took root in Italy with great difficulty and strong changes, which marked the beginning of the "Italian Gothic". At the end of the 14th century, this architectural style was transformed into the so-called "International Gothic".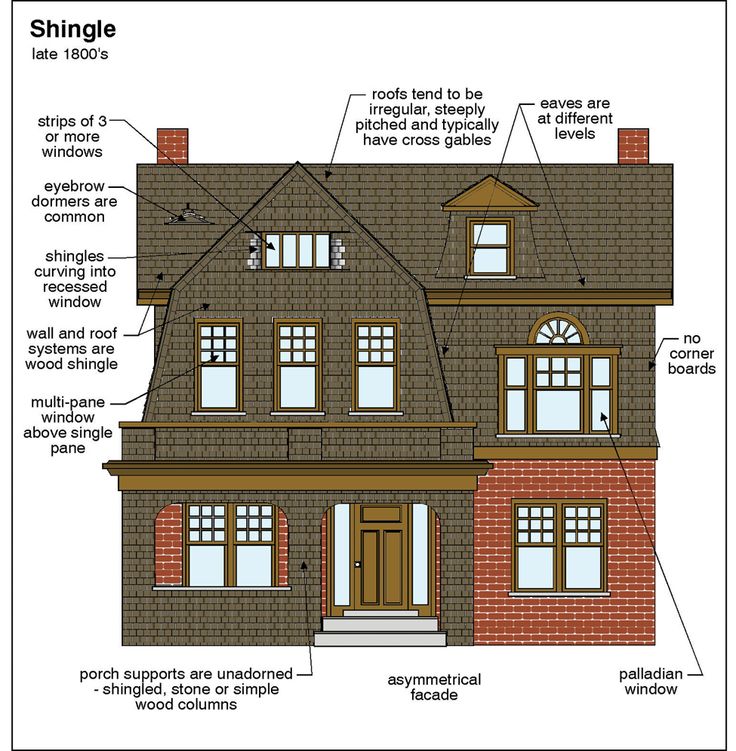
For those interested in more details in the article Gothic style in architecture. The article Gothic Cathedrals of the Middle Ages describes 6 of the most striking examples of Gothic in Europe. An example of radiant Gothic is given in the article on Cologne Cathedral.
Renaissance or Renaissance architectural style
The Renaissance began in Italy and spread throughout Europe. The humanistic orientation of the period 1425 - 1660 was characterized by attention to human activity, and a revival of interest in antiquity.
In architectural buildings this is reflected in the arrangement of columns, pilasters and lintels. Asymmetrical medieval features are replaced by semi-oval arches, hemispherical domes and niches (edicules). Ancient forms are returning to architecture again. nine0003
In the Renaissance there is a fusion of Gothic and Romanesque styles.
After the crisis of ideas in the 16th century, the Renaissance is replaced by Mannerism and Baroque.
Mannerism
The style replaced the late Renaissance with unstable moral, social and religious phenomena. In architecture, he expressed himself through the violation of the Renaissance balance, elements of the grotesque, the use of conceptual solutions that can cause a feeling of anxiety. nine0003 Example of Mannerism: Palazzo Massimo alle Colonne, Rome, Italy
Some art historians call it early Baroque. Origins: Florence, Rome and Mantua in Italy (it. maniera - manner). But most importantly, it became a reflection of the transformation of medieval art in modern times.
Baroque
The Baroque style was born by the Italian architects Borromini and Bernini. Its appearance at the end of the 16th century marks the era of the Late Renaissance. Also called the ornate development of the Renaissance. nine0003
This style was opposed to rationalism and classicism. His task was to create an impression of wealth and power. Find out what architectural illusions in the Vatican are created by architects.
His task was to create an impression of wealth and power. Find out what architectural illusions in the Vatican are created by architects.
It is characterized by large colonnades, an abundance of various sculptures and pilasters, the presence of telamones (atlantes), caryatids and mascarons (full face of a human or animal head). It is marked by multi-tiered complex domes (St. Peter's Cathedral, Rome).
Beloved by the Catholic Church (see Birthplace of the Vatican), the Baroque style is quickly becoming popular with the Spaniards and the French, the Germans and the Netherlands, the Russians and the Poles. It is also accepted in South America. nine0003 Baroque style in the architecture of Rome, Italy
Read also How Baroque was born on the Zen channel Architecture.
In the article Baroque style in Europe, the most striking examples in different periods of development of the direction, from early to late, are briefly considered.
You can find out very briefly about the features and history of the development of the Baroque in Europe on the Zen Architecture channel by clicking on the link.
At the end of its development, the baroque thinned into rococo.
Rococo
The birthplace of this style is France, where it appeared at the beginning of the 18th century. Rococo is distinguished by lightness, friendliness, playfulness. Architecture completely arbitrarily combines and distributes the parts of the structure, without thinking about the forms and their expediency. There is no strict symmetry, but there is an endless enumeration of numerous details of the ornament and their division. nine0003
The complete lack of rationality in dealing with the arrangement and harmonious combination of elements, capriciousness, refinement and burdened forms on the Rococo monuments make them original and sloppy. The masterpieces of Rococo architecture in Italy, Germany, England have their own differences. They remind us of the times when powdered wigs, flies, blush and white were in fashion.
Helbling House in Innsbruck, Austria. Photograph by James Davies/Corbis Read more in Rococo in Architecture: What You Need to Know. nine0105 Rococo masterpieces in Italy are briefly described on the Architecture Zen channel, and there is also a description of the Rococo monuments in England and in the architecture of Germany.
nine0105 Rococo masterpieces in Italy are briefly described on the Architecture Zen channel, and there is also a description of the Rococo monuments in England and in the architecture of Germany.
Architectural styles of classicism
At the end of the Renaissance Palladio and Scamozzi (Italian architects) expressed in architectural language the direction of classicism . The basis of the classical style: rationalism and the use of only functional details.
Architect A. Palladio. Villa La Rotonda, Vicenza, Italy. Classical style in architectureDue to the adherence to strict canons, the buildings are distinguished by
- correct planning,
- clear forms,
- symmetrical compositions and
- restrained decoration.
The aestheticism of classicism was supported by large-scale urban development projects, which resulted in the ordering of urban buildings.
In different countries this trend manifests itself with some peculiarities.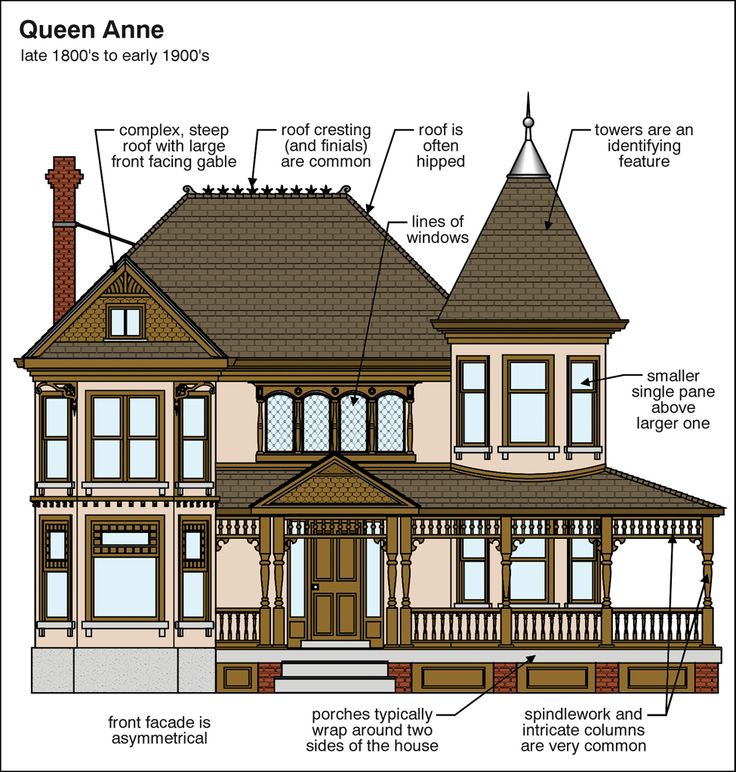 Italy, France, England, Germany, USA expressed the classics as:
Italy, France, England, Germany, USA expressed the classics as:
- Palladian or early classicism,
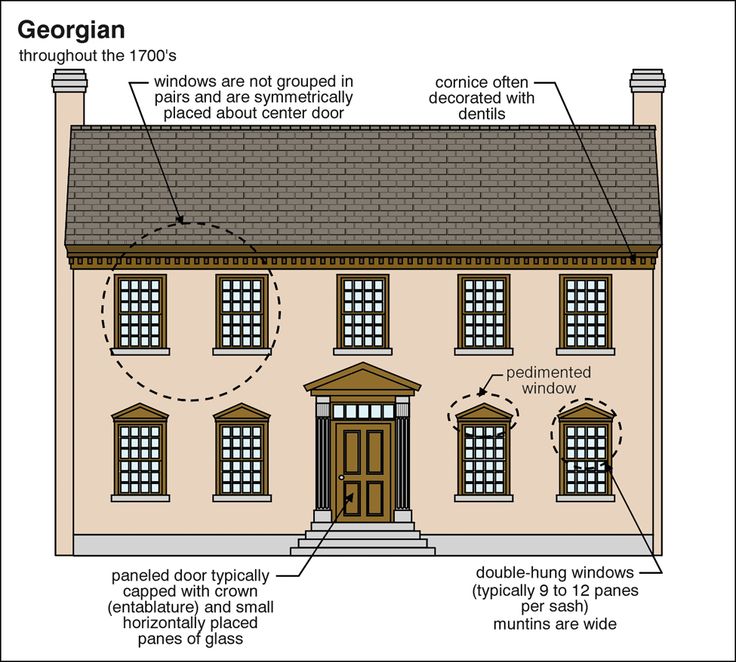
- Georgian architecture,
- Empire style,
- Regency,
- Biedermeier,
- Federal architecture.
The article Classicist Architects in England traces the evolution of architectural styles in this country.
Classicism means "exemplary". The Rational Methodology of the European Philosopher René Descartes (1596 - 1650 years) "from simple to complex" found expression in the architectural masterpieces of the classical style of buildings of the 17th - 19th centuries.
The architectural styles of this direction are described in more detail in the article "Classicism in architecture".
Styles of Historicism in Architecture
This direction tends to consciously recreate the forms and content of the historical styles of architecture of the past. It can simultaneously combine several old trends and introduce new elements. This is, in a way, a smooth dissociation from classicism, the time of eclecticism in architecture. nine0003 Sint-Petrus-en-Pauluskerk, Ostend, Neo-Gothic, 1899 - 1908 Belgium
It can simultaneously combine several old trends and introduce new elements. This is, in a way, a smooth dissociation from classicism, the time of eclecticism in architecture. nine0003 Sint-Petrus-en-Pauluskerk, Ostend, Neo-Gothic, 1899 - 1908 Belgium
It includes
- subjective interpretations of Neo-Gothic and Neo-Renaissance with elements new to them,
- combinations with Neo-Moorish or Byzantine styles,
- variations on a theme - neo-baroque
- and the theme of the Greek style - neo-Greek.
Historicism in Russia took shape in the "pseudo-Russian style".
A harmonious combination of forms of past styles is characteristic of pure historicism . It is inherent in late historicism to focus on the baroque period in the revival - neo-baroque.
Modern architecture, using this style in our time, has created another look, which is called Neo-historicism.
For a more complete description of the architectural styles of this period, read and see the articles "Historicism in Architecture" and "Eclecticism in Architecture".
Art Nouveau Architectural Styles
Although art historians in Great Britain unequivocally define Art Nouveau as a Victorian style, its birth heralded the beginning of the Art Nouveau era. And that was in 1861. nine0003
Art Nouveau (Art Nouveau)
This architectural style developed from the late 19th century to the mid-20s of the 20th century. The founder of Art Nouveau is the Englishman William Morris (1830-1896), a well-known leader of the Arts and Craft movement, and Pre-Raphaelite artists.
Despite the different names, "liberty", "art nouveau", "tiffany", "metro" and others, it is easily recognizable, because draws its inspiration from nature. Its main characteristic is ornaments filled with stylized motifs of plants and flowers, birds, insects, fish. nine0003
Smooth curved lines and shapes dominate; often there are female silhouettes and neoclassical elements. You can learn more about this style in the article Modern in architecture.
Art Deco (Art Deco)
This dynamic and bold continuation of Art Nouveau . Luxury is limited by strict regularity and lack of bright colors in the design. The main focus is the beauty of the material. Art Deco gained international recognition in the 1930s and 1940s. 1930-1937 Art Deco gently flows into Rational Modern. This style emphasizes curved, horizontally elongated forms and elements of ship architecture. Industrial designers stripped Art Deco of ornamentation in favor of clean lines, sharp angles were replaced by aerodynamic curves, and exotic woods and stone were replaced by cement and glass. nine0003 Pharmacy Building, Kansas City, Missouri, USA, Art Nouveau. The global movement in architecture and design of the 20th century, which united the emerging architectural styles based on innovations in building technology, new materials, reinforced concrete, steel and glass, was called international style . Characteristics: He rejects the ornamentation, the neoclassical approach to architecture and the Beaux-Arts (beaux-art), which means "delicate architecture", and favors the minimalism of . Basic elements: In different countries, their features acquired their own sound. But the same principles are observed in all: There are no national cultural signs in the buildings, no decor, but there are glass and metal surfaces. International style covers modern trends in architecture such as: The architectural styles of this trend are discussed in more detail in the article Modernism in Architecture. An amalgamation of architectural trends that emerged in the 1960s as a reaction to austerity, formalism and a lack of diversity is postmodernism. His heyday was on 1980s. The recurrence of various principles contained mainly in the classical architecture of the past and their application to modern structures has given rise to the architecture of historical allusion (a stylistic device that alludes to something well-known). The search for uniqueness, the creation of new forms, the idea of harmonizing architecture in accordance with the environment are distinctive features in the work of postmodernists. The desire to maintain proportions and symmetry, to express the imagery of buildings, the introduction or revival of decor (bas-reliefs, murals) are actively used in exterior decoration. Since the late 1990s, it has been splitting into new trends in high-tech architecture, neoclassicism and deconstructivism. High Tec - high technologies. It arose in the 1970s on the basis of high-tech elements in industry and engineering. These changes have been made and implemented by style key architects Norman Foster and Richard Rogers since the 1970s. These strange, distorted, almost impossible buildings are actually part of a very specific, non-straightforward approach to design. By focusing on freedom of form rather than functional issues, the deconstructivists aim to impress the visitor by making their stay in their space memorable: the interior is just as captivating as the exterior. nine0003 This fragmented style is said to have developed out of postmodernism that began in the late 1980s. While postmodernism was returning to historical roots that modernism had shunned, deconstructivism rejected postmodern acceptance of such references and took a bold step towards extraordinary innovation in architecture. Green building seeks to minimize the negative impact of construction on nature. This current strives for a moderate and efficient use of materials, energy and space in order to organically develop the ecological system as a whole. nine0105 A key factor in green architecture: the use of environmentally friendly technologies and resources at every stage of construction, from idea and planning, ending with destruction. The 20th century architect F. L. Wright first used the term "organic architecture", formulated its principles and adhered to them in his works. He knew how to combine the desires of customers with the uniqueness of the environment. You can be convinced of this by getting acquainted with examples of the works of a talented master. nine0003 But no less (and perhaps more) organic is the architecture of another great architect, Antoni Gaudí. A new global style called Parametricism appeared relatively recently with the advent of affordable powerful computers and programs. Such design methods were widely used only in 90s of the last century. Galaxy SOHO[d] complex (2009-2012). Beijing, China. Architect Zaha Hadid (2008-2012) Photo: Rob Deutscher - Flickr, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=54734274 Dalian International Convention Center Building (2008-2012) ). Dalian, China. Architectural bureau Coop Himmelb(l)au, Austria. Photo: 準建築人手札網站 Forgemind ArchiMedia — https://www.flickr.com/photos/eager/14302092083, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=36644368 The style was named by the architect Patrick Schumacher in 2008. In his article "Parametricism - A New Global Style for Architecture and Urban Design", he points out that in this style all architectural elements should be parametrically linked into a system. In the second decade of the 21st century, parametricism began to claim a leading role among modern architectural trends. The first sprouts of parametricism can be seen in the architecture of Antonio Gaudí (beginning of the 20th century). Representatives of parametricism: Greg Lynn, Jan Kaplicki, Santiago Calatrava, Zaha Hadid, Kostas Varotos. nine0003 The future of architecture is inextricably linked to design automation. Architecture in its development crossed the threshold when all the necessary knowledge could fit in a person's head. Now you know the architectural styles in chronological order. What is missing from this list? nine0003 Author: Jelena Shilyaeva M.A. in History of Art, University of Glasgow Share your opinion about the article in the comments. Publications of the Architecture section Eldar Ryazanov in the film "The Irony of Fate, or Enjoy Your Bath!" somewhat exaggerated how similar Russian streets are to each other. However, there are buildings of the same architectural trends in many Russian cities. "Culture.RF" has compiled a short guide to the main styles that can be seen in almost any city in our country . St. Sophia Cathedral, Veliky Novgorod. Photo: Zazelina Marina / photo bank "Lori" Church of the Intercession on the Nerl, Vladimir. Photo: Yakov Filimonov / Lori photo bank Very few civil monuments of the 11th-17th centuries have survived, but churches from this period can be seen in cities over 400 years old. As a rule, these are rectangular buildings, the walls of which are oriented to the cardinal points. The churches are crowned with domes, the number of which can vary, the most common are one-, five-, nine- and thirteen-domed churches. For example, St. Sophia Cathedral in Veliky Novgorod has five domes, while the Church of the Intercession on the Nerl is crowned with one dome. But no matter how many domes a temple has, there is always one main one: it is raised on a special base - a drum. nine0003 Church of the Ascension, Kolomenskoye. Photo: panoramio.com Tent belfry, Kizhi. In the 16th century, domes were replaced by a purely Russian invention that has no analogues in church architecture in other countries: a tent is the completion of a temple in the form of a multifaceted pyramid, not a dome. It is likely that the appearance of tent architecture is associated with technical difficulties: many churches in Rus' were built of wood, and it is not easy to make a dome from this material. Later, this architectural feature spread to stone construction. To imagine a hipped temple, it is enough to recall the Church of the Ascension in Kolomenskoye and the hipped bell tower in Kizhi. nine0003 Winter Palace, St. Petersburg. Photo: Vitas / photo bank "Lori" Church of the Sign, Dubrovitsy. Photo: gooper.ru This architectural style came to Russia at the very end of the 17th century. The first buildings appeared in Moscow, then St. Petersburg was actively built up with baroque buildings. The Baroque style is easy to define: its main features are complex shapes and an abundance of decorations. Chinese Palace, St. Petersburg. Photo: Igor Litvyak / photo bank "Lori" Roller Hill, St. Petersburg. Photo: Igor Litvyak / Lori photobank In general, the Rococo style, popular in the second half of the 18th century, has much in common with the Baroque. The main differences lie in the details. Rococo buildings are richly decorated with sculptural decorations such as vases and flower garlands, masks or simply cute curls. There are few such buildings in Russia. These include the Chinese Palace and the Rolling Hill Pavilion in Oranienbaum. nine0003 Russian Rococo Tauride Palace, St. Petersburg. Photo: Ekaterina Ovsyannikova / Lori photobank Bolshoi Theatre, Moscow. Photo: Gennady Solovyov / photo bank "Lori" Classicist buildings can be found in many Russian cities. Russian Classicism See also: Cathedral of Christ the Savior, Moscow. Photo: strinplus.ru Tsaritsyno Estate, Moscow. Photo: Yuri Gubin / Lori photo bank Buildings in this architectural style, which appeared in the middle of the 19th century, are the most diverse. The main feature of historicism is the architect's appeal to the heritage of the past. House of the Singer company, St. Petersburg. Photo: spb-guide.ru Metropol Hotel, Moscow. Photo: liveinmsk.ru Art Nouveau buildings appeared in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The abundance of glass and iron, the use of mosaics and paintings on facades, unusual curved lines and asymmetry are all signs of modernity. The house of the Singer Company in St. Petersburg or the Metropol Hotel in Moscow are the most characteristic buildings in this style. House of Culture named after Rusakov, Moscow. Photo: Bala-Kate / photobank "Lori" Department store Mostorg on Krasnaya Presnya. Photo: Dmitry Danilkin / photobank "Lori" In the 1920s, the same revolutionary architectural style as the new government appeared in the Soviet state. Simple structures and lack of decor, glass and concrete - these were the avant-garde buildings. For avant-garde architects, the functionality of the building was important, not its aesthetic value. It is not surprising that, in addition to supporters, the style also had ardent opponents who called avant-garde buildings "concrete tumors" on the body of Moscow. So, for example, contemporaries appreciated the Melnikov House of Culture named after Rusakov. The Mostorg department store on Krasnaya Presnya, another well-known example of the avant-garde, was received more calmly. nine0003 Central Academic Theater of the Russian Army, Moscow. The main building of Moscow State University on Sparrow Hills, Moscow. Photo: Denis Larkin / Lori photo bank In Stalin's time, architects began to return to the classical heritage, although in a slightly different sense. The buildings of the 1930s and 40s were majestic and pompous - with columns and stucco, wall paintings and an abundance of decor with Soviet symbols. Columns are back in fashion. One of the interesting reflections of the classicism style in Stalin's time was the Central Academic Theater of the Russian Army in the form of a five-pointed star and the Main Building of Moscow State University on Sparrow Hills. nine0003 Typical architecture of the Khrushchev times. Photo: kp.ru Typical architecture of the Brezhnev era. Business center "Smolensky", St. Petersburg. Photo: mhi-russia.ru Together with the era of Stalin, the era of "architectural excesses" and monumentalism also ended. He does not reject neoclassicism, but welcomes modern technology and aerodynamic elements. Transforms the smooth lines of the previous style into geometry, angular ornaments and ethnographic patterns. Prefers expensive materials, such as rare woods, ivory, aluminum and silver. nine0003
He does not reject neoclassicism, but welcomes modern technology and aerodynamic elements. Transforms the smooth lines of the previous style into geometry, angular ornaments and ethnographic patterns. Prefers expensive materials, such as rare woods, ivory, aluminum and silver. nine0003 Modern Rational
Architectural styles of modernism

Modernism. Palace of Gustavu Capanema, Rio, Brazil Postmodern Architectural Styles
 They are characterized by bright colors, classical motifs, a variety of structures, materials and shapes. nine0003
They are characterized by bright colors, classical motifs, a variety of structures, materials and shapes. nine0003 High-tech in architecture
The concept of High Tech developed from British modernist architecture of the late 19th60s. Prefers lightweight materials and clean, smooth, impenetrable surfaces, often glass. Characterized by pronounced open steel structures, exposed pipes, ducts, etc., flexibility to create indoor areas and interiors. 
Deconstructivism
Deconstructivism is characterized
Green, organic architecture
 He was inspired by the forms observed in nature and transferred them to his creations. The Sagrada Familia is a prime example of this.
He was inspired by the forms observed in nature and transferred them to his creations. The Sagrada Familia is a prime example of this. Parametricism - a new look at architecture
 Instead of classic geometric shapes - lines, rectangles, cylinders and pyramids - parametric projects use fundamentally new dynamic elements based on
Instead of classic geometric shapes - lines, rectangles, cylinders and pyramids - parametric projects use fundamentally new dynamic elements based on
Architectural styles in chronological order: list
 - 4 in n. e.
- 4 in n. e.
Rate the article by selecting the desired number of stars below.
Take it to your wall in a social network so as not to lose it. Or bookmark (Ctrl+D). old Russian architecture, baroque, rococo, classicism, avant-garde.

Old Russian cross-domed architecture
Old Russian tent architecture
 Photo: streamphoto.ru
Photo: streamphoto.ru
Baroque
 Actually, the very term "baroque" in translation from Italian means "bizarre, strange." Examples include the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg and the Church of the Sign in Dubrovitsy in the Moscow region. nine0003
Actually, the very term "baroque" in translation from Italian means "bizarre, strange." Examples include the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg and the Church of the Sign in Dubrovitsy in the Moscow region. nine0003
Rococo
Classicism
 This architectural trend was widespread at the end of the 18th - the first half of the 19th century. Palaces and estates, theaters and even warehouses were built in the classical style. The key detail, by which one can easily identify a monument of the era of classicism, is the column. More precisely, a lot of columns. Also, buildings in this style are characterized by restraint, symmetry and laconic decor. Such, for example, are the Tauride Palace in St. Petersburg and the Bolshoi Theater in Moscow. nine0003
This architectural trend was widespread at the end of the 18th - the first half of the 19th century. Palaces and estates, theaters and even warehouses were built in the classical style. The key detail, by which one can easily identify a monument of the era of classicism, is the column. More precisely, a lot of columns. Also, buildings in this style are characterized by restraint, symmetry and laconic decor. Such, for example, are the Tauride Palace in St. Petersburg and the Bolshoi Theater in Moscow. nine0003
Historicism
 The past could be, for example, Byzantine - then neo-Russian style buildings appeared, like the Cathedral of Christ the Savior. It could have been Gothic - this is how the Tsaritsyno estate in Moscow was built. And it could be a reflection of the heritage of the Renaissance - like the Moscow and Leningrad stations. It is rather difficult to formulate the key external features of historicism: the buildings of this style are not similar. If you see a building that "wants to appear older than it really is" - this is probably a monument of historicism. nine0003
The past could be, for example, Byzantine - then neo-Russian style buildings appeared, like the Cathedral of Christ the Savior. It could have been Gothic - this is how the Tsaritsyno estate in Moscow was built. And it could be a reflection of the heritage of the Renaissance - like the Moscow and Leningrad stations. It is rather difficult to formulate the key external features of historicism: the buildings of this style are not similar. If you see a building that "wants to appear older than it really is" - this is probably a monument of historicism. nine0003
Modern
 nine0003
nine0003
Avangard
Stalinist Neoclassicism
 Photo: Aleshina Oksana / Lori photobank
Photo: Aleshina Oksana / Lori photobank
Typical architecture of the Khrushchev and Brezhnev times

Learn more