Period house styles
13 beautiful illustrations depicting the different types of British houses through the ages
The home is an important concept for the British, reflected in the famous saying "an Englishman's home is his castle".
Britain's homes have changed dramatically through the ages, in size, architectural design and features.
In light of this, Made.com have created an infographic, named Brits & Mortar, to reveal the variety of house types we have seen over the last 500 years. They acquired the help of historical architectural expert and author, Trevor Yoke, to discover some insightful knowledge about the historical background about each of the eras.
Which type of home do you live in? Take a look at the beautiful illustrations below to find out more about the various styles of architecture.
1. TUDOR: 1485 - 1560
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
Britain became more isolated after Henry VIII founded the Church of England and therefore was less influenced by architectural styles flourishing across continental Europe. In 16th-century Britain, housing was characterised by thatched roofs and exposed timber frames, and built largely with practicality in mind.
2. STUART: 1603 - 1714
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
In contrast to the times of Henry VIII, the Stuart era had Catholic leanings, which opened the country up to European influences again. Inigo Jones became the first architect to apply this style to buildings for the royal family. However, it would not be until after 1660 that this style would begin to transform housing. Households with more money were increasingly building houses from stone and brick, rather than timber.
3. GEORGIAN: 1714 - 1790
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
The Palladian style of Georgian homes was inspired by the designs of the 16th-century Italian architect, Andrea Palladio, and the work of Inigo Jones.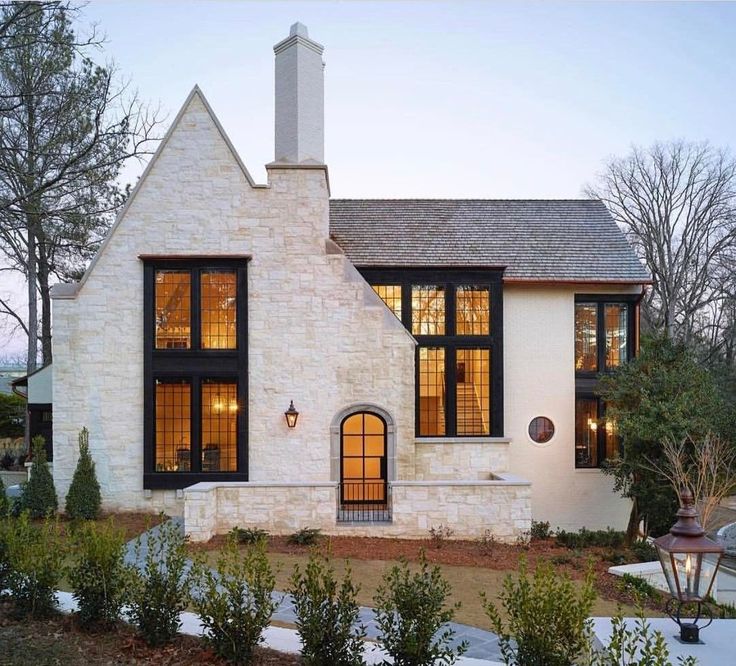 This period saw elegant homes with symmetrical facades and ornate decorations. Greek motifs also became very popular in the late 18th and early 19th century.
This period saw elegant homes with symmetrical facades and ornate decorations. Greek motifs also became very popular in the late 18th and early 19th century.
4. VICTORIAN: 1839 - 1900
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
During the Industrial Revolution, a Gothic Revival took place in architectural styles for the home. Augustus Pugin and John Ruskin were the key figures in this movement.
During the Victorian period, homes were designed asymmetrically, with pointed arches and patterns. Brick was the material of choice. Ornate designs and lavish decorations were a way for the growing middle classes to show off their wealth and status.
Though this era is seen as pivotal in terms of British architecture, most of the population lived in small cottages or houses.
5. QUEEN ANNE: 1880 - 1900
QUEEN ANNE: 1880 - 1900
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
The houses of this distinct epoch were famous for the Queen Anne Style which was inspired by the Dutch-designed buildings popular in Britain from the 1680s to1720s. Mostly popular in London, these homes featured timber hoods over the door, windows with glazing bars, and were reminiscent of old farmhouses. Terracotta tiles and panels, and rich red brick were common.
6. EDWARDIAN: 1900 - 1918
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
Edwardian homes were colourful and decorative with carvings and patterns, though not as showy as in Victorian architecture. Interiors became lighter and brighter in this era due to the arrival of electric lighting, which resulted in cleaner houses.
Many public buildings were built in the Baroque style of the late 17th century. The period also saw the Arts and Crafts movement take hold, which consisted of homes with timber framing, pebbledash, hanging tiles, white painted timber porches and balconies.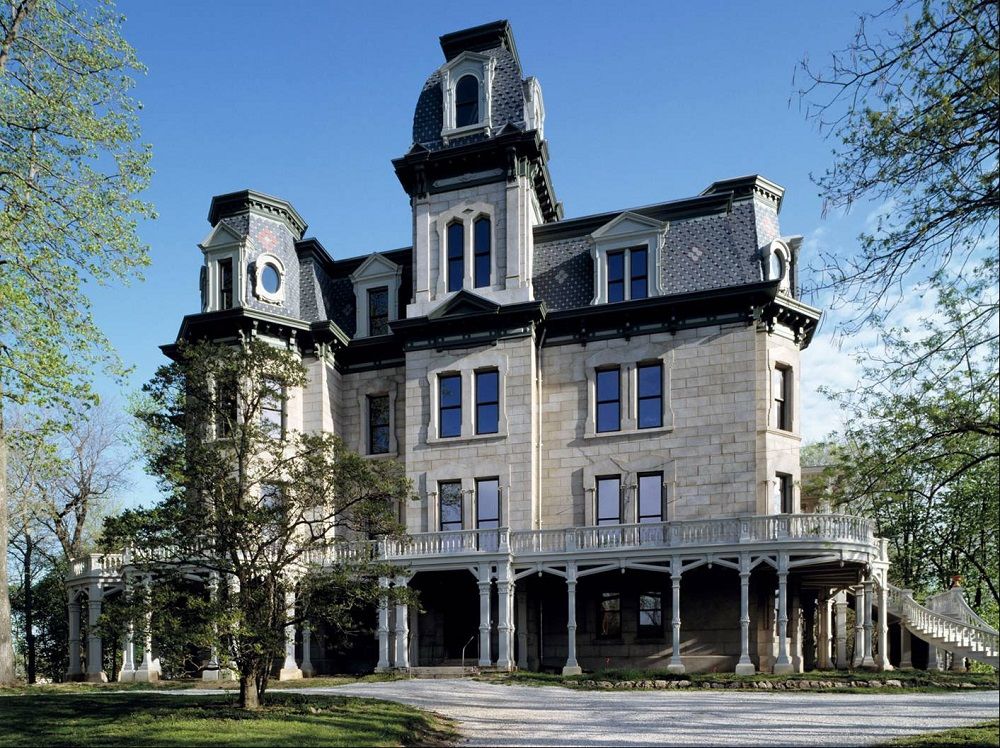
7. ADDISON HOMES: 1919
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
After the First World War, housing for working class families became a government issue, calling for affordable but decent living conditions. The designs were influenced by the Arts and Crafts movement and resembled countryside cottages.
When Christopher Addison, passed the 1919 Housing Act, homes were designed to allow lots of natural light into the house. The properties were also often organised along avenues, crescents and cul-de-sacs.
8. 30s SEMI: 1918 - 1939
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
A distinctive architectural style of this period consisted of homes with pebbledashed walls, recessed porches, and mock timber framing, inspired by the Arts and Crafts designs. The 1930s semi is one of the most common housing styles you see in Britain today and is recognised by a hipped roof and curved bay windows.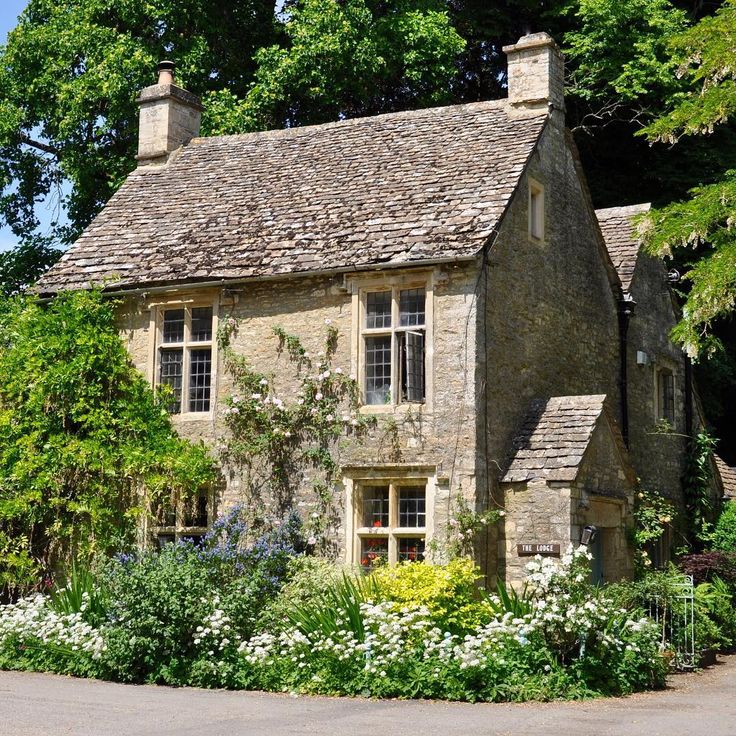
The countryside was becoming more accessible in this period due to increased railways and tram lines. The land running along these links was much more affordable than in the cities so many semi-detached properties were built here.
9. ART DECO: 1920 - 1940
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
The most fashionable Art Deco homes had several influences. Many of the architects within this era experimented with new materials and ideas. The designs had an emphasis on welcoming in sunlight, open interiors, flat roofs, plain white walls, and Egyptian style motifs.
10. AIREY HOUSES: 1940s
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
During the 1940s after the Second World War, materials were at a low and thousands of homes needed to be rebuilt. This led to houses being mass produced in factories, transported and set up on site.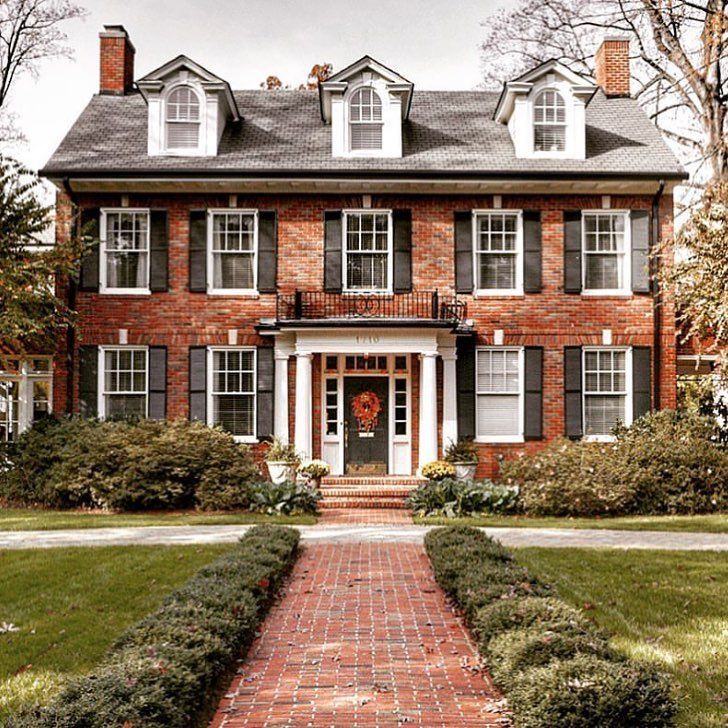 This included a design by Sir Edwin Airey. It focused on concrete columns and metal tubing, with smaller windows and plain glass.
This included a design by Sir Edwin Airey. It focused on concrete columns and metal tubing, with smaller windows and plain glass.
11. 70s TERRACE: 1970s
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
Affordable terraced homes became popular in the 60s and 70s. They had central heating, and often had a garage. The facades of these buildings were clad with traditional hanging tiles and weatherboarding to add more character.
12. 90s NEW BUILD: 1990s
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
By the 1990s, many Brits wanted their homes to have traditional features and rejected modernism. This meant that new builds often reflected older styles with mock timber framing, rendered walls and cottage features. Double glazing and insulation were also becoming standard parts to new homes.
13. MODERN MINIMALIST: Present day
MODERN MINIMALIST: Present day
Bear Grylls//Digital Spy
In our current day, modernist architecture has become popular once again. Eco-friendly and minimalist living are often sought after, resulting in homes that prioritise sunlight with solar panels, and are energy efficient, with open plan interiors, exposed steelwork and lots of glass.
British house styles across the ages
Your home is your castle, so the saying goes; and there’s no doubt that Britain has a rich architectural history. Houses here range in style from thatched Tudor cottages, right through to today’s new build, eco-friendly homes.
We’ve charted the ever-evolving architectural styles of British homes since the 1400s via a series of illustrations, which depict how British homes have changed over more than 500 years.
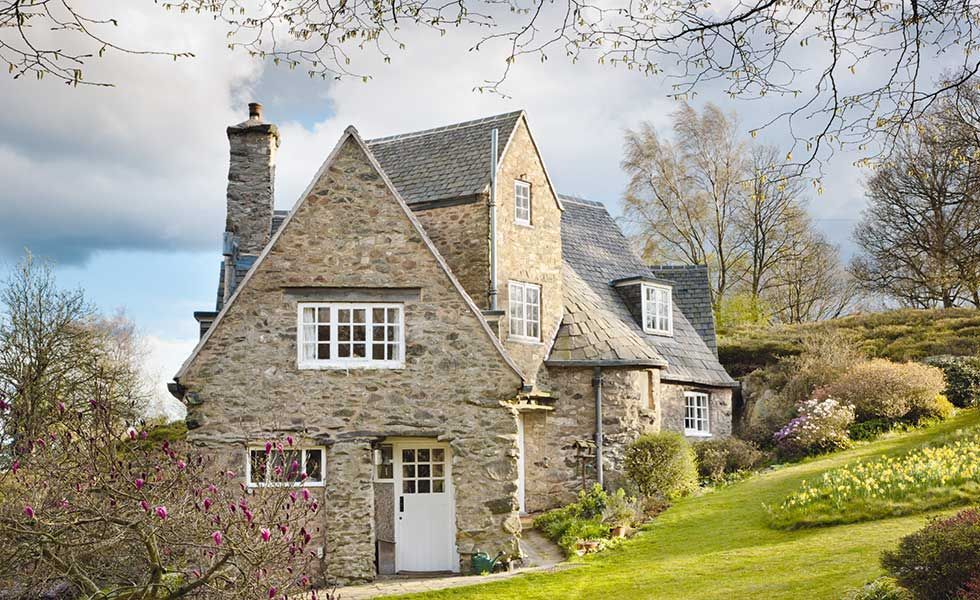
Tudor houses
1485-1560
When Henry VIII founded the Church of England, Britain was largely cut off from the architectural fashions of continental Europe.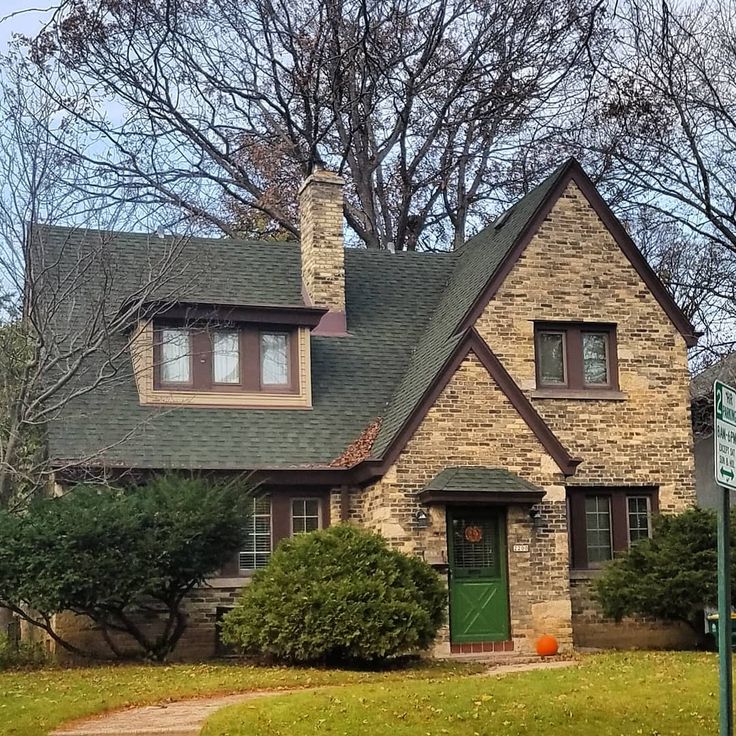 As such, the rebirth of classical art and architecture which was flourishing in Italy and France had little influence on 16th century British housing.
As such, the rebirth of classical art and architecture which was flourishing in Italy and France had little influence on 16th century British housing.
Characterised by their thatched roofs and exposed timber frames, and built largely with function in mind, the exteriors of these homes reflected the size and the use of the rooms within, and there was little concern for symmetry. As such, Tudor homes were not generally subject to much in the way of embellishment. Nevertheless, there were some exceptions: close studding (tightly set vertical timbers) denote wealth in the South and East of the country; and small square panels, (some with decorative patterns within), denote wealth in the West and North.
Explore Tudor houses:
- A careful restoration of a characterful Tudor cottage
Stuart houses
1603-1714
Unlike Henry VII, the Stuart Kings with their Catholic leanings were more open to the architectural fashions from Europe.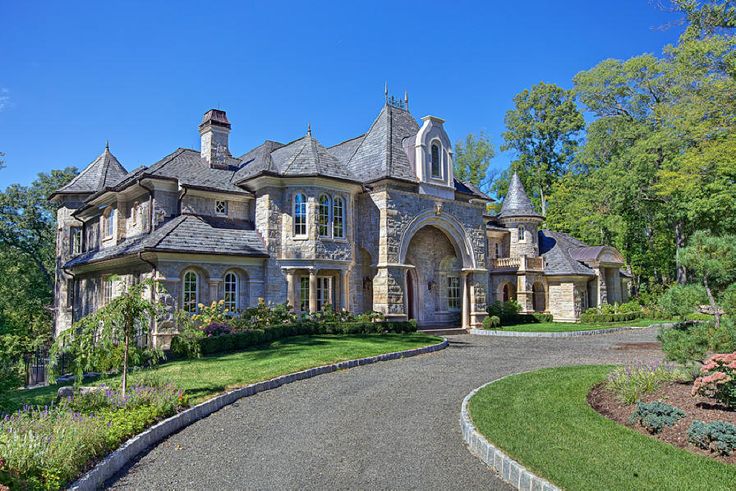 Inigo Jones became the first architect to apply this style to buildings for the Royal family. However, it would not be until after 1660 that this style would begin to transform housing.
Inigo Jones became the first architect to apply this style to buildings for the Royal family. However, it would not be until after 1660 that this style would begin to transform housing.
More like this
Timber framed homes were still popular with merchants and farmers in the countryside during this period, however, the homes of those who were better off were increasing built of stone and brick, particularly in Eastern and Southern counties; and two storey homes with a couple of bedrooms above two ground floor rooms became more common.
After William of Orange took the throne in 1689, Dutch houses with hipped roofs, deep white cornices and richly decorated hoods over the doors became increasingly fashionable.
You might also like everything you need to know a out listed buildings
Georgian houses
1714-1790
As the 18th century saw the beginnings of the Agricultural and Industrial Revolution, a new middle class rose, and London especially began expanding rapidly with Georgian style homes.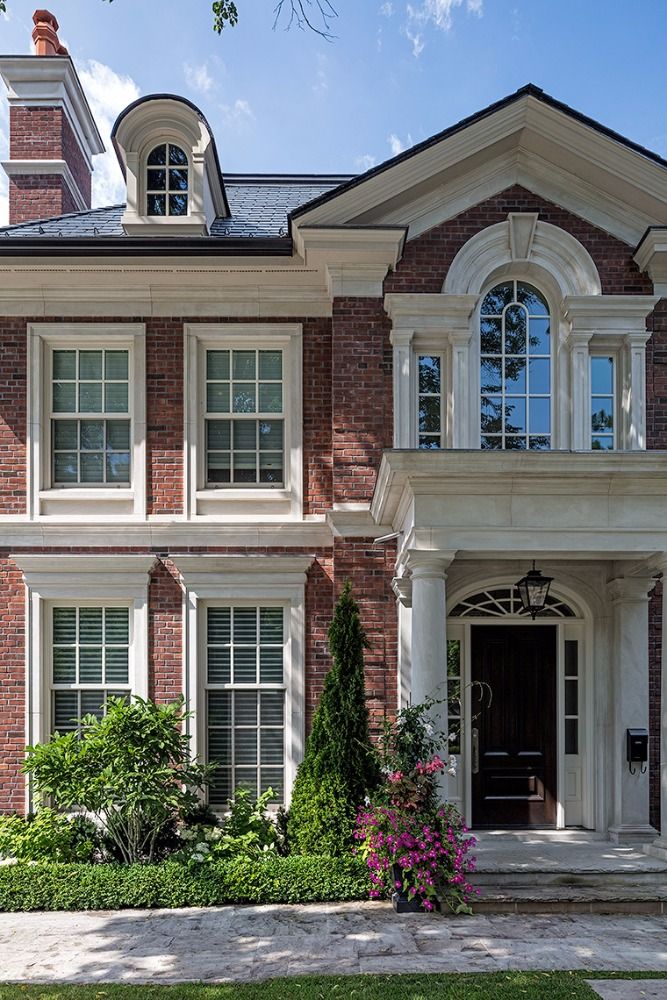
The Palladian style which they championed was based upon the designs of the 16th century Italian architect, Andrea Palladio, and the work of Inigo Jones. Symmetrical facades became a must for homes in this period and most urban homes and large houses were now double piled (two rooms deep). New discoveries of buildings in Ancient Greece from the 1760s made Greek motifs popular in the late 18th and early 19th century.
It is recognised as a period which featured refined, elegant buildings which unlike the Baroque era, was devoid of lavish decoration.
Explore Georgian houses:
- A careful restoration of a Georgian home on the coast
- Dennis Severs' house: inside a Georgian Christmas home
Victorian houses
1839-1900
With the rapid rise of the Industrial Revolution, Augustus Pugin and John Ruskin were the leading lights who promoted the Gothic Revival within domestic architecture.
Homes were designed asymmetrically, and brick once again became fashionable.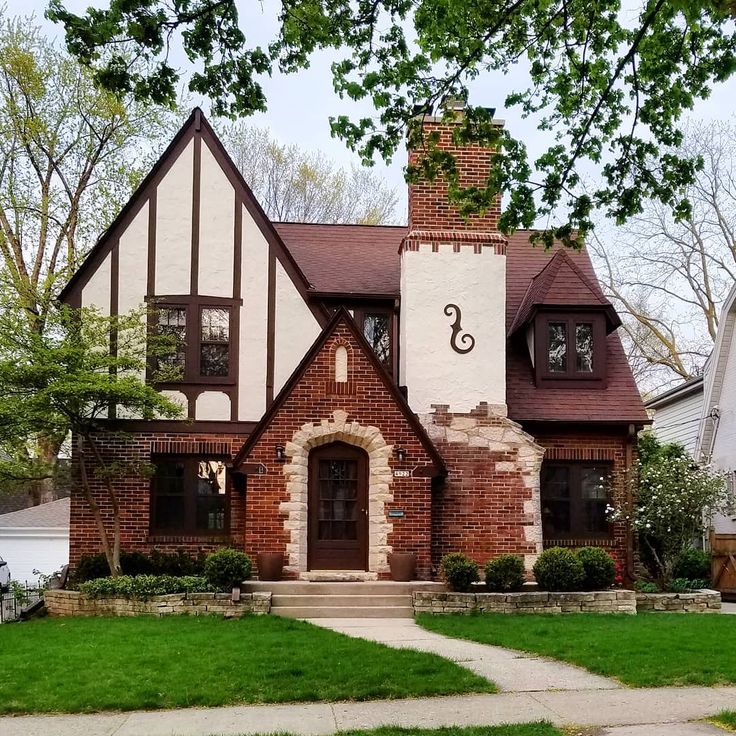 As the middle classes grew in size and wealth so they sought to display their status with lavish decoration and displays of colourful brickwork.
As the middle classes grew in size and wealth so they sought to display their status with lavish decoration and displays of colourful brickwork.
Victorian homes are frequently considered a defining attribute of British architecture, however during this period the vast majority of the working population continued to live either in small cottages or back-to-back homes recognised today as terraced houses.
Explore Victorian houses:
- Annie Sloan's colourful Victorian house
- A timeless renovation of a London Victorian home
- A Victorian property with vibrant vintage decor
- A moody Victorian flat filled with art and antiques
- Restoring and renovating a Victorian B&B
Queen Anne houses
1880-1900
After an era of pointed arches and busy patterns, architects began to tire of the Gothic Revival style and started studying old farmhouses and manor houses from the 17th century rather than medieval churches.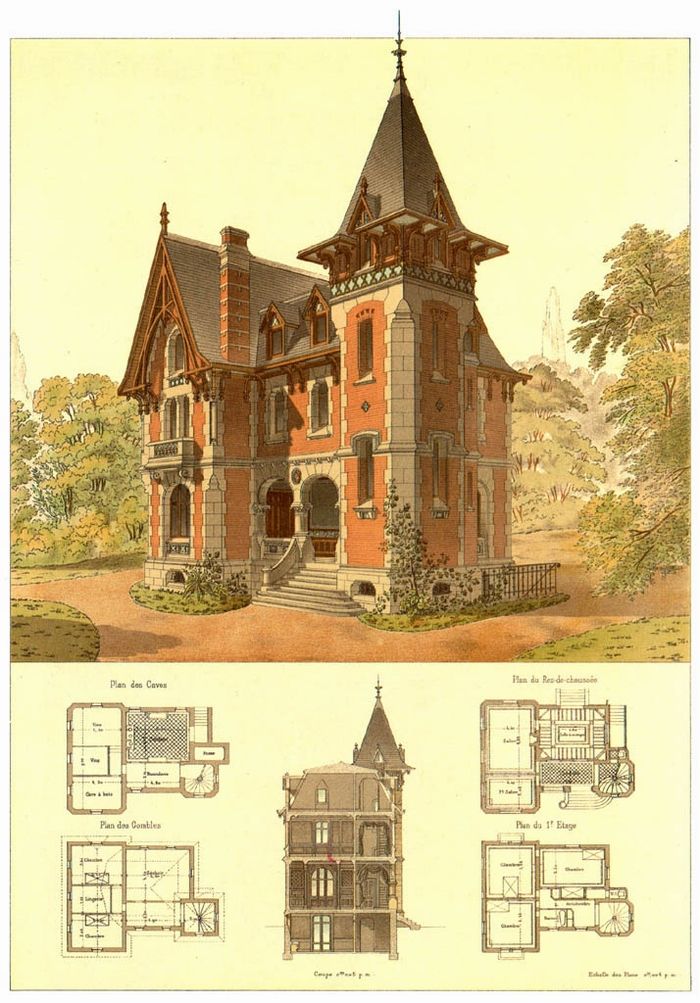
Architect, Richard Norman Shaw, popularised the Queen Anne style based on the Dutch influenced buildings which were popular in Britain from the 1680s -1720s (Queen Anne only reigned from 1702-1714). There was a strong resurgence in ‘Dutch’ gables; windows with glazing bars and timber hoods over the door. Homes were usually built with rich red brick, with windows and timber work painted white. Terracotta tiles and panels were also popular.
The Queen Anne Style was common particularly in London, and can still be found in neighbourhoods like Chelsea, Bayswater and Kensington today.
Explore Queen Anne houses:
- A stylish Scandi home filled with vintage finds
Edwardian houses
1900-1918
During the Edwardian era, the monumental Baroque style of the late 17th century was adapted for grand houses and public buildings.
As many rejected the mass produced goods of the industrial age, craftsmanship and traditional forms of building were revived.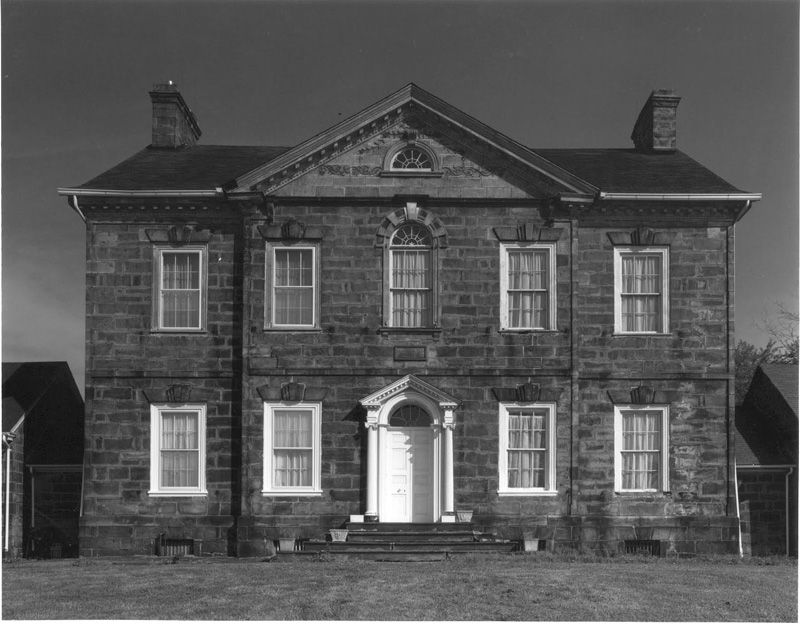 It was during this time that the Arts and Crafts Movement led to a rise in vernacular architecture and timber framing, pebbledash and hanging tiles could be found on most Edwardian terraces. White painted timber porches and balconies with intricate fretwork and balusters were also popular.
It was during this time that the Arts and Crafts Movement led to a rise in vernacular architecture and timber framing, pebbledash and hanging tiles could be found on most Edwardian terraces. White painted timber porches and balconies with intricate fretwork and balusters were also popular.
The exterior of Edwardian homes were still colourful and decorative but the patterns and carvings were generally more subdued than in the Victorian era. With the arrival of gas, and eventually, electric lighting, houses did not get as dirty, encouraging people to decorate with lighter, brighter wallpapers and curtains.
Explore Edwardian houses:
- An opulent Edwardian home filled with antiques and original features
- Discover a playful Edwardian home that mixes dark colours with vintage accessories
- John Sutcliffe's creative upcycled home
Addison Homes
1919
After the First World War, the government made its first attempt to improve housing for working class families.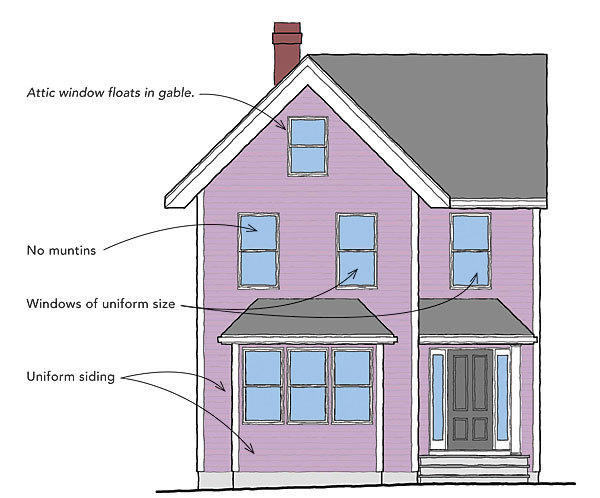 The Tudor Walters Report instigated in 1917 created plans for cheap housing which could be erected by local authorities. The designs were influenced by the Arts and Crafts movement and although they were devoid of decoration, their form and setting was designed to resemble rural cottages.
The Tudor Walters Report instigated in 1917 created plans for cheap housing which could be erected by local authorities. The designs were influenced by the Arts and Crafts movement and although they were devoid of decoration, their form and setting was designed to resemble rural cottages.
When Christopher Addison, passed the 1919 Housing Act, the first houses built used the Tudor Walters Report as a blueprint. They were designed to maximise the amount of sunlight entering the house, and the homes themselves were laid out along avenues, crescents and cul-de-sacs with open green spaces at the centre of estates. As the economy took a turn for the worse in the early 1920s, homes were reduced in size and designs were further simplified to lower building costs.
Art Deco houses
1920-1940
The most fashionable Art Deco homes, designed by leading architects, were influenced by a number of sources. The discovery of Tutankhamun’s tomb in 1922 created an interest in the forms and decoration of ancient Egypt.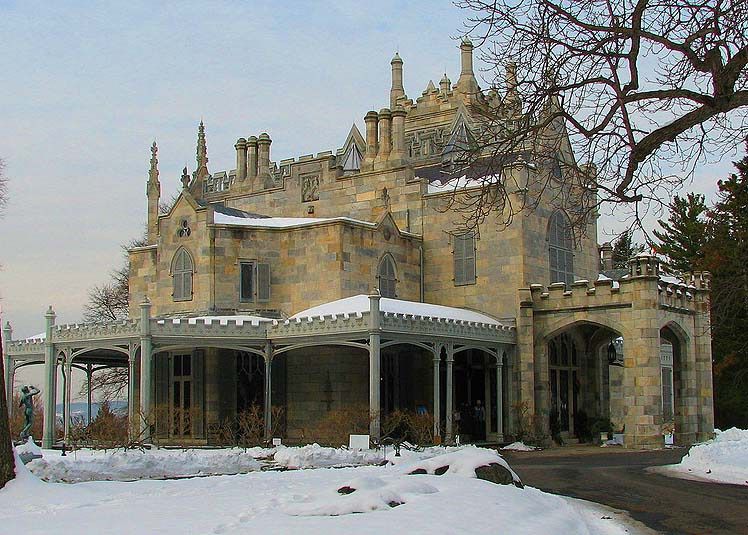 At the same time, many architects were experimenting with new forms which rejected historicism and embraced the structural possibilities of new materials like concrete and steel.
At the same time, many architects were experimenting with new forms which rejected historicism and embraced the structural possibilities of new materials like concrete and steel.
Modernist architects created new homes which welcomed in sunlight and opened out the interior; doors were plain but with a geometric shaped glazed upper section which allowed for light. Added to this was the excitement surrounding the streamlined forms of US architecture, which could be seen by all at the cinema.
These strands came together in the late 1920s and 30s with daring flat roofed houses, featuring plain white walls, curved suntrap windows and Egyptian style motifs.
Explore Art Deco houses:
- Inside an original Art Deco house
30s Semi houses
1918-1939
After the war, many rural areas were suffering from the effects of agricultural depression and many aristocratic families were selling off their estates. At the same time railways, the underground, and new tram lines made the countryside which surrounded towns and cities accessible.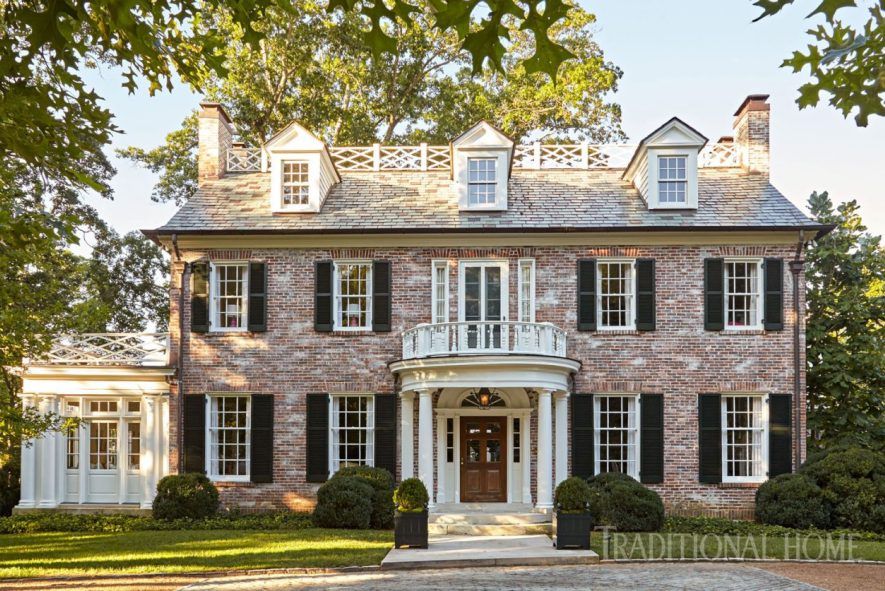
As a result, the land alongside these new transport links could be purchased at a much lower price than in the cities. It therefore made economic sense to build on this land, and the boxy, semi-detached house with its hipped roof and curved bay windows became distinctive of the period.
Some elements of the Arts and Crafts style can still be recognised in 1930s semis: mock timber framing in gables, pebble dashed walls, hanging tiles and recessed porches are commonly found. These houses remain one of the most common architectural styles you see in Britain today.
Airey Houses
1940s
After the Second World War, there were thousands of houses to rebuild and a desire to finally provide housing fit for all. However, the skills and materials required weren’t readily available, and so new system-built homes were designed, which could be mass produced in factories and quickly erected on site.
One such system was designed by Sir Edwin Airey.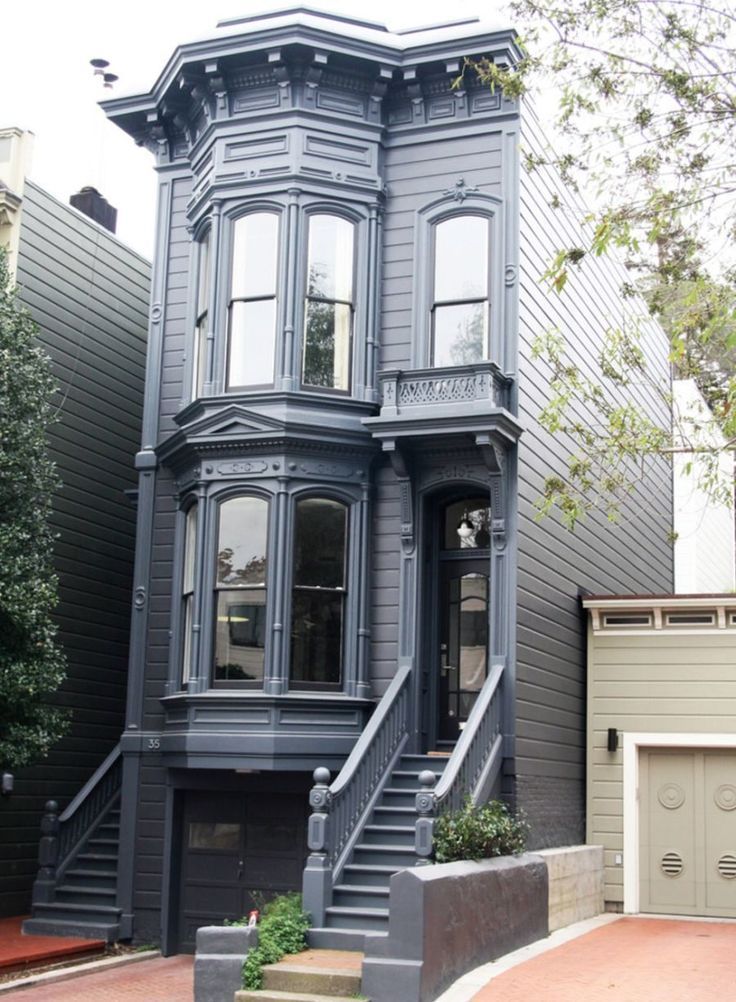 It used concrete columns reinforced with metal tubing which supported horizontal concrete slabs to form the outer skin of the house. They were popular in many rural areas as the parts were easily transportable.
It used concrete columns reinforced with metal tubing which supported horizontal concrete slabs to form the outer skin of the house. They were popular in many rural areas as the parts were easily transportable.
Once the shortage of building materials was over in the early 1950s, most houses were re-built. However, to keep costs down, the simple form of these prefabricated homes was retained. Hence roofs were pitched and not hipped, windows were smaller and had plain glass, and bay windows were a rarity.
70s Terrace houses
1970s
By the late 1950s, the new generation were keen to throw out the old and embrace all things modern. This was the Space Age, and many desired homes with interiors which were fresh, colourful and open-plan.
New forms of houses were built so that even those on a tight budget could experience the future, and these terraced homes became incredibly popular in the 1960s and 70s. However, the builders who erected these homes understood that many buyers still had conservative tastes, and so they clad these homes with traditional hanging tiles and weatherboarding to broaden their appeal.
Central heating systems were introduced so chimneys were no longer required, and, by this point, garages were now a standard feature on most homes.
90s New Build houses
1990s
The collapse of the Ronan Point flats in 1968 exposed the shortcomings of some of Britain’s popular modernist structures. At the same time, there was a growing movement against the wide scale demolition of Victorian buildings to make way for new developments.
By the 1990s, people desired traditional features, and as a result new build houses outwardly reflected older buildings once again: mock timber framing, rendered walls and cottage features all appealed to buyers.
Insulation was introduced into walls and in loft spaces, and double glazing began to be retrofitted into most homes. Safety standards were highly improved in homes during this period and more elaborate security measurements such as fire and gas safety (amongst many others) were implemented. These new build estates were often laid out at angles or staggered back so as to resemble villages.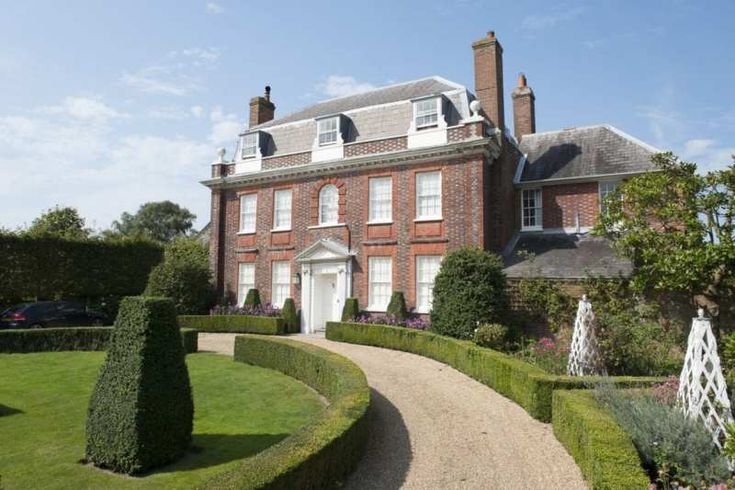
Modern Minimalist houses
Present day
The 1990s saw modernism rejected, but today modernist architecture has risen in popularity once again; and this, alongside people’s desire to live in a more sustainable, environmentally-friendly way, has led to the modern minimalist style.
The form and shape of these homes consider the importance of sunlight and shade (in addition to how the rooms within might be used), and homes can now be built as sealed units to minimise heat loss, with heat exchangers to provide warmth and fresh air. Solar panels are often fitted in new homes, and open plan interiors can also be designed without the problems of draughts.
Timber cladding and exposed steelwork are common features as are large expanses of glass, which, thanks to new double and triple glazing technology, can be fitted whilst maintaining thermal efficiency.
10 architectural styles for country houses
home Articles Styles in construction 10 architectural styles for building modern country houses
The first and most important thing to decide before you start choosing a country house project is how you want to see your future home. When choosing a specific type of cottage design, in addition to your own desires, the features of the area, as well as many other factors, are taken into account. Certain architectural styles fit where others would not. Of course, it is almost impossible to understand in detail all the types of private houses, but familiarity with the most popular architectural styles can help you choose the house that is most suitable and comfortable for you.
When choosing a specific type of cottage design, in addition to your own desires, the features of the area, as well as many other factors, are taken into account. Certain architectural styles fit where others would not. Of course, it is almost impossible to understand in detail all the types of private houses, but familiarity with the most popular architectural styles can help you choose the house that is most suitable and comfortable for you.
Classic style
As a rule, classical architecture is associated primarily with something massive, solid, fundamental. And this is understandable, because the main source of classics is ancient culture, from which it adopted its distinctive features: proportionality, symmetry and, in a sense, ingenious simplicity. The clarity of outlines and harmony in every detail - that's what distinguishes the classic style from all the others.
Such cottages are characterized by pitched tiled roofs, columns and balustrades, many forged details and balconies.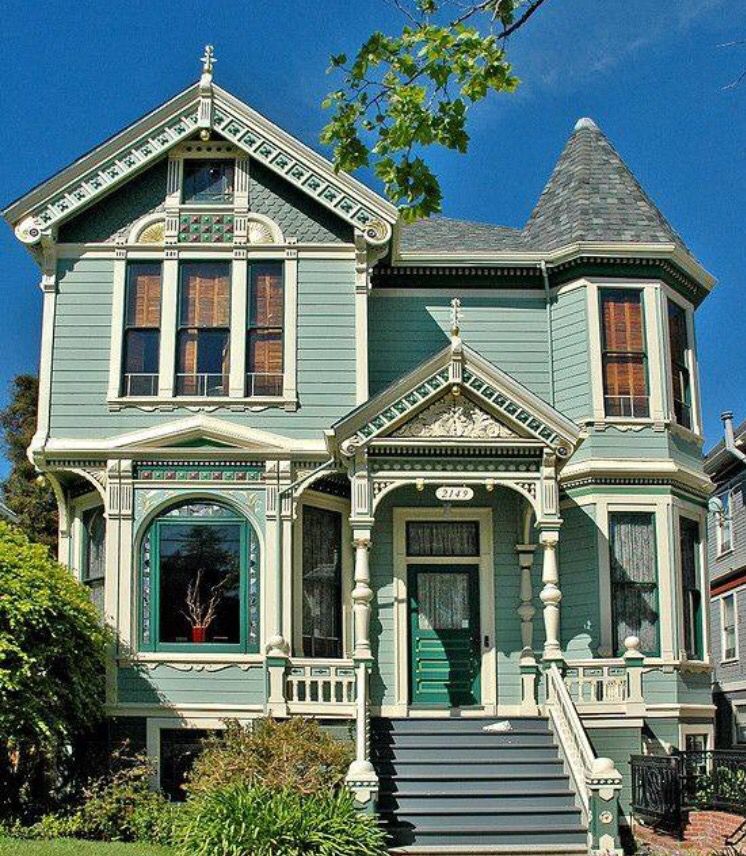 The facades of houses in the classical style are created using light modern building materials. The exterior of the building after such a finish becomes more attractive, and the structure itself does not look overloaded. In the cladding of buildings, as a rule, natural stone and facade plaster are used.
The facades of houses in the classical style are created using light modern building materials. The exterior of the building after such a finish becomes more attractive, and the structure itself does not look overloaded. In the cladding of buildings, as a rule, natural stone and facade plaster are used.
Classical architecture is more often used in the construction of large, capital houses. And even today, despite the advantage of house designs in modern architectural styles on the market, classical themes remain in demand and popular. After all, such a building will always look noble and aristocratic. But, before decorating the facade of the house in a classic style, you should make sure that the landscape of the adjacent territory is in harmony with it.
Examples of classic style houses
D1304 - project of a house with a sauna
D1307 - project of a house with a spacious living room, a small covered terrace and a garage
D230 - cottage project with pool and garage
Modern
The Art Nouveau style is some rethinking of classical architecture.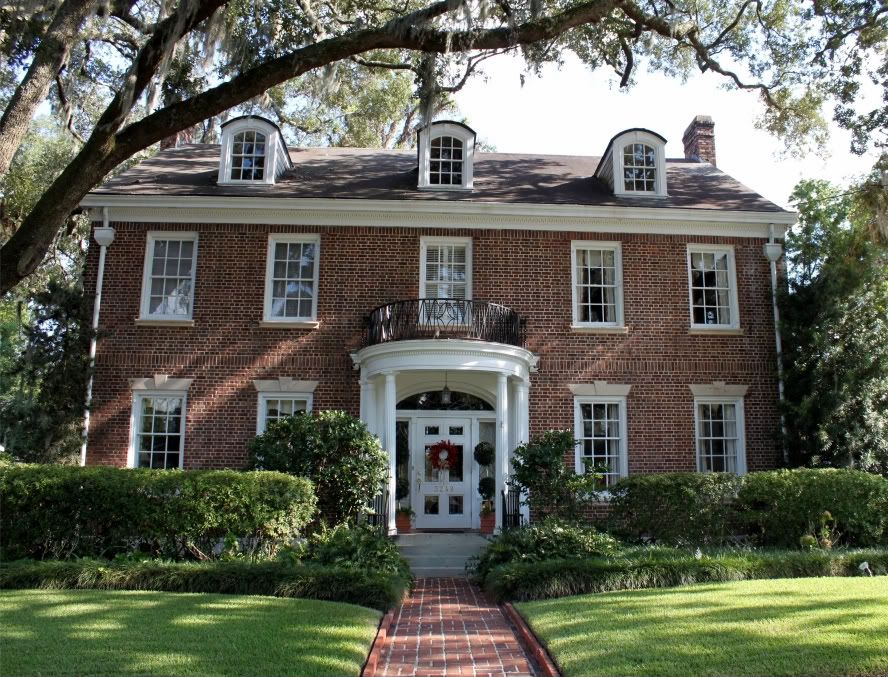 It appeared at the end of the 19th century, as the embodiment of the idea of creating beautiful, but at the same time functional buildings. Symmetry and dry proportionality in it are replaced by naturalness and quirkiness of “natural” forms, a plant theme appears in the design. In the decoration of houses, completely different materials are used: glass, ceramic tiles and even bronze. Mosaics and stained-glass windows appear on buildings, roofs take on unusual shapes. The appearance of this style in architecture brought something completely new to it. Today, this style has received many branches, which are often used in the construction of country houses. And despite the fact that the peak of the popularity of Art Nouveau fell on a time far from us, even now in almost every house you can notice its distinctive features.
It appeared at the end of the 19th century, as the embodiment of the idea of creating beautiful, but at the same time functional buildings. Symmetry and dry proportionality in it are replaced by naturalness and quirkiness of “natural” forms, a plant theme appears in the design. In the decoration of houses, completely different materials are used: glass, ceramic tiles and even bronze. Mosaics and stained-glass windows appear on buildings, roofs take on unusual shapes. The appearance of this style in architecture brought something completely new to it. Today, this style has received many branches, which are often used in the construction of country houses. And despite the fact that the peak of the popularity of Art Nouveau fell on a time far from us, even now in almost every house you can notice its distinctive features.
Examples of modern house designs
D924 - project of a cottage with a swimming pool and a winter garden
D722 - project of a plastered two-storey cottage
D129 - compact cottage project
Wright Style
Frank Lloyd Wright is a legendary American architect who created "organic architecture" and "prairie houses", as pitched-roof houses are often called.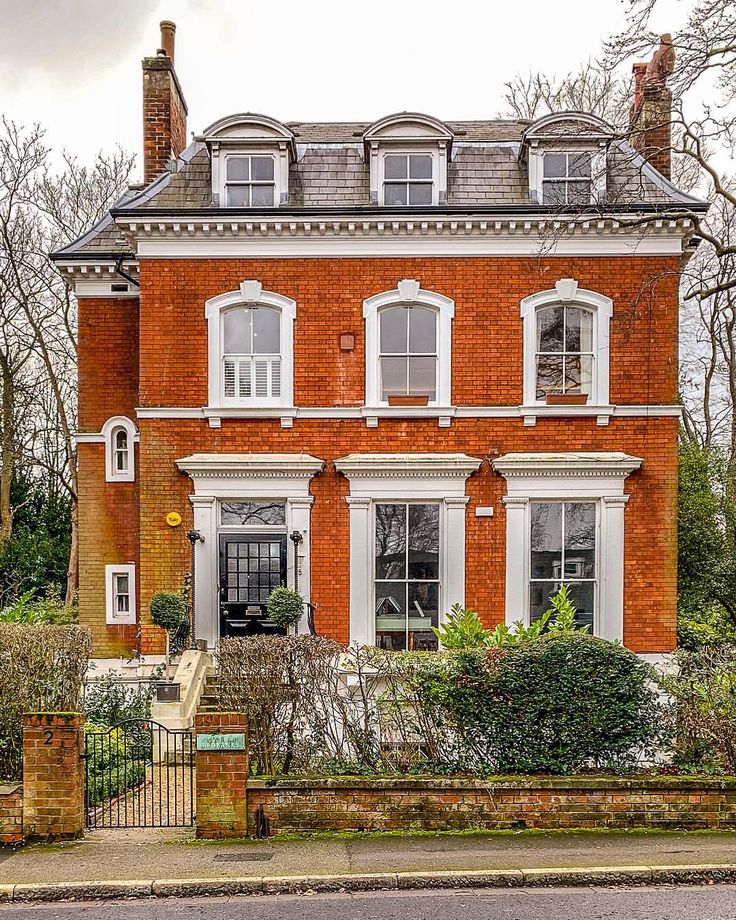 The philosophy of Wright's style lies in the maximum visual fusion of the building with the general landscape, the desire to "let in" the surrounding nature into the house. This effect is achieved largely due to large-scale glazing, the predominance of horizontal surfaces and lines, as well as large open spaces. It is in this architectural style that functionalism begins to naturally harmonize with the aesthetics of proportionality. Simplicity of lines, minimal decor, lightness and naturalness of interior decoration, large free space inside each room. For the decoration of the facades, natural materials are used here: stone, wood. Sloping roofs are most often covered with seamed copper sheet. Elements of Wright's style are found in many modern homes.
The philosophy of Wright's style lies in the maximum visual fusion of the building with the general landscape, the desire to "let in" the surrounding nature into the house. This effect is achieved largely due to large-scale glazing, the predominance of horizontal surfaces and lines, as well as large open spaces. It is in this architectural style that functionalism begins to naturally harmonize with the aesthetics of proportionality. Simplicity of lines, minimal decor, lightness and naturalness of interior decoration, large free space inside each room. For the decoration of the facades, natural materials are used here: stone, wood. Sloping roofs are most often covered with seamed copper sheet. Elements of Wright's style are found in many modern homes.
Wright style house designs
D4 - project of a two-story square house with an open terrace
D2837 - project of a one-story house with a terrace and a carport
D238 - project of a one-storey house with a panoramic window to a covered terrace
Minimalist
Minimalism is not just a style, but a whole trend in architecture.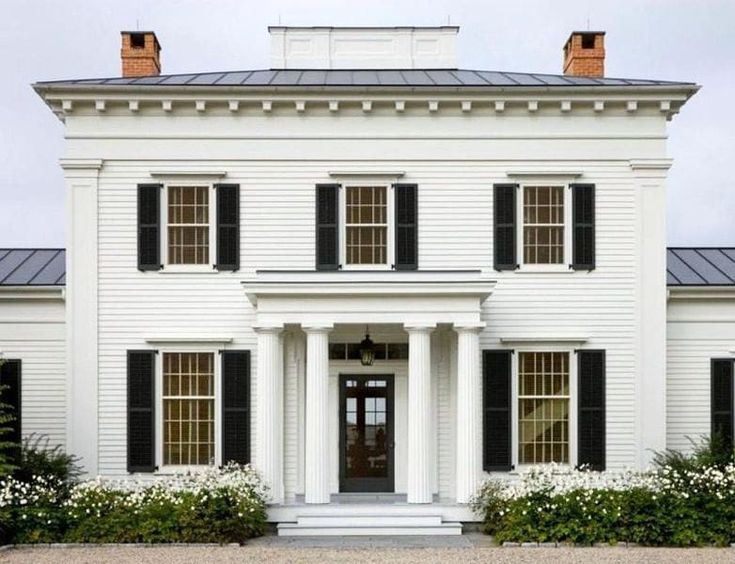 The whole essence of this style lies in its name. "Minimal art" - the desire to reduce the number of unnecessary details in architecture, the absence of "clutter". By minimalist standards, any art, including architecture, should be as functional as possible. Minimalism takes its basis in modernity, but it goes from unusual, ornate lines to the maximum possible simplicity, observance of the basic rules of composition, the use of natural materials and a single color scheme. Today, minimalism is developing at an amazing rate, gaining more and more fans and followers.
The whole essence of this style lies in its name. "Minimal art" - the desire to reduce the number of unnecessary details in architecture, the absence of "clutter". By minimalist standards, any art, including architecture, should be as functional as possible. Minimalism takes its basis in modernity, but it goes from unusual, ornate lines to the maximum possible simplicity, observance of the basic rules of composition, the use of natural materials and a single color scheme. Today, minimalism is developing at an amazing rate, gaining more and more fans and followers.
Minimalist house designs
D220 - a project of a laconic attic house with a strict finish
D2527 - aerated concrete house project with a courtyard
D2915 - a small attic house made of aerated concrete
European style
European style is commonly referred to as the modern style of architecture throughout Europe. It, in turn, is divided into Swedish, German, Scandinavian and English.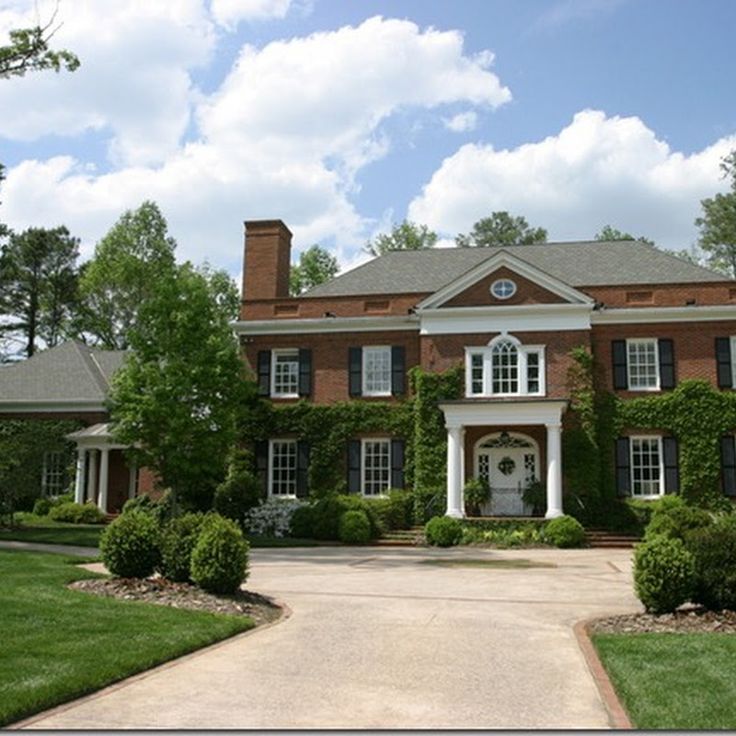 The characteristic features of houses in each of the countries depend on the characteristics of life, weather conditions, habits and traditions. Nevertheless, all modern European architecture is based on the same principles of rationalism and practicality, so each of the styles of these countries has something in common. The project of any European house is based on the correct geometric shapes and the absence of any frills in the layout. Windows in houses also have a geometric shape, most often rectangular, which is also striking. In the decoration of such buildings, natural stone, plaster of various types, and bricks are used. Now the vast majority of country houses in Europe and Russia are being built in the European style.
The characteristic features of houses in each of the countries depend on the characteristics of life, weather conditions, habits and traditions. Nevertheless, all modern European architecture is based on the same principles of rationalism and practicality, so each of the styles of these countries has something in common. The project of any European house is based on the correct geometric shapes and the absence of any frills in the layout. Windows in houses also have a geometric shape, most often rectangular, which is also striking. In the decoration of such buildings, natural stone, plaster of various types, and bricks are used. Now the vast majority of country houses in Europe and Russia are being built in the European style.
European style house designs
D2 - European style house project with basement
D204 - house project of a one-story house with an attic floor, a bay window, balconies in the bedroom
D1177 - project of a house with a garage for one car, with a gym and a shower room on the second floor
German style
German architecture has always been known for its beauty and rationality.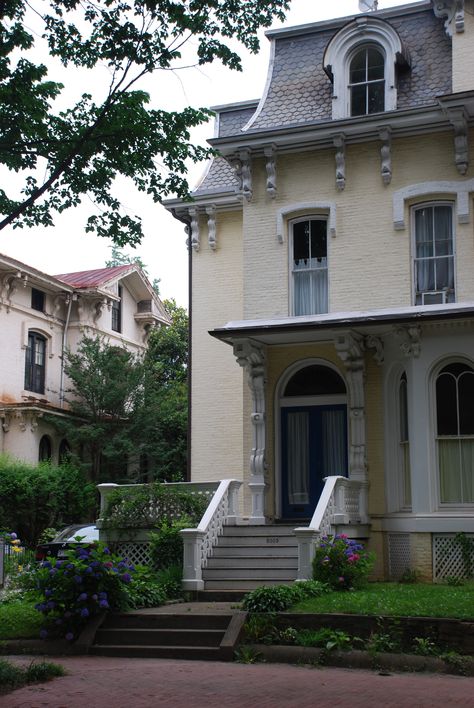 Due to its solidity and practicality, it has become a symbol of high quality all over the world. Today, many people give their preference to the projects of German houses and cottages. Buildings usually have a classic rectangular or square shape, and a smooth surface makes their appearance more noble and rich. Finishing a house in the German style is often done after the completion of the construction itself, which is a definite plus. Unlike classical German architecture, the style of a modern house in this style relies heavily on the principles inherent in functionalism and minimalism. The projects of such buildings are distinguished by simple decor, the absence of bright colors, catchy patterns, sculptures and stucco moldings. The traditional German cottage is decorated with small bay windows, and the main decorative elements are attics and balconies. The plinth is finished with natural stone, which is very popular in Germany.
Due to its solidity and practicality, it has become a symbol of high quality all over the world. Today, many people give their preference to the projects of German houses and cottages. Buildings usually have a classic rectangular or square shape, and a smooth surface makes their appearance more noble and rich. Finishing a house in the German style is often done after the completion of the construction itself, which is a definite plus. Unlike classical German architecture, the style of a modern house in this style relies heavily on the principles inherent in functionalism and minimalism. The projects of such buildings are distinguished by simple decor, the absence of bright colors, catchy patterns, sculptures and stucco moldings. The traditional German cottage is decorated with small bay windows, and the main decorative elements are attics and balconies. The plinth is finished with natural stone, which is very popular in Germany.
German style house designs
D1354 - a house with a semicircular bay window, an adjacent hall, a living room and a dining room
D157 - cottage project with a convenient layout
D151 - project of a cottage with a bay window and a balcony
Scandinavian style
The hallmark of all Scandinavian interiors is simplicity and minimalism.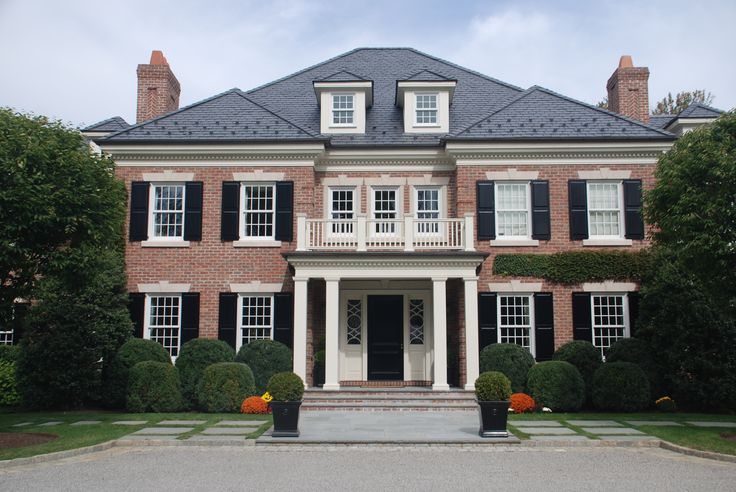 The Scandinavian style combined elements of the architecture of the Finns, Norwegians, Swedes and Danes. Due to harsh winters and short sunny days, the inhabitants of these countries had to abandon dark colors in the interior, but they learned how to skillfully combine white with other pastel colors. In addition to white, brown, beige, golden colors are used in the design of cottages; a variety of types of wood are used for decoration. Large panoramic windows are another sign of the Scandinavian style of cottages. They are not only the main decoration of the house, but also provide good illumination even on cloudy days.
The Scandinavian style combined elements of the architecture of the Finns, Norwegians, Swedes and Danes. Due to harsh winters and short sunny days, the inhabitants of these countries had to abandon dark colors in the interior, but they learned how to skillfully combine white with other pastel colors. In addition to white, brown, beige, golden colors are used in the design of cottages; a variety of types of wood are used for decoration. Large panoramic windows are another sign of the Scandinavian style of cottages. They are not only the main decoration of the house, but also provide good illumination even on cloudy days.
Modern options for facing the facade of a Scandinavian-style house are very diverse. The walls of the buildings are sheathed with clapboard or wooden boards, and on top they are covered with varnishes, tint solutions. When designing the facade, it is not necessary to adhere to strict natural monochrome, but at the same time, the colors should not completely hide the texture of the wood.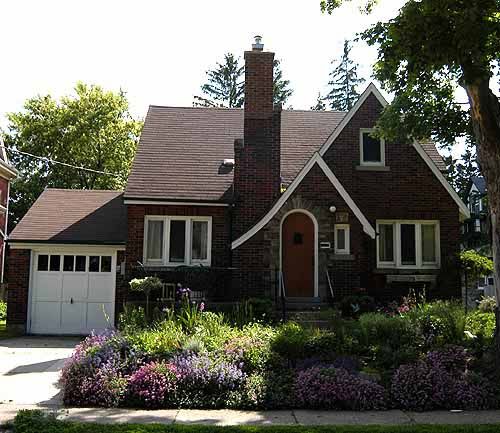 Designers use black, blue, dark green for coloring.
Designers use black, blue, dark green for coloring.
The facade of the house in the Scandinavian style can be decorated after construction is completed. The most important thing is to avoid pretentiousness in the exterior, use natural materials for decoration.
Scandinavian style house designs
D1208 - project of a brick house with a two-material finish
D2156 - a project of a two-story house made of glued laminated timber with panoramic windows
D1344 - project of a brick house with a balcony
English style
The facade of the house in the English style is distinguished by its elegance and versatility. Cottages designed in this way will ideally fit both in the metropolis and in a country cottage village. Modern English style includes elements of Tudor, Victorian, Georgian styles. In each individual project, an emphasis on one of these eras is possible. The facades are characterized by the presence of small columns, restrained colors, straight walls and the obligatory presence of an attic, the absence of drawings and complex carvings. But of course, a real English cottage is not just a building itself, but also a properly designed area around it.
But of course, a real English cottage is not just a building itself, but also a properly designed area around it.
Examples of English style houses
D332 - laconic cottage project
D2685 - project of a two-storey house with an attic, a terrace, a swimming pool
D2081 - project of a country house with a bay window, with a garage for two cars
Country
Country style originates in the traditional village housing of different peoples, adjusting to their national characteristics. However, as a rule, it consists of many different types of log houses that combine conciseness and functionality. When building such a house, a large amount of wood and other natural materials are always used. The roofs are usually covered with tiles. Country-style houses are distinguished by a natural color palette, involving the use of the most soft and harmonious pastel colors. The facade of the house is also decorated with natural materials, and for decoration they use paints and varnishes of dark colors, decorated with handmade accessories.
Today, Country style is one of the most popular among metropolitan residents who want to build a country house for themselves, in an effort to get away from urban stress.
Country house designs
D172 - project of a spacious cottage
D1083 - a country house with a billiard room and a gym in the basement
D46 - project of a house with a spacious living room and a kitchen-dining room, a terrace with a barbecue
Fachwerk
This type of decoration was popular in Germany in the 15th century, but today, formally, only fachwerk imitation is popular, because it is too difficult and pointlessly expensive to build cottages from beams using the old technology. The main feature of half-timbered houses is that the frame protruding from the outside is both a technical component of the building and the main decoration of the house. With the help of inclined wooden beams, a pattern is formed, most often in the form of any geometric shapes.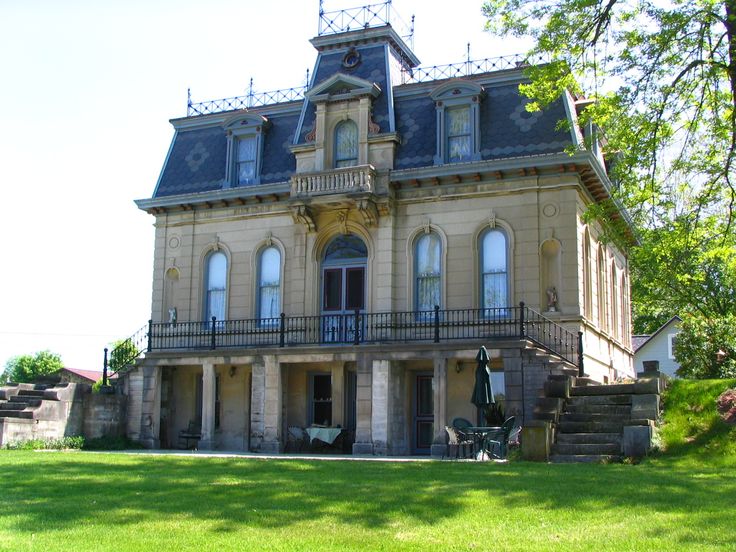 This is what makes the houses so recognizable. Usually houses in this style are faced in light shades, the facade is decorated with wood, natural stone or plaster. Also, modern half-timbered houses are decorated with panoramic windows, which, in addition to excellent lighting of the rooms, can provide access to the street. Such buildings simultaneously combine all the advantages characteristic of any beam structures and an unusual, colorful appearance.
This is what makes the houses so recognizable. Usually houses in this style are faced in light shades, the facade is decorated with wood, natural stone or plaster. Also, modern half-timbered houses are decorated with panoramic windows, which, in addition to excellent lighting of the rooms, can provide access to the street. Such buildings simultaneously combine all the advantages characteristic of any beam structures and an unusual, colorful appearance.
Examples of half-timbered houses
D1011 - brick house project
D468 - project of a two-storey house with three bedrooms
D982 - a project of a two-story brick house with a non-standard living room
Chalet
The chalet, also called Alpine style, originated in the French Alps in the 19th century. Initially, such houses had one purpose - to be a reliable home, allowing local residents to hide from any bad weather that could overtake in the mountains. Subsequently, this style, due to its functionality combined with the aesthetic appearance, became more and more popular not only in France, but throughout the world.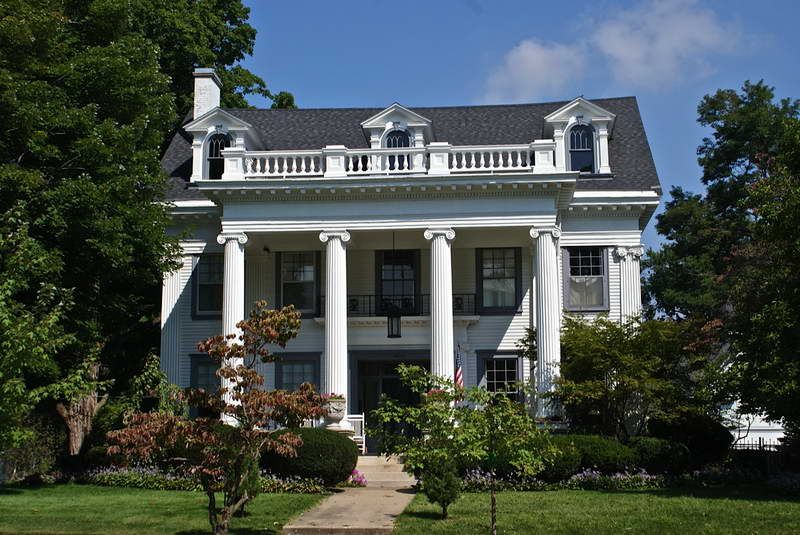 A distinctive feature of cottages designed in this way are small dimensions. Chalet-style houses look elegant and miniature, and the upper floors have more space than the lower ones. Wide roofs, strongly protruding beyond the edges of the walls, began to have a decorative character. Under such roofs, it is customary to build large, cozy balconies. The abundance of horizontal lines gives the appearance of houses organic and allow them to fit organically into the overall landscape. Such cottages will look very picturesque in hilly and mountainous areas.
A distinctive feature of cottages designed in this way are small dimensions. Chalet-style houses look elegant and miniature, and the upper floors have more space than the lower ones. Wide roofs, strongly protruding beyond the edges of the walls, began to have a decorative character. Under such roofs, it is customary to build large, cozy balconies. The abundance of horizontal lines gives the appearance of houses organic and allow them to fit organically into the overall landscape. Such cottages will look very picturesque in hilly and mountainous areas.
Chalet-style house designs
D116 - project of a one-storey house with a barbecue on a large terrace
D2297 - project of a house with a garage and a carport
D1803 - project of a frame house with a large balcony
Hi-tech
Most often, it is customary to combine the high-tech style with minimalism close to it in spirit, because they both took their origins in modern and Japanese architecture, but at the same time they are different directions from each other.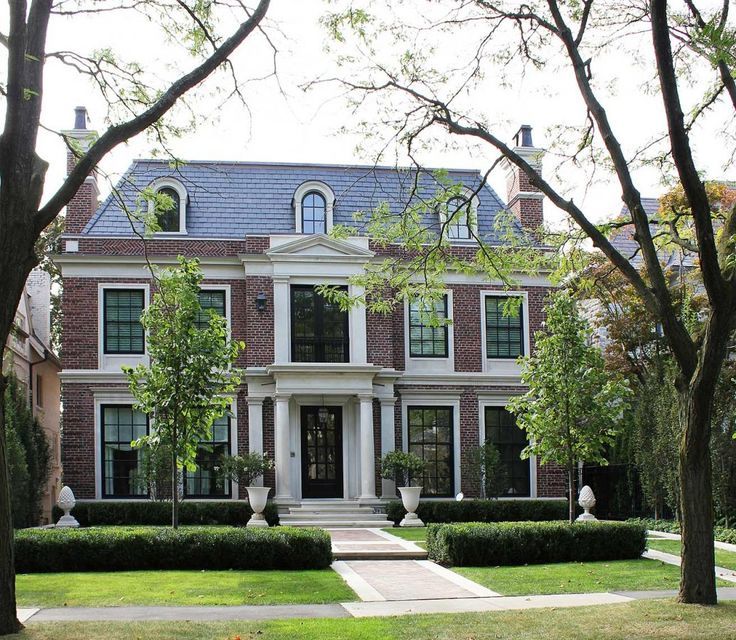 In combination, these two styles greatly transform any building. In hi-tech, you can see the presence of not only straight lines, but also very unusual shapes. This style is distinguished by a complete lack of symmetry. Despite this, conciseness and restraint reign here in absolutely everything: both in decor and in the very architecture of the structure. Small architectural details are not welcome, and the emphasis is on functionality, practicality, and convenience.
In combination, these two styles greatly transform any building. In hi-tech, you can see the presence of not only straight lines, but also very unusual shapes. This style is distinguished by a complete lack of symmetry. Despite this, conciseness and restraint reign here in absolutely everything: both in decor and in the very architecture of the structure. Small architectural details are not welcome, and the emphasis is on functionality, practicality, and convenience.
The main color in this style is metallic gray, as well as all the colors that are in harmony with it. In the architecture of the house and in the decoration, a lot of metal is also used, precisely as a technical material: here it replaces plastic, glass, and wood.
High-tech house designs
D757 - project of a domed house with 4 bedrooms and a view living room
D707 - a project of a foam block house with an unusual finish
D2212 - project of a round house with large bedrooms
Modern style
Modern style combined a huge variety of architectural trends that appeared and began their development at about the same time.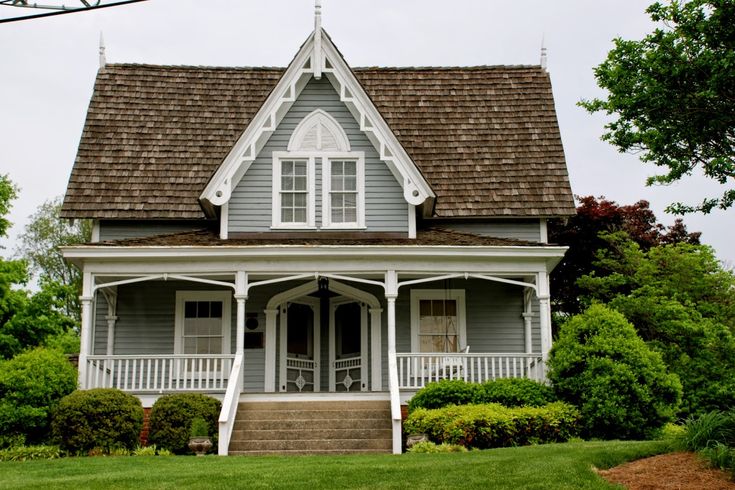 This includes functionalism, high-tech, constructivism and deconstructivism, avant-garde, biotech. Modern architecture implies both a rejection of any excesses towards functionality and practicality, and an open space for new forms and ideas. Houses built in a modern style are usually very practical, each square meter has its own purpose, a rational approach is visible in everything. Today, almost 80% of new cottages are built in this style, and it can rightfully be considered ideal for building a private country house for the whole family.
This includes functionalism, high-tech, constructivism and deconstructivism, avant-garde, biotech. Modern architecture implies both a rejection of any excesses towards functionality and practicality, and an open space for new forms and ideas. Houses built in a modern style are usually very practical, each square meter has its own purpose, a rational approach is visible in everything. Today, almost 80% of new cottages are built in this style, and it can rightfully be considered ideal for building a private country house for the whole family.
Examples of modern house designs
D1092 - project of a two-storey house with stucco cladding
D1131 - project of a house with a large open terrace, a carport for one car, a second light
D1391 - project of a house with a garage for two cars, a terrace, a sauna, two balconies
In conclusion, it is worth emphasizing that today the features and elements of one style are often borrowed by others, which gives rise to many new architectural trends.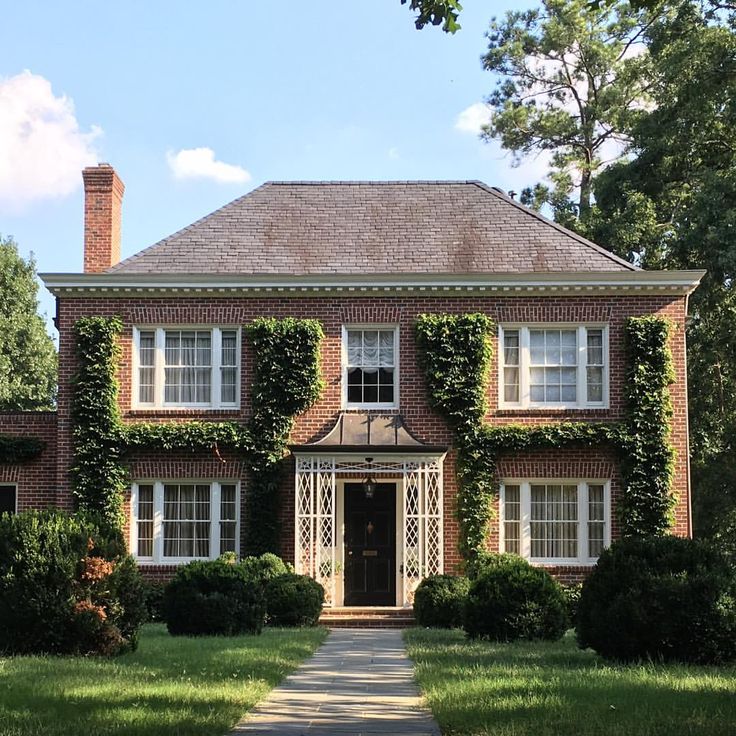 When choosing a project for a country house, you should rely primarily on your needs and desires, then there will be no problems with determining the desired architectural style.
When choosing a project for a country house, you should rely primarily on your needs and desires, then there will be no problems with determining the desired architectural style.
19 architectural styles of private houses with names and features
There are several dozen architectural styles of houses on the construction market: from avant-garde to modern processing of classics. Each project contains elements of non-standard architectural solutions that allow houses to stand out against the general background. The choice of style depends on the local climate, budget, individual preferences of the future owners of the house and their ideas about comfort.
Contents
Scandinavian style
The style is functional, full of natural light and stylish practicality while maintaining comfort. Scandinavian architecture helps to stay close to nature even in urban environments. The style is dominated by simplicity and conciseness.
The architectural direction arose in countries with a harsh climate similar to Russia - Denmark, Sweden, Norway.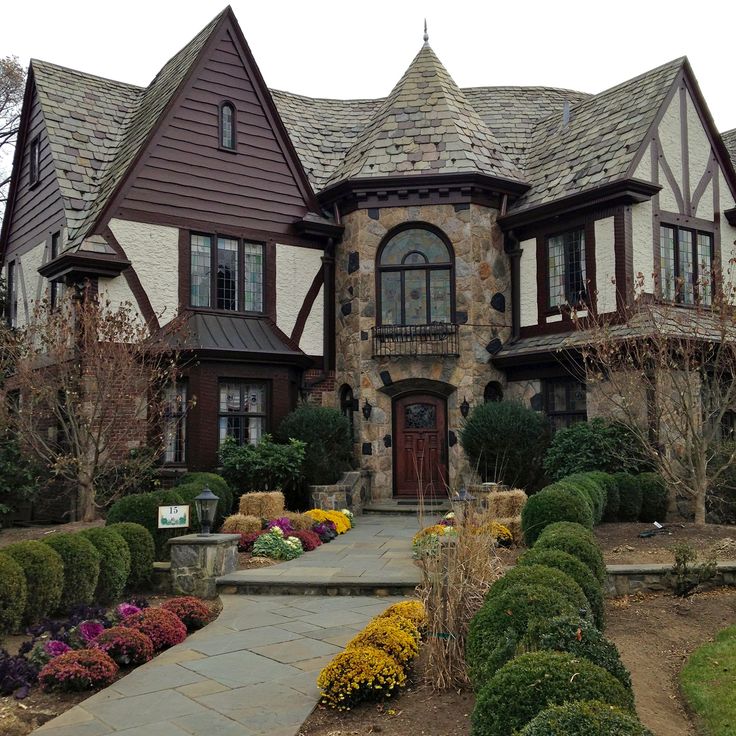 The facade is made of wood. The skin is treated with protective compounds to preserve the natural structure of the material. A characteristic feature of the buildings: a large porch, a terrace, gable roofs with a steep slope with an asymmetric or classical shape, large windows or panoramic windows.
The facade is made of wood. The skin is treated with protective compounds to preserve the natural structure of the material. A characteristic feature of the buildings: a large porch, a terrace, gable roofs with a steep slope with an asymmetric or classical shape, large windows or panoramic windows.
Wooden window frames or double-glazed windows with a wood-like finish are desirable. The roof is covered with polymeric materials or metal tiles. The buildings are distinguished by soft natural shades: terracotta, dark green, gray, brown.
Hi-tech
This direction involves the use of modern materials and stylization of the project as an industrial building. Practical and comfortable style was born in 1970. Architectural objects of this direction have metal frames with glass enclosing structures.
Most of the projects involve the removal of utilities to the facade of the house. Distinctive features of the architectural direction: an abundance of metal structures, simple, clear lines, flat roofs with dark roofing, large windows.
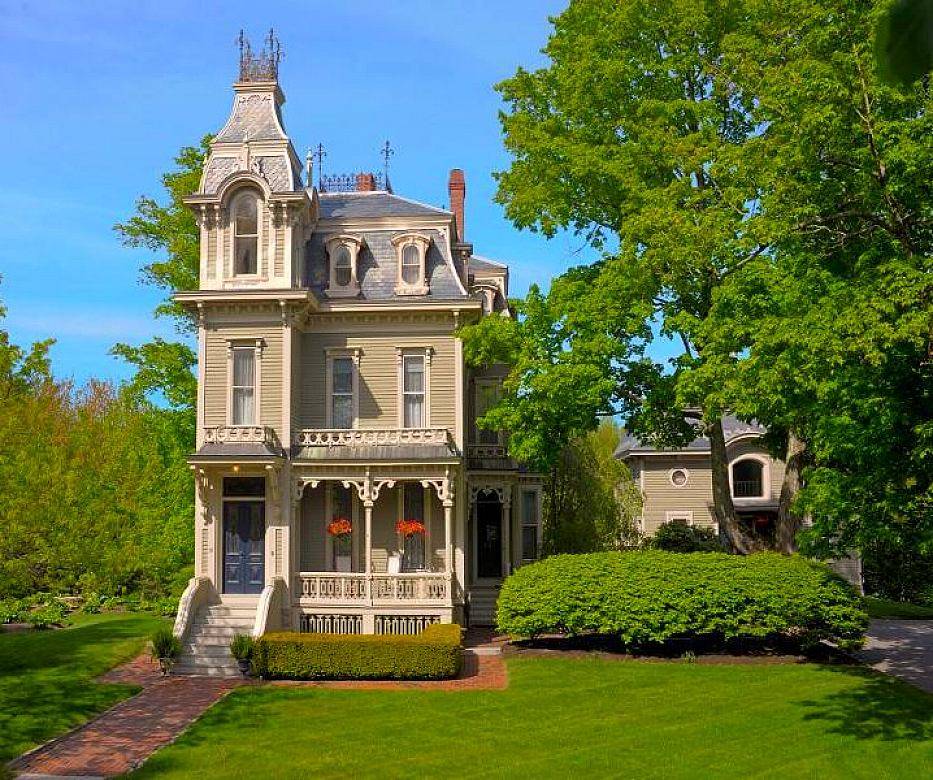
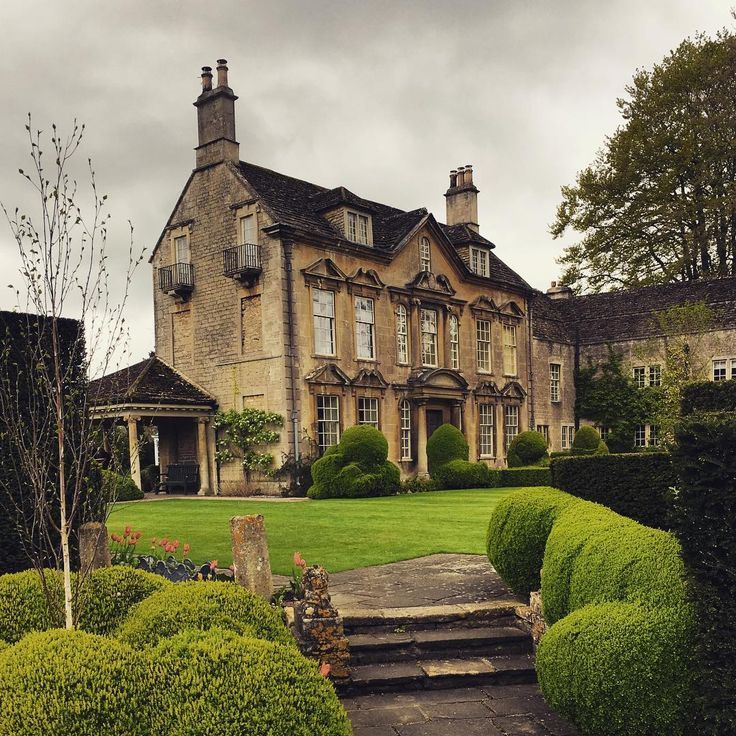
Victorian architecture
The style originated between 1830 and 1910 during the reign of Queen Victoria. Key Features: Dollhouse effect, thoughtful finishes, steep tiled mansard roof, asymmetrical shape, porch, bright saturated colors, pillared balconies, majestic towers and turrets, ornate railings.
Victorian houses are usually two-story compact buildings with intricate decor and multi-stage sloping roofs, often decorated with spiers. The stylistic direction originated in Great Britain and spread not only within the country, but also to the English colonies. Houses in this architectural style are distinguished by an asymmetrical facade. For decoration within the framework of the stylistic direction, plaster, siding, brick are used.
Japanese style
The architecture of the Land of the Rising Sun is the result of the centuries-old war of the Japanese with nature. The main features of the style were borrowed from the Chinese.
The basic architectural elements of the Japanese style are not determined by fashion trends, but by vital necessity. Both in antiquity and now, the main principle of architecture is the unity of buildings and the surrounding nature. Functionality is a priority, while aesthetics fade into the background. Characteristic features of Japanese houses: a small amount of decor, practicality and rationalism.
Japan used to build houses out of wood and rice paper. Today, fiber cement boards and ceramic siding are used. A feature of the Japanese style is a terrace with plank flooring. For greater authenticity, the terrace is decorated with container gardening.
American style
The style is an adaptive variation of a pre-existing European architectural trend. From the desire of the first settlers to demonstrate the scale and richness of the house, there was a need to create not modest dwellings, but a whole architectural complex.
The style is distinguished by a minimum of relief details, a predominance of straight lines, symmetry, light calm colors, many windows, horizontal extension, an asymmetric roof.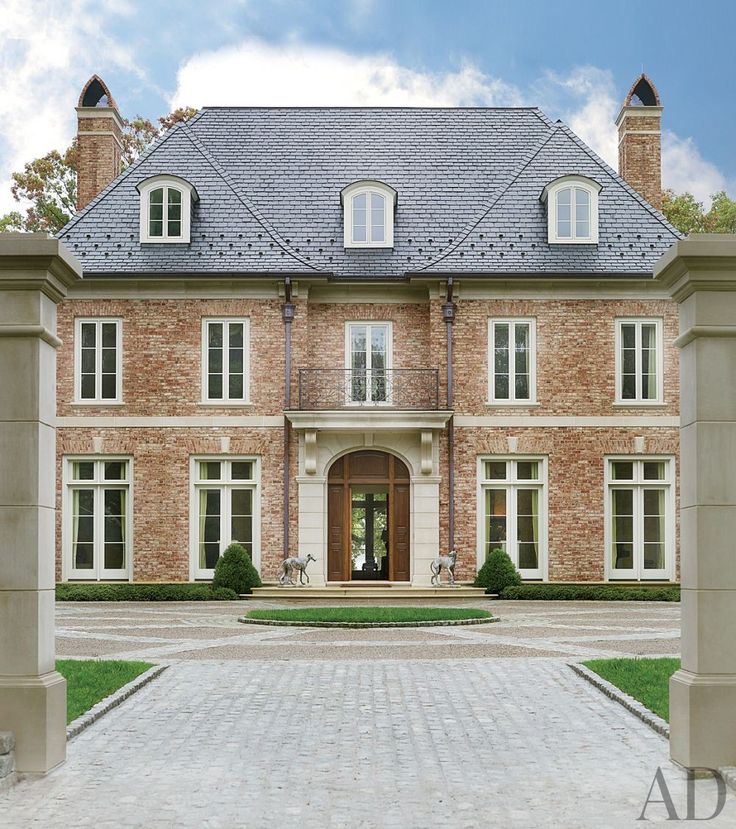 Currently, this stylistic direction is a mixture of architectural styles. General concept: to build a spacious comfortable house where everyone will feel comfortable. Usually this is a frame one-two-story house with a low foundation with a veranda or a spacious porch.
Currently, this stylistic direction is a mixture of architectural styles. General concept: to build a spacious comfortable house where everyone will feel comfortable. Usually this is a frame one-two-story house with a low foundation with a veranda or a spacious porch.
Country style
The main features of the country style are naturalness and simplicity. The direction reflects the folk traditions of their country, is distinguished by deliberate rudeness, proximity to nature.
The rustic-style building looks authentic, natural materials (stone, wood) and natural shades are used in the exterior. Usually a house in this style is built with a veranda or a massive porch. If the building has two floors, a spacious balcony is built over the porch, in harmony with the general style of the facade. Characteristic features of the Russian rural style: log walls, windows with carved platbands.
Wright Style
The style originated in the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.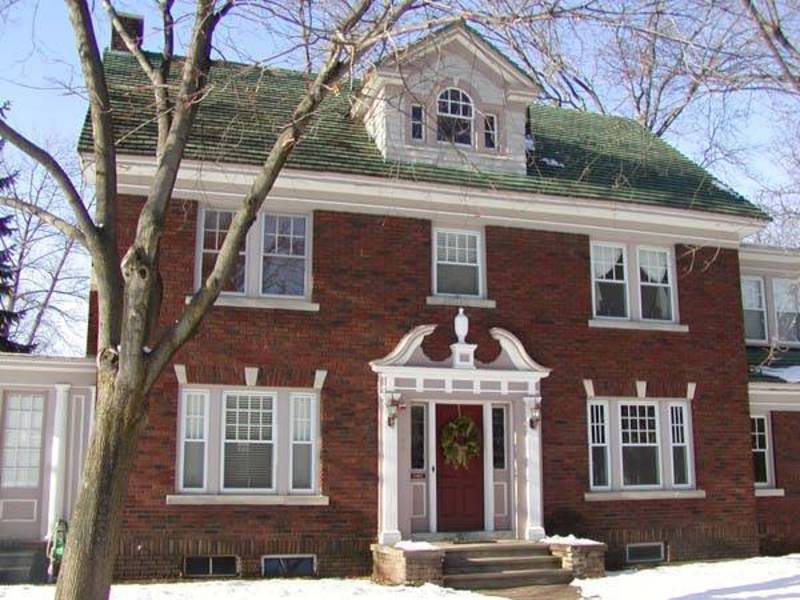 The ancestor of the direction was the architect Frank Lloyd Wright . Wright's style is also known as Prairie Style .
The ancestor of the direction was the architect Frank Lloyd Wright . Wright's style is also known as Prairie Style .
Wright advocated purity and simplicity of lines, a building whose exterior is integrated into the surrounding landscape. Prairie-style houses blend in seamlessly with the natural setting for a western film. Key features of the style: long horizontal lines, minimalist facade decoration, hipped or flat roofs, glazed galleries.
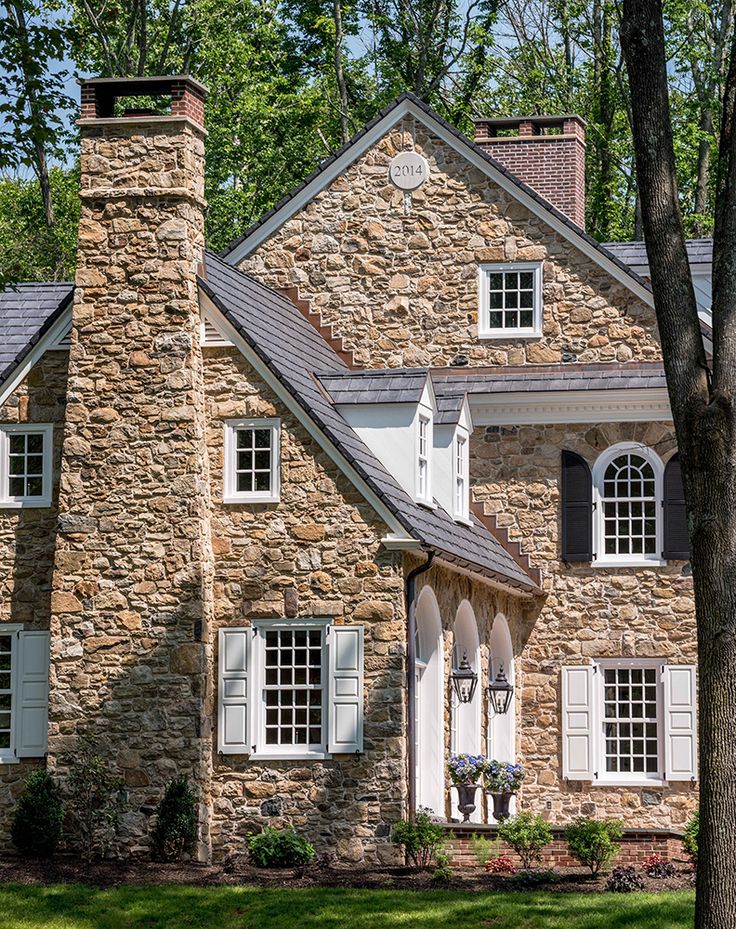
Chalet
Alpine house style is chosen by those who dream of an atmosphere of security, harmony and tranquility.
The direction spread from the ancient province in the south-east of France. Buildings in this style are adapted to the harsh climate and therefore are best suited for Russia. Today, the chalet is a relevant and sought-after style for functional suburban housing.
Cornerstones of the style: a solid stone foundation and a wooden top, the use of high-quality environmentally friendly materials, a sloping roof with a large angle of inclination, a terrace.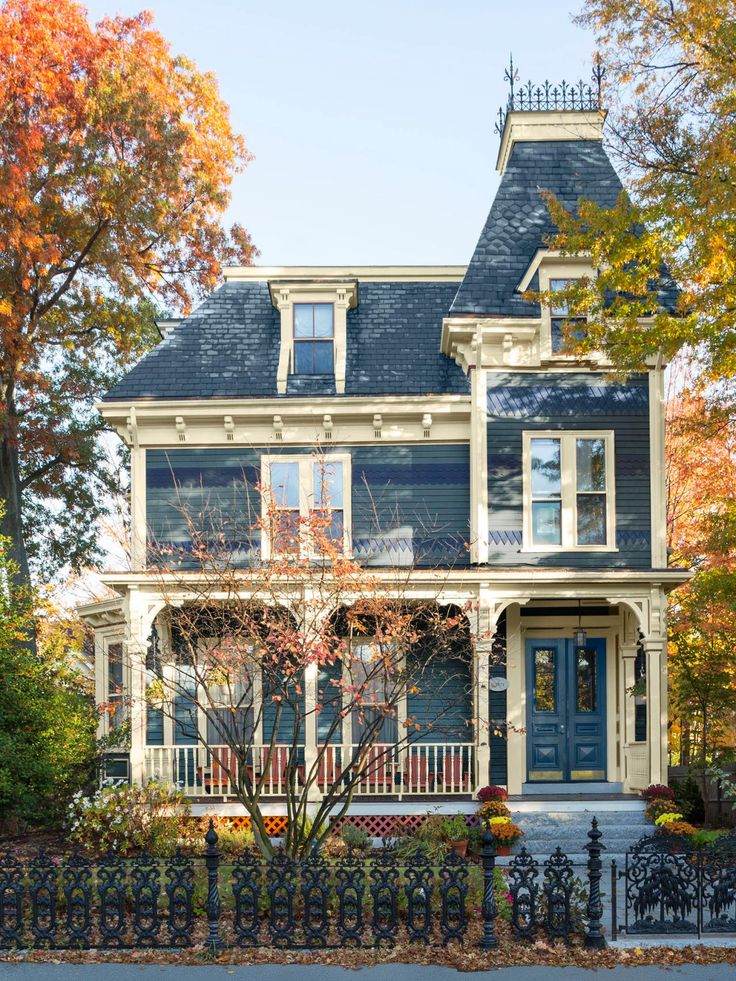 Another feature is the multi-level architecture, since the original chalets were mainly built in the mountains and repeated the uneven terrain. For this reason, the chalets fit perfectly into the site with a significant slope. The roof of the shepherd's house uses flexible, ceramic, wooden shingles to preserve authenticity. The modern dwelling of the Alpine shepherds is built in 1-2.5 floors.
Another feature is the multi-level architecture, since the original chalets were mainly built in the mountains and repeated the uneven terrain. For this reason, the chalets fit perfectly into the site with a significant slope. The roof of the shepherd's house uses flexible, ceramic, wooden shingles to preserve authenticity. The modern dwelling of the Alpine shepherds is built in 1-2.5 floors.
German style
This architectural direction is chosen by those who value solidity, simplicity and elegance. The nuances of building facades in the Bavarian or German style: the severity of lines, the lack of redundancy of decorative elements, restrained colors, the use of inexpensive materials.
This style inherits German neatness and order. Despite this, the houses resemble charming fairy-tale houses that have descended from the pages of fairy tales. The German-style building is designed as a square or rectangle with a gable roof.
Walls are painted in white, sand, gray or other discreet colors.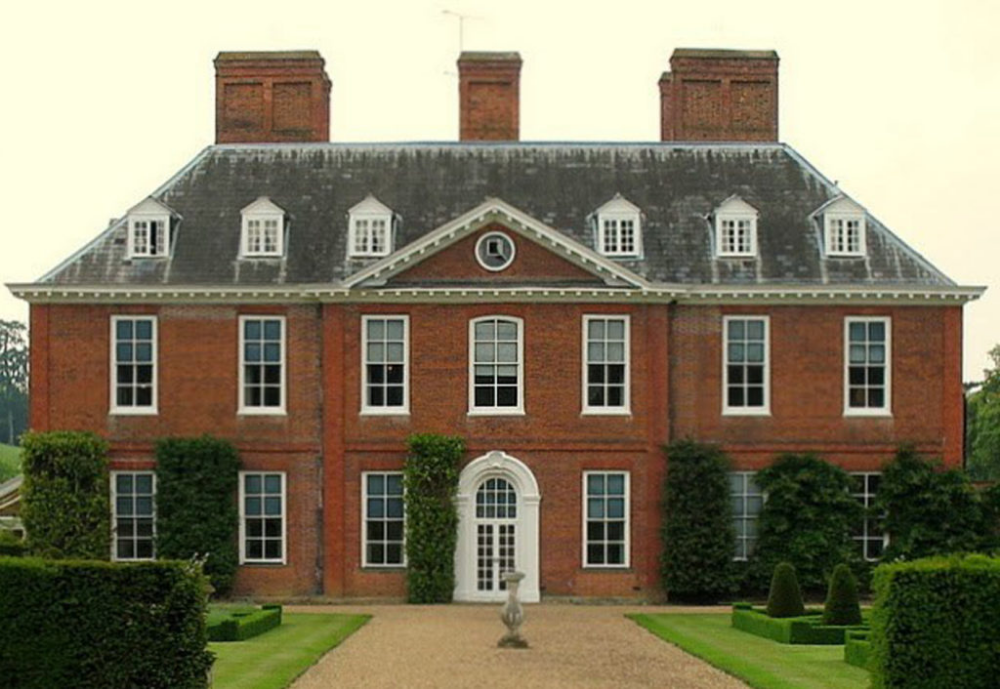 The tiled roof is traditionally done in brown or red. The shape of the windows is rectangular or arched, the glazing is divided into several square or rectangular sections, the windows are sometimes complemented by shutters.
The tiled roof is traditionally done in brown or red. The shape of the windows is rectangular or arched, the glazing is divided into several square or rectangular sections, the windows are sometimes complemented by shutters.
English style
Style is a combination of refined taste and restraint. The cornerstones of the architectural direction: symmetrical rectangular plan, red brick walls, low entrance with a portico.
At present, the architecture of an English mansion is dominated by elements characteristic of the architecture of a particular historical era. The key features of the eclectic style are: a roof with a dormer and a steep slope, low-lying windows, walls made of brick or stone.
Fachwerk
The style originated in the 15th century in Germany. The half-timbered house is an example of German quality and practicality. Buildings in this type of architecture suggest the presence of an external frame of vertical, horizontal and diagonal beams.
Style feature: the second floor overhang over the first. The main material of half-timbered houses is wood. Since wooden houses are flammable materials and require antifungal treatment, nowadays half-timbered houses are imitation with polyurethane panels that give the impression of wooden beams.
Gothic style
Gothic houses have their own characteristics: strict geometric shapes, resemblance to a defensive fortress with one to four high towers, pointed roof, elongated lancet windows, stained-glass glazing, modest facade decoration, contrasting combination of roof and wall colors . The building material of Gothic houses is stone or brick. Buildings have at least 3 floors. Gothic-style houses look authentic on the edge of a forest or in a mountainous area.
Baroque
Baroque houses look like miniature palaces. The buildings are distinguished by their monumental appearance, an abundance of stucco work, and an intricately decorated façade, reminiscent of buildings of the late Middle Ages.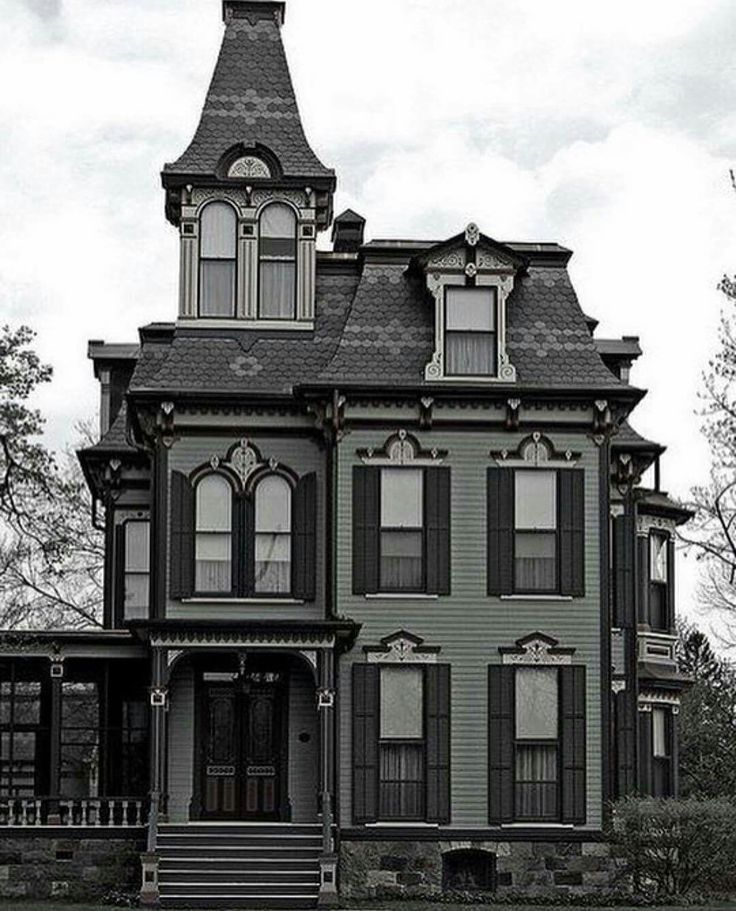 The baroque style is chosen by fans of classical architecture, connoisseurs of luxury and elegance.
The baroque style is chosen by fans of classical architecture, connoisseurs of luxury and elegance.
Pilasters, arched windows, embossed cornices, balustrades, a high massive porch, a staircase with railings, decorative cornices under the roof and above the windows are also distinctive characteristics of the architectural trend. The style involves finishing the facade in cream, white, beige, golden, gray tones.
Modern
Extravagant style rethinks the principles of standard architecture. The originality of this design lies in the combination of building materials such as metal and glass, concrete and stone, a combination of asymmetric lines and broken shapes.
- The architectural trend is based on a harmonious combination of man-made elements and natural forms, the presence of plant motifs, and the absence of symmetry.
- The style attracts with its polygonal shapes, voluminous architecture, wavy recesses.
- Architectural modernism combines simplicity of design and a rich choice of color schemes.

The facade of the building looks organic and integral. Projects of houses in the Art Nouveau style are picturesque and significant. To create structures, various building materials are used: metal, concrete, natural and artificial stone, tempered glass, as well as polycarbonate, metal tiles can be used for roofing.
Provence
The style of rural houses in the southern French province originated in the 19th century. The architecture of Provence is consonant with those who can see the beauty in everyday life. A characteristic feature of the decor in the Provence style is some negligence and aged materials for the exterior decoration of the facade.
Distinctive features of the style are a high spacious terrace, wrought iron and carved details, wooden shutters and windows, a tiled roof with several slopes, a balcony with columns and balusters, massive doors with metal hinges. Exterior wall decoration is done in light pastel colors.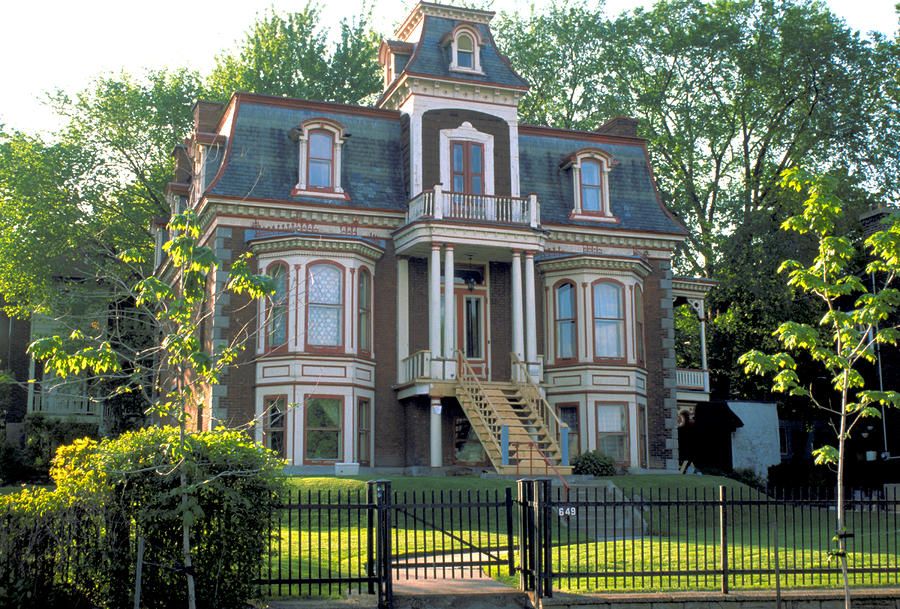 The advantage in the decoration of the facade is given to natural materials: wood and stone, with a small budget they are replaced with high-quality imitation.
The advantage in the decoration of the facade is given to natural materials: wood and stone, with a small budget they are replaced with high-quality imitation.
Casa Batlló
An example of Art Nouveau architecture from the early 20th century built in 1877. In 1904-1906, the building was completely rebuilt by the brilliant architect Antonio Gaudí. Both the façade and the interiors have been reconstructed.
The building, due to the many design techniques used, stands out for its stylistic heterogeneity and is a real Barcelona landmark. The exterior of the house is distinguished by the decoration of glass mosaics, the predominance of asymmetry, natural motifs, religious symbols, colorful pure colors, balconies with railings in the form of the pelvic bones of the human skeleton. Gaudí radically redesigned the seven-level structure, giving the façade a flowing shape and the roof a silhouette of the curved back of a dragon.
Loft style in architecture
The birthplace of non-standard trends in the interior and exterior design of houses is the USA.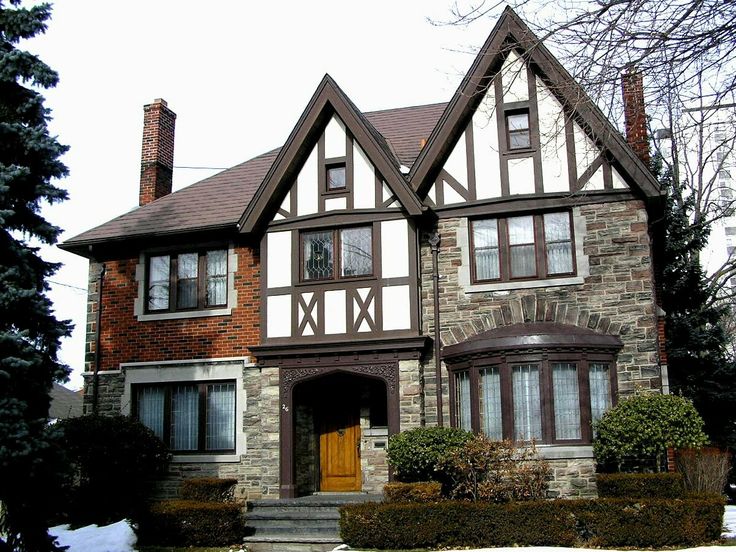 Initially, these were factories, warehouses, factories converted into residential premises. Loft objects have an industrial, authentic look.
Initially, these were factories, warehouses, factories converted into residential premises. Loft objects have an industrial, authentic look.
Conceptual features of the architectural style:
- Dirty gray, red-brown color scheme and metallic shades.
- Severity of lines and simplicity of geometric shapes with minimal decor.
- Fragments of industrial structures for industrial use in the form of metal stairs, factory pipes, ventilation systems.
- Unusual combinations of aged red brick and panoramic glazing, raw or roughly plastered concrete and ferrous metal for a residential building.
Loft-style houses are preferred by creative individuals with a non-standard approach to life. Architectural objects that claim to belong to the Loft are distinguished by extraordinary exteriors, referring to the industrial past.
Minimalism
The classic minimalist home is a small house with a simple symmetrical design.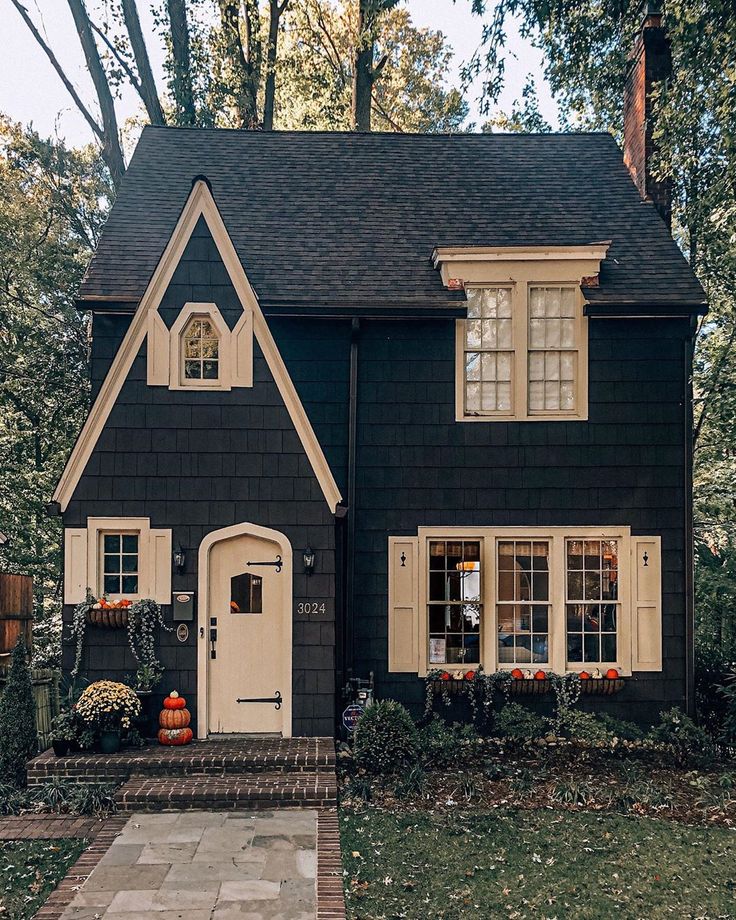 This style direction is characterized by the absence of decorative elements and the maximum simplicity of lines, geometric shapes and natural textures. Style concept: cut off all unnecessary and leave rational.
This style direction is characterized by the absence of decorative elements and the maximum simplicity of lines, geometric shapes and natural textures. Style concept: cut off all unnecessary and leave rational.
Basic features of minimalist houses: large window openings, horizontal roof, combination of vertical and horizontal lines. The basic colors of such architectural objects are light, neutral. The geometry of the architectural solution is emphasized in black. Dwellings in a minimalist style are built in one or two floors. Materials used in construction: concrete and glass, natural wooden boards and clinker tiles are used for decoration.
Barnhouse
An architectural style inspired by loft, minimalism and bio-tech. These are the so-called barn houses with one or two floors. Conceptual features of houses in this style:
- Strict simplicity of form and texture.
- Presence of open wooden terraces.
- Rectangular stable shape.









