Is it easy to grow spinach
How to Grow Spinach | BBC Gardeners World Magazine
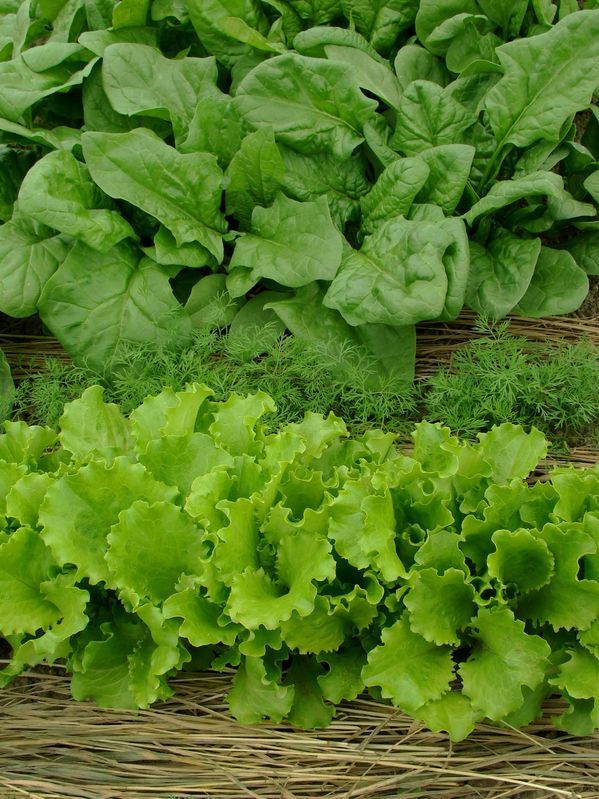
Spinach is high in nutrients and is fast and easy to grow as a cut-and-come again ‘baby-leaf’ vegetable or for larger leaves.
It can be grown all year round if you choose the right varieties and works well in containers too. It tastes delicious when wilted in the pan or as young fresh leaves in a salad.
How to grow spinach
Grow spinach in moist but well-drained soil or compost in partial shade. Sow seeds in a shallow moist drill and cover lightly with soil. Sow spinach successionally every few weeks to ensure a continuous crop. Harvest baby leaves for use in salads or mature leaves to wilt for use in soups and stews.
More on growing spinach:
- Winter veg crops to sow in August
- Vegetable seeds to sow in September
- 10 microgreens to grow
How to sow spinach seeds
How to grow spinach - sowing spinach in a seed drill
Make a shallow drill in well-prepared, fertile soil in a sunny spot and sow your spinach seeds thinly, approximately 1. 5cm deep. Cover seeds with soil and water well. If sowing in rows sow 40cm apart. Cover with cloches or protection if the weather is still cool. Sow a batch every three to four weeks for a regular supply through the growing season.
In this video clip from Gardeners' World, Monty Don explains how to sow spinach, beetroot and chard seeds and then look after the crops over the coming weeks:
How to care for spinach
How to grow spinach - watering young spinach plants
Spinach thrives in fertile soil that doesn't easily dry out. In hot weather, set up temporary shade for your spinach crop to stop the soil drying out and the crop bolting (running to seed).
After thinning your sowings to 15cm apart, the most important thing is to keep your spinach well watered. For sowings later in the year, protect your spinach seedlings with fleece or a cloche for a supply through the winter months.
Growing spinach: problem solving
How to grow spinach - thinning out spinach
Protect young spinach seedlings from slugs, snails and birds.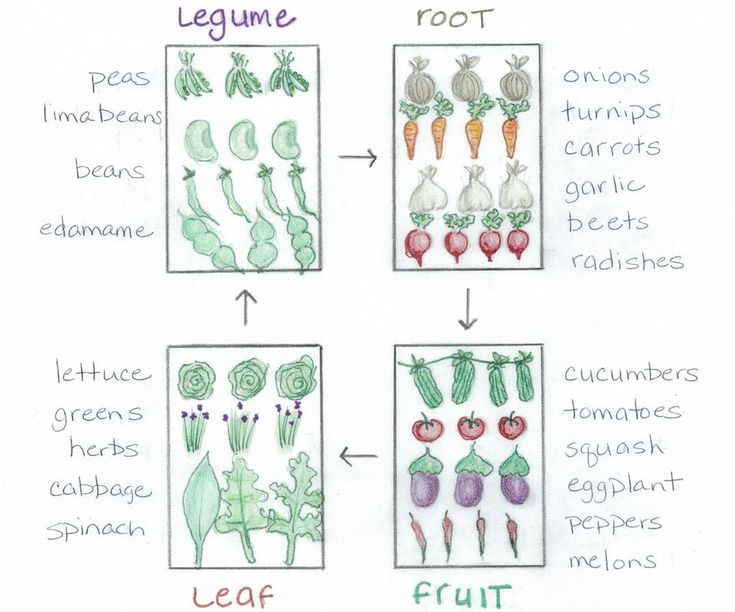 Spinach is also prone to downy mildew, which is worse in humid weather. Mildew-resistant varieties are available but the best method of prevention is good spacing around plants to help the air to circulate, and to target your watering at the base of the plants.
Spinach is also prone to downy mildew, which is worse in humid weather. Mildew-resistant varieties are available but the best method of prevention is good spacing around plants to help the air to circulate, and to target your watering at the base of the plants.
Check out these tips on stopping slugs from eating young plants.
How to harvest spinach
Picking spinach leaves
Spinach is ready to harvest 6-10 weeks after sowing. As a general rule, you can pick summer varieties from May to October and winter ones between October and April. But keep an eye on your crop as spinach usually grows quicker in warmer weather. Cutting back to just above the base of the plant can encourage more leaves to grow for a second crop.
More like this
Looking for inspiration on how to use your crop? Our friends at olive have curated a delicious collection of spinach recipes, including a vibrant pea, spinach and crab risotto.
How to store spinach
Spinach is best eaten fresh when it's highest in nutrients. But it can be frozen for later use in soups and omelettes – there's no need to blanch the leaves.
But it can be frozen for later use in soups and omelettes – there's no need to blanch the leaves.
Organic tip
Spinach is a good crop to grow in between beans, peas or sweetcorn if you only have a small growing space. But it's important to move your spinach crops around your vegetable plot as the spores of downy mildew can remain in the soil and will re-infect your crop.
Spinach varieties to grow
How to grow spinach - spinach 'Medania'
- ‘Medania’ RHS AGM – a good, healthy spinach variety, producing lots of dark green leaves with a soft texture and good flavour whether eaten as a baby leaf or mature crop
- ‘Perpetual’ – a good variety that doesn't bolt easily and will grow on drier soils. Good for summer, autumn and winter crops
- ‘Apollo’ – this variety gives a good yield with leaves that taste good either as a baby leaf crop or when mature. Good bolt-resistance and good in containers
- ‘Palco’ RHS AGM – a mildew-resistant variety that’s slow to bolt
- ‘Atlanta’ RHS AGM – a hardy, winter variety that produces a good crop of leaves
How to grow spinach: indoors or outdoors for healthy leaves
(Image credit: Poungpeth EyeEm/GettyImages)
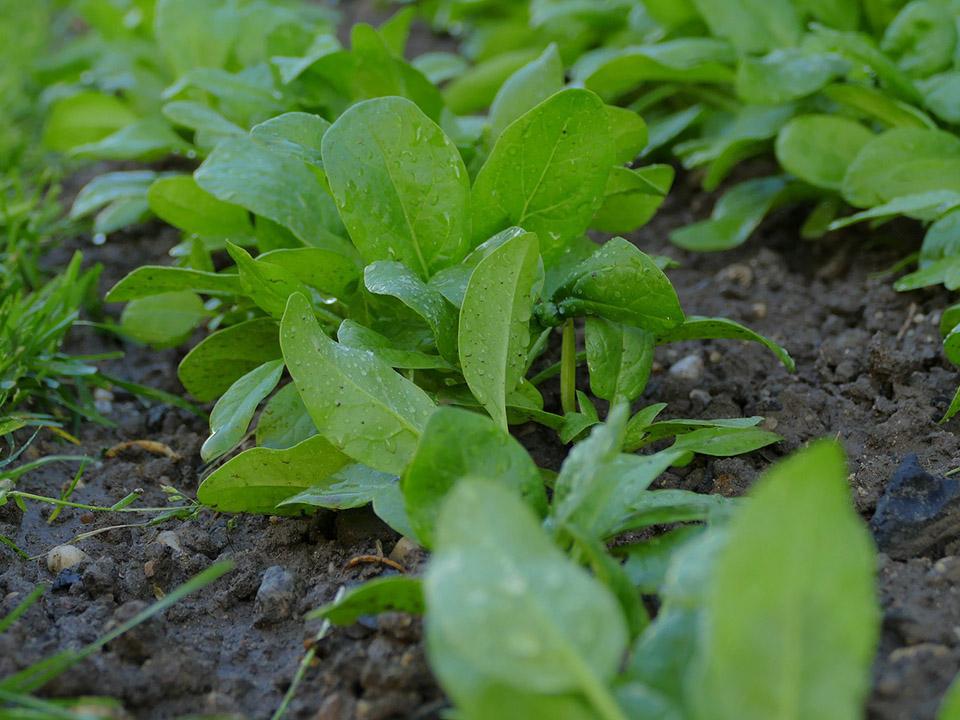
It is easy to learn how to grow spinach and the tasty homegrown leaves are packed with nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, iron and calcium and 13 compounds that function as antioxidants and cancer fighting agents – making it an excellent choice to add to your vegetable garden ideas.
Quick and easy to grow, you could be enjoying spinach leaves within six to eight weeks of planting. With many different varieties to choose from, if you plan carefully, and sow different types successionally, you could enjoy the green nutritious leaves year round.
An ideal crop for vegetable garden container ideas, spinach can be grown as cut-and-come-again baby leaves to enjoy in salads or sandwiches, or leave the leaves to grow larger and mature to use in cooking, such as to add to pasta dishes or use as a side vegetable. It is a productive and highly versatile crop, making growing spinach a popular choice for small vegetable garden ideas, where every inch of space needs to be used to the best advantage.
How to grow spinach
(Image credit: Sigmund/Unsplash)
There are a number of options for how to grow spinach. You could grow it indoors or outdoors, in pots on a terrace or courtyard along with other salad leaves such as lettuce, among other crops as part of your kitchen garden ideas, or in raised garden beds.
'Select from one of three types of spinach. The curly leafed savoy, flat leafed or the slightly curly semi-savoy. The flat leafed types generally have the mildest flavor and their smallest leaves are sold as baby spinach,' explains gardening expert Melinda Myers .
When is the best month to plant spinach?
The best month for growing spinach will depend to a certain extent on the hardiness zone where you live. However, you want to be growing spinach during the cool weather of spring and fall, as it is a cool weather crop.
Summer spinach cultivars: Plant summer varieties of spinach every few weeks from early until late spring.
Winter spinach cultivars: Sow hardy winter cultivars from mid summer to early fall.
The experts at Bonnie Plants provide the following advice for growing spinach twice a year: plant it about four to six weeks before the last frost in the spring, and again six to eight weeks before the first frost in the fall.
By sowing spinach seeds every three to four weeks as part of your planning of when to plant vegetables, you can enjoy a constant supply through the growing season.
How to grow spinach from seed
(Image credit: Getty Images)
First decide on where you want to grow your spinach crops, as some of the smaller varieties are particularly well suited to containers, for instance.
For success in growing spinach, before sowing the seeds enrich the soil, such as by digging in homemade garden compost and a general fertilizer. This will both help the spinach to grow well, and also prevent the leaves tasting bitter.
'There is no such thing as putting too much compost in garden soil. Mix at least 2-4 inches of compost in the row before planting,' advises Simon Crawford, breeder at Burpee Europe .
'The key to success begins with getting the plants off to a good start. Plant the right varieties in a rich, organic soil. Supply lots of moisture, and don't be shy about fertilizing. Vigorous spinach is tasty spinach,' adds Simon.
Vigorous spinach is tasty spinach,' adds Simon.
Follow these steps for how to grow spinach from seed:
- Grow spinach in moist but well-drained soil or compost.
- Winter spinach cultivars need a sunny position; summer spinach varieties are better in partial shade so are among the easiest vegetables to grow in shade
- Sow seeds thinly in a shallow drill – about 1inch deep.
- If sowing more than one row then space each row about 14 inches apart.
- Cover seeds lightly with soil.
- After the seeds germinate thin them to 3-5 inches apart. 'Thinning is very important and you must be ruthless,' says Simon Crawford.
- Fertilize plants regularly with a water-soluble plant food.
- Sow seeds every three to four weeks for a regular supply through the growing season.
- Keep spinach crops well watered – watering at the base of the plant.
‘Spinach can be cut again and again and last for months and months. I sow seeds deliberately quite thickly as a cut and come again salad crop. It’s important to keep them well watered and that way you will get delicious growth,' advises Monty Don in a video for Gardeners' World .
I sow seeds deliberately quite thickly as a cut and come again salad crop. It’s important to keep them well watered and that way you will get delicious growth,' advises Monty Don in a video for Gardeners' World .
Growing spinach in raised beds
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Choosing raised beds for growing spinach can get round the problem of your garden having poor soil or the wrong soil type for crops to grow successfully – as spinach prefers a neutral to alkaline soil.
Raised beds offer good drainage and are also easily manageable as a low maintenance garden border idea. You can fill them with rich, organic soil, working in 2-4 inches of compost prior to planting spinach seeds.
As above, sow spinach seeds in a shallow drill about 1 inch deep, each row about 14 inches apart. When seedlings are large enough to handle, thin them out to about 3 inches apart. Water and fertilize the plants regularly.
How to grow spinach in pots
(Image credit: Getty Images)
For how to grow spinach in pots, choose a wide pot or trough so that you can space out the spinach plants, and one that is about 6-8 inches deep. Spinach works well growing in pots alongside herb planter ideas.
Spinach works well growing in pots alongside herb planter ideas.
- Use quality potting mix rich in organic matter.
- Well-draining soil is important for spinach to grow well in pots.
- Sow seeds 1/2 inch deep in containers.
- Seedlings should germinate in five to 14 days depending on the variety and growing conditions.
- Space each spinach plant at least 3 inches apart - or slightly further apart if you want to harvest larger leaves.
- Keep the pot in a sunny spot when growing spinach in the fall.
- When growing spinach in spring and summer keep the containers in semi shade.
- Do not let the spinach plants sit in wet soil – keep the soil moist but not wet – so make sure the pot has good drainage.
- Fertilize the soil regularly.
'One of the great advantages of container growing is that it is easy to extend the growing season. Many plants will benefit from the additional warmth found close to the house,' says Aaron Bertelsen, gardener and cook at Great Dixter and author of Grow Fruit & Vegetables in Pots: Planting advice and recipes from Great Dixter .
How to grow spinach indoors
(Image credit: Angèle Kamp/ Unsplash)
It is easy to grow spinach indoors on a windowsill. If you are growing herbs indoors then place your spinach crops by these so you can tend to them all at the same time.
If planting in fall, place the pots on a sunnier windowsill as there are fewer hours of sunlight. Do not allow the plants to get too cold or too hot – so do not place directly above a radiator, for instance.
If planting spinach in spring, then position the pot where it will get some shade.
Sow spinach seeds in a pot at least 6 inches deep, and plant seeds at a depth of 1/2 inch, with each plant spaced about 3 inches apart. Keep the spinach plants well watered, although do not allow the soil to get waterlogged.
(Image credit: Getty Images)
How often should you water spinach?
You should water and fertilize spinach plants regularly, but try to avoid getting the leaves wet. The is to keep the soil moist but not soggy. Regular watering is especially important in periods of warm weather to prevent the plants from 'bolting' or producing flowers – if they do so the leaves will taste bitter.
Regular watering is especially important in periods of warm weather to prevent the plants from 'bolting' or producing flowers – if they do so the leaves will taste bitter.
Other ways to care for spinach include:
- Protect spinach seedlings sown in the fall from the cold by covering with fleece or a cloche.
- Shade spinach crops in hot weather to stop the soil drying out and the spinach plants bolting. You can do this through companion planting them next to pole – or runner – beans which as they grow will provide shade to protect the tender spinach plants from the heat of the sun.
- Protect young spinach seedlings from slugs, snails and birds.
Harvesting spinach
(Image credit: Getty Images)
You can harvest spinach between 6 to 10 weeks after sowing. If you sow successionally in spring and fall, you can have spinach to harvest throughout the year.
Summer spinach cultivars – you can generally pick summer varieties of spinach from May to October, depending on the climate in the area where you live.
Winter spinach cultivars – these can be harvested between October and April.
'Harvest a few leaves at a time from each plant. This will allow the plants to continue producing all season,' advises Simon Crawford.
This makes spinach a great crop to grow when gardening with children as they can continue to enjoy the fruits of their labors. This is the same as for other cut-and-come-again salad leaves, or if you're growing basil, or other leafy herbs.
Others gardening experts advise to harvest every alternate plant for use in the kitchen, giving the rest more room to grow.
Keep an eye on spinach crops as the plants usually grow quicker in warmer weather.
There are options for how to pick the leaves for a later harvest, much in the same way as when harvesting swiss chard. 'You can cut individual outer leaves when the plants are 3 inches tall and allow the inner leaves to continue to grow for later harvests. Or cut the whole head when the plant is 6 inches tall and wait several weeks for regrowth and a second harvest,' advises Melinda Myers,
Baby spinach leaves are great for use in salads, whereas mature leaves can be wilted into soups, stews, pasta or risotto dishes, to name but a few.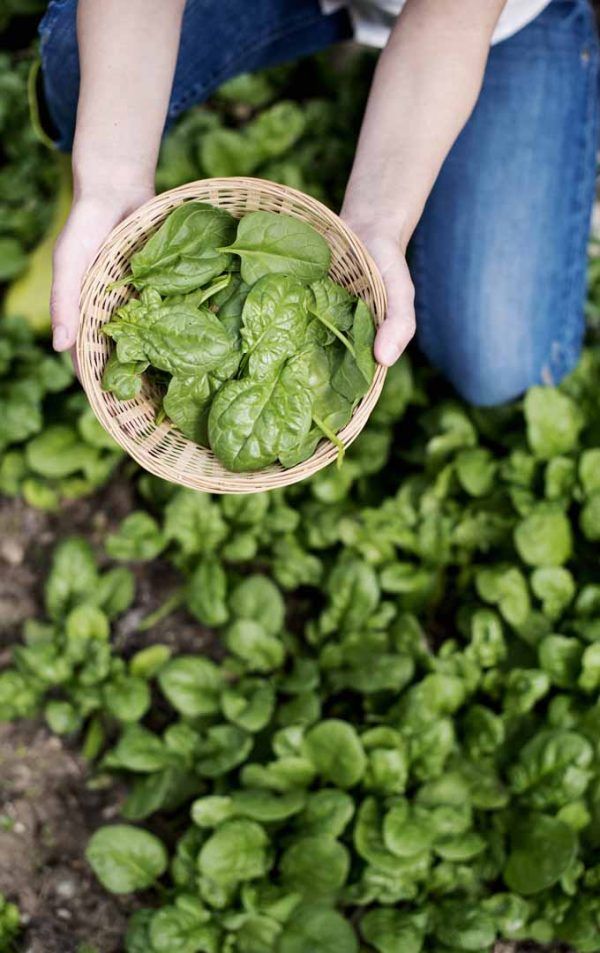
Leaves are ideally used directly after harvesting for the best flavor, and any extras can be stored in the fridge for up to 14 days.
Is spinach easy to grow?
If you've ever wondered if spinach is easy to grow, the simple answer is, yes. Like beets, it is a cool weather crop and requires minimal fuss.
It can be grown all year round if you choose the right spinach varieties and works well in containers, too. While the most cost effective method is to grow spinach from seed, you can buy transplants often at local nurseries, or online, too, in the main growing seasons. 'These young plants will already be well on their way to maturity when you put them in your garden,' explains the experts at Bonnie Plants .
How long does it take to grow spinach?
Spinach takes about six weeks to grow from being sown to harvesting.
There are both winter cultivars and summer cultivars of spinach, which are sown and harvested at different times. Choose a variety of each to sow and you can enjoy the leaves all through the year.
'A fast-growing plant, spinach yields many leaves in a short time in the mild weather of spring and fall. The main trick in how to grow spinach lies in making it last as long as possible, especially in the spring, when lengthening days shorten its life,' explain the Bonnie Plants experts.
Does spinach like full sun?
If you are growing winter cultivars of spinach in fall then these prefer full sun to grow well. Summer varieties prefer partial shade as otherwise the leaves can get scorched by hot sun in summer.
Will spinach regrow after cutting?
Spinach will regrow after cutting and if you keep harvesting the leaves, a few at a time, it will continue producing leaves through the season.
Rachel is senior content editor, and writes and commissions gardening content for homesandgardens.com, Homes & Gardens magazine, and its sister titles Period Living Magazine and Country Homes & Interiors. She has written for lifestyle magazines for many years, with a particular focus on gardening, historic houses and arts and crafts, but started out her journalism career in BBC radio, where she enjoyed reporting on and writing programme scripts for all manner of stories. Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
growing from seeds in open ground and at home, harm and benefits, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/en/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: garden plants reprinted: Last amendments:
Content
- Planting and care for spinach
- Plant Spinach - Description
- Spinach sowing
- When to plant spinach
- Growing spinach from seeds
- Growing spinach on the windowsill
- How to grow spinach at home
- Growing spinach in open ground
- when
- Planting spinach in soil spinat Spinach nutrition
- What to plant after spinach
- Spinach pests and diseases
- Spinach diseases
- Spinach pests
In the middle of the 7th century, along the Great Silk Road, spinach came to China, where it was called the “Persian vegetable”.
In Christian Europe - first in Sicily and Spain - spinach became known around the 13th century, but then a form of the plant was cultivated that is now forgotten. In Italy of the 15th century, green spinach was eaten during Lent, and in France, the Italian Catherine de Medici introduced the fashion to serve spinach at the table. Since the middle of the 16th century, spinach of the modern type has already been grown in Europe: broad-leaved, without bitterness and with round seeds.
In the first third of the 20th century, spinach boomed in popularity in the United States and Western countries because it was mistakenly believed to contain an incredible amount of iron. Remember cartoons about the sailor Popeye? However, later it turned out that there is 10 times less iron in spinach: the researcher simply forgot to put a comma in the number ... The excitement around spinach gradually subsided, but nevertheless, its producers erected a monument to the sailor Popeye in Texas in gratitude for popularizing the vegetable.
In Russia, spinach began to be eaten in the middle of the 18th century, but until the end of the next century it remained a little-known "master's" vegetable, which was served at the table with croutons and an egg, and even then spinach in Russia failed to gain wide popularity.
Currently, this crop is most in demand in China and the United States, and in America, three-quarters of the spinach crop is sold fresh. Spinach consumption in the United States has almost returned to the levels of the middle of the 20th century. Today, young spinach, the so-called baby spinach, with tender leaves up to 5 cm long, is gaining ground on the market.
Planting and caring for spinach soil - in the second half of May. Sowing seeds of early varieties directly into the ground - at the end of April, after which seeds can be sown by the conveyor method every two weeks: from sowing to harvesting - 5 weeks. Late varieties can be sown until mid-August to harvest in 6-7 weeks. Before winter, spinach seeds can be sown 6-8 weeks before the first frost - in mid-October.

- Lighting: bright sunlight, partial shade and even shade.
- Soil: well-drained, slightly acidic loam, pH 6.5-7.0.
- Watering: for each m² of garden watering can with a sprinkler or a hose with a sprinkler head, a bucket of water is poured. In heat and drought, spinach is watered three times a week.
- Top dressing: if spinach growth is slow, apply nitrogen fertilizer to the soil, but if the soil was fertilized before sowing, top dressing is unlikely to be needed.
- Propagation: seed - seedling and non-seedling.
- Pests: mining and beet flies, gamma cutworm caterpillars, aphids, common mole crickets and boletus flies.
- Diseases: fusarium, peronosporosis, anthracnose, curliness, viral mosaic, ascochitosis, cercosporosis and ramulariasis.
- Properties: Spinach is the most valuable dietary product with a laxative, diuretic, anti-inflammatory and tonic effect.

Read more about growing spinach below
Spinach plant - description
What does spinach look like? The height of the plant is from 25 to 50 cm or more. Its stems are bare, simple and branched. The lower basal leaves of spinach are petiolate, triangular-lanceolate, often with elongated lateral ears, or oval, oblong-ovate, entire, contracted into a petiole. The upper, and often the middle leaves are oblong, pointed, with a wedge-shaped base. Anther flowers with four stamens form a spike-paniculate inflorescence, and pistillate flowers are in dense glomeruli located in the axils of the leaves. The fruits of spinach are spherical or two-horned, sometimes soldered together, but, nevertheless, do not form seed.
Rosettes of spinach leaves, which form at the very beginning of the growing season, are used as food.
Sowing spinach for seedlings
When to plant spinach
Spinach, like any other herb, can be grown in a greenhouse, at home or in open ground.
 You can get the earliest greens if you pre-grow spinach seedlings. To do this, in late March or early April, spinach seeds are sown in boxes, paper or plastic cups filled with a moist, loose, disinfected substrate consisting of biohumus (1 part) and coconut fiber (2 parts). A layer of expanded clay 2-3 cm thick is placed under the substrate.
You can get the earliest greens if you pre-grow spinach seedlings. To do this, in late March or early April, spinach seeds are sown in boxes, paper or plastic cups filled with a moist, loose, disinfected substrate consisting of biohumus (1 part) and coconut fiber (2 parts). A layer of expanded clay 2-3 cm thick is placed under the substrate. Stubborn spinach seeds with a dense shell are soaked in water for two days before sowing, changing it every 6-8 hours. Then they are placed for disinfection for several hours in a pink solution of potassium permanganate, after which they are dried to flowability.
- The right choice of seeds is the key to a good harvest
Growing spinach from seeds
Spinach is sown to a depth of 1-1.5 cm, then the surface is slightly compacted, the crops are covered with film or glass and kept in a warm place until germination. As soon as the seeds begin to germinate, the film is removed, and the container is moved to the southeast or south window sill - the seedlings that have appeared will need a lot of light.
 But spinach seedlings are undemanding to warmth: it can be grown even on an unheated loggia. Another condition for the successful development of seedlings, in addition to good lighting, is to keep the substrate slightly moist.
But spinach seedlings are undemanding to warmth: it can be grown even on an unheated loggia. Another condition for the successful development of seedlings, in addition to good lighting, is to keep the substrate slightly moist. Spinach is planted outdoors when the soil is warm. After transplanting, install metal arcs above the bed at a height of about 20 cm and cover the seedlings with agrofibre in case of night frosts and intense spring sun.
Growing spinach on the windowsill
How to grow spinach at home
If you want to grow spinach on the windowsill, keep in mind that the life of the bush is no more than two months: after a few cuts, the spinach releases a flower arrow, and its leaves lose their necessary for food quality. How to grow spinach at home? When growing a crop in the spring-summer period, the seedlings do not require supplementary lighting, but if spinach is grown from seeds in the autumn or winter, it can give a good harvest only if you organize daily additional lighting for it for 2-3 hours after the Sunset.

Sowing of prepared spinach seeds is carried out to a depth of 1-1.5 cm in the same substrate in which spinach seedlings are grown. Under the substrate, a layer of drainage 2-3 cm high is laid in the dishes. Spinach can be sown in boxes or containers at least 15 cm deep or in 1-2-liter pots, or you can grow seedlings in small cups, and in the development stage of seedlings 2- 4 real leaves, pick them into a permanent dish. Crops are covered with a film until germination.
Growing and caring for spinach at home is very easy. The optimum temperature for the development of spinach seedlings is 15 to 18 ºC, watering should be regular and sufficient, especially in summer, as drying out of the substrate provokes premature bolting. In addition, you will need to spray your spinach daily in the early morning or after sunset. As for dressings, when sowing spinach in fertile soil, they are not needed. Spinach greens for cutting will ripen, depending on the variety, 3-5 weeks after sowing, but after 1-2 months the bush will go into the arrow and new greens will stop growing.

Growing spinach outdoors
When to sow spinach outdoors
Since spinach is a hardy plant, it can be grown outdoors without the seedling stage. For a spring harvest, spinach is sown 4-6 weeks after the last spring frosts, and for an autumn harvest, 6-8 weeks before the first autumn cold. In the spring, as soon as it warms up and the sun shines for 14 hours a day, small flowers will appear on the spinach - a process called flowering or shooting, and it makes the leaves of the plant unfit for consumption. Therefore, many gardeners prefer to sow spinach in the fall. In the spring, at the end of April, early varieties of spinach are sown. You can sow the plant several times every 15-20 days. No more than 5 weeks pass from sowing to harvesting. Late varieties are sown until mid-August - they give a harvest in 6-7 weeks.
You can also sow spinach before winter - in mid-October. Before the onset of winter, the plant manages to form small rosettes, and in the spring, spinach left to winter in the ground will sprout very early, and in a couple of weeks you can include it in your diet.

- We grow large carrots - consider what grew to carrots in this area and follow the recommendations
Planting spinach in the ground
Planting and caring for spinach in the field is quick and easy. The site for the plant should be sunny, and although the plant will also grow well in the shade, its productivity will be lower than when grown in the sun. Spinach prefers drained slightly acidic loamy soils with a pH of 6.5-7.0. You can adjust the acidity of the soil by adding limestone to it: dolomitic limestone is added to soil that contains little magnesium, and calcite limestone is added to soil with a high magnesium content. Do this in the fall or at least 2-3 months before sowing.
Since the soil for spinach needs to be rich in organic matter, alfalfa, soybean or blood meal is added to the soil for deep digging. Or they dig up a site with mineral fertilizers from the following calculation: 30 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium chloride per 1 m².
Before spring sowing, urea is introduced into the soil - 20 g per 1 m².
Spinach is sown in rows to a depth of 2 cm with row spacing of 20-30 cm, placing the seeds at a distance of 5-8 cm from each other. After planting the seeds, the surface is slightly compacted with the back of the rake, watered, covered with burlap for 3-4 days, and a plastic film is thrown onto the arched supports installed in advance at a height of about 20 cm. Seeds germinate at a temperature of 2 to 5 ºC in about 10-14 days.
When the seedlings have formed a rosette of 2-3 leaves, thin out the spinach - ideally the bushes should grow at such a distance from each other that they barely touch the leaves. Spinach care consists of regular watering, weeding, loosening the soil around the plants and protecting the spinach from the sun with a shade net when the air temperature rises to 26 ºC.
Watering spinach
Spinach is very moisture-loving. For watering it, it is better to use a hose with a sprinkler nozzle or a garden watering can with a splitter, but remember that with strong pressure you can wash away fragile shoots.
Approximately one bucket of water is consumed per m² of beds. In dry, hot weather, watering is carried out at least three times a week, and in order to prevent water from spreading, make a furrow around the perimeter of the beds. After watering, when the water is absorbed and the surface of the soil is slightly dry, loosen the soil around the plants and remove the weeds. If you notice flower arrows on spinach, break them off.
Fertilizing spinach
If spinach grows well in the field, then it has enough nutrients in the soil, but if spinach grows slowly, feed it with a nitrogen fertilizer: cudweed meal or blood meal. Fertilizers are applied to a depth of several centimeters, after which the site is watered. In general, spinach needs top dressing only if the area was not fertilized before sowing or planting seedlings.
What to plant after spinach
To prevent soil depletion, spinach can be grown on one plot with a break of 3-4 years. According to the laws of crop rotation, roots are usually grown after tops, that is, after spinach, you can plant Jerusalem artichoke, swede, radish, radish, daikon, katran, turnip and other tuberous or root plants.
- An important April top dressing for peppers - which of the two preparations to choose?
Spinach pests and diseases
Spinach diseases
The most harmful diseases of spinach are fusarium, downy mildew, anthracnose, curl and viral mosaic. Spinach can also be affected by diseases such as ascochitosis, cercosporosis and ramulariasis.
Fusarium wilt, or root rot is a dangerous fungal disease that affects seedlings and young plants. In specimens affected by Fusarium, the color becomes dull, they begin to lag behind in growth, their leaves lose turgor, turn yellow, and the plants die. The process begins with the lower leaves, and when the plant is dug up, its roots are found to be rotten. You will not succeed in curing spinach from fusarium, especially if the process has covered the entire plant, so the affected bushes must be removed from the garden. As a preventive measure, you need to grow disease-resistant varieties of spinach, make sure that the bushes do not grow too close to each other, regularly loosen the soil around them and remove weeds, and the seeds must be disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate before sowing.

Downy mildew, or Downy mildew is a fungal disease that appears as yellowish spots on the upper side of spinach leaves, while a grayish coating forms on their underside. Then the spots acquire a brown-brown hue, the leaves droop, wrinkle, dry out and crumble. The disease progresses in cool damp weather. Ways to protect against peronosporosis, as well as from root rot, are mainly preventive, since when using chemical preparations, the toxic substances contained in them, accumulating in the leaves, will make them unsuitable for food. Folk remedies for fighting fungal diseases can come to the rescue:
- treatment of plants with a solution of 10 drops of 5% pharmacy iodine in 1 liter of milk, which is then mixed with 9 liters of water;
- treatment of spinach with an ash solution: 2 cups of ash are brewed with three liters of boiling water, allowed to cool, filtered through a triple layer of gauze, diluted with 10 liters of water and spinach is treated with this solution;
- 200-300 g of onion peel are poured into 10 liters of water, brought to a boil, allowed to infuse for 1-2 days, filtered and treated with infusion of the plant;
- 1-1.
 5 g of potassium permanganate is diluted in 10 liters of water and sprayed with a solution of spinach.
5 g of potassium permanganate is diluted in 10 liters of water and sprayed with a solution of spinach.
Anthracnose covers the leaves and their petioles with rounded dark spots, in the center of which there are black raised pads.
Cercosporosis also affects the leaves and stems of spinach. First, rounded spots with a diameter of 2-4 mm are formed on them - red-brown with an ashy middle. Then the spots grow, merge with each other, the tissue inside the spots becomes thinner, dries and spills out, leaving holes in the leaf plates.
With ascochitosis , spots also appear on leaves and stems: convex, of various shapes and colors, but most often brown with a dark border. Affected tissues gradually dry out.
Ramularia blight, or leaf spot covers spinach leaves with grey-brown spots with dark edges. With the development of the disease, the leaves die.
Cucumber mosaic viruses and can be stored in soil, on seeds and plant debris and transmitted by sucking insects.
 Viruses penetrate the plant through damaged tissues, their presence is manifested by the formation of yellow or light green strokes and star-shaped spots on spinach leaves, which gradually merge with each other. The leaves are deformed, stunted, become dwarfed.
Viruses penetrate the plant through damaged tissues, their presence is manifested by the formation of yellow or light green strokes and star-shaped spots on spinach leaves, which gradually merge with each other. The leaves are deformed, stunted, become dwarfed. Leaf curl results in thickening and uneven growth of the leaf tissue, causing the leaf to curl, become wavy and blistered. Curly hair is often accompanied by necrosis, spinach leaves dry up and fall off.
Curly and Mosaic are viral diseases and there is no way to cure them - the plants must be destroyed. And with fungal diseases, you can fight with preventive methods and folk remedies, which we have already described to you.
Spinach pests
Spinach pests are also numerous. Among them are mining and beet flies, gamma scoop caterpillars, aphids, common bears and babanukhs.
Miner fly lays its eggs in the leaves of the plant, and the larvae that appear in June eat their flesh, which kills the spinach.
 You can scare away the pest by alternating rows of spinach with rows of beets, which the fly does not tolerate. However, do not sow spinach in an area where the beets have just been harvested, as it can get root rot.
You can scare away the pest by alternating rows of spinach with rows of beets, which the fly does not tolerate. However, do not sow spinach in an area where the beets have just been harvested, as it can get root rot. Green or brown cutworm is one of the worst leaf-destroying pests of spinach. You can fight caterpillars by treating bushes with tobacco or pepper infusion, as well as infusion of tomato tops. And don't forget to weed the garden regularly.
Beet fly also lays eggs on spinach leaves. Destroy it by treating the plant with a two percent solution of Phosphamide.
Aphid is a sucking insect that makes punctures in young leaves of plants, sucking juice out of them, and often infecting them with viral diseases. Processing spinach with an ash-soap solution will help you cope with aphids: 200-300 g of ash should be boiled in a bucket of water for 30 minutes, then cool, strain and add 40 g of grated soap or liquid dishwashing detergent.
 Most likely, you will not be able to get rid of aphids at once, but if you spray the spinach with an ash-soap solution 4-5 times with an interval of several days, the aphids will disappear.
Most likely, you will not be able to get rid of aphids at once, but if you spray the spinach with an ash-soap solution 4-5 times with an interval of several days, the aphids will disappear. Medvedka is a large and dangerous pest that feeds not only on plants, but also on small insects. She can move underground, on the ground and even through the air, which makes it very difficult to fight her. Nevertheless, it must be destroyed, since not only spinach, but also other garden and garden plants can suffer from this pest. The main thing is to find its nest and all the passages to it in the footsteps of the bear, and the tracks are best seen after rain. The discovered nest must be very carefully dug out so as not to frighten away the insect in it, put into a bucket and burned, and a drug to destroy the bear or pour soapy water into each passage in case there is no pest in the nest.
Babanukha is a cabbage or horseradish leaf beetle that also eats spinach leaves with pleasure.
 These bugs are best picked by hand and destroyed, and after harvesting, it is advisable to dust the spinach with a mixture of wood ash with hot red pepper powder and dry mustard.
These bugs are best picked by hand and destroyed, and after harvesting, it is advisable to dust the spinach with a mixture of wood ash with hot red pepper powder and dry mustard. Types and varieties of spinach
According to the maturation period, garden spinach varieties are divided into early-ripening, mid-ripening and late-ripening. The best early maturing varieties include the following:
- Gaudry is a variety ripening for food in 2-3 weeks. It can be sown both in early spring and late autumn, both in open and closed ground. The diameter of the rosette of leaves of the Gaudri variety is about 23 cm;
- Gigantic is one of the most well-known cultivars producing leaves two weeks after sowing. This variety is one of the best for canning. Rosette of elongated fleshy leaves sometimes reaches a diameter of 50 cm;
- Virofle - an early maturing French variety, prone to the early formation of a flower arrow.
 The rosette of oval, fleshy, tender and smooth, greenish-yellow leaves reaches a diameter of 30 cm. The plant is resistant to cold, so it can be sown in early spring;
The rosette of oval, fleshy, tender and smooth, greenish-yellow leaves reaches a diameter of 30 cm. The plant is resistant to cold, so it can be sown in early spring; - Stick is a high-yielding variety cultivated in our country since 1995, used both for fresh consumption and for canning. The rosette of leaves up to 19 cm long and up to 14 cm wide is half raised and reaches a diameter of 30 cm.
Of the mid-season varieties most often grown:
- Matador - frost-resistant and moisture-loving, as well as not prone to early bolting, a productive variety of Czech selection, which gives leaves already three weeks after sowing. The plant has a medium-sized compact semi-vertical rosette consisting of smooth, glossy oval grey-green leaves;
- Bloomsdalesky is a new variety of Dutch selection, resistant to bolting, with a high rosette with a diameter of about 25 cm. Leaves of deep dark green color, smooth, juicy and fleshy, in slightly pronounced bubbles;
- Krepysh is a high-yielding frost-resistant variety, not prone to early bolting, with a rosette of about 25 cm in diameter of semi-raised, glossy, obovate green leaves with slight vesicles.

Late-ripening varieties of spinach include:
- Victoria is a moisture-loving and high-yielding variety with resistance to peronosporosis and bolting, which gives foliage 30-35 days after sowing. This plant has a compact rosette with a diameter of 14-19cm with dark green with a bluish tinge, strongly bubbly leaves up to 10 long and up to 7 cm wide;
- Spokane is a high yielding hybrid dutch variety that is resistant to flowering and is recommended for both fresh consumption and canning. It has rounded, wavy, wrinkled-bubbly dark green leaves 10-14 cm long and 6-11 cm wide, collected in a compact medium-sized rosette;
- Varyag – a variety with an elevated compact rosette of large green oval medium-bubbly leaves of a slightly sour taste with medium-length petioles. The variety is suitable for salads and soups.
In addition to those described, spinach varieties such as Khorovod, Povar, Zhirnolistny, Popeye, Nikitos, Normal, Prima, Casta, Melodiya, Mazurka, Virtuoso, Tarantella, Ladya and Dolphin, Puma, Space, Emerald hybrids have proven themselves well.

Also known in cultivation is the so-called New Zealand spinach, or tetragonia, an annual plant of the Aizaceae family. This plant is not related to spinach, although the nutritional value and taste characteristics of these plants are very similar, and in some respects tetragonia even surpasses spinach.
But many-leaved spinach, or zhminda, or spinach-raspberry is a relative of garden spinach and is valuable not only for tasty and healthy leaves that are added to soups and salads, but also for berries similar to mulberry, from which jelly, compote and jam are cooked.
Malabra or Ceylon spinach, or Basella, from the Basella family, is a herbaceous plant, a creeper whose fleshy leaves are tasty both raw and cooked. A refreshing drink is obtained from the infusion of the leaves. In nature, Basella grows in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and America, and in our climate it can be grown in the garden as an annual plant.
Benefits and harms of spinach
Medicinal properties of spinach
Spinach has many medicinal properties.
 Why is spinach useful? What valuable substances are contained in its leaves? They include carbohydrates, proteins and fats, fiber, organic, unsaturated and saturated acids, sugars, starch, vitamins A, C, H, E, PP, K, B vitamins, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, copper , iodine, zinc, potassium, selenium and manganese.
Why is spinach useful? What valuable substances are contained in its leaves? They include carbohydrates, proteins and fats, fiber, organic, unsaturated and saturated acids, sugars, starch, vitamins A, C, H, E, PP, K, B vitamins, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, copper , iodine, zinc, potassium, selenium and manganese. It is important that vitamins C and A contained in spinach are retained even after cooking. And the iron in spinach is in a form that is easily absorbed by humans and prevents the formation of cellulite. Due to the fiber contained in spinach, the intestines are cleansed, which helps to get rid of excess weight. Spinach normalizes peristalsis and eliminates constipation.
Spinach is recommended for diseases of the nervous system, anemia, malnutrition, diabetes, enterocolitis, gastritis, hypertension and anemia. Since the plant has a laxative, diuretic, anti-inflammatory and tonic effect and is perfectly absorbed by the body, it is useful for those recovering from a serious illness, pregnant women and children.

Spinach strengthens the heart muscle and relieves insomnia, and due to the lutein contained in the leaves, it clarifies vision, reduces fatigue and increases efficiency.
Fresh spinach juice helps cleanse the body, replenishes energy reserves, stimulates the functioning of organs - the liver, intestines, kidneys. With inflammation of the gums, they rinse their mouth, and with sore throats - the throat. Fresh chopped spinach leaves are applied externally for abscesses and stings of bees, wasps and other insects, and a paste of spinach leaves boiled in olive oil treats eczema and burns, removes freckles and whitens the skin of the face.
Spinach is eaten fresh, boiled or baked and is used in many complex dishes, snacks and sauces.
Spinach - contraindications
Spinach contains large amounts of oxalic acid, therefore it is contraindicated for people with problems with the urinary tract, suffering from urolithiasis, nephritis and similar diseases.
 Spinach is not useful for gout, diseases of the duodenum, liver, biliary tract and rheumatism.
Spinach is not useful for gout, diseases of the duodenum, liver, biliary tract and rheumatism. It should be said that there is not so much oxalic acid in young leaves - it accumulates in mature leaves, so problems can be avoided by eating only young leaves of the plant, that is, the so-called baby spinach.
Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Peculiarities and other plants of the family Amaranthaceae
- List of all species on The Plant List
- More information on World Flora Online
For large garlic: what fertilizer is important at this stage?
Sorrel: growing in the garden, propertiesSections: Garden plants Amaranth (Schiritsaceae) Plants on Ø Leaf
After this article is usually read
Add a comment
planting and care in the apartment
As a rule, spinach is grown in open ground , but in order to get useful macro- and microelements even in the middle of winter, many people sow spinach seeds at home and grow them on the windowsill.
 If you can follow the simple rules of sowing and maintenance (create the necessary light and temperature conditions), you will have fresh and juicy greenery all year round, even if you do not have a summer house.
If you can follow the simple rules of sowing and maintenance (create the necessary light and temperature conditions), you will have fresh and juicy greenery all year round, even if you do not have a summer house. How to grow spinach at home on the windowsill will be described in detail below.
By the way! Many people don't like spinach because it tastes like "grass with grass" (not sour like sorrel). Indeed, this is a tasteless plant. But the neutral taste is great, you can make such delicious dressings! For example, the Caesar salad with spinach is very unusual.
Contents
- 1 What varieties of spinach are suitable for growing on a windowsill
- 2 How to plant spinach on the windowsill: Features, conditions and step -by -step instructions
- 2.1 Capacity for growing
- 2.2 In what soil to plant
- 2.3 Pre -preparation of seeds
- 2.4 Direct landing
- 3 Cross -poll pot for growing in an apartment
- 4 How to care for spinach on the windowsill at home
- 4.
 1 What should be the place for growing: light and temperature
1 What should be the place for growing: light and temperature - 4.2 Watering
- 4.
- 5 Emergence and Harvest Timing of Homemade Spinach
Which Spinach Varieties Are Suitable for Windowsill GrowingAnd for this, first of all, carefully study the instructions on the package - familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the varieties in order to choose the most suitable for indoor cultivation.
As a rule, the following varieties of spinach are used for sowing, which tolerate greenhouse conditions well and give a bountiful harvest:
- Fat-leaved.
- Gigantic .
- Matador.
- And also many others, for example, Krepysh, Virofle, Stoik, Victoria, Ilya Muromets. There is even a very interesting strawberry spinach .
To determine the most suitable variety, it is worth planting several packages of seeds in different containers.
 Only after that you can understand which kind of spinach will suit you the most according to all criteria.
Only after that you can understand which kind of spinach will suit you the most according to all criteria.
How to plant spinach on the windowsill: features, conditions and step-by-step instructionsAfter choosing the desired variety, you should start sowing work, namely: preparing the container, growing soil, soaking the seeds. To do this, planting spinach at home requires approaching with skill and performing all stages of cultivation according to certain rules.
Growing containerThe root system of spinach, for example, unlike sorrel, is quite shallow, so the container requires a small depth (12-15 cm).
Naturally, the pot must have drainage holes to drain excess moisture.
In addition, you can add a small layer of expanded clay or foam to the bottom of the planting container as drainage.
What soil to plant inSpinach will grow well only in neutral soil.

In other words, spinach loves soil with an acidity level of around 6-7 pH!
You can purchase ready soil for growing vegetables such as cabbage, pumpkin, beans, peas.
Or make your own. To do this, take a neutral garden soil and mix it with compost or humus, as well as river sand.
Tip! It is recommended to decontaminate any soil, even purchased soil, in advance using one of the methods, for example, by steaming the oven so that all soil pests die under the influence of high temperatures. Then additionally shed with a solution of Fitosporin .
Seed preparationIt is not recommended to plant spinach with dry, unprepared seeds (unless it is pelleted, i.e. already processed seeds). The seeds have a dense external structure, so they should be pre-soaked for a day or two in water at room temperature (above 18 degrees).

And then (optional) hold for another 20-30 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect seedlings from diseases.
Direct plantingStep-by-step instructions for sowing spinach seeds for further cultivation at home:
- Drainage and soil are poured into the planting container.
- Barbs are made 1.5-3 cm deep.
- Sowing seeds at a distance of 2-3 centimeters from each other.
- Next, you need to fill the rows with soil.
- Spend it (soil) moistening. For example, you can spray from a spray bottle.
- To create greenhouse conditions, the container is covered with film or glass.
- The pot is placed in a warm (+18..+20 degrees) and dark place.
- When shoots appear, the shelter (greenhouse) is removed, and the container itself is moved to a bright place - on the windowsill.
Please note! In the next video, the author uses unsuitable soil to grow spinach (wrong acidity).
 In general, everything is shown very well and clearly.
In general, everything is shown very well and clearly. Video: sowing spinach seeds for growing on the windowsill
Transplanting spinach from the open field into a pot for growing in the apartmentBy the way! It is not necessary to grow spinach from seeds, it is much easier to take and transplant it from the garden.
All you need is to dig up the bushes in autumn and transplant them into a pot.
Further care and cultivation are carried out similarly to those sown with seeds (more on this later).
How to care for spinach on the windowsill at homeSpinach care is quite simple - maintain optimal light and temperature conditions, as well as water on time.

What should be the place to grow: light and temperatureSpinach is a relatively light-loving plant. For him, it is recommended to choose a well-lit southern window sill (either western or eastern, but better at least southwestern or southeastern) .
Optimum day length is 12-14 hours.
But in order for the sun to not burn too much on especially hot days, burning tender leaves, it is recommended to shade it.
By the way! Spinach generally does not like direct sunlight and a lot of sunlight, besides, it becomes bitter …
In late autumn, winter and early spring days, the shrub does not have enough daylight hours, especially when it is raining or just overcast outside. Therefore, for growing spinach indoors, it is recommended to additionally install phytolamps or full-spectrum LED lamps.
Spinach does not require very warm conditions.
 At a temperature regime of +15..+18 degrees , the leaves of the plant quickly gain strength and grow to optimal sizes.
At a temperature regime of +15..+18 degrees , the leaves of the plant quickly gain strength and grow to optimal sizes. A grown plant with 4-5 leaf blades can be grown at a lower temperature of +10..+14 degrees, but in this situation the growth of leaf blades will be somewhat slowed down.
Therefore, an insulated balcony or loggia, where the temperature is slightly lower than room temperature, is quite suitable for growing.
In too warm conditions, spinach stalks will quickly wither, so it is recommended to maintain an optimal cool temperature.
WateringWatering should be carried out quite often and plentifully, spinach does not tolerate drying out of the soil.
It is strongly recommended to periodically spray overgrown leaf blades. This will saturate them with nutrient moisture and improve their appearance.
The low level of humidity provokes bolting, spinach throws out flower stalks, which should be promptly disposed of so that the plant does not waste extra energy.

Spinach does not require any special feeding.
Germination and harvesting time of domestic spinachAfter sowing spinach, you can see its first shoots, even with pre-treatment (soaking), in about a week (sometimes earlier).
And the actual cutting of foliage (harvesting) will begin only when the plants have fully formed succulent leaves. There will be 5-8 pieces, 8-10 centimeters long. In early ripening varieties, this moment occurs approximately 30 days after the first shoots.
Tip! In order not to interrupt the process of constantly obtaining useful spinach foliage, you can regularly make new crops.
At harvest time, the leaves can be cut off completely, leaving only the outermost young leaves.
Harvest by gently breaking the stem or cutting with scissors.
Do not pull or pluck the foliage as this may damage the root system.











