How to protect your plants from cold weather
Frost Covers & Cold Snap Care
Whether you fell under the spell of some eye-catching color at the garden center or just wanted to get a jump on the gardening season, planting too early can create a crisis when a cold snap threatens. Helping your seedlings survive the big chill isn't impossible, but it does require some preparation.
In most cases, you can count on makeshift methods to protect plants when the thermometer dips. But for larger plantings, such as a vegetable garden, you'll need to arm yourself ahead of time with the right gadgets to guard plants against frosty mornings.
Know The Limits
In order to understand what steps to take when freeze warnings threaten, you need to know the point at which treasured greenery fades to frost-burned brown. The general rule of thumb is that most plants freeze when temperatures remain at 28°F for five hours.
Of course, there are exceptions to this rule. Seedlings, with their tender new leaves, often give up the ghost when temperatures dip to 32-33°F. Tropical plants have differing low-temperature thresholds. Some keel over when temps fall to 40°F; others crumble at 35°F. Other plants are just hardy by nature and can withstand temperatures as low as 18-20°F. To find the threshold for your plants, search garden books and online resources.
Quick Fixes For Frost Warnings
Pick It Up – The easiest cold-protection scheme is to move plants out of harm's way. This works with seedlings in flats and potted plants. Moving plants under a deck, into a garage or shed, or onto a porch with a roof often offers ample protection.
Count On Water – Water soil just before sundown to raise overnight air temperature around plants as the water evaporates. Fill gallon jugs or buckets with water and place them in the sun during the day. At night, move them near endangered plants. The water will moderate air temperatures; if it freezes, it will release heat. For greatest effect, paint a few water-holding containers black to maximize daytime heating.
Keep Air Moving – Cold, still air does the most damage to plants. Stir a breeze all night with an electric fan to keep frost from forming on plants. Remember to protect electrical connections from moisture.
Cover Plants – Protect plants from all but the hardest freeze (28°F for five hours) by covering them with sheets, towels, blankets, cardboard or a tarp. You can also invert baskets, coolers or any container with a solid bottom over plants. Cover plants before dark to trap warmer air. Ideally, coverings shouldn't touch foliage. Anchor fabric coverings if windy conditions threaten.
In the morning, remove coverings when temperatures rise and frost dissipates. Heat from the sun can build beneath solid coverings, and plants can die from high temperatures.
Break Out Blankets – Keep gardening blankets, often called row covers, on hand. These covers are made from synthetic fibers or plastic in varying thicknesses. Lay row covers directly on plants, or create a tunnel by suspending them over a bed using stakes.
Turn On Lights – An incandescent light bulb generates sufficient heat to raise nearby air temperature enough to protect a plant from the deep freeze. Bulbs must be close to plants (within 2-3 feet) for this technique to work. (Fluorescent bulbs don't generate enough heat for this chore.)
Protect Individual Plants – Install hot caps – rigid plastic containers with venting holes – over individual seedlings at planting time. Hot caps act like cloches (mini greenhouses), but venting holes eliminate the daily chore of placing and removing the covering. Create the equivalent of a hot cap using plastic two-liter bottles or gallon jugs with bottoms cut off and lids removed (but saved). Replace lids at night when cold temperatures swoop through.
A twist on the hot cap idea is a Wall O'Water tepee, which encircles individual plants with a sleeve of water-filled tubes. The water absorbs the sun's heat during the day. At night, as the water slowly freezes, it releases the stored radiant heat of the sun, keeping air inside the tepee frost-free.
More Lawn Solution Articles for You
Winter Garden Checklist For Mild Climates
Winter garden checklist during mild climates. Winter doesn't signal the end of gardening season. There is many chores such as planting,...
read more
How To Prepare Your Garden For Frost
If winter is coming soon, this simple to-do list will help you prepare your garden for frosty weather, from harvesting, to draining hoses to...
read more
Planting After Danger Of Frost
For a successful spring planting, be aware of the danger of frost. It can kill young seedlings. Knowing the last frost date in your area can...
read more
Copyright © 2022 bioadvanced. com All Right Reserved.
com All Right Reserved.
How to protect plants from frost: 10 quick and easy methods
(Image credit: Getty Images)
As the cold weather sets in, it's important to know how to protect plants from frost, as tender and young plants in particular can be wiped out by a sudden cold snap.
There are many quick ways you can protect more vulnerable plants and it's definitely better to be safe than sorry – there is nothing more devastating than seeing the beautiful plants you have lovingly nurtured destroyed seemingly overnight by a visit from Jack Frost.
Unless you live in a warm zone, it is likely that some of the ornamental plants and crops you have included in your garden ideas will be in need of some protection, so read on to find out how you can help their survival through the colder months.
How to protect plants from frost – which plants to protect
(Image credit: National Trust)
Not all plants in your backyard will need protection from the frost, but there are certain categories that will. These include:
These include:
- Young seedlings and new growth
- Tender perennials
- Half-hardy varieties
- Tropical and subtropical plants such as palms and banana plants
Signs of frost damage include blackened, distorted or limp growth and the leaves turning green on evergreen plants and shrubs.
If in any doubt, research the conditions and hardiness of specific plants. Err on the side of caution and include frost protection in your winter garden ideas if cold weather is forecast in your state or area.
(Image credit: Getty Images)
In terms of vegetable crops, there are some that actually benefit from a dose of frost and can taste better afterwards. 'There are some veg crops that are frost tolerant, if not frost resistant,' explains Nicole Burke, author of Rooted Garden .
If you live in a colder zone, it is therefore worth learning how to grow kale and other frost tolerant vegetable crops.
1. Bring potted plants indoors
(Image credit: Future)
There are many quick ways for how to protect plants from frost, and among the easiest is to bring potted plants indoors, especially tender container plants.
Potted plants are more susceptible to frost damage because they don't have the insulated benefits of of those planted in the ground.
Use a conservatory, garden room, garage, porch or frost-free greenhouse to overwinter potted plants – not somewhere that is too warm.
This can be a suitable option if you're wondering how to overwinter fuchsias in pots, or how to winterize hydrangeas, for example.
2. Add a layer of mulch on garden beds
(Image credit: Alamy)
'Apply dry mulch, such as chipped bark or straw around borderline-hardy plants, such as agapanthus, phygelius (cape fuchsia), hedychium and the architectural melianthus to protect the crown,' advises plant expert Sarah Raven .
You could also use leaf mold or piles of leaves to add some extra protection on garden beds and provide a barrier against the cold.
Find out how to make leaf mulch to protect tender and emerging plants.
3. Cover plants with fleece
(Image credit: Getty Images)
You may wonder how to protect plants from frost when they are planted in the ground? One method – which is useful for larger garden plants and shrubs – is to cover them with horticultural fleece. You could use blankets or bubble wrap, too, to create a protective cover. These Amazon plant covers come highly recommended by reviewers.
You could use blankets or bubble wrap, too, to create a protective cover. These Amazon plant covers come highly recommended by reviewers.
Place several stakes around your plants and then cover these with the chosen material to create a tent-like structure. Weigh down the corners to prevent the coverings from blowing away in the night and remove the covers during the day.
You can use this method for plants that require winter protection, such as agapanthus, cordyline and tree ferns.
'Fleece is very effective, but if you prefer something less obtrusive, a circle of wire netting filled with bracken or leaves will keep the cold at bay, too' advises Sarah Raven.
You can also wrap the trunks of young trees with horticultural fleece or blankets, such as if you're growing some of the best fruit trees or have mastered how to grow lemon from seed.
4. Place tender plants in a sheltered spot
(Image credit: Getty Images)
The mantra 'right plant, right place' is relevant when considering how to protect plants from frost.
'Always plant half hardy and frost tender plants in a sheltered position, preferably near a south or west-facing wall, which will absorb heat during the day and radiate it at night,' advise the experts at Jacksons Nurseries .
'Eliminating the wind chill factor can substantially reduce the amount of frost damage incurred,' they add.
Other sheltered positions will include next to fences, under large evergreen trees for gardens, under the protection of pergola ideas or in patio or courtyard areas, as long as these also receive plenty of sunshine.
While a sunny, sheltered spot is ideal for many tender plants, do not place early-flowering plants, such as magnolias and camellias, so that they are exposed to the morning sun. 'The rapid thawing of frozen buds can result in blackening and bud drop,' advises Guy Barter, horticultural expert at the RHS .
5. Lift and store tender perennials
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Tender perennials that have bloomed and died down can be lifted to protect them from frost.
Store the roots, bulbs, tubers and corms in a cool but frost-free place, such as a potting shed or greenhouse. There are lots of mini greenhouses to shop at Amazon , should you only have a few tender perennials to protect.
This is a suitable method for how to overwinter dahlias or how to overwinter begonias.
6. Protect tender plants with a cloche
(Image credit: Future / Michelle Garrett)
If you're wondering how to protect plants from frost in the vegetable patch, then a cloche is one of the best methods. A cloche can be used to protect seedlings and smaller plants from frost.
Cloches are bell-shaped covers made from glass or plastic that can be placed over the plants. You can buy cloches or even make your own out of recycled objects. They also sell a range of cloches on Amazon .
'Cut-off large plastic bottles or milk containers can be turned into homemade cloches to embed into the soil around small plants and seedlings to provide protection,' advise the experts at Jackson Nurseries.
Remove them during the day to allow the plants to benefit from the warmth and energy of the sun.
Cloches are ideal for use with young vegetable crops that are sown in fall, such as broad beans, spinach, scallions or spring onions and asparagus.
7. Move plants into a cold frame
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Young hardy annuals that are sown in fall may also benefit from some protection from frost.
Place them in the shelter of a cold frame over winter, although ensure they have good ventilation on warmer days.
You could make your old cold frame if you don't already have one, advise the experts at Jacksons Nurseries.
To make your own temporary cold frame:
- Bend slender, metal rods into loops – you could use wire coat hangars for this
- Insert the ends of the metal loops into the ground either side of a row of crops or plants
- Lay a sheet of clear plastic over the frame and secure it in place to protect the plants below
8.
 Water plants in the morning
Water plants in the morning(Image credit: Getty Images)
You probably wouldn't think that your routine for watering plants could make a difference when considering how to protect plants from frost – but in fact it can help support any protective measures you take.
It is best to water plants in the morning during winter and when there is a risk of frost, because wet soil actually absorbs heat during the day and has an insulating effect.
9. Wrap containers
(Image credit: Ian West / Alamy Stock Photo)
If you are unable to move containers indoors as a method for how to protect plants from frost, then try to protect them from the elements outdoors by placing the pots in sheltered areas, and where possible grouped together for added protection against the cold and wind.
Container plants are more likely to suffer from their roots freezing. To prevent this, 'wrap the containers with bubble wrap from Amazon or straw, or bury the pots in the ground with just the rim showing, to benefit from the insulating properties of the ground,' advise the RHS experts.
Also raise containers using pot feet or by resting them on bricks to allow water to drain away more easily, and prevent plants sitting in icy water.
10. Choose the right plants for your backyard
(Image credit: Future / Camilla Reynolds)
Rather than trying to protect plants that are not suited to the climate of your backyard, instead choose those that are reliably hardy in the zone where you live. This will prevent the disappointment of losing plants when they aren't adequately protected.
Many evergreen shrubs and plants are fairly hardy. Plants will have a hardiness rating ranging from fully hardy – able to withstand temperatures of 0-10 °F (-18 -12 °C) – to frost tender, which might not survive being exposed to temperatures below 40-50 °F (4-10 °C).
While this might limit to some extent the plants or crops you can include in your garden, there will still be plenty of options suitable to you hardiness zone.
You can also include some of the best winter flowers to plant for color and interest in the colder months, or best winter plants for pots and borders.
What can I cover my plants with to prevent frost?
There are many materials that you can use to cover plants with to prevent frost.
You can find many permeable horticultural fleeces and frost protection products on the market, but can also use materials that you can find around the house – just make sure they are lightweight, breathable and insulating.
Options to use include:
- Straw
- Bubble wrap
- Blankets, bed sheets, towels
- Newspaper
- Leaves or other organic materials
What temperature should I cover my plants for frost?
The temperature that you should cover your plants from frost to protect them will depend on the individual plants and the conditions and position in which they are planted.
Frost occurs in temperatures below 32°F (0°C) so this is the point at which you need to be protecting plants in winter.
Most plants will need protecting from temperatures of 30°F (-2°C) or lower, but frost tender specimens should be protected before temperatures dip this low.
Can I use plastic bags to cover plants from frost?
It is not advisable to use plastic bags to cover plants from frost. This is because plastic can damage your plants if it makes contact with foliage, as it holds water against the plant and causes more damage from freezing.
It also isn't a very insulating material, nor is it an eco-friendly or a sustainable option, so look for alternatives when deciding how to protect plants from frost.
Rachel is senior content editor, and writes and commissions gardening content for homesandgardens.com, Homes & Gardens magazine, and its sister titles Period Living Magazine and Country Homes & Interiors. She has written for lifestyle magazines for many years, with a particular focus on gardening, historic houses and arts and crafts, but started out her journalism career in BBC radio, where she enjoyed reporting on and writing programme scripts for all manner of stories. Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
How to protect plants on the site from frost?
Dmitry Krylov
Expert in private houses. Experience of country living: 30 years.
Severe frosts can cause many plants to die quickly, so proper protection is essential. Fortunately, there are many methods that will allow them to survive the difficult winter period. We will talk about them in this article.
Protection of plants from frost. What should be done?
Before taking the first steps to protect plantings from frost, it is worth considering when we should really think about protecting plants in our garden. Indeed, if we do everything in this matter at the wrong time or too hard, we can do more harm than help - a protective layer at too high temperatures will lead to plant infection. nine0003
nine0003
Therefore, protective mats and mats for plants are recommended to be used only at temperatures below -5 degrees. A certain indicator for us can also be the condition of the soil - if its top layer begins to freeze slightly, this is a signal for us that it is time to start appropriate preparation of our garden for winter.
It is important to pay attention to all newly planted young plants that are not yet sufficiently established. They are especially vulnerable in low temperatures and cold winds, and also need protection. In the case of perennial trees or plants resistant to frost, protection will be correspondingly less (and some of them will not need it at all). nine0003
How to protect plants in winter?
As noted above, there are many methods and products that we can use.
Mulching
This activity not only nourishes the soil and protects it from the development of various weeds, but also provides protection in case of strong temperature fluctuations and drying of the soil.
What is mulching? This is the process of covering the soil around plants with litter, that is, a variety of material - both natural and synthetic. This material essentially acts as a "coat" for our plants, and effectively protects the roots of plants from many harmful factors. nine0003
Before mulching, it is very important to choose the right materials, they are divided into organic and synthetic.
Organic Mulch Materials:
- Grass Clippings - Suitable for frost protection for most horticultural crops. Its layer should not be too thick, otherwise it will begin to rot;
- Pine bark - It is used primarily to protect coniferous trees. It should not be used for those plant species that grow in alkaline soil; nine0035
- Straw - usually covered with strawberries. Straw heats strawberry bushes and protects them from external factors;
- Nettle - used to feed plants (contains a large amount of potassium).
 Remember that nettles must be used without seeds;
Remember that nettles must be used without seeds; - The leaves of are mainly perennials, which are not threatened by limited air access. The leaves form a very dense coating, thanks to which they maintain a favorable temperature even during severe frosts. Their disadvantage is that they can be a source of various diseases, so the leaves are not suitable for covering plants with poor resistance. What's more, they are the perfect hiding place for mice and voles. These animals eat tubers and bulbs of plants; nine0035
- Sawdust - due to the correct thermal insulation properties, it is recommended to cover the roots of young shrubs and trees with sawdust;
- Peat - used to cover beds;
- Coniferous branches . The biggest advantage of this type of mulch is that it is very breathable, which is why coniferous branches are widely used by gardeners today as a protection for all kinds of plants.
 It's also worth mentioning that we won't find mice or voles in them; nine0035
It's also worth mentioning that we won't find mice or voles in them; nine0035 - Earth mounds — formed around the trunks of small trees, shrub shoots. Their height usually reaches about 30 centimeters.
Synthetic Mulch Materials:
- Mulching Film - effectively protects crops from severe frost, but can also act as a shield against various chemicals;
- Foil mat - mainly used for protecting plants and vegetables; nine0035
- Paper is a cheap and quick solution, but has poor durability and questionable aesthetics. Although the same beds and tree trunks, paper protects well;
- Nonwoven Synthetic is a special frost protection material that perfectly insulates plants from cold temperatures and gusty winds;
- Mesh - mainly used to protect trees and shrubs from frosty wind. It can also be used as a plant drying cover; nine0035
- Styrofoam - it protects plants on the terrace, and also insulates flower pots.
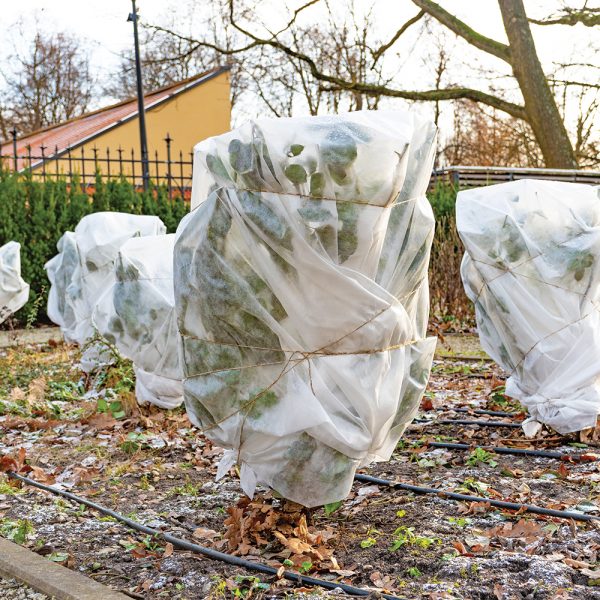 For the same purpose, you can use bubble foil and cardboard.
For the same purpose, you can use bubble foil and cardboard.
How to protect the plants on the site in winter?
In addition to the above materials, gardeners recommend considering ways to protect specific plant species:
How to protect perennials in winter?
Perennial plants, for the most part, tolerate frost well, and care for them does not cause any special problems. To protect perennials in winter, we can use leaves, sawdust, strois or bark. Do not forget to cover them very carefully - in frosts with temperatures below -5 degrees, the protective layer should be at least 10-15 cm thick. Another 10 cm should be added when the temperature drops below 10 degrees. In addition, it is recommended to regularly trim the shoots of perennials, until winter. nine0003
How to protect evergreens in winter?
Conifers and other evergreens are very cold tolerant, but the sun during this period can cause water to evaporate from them, which can cause plants to wilt because they cannot hydrate from the frozen soil.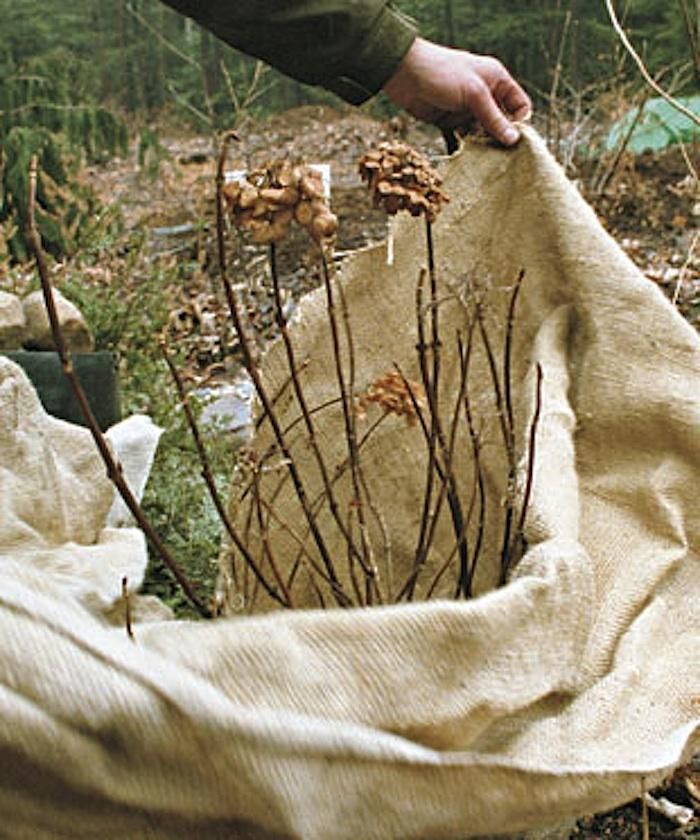
All this means that evergreen shrubs and trees must also be protected in winter. To protect them, it is best to use a coating of non-woven fabric. Sawdust, bark and peat can also be effective. However, in no case should the leaves be used to shelter evergreens, because this will lead to rotting of the plants. Do not forget about intensive watering in the fall. nine0003
How to protect trees and bushes in winter?
With trees and shrubs in winter, everything is simple. At their base, you need to lay out earthen mounds, reinforced with a layer of leaves, bark or sawdust. You can also use an additional coating in the form of corrugated cardboard or non-woven mulch - these are special covers, usually made of straw. Thus, we guarantee trees and shrubs effective protection against severe frosts.
How to protect roses in winter?
Roses are delicate flowers and therefore need special protection in winter. Firstly, it is recommended to build earth mounds around them (preferably more than 30 cm high), and then fix their shoots. How? We can use nonwovens, corrugated board and straw mats. nine0003
How? We can use nonwovens, corrugated board and straw mats. nine0003
How to protect your lawn in winter?
Preparing the lawn for winter is an extremely important step for every owner of the site, unless, of course, he wants to get unsightly rotted grass with melted snow in the spring.
How to avoid this? First of all, we must remove all fallen leaves from the surface of the lawn, which can rot and destroy its structure. Just before the winter cold, the grass should also be cut. If it turns out to be too high, such grass will become an ideal place for the development of various diseases, especially the so-called snow mold. Then it is worth using special fertilizers with a high content of potassium and phosphorus. Thanks to this, the grass will be reliably protected from the effects of particularly high temperatures. nine0003
How to protect plants in pots and containers in winter?
Many potted plants can overwinter not only on terraces. but also in the field. If the task is to take care of plants and flowers on the terrace, we can cover them from the cold with foam, ordinary foil or cardboard. If the plant is left to winter in the ground, it is better to cover it with tree bark or peat. For flowers wintering in large containers, the best solution would be to cover them with salt.
If the task is to take care of plants and flowers on the terrace, we can cover them from the cold with foam, ordinary foil or cardboard. If the plant is left to winter in the ground, it is better to cover it with tree bark or peat. For flowers wintering in large containers, the best solution would be to cover them with salt.
In addition to all the above protection measures, in winter we should carefully observe whether the plants are damaged by fungi, insects and typical winter diseases. If the plants are infected, treatment should be started immediately, because diseased plants will not be able to withstand frost and will definitely die. nine0003
If the winter in your region is without snow, rather dry and sunny, you should not forget about regular watering of evergreens. Otherwise, the water will evaporate, causing them to dry out. Constant monitoring of the condition of plants in winter will save them from many problems, including with the beginning of the spring season, so it is wiser to take into account all these recommendations and, if necessary, carry out their timely prevention.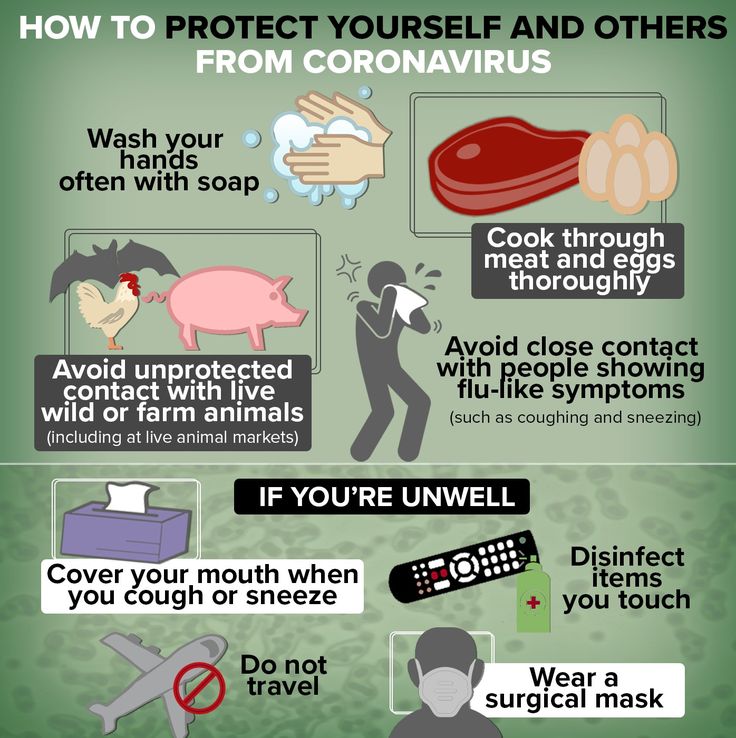
Was this article helpful to you? Please share it on social networks:
Don't forget to bookmark the Nedvio site. We talk about construction, repair, suburban real estate in an interesting, useful and understandable language.
Protection of plants from cold, sun and wind
Contents
The wind ruffled the delphinium and broke the godetia. The delicate leaves of the clarkia were burned in the sun. The foliage of dahlias and marigolds suffered from the night cold. Petunia and Lobelia were killed by hail. Garden plants get from the whims of the weather. It is bitter to see broken flower beds and seedlings that died from spring frosts. nine0003
Young plants planted in beds in spring are especially affected. They have not yet grown stronger, poorly rooted in the ground. Cold, wind, downpour, burning sun can break and destroy plantings.
My plot of land is located in an open area, next to a field. Strong winds are not uncommon. Cold nights and rains bring a lot of trouble. Therefore, the issue of protecting plants in open ground is very relevant for me.
Cold nights and rains bring a lot of trouble. Therefore, the issue of protecting plants in open ground is very relevant for me.
Over time, I have built up my arsenal of tools and items that help protect outdoor plants from inclement weather, hot sunny days and cold snaps. Most of them can be prepared and made independently. nine0003
Pipe cuttings Pipe cuttings for plants
Plastic pipes left after construction. We cut them into pieces, 30 cm high. It turned out to be an indispensable device for protecting ornamental plants. Pipe cuttings reliably protect young seedlings from wind damage, shade low plants from the sun.
Fragile godetia breaks easily. In pipe cuts, it looks like in a flower pot and is protected from gusts of wind. When it gets cold, the top of the pipe can be covered with a cloth or wooden board. And they are also able to protect flowers and dwarf conifers from damage by a trimmer while mowing grass. nine0003
Homemade boxes made of polycarbonate Homemade box for sheltering plants
Initially, we made these boxes from leftover polycarbonate for young roses, as a shelter for the winter from frost and moisture. Drawers let in light and retain heat. They protect plants from wind, cold, and soaking.
Drawers let in light and retain heat. They protect plants from wind, cold, and soaking.
Old containers Protecting plants from the wind with a container
Old trash in the form of broken containers can also benefit garden plants. It will protect from gusts of wind and protect from low temperatures, if covered with plywood from above at night. A large container will shelter several plants from inclement weather at once. nine0003
Garden Umbrellas Garden Umbrellas
Folding Garden Umbrellas are a great thing and provide versatile protection for seedlings and flowers throughout the season. Long service life, do not take up much storage space. Plants are comfortable and light in them. Protect from frost, wind, rain and hail. Petunias under an umbrella during the rain look cool and retain a decorative, well-groomed appearance.
Transparent bottles Wind and cold protection bottles
The bottom of a 19 liter water bottle was cut off to create a mini greenhouse.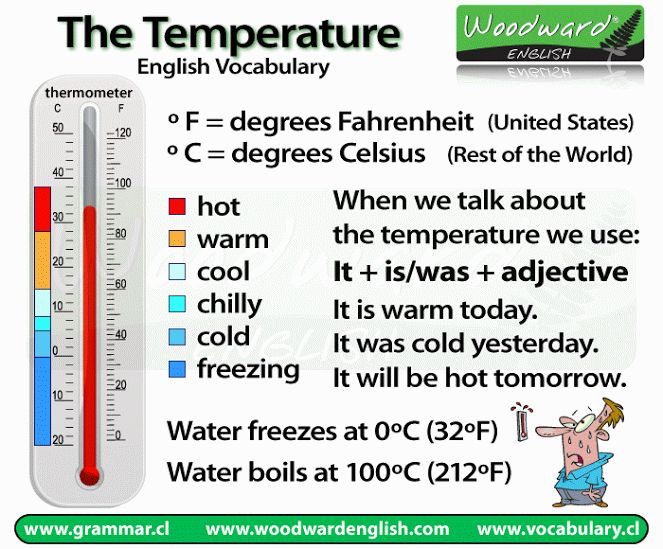 Seedlings are very comfortable in them. Light, warm. The wind does not shake, the air enters. Full protection is provided from all manifestations of capricious weather, even from frost. A good replacement for expensive garden umbrellas. Five liter cans can also be used. But they are light, the wind blows them away. Large bottles are more spacious, firmer, more securely fixed in the ground. Their size is enough to cover the bushes of seedlings of cabbage or root celery in cold weather. With large bottles from the wind and cold, I protected the seedlings of the budley of David and mock orange all spring. nine0003
Seedlings are very comfortable in them. Light, warm. The wind does not shake, the air enters. Full protection is provided from all manifestations of capricious weather, even from frost. A good replacement for expensive garden umbrellas. Five liter cans can also be used. But they are light, the wind blows them away. Large bottles are more spacious, firmer, more securely fixed in the ground. Their size is enough to cover the bushes of seedlings of cabbage or root celery in cold weather. With large bottles from the wind and cold, I protected the seedlings of the budley of David and mock orange all spring. nine0003
Greenhouse made of covering material Greenhouse made of fabric and garden poles
Greenhouses are easily assembled from covering material, garden poles and clips. Optimal weather protection for all crops. The main thing is to securely fasten the fabric on the arcs, and the greenhouse itself on the ground.
I always plant marrows, pumpkins, squash in the garden under such cover. They live in it until the end of the first decade of June. Vegetables calmly endure a drop in temperature, are protected from swaying by the wind. This shelter gives them time to take root and gain a foothold in the ground. nine0003
They live in it until the end of the first decade of June. Vegetables calmly endure a drop in temperature, are protected from swaying by the wind. This shelter gives them time to take root and gain a foothold in the ground. nine0003
Pumpkins and marrows are thermophilic, but the leaves in the sun immediately bind. For seedlings, this is stressful. Homemade greenhouses will protect from frost, wind, heavy rain, cold nights. The fabric transmits light well, retains heat. Shades plants on a sunny day. Greenhouses on arcs can cover the entire vegetable garden or flower bed. This is convenient when you need to protect a lot of plants.
Cover material is indispensable when plants need protection from the sun. Especially the young, not accustomed to the fresh air. Sunburn, wilted leaves - the problems of the beginning of the season. On sunny days, with pieces of fabric, like screens, I cover the planted seedlings so that they gradually get used to it, do not wither and successfully take root in the open field. It is convenient to fix the covering material on garden arches using clips. nine0003
It is convenient to fix the covering material on garden arches using clips. nine0003
Plastic buckets Plant protection with plastic buckets
A few years ago I did an experiment: I planted greenhouse tomatoes in plastic buckets. Large holes were made in them for the roots. Now I don’t plant tomatoes like that, but the buckets remain. In early June, thanks to them, I saved marigolds and amaranths from night frosts. The buckets are not transparent, but due to the wide opening they let some light through. Therefore, on a cold day, you can not remove them, but cover them with a brick or board at night to keep warm. Plastic buckets will protect from wind or hail. To prevent such protection from being demolished from the garden, it is advisable to put something heavy on top, for example, a stone, a brick, a piece of slate. nine0003
DIY metal poles Tall plant poles
Metal poles can be made by yourself if you know how to weld. Solid structures are necessary for tall perennials to protect against windy weather. I have a two-meter delphinium and huge lilies, 1.5 meters high. Without such support, it would be impossible to avoid breakdowns, maintain the decorativeness and integrity of the bushes during heavy rains and strong winds. For the manufacture of supports, metal rods or corners, a welding machine are needed. nine0003
Solid structures are necessary for tall perennials to protect against windy weather. I have a two-meter delphinium and huge lilies, 1.5 meters high. Without such support, it would be impossible to avoid breakdowns, maintain the decorativeness and integrity of the bushes during heavy rains and strong winds. For the manufacture of supports, metal rods or corners, a welding machine are needed. nine0003
Plastic garden net Plastic net for a tidy flower garden
Plastic garden net keeps the flowers compact and prevents them from falling apart in the rain or ruffled in the wind. Plants in the grid are well ventilated. In the garden, the mesh-support looks organic and unobtrusive. Lichnis bushes framed in a mesh support look pretty.
After flowering, the foliage of daffodils lives for a long time, until mid-July. Their thick hair prevents other flowers from growing, takes up a lot of space in the flower bed. I collect the leaves of daffodils into a net, fixing it around the perimeter in the ground with a few pins. It will not be difficult to cut a plastic mesh of the desired height and length. nine0003
It will not be difficult to cut a plastic mesh of the desired height and length. nine0003
Prefabricated supports and garden arches Supports for peony bushes a
Prefabricated garden supports are needed to support roses, poppies, peonies and other spreading plants. Under the weight of large flowers, peonies fall to the ground just like roses wet after rain. Plants with such a support look beautiful and elegant. Reliably protected in windy, rainy weather all summer long.
Garden polesGreenhouse poles are also used to support and protect bulky ornamental shrubs and flowers from breakage. nine0003
Support poles Tie lilies and sunflowers to support poles
The easiest way to fix plants and protect them from damage. You need rope and sticks. Metal, plastic or wood. The whole stem or bush is tied around with a rope and tied with a figure-eight loop to a stick. The stem will not break, the plants will remain compact in wind or rain. Such supports are relevant for lilies, delphiniums, sunflowers and other tall plants. nine0003
Such supports are relevant for lilies, delphiniums, sunflowers and other tall plants. nine0003
Studs and staples Wind protection for plants with staples and studs
Studs can be made from hard wire, metal bars. Staples are sold in hardware stores. They are convenient to pin garden and garden plants to the ground in windy areas. So that the wind does not tear the whips of pumpkins, I fix them with pins and staples to the soil. Several bushes of Godetia did not have enough pipe trimmings. Helped homemade studs. She pinned the long branches of the godetia to the ground, and she safely survived several days of windy weather. nine0003
Without timely protection from external conditions, garden and garden plants will have a hard time. Do not wait until the peony bush grows. Put a support under it in advance. Enclosing a grown plant, it can be accidentally broken off.
Before planting seedlings in the ground, think about how to protect it from cold, frost, burnout.