How to protect outdoor plants from frost
Frost Covers & Cold Snap Care
Whether you fell under the spell of some eye-catching color at the garden center or just wanted to get a jump on the gardening season, planting too early can create a crisis when a cold snap threatens. Helping your seedlings survive the big chill isn't impossible, but it does require some preparation.
In most cases, you can count on makeshift methods to protect plants when the thermometer dips. But for larger plantings, such as a vegetable garden, you'll need to arm yourself ahead of time with the right gadgets to guard plants against frosty mornings.
Know The Limits
In order to understand what steps to take when freeze warnings threaten, you need to know the point at which treasured greenery fades to frost-burned brown. The general rule of thumb is that most plants freeze when temperatures remain at 28°F for five hours.
Of course, there are exceptions to this rule. Seedlings, with their tender new leaves, often give up the ghost when temperatures dip to 32-33°F. Tropical plants have differing low-temperature thresholds. Some keel over when temps fall to 40°F; others crumble at 35°F. Other plants are just hardy by nature and can withstand temperatures as low as 18-20°F. To find the threshold for your plants, search garden books and online resources.
Quick Fixes For Frost Warnings
Pick It Up – The easiest cold-protection scheme is to move plants out of harm's way. This works with seedlings in flats and potted plants. Moving plants under a deck, into a garage or shed, or onto a porch with a roof often offers ample protection.
Count On Water – Water soil just before sundown to raise overnight air temperature around plants as the water evaporates. Fill gallon jugs or buckets with water and place them in the sun during the day. At night, move them near endangered plants. The water will moderate air temperatures; if it freezes, it will release heat. For greatest effect, paint a few water-holding containers black to maximize daytime heating.
Keep Air Moving – Cold, still air does the most damage to plants. Stir a breeze all night with an electric fan to keep frost from forming on plants. Remember to protect electrical connections from moisture.
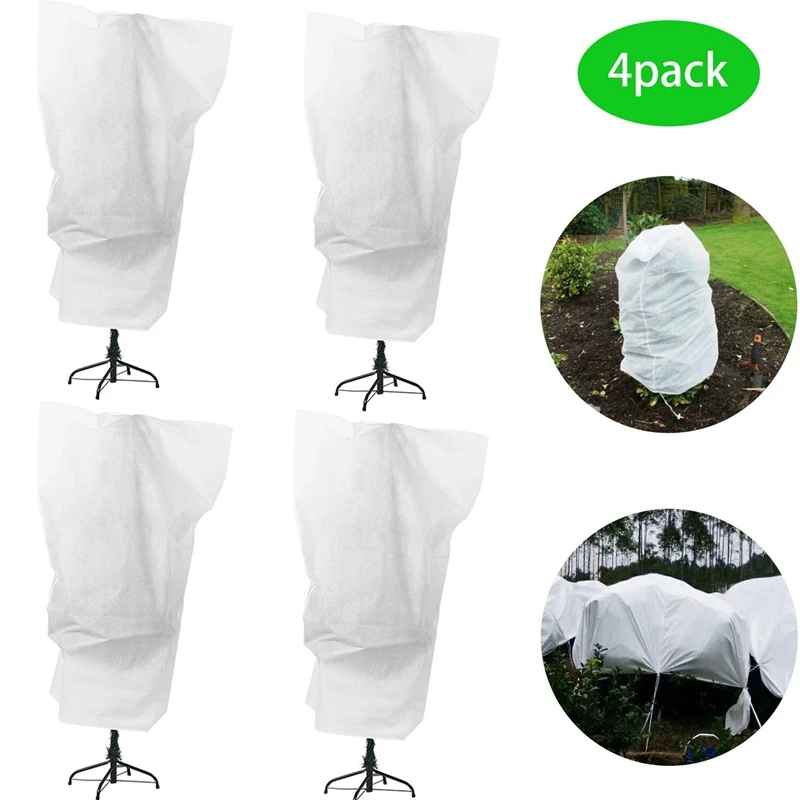
Cover Plants – Protect plants from all but the hardest freeze (28°F for five hours) by covering them with sheets, towels, blankets, cardboard or a tarp. You can also invert baskets, coolers or any container with a solid bottom over plants. Cover plants before dark to trap warmer air. Ideally, coverings shouldn't touch foliage. Anchor fabric coverings if windy conditions threaten.
In the morning, remove coverings when temperatures rise and frost dissipates. Heat from the sun can build beneath solid coverings, and plants can die from high temperatures.
Break Out Blankets – Keep gardening blankets, often called row covers, on hand. These covers are made from synthetic fibers or plastic in varying thicknesses. Lay row covers directly on plants, or create a tunnel by suspending them over a bed using stakes.
Turn On Lights – An incandescent light bulb generates sufficient heat to raise nearby air temperature enough to protect a plant from the deep freeze. Bulbs must be close to plants (within 2-3 feet) for this technique to work. (Fluorescent bulbs don't generate enough heat for this chore.)
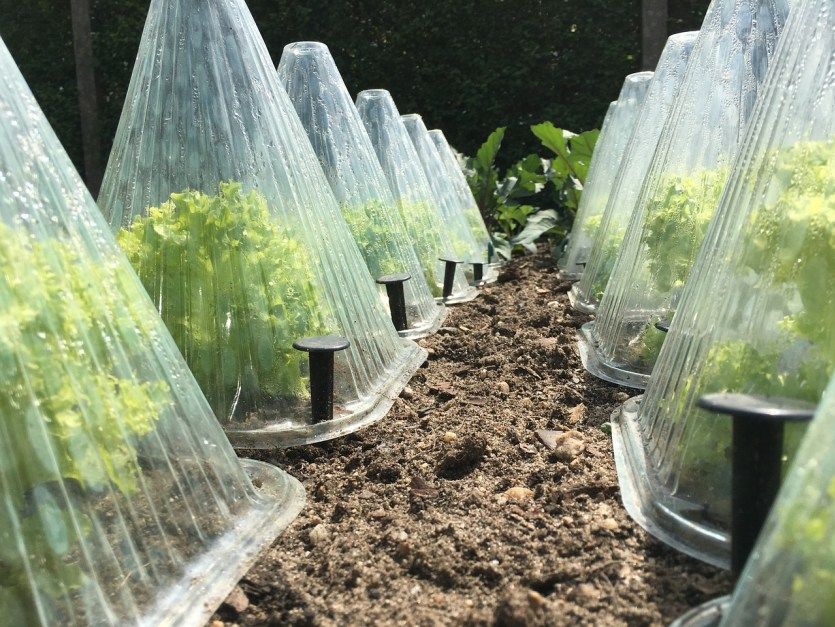
Protect Individual Plants – Install hot caps – rigid plastic containers with venting holes – over individual seedlings at planting time. Hot caps act like cloches (mini greenhouses), but venting holes eliminate the daily chore of placing and removing the covering. Create the equivalent of a hot cap using plastic two-liter bottles or gallon jugs with bottoms cut off and lids removed (but saved). Replace lids at night when cold temperatures swoop through.
A twist on the hot cap idea is a Wall O'Water tepee, which encircles individual plants with a sleeve of water-filled tubes. The water absorbs the sun's heat during the day. At night, as the water slowly freezes, it releases the stored radiant heat of the sun, keeping air inside the tepee frost-free.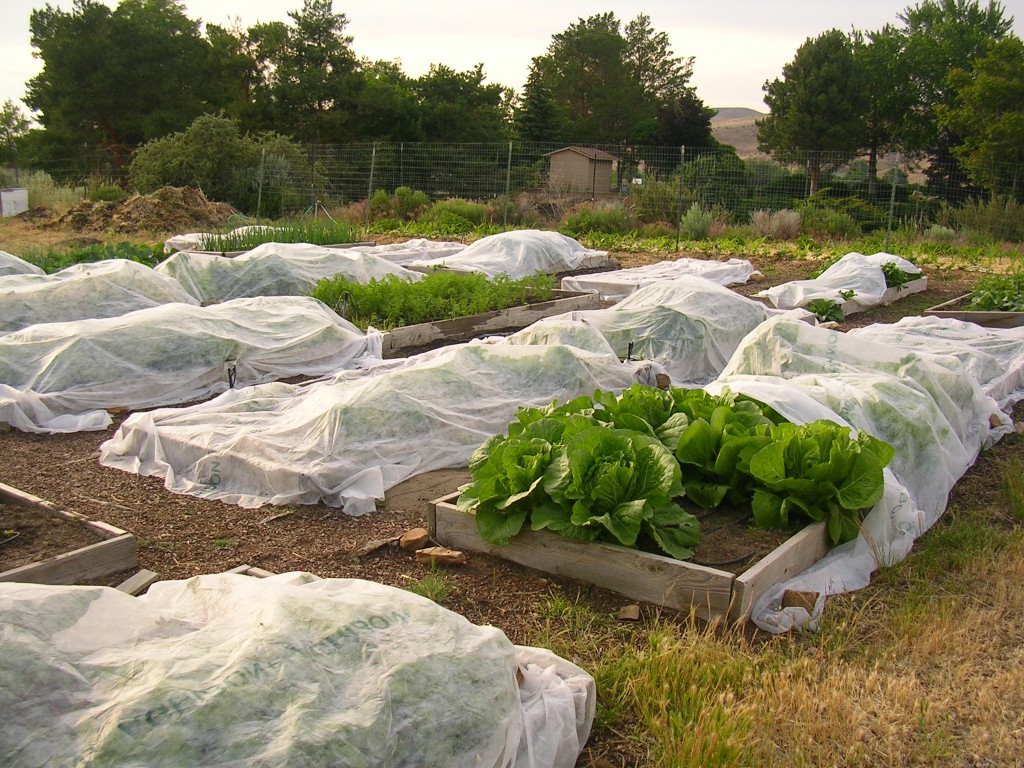
More Lawn Solution Articles for You
Winter Garden Checklist For Mild Climates
Winter garden checklist during mild climates. Winter doesn't signal the end of gardening season. There is many chores such as planting,...
read more
How To Prepare Your Garden For Frost
If winter is coming soon, this simple to-do list will help you prepare your garden for frosty weather, from harvesting, to draining hoses to...
read more
Planting After Danger Of Frost
For a successful spring planting, be aware of the danger of frost. It can kill young seedlings. Knowing the last frost date in your area can...
read more
Copyright © 2023 bioadvanced. com All Right Reserved.
com All Right Reserved.
How to protect plants from frost: 10 quick and easy methods
(Image credit: Getty Images)
As the cold weather sets in, it's important to know how to protect plants from frost, as tender and young plants in particular can be wiped out by a sudden cold snap.
There are many quick ways you can protect more vulnerable plants and it's definitely better to be safe than sorry – there is nothing more devastating than seeing the beautiful plants you have lovingly nurtured destroyed seemingly overnight by a visit from Jack Frost.
Unless you live in a warm zone, it is likely that some of the ornamental plants and crops you have included in your garden ideas will be in need of some protection, so read on to find out how you can help their survival through the colder months.
How to protect plants from frost – which plants to protect
(Image credit: National Trust)
Not all plants in your backyard will need protection from the frost, but there are certain categories that will. These include:
These include:
- Young seedlings and new growth
- Tender perennials
- Half-hardy varieties
- Tropical and subtropical plants such as palms and banana plants
Signs of frost damage include blackened, distorted or limp growth and the leaves turning green on evergreen plants and shrubs.
If in any doubt, research the conditions and hardiness of specific plants. Err on the side of caution and include frost protection in your winter garden ideas if cold weather is forecast in your state or area.
(Image credit: Getty Images)
In terms of vegetable crops, there are some that actually benefit from a dose of frost and can taste better afterwards. 'There are some veg crops that are frost tolerant, if not frost resistant,' explains Nicole Burke, author of Rooted Garden .
If you live in a colder zone, it is therefore worth learning how to grow kale and other frost tolerant vegetable crops.
1. Bring potted plants indoors
(Image credit: Future)
There are many quick ways for how to protect plants from frost, and among the easiest is to bring potted plants indoors, especially tender container plants.
Potted plants are more susceptible to frost damage because they don't have the insulated benefits of of those planted in the ground.
Use a conservatory, garden room, garage, porch or frost-free greenhouse to overwinter potted plants – not somewhere that is too warm.
This can be a suitable option if you're wondering how to overwinter fuchsias in pots, or how to winterize hydrangeas, for example.
2. Add a layer of mulch on garden beds
(Image credit: Alamy)
'Apply dry mulch, such as chipped bark or straw around borderline-hardy plants, such as agapanthus, phygelius (cape fuchsia), hedychium and the architectural melianthus to protect the crown,' advises plant expert Sarah Raven .
You could also use leaf mold or piles of leaves to add some extra protection on garden beds and provide a barrier against the cold.
Find out how to make leaf mulch to protect tender and emerging plants.
3. Cover plants with fleece
(Image credit: Getty Images)
You may wonder how to protect plants from frost when they are planted in the ground? One method – which is useful for larger garden plants and shrubs – is to cover them with horticultural fleece.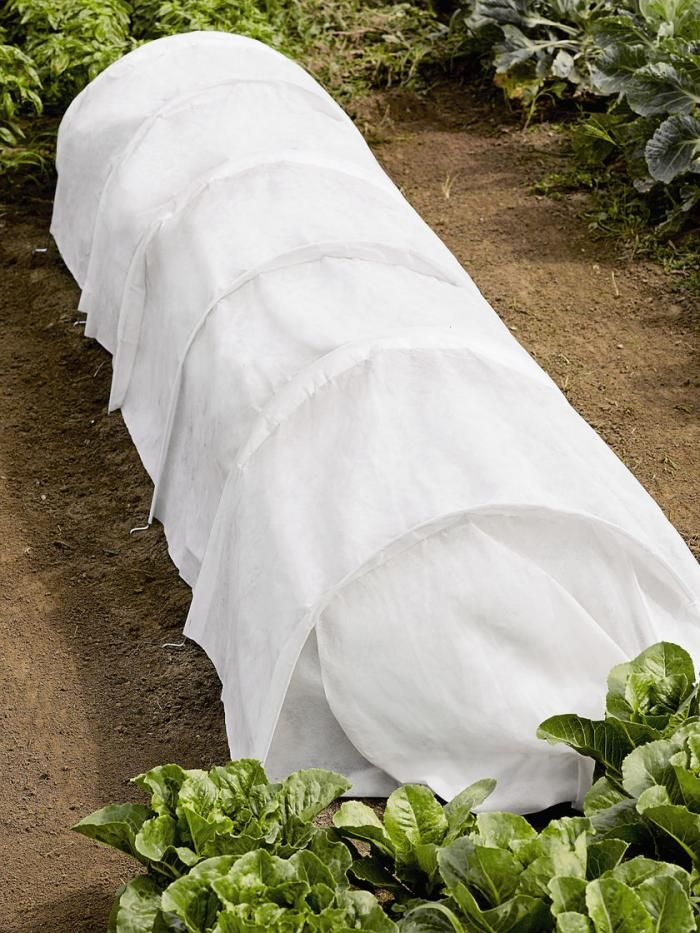 You could use blankets or bubble wrap, too, to create a protective cover. These Amazon plant covers come highly recommended by reviewers.
You could use blankets or bubble wrap, too, to create a protective cover. These Amazon plant covers come highly recommended by reviewers.
Place several stakes around your plants and then cover these with the chosen material to create a tent-like structure. Weigh down the corners to prevent the coverings from blowing away in the night and remove the covers during the day.
You can use this method for plants that require winter protection, such as agapanthus, cordyline and tree ferns.
'Fleece is very effective, but if you prefer something less obtrusive, a circle of wire netting filled with bracken or leaves will keep the cold at bay, too' advises Sarah Raven.
You can also wrap the trunks of young trees with horticultural fleece or blankets, such as if you're growing some of the best fruit trees or have mastered how to grow lemon from seed.
4. Place tender plants in a sheltered spot
(Image credit: Getty Images)
The mantra 'right plant, right place' is relevant when considering how to protect plants from frost.
'Always plant half hardy and frost tender plants in a sheltered position, preferably near a south or west-facing wall, which will absorb heat during the day and radiate it at night,' advise the experts at Jacksons Nurseries .
'Eliminating the wind chill factor can substantially reduce the amount of frost damage incurred,' they add.
Other sheltered positions will include next to fences, under large evergreen trees for gardens, under the protection of pergola ideas or in patio or courtyard areas, as long as these also receive plenty of sunshine.
While a sunny, sheltered spot is ideal for many tender plants, do not place early-flowering plants, such as magnolias and camellias, so that they are exposed to the morning sun. 'The rapid thawing of frozen buds can result in blackening and bud drop,' advises Guy Barter, horticultural expert at the RHS .
5. Lift and store tender perennials
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Tender perennials that have bloomed and died down can be lifted to protect them from frost.
Store the roots, bulbs, tubers and corms in a cool but frost-free place, such as a potting shed or greenhouse. There are lots of mini greenhouses to shop at Amazon , should you only have a few tender perennials to protect.
This is a suitable method for how to overwinter dahlias or how to overwinter begonias.
6. Protect tender plants with a cloche
(Image credit: Future / Michelle Garrett)
If you're wondering how to protect plants from frost in the vegetable patch, then a cloche is one of the best methods. A cloche can be used to protect seedlings and smaller plants from frost.
Cloches are bell-shaped covers made from glass or plastic that can be placed over the plants. You can buy cloches or even make your own out of recycled objects. They also sell a range of cloches on Amazon .
'Cut-off large plastic bottles or milk containers can be turned into homemade cloches to embed into the soil around small plants and seedlings to provide protection,' advise the experts at Jackson Nurseries.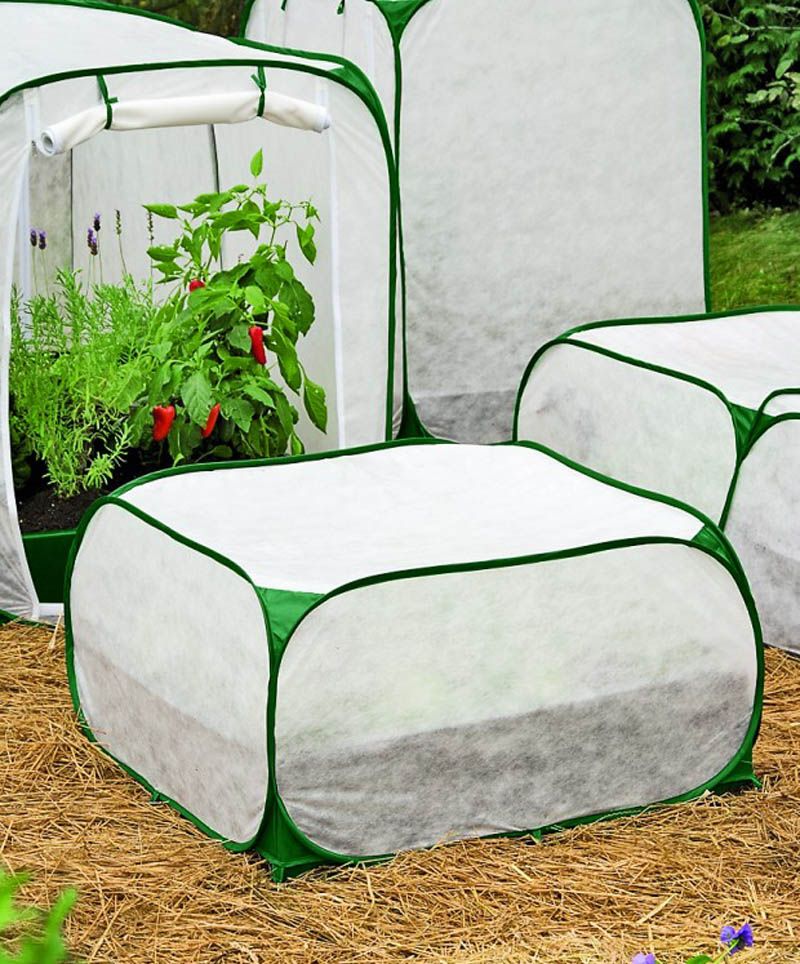
Remove them during the day to allow the plants to benefit from the warmth and energy of the sun.
Cloches are ideal for use with young vegetable crops that are sown in fall, such as broad beans, spinach, scallions or spring onions and asparagus.
7. Move plants into a cold frame
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Young hardy annuals that are sown in fall may also benefit from some protection from frost.
Place them in the shelter of a cold frame over winter, although ensure they have good ventilation on warmer days.
You could make your old cold frame if you don't already have one, advise the experts at Jacksons Nurseries.
To make your own temporary cold frame:
- Bend slender, metal rods into loops – you could use wire coat hangars for this
- Insert the ends of the metal loops into the ground either side of a row of crops or plants
- Lay a sheet of clear plastic over the frame and secure it in place to protect the plants below
8.
 Water plants in the morning
Water plants in the morning(Image credit: Getty Images)
You probably wouldn't think that your routine for watering plants could make a difference when considering how to protect plants from frost – but in fact it can help support any protective measures you take.
It is best to water plants in the morning during winter and when there is a risk of frost, because wet soil actually absorbs heat during the day and has an insulating effect.
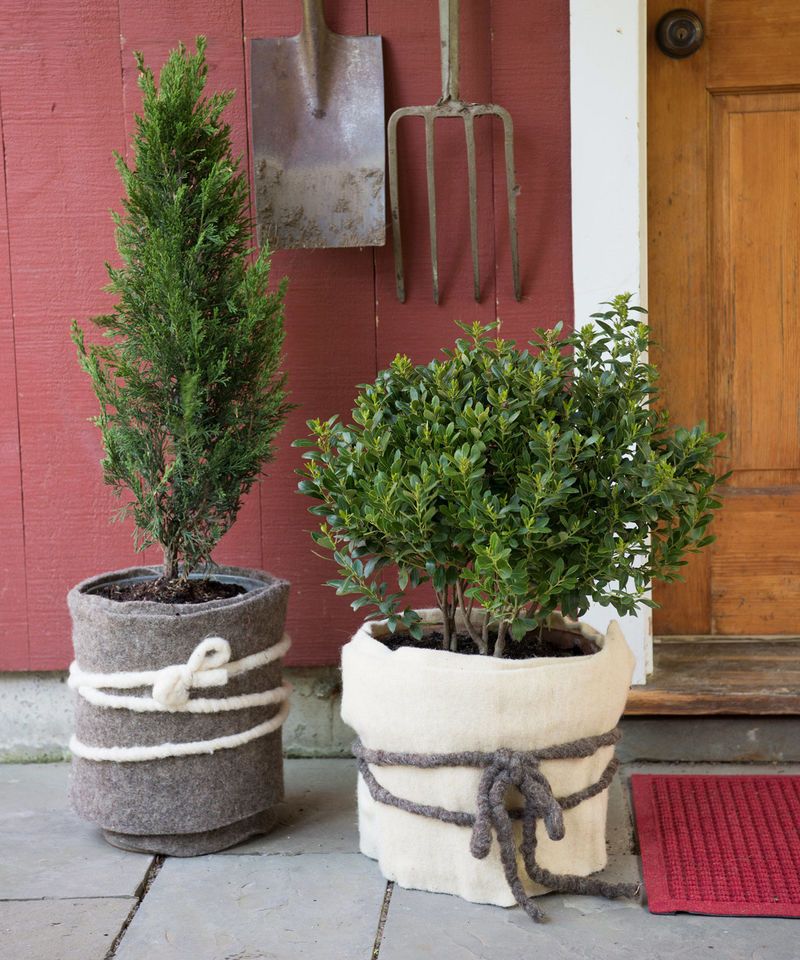
9. Wrap containers
(Image credit: Ian West / Alamy Stock Photo)
If you are unable to move containers indoors as a method for how to protect plants from frost, then try to protect them from the elements outdoors by placing the pots in sheltered areas, and where possible grouped together for added protection against the cold and wind.
Container plants are more likely to suffer from their roots freezing. To prevent this, 'wrap the containers with bubble wrap from Amazon or straw, or bury the pots in the ground with just the rim showing, to benefit from the insulating properties of the ground,' advise the RHS experts.
Also raise containers using pot feet or by resting them on bricks to allow water to drain away more easily, and prevent plants sitting in icy water.
10. Choose the right plants for your backyard
(Image credit: Future / Camilla Reynolds)
Rather than trying to protect plants that are not suited to the climate of your backyard, instead choose those that are reliably hardy in the zone where you live. This will prevent the disappointment of losing plants when they aren't adequately protected.
Many evergreen shrubs and plants are fairly hardy. Plants will have a hardiness rating ranging from fully hardy – able to withstand temperatures of 0-10 °F (-18 -12 °C) – to frost tender, which might not survive being exposed to temperatures below 40-50 °F (4-10 °C).
While this might limit to some extent the plants or crops you can include in your garden, there will still be plenty of options suitable to you hardiness zone.
You can also include some of the best winter flowers to plant for color and interest in the colder months, or best winter plants for pots and borders.
What can I cover my plants with to prevent frost?
There are many materials that you can use to cover plants with to prevent frost.
You can find many permeable horticultural fleeces and frost protection products on the market, but can also use materials that you can find around the house – just make sure they are lightweight, breathable and insulating.
Options to use include:
- Straw
- Bubble wrap
- Blankets, bed sheets, towels
- Newspaper
- Leaves or other organic materials
What temperature should I cover my plants for frost?
The temperature that you should cover your plants from frost to protect them will depend on the individual plants and the conditions and position in which they are planted.
Frost occurs in temperatures below 32°F (0°C) so this is the point at which you need to be protecting plants in winter.
Most plants will need protecting from temperatures of 30°F (-2°C) or lower, but frost tender specimens should be protected before temperatures dip this low.
Can I use plastic bags to cover plants from frost?
It is not advisable to use plastic bags to cover plants from frost. This is because plastic can damage your plants if it makes contact with foliage, as it holds water against the plant and causes more damage from freezing.
It also isn't a very insulating material, nor is it an eco-friendly or a sustainable option, so look for alternatives when deciding how to protect plants from frost.
Rachel is senior content editor, and writes and commissions gardening content for homesandgardens.com, Homes & Gardens magazine, and its sister titles Period Living Magazine and Country Homes & Interiors. She has written for lifestyle magazines for many years, with a particular focus on gardening, historic houses and arts and crafts, but started out her journalism career in BBC radio, where she enjoyed reporting on and writing programme scripts for all manner of stories. Rachel then moved into regional lifestyle magazines, where the topics she wrote about, and people she interviewed, were as varied and eclectic as they were on radio. Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
Always harboring a passion for homes and gardens, she jumped at the opportunity to work on The English Home and The English Garden magazines for a number of years, before joining the Period Living team, then the wider Homes & Gardens team, specializing in gardens.
How to protect plants from frosts in spring
Even when weather forecasters promise a warm spring, no one cancels return night frosts. In the Middle lane and more northern regions, you need to be ready for them until the first decade of June. Flowers, fruit trees, and especially newly planted seedlings can be severely damaged by a sudden frost. They may also die. Do you know how to protect plants from spring frosts? If not, no problem. Now we will talk about the most popular and effective "insulation" of the garden and vegetable garden. nine0003
Which crops are afraid of frost and which are not?
By and large, any plant suffers from frost. Cell sap freezes, turning into crystals that damage cell membranes. Cells shrink, deform, their work is disrupted. But some plants are able to recover from such metamorphoses, while others simply die.
Cells shrink, deform, their work is disrupted. But some plants are able to recover from such metamorphoses, while others simply die.
The most sensitive are thermophilic vegetables and trees. Eggplants, peppers, watermelons and melons begin to die already at low positive temperatures - + 1 ° С ... + 2 ° С. Tomatoes, zucchini and cucumbers die at temperatures below 0°C. nine0003
Even if the plant itself is more or less resistant to frost, at some stages of the life cycle it can be very vulnerable. For example, at the seedling stage. Any newly planted seedlings that have not really “grabbed the ground” without protection will freeze even with a slight frost.
Another example is flowering. Strawberries can survive frosts down to -8°C, but its flowers and buds will freeze at -2°C. Flowers of fruit trees are also afraid of return frosts. Pear and apple blossoms will not survive -2°C (buds can survive down to -4°C). Cherry blossoms will not survive even -1°C. But the survival limit for plum buds reaches -5 ° C. nine0003
nine0003
In the reference table, we told you what kind of frosts certain crops can survive. Do not miss!
The most annoying thing is that sometimes the flowers after freezing can look quite normal on the outside and it seems like everything is in order. But in fact, the frost has damaged the pestle, and the fruits will no longer be tied.
And one more important point: even frost-resistant crops have a hard time in frost. Plants that survive will need time to recover. And our help. But we will return to this later. nine0003
How to understand that there will be frosts at night
During the summer season, the weather forecast becomes the most important news for any gardener. And during the period of return frosts - even more so. We compare weather forecasts from different sources and prepare for the worst-case scenario. Along the way, we observe nature. If by eight in the evening the temperature dropped sharply to + 4 ° С ... + 5 ° С and by midnight it reached + 1 ° С .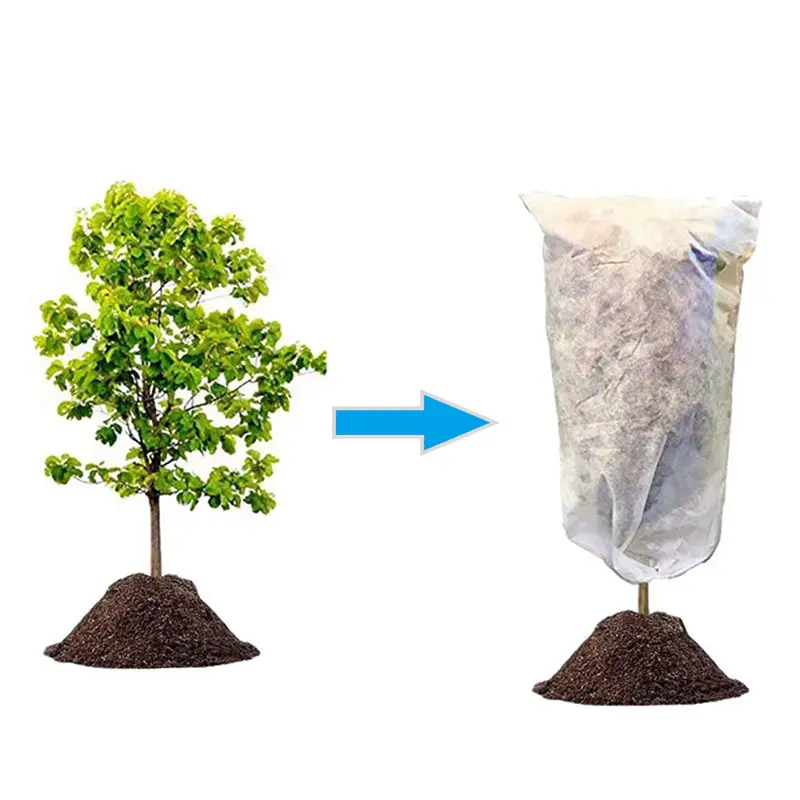 .. + 2 ° С, it will definitely be below zero at night. If the rain stopped, the wind subsided, the sky cleared up and it became very quiet in the evening, there is also a chance of frost. Moreover, the strongest drop in temperature does not occur at night, but in the early morning - before sunrise. nine0003
.. + 2 ° С, it will definitely be below zero at night. If the rain stopped, the wind subsided, the sky cleared up and it became very quiet in the evening, there is also a chance of frost. Moreover, the strongest drop in temperature does not occur at night, but in the early morning - before sunrise. nine0003
But when the weather is cloudy, dew falls or the wind blows, frost is not expected.
Ways to protect plants from frost
Summer residents try to protect plants from frost by various methods, as best they can. Let's talk in more detail about each.
Sprinkling or watering
One of the most effective ways to combat frost is sprinkler irrigation. That is, watering plants from a hose with a fine spray. Sprinkling works especially well on fruit trees, bushes and strawberries. It would seem, how dousing plants with cold water can protect against freezing? Nevertheless, this is a fact. The fact is that when the water freezes, it begins to evaporate and releases heat. This heat slightly raises the temperature of the surrounding air, and just this "little" helps the plants survive, and we - to save the crop. At the same time, the plants themselves can become covered with ice on the outside, but the fluids inside the cells still do not freeze. Not surprisingly, this sprinkling technique was called "Ice Shell". nine0003
This heat slightly raises the temperature of the surrounding air, and just this "little" helps the plants survive, and we - to save the crop. At the same time, the plants themselves can become covered with ice on the outside, but the fluids inside the cells still do not freeze. Not surprisingly, this sprinkling technique was called "Ice Shell". nine0003
The technology is as follows: in the late evening, when the temperature has already dropped to 0 ° C, the plants must be very well poured with water, as they say, “from head to toe”. At three in the morning, it is advisable to do this procedure again. You need to water a lot and for a long time. Therefore, sprinkling is very convenient for those who have sprinklers installed around the site.
And when there are no waterers, even the usual fine watering with a hose on the eve of frost is better than nothing. Because dense moist soil cools more slowly than loose and dry. nine0003
Sprinkler irrigation can be successfully used in frosts down to -5°C.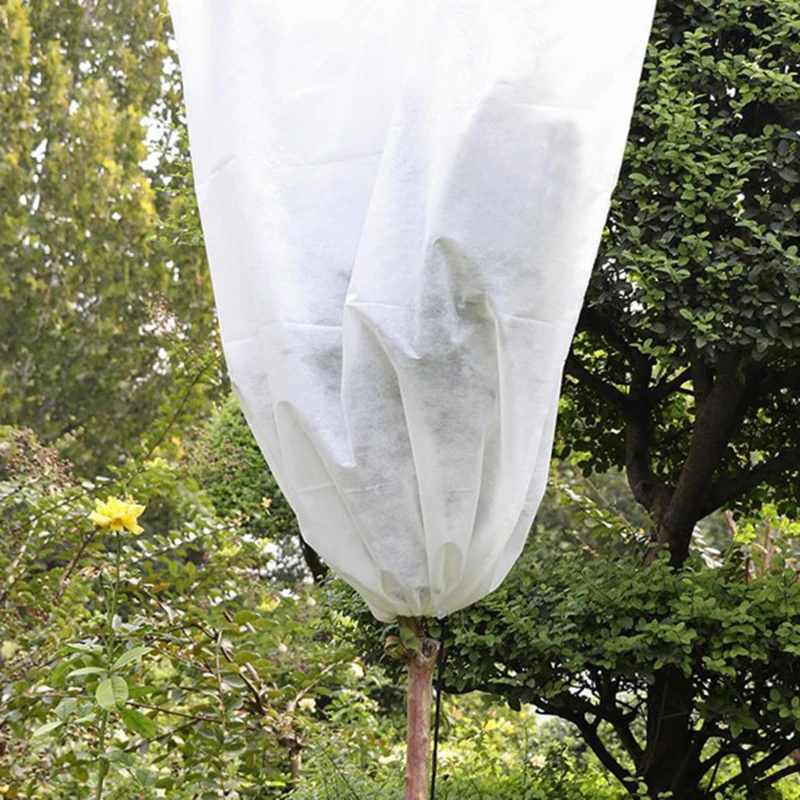
Smoke
An old, one might say, centuries-old way to protect flowering gardens from frost is to make smoking fires around the perimeter. Neighbors will not thank you, and in some regions they can even fine you. Nevertheless, it is impossible not to talk about this technique.
So, the gardener's task is to arrange fires throughout the area so that the smoke from them envelops the fruit trees to the maximum. For each hundred square meters, you will need a fire 1.5 meters in diameter and 40-60 centimeters in height. The bottom layer of the future fire is dry firewood, branches, paper. Then wet sawdust, half-rotted leaves, fresh grass, damp wood, tops, weeds are poured to the desired height. The entire structure is sprinkled with earth from above, leaving an exit for smoke in the center. nine0003
It is important that the fires do not burn out quickly, but smolder and smoke well. Therefore, a sleepless night is guaranteed for a gardener: you need to monitor the condition of the fires, add fuel, etc.
Much easier (but more expensive) to use smoke bombs instead of fires.
Heating
This variant is also commonly used in the garden. Trees are simply heated with a potbelly stove. The stove is placed next to the tree, but in such a way that it does not accidentally burn or burn the branches, and they flood it. In this way, you can save the color in case of a serious cold snap, up to -5 ° C. True, the stove (if there is one at all) is not enough for all the trees. But, for example, for the sake of an apricot or a pear, which you really want to keep, you can try. nine0003
Shelter
The most popular and well-functioning method of saving from low temperatures is to cover crops with film, agrofibre, cloth, paper, spruce branches, etc.
Usually, arches are installed above the beds at a distance of fifty centimeters from each other. Arcs are made of thick wire, metal-plastic pipes or even willow branches.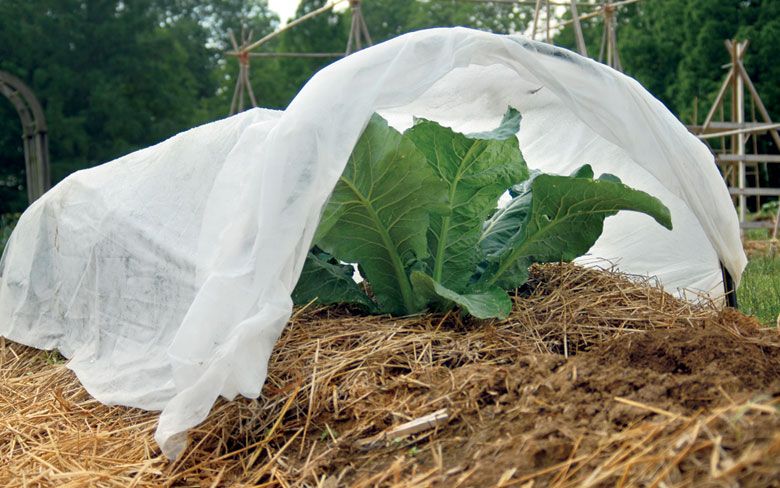 A film, spunbond or old sheets are pulled over the arcs, sometimes in several layers. In most cases, 60gsm spunbond is ideal because you can leave a bed underneath for a few days. The material transmits light and does not allow moisture to evaporate quickly. nine0003
A film, spunbond or old sheets are pulled over the arcs, sometimes in several layers. In most cases, 60gsm spunbond is ideal because you can leave a bed underneath for a few days. The material transmits light and does not allow moisture to evaporate quickly. nine0003
Cover small plants or seedlings with cut plastic bottles. Thus, they create their own mini-greenhouse for each plant. Instead of bottles, paper or plastic bags, cardboard boxes, buckets, glass jars are suitable.
Frost-fighting fertilizers
Plants will survive cold weather more easily if you feed them 10-24 hours before frost. Spraying on the leaves with a solution of potassium-phosphorus or complex fertilizer will work best. After feeding, the juice in the plant cells becomes more saturated, this one freezes more slowly. It's like with sea and ordinary water. If fresh water freezes at 0°C, sea water freezes at -1.8°C. nine0003
Instead of fertilizer, you can spray with Epin's solution.
Mulching
Mulch (straw, grass clippings, sawdust, pine needles, seed husks) retains heat in the soil and protects the root system of plants. She, of course, will not save from dead flowers and ovaries. But as an additional measure, it does not hurt. The tangible effect of mulching can be in the greenhouse.
Smaller plants (eg strawberry bushes) can be covered whole with mulch. True, in the morning you will have to carefully dig them out so as not to damage the stems and leaves. The exception is potato shoots. In general, they can be spudded with earth before freezing and not worry - the shoots will make their own way up. nine0003
Important! Potato seedlings grown from seeds, as well as potatoes from mini-tubers or layering, are not recommended to fall asleep. These sprouts are not strong enough to get out of the ground on their own.
Warm beds
This method is, of course, more preventive. Compost beds made from plant residues are called warm for a reason. The soil in them is really warmer. It warms the plants from the inside. And there are enough nutrients in such a ridge to make it easier to survive the unfavorable period. If you don’t have warm beds in your garden yet, try making at least one. Zucchini, pumpkins, cucumbers in such beds grow by leaps and bounds. nine0003
About what and how to build a warm bed, read here: Making a warm bed with your own hands: device, schemes outside. Nevertheless, greenhouse crops will also have to be saved from freezing. We have already mentioned that peppers, eggplants and even tomatoes react very badly to low temperatures, even to positive ones. The cold outside may not kill them, but the yield will drop significantly. nine0003
In order not to lose most of the crop, we will defend ourselves!
Covering plantings
The most obvious way is to build a temporary shelter in the greenhouse according to the same principle as in the open area.
Several layers of agrofibre will allow the plants to safely survive frosts. And if you come to the site only on weekends, arranging a greenhouse inside the greenhouse is perhaps the best option.
We heat the greenhouse
Infrared or any other heater is the simplest and most effective solution. In this case, you need to prepare for additional electricity costs or save. For example, turn on only in the coldest pre-morning hours or according to the “two hours of work - one hour of rest” scheme. nine0003
Someone uses homemade stoves to heat greenhouses. For example, they leave a closed brazier (bucket) with hot coals for the night. Or they build a semblance of a stationary furnace from an enameled bucket: a hole is made in the lid and a pipe is inserted. This pipe is taken out of the greenhouse. If necessary, coals are lit in a bucket.
Smoke can protect against frost
It is very often recommended to smoke greenhouses with tobacco bombs. The checker is placed in an iron bucket, set on fire with the onset of freezing and left to burn.
It burns for about an hour and a half, and for a couple of hours the smoke will stand in a closed greenhouse. Protects against slight frosts. The main thing is not to confuse a tobacco checker with a sulfur checker. The smoke of the latter can adversely affect the metal frame of the greenhouse. nine0003
Insulating the roots
In case of short-term frosts, "bed heaters" - water bottles or cobblestones - help out a lot. They need to be laid out next to the plants in advance. Then during the day they will heat up, and at night they will give off heat.
Finally, no one prevents us from combining. And spread out the bottles (preferably dark ones) with water, and cover the bushes on top, and even spray the plantings with Epin for safety net. In the fight against bad weather, all means are good!
And as a very effective preventive measure, I would like to recommend this: objectively assess your capabilities. It is clear that planting tomato seedlings in a greenhouse in the Moscow region at the end of April is cool.
Many do this and are satisfied with the harvest. But if you don't live near a vegetable garden, if you don't have a heater ready "just in case," maybe you shouldn't be in a hurry? nine0003
For some, it is much more convenient to postpone planting seedlings or delay the flowering of fruit trees for a week than to build temporary greenhouses or watch fires all night long.
Let's thaw together: how to save plants that have fallen under frost
And what to do when the plants still got frost? The weather forecast is not always 100% correct, and signs do not guarantee anything. If early in the morning you notice frost on the leaves, do not rush to despair. Let's try to resuscitate the victims. nine0003
Water and shade
First of all, the "frozen" ones should be sprayed with cool water and shaded. The bright sun is now only to their detriment. In the shade, the leaves will thaw slowly and possibly fully recover.
In the middle of the day, inspect the plants. It will already be clear which leaves have climbed out and which ones need to be cut.
Spraying with stimulants
Our indispensable Epin, Zircon, Fitosporin and other biostimulants are again in a hurry to the rescue. They activate the recovery processes in cells, helping the plant to cope with stress faster. Preparations are used for both vegetable and fruit crops. nine0003
First, let's prepare a "rescue" composition:
- Option 1. In 5 liters of water we dissolve an ampoule of "Epin-extra" and a teaspoon of vinegar to acidify the water
- Option 2. In 10 liters of water we dilute Zircon
We advise you to generously spray the branches and leaves damaged by frost, not forgetting to moisten the lower part of the leaf. This should be done early in the morning or late in the evening, because under the influence of sunlight, the active substances of the drugs are destroyed.
After spraying for 2-3 days, forget about watering. Thus, the plants will have to be processed four times with an interval of a week. nine0003
With the help of Zircon, gardeners managed to resurrect tomatoes that fell under -8°C. The entire ground part of the plants was cut off, leaving only 3 cm stumps. And poured under the root with a solution of Zircon 1: 8. From the root new shoots began to grow.
Mineral fertilizers
Fertilizing with mineral fertilizers also contributes to the rapid recovery of damaged crops. The only condition is not to overdo it. Small doses of fertilizers in this case will bring more benefits. nine0003
So, nitrogen fertilizers are applied under frozen potatoes: urea, ammonium nitrate, nitrophoska and others. When hilling, they fall asleep in the aisles, halving the dose recommended on the package.
Vegetable crops are fed with nitrophoska or other complex fertilizer at the rate of 10 grams per 1 square meter.

Nitroammophoska helps frozen strawberries. A tablespoon of fertilizer is dissolved in 10 liters of water and 500 milliliters are poured under each bush.
The same fertilizer is used for watering fruit trees and berry bushes. Take 50 grams of nitroammophoska per 10 liters of water.
Feeding is best done in the evening.
Be vigilant, dear gardening friends! Spring warmth is often deceptive, and return frosts are sudden. We hope that all the recommendations and tips will help you cope with spring frosts without significant losses.
We wish you success and great harvests!
Effective methods for saving plants from recurrent frosts
As spring approaches, all summer residents and gardeners start preparing for the new sowing season. One of the main activities at this time is the preparation for return frosts. A sharp drop in temperature in May and early June is a common occurrence for Russian latitudes. The situation is dangerous because trees, shrubs, sown vegetables, planted flowers and berries can die from a cold snap.
Heat-loving crops are especially affected. Consider how to protect plants from spring frosts. What to do to enjoy a rich harvest in the fall. nine0003
Which plants tolerate frosts more easily
Crop name
Low t withstand, o C
Peas, legumes, celery, garlic, parsnips
Seedlings are able to survive a decrease in air temperature and on the ground to -5 without consequences.
Raspberry bushes
Within 2-3 days, it will withstand the onslaught of frosts up to -3-4. On the third day, do something urgently. Otherwise, the bed cannot be saved.
Strawberries and strawberries
You will be able to survive the temperature drop to -9 painlessly.
Carrot, parsnip, parsley
Radish, cabbage, horseradish
Spinach, onion, rhubarb and sorrel
Able to withstand and not die when t drops to -5-6.

Blackberry, raspberry
Rarely affected by frost attacks. Saves shrubs late flowering.
Cold-sensitive crops
- Early flowering stone fruit, especially planted in lowlands, away from water bodies. Also weakened and sick specimens, which are the first to be at risk. nine0154
- Apricots, apples, plums and cherries are considered cold sensitive. Also cherry, pear.
- Grapes, gooseberries and blueberries do not tolerate frost well.
- Easily freezes early planted seedlings of vegetable crops. These are eggplant, tomato and pepper grown from seeds.
- A sharp cold snap is detrimental to strawberries, strawberries, gourds. They begin to suffer from cold when the thermometer falls to -1 about S.
- Even if the berries grown from mustaches or seeds were strong, the consequences cannot be avoided. After freezing, the bushes stop growing, leave for a long time and painfully.
But still, part of the crop can usually be saved. This is due to the fact that the culture has a fairly long flowering period. Even if the early flower buds suffer from the cold, fall off, after resuscitation, the plants will again throw out the flower stalks and delight with ripe berries.
- A number of heat-loving varieties of garden flowers also suffer from spring cold. Drop in air and soil t to -2 about C causes a halt in growth and development. As a result, even if the flowers do not die, flowering is still delayed by about 1.5-2 weeks.
- Perennial salvia and rose do not tolerate spring cold. Annuals dahlias, nasturtiums, chrysanthemums grown for seedlings from seeds of marigolds and zinnias. It is recommended not to rush to transfer them to the ground. It is better to wait until the threat of May frosts completely disappears.
Food for thought! The degree of susceptibility to sudden changes in temperature largely depends on what stage of blooming the buds are in.
The ovaries withstand temperatures down to -1 about C. The buds fall off already at a frost of -3 about C. Blossoming buds die at -3.3-3.5 about C. Blossoming buds darken and fall off if it gets colder to -2 about C. In the flowering stage, plants become the weakest, most susceptible. Fruits will not set if a flowering tree, bush or flower had to survive a frost of up to -1.5 about C.
How to protect the beds from return frosts
It is believed that the last decade of May, the beginning of June is the time when frosts are no longer scary. However, it is not. nine0003
- First of all, there are regions in Russia where the spring is protracted and the years are short and do not come soon.
- Secondly, today the climate is changing rapidly. Even the southern regions are not immune from sudden changes in temperature, night cooling.
What is a return frost? This is when at night the temperature drops for a certain time, falling to 0 about C.
Basically, such surprises occur at night or in the early morning, before sunrise. nine0003
How to protect the beds, especially those that are sensitive to cold? There is a set of measures that have proven useful and effective in practice:
Event
How to organize, conduct
Mulching
Ideal for garden beds.
- Use organic matter as mulch: dried grass, straw or compost. nine0154
- Beds and seedlings leaning towards the ground are covered with natural covering material.
Mulching helps conserve heat by reducing soil heat transfer and increasing moisture above the soil surface. When to line? Best in the evening, after watering. For greater effect, a layer of agrofibre should be laid on top of the organic mulch carpet. Then the beds will not be afraid of any frost.
Hilling
Mostly used for potatoes.
- Armed with a chopper, it is necessary to form mounds around each bush.

- Cover the sprouts with leaves well.
- The thickness of the soil layer should be approx. 8-10 cm.
Covering materials
A simple and effective way to save almost any vegetable garden. It consists in creating a mini-greenhouse from special covering materials, any bottles, boxes and containers that are at hand. nine0003
- beds are covered with spunbond or polyethylene film.
- Flowering strawberries and strawberries are covered with agrofiber, agrospan.
- Seedlings are covered with cut plastic containers: bottles, boxes, containers, caps, etc.
- Use any cardboard box as a covering. Cones and covering caps are made from cardboard and thick paper.
- To protect against frost, each bush can be covered with glass containers: jars, bottles, bottles, any other containers. nine0154
- To protect ornamental shrubs, special covering materials or ordinary burlap are used.
- Medicinal plants sown in the soil are protected by covering the seedlings with cut plastic bottles, buckets, disposable cups.

Any type of shelter will reliably protect the beds from harmful contact with the outside world.
Important! When constructing any protective devices, using covering materials and containers, try to keep them less in contact with the leaves, tops of plants. Therefore, mini-greenhouses are built for relatively tall seedlings, young bushes and trees. nine0003
- The frame is first formed from bent metal pipes. The length of the sections is at least 45 cm.
- After that, any non-woven material or film is attached to the structure.
- Preferably 2-3 coats. The number of layers will directly depend on the degree of the predicted degree of cooling.
Only use transparencies! Black and any dark ones will not let heat through to the roots of seedlings.
Fertilizer spraying
Preparing potassium-phosphorus top dressing.
- Take 75 g of double superphosphate for 1.5 liters of hot water.

- The mixture is infused for 3.5-4 hours.
- After the solution is filtered, diluted in 15 liters of water.
- Add 30 g of potassium nitrate to the finished composition.
The resulting mixture is sprayed on trees, shrubs, flowers and other horticultural crops a day before the predicted frost. nine0003
Root applications
Landings are watered at the roots with fertilizer solutions with a high content of potassium, phosphorus. Top dressing will help if they are applied 10-11 hours before the frost hits.
Smoke
The easiest way, but has some peculiarities. The essence is as follows:
- Fires are lit on the leeward side of the site. Based on each hundred square meters, one. Bonfire size: width up to 1.3-1.5 m, height - not less than 0.5-0.7 m.
- They set fire to everything that smolders well: straw, dry branches and leaves, cut grass, etc.

- The fire is kindled in advance with the expectation that the strongest frosts occur in the early morning. Maintain smoldering by checking if there is heat.
Smoke creates a curtain, an obstacle between cold and plants, warms the air by several degrees. What are the features of the method? It will help with frosts not lower than -4 about C. This method of protection can cause indignation of the neighbors if the smoke is blown into their garden. nine0003
Sprinkler or irrigation
The method is more convenient, more efficient than sprinkling, therefore it is considered quite popular. To do this, you need a hose with a nozzle for watering. Ideal if the site has a stationary irrigation system with sprinklers. What are they doing.
- Irrigate the plants a few hours before expected frost.
- They do it late at night, since in most cases the most severe frosts occur before dawn. nine0154
What does it do? The moisture that has fallen on the seedlings at minus begins to actively evaporate.
As a result of active evaporation, the air around is warmed up, not allowing the cold to fall close to the ground, where the roots of the plants are. The method is effective, it saves even in cases when it gets colder to the mark of -5-7 about C. The main thing is to water a few hours before the cold snap. Otherwise, the moisture will begin to evaporate early, all efforts will be nullified.
Heavy or wet irrigation
The method is applicable to all plants, for example, seedlings from vegetable seeds, young and adult berries, etc. But it is especially effective for shrubs and trees.
- Up to 5-10 buckets of warm water, heated to +10 about C, are poured under each tree or bush.
- Treat crops additionally by irrigation or sprinkling. nine0154
The protection method works similarly to the previous one. Moisture begins to evaporate, warms the air and prevents plantings from freezing.
Green manures
Green manure seeds are sown in advance between rows, in areas where vegetables, flowers, berries, any heat-loving varieties are planted.
Green manure with a living wall will protect plantings from extreme temperatures. After, when warm weather sets in, they are cut off, leaving between the rows like mulch. nine0003
Landing planning
- Stone fruit trees are capricious, react negatively to lower temperatures. It is recommended not to plant them in the lowlands, where it is always 2-3 about C colder than in the rest of the territory.
- Before transshipment of vegetable seedlings in open ground, it must be hardened off. During the day, take out to the street, at night - the house. In general, do not rush to plant vegetables in the garden. Wait until warm weather sets in. Otherwise, the plants can not be saved. nine0154
- When choosing seeds for shrubs and trees, vegetables, flowers and other crops, choose varieties that are suitable for the climate in your area. Today, most breeders have such seed. A striking example is the seeds "Gavrish" and "Agroelita".

Weatherman himself
It's good to be interested in the weather forecast, but we all know that meteorologists often make mistakes. Not because they are incompetent. It's just that often they give out data not for a single region or city, but in general, for the region. That is why the weather varies so much in individual places located in the same region. What to do? Learn on your own, determine what the weather will be like in the coming days. Become a weather forecaster and do everything to prevent freezing of plants. nine0003
Nature and folk wisdom will help
Sign, natural phenomenon
What will happen (probable course of events)
Early spring, warm first half of the season
In May there is a great threat of cooling. Moreover, a significant drop in temperature is likely to occur closer to the end of May, beginning of June.

Early spring, warm
Expect return frosts May 1-5, 15-20. In addition to freezing of the soil, wet snow is possible.
Warm during the day, very cold in the evening
Wait for cold weather if a sharp drop in temperature occurs against the background of such factors:
- cloudless, clear sky;
- calm, calm weather; nine0154
- dry air and no morning dew.
The probability is especially high if at 19:00-20:00 the temperature begins to drop sharply, and by 21:00 the thermometer already shows +3-4 about C.
Moon yellow like a head of cheese
Expect frost in the air and on the ground.
Sparrows sit silently, ruffled and hiding their tails. nine0003
High chance of rain with sleet. The cold will come soon.
The weather is cloudy, but it clears up closer to the night
Cooling will be for sure.

The fish does not bite and goes to the depth
A sharp cold will come in a day.
The frogs have stopped croaking, they are silent
There will be a cold snap, frosts on the ground.
Water lilies on ponds raised leaves
No more cooling. You can start planting heat-loving crops, sowing seeds of flowers and vegetables in open ground.
nine0193 Viburnum blossoms in a riotous color
The threat has passed. There will be no more cold snaps and frosts.
Red willow blossoms
The earth is ripe, there will be no sharp drops in temperature. It's time to go to the field, sow the soil.
Willow and aspen blossomed
It's time to sow carrot seeds in the garden. At the same time it is already possible to sow:
- parsley, dill;
- radish, radish;
- turnips and onions.
Maple blossoms
It's time to plant the beet seeds.
Lilac and rowan blossoms
It's time to sow cucumber seeds outdoors. Plant seedlings:
- eggplant;
- tomatoes; nine0154
- peppers;
- physalis.
It's time for cherry plum, cherry and blackthorn to blossom
Time to sow corn seeds outdoors.
The cuckoo has flown in and is calling
Heat-loving crops can be sown outdoors.
Oak blossomed
It's time to sow peas.
Three frosts in May
When bird cherry blossoms, when apricot blossoms, the temperature drops especially when oak blossoms.
This is interesting! The people noticed. If March is dry, April is damp, and May is cold, expect a rich harvest in autumn.

Calculations help predict the weather
In one of the issues of the magazine "Country Secrets" a note was published by our compatriot, an experienced gardener Yu. M. Alekseev. Based on personal experience, he told how you can determine whether there will be frost in May.
- To do this, you need an ordinary outdoor thermometer, which is hung out in a shady place where the sun hardly gets.
- To predict changes in the weather, you need to fix the thermometer readings at 13:00 (daytime) and at 21:00 (evening). nine0154
- After you need to find the difference between the received numbers.
- Check the final number with the data given in the table.
- Thus, to find out how likely the threat of the return of frost is.
Factors affecting forecast accuracy
Forecast accuracy depends on a number of weather factors. They focus on changes that occur mainly in the evening or at night. What factors indicate that there will be no cooling, even if the thermometer shows otherwise:
- The wind increased, became gusty and cold.

- Cloudiness has sharply increased.
- Fog came out of nowhere.
- Dew has fallen on the grass and leaves of the trees.
Good to know! In cities, on hills covered with vegetation, the ambient temperature is usually 2-3 about higher than in hilly areas and in lowlands.
If the seedlings and seedlings are still frozen
Unfortunately, not all crops will be able to survive the cold snap. Even strong plants sometimes cannot stand frost and freeze slightly. What to do in this case? Is it possible to somehow revive the garden and vegetable garden?
- It is recommended to wrap seedlings, frozen trees and shrubs with hay, straw or rags. They will warm up, slowly thaw. There is hope that they will fully recover.
- Frozen seedlings and crops will help save the following method. In the morning, before sunrise, spray the damaged plants with a solution, where 2 g of boron, potassium permanganate and copper were thrown into 10 liters of water.
Spray completely every bush! The water should be cold, not warm. nine0154
- Experienced gardeners are advised to fluff up frostbitten beds, water the root zone of damaged plants with a weak solution of complex fertilizers. This method is good for grapes. And the tomatoes will help, albeit partially. Frozen tops are unlikely to come to life, but with 100% certainty we can say that powerful side shoots will grow.
- Wait a day after the frost, then water the bed with tomatoes and cabbage with water at room temperature. How much to pour? Under each bush 1 liter. Before watering, it is recommended to trim the damaged tops and leaves to a healthy, undamaged tissue. nine0154
- One day after watering, spray frozen seedlings with any growth activator. Suitable Kornevin, Epin, Epin-extra, Heteroauxin or analogues. Prepare the spray mixture strictly according to the instructions on the package. How much will be needed? Based on the calculation of 75-100 ml for each bush. The same solution is recommended to water the soil near the plants.
Pour about 175-200 ml under each seedling.
- After 3-4 days, it is recommended to make top dressing from 10 liters of water, where 1 tbsp. l. urea. nine0154
- After about a week, 8-9 days, feed the affected crops with a top dressing with a high content of potassium. The solution is prepared based on 10 liters of water 1 tbsp. l. fertilizers. Under each bush, approximately 175-200 ml is poured.
- If frost has affected potato seedlings, it is also worth trimming the tops and leaves to living tissue. Then spray each bush with a growth stimulator. In parallel with this, reinforce the seedlings with nitrogen fertilizers. To do this, prepare a solution of 10 liters of water and 20 g of ammonium nitrate. Pour 150-180 ml under each bush. nine0154
How to reanimate seedlings of vegetable crops
Here is how experienced gardeners recommend reviving seedlings of garden crops beaten by the May cold snap:
Comprehensive treatment, sanitary pruning will revive frozen seedlings.











