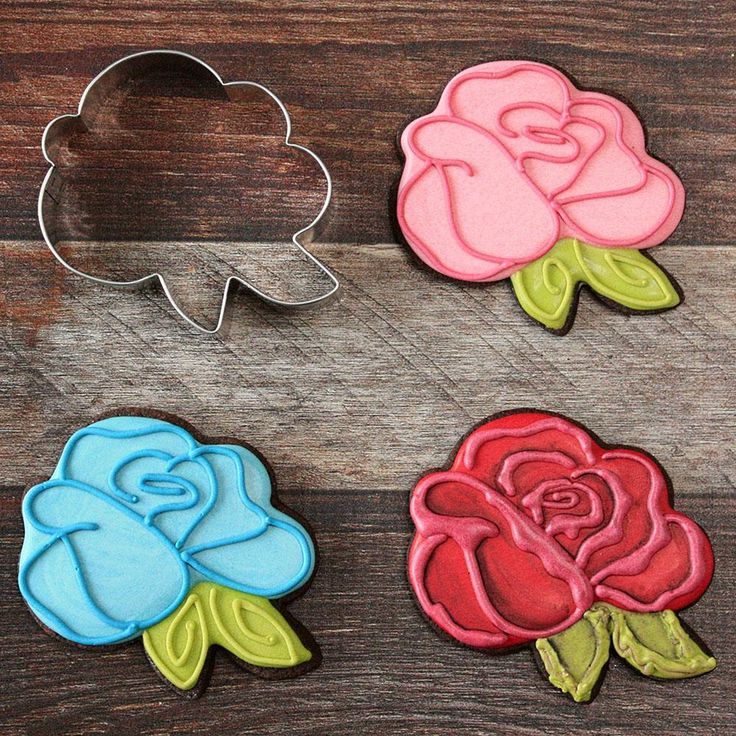
How to make a rose cutting
Grow Roses from Cuttings: 2 Best Ways to Propagate!
How to grow roses from cuttings easily! Compare the BEST & worst ways to propagate in water or soil, using potatoes, & root by air layering.
Maybe it’s a beautiful rose plant in the garden that you want to multiply, or a Valentines rose bouquet that you want to grow into more roses, it’s easy to want more colorful and gorgeous rose bushes and vines in our homes and gardens.
Many plant lovers have tried to grow roses from cuttings. There are many rose propagation methods such as rooting in soil or water, air layering, and some even try to grow rose cuttings in potatoes! Some of these methods are great, some actually don’t work very well.
Today we are going to compare which ways are the best and easiest to propagate roses from either a plant, cut flowers or even a bouquet. Wouldn’t it be nice to have more roses in our gardens or as gifts to share with friends? 🙂
Can you propagate patented roses?
* Some resources in article are affiliate links. Full disclosure here .
A plant patent lasts for 20 years, after which the plant is allowed to be propagated.
If the roses are patented within the last 20 years, it is illegal to propagate the rose without the consent of the patent holder. ( Source )
However, there are endless varieties of roses you CAN propagate. For example, the famous “New Dawn” and “Charlotte Armstrong” roses were patented over 50 years ago, and old-fashioned heirloom roses often root easier than modern hybrids.
Now you know which roses not to propagate, let’s look at the best and easiest methods to root rose cuttings! ( Source )
Best time to grow roses from cuttings
The best time to grow roses from cuttings is from spring through summer, when flexible new stems (current year’s growth) are actively growing. They are called softwood cuttings, who are the fastest and easiest to root when you select healthy stems.
Look at all the beautiful rooted rose cuttings by Vuon & Nha on YouTube! Video tutorial below:
The next best are semi-hardwood cuttings, taken in late summer and early fall, when new stems have partially matured.
Hardwood cuttings are most difficult type of cutting to root. They are taken in late fall or early winter, when the rose stems have matured and entered dormancy.
Grow roses from cuttings by air layering
Air layering is a fascinating propagation method being used for thousands of years! Nowadays there are easy products like these reusable air layering pods you can get, or make your own with simple materials such as small water bottles or plastic bags.
Air layering is the BEST way to propagate roses (and many woody plants) if the rose bush or vine that you want to multiply is already growing in your garden or in a friend’s garden. You don’t even have to use rooting powder with this method.
You don’t even have to use rooting powder with this method.
The best time for air layering roses is in late spring or summer when the weather is warm and the rose bushes are actively growing. ( Air layering rose video tutorial below. )
Select a stem that is about the thickness of a pencil and longer than a foot. Take a clean sharp knife, find a spot at about 1 foot for the top tip of the stem, remove leaves and thorns around this area, peel off about a 1 inch section of the green bark tissue to get to white wood.
You can also make a 2” long cut along the middle of the stem, and insert a little piece of plastic straw to prop the cut open, like shown in the above video tutorial by Vuon & Nha.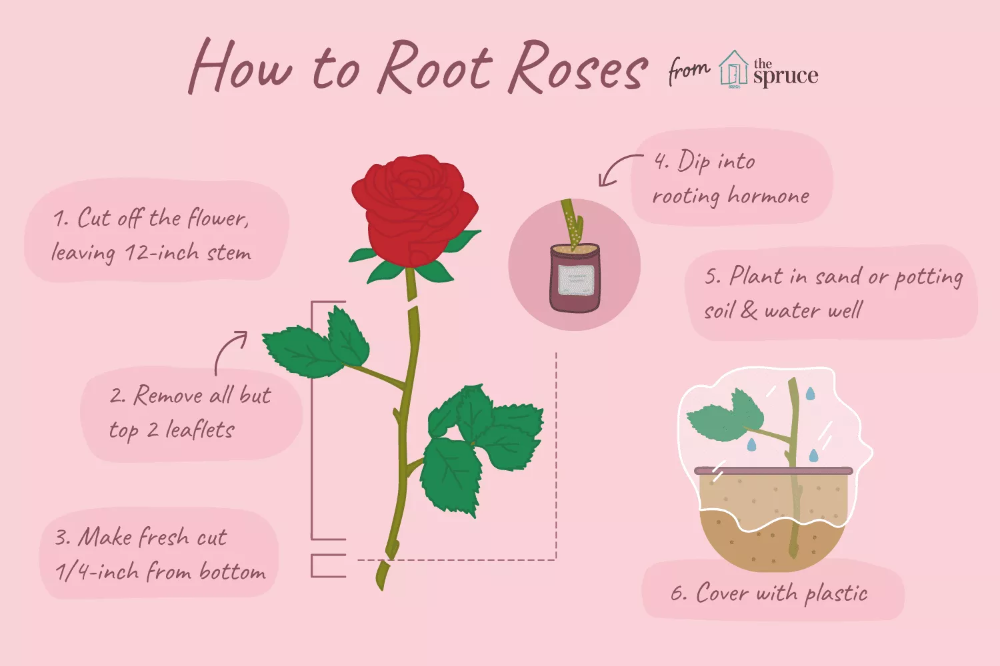
Don’t cut too deeply into the stem or it could break.
Dust the cut area with rooting hormone. You can skip this, but rooting hormone does help speeding up the process.
Next, make a 3” to 4” size pouch using either plastic wrap or a small plastic bottle filled with moist peat moss, coir, or potting soil. Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
The cut area should be completely covered with enough room for roots to develop. Video tutorial below by Vuon & Nha.
Secure top and bottom with strings or twist-tie (Not too tight so the plant can grow and expand). You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
Because the stem is still attached to the mother plant, it is receiving water and nutrients as the new roots are growing from the cut area. This greatly increases the propagation success rate to nearly 100%!
Most rose plants show their white roots in 3 – 5 weeks. When you see good root system develops with lots of healthy roots, clip the stem off below the layer.
Gently remove ties and covers. Carefully plant your new rose plants and keep them well watered and protected from direct sunlight for a couple of weeks so it can adapt.
Grow roses from cuttings in soil or medium
Fill some clean pots or containers rooting mix and water well so it’s moist and fully hydrated. You can use clean potting soil or a soil-less mix such as clean sand, peat moss, perlite, or Coco coir. ( Photo by Hedgerow Rose)
IMPORTANT: The containers should have drainage holes and never sit in water for too long. ( Photo by Grownups )
( Photo by Grownups )
Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
Take rose cuttings only from healthy plants that are well watered. Choose fresh healthy rose stems newly grown from the woody base, with at least 3-5 leaf nodes on the stem. Cut near the base at a 45-degree angle. Put cut stems in water immediately.
Video tutorial by Vuon & Nha on YouTube. How to propagate rose cuttings in coco coir!Cut longer stem into 6 inch to 8 inch long, and make sure each cutting have at least 3 nodes – where leaf meets stem. Remove all flower buds and leaves except for one set of leaves at the top of each cutting.
Dip the cutting’s bottom half in the rooting hormone powder or gel. Use a pencil to make a planting hole 3 to 4 inches deep in your rooting mix. Plant the rose cutting into the hole so at least two nodes are covered.
Keep the cuttings in a warm and bright place away from direct sun. Water when the rooting mix start to feel dry on the top inch. Pamela at Flower Patch farm used recycled coffee cups (above) and large jars (below ) as humidity tent. Such great ideas!
You can also use a propped- up plastic bag or a mini greenhouse. Here are 45 best DIY greenhouses you can make from tiny to big!
If you live in a warm humid climate with a shaded outdoor area, you can skip the humidity cover. ( Photo below by Hartwood Roses )
Most softwood rose cuttings will root within 2 to 6 weeks. If you see healthy leaves growing, and feel some resistance when you very gently tug on the cuttings (don’t do this too soon!) , it’s likely they have rooted.
Here’s a YouTube tutorial by Mike on how to use a humidity cover made from plastic bottles.
Now you can remove the humidity tent and let them grow for a couple more weeks before transplanting the cuttings. Below is another propagation example by Lilisim.
Can you root rose cuttings in water?
Rose cuttings do not propagate well in just water. Some cuttings will root, but the success rate is usually about 20%, while you can get 80% success by propagating rose cuttings in soil medium or by layering.
The rose cuttings tend to take a long time to root in water, and is prone to rotting.
However, some favorite plants can root very easily in water! Here are a couple of tutorials on how to propagate Fiddle Leaf Fig or Hydrangea cuttings in soil or water with almost 100% success!
Hydrangeas are some of the easiest flowers to propagate! Tutorial here!Can you grow rose cuttings using potatoes?
There are many viral images of rose cuttings in potatoes, but I have not seen any scientific or real life evidence of potatoes or dipping in honey making rose cuttings grow more quickly or successfully.
On the contrary, there are many reports of failures from gardeners who actually tried to grow rose cuttings in potatoes.
The potatoes may grow roots, which will not magically become rose roots. The rose cuttings need a medium that holds moisture and air, which isn’t really what a potato does.
That’s it! Use the first 2 methods, and happy gardening! 🙂
How to Propagate Roses From Stem Cuttings
By
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti is a life-long gardener and a veteran Master Gardener with nearly three decades of experience. She's also an author of three gardening books, a plant photographer, public speaker, and a former Cornell Cooperative Extension Horticulture Educator. Marie's garden writing has been featured in newspapers and magazines nationwide and she has been interviewed for Martha Stewart Radio, National Public Radio, and numerous articles.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
Updated on 10/11/22
Reviewed by
Julie Thompson-Adolf
Reviewed by Julie Thompson-Adolf
Julie Thompson-Adolf is a master gardener and author. She has 13+ years of experience with year-round organic gardening; seed starting and saving; growing heirloom plants, perennials, and annuals; and sustainable and urban farming.
She has 13+ years of experience with year-round organic gardening; seed starting and saving; growing heirloom plants, perennials, and annuals; and sustainable and urban farming.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
In This Article
-
When to Propagate
-
Before Getting Started
-
FAQ
Project Overview
Propagating herbaceous plants is often done by rooting green stem cuttings, but the process can also be successful with woody-stemmed plants, including some roses. Rooting stem cuttings of roses and other woody plants works best with so-called "wild" or "native" pure species, rather than hybrid shrubs. That's because many hybrids are created through a grafting process in which branches from showy but delicate species are melded onto rootstock from a sturdier species.
The result of grafting can be a spectacular plant with exceptional root hardiness. But if you propagate a new plant from a branch clipping, it will lack the parent plant's root hardiness. Thus, it's best to use stem clippings only to propagate non-grafted roses, which include many so-called shrub roses.
But if you propagate a new plant from a branch clipping, it will lack the parent plant's root hardiness. Thus, it's best to use stem clippings only to propagate non-grafted roses, which include many so-called shrub roses.
The stem clipping method is a bit tricky with woody plants, and you should expect that several attempts will end in failure. Take extra cuttings to ensure you have at least a few viable prospects. Still, if you take your cuttings from a healthy rose plant and follow the proper steps to root them, your odds of developing new plants will be high.
What Is a Shrub Rose?
The term "shrub rose" is defined by the American Rose Society (ARS) as “a class of hardy, easy-care plants that encompass bushy roses that do not fit in any other category of rose bush.” Many people use the term to refer to any type of non-hybrid rose, but there are several types of hybrid roses that do fit into the ARS's definition of shrub roses, including Moyesi hybrids, hybrid musk roses, Kordesii roses, English roses, and Knock Out roses. These join the many native rose species to form the category of shrub roses. However, any of these hybrid roses described as an "own-root" rose rather than a grafted rose may lend itself to successful propagation from stem cuttings.
These join the many native rose species to form the category of shrub roses. However, any of these hybrid roses described as an "own-root" rose rather than a grafted rose may lend itself to successful propagation from stem cuttings.
When to Propagate a Rose by Stem Cuttings
Rooting a stem cutting can be done almost any time, but cuttings taken from new growth that has recently flowered (rather than old, hardened wood) are more likely to root successfully. Spring or fall is the best time to take softwood stem cuttings. Select them in the early morning hours when the plant is well hydrated. Moreover, avoid taking cuttings when your plant is heavily blooming. At this time, the plant is putting most of its energy into flower production rather than root development, so cuttings won't readily root.
Before Getting Started
Sharp pruners are necessary when taking rose cuttings. Dull tools can crush the rose's woody stems instead of forming a clean slice, which can make the cutting susceptible to fungal rot. Furthermore, make sure to clean your pruners before and after each cutting to avoid transmitting any diseases.
Furthermore, make sure to clean your pruners before and after each cutting to avoid transmitting any diseases.
Be patient when growing roses from cuttings. It can take several years for your new rose to produce flowers.
Click Play to Learn How to Grow Roses From Cuttings
Equipment / Tools
- Pruning shears
Materials
- Mature rose plant for cuttings
- Powdered rooting hormone
- Plant pot
- Sand and vermiculite or a rose potting mixture
- Plastic bag or plastic wrap
The Spruce / Michela Buttignol
-
Take Cuttings
Start by taking a 12-inch segment of a new stem that has recently bloomed, cutting it from the plant at a 45-degree angle. The stem should be about the width of a pencil. The best cuttings for rooting usually come from the sides of the bush, rather than the center.
Remove any flowers or flower buds along the cut stem. Flowers or buds on the cut branch will consume energy, and you want to encourage the stem to refocus its survival energy on sending out new roots.
 If you're taking multiple cuttings, place them in a container of water to keep them hydrated until you're ready to propagate them.
If you're taking multiple cuttings, place them in a container of water to keep them hydrated until you're ready to propagate them. The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Remove Most Leaves
Remove all but the top two sets of leaves on the stem. Then, cut off the remaining portion of the stem just above this top set of leaves. Removing the excess leaves will help the cutting divert its energy to root production.
-
Prepare the Stem for Rooting
Using sharp pruning shears, make a fresh cut on the bottom of the stem just below a stem node (a bump where new growth typically forms). Then, slice into the bottom of the stem about a 1/4 inch up, splitting the stem into open quarters.
Apply Rooting Hormone
Although not absolutely necessary, applying a rooting hormone can help spur your rose plant into developing new roots. Rooting hormones can be found in powder, liquid, and gel form—you'll have the best success with the powder version when working with roses.
 To apply, slightly moisten the split end of the rose cutting, and then dip it into the powdered rooting hormone. Shake off any excess.
To apply, slightly moisten the split end of the rose cutting, and then dip it into the powdered rooting hormone. Shake off any excess. -
Plant the Cutting
Fill a small pot with at least 6 inches of a potting mix formulated especially for roses. Poke a hole in the potting medium, and then insert the stem sliced-side down, taking care not to rub off the rooting hormone. Gently pack the soil around the stem, and water well.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Cover the Cutting
Loosely cover the cutting, pot and all, with a plastic bag or plastic wrap to help retain soil moisture. Be sure not to let the plastic touch any remaining leaves on the stem, which can cause them to remain wet and susceptible to fungal disease. Putting a tall stake into the pot can help hold the plastic away from the leaves. The bag also needs to be slightly vented, so condensation can escape—if you seal the bag too tightly, the stem can rot. Place the cutting under grow lights or near a bright window.

-
Monitor the Cutting
Keep the soil moist until roots begin to form, which usually takes about two weeks. Check for roots by gently tugging on the stem—if there's resistance, roots are probably present.
Your cutting can be transplanted into a pot or the ground as soon as the roots are firmly established or when new leaf sprouts begin to appear along the stem. Make sure to harden off the new rose—i.e., gradually expose it to outdoor conditions—before planting outside.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
How to Get More Blooms From Your Roses
How to grow a rose from a cutting
Sooner or later, the presented bouquet of roses will wither and have to be thrown away. This fate befalls all freshly cut flowers. But, fortunately, you can save the memory of roses not only in photographs, you can breathe new life into a bouquet of roses, and then the flowers will delight you with their beauty and fragrance for a very long time. And for this, roses need to be rooted correctly and on time. If you want to order the Queen of Flowers in Vinnitsa, take a look at our catalog and you will definitely have plenty to choose from. Spectacular roses will not leave anyone indifferent.
And for this, roses need to be rooted correctly and on time. If you want to order the Queen of Flowers in Vinnitsa, take a look at our catalog and you will definitely have plenty to choose from. Spectacular roses will not leave anyone indifferent.
What are the best cuttings to root
Surprise your beloved!
Growing roses is very popular today. A rare summer resident will miss the opportunity to plant a beautiful bush on his site. Moreover, roses are universal holiday flowers. They are given for any reason and without it. As a rule, roses at home are propagated by cuttings (the part of the leaf that connects it to the stem). But in order for everything to work out, you need to know which cuttings are most likely to take root. So, the most important rule is that the fresher they are, the higher your chances of growing new plants, from which then original bouquets will turn out. Secondly, the variety of roses is important. All imported flowers root very poorly, because they undergo multi-stage processing with various chemicals that increase their shelf life. Therefore, you can not try to root a cut rose of Dutch origin. But with local varieties, things are much better. The period of the year when the flower was grown is also important. So, most likely, the summer stalk will take root, then the spring, autumn, and lastly the winter.
Therefore, you can not try to root a cut rose of Dutch origin. But with local varieties, things are much better. The period of the year when the flower was grown is also important. So, most likely, the summer stalk will take root, then the spring, autumn, and lastly the winter.
How to properly prepare a cutting for planting
Bouquet of roses "Charm"
Planting roses is a delicate matter, and you need to approach it responsibly. So, first of all, take roses that already have formed shoots. Next, carefully cut off the leaves, buds and thorns from them. Now you can cut off the cutting itself (about 10-15 cm will be enough) and immerse it in water. Important: the cut on the handle should be as even as possible. So arm yourself with the sharpest knife. Cut the stem at an angle of 45 degrees, taking into account that the distance from the kidney should be about 1 cm. It is in this part of the stem that a large accumulation of nutrients is located. They then stimulate the growth of a new flower. It will be a huge plus if you treat the cuttings with a special hormone that stimulates the growth of shoots. You can find such a tool in any gardening store, where you will certainly be advised.
It will be a huge plus if you treat the cuttings with a special hormone that stimulates the growth of shoots. You can find such a tool in any gardening store, where you will certainly be advised.
How to grow cuttings in a pot with earth
Bouquet "For my Queen"
First, hold the cuttings in a container of water for about a day. Then plant the lower cut into the ground vertically (it is important that the upper buds are above the soil surface). Water the soil generously with water and place the pot on a windowsill that faces south. The optimum temperature regime is up to 20 degrees above zero. You can insert wooden chopsticks into the pot (unnecessary pencils or Japanese chopsticks will do). In the future, they will become a support for the process on the stem. Then stretch a film or bag over the sticks to create a kind of greenhouse for the cuttings. And that's all. Now we wait about a month and check if the flowers have rooted. It is very simple to do this: slightly pull the stem with your fingers, if there is some resistance, then everything is going according to plan and the stalk has taken root.
Method of growing cuttings in potatoes
Bouquet "Gift for a Beloved"
The method of growing roses in potatoes is the most popular and very effective. But it is advisable to use it only in the spring. The meaning of the method lies in the fact that a young potato tuber will create a moist environment for the stem and nourish it with useful microelements. Keep in mind that the length of the handle should be no more than 20 cm, and the potato itself should be medium in size and without “eyes”. We make a hole for the stem, plant the potatoes in the ground, pour water and cover with any unnecessary jar. In this form, the stalk will not only receive everything necessary for rapid growth, but will also be protected from pests. Do not forget to periodically moisten the soil (but do not flood), and moisten the cutting itself with water a couple of times a day. Once every five days, it is a good idea to water the shoot with sweetened water (2 teaspoons of sugar per glass of water).
Method for growing cuttings in greenhouse conditions
15 red roses
In greenhouses, ripened lignified shoots that have survived the winter indoors are usually rooted. So, take a container and add to it a mixture of fertilizers that are usually used in normal planting in open ground. Plant a prepared cutting there and follow some simple recommendations. So, the temperature regime in the greenhouse should be in the range of 24-25 ° C, the humidity should be high (above 90%), and access to sunlight is limited. The leaves of the cuttings should be regularly moistened, which is why watering will have to be done 10 times a day. When growing roses on a large scale, it is better to get sprinklers for this purpose. After 3 weeks, you can reduce watering, remove shading and start airing the greenhouse (the so-called hardening of cuttings).
Method of growing cuttings in water
Bouquet "Our happiness!"
Growing rose cuttings in water is the easiest method. Carefully cut the stems and place them in a container of boiled water at a temperature of 20-25 ° C. Place the tank in a place with good shade. Change water daily. After three weeks, at the end of the cutting, you can see the beginnings of roots.
Carefully cut the stems and place them in a container of boiled water at a temperature of 20-25 ° C. Place the tank in a place with good shade. Change water daily. After three weeks, at the end of the cutting, you can see the beginnings of roots.
Method for growing rose cuttings in a bag
25 red roses with hearts
This method is also called “burrito”. Now you will understand why. All you need is unnecessary newspapers and a bag. Prepare the cuttings (preferably treated with growth stimulants), lay them on a newspaper and wrap. Now moisten the bundle liberally and place it in the bag. In this form, the cuttings should be stored in a dark place at a temperature of about 20 ° C. About once every ten days, unroll the bundle, inspect the stems, remove the rotten ones, change the newspaper for a new one, treat it with water and put it back in place. After 3 weeks, the root system should germinate on the cuttings.
Useful tips on how to plant a rose
Basket "In love with you"
In conclusion, we want to tell you some secrets of cuttings so that growing roses at home is as effective as possible.
- Do not plant more than 3 cuttings in one pot.
- Prefer opaque containers.
- Don't over water to prevent rot.
- When the water begins to evaporate, do not replace it completely, it is better to add a little new water.
- If there are no leaves on the stems, the root system can also form in the dark. But if at least one leaf has grown, light is needed.
- Roses are light and heat-loving varieties of flowers that do not tolerate drafts and white walls.
If you fail to grow a rose from cuttings the first time, don't give up. This does not mean at all that you are not given to be the owner of the rosary. Keep trying, experimenting and you will definitely succeed.
methods of cuttings in winter, spring, autumn with photo and video
Rules for propagation of roses by cuttings
Cuttings are one of the main methods of rose propagation. There are two options - green and cuttings and lignified. The first case is used for summer propagation of garden roses. The second is for winter and spring. And he is the most popular. And in this way you can propagate roses from a bouquet, because in flowering shoots the lower part of the shoot is always lignified.
The first case is used for summer propagation of garden roses. The second is for winter and spring. And he is the most popular. And in this way you can propagate roses from a bouquet, because in flowering shoots the lower part of the shoot is always lignified.
Cutting cuttings
Rooting cuttings can be cut from any part of the shoot, except for the top with a flower. Each cutting should have 2 nodes - this is the place where the leaves are attached to the stem and where the buds are. The thickness of the cutting should be at least 5 mm - too thin will not take root.
The bottom cut should be oblique - it is made just below the knot, stepping back about 5 mm. Why oblique? But because the callus (the tissue from which the roots then grow - a kind of white growth) is best formed around the cut. And the larger its area, the larger the callus. And one more thing: it is very important to make cuts with a sharp knife - if the tissues of the shoot are wrinkled, it will most likely rot and will not give roots.
Here, the top cut must be straight. They do it by stepping back from the node the same 5 mm. Why direct? Moisture escapes through the wound, and besides, it is an open gate for infection. That is why the area of the upper cut should be minimal.
Preparing the cuttings
Remove the lower leaves from the cut cuttings. And the upper ones are shortened - rose leaves usually consist of 3 or 5 segments, and only 2 are needed. For reliability, it is useful to cover the upper cut with children's plasticine.
Soil for rooting cuttings
Rose cuttings give roots, but not as easily as, for example, currant twigs - just putting them in water is not enough. It is best to root them in the ground. And there are options.
And there are options.
River sand. It is light, fluffy and very well breathable, which is necessary for the formation of roots. But there is a problem - the sand dries up very quickly. Therefore, it will need to be watered frequently. Or add perlite to it, which retains moisture.
Soil mixtures. There are 2 classic versions:
- river sand with peat in a ratio of 1:1;
- river sand with sheet earth in the ratio 1:1.
The sand in this case is the baking powder. And peat or earth provide moisture capacity, that is, planted cuttings will have to be watered less often.
Rooting conditions for cuttings
Cuttings are buried in the substrate by about 1 cm. You need to make holes with a stick or pencil, insert the cuttings there and lightly compress the soil with your hands.
Then the cuttings should be well watered. And be sure to cover with either a jar or a plastic bag so that there is constantly high humidity around the planted cuttings. But! It is necessary (required!) Once a day to remove the jar (package) so that the cuttings are ventilated - otherwise they will become moldy and rot.
But! It is necessary (required!) Once a day to remove the jar (package) so that the cuttings are ventilated - otherwise they will become moldy and rot.
Another important point: the soil temperature should be about 21 °C, and the air temperature should be 2-3 °C lower (2). There is no place for cuttings on the windowsill - it is always cooler than necessary, and cold soil, combined with high humidity, always leads to an outbreak of fungal diseases.
Photo: pixabay.comAnd, of course, cuttings need a lot of light. But not direct sunlight is the best - they will provoke increased evaporation of moisture from the leaves, as a result of which the cuttings can dry out.
Methods for cutting roses
Roses can be propagated by cuttings at almost any time of the year. And there are some interesting methods that allow you to propagate roses more efficiently.
Cuttings of roses from a bouquet
The life of bouquets given on March 8 is short-lived - in most cases they will last no more than a week. And so we want this beauty to be with us always ... But this is possible! For example, you can cut cuttings from roses from a bouquet, and then grow them in the garden.
And so we want this beauty to be with us always ... But this is possible! For example, you can cut cuttings from roses from a bouquet, and then grow them in the garden.
Cuttings will only take root if the roses in the bouquet were fresh. It is useless to root dried shoots. But how to understand how fresh a flower is?
- The first thing you need to pay attention to is the sepals, small green “leaves” at the very base of the flower, advises agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova. - If they are raised up, literally "hug" the bud, then the flower is fresh. If they are lowered down, then the rose has been cut long ago.
The second indicator of freshness is leaves.
– If you pick up a flower and the leaves begin to fall off, then the rose is not fresh, says Svetlana Mikhailova.
By the way, many buyers are guided by the degree of dissolution of the flower. They think that if the rose is still in bud, it means that it was cut recently. Nothing like this!
Nothing like this!
– Roses are stored in the refrigerator until they are sold, explains Svetlana Mikhailova. - They are even transported in refrigerators. Under such conditions, the bud will not open. Moreover, flowers are always stored and transported "dry", without water - they are simply packed in paper. And how much the rose spent in this form, no one knows.
It happens that without water and in the cold, roses spend a week or more. The buds will remain unopened, but the plant has already died. And so you bring home a bouquet, put it in water, hoping that now the flowers will bloom. But their heads just hang, never opening. They are dead. And it is pointless to cut such roses.
- This is often the case with Dutch roses, - says Svetlana Mikhailova, - because they are brought from afar. But now there are a lot of Russian greenhouse roses on the flower market. They are usually much fresher.
And that's the easiest way to cut them.
Cuttings of roses in winter
In winter, you can cut cuttings from purchased roses, for example, from the same bouquets. Or specially buy a flower you like in the store. In this case, the method of propagation by semi-lignified cuttings is used.
Or specially buy a flower you like in the store. In this case, the method of propagation by semi-lignified cuttings is used.
Cuttings of roses in spring
Experts do not advise radical pruning of roses in autumn, it is better to pin the shoots to the ground for the winter, and if you use this technology, then spring cuttings of roses are your option. After the winter shelter has been removed from the plants, they need to be cut off - cut out frozen branches and remove excess stems. So these very extra stems are excellent material for cuttings.
In this case, the standard method of propagation by semi-lignified cuttings is also used.
Cuttings of roses in summer
In summer, roses actively grow shoots, and at this time you can use the second method of propagation - green cuttings. They are cut from May to July, but it is better in the budding phase (3).
The shoot intended for cuttings must be strong, fully green. The cuttings are cut about 10 cm long, but it is important that they have 2-3 buds. The top cut is made directly above the kidney. The lower one is oblique, just below the kidney. The lower leaves should be removed, leaving a couple of the top ones. And cut them so that out of 3 - 5 plates only two remain.
The top cut is made directly above the kidney. The lower one is oblique, just below the kidney. The lower leaves should be removed, leaving a couple of the top ones. And cut them so that out of 3 - 5 plates only two remain.
Before planting, the cuttings should be soaked in a Heteroauxin solution for 12 hours to stimulate root formation.
Prepared cuttings are planted in a school - a secluded quiet place with fertile soil, deepening by 1.5 - 2 cm. Water well and cover with foil. Roses are photophilous plants, however, under the scorching rays of the sun, the cuttings begin to evaporate moisture too actively and dry out rather than give roots. Therefore, the shkolka should be done either under the light shade of trees, or the cuttings should be shaded with coniferous branches or burlap.
Planted cuttings should be watered frequently - the soil should be moist all the time. And in hot weather, it is useful to rinse the film with cold water.
Roots of green rose cuttings usually form after 3-4 weeks - new leaves speak for this. After that, the film must be gradually opened so that the plants get used to the open air - first for a couple of hours in the morning, then longer and longer. After 2 weeks, the film is removed completely.
After that, the film must be gradually opened so that the plants get used to the open air - first for a couple of hours in the morning, then longer and longer. After 2 weeks, the film is removed completely.
In the future, young roses should be constantly watered, and carefully covered for the winter. In the spring they can be planted with a clod of earth in permanent places.
Potato rose cuttings
Both green and semi-woody cuttings can be rooted in this way. They are prepared in a standard way, but before planting they are stuck into potatoes, and only then, together with the tuber, they are planted in a school in the garden.
Why do they do it? And in order for the cuttings not to dry out, if it is not possible to water them often, this method is useful for weekend summer residents. Juicy potatoes. The moisture in it remains for a very long time, and even if the soil is dry, the cutting will not die.
Rose cuttings using the burrito method
This method of rooting cuttings is becoming more popular year by year. And it got its name from the Mexican analogue of shawarma - burrito. And you will understand why.
And it got its name from the Mexican analogue of shawarma - burrito. And you will understand why.
The point is this. The lower cut, as with traditional cuttings, is dusted with a root formation stimulator. Then several pieces of cuttings (usually 5-10 are recommended) are wrapped in 2-3 layers of newspaper or paper towels, moistened with water so that the paper is moist, but not wet, and then loosely (it is important that air penetrated inside) wrapped in polyethylene. It turns out a kind of bundle, similar to the same shawarma burrito. It is cleaned in a dark, cool place with a temperature of 14 - 18 ° C.
This is important! If the temperature is lower, the roots will not form. And if it is higher, the cuttings will either dry out (even constant moisture often does not save), or they will become moldy and begin to rot.
As a rule, the callus on the cuttings is formed after 3 weeks. If this does not happen, the cuttings are again wrapped in paper (if it has dried up, it must be moistened again) and the film and again sent to a dark, cool place.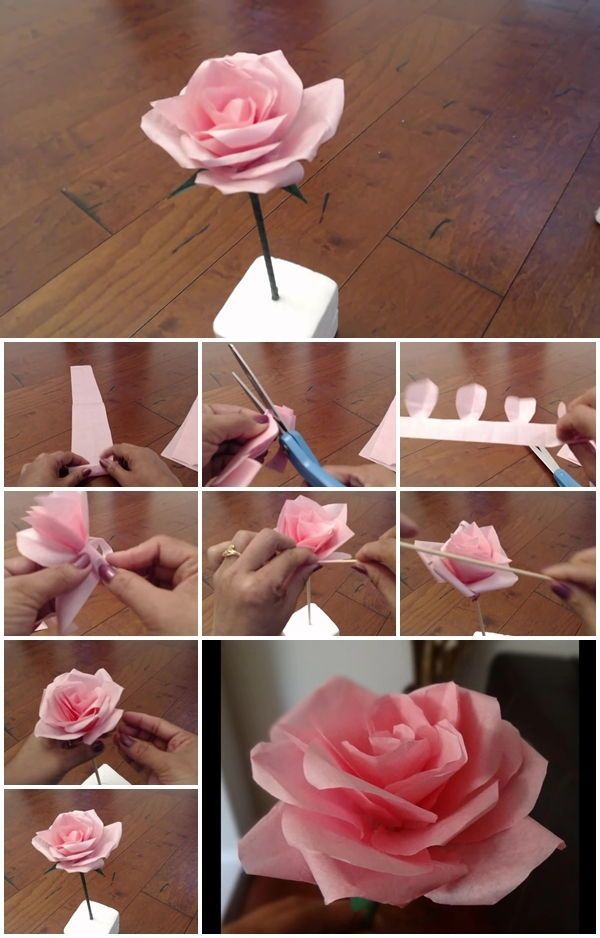
When the callus is formed, the cuttings are planted one at a time in pots in light nutrient soil (traditional rooting mixtures are suitable) so that only 1 bud is above the soil surface, watered and covered with a jar or bag. And now they need to be placed in a bright (but not under direct sunlight) and warm place - the temperature should be 23 - 25 ° C.
The burrito method has been shown to give a higher percentage of rooting. And even varieties of roses that are difficult to propagate by cuttings, with this method, give roots much more readily.
Popular Questions and Answers
We talked about the propagation of roses by cuttings with agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova.
Can all varieties of roses be propagated from cuttings?
Easily rooted cuttings of polyanthus (Border King, Paul Crampel, Holsiein), climbing (Bobbie James, Snow goose, Polka) and floribunda (Apricola, Edelweiss, Tequila) roses. Hybrid teas take root worse and give a weak root system.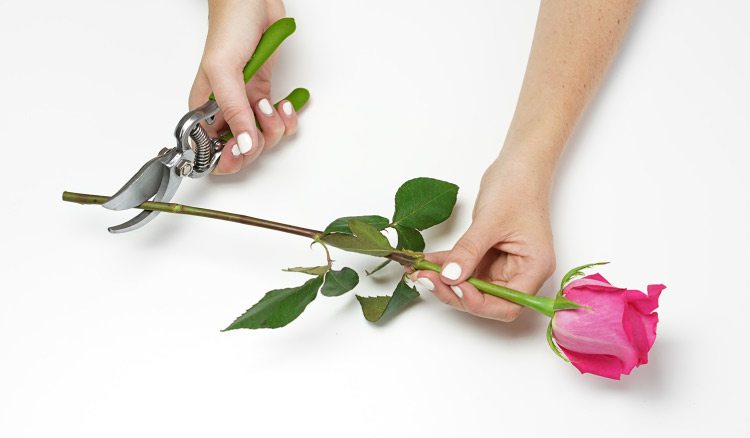 Roses with yellow flowers take root poorly (Papillon, Golden Tower, Yokey Dokey).
Roses with yellow flowers take root poorly (Papillon, Golden Tower, Yokey Dokey).
When to prune roses grown from cuttings?
They do not need to be trimmed in the first year of planting. The first pruning can be done next spring, cutting out dry and frozen branches. A cardinal pruning is best done from 3 years.
Which roses are better: grafted or own-rooted?
Both have their pros and cons. Own-rooted ones do not give wild shoots, however, their root systems are weaker and may suffer in a frosty snowless winter.
Roses grafted onto wild roses winter better, their roots are strong, but wild shoots constantly grow from the stock, which must be removed. And often the vaccine is short-lived.
Sources
- State catalog of pesticides and agrochemicals permitted for use on the territory of the Russian Federation as of July 6, 2021 // Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation https://mcx.gov.ru/ministry/departments/ departament-rastenievodstva-mekhanizatsii-khimizatsii-i-zashchity-rasteniy/industry-information/info-gosudarstvennaya-usluga-po-gosudarstvennoy-registratsii-pestitsidov-i-agrokhimikatov/
- Kudryavets D.











