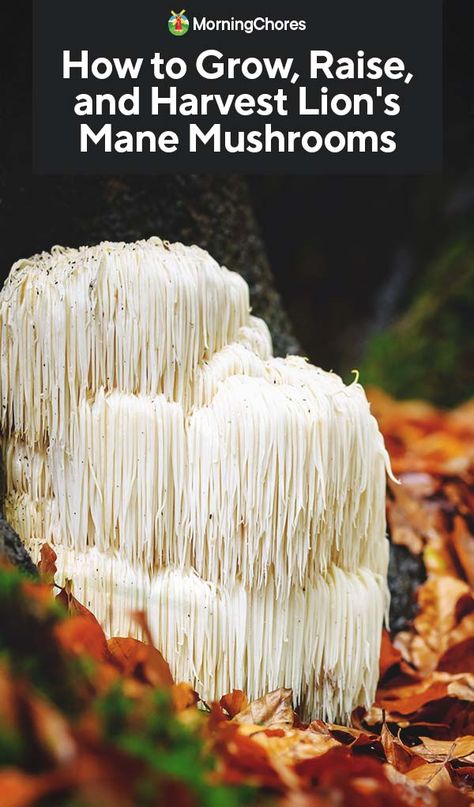
How do you grow mushrooms
How to Grow Mushrooms | BBC Gardeners World Magazine
Mushrooms are an unusual grow-your-own crop that's increasing in popularity. Mushrooms take more effort than most crops to grow, but mushroom growing kits offer easier growing methods, and give you the opportunity to grow ‘gourmet’ varieties such as oyster and shiitake, as well as the more usual button mushrooms.
Mushrooms can be grown indoors or outdoors in prepared beds or boxes, or on hardwood logs outdoors. Indoor growing in a controlled environment usually gives the best results. Outdoors, weather conditions have a strong influence on the success or failure of mushrooms grown in beds, although log-grown mushrooms tend to be more successful.
How to grow mushrooms
There's a number of ways to grow mushrooms. You can buy mushroom spawn to grow in beds or boxes filled with manure or compost. Alternatively choose a 'mushroom growing kit' that usually includes the spawn and growing media (such as wood shavings or straw). If you have access to recently chopped logs, you can buy wooden dowels or plugs that have been impregnated with spawn, which you tap into pre-drilled holes in the log.
Where to grow mushrooms
Shiitake mushrooms, Lentinula edodes growing kit in home kitchen counter. Getty Images
Mushrooms are best grown under-cover, where temperature and moisture can be controlled. A shed, garage, garden cold frame or cellar will work well – anywhere out of the sun where it's possible to give mushrooms their optimum growing temperature of around 15°C (the temperature shouldn’t go below 10°C or above 20°C). Outside, grow mushrooms in beds, on compost heaps, or in logs, again away from sunlight.
More like this
Growing mushrooms in beds or boxes
A rich, fertile, moisture-retentive growing medium is needed for mushrooms. The traditional material for growing mushrooms is horse manure and you can buy this from your local garden centre or nearby stables. If the manure is fresh, pile it into a heap and fork it over to mix well every couple of days for a fortnight until the heap has cooled and settled.
If the manure is fresh, pile it into a heap and fork it over to mix well every couple of days for a fortnight until the heap has cooled and settled.
Ensure the growing medium is moist. Spread the spawn across the surface and mix it 5-8cm deep, then cover with damp newspaper. After several weeks when white thread-like mycelium has appeared, take off the newspaper and cover the mycelium with a 2-3cm layer made up of 50 per cent garden soil or compost mixed with 50 per cent lime. Water as required to keep this evenly moist, using either a hose fitted with a spray attachment, or a watering can fitted with a fine rose. Mushrooms should start appearing from several weeks after sowing.
How to grow mushrooms on logs
How to grow mushrooms - mushroom log kit
Growing mushrooms on logs is easy as the logs need little attention once the dowels are inserted. However, you do need to supply and drill your own logs. These need to be hardwood, not conifers, and cut from healthy wood. Logs need to be freshly cut and the dowels implanted no more than six weeks after cutting. The best woods to use are oak, beech, hornbeam, chestnut, hazel, birch, maple or holly. Logs should have a diameter of 10-15cm and be 45-60cm long.
Logs need to be freshly cut and the dowels implanted no more than six weeks after cutting. The best woods to use are oak, beech, hornbeam, chestnut, hazel, birch, maple or holly. Logs should have a diameter of 10-15cm and be 45-60cm long.
Drill holes along the length of the log, 15cm apart and in rows 8cm apart. Insert the impregnated dowels fully into each hole. Some kits come with sealing wax, so seal each one with wax if directed to. Place the log in a shady spot, under trees or shrubs, with one end on the ground and the other propped up, and ensure it stays moist. Mushrooms can take up to 18 months to appear.
How to grow oyster mushrooms
Oyster mushrooms. Getty Images
Buy a pack of oyster mushroom spawn, along with some straw. Soak the straw in water overnight to make sure it's thoroughly damp, discarding excess water. Mix the mushroom spawn with the damp straw and then pack into a polythene bag such as a bin liner. Seal and leave for six weeks in a damp, sheltered spot between 20-25ºC, such as near your compost heap. As the straw breaks down, the mushroom spawn will grow into it, colonising the straw.
As the straw breaks down, the mushroom spawn will grow into it, colonising the straw.
Here, Monty Don demonstrates how to grow oyster mushrooms in straw:
After six weeks the oyster mushroom spores will have colonised the straw in the plastic bag. Move the bags into a light, warm and moist environment, such as your greenhouse. Cut slits in the bag so the oyster mushrooms can grow through them.
Monty Don checks on the progress of his oyster mushrooms:
After two weeks, check the bag to see if oyster mushrooms have developed. The straw should continue to produce mushrooms for several weeks.
Advice on buying mushrooms
Mushroom spawn and dowels are available by mail order from specialist mushroom suppliers and from some vegetable seed suppliers
Make sure you buy the right mushroom kit for your needs and space. Success depends on providing the perfect conditions for your mushrooms to grow
Where to buy mushrooms
- Gourmet mushrooms
- Suttons
- Thompson & Morgan
Looking for inspiration on how to use your crop? Our friends at olive have curated a delicious collection of mushroom recipes, including a creamy mushroom risotto.
How to Grow Mushrooms at Home
istockphoto.com
Nothing compares to the flavor of vegetables you’ve grown yourself. Unlike most vegetables, mushrooms actually grow well indoors because they thrive in cool, dark, and damp environments. Mushrooms can grow outside, of course, but inconsistent growing conditions may cause the process to take up to three years. The best place to grow them at home is in a basement or under a sink where they won’t be exposed to bright light. Even apartment dwellers with limited space can grow mushrooms.
Nearly any type of mushroom—including portobello, shiitake, button, oyster, cremini, and enoki—can be grown indoors, but each variety requires a different growing medium. This guide will explore how to grow white button mushrooms, which are actually the same species as cremini and portobello mushrooms.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
The process of cultivating mushrooms differs from that of most other vegetables. Before we describe the growing process, it’s important to go over a few key terms.
- While most plants are grown from seeds, mushrooms and other fungi are grown from spores.
- When mushroom spores mix with soil or another growing medium, a white, root-like substance called mycelium grows.
- A mushroom substrate is a substance that mycelium can grow on. For white button mushrooms, the recommended substrate is a mixture of compost and manure.
- Mushroom spawn is a substrate that already has mycelium growing on it.
Rather than buying their own mushroom spores, beginners may prefer to purchase a mushroom growing kit. These kits include a growing medium as well as mushroom spawn that has already been incubated. If using a kit, skip to Step 3.
Tools & Materials- Planting trays
- Seedling heat mat
- Mushroom spores
- Compost and manure mixture
- Potting soil
- Soil thermometer
- See full list «
- Sharp knife
STEP 1: Add the spores to the growing medium.

The first step is to set up the substrate, or growing medium. To do this, start with a planting tray that measures approximately 14 by 16 inches with a 6-inch depth. The tray can be made of wood, plastic, or metal. Fill the tray with a mixture of compost and manure, leaving an inch of space at the top of the tray. Then, spread the spores on top.
Advertisement
For best results, try to keep conditions sterile during this step so that other types of mold and fungi aren’t introduced to the substrate. Be sure to clean your hands thoroughly before working with the substrate, for example, and sterilize the knife and any other tools used.
Photo: istockphoto.com
STEP 2: Make sure the soil is moist all the time.
Mushrooms thrive in humid environments, so it’s essential to ensure that the soil remains moist throughout the growing process. To keep your growing medium moist, spray or mist it once or twice each day or cover it with damp towels.
RELATED: The Best Soil Moisture Meters for Your Gardens
STEP 3: Incubate the spores.

For the first three weeks, the soil temperature must be incubated at 70 degrees in order to promote growth. This can be done by keeping the trays in a warmer area of the house, or you can place the tray on a seedling heat mat. Choose a heating pad that has precise temperature controls and place it under the tray. Using a soil thermometer, make sure that the temperature of the soil never rises above 70 degrees because higher temperatures can kill the spores.
STEP 4: Lower the temperature to between 55 and 60 degrees.
Soon white, rootlike growths—or mycelium—will appear on top of the soil. When the entire tray is covered, it’s time to lower the temperature. While many vegetables have to be grown in the summer, growing mushrooms is a great winter project because they thrive in cooler temperatures. Lower the temperature of the soil to between 55 and 60 degrees (to do so, you will probably need to remove the heating pad from under the tray), and cover the mycelium with about an inch of potting soil.
After a few days at this temperature, tiny mushrooms known as primordia will begin to sprout.
Advertisement
Photo: istockphoto.com
STEP 5: Harvest the mushrooms and enjoy!
Button mushrooms should be fully grown after three or four weeks. You’ll know they’re ready to be harvested when the caps open fully and separate from the stems. If they’re allowed to grow longer, they will turn brown and be categorized as cremini mushrooms. In their final stage of growth, they become even larger portobello mushrooms. In order to harvest the mushrooms, use a sharp knife to cut the stem. Do not pull mushrooms from the soil because the surrounding growth can be damaged in the process.
Mushrooms will grow continuously for approximately six months if they are harvested daily because each mushroom will release its own spores. When growth ceases, more mushroom spawn can be added to the existing growing station. It’s important to note that fresh mushrooms won’t last for long after they’re cut, so they should be cooked or eaten within a couple of days.
Use this method to easily grow tasty mushrooms for topping pizza, turning into a creamy soup, or eating in salads.
RELATED: Keep Your Green Thumb Going Indoors with a Garden Tower
istockphoto.com
Advertisement
instructions for growing porcini mushrooms, champignons
Where to buy mushrooms for home growing
Many imagine that in order to grow a mushroom, you must first find it in the forest, dig it up, chop it, sow it in the garden. Now it's all much easier. In any garden store - whole showcases of packs of mushrooms with mycelium.
Simply buy a pack, on the back of which you will find step-by-step instructions on how to properly breed and care for this particular type of mushroom. nine0005
Growing conditions
Some mushrooms, such as oyster mushrooms and champignons, can be grown at home in a cellar or pantry. But it is much easier to breed them in the garden.
Growing mushrooms is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. First of all, you need to decide which ones you want - milk mushrooms, mushrooms, boletus, mushrooms or champignons. If your site has a piece of forest - that would be ideal. However, you need to understand which forest is deciduous or coniferous. It depends on which mycelium can take root there and form a fruiting body. But even if there is no forest nearby, it does not matter, each site has a garden. nine0005
First of all, you need to decide which ones you want - milk mushrooms, mushrooms, boletus, mushrooms or champignons. If your site has a piece of forest - that would be ideal. However, you need to understand which forest is deciduous or coniferous. It depends on which mycelium can take root there and form a fruiting body. But even if there is no forest nearby, it does not matter, each site has a garden. nine0005
Stumps can be used for growing mushrooms. For example, there was a stump left from some tree, do not uproot - here you can breed a whole family of mushrooms. Buy mycelium - and go! There are even winter mushrooms with which the stump must be "infected" in the fall. Don't worry, they won't die. On the contrary, in the spring, as soon as the sun warms the shadow, they will begin to grow. You can also choose a summer variety - you can’t go wrong either.
Planting mushrooms
Planting mushrooms depends on the type of mycelium.
On stumps. Tree mushrooms such as oyster mushrooms, autumn mushrooms, shiitake, nameko and tremella ice mushrooms are sold as mycelium-infested sticks. They are grown on logs of certain tree species (indicated in the instructions) with a diameter of 10 - 20 cm and a length of about 1 m, in which holes must be made at a distance of 20 cm from each other and deeper than the length of the stick. The sticks are driven in to the stop, and the hole itself is sealed with wooden plugs, wax or clay - so that bacteria and mold spores do not get inside. nine0005 Shiitake. Photo: pixabay.com
They are grown on logs of certain tree species (indicated in the instructions) with a diameter of 10 - 20 cm and a length of about 1 m, in which holes must be made at a distance of 20 cm from each other and deeper than the length of the stick. The sticks are driven in to the stop, and the hole itself is sealed with wooden plugs, wax or clay - so that bacteria and mold spores do not get inside. nine0005 Shiitake. Photo: pixabay.com
The logs are removed to a dark, damp room, which should be well ventilated, and left to grow mycelium. After 2 - 4 months you will see a white "mold" - this is the mycelium. But until it appears, the logs need to be watered 2-3 times a week for 10-15 minutes.
After the mycelium has appeared, the logs are dug in the garden or in the greenhouse at an angle. And after about 1 - 2 weeks, the rudiments of fruiting bodies will appear on them.
There are other options for growing tree mushrooms. For example, oyster mushroom mycelium is on sale on a grain substrate (1), which is usually used for growing mushrooms in bags - they are filled with any plant material: leaves, sawdust, straw, buckwheat husks and even cardboard. And shiitake mushroom can be grown in pine sawdust (2). nine0005
And shiitake mushroom can be grown in pine sawdust (2). nine0005
In soil. Ground fungi, eg porcini, boletus, boletus, boletus, milk mushrooms are planted in the soil. And their mycelium is sold in the form of grains of cereals infected with mycelium. Each type of mushroom requires its own tree if they grow in symbiosis. What trees are needed - indicated in the instructions on the package.
To breed such mushrooms, make 3 holes around the tree with a diameter of 10 - 15 cm and a depth of 20 cm. They are half covered with compost, pieces of mycelium are placed on it, and the top is also covered with compost and lightly tamped. The holes are covered with moss, dry leaves and branches, after which the plantings are watered - in 1 bucket of water for each hole. In order for such a mycelium to take root well, it is useful to water it from time to time with a solution of sugar - 2 teaspoons per 10 liters of water. nine0005
“Be prepared for the fact that if you follow all the instructions, you will not get a harvest in the first year,” warns gardening expert Tatyana Kudryashova. - This will happen either next year or two later. Such a capricious mushroom! It is better to sow mushrooms in early spring, as soon as the snow has melted and the earth has warmed up. Until it gets hot, it's bad for survival. In the spring, there is a lot of moisture, it rains in sufficient quantities, and the sun is not so hot. It is also important that you need to water the mycelium not once a week, as many are used to, but as often as possible. nine0005
- This will happen either next year or two later. Such a capricious mushroom! It is better to sow mushrooms in early spring, as soon as the snow has melted and the earth has warmed up. Until it gets hot, it's bad for survival. In the spring, there is a lot of moisture, it rains in sufficient quantities, and the sun is not so hot. It is also important that you need to water the mycelium not once a week, as many are used to, but as often as possible. nine0005
Mushroom growth also depends on temperature. The lower, the longer the formation of mycelium.
White mushrooms
White mushroom. Photo: pixabay.comWhite mushrooms, or mushrooms, are more difficult to breed. The first step is to dig a groove deep and wide on the spade bayonet.
- Then dig a strip on the right and left, divide it into even squares and turn the turf over, - Tatyana Kudryashova shares her advice . - A humus bedding for a boletus is required, otherwise it will not survive. When the mycelium takes root and fruiting bodies of mushrooms appear, watering and care can be completely stopped. In this way it is possible to breed porcini mushrooms, boletus, boletus, boletus in the area. Mushrooms require good compost or semi-decomposed straw horse manure (3). These mushrooms are quite whimsical: they do not grow on the ground or in the open sun, they need shade, certain moisture and temperature conditions, so a place for them must be found somewhere in a shady corner of the garden. nine0005 Mushroom sprouts look like white mold, which gradually curls up into small knots - these are future mushrooms. Then a tiny stem and a hat the size of a pinhead appear, and then a mushroom. The yield of mushrooms grown from purchased mycelium can be quite solid. But if you want to increase your mushroom harvest, bring land from the forest. You just need to find a place with the mycelium of interest to us, for example, white or oily, carefully remove the soil 15 cm thick and bring it to your site. And on the site, remove the sod of exactly the same size and put forest soil on this place. And already on it sow the purchased mycelium. By the way, you don't have to buy mycelium. Bring an old or wormy mushroom from the forest, chop its hat, mix it with wood dust and scatter it under the trees. And after a while, mushrooms will appear in this place. nine0005 We talked about growing mushrooms with agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova - she shared details about growing different types of mushrooms. Mycelium of 2 types of porcini mushrooms can be bought at garden centers. White mushroom oak will grow under oak, linden and beech or hornbeam in the southern regions. White fungus pine - under the pines. Moreover, the trees must be young - no older than 10 years. nine0005 Oaks and birches are suitable for oaks, and beeches in the south. The optimal age of trees for breeding this fungus is 6 years. Chanterelles grow best under pine trees, where they produce the highest yields. White truffle, namely its mycelium, is most often sold in garden centers, grows well under young oaks and hazel. And in the southern regions - under the beeches. nine0005 There are various types of oyster mushrooms on sale, and everyone has their own preferences: Autumn and summer mushrooms can be successfully grown on logs of oak, birch, alder, poplar, ash, maple, beech, hornbeam and chestnut. nine0005 Sources Greetings. Content  Pieces of mycelium are laid on it and sprinkled with humus, covered with removed turf and carefully spilled with water. nine0005
Pieces of mycelium are laid on it and sprinkled with humus, covered with removed turf and carefully spilled with water. nine0005 Mushrooms
How to increase the yield of mushrooms in the garden
 For example, oil under one tree can be collected 6 - 17 pieces, boletus and boletus - 5 - 15 pieces, porcini mushrooms - 2 - 5 kg, shiitake - up to 4 kg per log, oyster mushrooms - 20 - 50% of the weight of the log. nine0005 Autumn mushroom. Photo: pixabay.com
For example, oil under one tree can be collected 6 - 17 pieces, boletus and boletus - 5 - 15 pieces, porcini mushrooms - 2 - 5 kg, shiitake - up to 4 kg per log, oyster mushrooms - 20 - 50% of the weight of the log. nine0005 Autumn mushroom. Photo: pixabay.com Popular questions and answers

Under which trees can porcini mushrooms be grown?
Under which trees can oak be grown?
Under which trees can chanterelles be grown?
Under which trees can truffles be grown?
On what tree species can oyster mushrooms be grown?
- ordinary, Indian, pink - birch, poplar, willow, alder, aspen, oak, maple, chestnut, beech, hornbeam;
- lemon and Colombian - birch, willow, poplar, maple, mountain ash, fruit trees, beech.
On what tree species can mushrooms be grown?
https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-vyraschivaniya-mitseliya-gribov-plearotus-ostreatus
https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/iskusstvennoe-vyraschivanie-griba-shiitake-lentinula-edodes-berk-pegler-na-hvoynyh-opilkah Growing mushrooms in the country and in the garden: ways for beginners
 Today I’ll talk about proven methods: how to grow mushrooms in the country, in different ways, but I’ll emphasize the methods I’ve tested. I will share with you what mushrooms can be grown in the country in the garden. I will tell you when to plant mushrooms in the country and in what ways. And following the recommendations for planting and care, even an inexperienced gardener can grow mushrooms. nine0005
Today I’ll talk about proven methods: how to grow mushrooms in the country, in different ways, but I’ll emphasize the methods I’ve tested. I will share with you what mushrooms can be grown in the country in the garden. I will tell you when to plant mushrooms in the country and in what ways. And following the recommendations for planting and care, even an inexperienced gardener can grow mushrooms. nine0005
What kind of mushrooms can be grown in the country
It would be a misconception that only champignons and oyster mushrooms are suitable for garden cultivation. On the site you can successfully grow a variety of mushrooms:
On the site you can successfully grow a variety of mushrooms:
- Ceps. In taste, these forest dwellers surpass all their brethren. The number of ways to prepare them is also great: stewing, frying, pickling, salting, drying. They are bred with mycelium, mycelium and special "mushroom seedlings" (spores).
- Aspen mushrooms. These forest mushrooms live in the same way as white mushrooms, only under symbiont trees. You can transfer the mycelium to the garden, breed "seedlings" or buy mycelium. nine0109
- Boletus, boletus, honey mushrooms. You can breed in the same ways - through mycelium, spores (soaking "seedlings") and forest mycelium.
- Morels. Spring mushrooms that will delight you with an early harvest.
- Oyster mushrooms. Cultivated mushrooms whose mycelium is very easy to find commercially.
Having decided on the desired mushrooms, we move on to other important issues.
When to plant mushrooms in the country
There are no clear terms for planting mycelium and mycelium - I breed them in summer and early autumn, from May to October.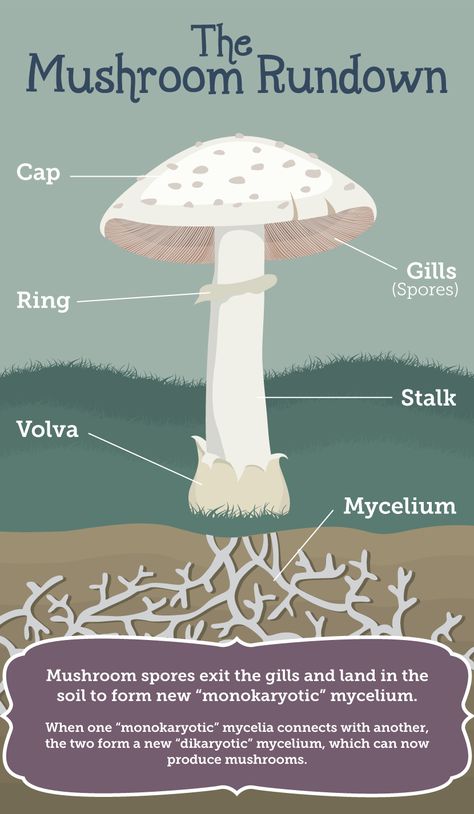 You will not be able to find mycelium in the forest at other times of the year. It is important to place it in the soil already warmed by the sun (at least up to 15 C). Landing "before winter" is not suitable - a young mycelium will not withstand the cold. nine0005
You will not be able to find mycelium in the forest at other times of the year. It is important to place it in the soil already warmed by the sun (at least up to 15 C). Landing "before winter" is not suitable - a young mycelium will not withstand the cold. nine0005
Do not grow mushrooms on a sunny, hot day, in dry weeks - your work will be in vain. I "root" the mycelium after a good rain - the earth should be well moistened, but not swampy. I choose a cool, cloudy and windless day. If the weather is sunny, I plan to land in the evening - after sunset.
Where to plant mushrooms in the country
When choosing a place on the site for a particular variety, I always study the conditions for its growth in natural conditions. If it grows under a birch, I make a plantation under a tree. If in the forest it prefers light partial shade, and in the garden I am looking for the same area. nine0005
I'll tell you about the general requirements for the place of growth:
- They prefer light, airy and fertile soil - it is best to get a real forest substrate for them, renew it as it is depleted.

- Symbiont mushrooms are planted only under those plants with which they "collaborate".
- Mycelium, mycelium are placed as close as possible to the roots of the symbiont - so that it quickly wraps around the root system, from which it will receive nutrition. The recommended distance from the tree trunk is at least 50 cm.
- Forest mushrooms don't like fruit trees. Therefore, if you hook them up to an apple tree or a pear, nothing will work.
The best option is to imitate a forest clearing in the garden. To do this, the top layer of garden soil is cut off under the trees by about 30 cm. It is replaced with a forest substrate. Such a soil mixture does not need to be fertilized - only moistened during dry periods, systematically updated. I also do not forget to collect natural mulch in the forest in the spring - foliage that has rotted over the winter. Its layer will reliably protect the "plot" from drying out. nine0005
How to get seed material
Mushrooms are a bit easier than growing garden plants - I got "seed" in three different ways:
- Spores.
 Mushrooms reproduce by means of spores - they can be called the distant ancestors of the seeds of flowering plants. The spores are located in the cap sponge - it is impossible to collect them manually, they are so microscopic. Therefore, I turn the caps of the necessary mushroom into gruel - this is how a kind of “seedling” is obtained.
Mushrooms reproduce by means of spores - they can be called the distant ancestors of the seeds of flowering plants. The spores are located in the cap sponge - it is impossible to collect them manually, they are so microscopic. Therefore, I turn the caps of the necessary mushroom into gruel - this is how a kind of “seedling” is obtained. - Mushroom picker. One of the most difficult material to obtain is that I went to the forest, looked for the fruiting bodies of the mushrooms I needed, dug them out along with the mycelium. But, as practice has shown, forest dwellers are easier to take root in the garden, if you use this method.
- Mycelium. The easiest, but already paid way. The mycelium of the variety of mushrooms you need can be purchased at a large garden center, ordered online from reliable suppliers.
The choice of one or the other "seed" depends on the type of mushrooms that you want to breed. nine0005 cultivation of champignons from mycelium
Soil preparation
Properly prepared soil mixture becomes the key to successful engraftment of "seed material".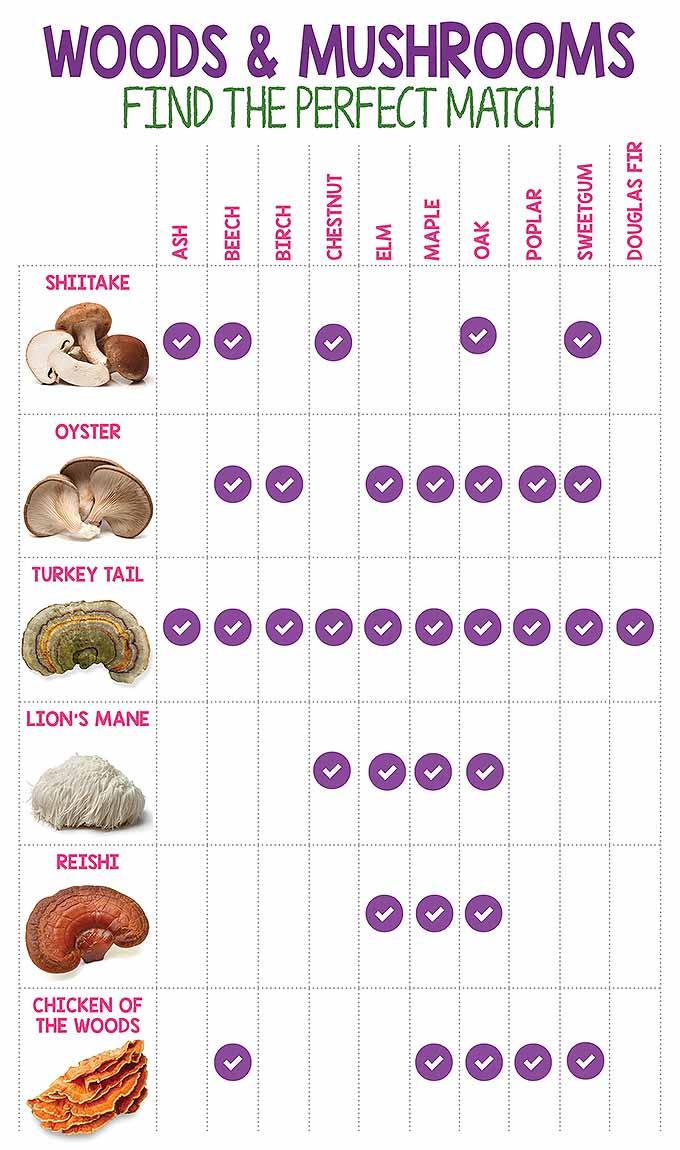 I will tell you about the most suitable substrates for mushrooms.
I will tell you about the most suitable substrates for mushrooms.
Straw
This material can be used both as a mushroom substrate and as a mulch. But mushrooms will not grow in straw alone - it must be mixed either with forest litter, or with rotten organic residues collected in the garden.
A fertile substrate for champignons is also prepared on the basis of straw:
- 50 kg of last year's manure - horse, cow;
- 15-20 kg of straw;
- 12 kg plaster;
- 12 kg lime.
I put all the components in a pile - I also add organic waste to it. It is important to properly compact the mass, spill it with water and wrap it in a film. A pile matures for 15-20 days. I judge its readiness by the strong smell of ammonia.
Logs
I'll tell you how I grow mushrooms on a log:
- I take only healthy wood - I soak it in water for 2-3 days. nine0109
- Then I move it to a warm and dry place - either in a heated garage or on a tarp in the sun.
 I'm waiting for the excess moisture to evaporate.
I'm waiting for the excess moisture to evaporate. - I cut small holes in a checkerboard pattern according to the scheme 10x10 cm - 4 cm deep, 0.5-1 cm in diameter.
- I put seed in them, wrap the log in a film. I make several holes in polyethylene for air access.
- I transfer it to a warm (10-20 C) and humid room: for 2-3 months the log will turn into mycelium - a thin white cobweb. nine0109
- In a place protected from the wind, in partial shade, I make a hole for a log - I bury it vertically for 30-50% of the length. For disinfection, I sprinkle the soil around with ashes. I "plant" the log as soon as the air temperature rises to 15-25 C.
- In dry weather, I water the ground around the log every 2-3 weeks.
I don’t dig out a log with mycelium in autumn - I warm it for the winter with compost and rotten leaves.
growing oyster mushrooms on stumpsSawdust
A popular type of potting mix for mushrooms is based on sawdust. You can mix them in equal proportions with compost, garden soil, rotted plant residues. Be sure to treat the mass with disinfectant suspensions - potassium permanganate, copper sulfate, boric acid. It will not be superfluous to shed it with a solution of a growth stimulator. nine0005
You can mix them in equal proportions with compost, garden soil, rotted plant residues. Be sure to treat the mass with disinfectant suspensions - potassium permanganate, copper sulfate, boric acid. It will not be superfluous to shed it with a solution of a growth stimulator. nine0005
Other substrates
I consider forest floor or its imitation to be the best option for mushrooms:
- dead leaves, needles;
- wood dust;
- rotten moss.
Some of the elements can be replaced with last year's garden compost. Wood ash will become a fertilizer and disinfectant for the substrate.
Features of growing some types of mushrooms in the country
Keep in mind that forest mushrooms are symbionts by nature. For life, development and formation of fruiting bodies, they need a continuous exchange of substances with the bodies of higher plants. In most cases - with their roots. Each forest mushroom has its own symbiont. The boletus has birch, the white fungus has coniferous trees, and the boletus has aspen.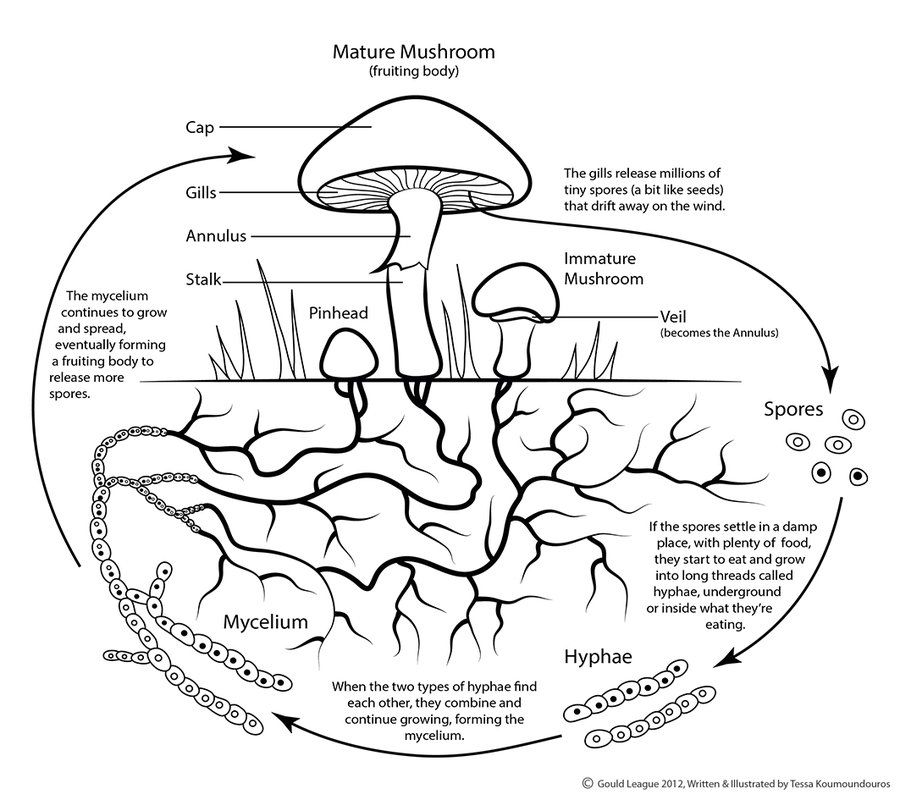 nine0005
nine0005
Accordingly, your site should have a tree that will allow the fungus to grow. Without this condition, the mycelium and mycelium will die without food. Do not think that fungi will damage the trees - they are not parasites. Symbiotic coexistence is equally beneficial for both the plant and the fungi.
Let me tell you about the peculiarities of growing some mushrooms:
- White. They take root next to a pine - it must be a developed tree at least 30 years old. The best type of breeding is through the forest mycelium. A big mistake is to plant them next to fruit trees. nine0109
- Aspen mushrooms. If you decide to engage in spore breeding, then you should cut off the flesh under the hat from the overripe one. Soak the mass in dechlorinated warm water for a day, and then bury it in the ground according to my advice.
- Oil mushrooms. If most forest mushrooms need a living, healthy symbiont tree, then these rotten, almost collapsed stumps are needed for development.
 Having uprooted such “wealth” in the forest, you can plant delicious garden mushrooms on it with great success. Another option is to carefully cut the bark sprinkled with mushrooms from the stump. Here it is more convenient to operate with a saw, a hacksaw. The "Mushroom Kingdom" can be planted in the shade of trees, overlaid with mosses, and then provide mushrooms with the necessary nutrition - wood dust. nine0109
Having uprooted such “wealth” in the forest, you can plant delicious garden mushrooms on it with great success. Another option is to carefully cut the bark sprinkled with mushrooms from the stump. Here it is more convenient to operate with a saw, a hacksaw. The "Mushroom Kingdom" can be planted in the shade of trees, overlaid with mosses, and then provide mushrooms with the necessary nutrition - wood dust. nine0109 - Morels. Spring mushrooms ready for April-May. At this time, you need to go to the forest to collect fruiting bodies and mycelium. Morels do not like the neighborhood of fruit trees, especially apple trees.
- Mushrooms. These are those mushrooms that do not require the presence of symbiont trees on the site. On the contrary, they tolerate the neighborhood with any higher plants, including fruit, fruit. They are grown on a special substrate with straw. They love champignons and manure, compost heaps, rich in organic matter. Prefer good moisture and shade. nine0109
- Oyster mushrooms, shiitake.
 Grow on trees, including dead ones. Therefore, you can grow them on rotten stumps, logs in the way that I described above. Oyster mushrooms are the most productive of cultivated mushrooms. The mushroom picker is not going through a frosty winter - you can harvest from one plantation for several years.
Grow on trees, including dead ones. Therefore, you can grow them on rotten stumps, logs in the way that I described above. Oyster mushrooms are the most productive of cultivated mushrooms. The mushroom picker is not going through a frosty winter - you can harvest from one plantation for several years.
I advise you to start with cultivated mushrooms, whose mycelium, along with detailed growing instructions, you can find in garden centers. Once this is obtained, you can start experimenting with forest ones. nine0005
Ways of growing mushrooms in the country
I will tell you about the most common methods of relocation to your site.
Breeding by spores
I prefer to use this method as a backup, belay. For example, if I bring a mycelium from the forest, I do not forget to “sow” spores in the neighborhood. The method of preparing "mushroom seedlings" is very simple:
- I separate the mushroom caps, finely chop them with a knife or pass them through a meat grinder.

- I fill it with dechlorinated water (preferably rain water), I insist for a day. nine0109
- About 0.5 m from the tree trunk I dig a hole 25-30 cm deep. Best of all is the one under which they grew in their natural environment.
- I pour the “seedlings” into a hole, cover it with a forest substrate - rotten leaves, wood dust.
- The first 1-2 weeks I don't touch the "landing" at all. Then I begin to water the breeding site with water by sprinkling.
This breeding method is waste-free. If after a trip to the forest you still have trimmings of spoiled mushroom caps, do not rush to throw them away. Prepare "mushroom seedlings" according to my recipe. If it does not take root, there is nothing to worry about - you will introduce useful fertilizer into the soil. nine0005
Mushroom seedlings are best suited for overripe caps, as they will contain ready-made spores. It's okay if they are wormy - when soaked, the pests will emerge. It is best to place the mushroom mass in heated and dechlorinated water.
A little secret: you need to start a process similar to the process of fermentation in the stomach of a forest animal that feeds on mushrooms - it is he who “revives” the spores. To do this, I add a couple of tablespoons of sugar, dry yeast or kvass sourdough - I start fermentation. During soaking, do not forget to stir the mass with a spoon. nine0005
Growing with mycelium
I have already written that breeding with mycelium is the most difficult, time-consuming, but also the most reliable way. I'll tell you step by step how I do it:
- 1-2 weeks before picking the mycelium I prepare the substrate - I mix last year's compost, rotted leaves and dust from the old stump in approximately equal parts.
- I always take a bag filled with this soil mixture, a bottle of water and a bayonet-shovel into the forest (I don’t forget to sharpen it well). nine0109
- Looking for the type of fruit bodies I need. If you are not an experienced mushroom picker, then first study the guide, find the necessary images on the Internet so as not to relocate inedible, or even poisonous mushrooms to your site.

- With a bayonet-shovel I remove the forest substrate in a diameter of 10-15 cm from the fruiting body until I reach the mycelium resembling a cobweb. It often intertwines with the roots of plants, so they have to be carefully cut (for this I sharpen the shovel). nine0109
- I take the mycelium together with a large clod of native substrate, put it in a bag with prepared soil mixture. It is important that it is poured in a deep layer.
- Moisten the mass a little with bottled water.
- Then my task is to bring the mycelium to the garden as soon as possible.
Mushrooms love the same substrates as in their native forest. In most cases - light, breathable, drained. But not waterlogged, caked, heavy. Having decided on the landing site, I act as follows:
- At a distance of 40-60 from the trunk of the symbiont tree I remove the top layer of soil (25-30 cm).
- I fill the bottom of the recess with a mixture of humus, plant residues, wood dust.

- Carefully place the mycelium on this mat.
- I sprinkle with the same layer of rotted leaves, dust and humus.
- Lightly moisten the landing site.
If the mycelium has taken root, then you will notice the first signs of life in 2-3 weeks.
Mycelium cultivation in the garden
This method is the most professional of those listed. It should be noted its simplicity, as well as the high probability of mycelium engraftment. The latter is divided into two varieties:
- Grain. For planting, the mass is mixed with compost or garden substrate.
- Compost. Pour in water, stir until the consistency of sour cream, and then planted.
I recommend proceeding with the purchase according to the following instructions:
- Buy mycelium on a specialized website or in a gardening store. Carefully study the annotation to it - whether the "seed material" is suitable for your region, the type of soil on the site.
 Here I prefer not to save - I buy a little more mycelium than I need. nine0109
Here I prefer not to save - I buy a little more mycelium than I need. nine0109 - I store the mass in the refrigerator until planting. Before the “sowing” itself, I test its viability - I transfer it to a warm place for 3-4 days. If it is active, it begins to increase, smell like mushrooms. If not, it will not show signs of life, it will envelop with a sour smell.
- I choose a place for planting - in partial shade, on the roots of trees. I remove the upper layer of the substrate by 30-40 cm. At the same time, I retreat from the tree trunk by about half a meter. The area of the recess depends on the volume of the purchased mycelium. nine0109
- At the bottom of the hole I lay a mixture of humus, tree dust, sawdust and ash (15 cm). Then - a thin layer of fertile black soil.
- I lay the mycelium on the bedding, distribute it, smooth it with my hands. For better engraftment, it even needs to be tamped a little into the ground.
- I cover with the same soil mixture, with a layer of rotten leaves, lightly water.

Mycelium does not need further special care - only watering (by sprinkling) every 2-3 weeks. If the summer is rainy, then additional water procedures are not required. nine0005
Caring for mushrooms in the garden
They do not require the same care as cultivated flowering plants. Our task is to bring the conditions of their existence in the garden as close as possible to natural, forest ones. I do it in the following ways:
- Watering. Since childhood, we know the saying "Growed up like mushrooms after the rain." But this does not mean that mushrooms love waterlogged soil. They feel comfortable only in a moderately moist substrate - so we never look for them in a swampy forest. I water them by sprinkling only when the soil mixture dries out. I try to use natural water - melt, rain, well. nine0109
- Fertilizers. Under natural conditions, mushrooms have enough nutrition from the roots of their symbionts. In the garden, they will not be harmed by periodic feeding with compost, ash, organic residues - I just scatter dry fertilizers over the mushroom plantation, and then water it.

- Growth promoters. Mushrooms respond well to humates, "Epin", "Zircon". Therefore, in the spring, in order to awaken the mycelium, I water it with solutions of growth activators.
In order to save the mycelium for the next year, do not forget to insulate it in the fall with a “cap” of decomposed leaves or plant remains. If winter is expected to be cold, I additionally cover it with a piece of slate, linoleum, roofing material. In the winter months, I insulate with a snow “pillow”. nine0005
If the mycelium survives the winter, you won't need to buy mycelium or breed "seedlings" - the crop will "keep pace" for several years in a row. The mushroom picker is a living organism: in comfortable conditions, it grows, gradually being replaced by a younger one.
What difficulties may arise when growing mushrooms in the country
Mushrooms, like plants, suffer from diseases and pests. Moreover, under unnatural conditions, gardens become more susceptible to viruses and bacteria. nine0005
nine0005
Pest control
In addition to the well-known worms that spoil the fruit bodies of mushrooms, there are other enemies:
- Mushroom mosquito. This pest gnaws passages in the fruiting body of the fungus, laying larvae there. To protect my plantations from it, I periodically treat them with insecticides. Another way to fight is to buy a small mosquito net, cover the mushroom "beds" with it. If the insect has already struck the fruiting body, it remains only to destroy it.
- Mushroom mite. May appear on a mushroom plantation when fertilized with fresh manure. The pest gnaws passages and tunnels in the fruiting body, making it inedible. Such a spoiled crop can only be thrown away. Prevention of ticks - treatment of the soil mixture with acaricides, calcination of the earth at high temperatures.
If you use acaricides, insecticides, carefully read the instructions for the preparations. Not everything that is used for cultivated plants is applicable to fungi. Be sure to consult with the seller about the possibility of using the product, the required waiting period. nine0005 fungus mosquito
Be sure to consult with the seller about the possibility of using the product, the required waiting period. nine0005 fungus mosquito
Disease prevention
Here are the common fungal diseases:
- Carmine mold. One of the most common fungal diseases. First, individual white threads appear on the hat, and then a whole edge. With the development of the disease, it changes color from snow-white to cherry. There is no cure for the disease - the fruiting bodies are cut off, the mycelium is dug up. The place of its sowing is treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and potassium permanganate. To prevent this problem from damaging the next crop, carefully follow the watering schedule, do not overfeed the mushrooms with nitrogen-containing substances. nine0109
- Mycogonosis (white rot). The consequence of improper watering, inappropriate temperature conditions. The infected mushrooms themselves cannot be saved - the fruiting bodies are cut off, and the place of the mycelium is shed with a strong (raspberry) manganese solution.
 If you grew mushrooms indoors, do not enter it without a respirator - inhalation of spores is dangerous for humans. Be sure to treat the barn, cellar or garage with chemicals from mycogonosis.
If you grew mushrooms indoors, do not enter it without a respirator - inhalation of spores is dangerous for humans. Be sure to treat the barn, cellar or garage with chemicals from mycogonosis. - Rust spot. The result of an incorrect humidification schedule. If you notice strange rust spots on the fruiting bodies, remove them as soon as possible. Spill the mushroom plantation with a disinfectant solution of potassium permanganate, treat uninfected fruiting bodies with this suspension - both hats and legs. nine0109
- False truffle disease. The mycelium of cultivated mushrooms is affected by the mycelium of the false truffle. Such a parasitic neighborhood gradually leads to its death. It is impossible to save the mycelium - it remains only to destroy it. Therefore, before sowing, I always treat the soil mixture - I spill it with iodine (a few drops) or manganese (a few crystals) solution. Another disinfection option is a 1% solution of copper sulfate. Chernozem can also be calcined in the oven or microwave.

Learn more










