How deep does a garden bed need to be
How Deep Should A Raised Garden Bed Be? – Vego Garden
When deciding on a raised garden bed, one of the major factors is the depth requirements of the raised garden bed. If you’re placing your raised bed on a patio or a terrain where the soil underneath is not conducive to growth, then it is important to grow your plants within the parameters of the bed itself. A raised bed should be able to blend in well with its surroundings as well as adequately support the roots of your plants. The required soil depth depends on the types of plants grown, the soil conditions, and desired aesthetic. Other important considerations include the shape, size, and material chosen for the raised garden bed. Since there are a dazzling array of designs available worldwide, choosing one can be a tough decision to make.
However, the large variety of patterns available guarantees that there is a match for every type of landscape, budget and style. A raised bed can either be informal or formal, depending on your preference and garden situation. We recommend displaying vegetable gardens in modern, industrial metal beds, which can prove to be an attractive focal point of your garden, and significantly brighten up dull spaces or outdoor dining areas. It is important to keep in mind that the size of the bed should be proportional to the space around it. If you have limited space, it is best to buy modular raised garden kits, which will allow you to customize your beds based on your available space. This article examines the soil depth requirements for various types of yards and plants.
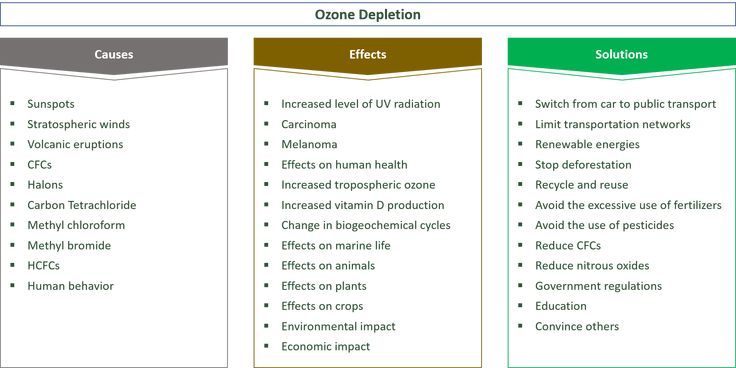
Drainage: Whether it be an irregularly-shaped perennial border garden that sits behind a dry-stone wall, or a metal raised bed in a vegetable garden, one should always consider the depth of the raised bed carefully. A raised bed does not always require a significant depth for it to be effective. They should have at least 8 inches of soil depth to accommodate the root systems of plants, because the majority of plant roots require 6 – 8 inches of soil for healthy root growth. A depth of 8 – 12 inches will suffice for most gardening situations.
A depth of 8 – 12 inches will suffice for most gardening situations.
Because of the excellent drainage properties of raised beds, it is possible to grow an abundance of vegetables in a limited amount of space. In cases where drainage is an issue, or if the plants that you are planning to grow prefer an environment with drier soil, then the depth of your raised garden bed can be taller, which can then be filled up with a porous growing medium.
Material: The material you use for a particular raised bed should be durable, attractive and stable. It is important to consider the material of your garden bed, which determines how well it blends in with the landscape. The sides of the bed lend structural support to the and help contain the soil in a particular space. The sides of raised garden beds can be metal panels, wood, or brick and stone. While it is important to consider the depth of your raised garden beds when browsing for raised garden bed designs, it is also important to consider the material of your garden bed.
Traditional metal panels, while easy to install, can rust over time, diminishing its attractiveness and usefulness. Wood will rot in as little as one season. Stone and concrete blocks can be expensive to install. Also, many gardeners do not want the hassle of buying raw material and assembling them for a DIY raised garden bed project. We recommend Vego Garden beds for an easy solution. Vego raised garden beds are made of a specialized rust and corrosion resistant metal and lend a clean, modern aesthetic to your garden. Our kits are easy to assemble, and complete with heavy duty rubber edging along the top to ensure a safe and fun experience.
Double Digging: Some gardeners choose to dig below the ground using their shovel to create more space for their roots, especially if they have a crowded or shallow garden bed. This process, known as double digging, can be time consuming and arduous. Vego Garden beds are tall enough that you don’t have to dig into the ground. You can simply place your raised bed anywhere in your yard after clearing the ground of debris.
Gardeners should slightly overfill their gardening beds, because the soil will compact over time with watering. As a tip, you should add an extra 2 inches of soil over your garden bed, and water the soil to see how much it compresses.
Vegetable Beds: On the other hand, when it comes to vegetable beds, the bed must be approximately 12 to 18 inches deep to ensure adequate depth for the roots of your plants. This is especially important if your raised bed is placed on cement or the patio, which will inhibit roots from growing deeper into the ground. Below are the root depth requirements of a few common garden plants. Since our garden beds are 17″ and 32″ deep, they are deep enough to cultivate a medley of vegetables, including those with deep root systems. A deeper bed also allows for more moisture retention, leading to less watering and chance of drying out.
The following plants have 12 - 18″ roots
- Garlic, onions, chives
- Lettuce, brussels sprouts, spinach
- Corn, cabbage, radishes
- Strawberries
The following plants have 18 - 24″ roots
- Beans, peas
- Cantaloupes, squash, eggplants
- Carrots, turnips, beets
- Potatoes
Below are plants with deeper systems of 24 - 36″ roots
- Artichokes, asparagus
- Parsnips, rhubarb
- Sweet potatoes, pumpkins
- Watermelons
When planning out the components of your raised garden bed, it is important to orient your crops so that taller plants don’t block shorter plants from receiving sunlight. Beds should face South horizontally, which optimizes sun exposure across the bed and prevents neighboring plants from shading each other as the sun moves from East to West. If you are growing a variety of plants, you can orient your bed vertically (North to South), positioning the taller plants in the back to prevent them from shading shorter plants. Do not situate your garden bed in windy locations or near wet and marshy areas.
Beds should face South horizontally, which optimizes sun exposure across the bed and prevents neighboring plants from shading each other as the sun moves from East to West. If you are growing a variety of plants, you can orient your bed vertically (North to South), positioning the taller plants in the back to prevent them from shading shorter plants. Do not situate your garden bed in windy locations or near wet and marshy areas.
It is important to know the height of each crop at maturity in order to plan out your planting arrangements. To illustrate, shorter plants such as lettuce and radishes should be planted on the south side, while the tallest plants should be planted on the northern side of the area. If you have a trellis, it is important to keep it near the rear wall, as those plants can block out a large amount of light. Below are the heights of some popular vegetables at maturity:
| Vegetable | Size at Maturity | Vegetable | Size at Maturity |
| Artichokes | 4' - 5' | Leeks | 12" – 24" |
| Arugula | 8" - 10" | Lettuce | 6" – 12" |
| Garlic | 12" – 24" | Onions | 8" – 24" |
| Corn | 4' – 8' | Peas | 2' – 6' |
| Beans (lima) | 24" – 36" | Watermelon | 12" – 36" |
| Beans (pole) | 8' – 12' | Parsnips | 6" – 18" |
| Tomatoes | 2' – 8' | Potatoes | 12" – 30" |
| Cabbage | 12" – 18" | Turnips | 6" – 12" |
If you experience mobility issues, back strain, or simply dislike bending over, a taller raised garden bed will improve your gardening experience. Our extra tall 32″ garden bed kits significantly reduce back strain when you are tending or harvesting your garden. Whether you are a more experienced gardener or a beginner, we definitely recommend you invest in a raised garden bed to reduce the toll that straining your back can have on your health.
Our extra tall 32″ garden bed kits significantly reduce back strain when you are tending or harvesting your garden. Whether you are a more experienced gardener or a beginner, we definitely recommend you invest in a raised garden bed to reduce the toll that straining your back can have on your health.
32" Extra Tall 9 In 1 Modular Metal Raised Garden Bed Kit
$299.95 $269.95
Our extra tall 32" height eliminates bending and strain on your back when you tend to your garden, as well as creates plenty of space for healthy roots. …
About Vego
At Vego Garden, our goal is to redefine Raised Garden Beds. The company was founded with the goal of launching a modular metal garden bed system with a 20+ year life expectancy, utilizing eco- friendly metal materials instead of cutting down trees. We emphasize innovative design and high quality with our products. The name vego carries the spirit of DIY modular raised beds suitable for growing vegetables.
Read More >>
Featured Posts
12 Gardening Resolutions to Stick To in 2023
December 31.2022
Lessons We've Learned in 2022
December 26.2022
Get A $15 OFF + Free Shipping*
Be the first to know about our discounts, and get $15 off your next order of $199 + free shipping
How Deep Should Your Raised Garden Beds Be? • Gardenary
raised beds
Published May 19, 2022 by Nicole Burke
Filed Under:
raised gardens
raised kitchen garden
raised vegetable garden
garden design
Raised garden beds allow us to maximize our growing space, improve drainage, increase productivity, and tend our plants with greater ease. If you're new to the idea of growing in raised beds, explore three reasons raised beds are better for gardening.
My six main beds (pictured above) are two feet tall, as are the majority of the raised beds my Houston-based company Rooted Garden designs.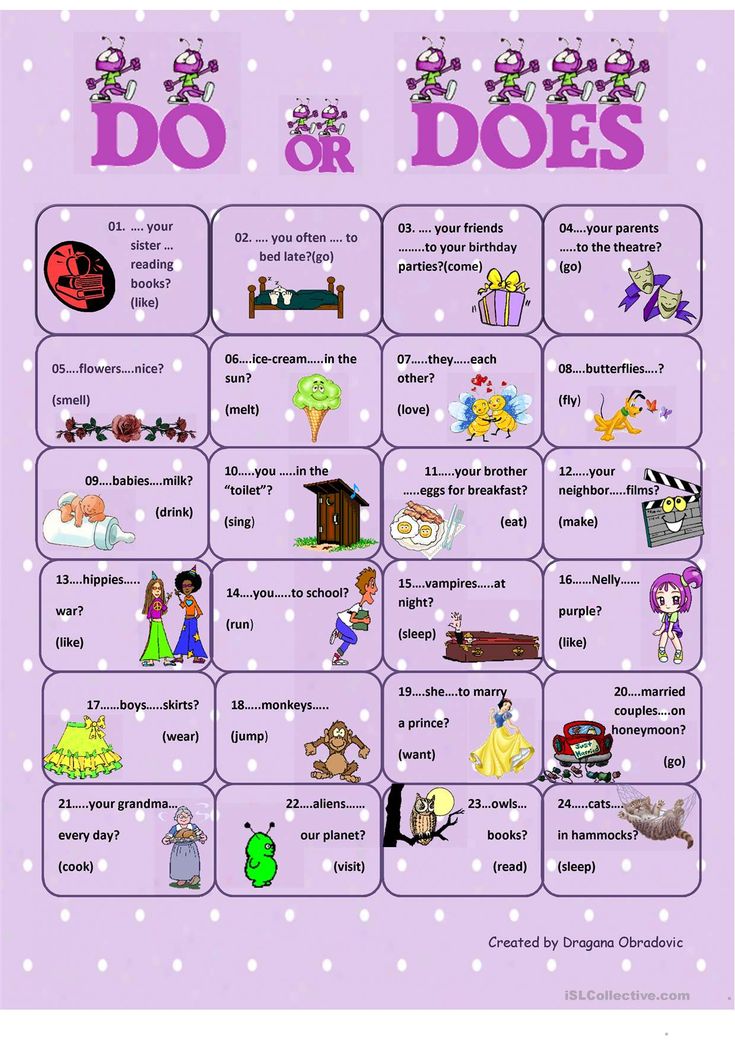 While two-foot beds aren't required to have a beautiful and productive garden, you do need at least 18 inches to grow certain plants.
While two-foot beds aren't required to have a beautiful and productive garden, you do need at least 18 inches to grow certain plants.
Ideal raised bed depth based on the plants you want to grow
Let's look at how deep vegetable plant roots grow and how deep a raised bed would therefore need to be to accommodate the root balls of those plants.
- herbs - 6 inches deep
- lettuce - 6 inches deep
- carrots - 12 inches deep
- radishes - 12 inches deep
- peppers - 12 inches deep
- tomatoes - 18 inches deep
- cucumbers - 18 inches deep
- squash/zucchini - 18 inches deep
- kale - 18 inches deep
Now, let's break down each of these raised bed heights, and then I'll explain why I converted to two-feet-tall raised beds.
What can you grow in a six-inch-deep garden bed?
Six inches is the minimum height I’d recommend. The very first raised bed my family ever put together was only four inches tall, and that height just didn't hold enough good soil we could grow in.
Six inches is enough to grow lettuce greens, herbs, and plants with very shallow root structures.
If you're not quite ready to commit to building a full raised bed, try grabbing a six-inch deep container that's at least a foot wide, and try growing your own lettuce plants. Here are my picks for the best containers to grow salad greens.
What can you grow in a 12-inch-deep garden bed?
One-foot-tall beds are pretty standard in the gardening world. You'll be able to grow plants with deeper roots like carrots, radishes, celery, and peppers, though you might struggle with things like tomatoes, kale, and eggplants, which have really deep root structures.
Personally, I find this height of raised bed hard to tend since you have to bend over more from the waist to reach down.
Shop Gardenary's Raised Bed Kits
What can you grow in an 18-inch-deep garden bed?
Eighteen inches is the minimum height needed for plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, zucchini, and kale—plants that have a bigger root base and need more nutrients and space to spread out.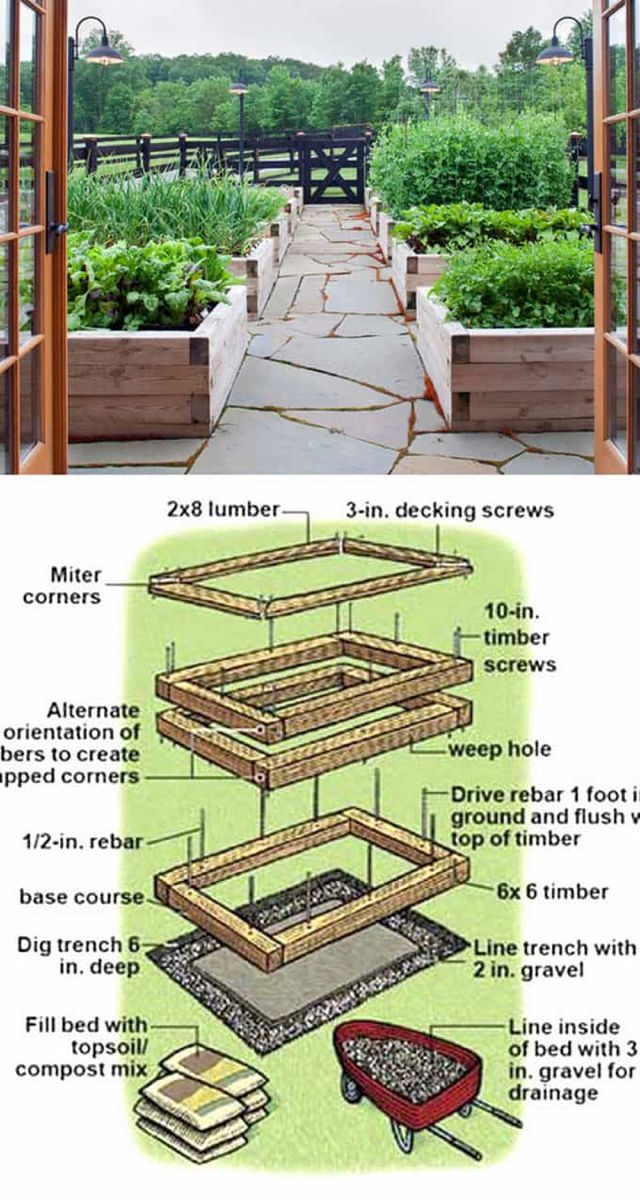
This height also allows for better drainage. Most edible plants hate having their roots stay wet. In-ground plants are more likely to sit in water for longer than plants in a raised bed structure because the soil allows for faster draining, even when there's heavy rain.
What can you grow in a two-foot-deep garden bed?
You can grow just about anything you want in a two-foot-tall raised kitchen garden bed. Few plants really need two feet of depth for their roots, so the extra height is mostly just for the ease and convenience of the gardener. I find the closer a bed is to two feet, the easier it is to tend and harvest from your plants. You bend over from the waist and are at the plant’s level. Garden work should be an enjoyable part of your daily routine, not a chore that hurts your knees and back.
I also prefer this height for aesthetic reasons. Two feet of stone, brick, Corten steel, or cedar planks adds beauty and way more vertical interest to a landscape.
It’s not necessary to have anything over two feet, unless you have a specific reason, like a dog you want to keep out of your beds.
What do you put in the bottom of a raised garden bed?
I get asked this question a lot. The answer is new soil.
This is your opportunity to start fresh with clean, nutrient-rich soil and organic matter. I've seen suggestions to add plastic bottles or trash bags as filler to the bottom of raised beds to save money on soil, but that kind of defeats the purpose of giving your plants' roots all the growing room they need. We want to make sure we're filling up our raised beds from the bottom all the way to the top with great organic matter that will feed our plants, not something that will break down slowly and contaminate your soil with plastic particles.
Before you shovel your new soil in, add some weed barrier cloth to the bottom of your bed to keep weeds out and to prevent your soil from washing out of your bed with the first heavy rain. If you have pests that like to burrow from the ground and eat your plants, add an extra barrier with hardware cloth, as well.
Discover your own gardening strengths and find inspiration to grow your self further with our fun and brief Green Thumb Quiz.
take the quiz
How much soil do I need to fill a raised bed?
Here's a simple soil calculator to add up exactly how much soil you need to fill up your raised bed garden:
STEP 1
Calculate the total width of your garden in feet = W
STEP 2
Calculate the total length of your garden in feet = L
STEP 3
Calculate the total height of your garden in feet = H
STEP 4
Multiply all three together: W x L x H
The answer for this equation is the TOTAL CUBIC FEET of soil you need for your raised beds.
Example
Let's practice with my own six raised garden beds, each measuring 2.5' x 7' x 2'.
To calculate the cubic feet of each bed, we'll use our soil calculator: 2.5 x 7 x 2 = 35 cubic feet for each bed.
Because this setup includes six gardens that all have the same measurement, the total calculation for the full amount of soil needed for these raised beds is: 6 x (2.5 x 7 x 2) or 6 x (35) = 210 cubic feet.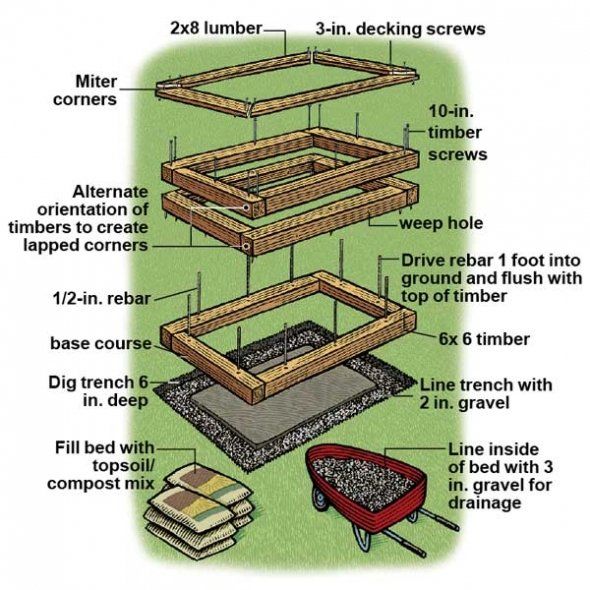
Read our full directions on how to calculate soil for raised beds, plus whether you should buy soil bags or order a truck delivery to fill your total soil requirement.
Not only are raised beds more practical, but they add another layer of beauty as you step into your kitchen garden day after day. I'm confident that you're going to love having raised beds if you choose to install them in your outdoor space, and we've got tons of resources to help you build your own gardening haven and start growing!
Gardenary 365
Gardenary 365 includes full access to our complete Gardenary content library, including Intensive Planting, Herb Garden Guide, Salad Garden School, Microgreens, and Seed Starting Indoors. You'll also learn how to design and build your own raised beds with comprehensive step-by-step guides.
start your 1st lesson
Previous
Next
The Author
NB
Nicole Burke
As founder of Rooted Garden, I've consulted with hundreds of new and experienced gardeners and designed all kinds of kitchen gardens from large to small and everything in between.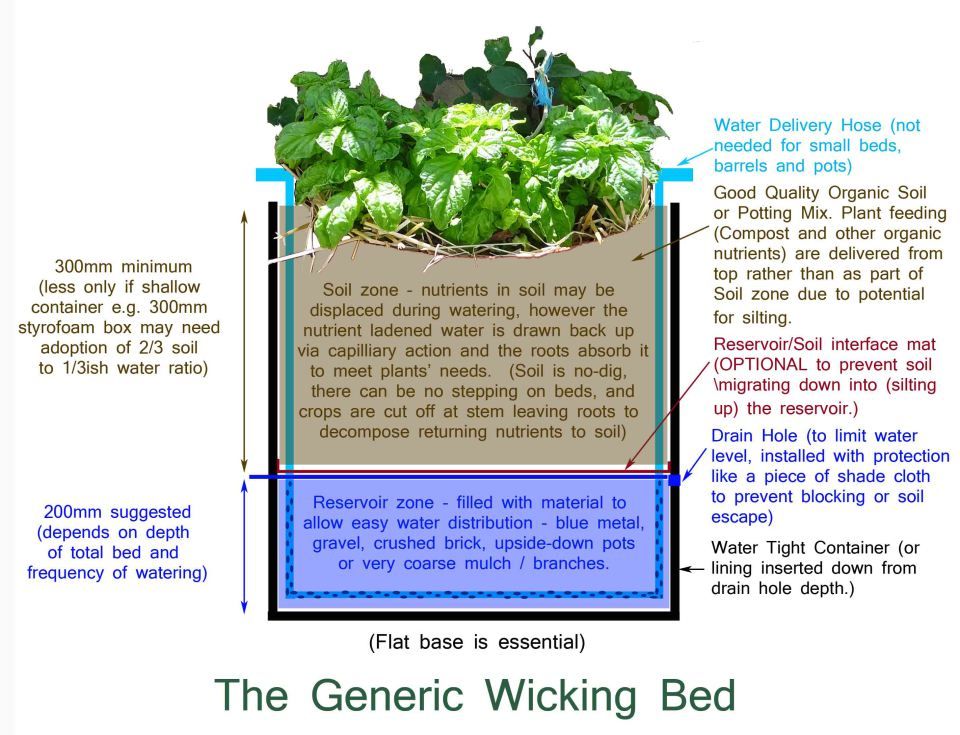
What should be the ideal garden bed
For gardeners, the spring season always starts like a blueprint: dig up the ground, cover the beds with fertile soil, and wait until the soil warms up completely, plant seedlings and start a viscous fight against pests and weeds. However, if you make innovative solutions, you can get a rich harvest with little time, effort and money. The beds provide invaluable assistance in cultivating the land, its processing and harvesting. From the article you will learn what should be the ideal garden bed and how to build it in a summer cottage.
Optimal bed sizes
Length, width and height
On the web you can find a lot of recommendations on the question " What height and what width should be the correct bed? ".
There is no single answer, but there are a number of parameters that can be called universal. If the bed can be processed on both sides, then the width can be laid from 80 to 100 cm. Making a bed less than 80 cm wide is not economically justified. Setting the bed width to more than 100 cm also does not make sense, because labor costs will increase, since it will be more difficult to get to the middle of the bed. If it is possible to process the bed on only one side, the width can be set within 50-60 cm.
Making a bed less than 80 cm wide is not economically justified. Setting the bed width to more than 100 cm also does not make sense, because labor costs will increase, since it will be more difficult to get to the middle of the bed. If it is possible to process the bed on only one side, the width can be set within 50-60 cm.
Usually the height of the beds rises 15-20 cm above the ground, however, you can build beds more than half a meter in height and take care of the plants while standing, but this will significantly increase the time and cost. However, if you build beds 30-40 cm high, then you can take care of them while sitting on a chair in the aisle! In such a bed, an important role is played by the warming bottom layer, which is rich in fertilizers, vitamins and minerals. The undeniable advantage of such beds will be, among other things, the convenience of tillage. nine0005
The length of the bed can be completely different. You need to proceed from the specifics of your area. Usually the length of the beds varies between 4-8 meters. It is recommended to arrange the beds from south to north. In this case, the sun will evenly illuminate the plants in the garden. Remember! To improve the quality of tillage and promote a richer harvest, the right size of the beds will help!
Usually the length of the beds varies between 4-8 meters. It is recommended to arrange the beds from south to north. In this case, the sun will evenly illuminate the plants in the garden. Remember! To improve the quality of tillage and promote a richer harvest, the right size of the beds will help!
Track width
We are often asked: " How far apart should the beds be? "The main criteria for answering will be the convenience of moving between the beds. Usually the paths between the beds are 40 cm. This is the necessary minimum. The width of the paths directly depends on the height of the beds. The larger it is, the wider the width of the paths needs to be laid. For example, between the beds, the height of which is 50 cm, the width of the paths must be at least 50 cm. , mold and insects. Ideally, fencing materials should last a long time and have a low cost. A wide variety of materials are used for fencing. In this article, we will consider those that have earned the trust of most gardeners: wooden boards and flat slate.
Wood
Plank is the most common material for making perfect beds! Wooden boards with a section of 40x200 are ideal for fencing the edges of the beds. A significant drawback of wood is its fragility and susceptibility to decay. And if the site is located in an area with high humidity, these processes proceed even faster. Of course, you can treat the boards with special impregnations, varnishes or paints. However, all this chemistry will soon be in your garden, and then on the table in vegetables and fruits. In addition, hordes of ants are very fond of settling in wooden boards, which are considered by gardeners to be a real unfortunate disaster. nine0005
Flat slate
Slate can be a good substitute for wooden planks. Slate is considered optimal, 8 mm thick. Durable is the most important trump card of this material. He is indifferent to frost and drought, sun and moisture. Ants and other insects will not settle in it; it will serve you forever. Another nice advantage is the availability of this material. The cost of flat slate in the markets is low, so the arrangement of a summer cottage will not hit the budget.
The cost of flat slate in the markets is low, so the arrangement of a summer cottage will not hit the budget.
Gardener with many years of experience Timofey Ivanovich:
- Even 2 years ago, I spent a huge amount of time and effort on the cultivation of beds. It was a real hard labor: I had to bend down and unbend a myriad of times. My back, neck, arms and legs hurt after every trip to the garden. The attending physician even warned that if I did not stop such gymnastics, sciatica would develop. The granddaughter and her husband presented two beds made of galvanized metal. I grow strawberries and tomatoes in them. I have never seen such a harvest in my garden. A month ago I ordered another frame. And today I am already preparing three beds for the new season, which, I am sure, will be rich in harvest. And I completely forgot about back pain! nine0005
Once you've been convinced by the benefits of raised beds, arm yourself with tools, stock up on supplies, and start building unique beds!
And if you want to order galvanized metal beds - please contact us!
← How to make beautiful beds with your own hands Border tape, as an element of decor for beds and lawns →
How to make the right beds in the garden - what is the optimal height and width
In this article I will share with you information about the beds, what they are, what they are for, how to make the right beds in the garden so that the harvest grows excellent.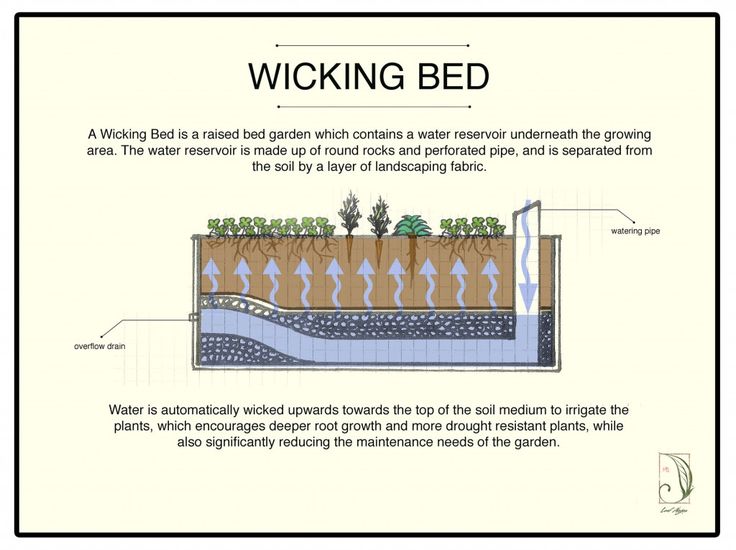 The garden bed should be warmed by the sun, be perfectly flat in order to be evenly moistened, but water should not stagnate on it.
The garden bed should be warmed by the sun, be perfectly flat in order to be evenly moistened, but water should not stagnate on it.
Sides
What to make beds from: it can be just earthen or wooden boards along the edges. The higher and narrower the bed, the better it warms up, drier, it is easier for air exchange to occur in it. nine0005
Bed height
On light, loose soil, you can make beds flush with the paths, but if the soil is heavy, the height of the beds should be increased. The height of the beds is also increased in areas with close groundwater.
In addition, it is very important for the Non-Black Earth region that high beds warm up faster in spring. Under normal conditions, it is difficult to provide the required soil moisture on a high bed.
Therefore, usually the height of the bed is no more than 10-15 cm (or even at the same level with the soil) to ensure good moisture. nine0005
nine0005
Carrot and radish beds
Higher beds are also used for deep-rooted vegetables such as carrots. But for radish, with its weak root system, it is more important to ensure constant soil moisture, so the bed should be low and even.
How wide should the bed be?
The optimal bed width is 0.45-1.2 meters. This is primarily in order to be able to reach from any side of it with your hands to the opposite side. nine0005
Most landowners want to grow not only flowers, but also vegetables and fruits. Is it possible to place all this on a small lawn in front of the house? See for yourself!
Option 1 - Vegetables in high beds
Why not plant a vegetable garden in high beds? Of course, this will require some physical and material costs, but then you can sow, weed, loosen and harvest crops without bending to death.
Around the garden, a strip of sod about one and a half meters wide was removed, which was used to fill boxes for beds. The land has been dug up and planted with berry bushes. You can get into the garden through an arch entwined with roses. A lattice fence on the border with neighbors also serves as a support for climbing beans in summer. nine0005
Organic waste is placed in the wooden compost box located in the right corner. Along the other border there is a rabatka with flowering perennials. Opposite the entrance to the garden is a place to relax with a bench and an arch, also entwined with roses.
How to make a high bed
To frame a bed 70-90 cm high and 130 cm wide, you will need 4 cm thick boards or beams. To protect against voles, lay a wire mesh on the bottom of the box. It’s good to line the inside with a film. Now fill the box with thick branches, grass clippings, vegetable waste, leaves, half-ripe compost, and garden soil. nine0005
Option 2 — Meadow with fruit trees and flower beds
The desire to have fruit trees even in a small garden is quite understandable. However, they require a lot of space and light, so we recommend planting trees along the boundaries of the site. At the same time, they will protect your garden from prying eyes of neighbors.
However, they require a lot of space and light, so we recommend planting trees along the boundaries of the site. At the same time, they will protect your garden from prying eyes of neighbors.
The free central part of the garden can now be planned according to your needs and taste. The solution proposed here visually enlarges the garden. This impression is achieved by a paved path laid diagonally, to the left and right of which square beds are broken. nine0005
You can plant vegetables, flowers, herbs on them. So that the soil is not depleted, crops should be changed annually in the beds, to the left and right of which square beds are broken. You can plant vegetables, flowers, herbs on them. So that the soil is not depleted, crops in the beds should be changed annually.
On the old wooden bench at the entrance to the pavilion it is pleasant to rest after righteous labors and admire the garden.
Option 3 - Strict order in everything
For lovers of clear forms, we recommend breaking up large rectangular beds framed by a low hedge (pictured - from boxwood). Inside, you can alternately plant vegetables, flowers and herbs. nine0005
Inside, you can alternately plant vegetables, flowers and herbs. nine0005
This is not only useful for plants, but also looks much more attractive than the usual narrow and long beds, especially if you put an obelisk in the center or a simple pyramid for clematis, or any climbing annuals.
Between the right flower bed and the boundary of the site, a wide arch-arbor was built. It can be made of wood or metal and entwined with roses, clematis or (in warm regions) wisteria, or you can use climbing vegetable plants like ornamental pumpkins, beans, cucumbers for the same purpose. nine0005
Work with beds in spring
In early spring, when all the snow has not yet melted, and only thawed patches have formed, we heat up our greenhouse bed and plant tomato seedlings there in a week. Between the rows of tomatoes we sow rows of early radishes or stick already sprouted bulbs into the soil with the bottom. We eat green onions with might and main in two weeks.
After another 2 weeks, we remove the radish. After harvesting onions and radishes, we immediately sow kibray leaf dill in all row-spacings. It will grow weak, because by that time the tomato seedlings are already growing great and blocking the light. But a small bunch of dill is enough for the table until the time when it starts in the open garden. nine0005
After transplanting tomatoes to a permanent place, when the greenhouse is completely free, we dig up the ground in it with the addition of fertilizers and plant seedlings of cucumbers. Now it's a cucumber patch for the whole summer .
We prepare such a bed in autumn, we always prepare a bed in the same place . Crop rotation is not needed here, because in the fall, after harvesting cucumbers, we disassemble the ridge, take all the land to potato strips, treat the place with Bordeaux liquid and fill it with ash. Only after that we proceed to the construction of a new ridge. The place is sunny, behind the wind. nine0005
nine0005
The bed is deepened by 20 centimeters (per shovel bayonet) . Along the perimeter we also put a frame 30 cm high from logs. We cover the inner walls with a used film.
Lay a 10 cm layer of cut raspberry stalks on the bottom of the bed. This is a very necessary layer, which in the spring isolates the denser upper layers from the frozen soil and allows the ridge to warm up faster.
Then we pour leaves, plant residues, layer them with sawdust and earth. From above we pour a 10-centimeter layer of earth. We're trying to get it all right. nine0005
The bed is piled flush with the log sides . Pour water over and cover with several layers of film. Then we cover the bed around with rags moistened with tar or carbolic acid, or sprinkle with bleach. This is to keep mice out of the garden.
In the spring, it remains to remove the film, thoroughly pour hot water over the bed 2-3 times and wrap it with film for 3 days.