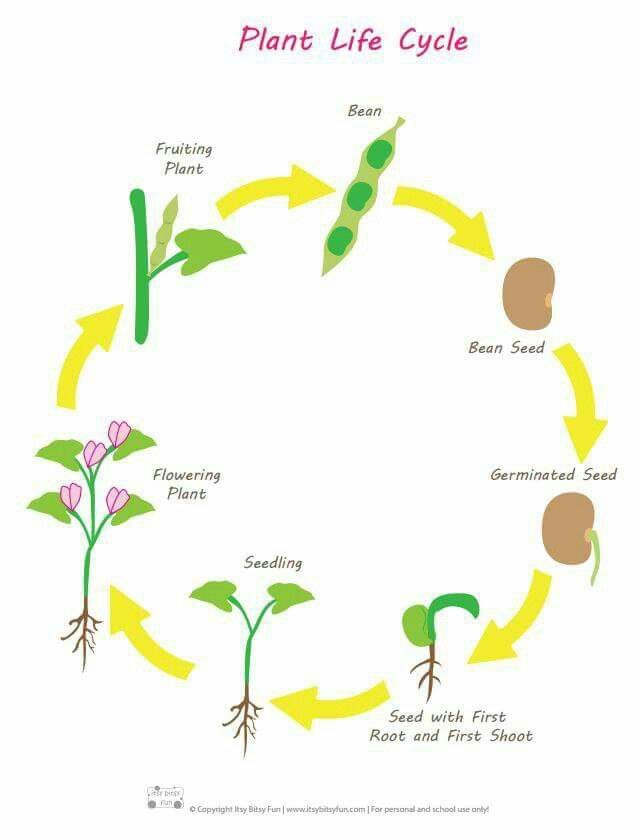
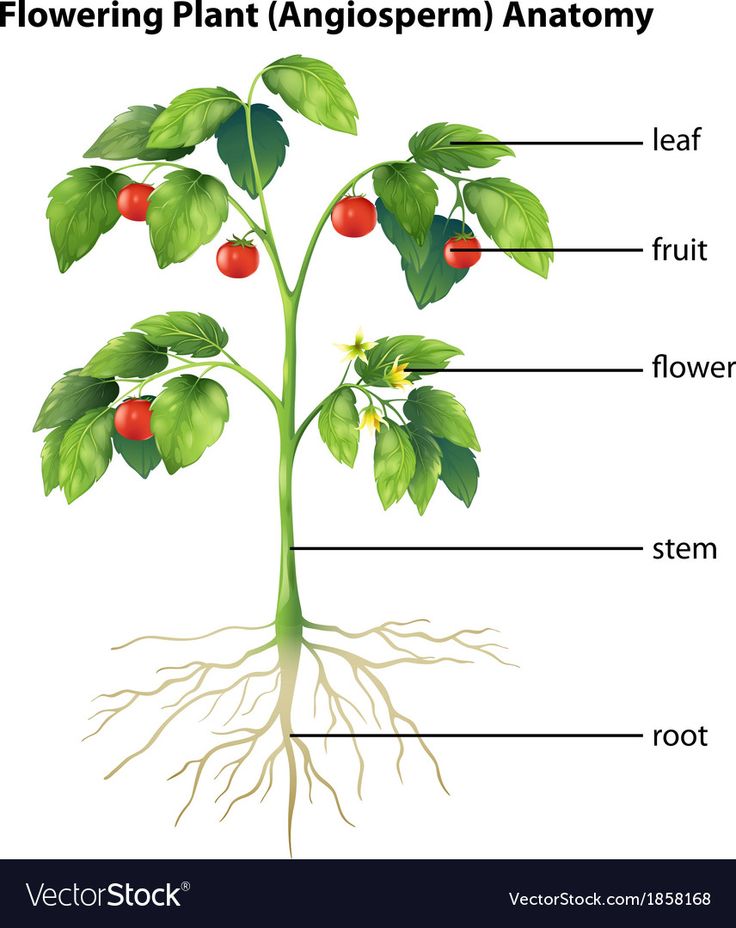
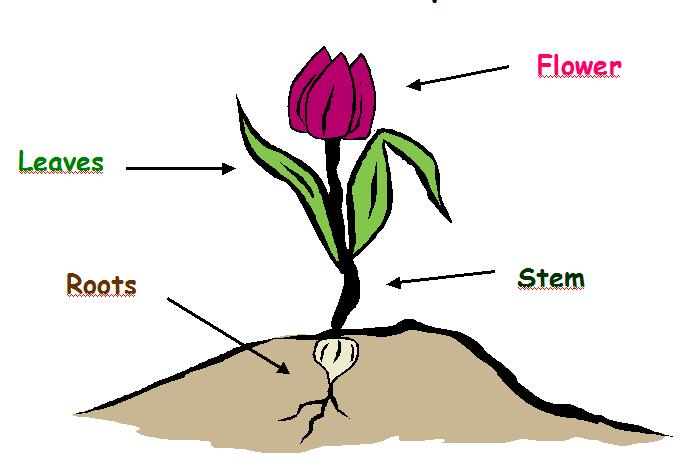
Can you root a rose stem
How to Propagate Roses From Stem Cuttings
By
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti
Marie Iannotti is a life-long gardener and a veteran Master Gardener with nearly three decades of experience. She's also an author of three gardening books, a plant photographer, public speaker, and a former Cornell Cooperative Extension Horticulture Educator. Marie's garden writing has been featured in newspapers and magazines nationwide and she has been interviewed for Martha Stewart Radio, National Public Radio, and numerous articles.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
Updated on 10/18/22
Reviewed by
Julie Thompson-Adolf
Reviewed by Julie Thompson-Adolf
Julie Thompson-Adolf is a Master Gardener and author. She has 30+ years of experience with year-round organic gardening; seed starting and saving; growing heirloom plants, perennials, and annuals; and sustainable and urban farming.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
In This Article
-
When to Propagate
-
Before Getting Started
-
FAQ
Project Overview
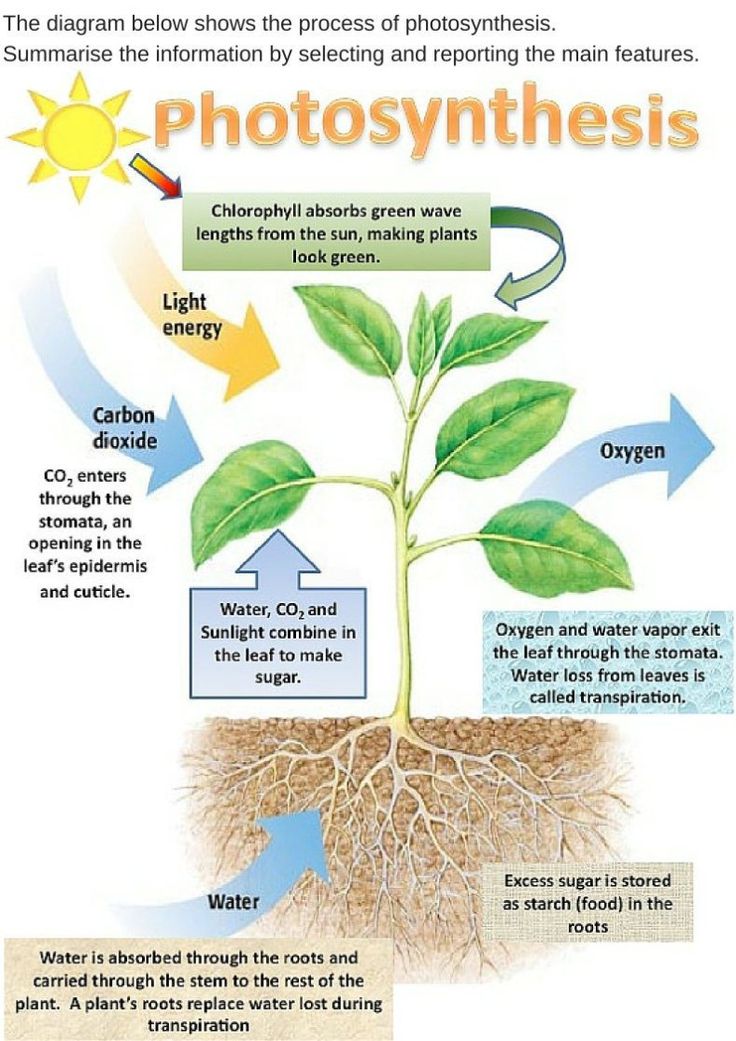
Propagating herbaceous plants is often done by rooting green stem cuttings, but the process can also be successful with woody-stemmed plants, including some roses. Rooting stem cuttings of roses and other woody plants works best with so-called "wild" or "native" pure species, rather than hybrid shrubs. That's because many hybrids are created through a grafting process in which branches from showy but delicate species are melded onto rootstock from a sturdier species.
The result of grafting can be a spectacular plant with exceptional root hardiness. But if you propagate a new plant from a branch clipping, it will lack the parent plant's root hardiness. Thus, it's best to use stem clippings only to propagate non-grafted roses, which include many so-called shrub roses.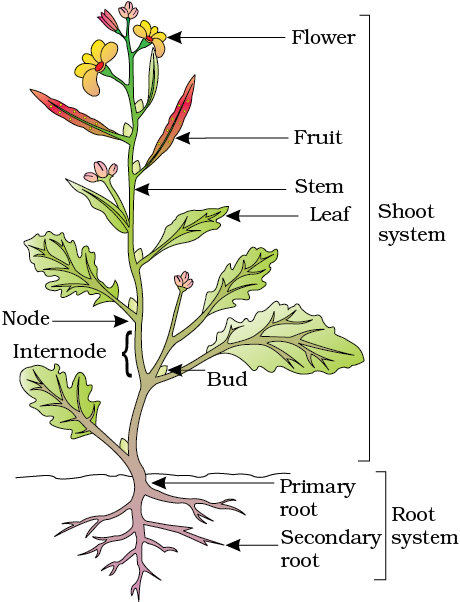
The stem clipping method is a bit tricky with woody plants, and you should expect that several attempts will end in failure. Take extra cuttings to ensure you have at least a few viable prospects. Still, if you take your cuttings from a healthy rose plant and follow the proper steps to root them, your odds of developing new plants will be high.
What Is a Shrub Rose?
The term "shrub rose" is defined by the American Rose Society (ARS) as “a class of hardy, easy-care plants that encompass bushy roses that do not fit in any other category of rose bush.” Many people use the term to refer to any type of non-hybrid rose, but there are several types of hybrid roses that do fit into the ARS's definition of shrub roses, including Moyesi hybrids, hybrid musk roses, Kordesii roses, English roses, and Knock Out roses. These join the many native rose species to form the category of shrub roses. However, any of these hybrid roses described as an "own-root" rose rather than a grafted rose may lend itself to successful propagation from stem cuttings.
When to Propagate a Rose by Stem Cuttings
Rooting a stem cutting can be done almost any time, but cuttings taken from new growth that has recently flowered (rather than old, hardened wood) are more likely to root successfully. Spring or fall is the best time to take softwood stem cuttings. Select them in the early morning hours when the plant is well hydrated. Moreover, avoid taking cuttings when your plant is heavily blooming. At this time, the plant is putting most of its energy into flower production rather than root development, so cuttings won't readily root.
Before Getting Started
Sharp pruners are necessary when taking rose cuttings. Dull tools can crush the rose's woody stems instead of forming a clean slice, which can make the cutting susceptible to fungal rot. Furthermore, make sure to clean your pruners before and after each cutting to avoid transmitting any diseases.
Be patient when growing roses from cuttings. It can take several years for your new rose to produce flowers.
Click Play to Learn How to Grow Roses From Cuttings
Equipment / Tools
- Pruning shears
Materials
- Mature rose plant for cuttings
- Powdered rooting hormone
- Plant pot
- Sand and vermiculite or a rose potting mixture
- Plastic bag or plastic wrap
The Spruce / Michela Buttignol
-
Take Cuttings
Start by taking a 12-inch segment of a new stem that has recently bloomed, cutting it from the plant at a 45-degree angle. The stem should be about the width of a pencil. The best cuttings for rooting usually come from the sides of the bush, rather than the center.
Remove any flowers or flower buds along the cut stem. Flowers or buds on the cut branch will consume energy, and you want to encourage the stem to refocus its survival energy on sending out new roots. If you're taking multiple cuttings, place them in a container of water to keep them hydrated until you're ready to propagate them.

The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Remove Most Leaves
Remove all but the top two sets of leaves on the stem. Then, cut off the remaining portion of the stem just above this top set of leaves. Removing the excess leaves will help the cutting divert its energy to root production.
-
Prepare the Stem for Rooting
Using sharp pruning shears, make a fresh cut on the bottom of the stem just below a stem node (a bump where new growth typically forms). Then, slice into the bottom of the stem about a 1/4 inch up, splitting the stem into open quarters.
Apply Rooting Hormone
Although not absolutely necessary, applying a rooting hormone can help spur your rose plant into developing new roots. Rooting hormones can be found in powder, liquid, and gel form—you'll have the best success with the powder version when working with roses. To apply, slightly moisten the split end of the rose cutting, and then dip it into the powdered rooting hormone.
 Shake off any excess.
Shake off any excess. -
Plant the Cutting
Fill a small pot with at least 6 inches of a potting mix formulated especially for roses. Poke a hole in the potting medium, and then insert the stem sliced-side down, taking care not to rub off the rooting hormone. Gently pack the soil around the stem, and water well.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
-
Cover the Cutting
Loosely cover the cutting, pot and all, with a plastic bag or plastic wrap to help retain soil moisture. Be sure not to let the plastic touch any remaining leaves on the stem, which can cause them to remain wet and susceptible to fungal disease. Putting a tall stake into the pot can help hold the plastic away from the leaves. The bag also needs to be slightly vented, so condensation can escape—if you seal the bag too tightly, the stem can rot. Place the cutting under grow lights or near a bright window.
-
Monitor the Cutting
Keep the soil moist until roots begin to form, which usually takes about two weeks.
 Check for roots by gently tugging on the stem—if there's resistance, roots are probably present.
Check for roots by gently tugging on the stem—if there's resistance, roots are probably present. Your cutting can be transplanted into a pot or the ground as soon as the roots are firmly established or when new leaf sprouts begin to appear along the stem. Make sure to harden off the new rose—i.e., gradually expose it to outdoor conditions—before planting outside.
The Spruce / Claire Cohen
How to Prepare for Rose Bloom Season
Grow Roses from Cuttings: 2 Best Ways to Propagate!
How to grow roses from cuttings easily! Compare the BEST & worst ways to propagate in water or soil, using potatoes, & root by air layering.
Maybe it’s a beautiful rose plant in the garden that you want to multiply, or a Valentines rose bouquet that you want to grow into more roses, it’s easy to want more colorful and gorgeous rose bushes and vines in our homes and gardens.
Many plant lovers have tried to grow roses from cuttings. There are many rose propagation methods such as rooting in soil or water, air layering, and some even try to grow rose cuttings in potatoes! Some of these methods are great, some actually don’t work very well.
Today we are going to compare which ways are the best and easiest to propagate roses from either a plant, cut flowers or even a bouquet. Wouldn’t it be nice to have more roses in our gardens or as gifts to share with friends? 🙂
Can you propagate patented roses?
* Some resources in article are affiliate links. Full disclosure here .
A plant patent lasts for 20 years, after which the plant is allowed to be propagated.
If the roses are patented within the last 20 years, it is illegal to propagate the rose without the consent of the patent holder. ( Source )
However, there are endless varieties of roses you CAN propagate. For example, the famous “New Dawn” and “Charlotte Armstrong” roses were patented over 50 years ago, and old-fashioned heirloom roses often root easier than modern hybrids.
Now you know which roses not to propagate, let’s look at the best and easiest methods to root rose cuttings! ( Source )
Best time to grow roses from cuttings
The best time to grow roses from cuttings is from spring through summer, when flexible new stems (current year’s growth) are actively growing. They are called softwood cuttings, who are the fastest and easiest to root when you select healthy stems.
They are called softwood cuttings, who are the fastest and easiest to root when you select healthy stems.
Look at all the beautiful rooted rose cuttings by Vuon & Nha on YouTube! Video tutorial below:
The next best are semi-hardwood cuttings, taken in late summer and early fall, when new stems have partially matured.
Hardwood cuttings are most difficult type of cutting to root. They are taken in late fall or early winter, when the rose stems have matured and entered dormancy.
Grow roses from cuttings by air layering
Air layering is a fascinating propagation method being used for thousands of years! Nowadays there are easy products like these reusable air layering pods you can get, or make your own with simple materials such as small water bottles or plastic bags.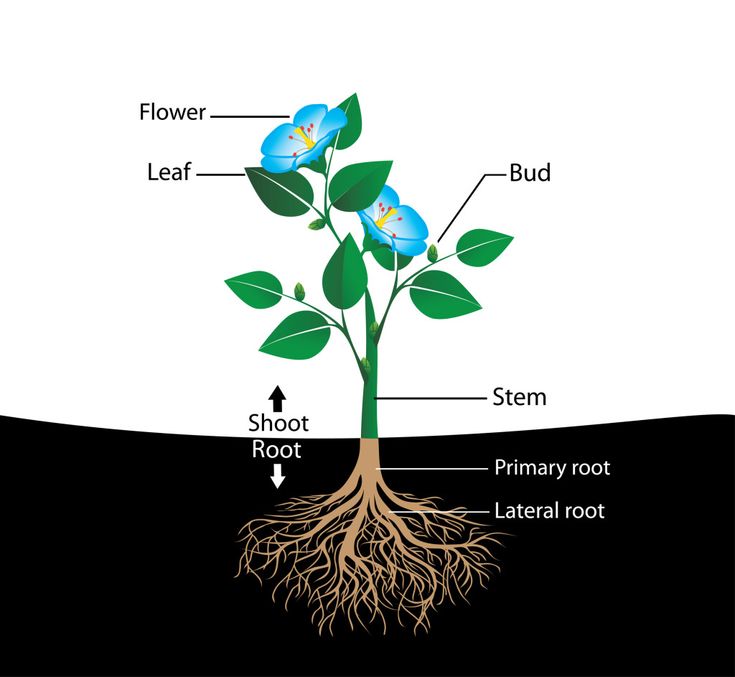
Air layering is the BEST way to propagate roses (and many woody plants) if the rose bush or vine that you want to multiply is already growing in your garden or in a friend’s garden. You don’t even have to use rooting powder with this method.
The best time for air layering roses is in late spring or summer when the weather is warm and the rose bushes are actively growing. ( Air layering rose video tutorial below. )
Select a stem that is about the thickness of a pencil and longer than a foot. Take a clean sharp knife, find a spot at about 1 foot for the top tip of the stem, remove leaves and thorns around this area, peel off about a 1 inch section of the green bark tissue to get to white wood.
You can also make a 2” long cut along the middle of the stem, and insert a little piece of plastic straw to prop the cut open, like shown in the above video tutorial by Vuon & Nha.
Don’t cut too deeply into the stem or it could break.
Dust the cut area with rooting hormone. You can skip this, but rooting hormone does help speeding up the process.
Next, make a 3” to 4” size pouch using either plastic wrap or a small plastic bottle filled with moist peat moss, coir, or potting soil. Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
The cut area should be completely covered with enough room for roots to develop. Video tutorial below by Vuon & Nha.
Secure top and bottom with strings or twist-tie (Not too tight so the plant can grow and expand). You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
You can also use these reusable air layering pods.
Because the stem is still attached to the mother plant, it is receiving water and nutrients as the new roots are growing from the cut area. This greatly increases the propagation success rate to nearly 100%!
Most rose plants show their white roots in 3 – 5 weeks. When you see good root system develops with lots of healthy roots, clip the stem off below the layer.
Gently remove ties and covers. Carefully plant your new rose plants and keep them well watered and protected from direct sunlight for a couple of weeks so it can adapt.
Grow roses from cuttings in soil or medium
Fill some clean pots or containers rooting mix and water well so it’s moist and fully hydrated. You can use clean potting soil or a soil-less mix such as clean sand, peat moss, perlite, or Coco coir. ( Photo by Hedgerow Rose)
IMPORTANT: The containers should have drainage holes and never sit in water for too long. ( Photo by Grownups )
( Photo by Grownups )
Coco coir is a great medium to root rose cuttings. It is sustainable and clean, which is important for propagation.
Take rose cuttings only from healthy plants that are well watered. Choose fresh healthy rose stems newly grown from the woody base, with at least 3-5 leaf nodes on the stem. Cut near the base at a 45-degree angle. Put cut stems in water immediately.
Video tutorial by Vuon & Nha on YouTube. How to propagate rose cuttings in coco coir!Cut longer stem into 6 inch to 8 inch long, and make sure each cutting have at least 3 nodes – where leaf meets stem. Remove all flower buds and leaves except for one set of leaves at the top of each cutting.
Dip the cutting’s bottom half in the rooting hormone powder or gel. Use a pencil to make a planting hole 3 to 4 inches deep in your rooting mix. Plant the rose cutting into the hole so at least two nodes are covered.
Keep the cuttings in a warm and bright place away from direct sun. Water when the rooting mix start to feel dry on the top inch. Pamela at Flower Patch farm used recycled coffee cups (above) and large jars (below ) as humidity tent. Such great ideas!
You can also use a propped- up plastic bag or a mini greenhouse. Here are 45 best DIY greenhouses you can make from tiny to big!
If you live in a warm humid climate with a shaded outdoor area, you can skip the humidity cover. ( Photo below by Hartwood Roses )
Most softwood rose cuttings will root within 2 to 6 weeks. If you see healthy leaves growing, and feel some resistance when you very gently tug on the cuttings (don’t do this too soon!) , it’s likely they have rooted.
Here’s a YouTube tutorial by Mike on how to use a humidity cover made from plastic bottles.
Now you can remove the humidity tent and let them grow for a couple more weeks before transplanting the cuttings. Below is another propagation example by Lilisim.
Can you root rose cuttings in water?
Rose cuttings do not propagate well in just water. Some cuttings will root, but the success rate is usually about 20%, while you can get 80% success by propagating rose cuttings in soil medium or by layering.
The rose cuttings tend to take a long time to root in water, and is prone to rotting.
However, some favorite plants can root very easily in water! Here are a couple of tutorials on how to propagate Fiddle Leaf Fig or Hydrangea cuttings in soil or water with almost 100% success!
Hydrangeas are some of the easiest flowers to propagate! Tutorial here!Can you grow rose cuttings using potatoes?
There are many viral images of rose cuttings in potatoes, but I have not seen any scientific or real life evidence of potatoes or dipping in honey making rose cuttings grow more quickly or successfully.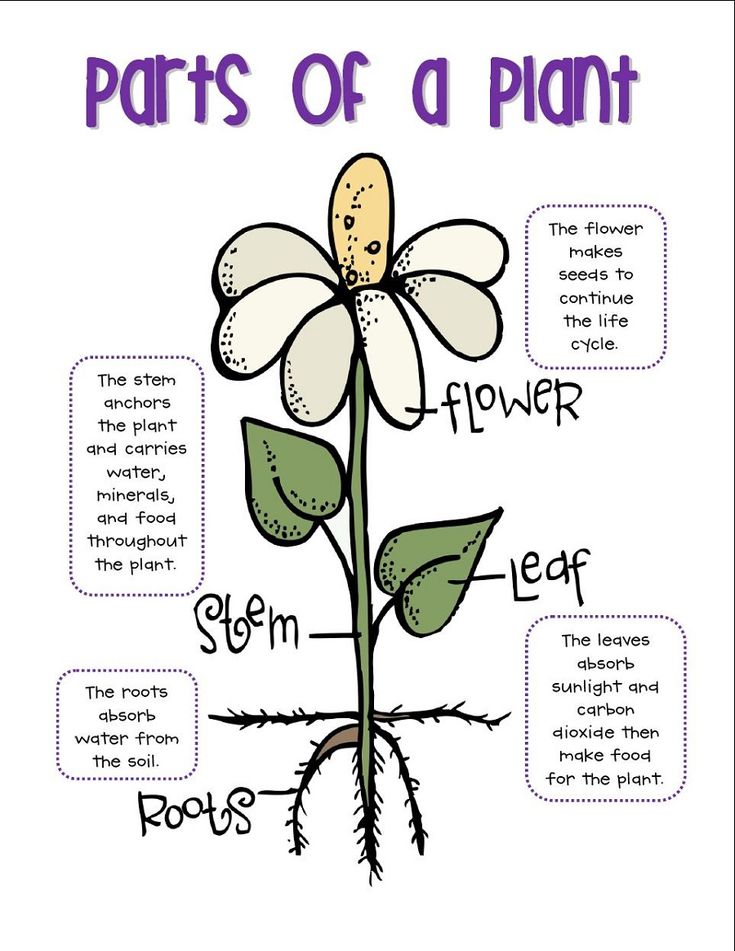
On the contrary, there are many reports of failures from gardeners who actually tried to grow rose cuttings in potatoes.
The potatoes may grow roots, which will not magically become rose roots. The rose cuttings need a medium that holds moisture and air, which isn’t really what a potato does.
That’s it! Use the first 2 methods, and happy gardening! 🙂
Rooting rose cuttings in water
You can buy rose seedlings, or you can propagate the variety you like on your own. You just need to find a suitable bush or bouquet. Growing roses from cuttings at home allows you to expand the rose garden for free. You can root a stem from a bouquet at any time of the year. Do not delay - if you like a rose, then the fresher the cut (no more than three days in a vase), the more successful the operation.
If the water in the vase has not been changed, then the multiplied microorganisms have already risen up the shoot and will cause decay instead of the formation of callus and roots.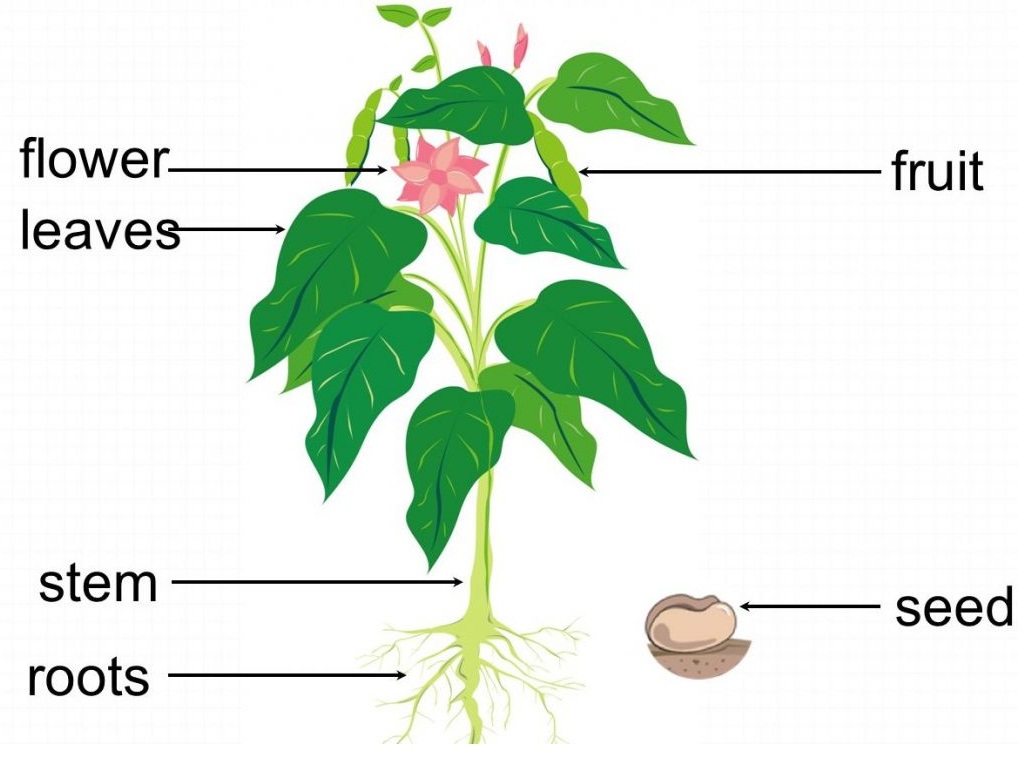 nine0004
nine0004
Rosehip - the wild ancestor of any rose - is a rooting champion. Any fragrant beauty has inherited this property to a greater or lesser extent. The vegetative method of reproduction (by shoot) provides considerable advantages:
- wild growth does not grow around the bush
- the flower does not freeze and lives longer than the grafted seedling
- method makes it possible to get the variety you like for free
The only drawback is that such a plant develops a little slower than a commercial graft. But over time, it catches up and is not inferior in habitus and flowering to purchased specimens. nine0004
What affects the rooting of rose cuttings in water
The success of reproduction depends on belonging to a group of varieties according to the classification. Climbing rooted best of all, in second place - miniature, polyanthus. The most capricious ones that are most often found in bouquets are hybrid tea.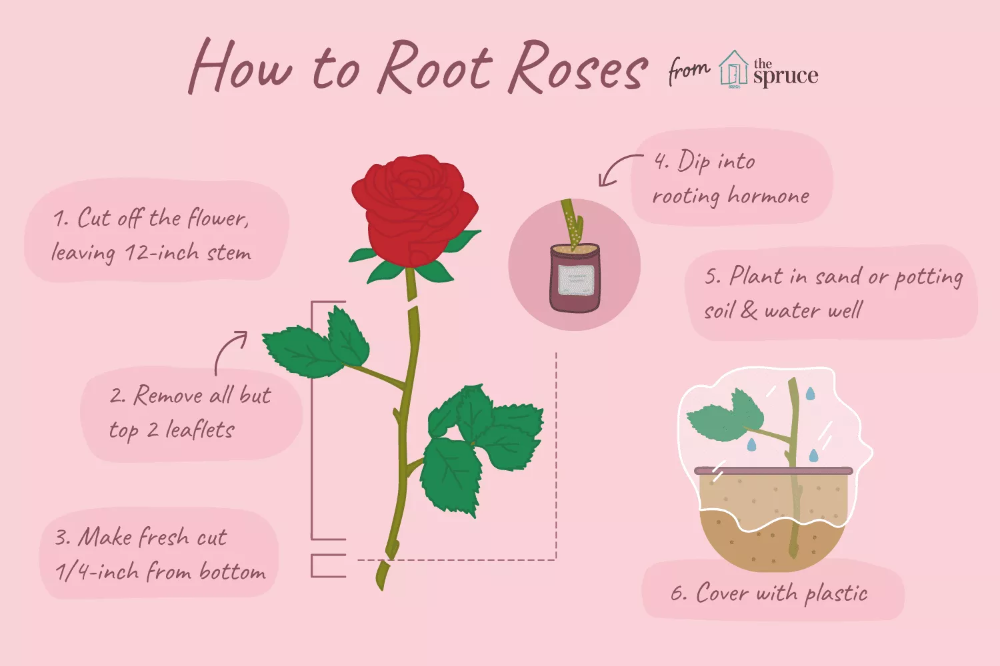
Willingly respond to the rooting of roses of domestic varieties or grown in your area. Imported varieties have almost lignified stems, a long cutting time - the journey of a beauty from Ecuador takes 5-7 days. The survival rate of cuttings is affected by stimulants and preservatives used in greenhouses. nine0004
It has been noted that pink and red varieties give a good result, yellow and orange ones are worse.
When and how to root a rose in water
It is best to cut the cuttings in spring, summer, early autumn - at this time the survival rate is maximum. Lighting is required in winter.
The material is chosen according to the following criteria: a bud, the leaves should not be withered, the average thickness of the stems is 0.5 cm (with a pencil), there should be buds in the axils of the leaves. There is little chance of rooting cuttings of roses in green and lignified stems - the latter are determined by thorns: if they come off easily, then they are late with reproduction. nine0004
nine0004
Cuttings are cut from the middle part of the stem, it is better to take a rose with a half-blown bud. The optimal length of the segment is 15-25 cm - this is one to three knots.
An oblique cut is made under the kidney (at an angle of 45˚), going down 1.5 cm. A horizontal cut is made above the upper kidney, retreating up one centimeter. Leaves are removed to minimize evaporation. Leave the top pair, but cut it in half. Rose seedlings are placed in water - you can and should change it, cover it with a bag. After the roots grow back, they are transplanted into the ground. nine0004
It will be correct to use stimulants: radipharm, rootin, kornerost, heteroauxin. The cut of the cutting is dusted with powder or soaked in a solution according to the instructions.
Alternative methods
There is an opinion that cuttings of roses in water can be replaced by sprouting in young potatoes. A hole is made in the tuber (with a nail, a skewer) and the prepared cutting is deepened to the lower kidney.
The advantages of the potato method are suitable humidity and root-forming auxins, growth phytohormones from sprouting eyes. But there are objections - young root hairs will not find their way through the dense tissues of the potato. But potatoes will grow from awakened eyes. It is possible that the method works as a way of holding for vaccination or transportation. nine0004
But a good result for roses from a bouquet gives the Burrito method: the formation of callus in wet newspapers or paper towels in the dark at a temperature of 14-18˚C. The technology is simple, but it is important to monitor compliance with the temperature regime.
So, the easiest and most cost-effective way to get your favorite variety is to propagate roses with cuttings in water. We wish you success in rooting and expanding the rose garden collection.
How to root a rose from a bouquet? nine0001
A bouquet of roses is undoubtedly a nice, but not very durable gift. The first few days, fresh buds delight with their heady aroma and beauty, and after that, they begin to fade.
Do not rush to throw the bouquet in the urn! The flowers you like can be easily rooted and turned into a houseplant. The cutting process is quite simple, does not require special skills or knowledge.
How to successfully root a rose from a bouquet: useful tips
In fact, the success of cuttings depends on many factors. It turns out that not all flowers can take root and take root in the ground. So that your time is not wasted, before rooting a rose from a bouquet, consider the following tips:
- Scarlet and white roses take root best of all. As for yellow, green, blue, the specificity of their selection makes germination almost impossible.
- Roses grown on the territory of our country take root much better. But Dutch, Kenyan or Ecuadorian roses, due to the large scale of production, are most often fed with chemistry, which complicates growth in the natural environment.
- The fresher the cut flower, the greater the chance of successful rooting of roses from the bouquet.
 For cuttings, a couple of stems will be enough for you, and the rest of the bouquet can continue to please the eye. nine0014
For cuttings, a couple of stems will be enough for you, and the rest of the bouquet can continue to please the eye. nine0014 - The success of rose rooting also depends on what time of year you are trying to grow the rose. The ideal period is summer. Further descending - spring, autumn, winter.
Even if all the above tips are followed, it is not a fact that the rose will instantly take root. Do not rush to get upset and give up, perhaps the next attempt will bring success!
Preparatory stage of rooting a rose from a bouquet
Preparing a cutting is one of the main stages in the rooting of a rose. The quality of this process depends on how quickly the flower takes root and takes root in the ground. nine0003 The process consists of 5 steps:
- Flower selection - the stem must be firm and greenish brown in color. The younger the branch, the less likely it is to take root. The ideal option is a stem that is already woody.
- Sections - we find 3 buds on the branch, which we will focus on.
 From the upper kidney, you need to retreat 2 cm and make an even cut, from the bottom - 1 cm and make a cut at an angle of 45 degrees.
From the upper kidney, you need to retreat 2 cm and make an even cut, from the bottom - 1 cm and make a cut at an angle of 45 degrees. - Removal of leaves - the bottom leaf must be completely removed and the top leaf cut in half. This procedure is mandatory, otherwise the leaves will take away nutrients and strength, which will clearly reduce the chances of roots appearing. nine0014
- Placement in water - finished cuttings must be placed in water exactly for a day. For greater effect, it is desirable to add "Kornevin" to the liquid. A special preparation contributes to a better formation of the root system.
What are the methods of rooting roses ?
Roses can be rooted using soil or a glass of water. Next, consider the most popular methods:
1. With the help of potatoes.
To do this, you need to take a medium-sized potato, peel it from the eyes, make an incision in the middle and place the stem there. Further, the entire structure must be placed in the ground and watered. Why are potatoes here? It protects the plant from bacteria and nourishes it with beneficial trace elements. nine0004
Why are potatoes here? It protects the plant from bacteria and nourishes it with beneficial trace elements. nine0004
2. Directly into the ground.
In this case, you immerse most of the cutting in the ground and water abundantly. To understand whether the plant has taken root will help the buds on the branches. After two weeks, they should begin to bloom.
3. Glass of water.
Place the cutting in a glass of water for 2 weeks, and then plant the plant in the ground. This is a more complicated process, because the water in the tank will need to be changed every day.
Optimal conditions for rooting roses from a bouquet
For rooting to be successful, care must be taken to create favorable conditions. There are quite a few requirements. Here are the key three:
- Indoor or outdoor temperature - +25 º. Too high a temperature will dry out the air, and a low temperature can slow down the growth process.
- Humidity 80-90% - for this you need to create a greenhouse effect.