When to sow potatoes
How to Grow Potatoes — Seed Savers Exchange Blog
Here are a few tips from SSE's gardening crew on how to grow potatoes for a healthy and bountiful harvest.
General Advice
Potatoes always do best in full sun. They are aggressively rooting plants, and we find that they will produce the best crop when planted in a light, loose, well-drained soil. Potatoes prefer a slightly acid soil with a PH of 5.0 to 7.0. Fortunately potatoes are very adaptable and will almost always produce a respectable crop, even when the soil conditions and growing seasons are less than perfect.
Always keep your potato patch weed-free for best results. Potatoes should be rotated in the garden, never being grown in the same spot until there has been a 3-4 year absence of potatoes.
When to Plant Potatoes
Potatoes may be planted as soon as the ground can be worked in the early spring, but keep soil temperatures in mind. Potato plants will not begin to grow until the soil temperature has reached 45 degrees F. The soil should be moist, but not water-logged.
Potatoes can tolerate a light frost, but you should provide some frost protection for the plants if you know that a hard, late season freeze is coming. If you want to extend storage times, and have a long growing season, you can plant a second crop as late as June 15 and harvest the potatoes as late as possible.
Cutting Potatoes Before Planting
A week or two before your planting date, set your seed potatoes in an area where they will be exposed to light and temperatures between 60-70 degrees F. This will begin the sprouting process. A day or two before planting, use a sharp, clean knife to slice the larger seed potatoes into smaller pieces. Each piece should be approximately 2 inches square, and must contain at least 1 or 2 eyes or buds. Plant smaller potatoes whole. A good rule of thumb is to plant potatoes whole if they are smaller in size than a golf ball. In a day or so your seed will form a thick callous over the cuts, which will help prevent rotting.
Planting Potatoes in the Garden
We find that potatoes are best grown in rows. To begin with, dig a trench that is 6-8 inches deep. Plant each piece of potato (cut side down, with the eyes pointing up) every 12-15 inches, with the rows spaced 3 feet apart. If your space is limited or if you would like to grow only baby potatoes, you can decrease the spacing between plants.
To begin with only fill the trench in with 4 inches of soil. Let the plants start to grow and then continue to fill in the trench and even mound the soil around the plants as they continue to grow. Prior to planting, always make sure to cultivate the soil one last time. This will remove any weeds and will loosen the soil and allow the plants to become established more quickly.
How to Water Potatoes
Keep your potato vines well watered throughout the summer, especially during the period when the plants are flowering and immediately following the flowering stage. During this flowering period the plants are creating their tubers and a steady water supply is crucial to good crop outcome. Potatoes do well with 1-2 inches of water or rain per week. When the foliage turns yellow and begins to die back, discontinue watering. This will help start curing the potatoes for harvest time.
Potatoes do well with 1-2 inches of water or rain per week. When the foliage turns yellow and begins to die back, discontinue watering. This will help start curing the potatoes for harvest time.
When to Harvesting Potatoes
Baby potatoes typically can be harvested 2-3 weeks after the plants have finished flowering. Gently dig around the plants to remove potatoes for fresh eating, being careful not to be too intrusive. Try to remove the biggest new potatoes and leave the smaller ones in place so they can continue to grow. Only take what you need for immediate eating. Homegrown new potatoes are a luxury and should be used the same day that they are dug.
Potatoes that are going to be kept for storage should not be dug until 2-3 weeks after the foliage dies back. Carefully dig potatoes with a sturdy fork and if the weather is dry, allow the potatoes to lay in the field, unwashed, for 2-3 days. This curing step allows the skins to mature and is essential for good storage. If the weather during harvest is wet and rainy, allow the potatoes to cure in a dry protected area like a garage or covered porch.
If the weather during harvest is wet and rainy, allow the potatoes to cure in a dry protected area like a garage or covered porch.
Storage Conditions
At Seed Savers Exchange. we are able to store potatoes well into the spring in our underground root cellar. Try to find a storage area that is well ventilated, dark, and cool. The ideal temperature is between 35 and 40 degrees F. Keep in mind that some varieties are better keepers than others. Varieties like Red Gold and Rose Gold are best used in the fall, and others like Carola and Russets are exceptional keepers.
Saving Seed Stock
Home gardeners can save seed for several generations. Save the very best potatoes for planting. You may find that after several years the size begins to decrease; this is typical. Potatoes are very susceptible to viruses. If you are looking for maximum yields it is best to start with fresh, USDA Certified Seed Stock every year.
In collaboration with University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers, SSE is working to eradicate viruses from heritage potatoes in order to safely preserve potato genetic diversity and to offer high quality seed potatoes.
Growing Potatoes: Planting, Growing, and Harvesting Potatoes
The taste and texture of homegrown potatoes are far superior to those of store-bought spuds! Garden “taters” also provide a bounty of nutrients. Here’s how to grow and harvest potatoes in your home garden.
About Potatoes
The potato (Solanum tuberosum) is a member of the nightshade family, which includes tomato, pepper, and eggplant. This cool-weather vegetable typically yields bigger crops in the northern portion of the U.S., however, they can be grown as a winter crop in warmer climates.
The edible part of the potato is the underground “tuber” which is an enlarged underground storage portion of the potato plant. The tuber develops from underground stems called stolons once the plants are 6 to 8 inches tall, or around 5 to 7 weeks after planting.
Potatoes are an ancient vegetable that was first documented by the Incas in Peru. According to the Maine Potato Board, this vegetable arrived in the American Colonies in 1621 when the Governor of Bermuda sent potatoes to the Governor of Virginia at Jamestown.
Now America’s #1 vegetable, potatoes are a fat-free, cholesterol-free source of carbohydrates (energy). But it’s the skin that you should not discard; the skin provides 45% of your daily vitamin C and 18% of potassium, as well as thiamin, riboflavin, folate, niacin, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, and zinc.
Learn more about planting potatoes below.
Planting
Plant potatoes in a sunny place with at least 6 hours of directly sunlight each day. The tubers need to grow in fertile, loose, well-drained soil; hard or compacted soil leads to misshapen tubers. Ideally, soil is slightly acid (pH 5.8 to 6.5) and the soil temperature is at least 45º to 55ºF (7° to 13°C). Before planting (preferably in the fall), mix compost or organic matter into the soil. Learn more about compost, soil amendments, and preparing soil for planting.)
When to Plant Potatoes
Garden potatoes can be planted as soon as the soil can be worked. For many gardeners, this is about 2 weeks after the last spring frost. But aware that early crops may be ruined by soil that’s too wet as the potato seeds will rot. Pay more attention to the soil than the calendar to determine planting time. The soil should not be so wet that it sticks together and is hard to work. Let it dry out a bit first. If you have a late and wet spring, you can plant later—through April (depending on location) or even June, especially in containers.
But aware that early crops may be ruined by soil that’s too wet as the potato seeds will rot. Pay more attention to the soil than the calendar to determine planting time. The soil should not be so wet that it sticks together and is hard to work. Let it dry out a bit first. If you have a late and wet spring, you can plant later—through April (depending on location) or even June, especially in containers.
In cooler regions, some gardeners will plant the first crop of “early-maturing” potatoes in early to mid-April, 6 to 8 weeks before the average last frost date. These varieties can withstand frost.
In warmer regions, potatoes can be grown as a winter crop and planting times range from September to February. Where winters are relatively mild, you can plant a fall crop in September. For example, in central Florida, gardeners plant potatoes in January, and in Georgia they plant in February.
See our Planting Guide for the best dates to plant by zip code or postal code.
How to Plant Potatoes
Note: Potatoes are usually planted in the ground, but they also can be grown in large containers or baskets. The same planting information applies.
The same planting information applies.
Use certified (disease-resistant) seed potatoes from which eyes (buds) protrude. (Do not confuse seed potatoes with potato seeds or grocery produce.
- One to 2 days ahead of planting, use a clean, sharp paring knife to cut large potatoes into golf ball-size pieces, with 1 to 2 eyes each. This time allows the pieces to heal, or form a protective layer over the cut surface, improving both moisture retention and rot resistance. Do not cut up seed potatoes that are smaller than a hen’s egg; plant them whole.
Preparing seed potatoes for planting. Photo by tanyss/Getty Images.
- Potatoes grow best in rows about 3 feet apart. With a hoe or round-point shovel, dig a trench row about 6 inches wide and 8 inches deep. Taper the bottom to about 3 inches wide. Spread and mix in aged manure, compost, and/or leaves.
- In each trench, place a seed potato piece cut side down every 12 to 14 inches and cover with 3 to 4 inches of soil.

- In 12 to 16 days after planting, when sprouts appear, use a hoe to gently fill in the trench with another 3 to 4 inches of soil, leaving a few inches of the plants exposed. Repeat as they grow (in several weeks), until the trench is at ground level.
- Mulch between rows to conserve moisture, control weeds, and cool the soil.
Favorable days of landing on the lunar calendar
Useful information on potatoes
| Planting terms | 1 - 10 (in some cases - from April 25 to June 10) |
| Scheme of landing | 50x50 cm, 60x30 cm, 60x30 cm |
| Tuber depth | 10 - 15 cm |
| Predecessors | • good - peas, beans, cucumbers, onions, carrots; • bad - potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants |
| Place | Well-lit area |
How to determine the timing of planting in your region
landing for it is standard throughout Central Russia - from May 1 to May 10.
Tuber sprouts appear from the ground on about the 20th day, at the very end of May - at this time frosts are already unlikely. But even if the temperature drops below 0 ° C, the potatoes are easy to save - just spud them "with their heads". And when it warms up - unwind.
Potatoes can be planted in the southern regions after 25 April. And the latest date for planting potatoes is June 10. But in this case, only early varieties can be planted - mid-ripening and late ones will not have time to ripen.
How to prepare tubers for planting
Many summer residents do not bother with preliminary preparation of tubers - they take them out of the cellar and immediately plant them. But the result is always sad - the harvest is small, the tubers are small, and the potatoes get sick during the summer. Therefore, preliminary preparation should not be neglected.
Therefore, preliminary preparation should not be neglected.
What does it include?
Rejection. Rotting, scab-ridden, too long or pear-shaped, cracked, discolored tubers are all unsuitable for planting. Ideal tubers should be even, weighing 50 - 80 g (the size of a chicken egg).
Germination. It is necessary for the seedlings to be friendly and strong. There are several ways to germinate tubers, but the easiest is to take potatoes out of the cellar 40 to 50 days (1) before planting and put them in a warm, bright room. At the same time, the tubers turn green, solanine accumulates in them, and it protects them from diseases.
Disease treatment. It is useful to treat germinated potato tubers before planting with a solution of boric acid and copper sulfate (1 g per 10 liters of water). Consumption: 1.5 - 1.8 liters of solution per 100 kg of tubers. Then the tubers are dusted with ash at the rate of 0.5 kg per 100 kg of planting material.
It is useful to treat germinated potato tubers before planting with a solution of boric acid and copper sulfate (1 g per 10 liters of water). Consumption: 1.5 - 1.8 liters of solution per 100 kg of tubers. Then the tubers are dusted with ash at the rate of 0.5 kg per 100 kg of planting material.
How to grow potatoes from seedlings
This method is used to propagate valuable and expensive varieties whose seed tubers are sold by the piece.
Sprouted tubers in late April - early May are tightly laid out in boxes in one row and covered with a layer of wet peat or humus 3 - 4 cm thick. The boxes are placed in a bright place with a temperature of 18 - 20 °C.
At the end of May, the tubers are removed from the boxes, the sprouts with roots are separated, they are immediately planted on the beds and well watered. Single sprouts will eventually produce fewer tubers from the bush, but in general there will be more from the seed potato plot.
Favorable days for planting potatoes for seedlings according to the lunar calendar: April 21 - 22, 25 - 26, May 2 - 4, 7 - 10.
How to plant potatoes
Photo: pixabay.comPotato planting scheme - 50 x 50 cm or 60 x 30 - 35 cm (2). Holes are dug on a spade bayonet. 1 tuber is placed in each, being careful not to break the sprouts. The holes are then covered with soil. After all the potatoes are planted, the plot is harrowed with a rake.
A little trick: if you put 1 tbsp. a spoonful of double superphosphate, there will be no wireworm.
The best precursors for potatoes are cabbage and table root crops. But after tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and other plants of the Solanaceae family, potatoes cannot be planted - they have common diseases (3).
Auspicious days for planting potatoes according to the lunar calendar: April 25-26, May 2-4, May 7-10.
Tips for caring for potatoes
Potato care is not difficult, all it needs is watering and hilling.
Watering Potatoes are watered only 2 times during the summer: immediately after germination and during flowering. This is more than enough to form a good harvest even in arid regions. Additional watering will not bring benefits, on the contrary, they can cause the tubers to start to hurt and be poorly stored. If they don't rot at all.
This is more than enough to form a good harvest even in arid regions. Additional watering will not bring benefits, on the contrary, they can cause the tubers to start to hurt and be poorly stored. If they don't rot at all.
Hilling. It is necessary because in many varieties the tubers come out as they grow. And they turn green, accumulating toxic solanine in themselves.
The first hilling is done when the plants reach a height of 15 - 20 cm - the earth is poured to the shoots up to the first leaves. Then over the summer they make another 2 - 3 hilling. As a result, the ridge should be 15 - 20 cm.
Popular questions and answers
We talked about planting potatoes with agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova - she answered the most frequent questions of summer residents.
Is it possible to plant cut potato tubers?
Usually large tubers are cut in half - this is quite acceptable, however, increases the risk of fungal infections. Therefore, it is necessary to cut the tubers not before planting, but in advance - 2 to 3 days in advance, so that the pulp is ventilated. And before planting, it is useful to powder the sections with ash - it will additionally protect against diseases.
Therefore, it is necessary to cut the tubers not before planting, but in advance - 2 to 3 days in advance, so that the pulp is ventilated. And before planting, it is useful to powder the sections with ash - it will additionally protect against diseases.
But it is still better to plant whole tubers the size of a chicken egg.
Should potatoes be greened before planting?
This is not a mandatory procedure, but it is very useful. In the light, solanine is formed in the tubers - this is a toxic substance, not only for people, but also for soil pests. And solanine reduces the risk of contracting fungal diseases.
Is it possible to grow potatoes from seeds?
After flowering, the potatoes form green berries from which seeds ripen. It is quite possible to grow potatoes from them, however, very small nodules are formed in the first year. A normal harvest can be obtained only in the second year.
The taco method is good because it will allow you to get clean, uninfected planting material.
Sources
- Fisenko A.N., Serpukhovitina K.A., Stolyarov A.I. Garden. Handbook // Rostov-on-Don, Rostov University Press, 1994 - 416 p.
- Yakubovskaya L.D., Yakubovsky V.N., Rozhkova L.N. ABC of a summer resident // Minsk, OOO "Orakul", OOO Lazurak, IPKA "Publicity", 1994 - 415 p.
- Group of authors, ed. Polyanskoy A.M. and Chulkova E.I. Tips for gardeners // Minsk, Harvest, 1970 - 208 p.
When and how to plant potatoes: expert advice
How to harvest a high yield of potatoes? The cultivation of this culture has its own characteristics, the knowledge of which is indispensable. How to plant potatoes correctly, the editors of the site tvtomsk.ru learned in the Agrarian Center of the Tomsk Region.
Variety selection
Getting high yields of potatoes largely depends on the right variety. Well-known varieties, for example, "blue-eye", of course, are very tasty, but are unstable to almost all types of potato diseases.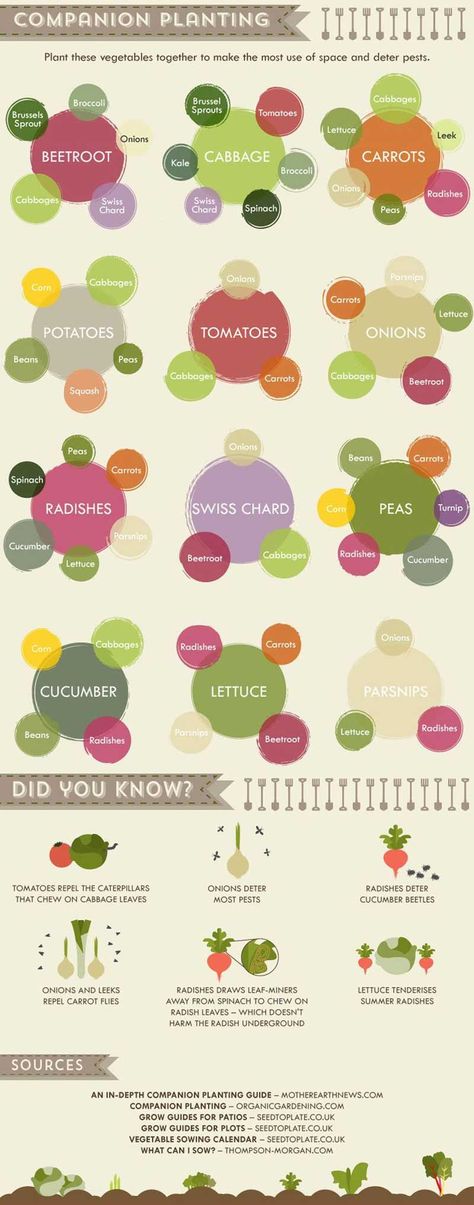
Experts note that late varieties have higher yields, but even a very good variety should not be planted for more than 8 or 10 years. It must be replaced by a new one.
The most common varieties of potatoes among the population of the Tomsk region: Nevsky, Zhukovsky early, In memory of Rogachev, Nakra, Rosara, Lina, Fresco, Antonina, Lyubava, Solnechny, Ketsky, Safo, Anniversary, Charm, Tomich, Sante, Ideal, Karatop, Feloks , Adretta, Lugovskoy, Tuleevsky, Udalets, Rozhdestvensky, Zekura.
Preparing the soil and potatoes for planting
The soil for potatoes for next year is already being prepared at the end of this summer. For digging, you can add urea, ammonium nitrate, double granular superphosphate or potassium salt.
Pure tubers should weigh between 55 and 100 grams. It is recommended to warm the tubers to room temperature for 3 days, then spread them out on the windowsill, in low boxes or on the floor near the window, so that the tubers get a little daylight.
Potatoes can be treated with copper sulphate, Energen, Buton or Agricola Vegeta biostimulants.
If the tubers are thick, strong and short shoots, they can be planted. Large potatoes should be cut with a knife so that at least 2 sprouts are located on the cut parts. Dry them for 2 days, then proceed to planting.
Planting potatoes
Potatoes are best planted after cucumbers, radishes, radishes, beans, green peas and green manure. It should not be placed after tomato and eggplant.
Potatoes should only be planted when the soil is warm to 8°C. Stick to a planting depth of 9-10 cm. Early varieties should be planted in early May. Plant mid-season potatoes in the 10th of May.
Planting methods
1. Smooth method. Plant the vegetable by spreading the potatoes in the furrow. The best potato growth is seen when the distance between the bushes is 65-70 cm and the aisles are wide. Row spacing and hilling should be loosened a week after planting.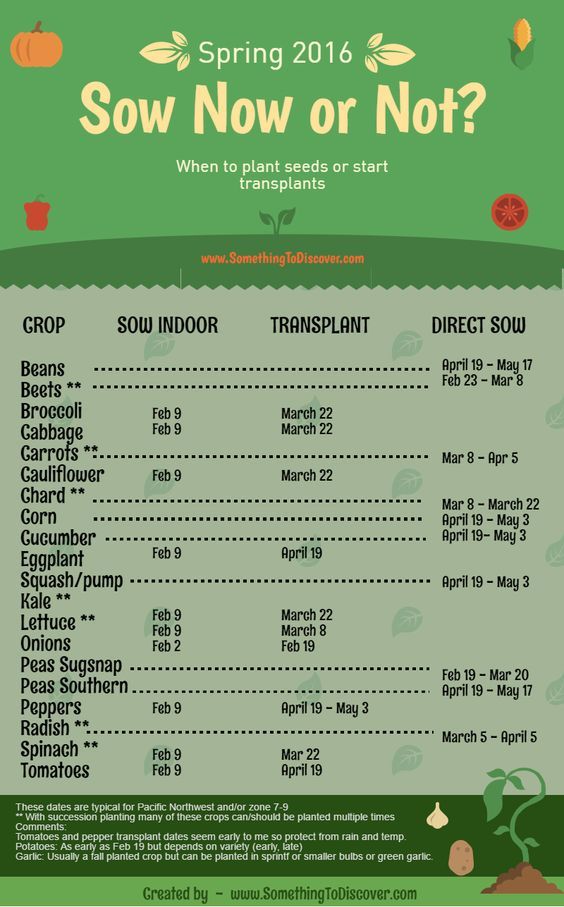
2. Comb method. Cut the ridges with a tractor cultivator or walk-behind tractor. Plant potatoes 8 cm on loamy soils and 11 cm on sandy soils. It should be moderately moist, loose and free of weeds. Potato hilling is carried out when the plant is 15-17 cm in height.
When plants develop slowly, remember to feed them and water them regularly. Weak development can be recognized by the state of the tops. For example, if there is not enough nitrogen, then there will be thin stems and small leaves, and the tops of a light green color.
End each watering by loosening the soil. When watering, keep the watering can close to the ground. The water temperature must be greater than the soil temperature.
Potato fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are the most valuable for potatoes. Not completely rotted manure is valid for 2-4 years. Manure that has decomposed to humus is 4 times more saturated with nitrogen than fresh manure. Therefore, it is better to choose rotten manure for fertilizer. It is also recommended to use slurry with water or humus. Use wood ash for digging, add to top dressing and to holes.
It is also recommended to use slurry with water or humus. Use wood ash for digging, add to top dressing and to holes.
How to properly store potatoes
Store potatoes in a cool, dry and well ventilated area. During storage, the main thing is not to let the tubers germinate or rot. Potatoes go bad especially in the spring.
Protection against pests and diseases
Diseases and pests of potatoes reduce its yield and quality of tubers. The main fungal diseases of this crop are early rot and late blight. Of the insects, the Colorado potato beetle and wireworms cause the greatest harm.
Late blight
The most common fungal disease of potatoes. It affects leaves, stems and tubers. On the surface of the tuber, brownish-grayish depressed spots are formed, inside it is painted in a rusty-brown color. The fungus enters the tubers during the harvesting period. The disease spreads in damp, moderately warm weather. To prevent the development of the disease, after harvesting, all affected plant residues are removed from the site and destroyed. When the first signs of disease appear, the plants are sprayed 90% solution of copper oxychloride.
When the first signs of disease appear, the plants are sprayed 90% solution of copper oxychloride.
Colorado potato beetle control
One of the methods of pest control in private farms is the cultivation of resistant potato varieties. The Colorado potato beetle affects the following varieties less: Pomegranate, Crystal, Lasunok, Spark, Loshitsky, Temp. Chemical control remains the most effective method of dealing with the beetle. Plants are usually treated when there are more than 15 larvae per plant in the plantings. For the first treatments, it is better to use insecticides such as "Commander" and "Iskra Zolotaya" - they provide protection for 20 days.
Wireworm control
Wireworm lives in the ground and damages stolons, roots, stem bases and especially tubers. Helps in the fight against wireworm early autumn digging of the soil. Deep loosening in the spring and summer contributes to the destruction of the larvae. Liming of acidic soils has an effective effect.