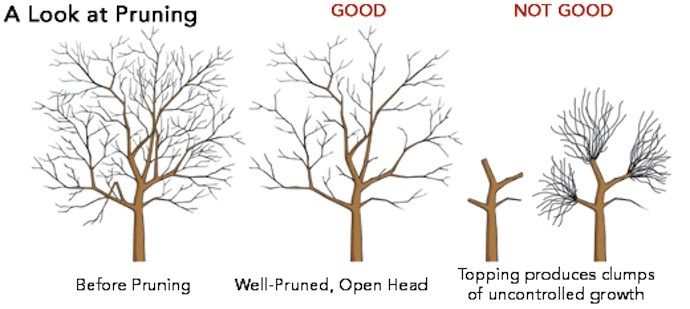
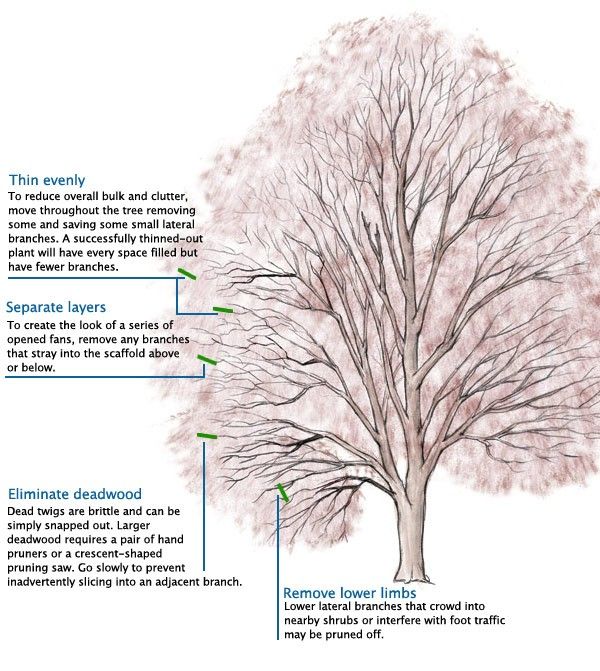
Sedum winter care
Sedum Winter Care | Plant Addicts
Sedums are a succulent plant that grows well in zones 3 to 9. Succulents are known for retaining water in its leaves, which makes sedum one of the hardiest succulents out there. Sedums can tolerate heat, dry soil, and cold weather conditions. Unlike most perennials, sedum will not require a lot of care over the winter.
As you prepare and prune your garden area for winter, sedums can be left unattended to. Sedums are hardy, tolerating frost and below freezing temperatures. Upright sedums will die back to the ground, but the remaining stalks with spent flowers will offer color and food for the birds. If you wish, you can prune the stalks to the ground. It will not harm the plant or the spring’s new growth.
Cutting Back Sedum For Winter
Pruning sedum in the fall is optional. Some find the plant attractive during the winter months. Pinching back the plant can be done to control the spread or size of the plant. If the sedum is diseased, you will want to cut it to the ground and discard any of the clippings. It will grow back in the spring.
Clumping sedums grow taller and have clusters of flowers that change color in the fall. If you want to enjoy the colors of the flowers over the winter, then leave them be. In the spring, cut the stalks to the ground to encourage new growth.
Creeping sedum grows lower to the ground. If the plant looks overgrown and loses its shape, you can prune it to promote next year’s growth. Snip the dead stems and flowers down to the ground.
Sedum Winter Care in Pots
Most sedum varieties are very hardy and can withstand the harsh winters. Depending on the material of the container, potted sedums can remain outdoors all winter. Ceramic or terracotta pots will crack under colder conditions, so we recommend using our resin containers. Place the pot in a sheltered area near a building for the winter. It is best for the plant to stay frozen and dormant during the cold and rebloom in the spring. Do not store the container in a sunny area.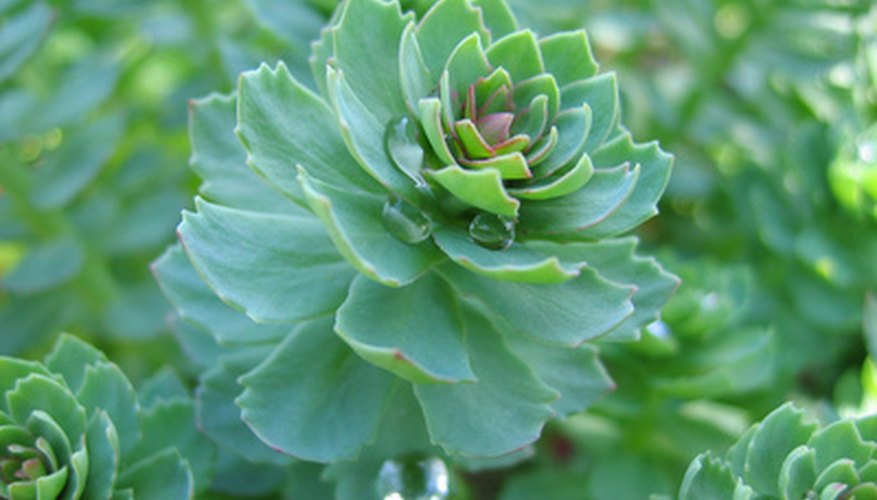 This can cause a thaw/freeze cycle which is not healthy for the roots. You can add protection to the roots of the sedum by wrapping the pot in burlap, burying the pot in the ground, or allowing snow to cover the container.
This can cause a thaw/freeze cycle which is not healthy for the roots. You can add protection to the roots of the sedum by wrapping the pot in burlap, burying the pot in the ground, or allowing snow to cover the container.
Watering Sedum in Winter
Once the growing season is complete, watering of the sedum should stop. Sedums like dry soil. Too much moisture can cause winter rot. A covering of snow will help to protect the sedum, but continuous precipitation and standing water is not good for the plant. If it is an unusually dry winter, you should water just enough so the soil is not completely dried out. Potted sedum will need more water than the in ground plants.
Growing Sedum Indoors
Sedums go dormant for the winter, and will survive outdoors in the brutal cold. It is possible for you to bring your container sedum indoors for the winter, but don’t expect blooming, as it is a dormant time. Sedum will still need 3-4 hours of sun each day and an occasional watering.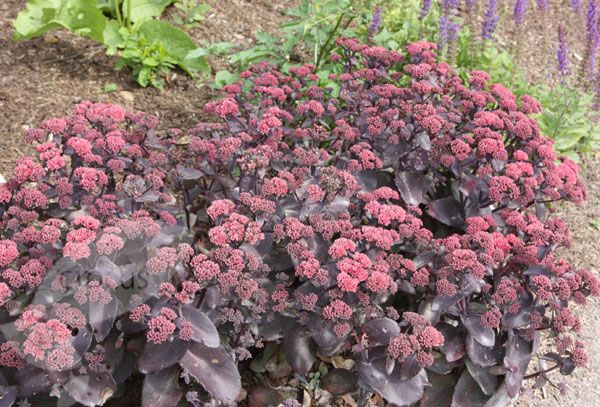
Tips to Care For Sedum in Winter
Sedums are very hardy succulent plants that can tolerate the cold winters. Rather than over care for them and cause damage, it is oftentimes, better to forget about them during the winter.
- Pruning is optional.
- Reduce watering. Water only if the soil is very dry.
- Potted sedums need a bit more watering.
- Too much moisture can cause root rot.
- Potted sedums will survive indoors or outdoors.
- Prune in the spring to encourage new growth.
This page contains affiliate links to products on Amazon. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links.
Winter Care of Sedum | Home Guides
By Karen Clark Updated February 23, 2018
At least 500 recognized cultivars of sedum (Sedum), a hardy succulent also referred to as stonecrop or as the genus Hylotelephium, grow along the ground or up to 2 feet tall. Most varieties thrive in U.S. Department of Agriculture plant hardiness zones 3 through 9 and are tolerant of cold, heat and dry soil. In colder climates, tall sedum dies back in winter and returns in spring. However, in warmer climates it remains a picturesque addition to the garden, showing off persistent green foliage and colorful flowers throughout the winter.
Most varieties thrive in U.S. Department of Agriculture plant hardiness zones 3 through 9 and are tolerant of cold, heat and dry soil. In colder climates, tall sedum dies back in winter and returns in spring. However, in warmer climates it remains a picturesque addition to the garden, showing off persistent green foliage and colorful flowers throughout the winter.
General Care
Sedum requires little care as long as you provide well-draining soil of just about any kind and plenty of sunlight. It even tolerates some shade, depending on the variety. Once established, sedum requires little watering, particularly in the winter, when you should water the plant just enough to ensure the soil doesn't completely dry out. Potted sedum requires more watering than those planted in the ground. It also should be brought indoors whenever the weather forecast calls for temperatures to dip below 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Upright Sedum
Autumn Joy stonecrop (Sedum spectabile 'Autumn Joy') is a popular variety often used in gardens or as potted plants because of its attractive fall color. It grows in zones 3 to 9 and reaches between 18 inches and 24 inches in height. During summer it produces tiny clusters of pink flowers that turn red in the fall. Its foliage and dead flowers retain color throughout the winter, so cutting them back isn’t necessary. When spring arrives prune off spent flowers and cut stalks to ground level to encourage new growth. During a particularly cold winter, the plant will die back. In that case, avoid watering until it returns in the spring. Autumn Joy sedum is best planted in a location where water won’t pool and the soil can dry out easily after winter rains.
It grows in zones 3 to 9 and reaches between 18 inches and 24 inches in height. During summer it produces tiny clusters of pink flowers that turn red in the fall. Its foliage and dead flowers retain color throughout the winter, so cutting them back isn’t necessary. When spring arrives prune off spent flowers and cut stalks to ground level to encourage new growth. During a particularly cold winter, the plant will die back. In that case, avoid watering until it returns in the spring. Autumn Joy sedum is best planted in a location where water won’t pool and the soil can dry out easily after winter rains.
Low-Growing Sedum
Certain types of sedum grow as a groundcover or small shrub, such as Dragon’s Blood (Sedum spurium 'Schorbuser Blut'). It reaches 6 inches in height with a generous spread of up to 2 feet wide. It performs best in USDA zones 4 to 9, where its tiny pink flowers bloom from August to September. Like the upright variety of sedum, this plant is evergreen throughout the winter in warmer climates. However, if the foliage begins to look overgrown or loses its attractiveness, removing dead stems and flowers down to the crown will promote next season’s growth. Avoid excess watering to ensure its healthy return in the spring.
However, if the foliage begins to look overgrown or loses its attractiveness, removing dead stems and flowers down to the crown will promote next season’s growth. Avoid excess watering to ensure its healthy return in the spring.
References
- Pacific Horticulture: Sedum Care and Propagation
- Brooklyn Botanic Garden: Sedum: Easy-to-Grow Succulents With Seasonal Interest
- eFloras.Org: Flora of North America: Sedum
- Colorado State University: Plant Talk Colorado: Sedum
- The National Gardening Association: Sedums: Plant Care and Collection of Varieties
- University of Illinois Extension: The Homeowners Column: Sedums – Tough Plants for Tough Areas
- University of California Cooperative Extension Master Gardeners of Sacramento County: Fall Plant List
- UC Master Gardener Program of Sonoma County: Sedum telephium ‘Autumn Joy’
- Monrovia Plant Catalog: Autumn Joy Stonecrop
- Portland Nursery: Evergreen Sedum: Stonecrop
- Santa Fe Botanical Garden: OCTOBER : Autumn Joy sedum : Hylotelephium telephium ‘Autumn Joy’ (synonym Sedum x ‘Autumn Joy’)
- Missouri Botanical Garden: Hylotelephium 'Herbstfreude' Autumn Joy
- Missouri Botanical Garden: Sedum spurium 'Schorbuser Blut' Dragon's Blood
Writer Bio
Karen Clark has been writing professionally since 2001. Her work includes articles on gardening, education and literature. She has also published short literary fiction in the "Southern Humanities Review" and has co-authored a novel. Her professional experience includes teaching and tutoring students of all ages in literature, history and writing. She holds a Bachelor of the Arts in political science and a Master of Fine Arts in writing.
Her work includes articles on gardening, education and literature. She has also published short literary fiction in the "Southern Humanities Review" and has co-authored a novel. Her professional experience includes teaching and tutoring students of all ages in literature, history and writing. She holds a Bachelor of the Arts in political science and a Master of Fine Arts in writing.
planting and care in the open field, propagation, species and varieties
The succulent plant Sedum (Sedum), or stonecrop, is a member of the Crassulaceae family. In the people, such a succulent is also called feverish or hernia grass. Under natural conditions, it can still be found in Eurasia, Africa, South and North America in meadows and dry slopes. The name sedum comes from the word "sedo", which is translated from Latin as "to subside", this is due to the fact that foliage in some species was used as an anesthetic. There is a myth about how Telephos, the son of Hercules, cured with such a plant a severe wound that Achilles inflicted on him with a spear. To date, more than 300 species of such a plant are known, while only about 100 species are cultivated, and there are also a large number of hybrids and varieties. Among them, there are garden plants (for example, a large stonecrop), and there are indoor plants (for example, Morgan's stonecrop).
To date, more than 300 species of such a plant are known, while only about 100 species are cultivated, and there are also a large number of hybrids and varieties. Among them, there are garden plants (for example, a large stonecrop), and there are indoor plants (for example, Morgan's stonecrop).
Content
- 1 Brief description of growing
- 2 Features of cleaning
- 3 Cleaning from seeds
- 3.1 Sowing 9000 3.2 Growing seedlings
- 5.1 Propagating stonecrop
- 5.2 Transplanting
- 5.3 Diseases and pests
- 6.1 Seeds
- 6.2 How to prepare for winter
 3 Stonecrop (Sedum acre)
3 Stonecrop (Sedum acre) Brief description of cultivation Sedum seeds are sown for seedlings in March or April, seedlings are transplanted into open soil in the last days of May.
 Experts do not recommend feeding the plant with fresh manure.
Experts do not recommend feeding the plant with fresh manure. Peculiarities of stonecrop
Sedum - this herbaceous succulent plant is a perennial or biennial, it is represented by shrubs or semi-shrubs. The leaf plates are alternately arranged, fleshy, entire and sessile, they can be opposite or whorled, they can also have a different shape, size and color. Lateral or apical inflorescences can have an umbrella-shaped, corymbose or racemose shape, they include bisexual star-shaped flowers of various colors. Flowering is observed in summer or autumn. Sedum is an excellent honey plant that attracts bees to the garden plot. At home, as a rule, tropical stonecrops are cultivated, while perennial frost-resistant species with erect or creeping shoots are grown in garden plots. All species are drought tolerant and photophilous, but they grow well in light shade. Sedum is a relative of Kalanchoe, juvenile, Echeveria and spotted.
Flowering is observed in summer or autumn. Sedum is an excellent honey plant that attracts bees to the garden plot. At home, as a rule, tropical stonecrops are cultivated, while perennial frost-resistant species with erect or creeping shoots are grown in garden plots. All species are drought tolerant and photophilous, but they grow well in light shade. Sedum is a relative of Kalanchoe, juvenile, Echeveria and spotted.
SEDUM, HARE CABBAGE unpretentious flower in the garden. Cultivation, care, reproduction.
Watch this video on YouTube
Growing sedum from seeds
Seeding
Outdoors, sedum can be grown from seed through seedlings. Sowing of seeds is carried out in March or April, the distance between them should be from 40 to 50 mm. To do this, containers or boxes are used, which must be filled with a soil mixture consisting of sand and garden soil, they are covered with coarse sand from above. The crops must be carefully moistened with a spray bottle, then they are covered with a film or glass on top, and then removed to the lower shelf of the refrigerator for stratification, while the air temperature should be from 0 to 5 degrees. As long as the crops are on the shelf of the refrigerator, they must be ventilated every day, and accumulated condensate must be removed from the surface of the shelter. The soil mixture should be constantly slightly moist. After half a month, the crops should be placed on the windowsill, while the required air temperature should be about 18–20 degrees. The first seedlings should appear after 15–30 days, until this happens, the crops must be systematically aired, condensate removed from the surface of the shelter, and the soil mixture should be moistened from the sprayer immediately after it dries.
As long as the crops are on the shelf of the refrigerator, they must be ventilated every day, and accumulated condensate must be removed from the surface of the shelter. The soil mixture should be constantly slightly moist. After half a month, the crops should be placed on the windowsill, while the required air temperature should be about 18–20 degrees. The first seedlings should appear after 15–30 days, until this happens, the crops must be systematically aired, condensate removed from the surface of the shelter, and the soil mixture should be moistened from the sprayer immediately after it dries.
Sowing seeds for seedlings, if desired, can be carried out before winter. This should be done in exactly the same way as described above, but the crops are not removed to the refrigerator shelf, but they are transferred to the greenhouse or buried in the ground, under these conditions the seeds will undergo natural stratification. Crops need to be brought into the room in April for germination.
Growing seedlings
The seedlings of this plant are very small. After the emergence of seedlings will be massive, the shelter is removed from the container. The picking of plants into individual small pots is carried out during the formation of their second true leaf plate. Caring for seedlings is very simple, for this it must be systematically watered and lightly loosen the surface of the soil mixture. When 7 days remain before transplanting into open soil, they begin to harden it, for this the plants are transferred to the street every day, while the duration of such a procedure must be increased gradually.
Stonecrop "Sultan" sowing seeds. Seeding result.
Watch this video on YouTube
Planting stonecrop in open ground
When to plant stonecrop in ground
Planting stonecrop seedlings in open ground is carried out in the last days of May after the threat of returning spring frosts is over. It is a picky plant, so you can choose both sunny and partial shade for its cultivation, but it grows best in the light. The site should be open and located away from deciduous shrubs and trees, the fact is that if the bushes are covered with foliage in the fall, then with the onset of spring it will not have the strength to break through it.
Planting rules
This plant is also unpretentious in terms of soil composition, it can be grown even on rocky soil, but in order for the bushes to be very effective, organic fertilizers (compost or humus) must be applied to the ground before planting. Planting holes should be made in the ground, while the distance between them should be about 0.2 m, then the plant is transplanted into them. Planted seedlings need abundant watering. The flowering of bushes grown from seeds begins at 2-3 years.
Evers stonecrop. Correct landing.
Watch this video on YouTube
Caring for sedum in the garden
Growing sedum in your garden requires weeding it quite often. However, there is a type of caustic soda, which is able to get rid of all weeds itself, in this regard, it is often used to frame alpine slides and flower beds. But almost all other species can suffer from weeds, so they need to be removed in a timely manner. Watering is carried out only during a period of prolonged drought. The growth of the stems must be monitored, and therefore they should be shortened in a timely manner, preventing them from growing. In order to preserve the decorative effect of the bushes, the inflorescences and foliage that have begun to wither must be immediately removed, while all the green stems must be cut out from the bushes with multi-colored shoots. In spring and autumn, sedum is fed with complex mineral fertilizer or liquid organic (bird droppings solution (1:20) or mullein infusion (1:10)). It is impossible to feed this plant with fresh manure.
However, there is a type of caustic soda, which is able to get rid of all weeds itself, in this regard, it is often used to frame alpine slides and flower beds. But almost all other species can suffer from weeds, so they need to be removed in a timely manner. Watering is carried out only during a period of prolonged drought. The growth of the stems must be monitored, and therefore they should be shortened in a timely manner, preventing them from growing. In order to preserve the decorative effect of the bushes, the inflorescences and foliage that have begun to wither must be immediately removed, while all the green stems must be cut out from the bushes with multi-colored shoots. In spring and autumn, sedum is fed with complex mineral fertilizer or liquid organic (bird droppings solution (1:20) or mullein infusion (1:10)). It is impossible to feed this plant with fresh manure.
Propagation of stonecrop
How to propagate this plant by seed was discussed at the beginning of this article. You can grow sedum from self-collected seeds, but it is likely that these plants will not inherit the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. The generative (seed) method of propagation is recommended only for initial cultivation, and it is also suitable for breeding new varieties. To propagate varietal bushes, it is best to use the vegetative method (dividing the bush or cuttings).
Ground cover species can be cut before or after flowering. The stalk is cut off from the stem, while its length should be about the size of a finger, all the lower leaf plates are cut off, and then planted in a loose soil mixture for rooting, while at least 1 node must be deepened into the substrate. After rooting, the cutting is transplanted to a permanent place. In the spring, cut cuttings should be immediately planted in open soil. In autumn, several stems are cut, and then they are put into a vase, like a bouquet, while keeping an eye on the water so that it does not stagnate, it should be systematically replaced.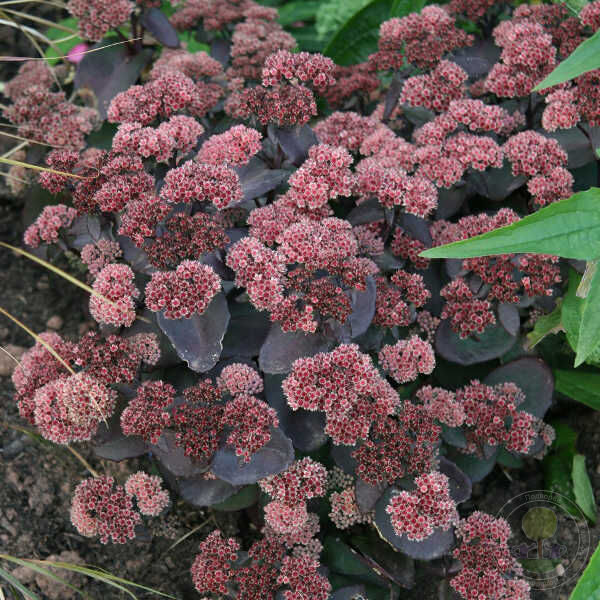 By the onset of the spring period, all cuttings should have roots, after which they can be planted in open ground. If the cuttings take root even in the middle of winter, they will need to be planted in separate pots, and in the spring they are transplanted by transshipment into open ground to a permanent place.
By the onset of the spring period, all cuttings should have roots, after which they can be planted in open ground. If the cuttings take root even in the middle of winter, they will need to be planted in separate pots, and in the spring they are transplanted by transshipment into open ground to a permanent place.
It should also be remembered that right on the spot you can root any part of the stem or the whole shoot. The surface of the soil, located directly under the stems, must be cleaned of weeds, then fertilizers are applied to the ground, leveled and tamped. After that, several stems are pressed to the surface of the prepared area, which are covered from above with a soil mixture consisting of sand and garden soil, which is then pressed a little. With this method of propagation, 7–10 cuttings out of 10 take root.
Vigorous shrubs, as well as those older than 4-5 years, can be propagated by division. To do this, at the beginning of the spring period, the sedum must be removed from the soil, all the earth is removed from its rhizome, after which the bush is divided into several parts, while taking into account that both buds and roots should be present on each division. The cut sites will need to be treated with a fungicidal preparation, after which the parts of the bush are cleaned in a cool, shaded place for several hours, where they should dry out. After that, the delenki are planted immediately in a permanent place.
Stonecrop prominent. Reproduction in spring and autumn.
Watch this video on YouTube
Transplantation
A bush can be grown in the same place for no more than 5 years, after which it must be rejuvenated. To begin with, all the old stems are cut off from him, then fresh soil and fertilizer are poured under the root, but if there is such an opportunity, then it is better to transplant the stonecrop. As a rule, during a bush transplant, it is divided into parts, how to do this is described in detail above.
Diseases and pests
This crop is highly resistant to diseases and pests. However, problems can also arise with it, for example, if watering is excessively frequent and plentiful, or if the summer period is quite cool and rainy. In this case, the bush may be affected by fungal diseases. The first sign that the bush is sick is the appearance of dark spots on its leaf plates. You can cope with the disease by treating with a fungicidal preparation. Those plants that are very severely affected are recommended to be removed from the soil and destroyed.
Aphids, sawfly caterpillars, weevils and thrips can live on sedum. To get rid of weevils, they must be collected by hand, for this white material is spread under the bush and at night, by the light of a flashlight, the pests are shaken off the plant, after which they must be destroyed. At the same time, caterpillars, aphids and thrips can be destroyed by spraying the plant with an insectoacaricide solution, for example, Aktellik.
Stonecrop after flowering
Seed collection
Before proceeding with the collection of stonecrop seeds, it must be taken into account that the plants obtained from them are not able to preserve the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. You also need to remember that the flowering of this plant continues until severe frosts, and in winter it leaves with green foliage, which will also make it very difficult to collect seeds. And you also need to remember that sedum is very easy to propagate by cuttings or dividing the bush.
How to prepare for wintering
After the first real frosts are behind, it is recommended to cut the bush, while cuttings should rise above the soil surface, the length of which should not exceed 30–40 mm. These trimmings must be covered with a layer of soil. The cut stems, if desired, can be rooted (see above), and in the spring they can be planted in a permanent place in open ground. If you like the look of stonecrop covered with snow, then you can not cut it. However, it must be taken into account that with the onset of spring, the bush should still be cut off, as it will lose its attractiveness.
Unpretentious garden flowers Stonecrop prominent and perennial aster
Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of stonecrop with photos and names
All types of stonecrop are divided into ground cover plants, which are stonecrops (Sedum), and stonecrops ( Hylotelephium), which are taller and they are separated into a subgenus of stonecrops. The most popular among gardeners are the types of sedum described below.
The most popular among gardeners are the types of sedum described below.
Stonecrop (Sedum telephium)
Or stonecrop, or sedum telephium (Hylotelephium triphyllum), or purple stonecrop (Sedum purpureum), or bean grass, or crow's fat, or live grass, or hare cabbage.
This perennial is a honey plant that reaches a height of 25–30 centimeters. His shoots are erect and thick. Oval sessile flat sheet plates can be opposite or alternately arranged, their edge is serrated. Flowering occurs from mid to late summer. At the tops of the shoots, lush corymbose paniculate inflorescences are formed, consisting of yellow-green or red flowers. Under natural conditions, such a plant can be found in the temperate climate of Europe and Asia, while it prefers to grow in glades, in pine forests, on forest edges, in shrubs and on the slopes of ravines. This species is medicinal, in alternative medicine its foliage is used as a tonic and tonic. This species has several subspecies:
- common legume dark purple flowers;
- common large - white-green or white-yellow flowers;
- common common ― this differs from the common large subspecies in the form of leaf blades, which taper towards the base;
- common Ruprecht - color of inflorescences is white-cream.

As a result of the work of breeders, a large number of varieties of this species have appeared and almost all of them are quite popular in culture. The following varieties are most popular:
- Matrona . The height of a powerful bush is about 0.6 m. Large greenish-blue leaf plates grow on dark purple shoots, with time their edge turns red. The flowers are painted pinkish.
- Black Jack . The height of the bush is about 0.4 m, its foliage is purple-blue. The composition of dense inflorescences includes flowers of pink color.
- Linda Windsor . The color of erect shoots is maroon, the foliage is dark red, and the flowers are ruby color.
- Strawberry and Cream . The height of such a hybrid plant is about 0.4 m. The leaf plates are green, the buds are pinkish-red, and the flowers are cream, which makes the inflorescences look bicolor.
- Picolette .
The height of a compact bush is about 0.3 m, it is decorated with small bronze-red leaf plates with a metallic sheen. The composition of dense inflorescences includes pink flowers.
Other popular varieties among gardeners are: Ruby Glow, Rosie Glow, Bon Bon, Vera Jamison, Green Expectations, Gooseberry Full, Heb Gray, Crazy Raffles, Xenox, etc.
White stonecrop (Sedum album), or soapwort
Either bee, or six-week, or living grass, or God's color.
Under natural conditions, this species can be found in the Caucasus, Asia Minor, Russia, Western Europe and North Africa. This species was called white stonecrop due to the fact that its fragrant flowers are painted white, they are part of paniculate inflorescences, which consist of several branches. Such an evergreen perennial plant forms a mat, which is about 50 mm high, its vegetative branches are short, and plump twisted oval-elliptical leaf plates grow on them, the length of which is about 10 centimeters.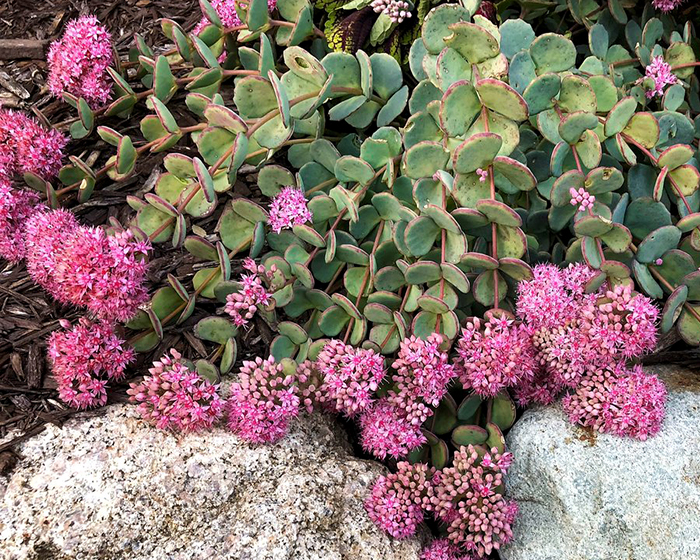 This species has several varieties:0003
This species has several varieties:0003
- small-flowered white - inflorescences in this form are white, while the spherical green leaf blades never turn red;
- wall white is a lush form with pink buds and bronze or purple leaf blades;
- wall white Cristatum - overgrown stem tips have a dense covering consisting of leaf blades.
Most popular varieties:
- Coral Carpet . The height of the bush is only about 50 mm. Its pale red foliage turns red in autumn.
- France . This tall plant is decorated with long green leaf plates, while in bright sunlight they turn pink over time.
- Laconicum . A tall bush is decorated with lush sessile green foliage, which in some cases can turn red.
Stonecrop (Sedum acre)
Either lamb, or goose soap, or wild pepper, or fever grass, or younger, or pimple, or blush, or chistik, or kernel.
In nature, this species is found in Western Siberia, Asia Minor, the European part of Russia, the Caucasus and North America. If the juice of such a plant gets on the skin, then ulcers can form on it, and the species name is associated with this. The height of the bush is about 10 centimeters, the shoots are branched and rounded. Naked, fleshy, alternately arranged leaf plates are green in color and about 0.6 cm long. The foliage does not fly around from the bush even in winter. Semi-umbellate inflorescences consist of yellow-golden flowers, which reach about 15 mm in diameter. This species has many different forms:
- Aureum - in this form, the tips of the stems are pale yellow in spring;
- Minus - this is a very short form with lush small foliage;
- Elegance - undersized bush is decorated with twisted leaf plates of variegated color.
Sedum spurium
In nature, this species grows in subalpine meadows, and also on the rocky slopes of Turkey, the Caucasus and Iran.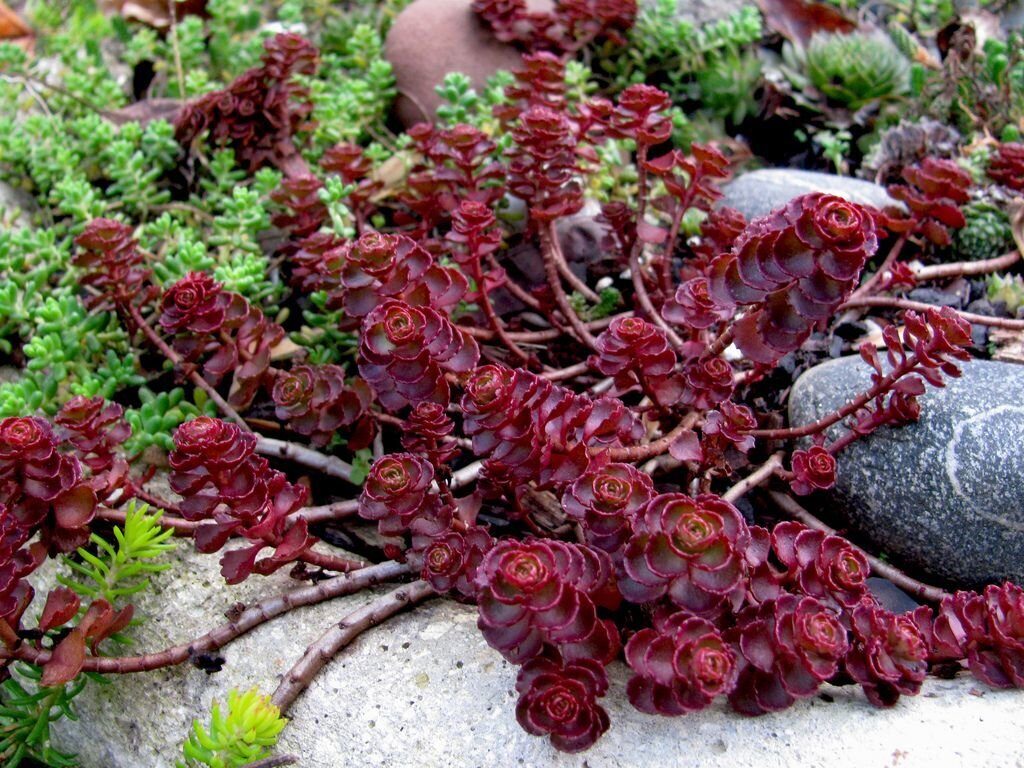 Such a frost-resistant perennial plant has creeping long rhizomes. Shoots can be ascending or creeping. Oppositely located fleshy leaf plates of a dark green color are ovate-wedge-shaped, while along the edge they are thick-toothed or crenate. The composition of the lush corymbs includes flowers of purple or pink color. This plant has been cultivated since 1816. The following varieties are most popular:
Such a frost-resistant perennial plant has creeping long rhizomes. Shoots can be ascending or creeping. Oppositely located fleshy leaf plates of a dark green color are ovate-wedge-shaped, while along the edge they are thick-toothed or crenate. The composition of the lush corymbs includes flowers of purple or pink color. This plant has been cultivated since 1816. The following varieties are most popular:
- Album - white flowers and green foliage;
- Bronze Carpet - color of inflorescences is pink, leaf plates become bronze by autumn;
- Ruby Mantle purple flowers and dark red foliage;
- Shorebuser Bluet - In the spring, the bush is decorated with foliage with a red border, while in the fall it turns red.
Gardeners also cultivate such varieties as: Erd Bluth, Fulda Glut, Purpurteppich, Koktsineum, Roseum, Salmoneum, etc.
Stonecrop (Hylotelephium spectabile)
This species is native to Japan, North Korea and Northeast China. The height of the bush is about 50 cm, while its rhizome is tuberous and thickened. Upright shoots adorn large bare sessile green-blue leaf plates, their shape is oval or spatulate, and the edge is serrated. The diameter of the semi-umbellate inflorescences is about 15 centimeters, they consist of flowers reaching 10 mm in diameter, which have a pinkish-lilac or carmine-purple color. In Asia, such a plant has been cultivated for a long time, and in Europe since 1853. A large number of varieties have been cultivated by gardeners:
The height of the bush is about 50 cm, while its rhizome is tuberous and thickened. Upright shoots adorn large bare sessile green-blue leaf plates, their shape is oval or spatulate, and the edge is serrated. The diameter of the semi-umbellate inflorescences is about 15 centimeters, they consist of flowers reaching 10 mm in diameter, which have a pinkish-lilac or carmine-purple color. In Asia, such a plant has been cultivated for a long time, and in Europe since 1853. A large number of varieties have been cultivated by gardeners:
- Iceberg - bush height about 0.35 m, white inflorescences;
- Brilliant is a relatively old variety with inflorescences of pink flowers with rich anthers and deep pink carpels;
- Septemberglut - large inflorescences consist of small dark pink flowers;
- Stardust, Snow Queen - inflorescences of these varieties are white;
- Meteor, Carmen - these 2 species are similar to each other, and they have purple flowers;
- Autumn Faye - about 50 cm high, grayish-green leaf blades and copper colored flowers;
- Neon - a bush about 0.
 35 m high is decorated with large inflorescences of rich pink color.
35 m high is decorated with large inflorescences of rich pink color.
Stonecrops such as spatula-leaved, Alberta, pale yellow, hybrid, thick-leaved, Spanish, Kamchatka, Kuril, carneum, linear, Lydian, vine-shaped, Middendorf, multi-stemmed, annual, Oregon, recurved, stonecrop, shoot-bearing, divergent, Rural, blue, opposite-leaved, dark red, thick-branched, thin, thin, Troll, narrow-leaved, Forster, six-row and subulate.
The most commonly grown types of stonecrop are: white-pink, anakampseros, blanching, viviparous, Siebold, Caucasian, false-representative, whorled, nautes, Tatarinova, poplar-leaved, Ussuri and Evers.
Stonecrop. Its varieties and care.
Watch this video on YouTube
Properties of stonecrop: benefits and harms
Medicinal properties of stonecrop
In alternative medicine, such medicinal types of stonecrop as prominent, ordinary (large, purple) and caustic are used.
Sedum vulgaris has anti-inflammatory, stimulating, wound healing, antitumor, regenerating, hemostatic and tonic effects. This type is considered a strong biogenic stimulant, which exceeds aloe in its activity, while it affects the body very gently and does not cause unwanted side effects.
Stonecrop large is used as an aid in the treatment of pneumonia, bronchitis, hepatitis, non-healing wounds and trophic ulcers, impotence, nervous disorders, kidney and bladder diseases, cancer.
A species of stonecrop is used for anemia, epilepsy, diseases of the digestive tract, ischemia and pulmonary insufficiency. It helps to stop bleeding, relieve inflammation and pain, neutralize the action of microbes and bacteria, sputum discharge, remove toxins from the body, restore joint mobility, lower blood pressure, calm the nervous system, heal wounds, dilate blood vessels, stimulate the endocrine glands, lower cholesterol and strengthening the immune system.
Stonecrop caustic is distinguished by its irritant and diuretic effect. It is used in the treatment of malaria, to enhance intestinal motility, increase blood pressure, heal wounds, burns and ulcers, treat catarrh of the upper respiratory tract, dropsy, anemia, jaundice, skin tuberculosis in children. Means made on the basis of caustic stonecrop have an analgesic effect.
Stonecrop heals, medicinal properties
Watch this video on YouTube
Contraindications
Only stonecrop is contraindicated, because its juice has an irritating effect. Preparations made from such a plant should not be used by hypertensive patients during pregnancy. When used externally, burning, irritation or redness of the skin can be observed, and if its juice is taken inside, this can cause nausea. In this regard, before using sedum for treatment, it is necessary to consult with your doctor.
Stonecrop (sedum). Care at home. Planting and propagation
Stonecrop (sedum) is a representative of succulents, and is also related to the well-known "Money Tree". These plants are directly related to Crassulaceae. Therefore, caring for such a plant is quite simple.
This genus is quite numerous, it includes at least 600 species. The largest number of them are found exclusively in their natural conditions. Several species adorn gardens and flower beds. On the windowsills, like houseplants, only a few grow. initially grown as a potted flower, they began to stonecrop Morgan and Weinberg. Then they included Gregg's stonecrop, compact and Siebold, as well as other
Most flower growers prefer to grow this plant as an ampelous (pending). The appearance of these flowers is quite different from each other, but they should be grown and cared for in the same way.
1 Sedum (sedum): home care
1.1 Location and lighting
1.2 Temperature
1.3 Watering and air humidity
1.4 Top dressing and fertilizing
1.5 Propagation
- 003
1.7 Healing properties
1.8 Caution
Locations and lighting
Sedum loves light very much. Most experienced flower growers claim that he is not afraid of the direct rays of the sun. However, this statement is not entirely true. In the event that the plant does not receive enough light, the color of the leaves will not be so saturated. And if the light is sorely lacking, then the leaves will fade altogether, and the flower itself will stretch out and take on a painful, stunted appearance.
The sedum flower needs direct sunlight for normal growth and development, but only in small amounts. However, it is worth considering here that in summer, in hot weather, if the stonecrop is placed on the windowsill on the south side with the window closed, then as a result the plant will simply “wither”. It is best to take the plant outside in the summer months, and if this is not possible, then open the window or at least shade it a little.
Sedum will not be able to feel comfortable if there is no clean and fresh air in the room. Therefore, it is so important to ventilate the room in which it is located, even if it is not inhabited.
Temperature
This plant differs from many others in that it can feel great both in warm and cool conditions. The most favorable temperature for sedum is from 8 to 26 degrees in the summer. If the flower is provided with careful care, then higher temperatures will not be afraid of it. Some types of stonecrop tolerate even slight frosts.
It is worth considering that in winter, sedum has a dormant period. Therefore, it is simply necessary to place it in a room where the temperature will be within 8-10 degrees. If the room is too warm, then the shoots of the flower will stretch out and undergo deformation.
Watering and air humidity
This plant is a succulent, so abundant watering is contraindicated. If the soil is heavily waterlogged, then the stonecrop may well die, especially in the winter period.
In spring and summer, watering is done only after the top layer of the substrate dries out. In winter, when the plant is at rest, it is watered once every 4 weeks (provided that the temperature is not higher than recommended). It is not necessary to moisten it at all and you need to do this only in order to wash off the dust.
Top dressing and fertilizers
In the spring-summer period, sedum should be fed with fertilizer for cacti and this should be done only once a month. In the autumn-winter period, feeding the plant is not required.
Transplantation
Young stonecrop needs to be transplanted quite often, about once a year. When he becomes an adult, then he can be transplanted every 3 or 4 years, or even less often. In general, sedum transplants are quite easy to transplant, but the problem is that it has very delicate leaves. They can fall off even with a light touch. Therefore, it is necessary to transplant the plant in case of emergency. For example, when the pot becomes too small for a flower.
Given that the root system of sedum is close to the soil surface, choose a pot that is not very high, but rather wide. You can choose almost any soil for transplanting. For this, land for cacti is quite suitable, which can be purchased at any flower shop or prepared independently. To do this, mix sheet and sod land, sand and brick chips in a ratio of 1: 1: 1: 0.5. It is also recommended to add some charcoal. It is very important to have good drainage.
Propagation
Sedum is propagated by cuttings. To do this, you need to cut off the stalk and plant it in pre-prepared soil (any special preparation of the stalk itself is absolutely not needed). Compost soil mixed with sand in a ratio of 1: 1, as well as a mixture of turf and leaf soil with sand, is suitable for planting a cutting. After 4 weeks, and maybe even earlier, the cuttings will have the first roots.
It is worth noting that there are several types of sedums, for example, Potozinsky sedum, which grow quite quickly and require annual renewal.
Healing properties
Sedum is a medicinal plant. So, it is able to quickly heal wounds, and it is also used to treat burns. And stonecrop has been used for medicinal purposes for a very long time.
Warning
Sedum Morgana is a rather dangerous plant.