Mature kale plants
Kale : Seed to Harvest
Learning Download: How to Grow Kale
Health nuts everywhere can grow their own kale, as it is an easy crop to grow. The leafy green vegetable is commonly known as a cool-weather crop best for growth in the spring and fall seasons, but kale is hardy and can adapt to warmer environments.
To plant:
Kale can be sown directly into the garden two weeks before the last frost date. Plant seeds 1/4 inch deep and 3 inches apart in rows set 18 inches apart. For a fall crop, plant kale seeds in the late summer.
To grow:
Once seedlings appear, thin them to 8 to 12 inches apart. Water regularly to keep the soil moist, as this keeps the leaves crisp and sweet. mulch around the plants to prevent dirt sticking to the leaves of the kale and potentially rotting it.
To harvest:
Kale can be grown to its full size or harvested when the leaves are small and tender. Kale is ready to harvest when its leaves are the size of your hand. It usually takes up to 95 days for kale to be ready after planting it from seed. Don’t pick the terminal bud at the top of the plant, but harvest one fistful of leaves each time you pick the kale. Kale can grow until temperatures reach 20 degrees, and frost adds to the taste. The small, tender leaves can be eaten raw. When using, cut up the larger leaves and remove the ribs prior to cooking.
What kale craves:
Upon planting the seeds, fertilize with a 5-10-10 fertilizer. Mix 1/5 cups of fertilizer with the top 3 to 4 inches of soil for a 25-foot row of kale. Throughout its growing season, you can fertilize kale with a side dressing of compost every six to eight weeks.
Where to buy kale seeds:
You can find many varieties of kale seeds, some with curled leaves and others with red stems at Urban Farmer.
Learning Download: Common pests and diseases: Kale
When growing vegetables, it is always exciting to care for the plant throughout its growing phase and harvest it for delicious recipes later on, but one thing to watch out for is pests and diseases. Different plants are susceptible to different types of pests and diseases, and it is important to make yourself aware so you can keep a watchful eye and also take any preventative methods to keep your plants safe throughout their lifespan.
Different plants are susceptible to different types of pests and diseases, and it is important to make yourself aware so you can keep a watchful eye and also take any preventative methods to keep your plants safe throughout their lifespan.
Kale can fall victim to several different pests and diseases, many of which are similar to the problems affecting greens.
Pests:
Some of the pests commonly affecting kale include the beet armyworm, cabbage aphids, cabbage loopers and more.
The beet armyworm will cause leaves to appear skeletonized due to heavy feeding. Use organic methods to control this insect such as Bacillus thuringiensis.
Cabbage aphids can stunt plant growth and even cause death. The insects are gray-green and will be visible on the leaves. These aphids only feed on cruciferous plants but can survive on related weeds. If the infestation isn’t bad, prune out the affected leaves. however, if the infestation is heavy, spray the sturdier plants with a strong jet of water to knock the aphids off the leaves.
Cabbage loopers will cause extensive damage in the leaves. The caterpillars are green and have white lines on each side of their body. They will overwinter in crop debris. Handpick the larvae off the plants, or apply Bacillus thuringiensis to kill the younger larvae.
Diseases:
Some of the most common diseases affecting kale include Alternaria leaf spot, anthracnose, damping off, downy mildew and others.
Alternaria leaf spot will cause small spots on the kale’s leaves which will then turn brown or gray. These spots may becomes brittle and then crack it in the center. To prevent this, plant pathogen-free seeds, rotate crops regularly and apply appropriate fungicides when needed.
Anthracnose will cause small circular dry spots that are gray or tan in color on the leaves. If there are too many spots, the leaves can die. This is caused by a fungus that can overwinter in leaf debris and on weeds. The disease prefers to emerge in moist, warm conditions. Treat seeds with hot water prior to planting, practice crop rotation and plant seeds in an area that has adequate soil drainage.
Treat seeds with hot water prior to planting, practice crop rotation and plant seeds in an area that has adequate soil drainage.
Damping off causes seedlings to die after germination. The stem will appear constricted and twisted. This disease is more likely to appear in seedlings when temperatures are cool.
Downy mildew will cause irregular yellow patches on stems which then turn light brown. There will be gray growth on the bottom of the leaves. The disease prefers to emerge when the conditions are cool and moist. To manage this disease, remove all crop debris after you harvest the kale. Also practice regular crop rotation and apply appropriate fungicides when needed.
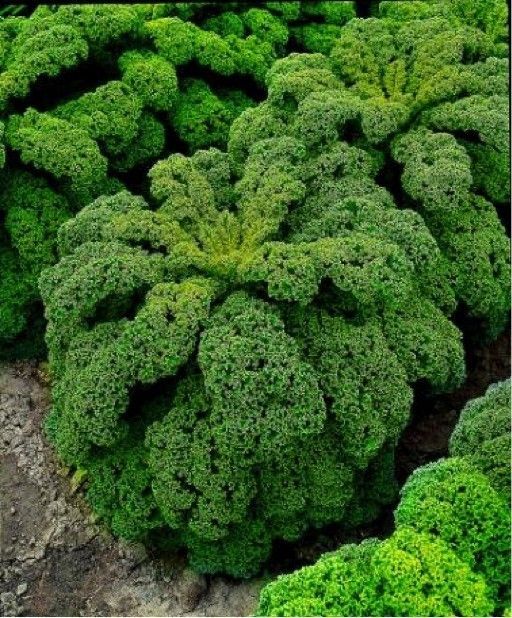
10 Tips for Growing Kale
It’s packed with fiber, iron, calcium, and vitamins K, A, and C. Plus, your favorite salads just aren’t the same without it. Yup, kale is pretty amazing — and a great way to get more of it is by growing your own.
Related Story
- 45 Quick and Easy Kale Recipes
Even if you’re not a seasoned gardener, it’s easy to find success with this green. Just three or four plants can supply a family of four with a nice weekly harvest. You don't even need a backyard; kale grows great in containers, too, like this Dura Cotta Planter Bowl. Just make sure your pot has at least a 12-inch diameter and use well-draining potting mix.
Just three or four plants can supply a family of four with a nice weekly harvest. You don't even need a backyard; kale grows great in containers, too, like this Dura Cotta Planter Bowl. Just make sure your pot has at least a 12-inch diameter and use well-draining potting mix.
Here’s how to grow your own kale, whether you’re planting directly into the ground or using a container garden.
Starting Kale Seeds
Though kale will produce in warm weather, it has a tendency to become woody and bitter. It’s best when allowed to mature in cool temps. Start spring seeds indoors approximately six weeks before the last frost to give plants a chance to mature before summer’s worst heat.
Direct seeds will mature in 55 to 75 days, while transplants will speed up the process, ready for harvest in about 30 to 40 days. Plant your crop again in the fall, six to eight weeks before the first expected frost — you can keep harvesting even after snowfall. Plant more seeds or transplants every two to three weeks for a long, continuous harvest.
Plant more seeds or transplants every two to three weeks for a long, continuous harvest.
Planting Kale
lauraag//Getty Images
If you’re planting during the cool season, do so where your crop will get full sun. If you’re growing during warmer temps, plant in partial shade.
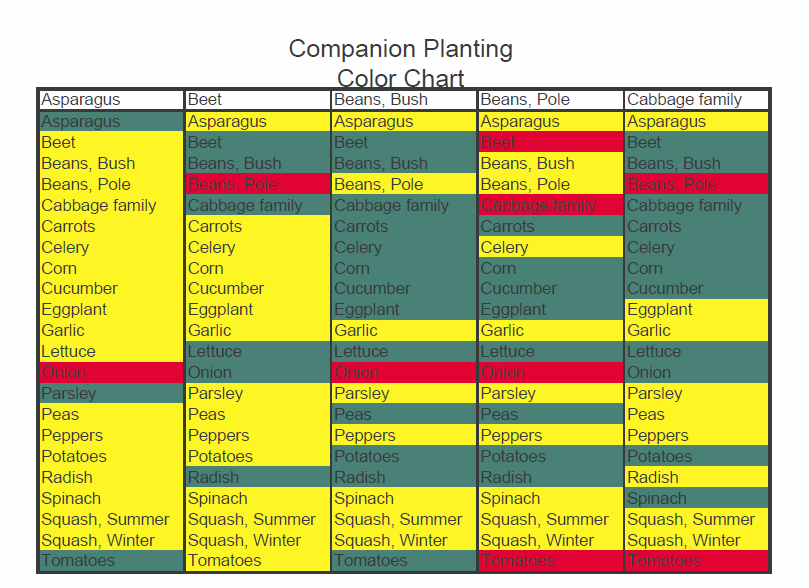
Kale is buddy-buddy with beets, celery, cucumbers, herbs, onions, spinach, chard, and potatoes. It isn’t happy growing next to beans, strawberries, or tomatoes.
Keep soil moist to encourage consistent growth. Dress your soil with compost every six to eight weeks. A seaweed emulsion, like Neptune’s Harvest Hydrolized Fish and Seaweed Fertilizer, can help boost growth when used lightly throughout the entire season.
Caring for Kale
Protect young plants with row covers like this Agfabric Floating Row Cover to stave off flea beetles and provide a buffer against any unexpected temperature dips. Picking off unhealthy-looking leaves and keeping your plants well-fed with compost and water will also reduce insect damage in your vegetable garden,
Picking off unhealthy-looking leaves and keeping your plants well-fed with compost and water will also reduce insect damage in your vegetable garden,
Kale’s roots run horizontally from the central stem. Use straw or grass mulch at the base of your plants to keep the soil cool, conserve moisture, and make it easier for roots to feed.
When things get really hot in the summer, pull plants up by their roots to make room in your garden for more heat-loving veggies until fall arrives for another round of planting.
Harvesting Kale
mphillips007//Getty Images
It’s time to harvest when the leaves are about the size of your hand. Pick them one by one, starting with the lowest, outermost leaves and working toward the center. Always leave a few of the small central leaves attached to encourage growth. In most cases, you’ll be able to harvest from the same plant again in five to seven days.
Diseases of cabbage, photo, description and treatment, in the open field and Greenhouse
Author Maria Chursina For reading 20 min. Views 51k. Posted by
Views 51k. Posted by
Cabbage is one of the most popular vegetables, along with cucumbers and tomatoes. To get a good harvest, it is important to detect and eliminate problems in your area, such as cabbage diseases or pests, in time.
Cabbage diseases do not have a specific regional status; gardeners, gardeners and farmers face them throughout Ukraine. Diseases spoil the presentation, reduce the yield on the site. They can infect the plant at all stages of plant development. nine0005
In this article you will find a brief description of each common cabbage disease, photo and description. In conclusion, recommendations will be given: how to treat cabbage from diseases, how to avoid their development.
Content
- Kila cabbage
- Root rot
- peronosporosis or false powdery mild of cabbage
- Fusarious wilting of cabbage (fusariosis, jaundice)
- cabbage
- Fittoros0015 Table of resistance of varieties and hybrids of cabbage to diseases
Kila of cabbage
Description
kohlrabi.
Kila is caused by a fungus. The source of infection can be soil and cruciferous weeds. Dangerous for both open ground and greenhouses. nine0005
The disease is dangerous because it makes white cabbage seedlings unsuitable for planting and negatively affects the development of adult plants. Actively progresses on waterlogged soils with high acidity.
Signs of cabbage damage by clubroot: swollen roots, formation of outgrowths on them, yellowed and sluggish leaves, poorly developed heads.
Methods of struggle with clubbed:
Agricultural technology:
General agrotechnical control measures for cabbage cultivation.
Agrochemistry:
Treatment of cabbage leaves with Phytosporin will reduce the chance of plants contracting this disease (3 g per 1 liter of water).
Preventive spraying of the soil with Fundazol (10-15 g per 10 liters of water) before planting seedlings.
Seed treatment with Prestige will not only help protect plants from pests, but also prevent fungal diseases. nine0005
Thiovit jet (90-100 g per 2-3 liters of water per 10 square meters)
Agronomist's comment: There are no drugs that treat keelah. There are products that reduce the acidity of the soil, thereby preventing the disease of cabbage with clubroot. Lime will help to equalize the acidity (2-3 tones per 1 ha, 20-30 kg per hundred square meters), but it is very important to know the pH of the soil for this. The disease is especially manifested in the permanent cultivation of cabbage in one place.
Recommended varieties and hybrids resistant to keel:
Dithmarscher, Kilastor F1, Bronco F1, Yamori F1.
Root rot
Description
These diseases of cabbage seedlings affect white, cauliflower, Beijing, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi and broccoli, severely damaging seedlings.
Root rot fungus lives in the soil and develops actively under favorable conditions.
Signs of root rot: brown color of seedling stems, formation of dark constrictions on it.
Blackleg control methods:
Agrotechnics:
Use of healthy seed. Removal of the remains of old and infected plants from the site. The correct sequence of planting vegetables in one place. Soil liming. Choosing the right irrigation system. Organization of a suitable light regime and temperature. nine0005
Agrochemistry:
An effective preventive measure against cabbage diseases is Trichodermin (biological) and similar fungicides containing the Trichoderma fungus (say, Mycohelp) and Previkur Energy - chemical.
Agronomist's comment: It mainly occurs when the seedlings are overcooled and flooded.
An effective measure of protection would be to shed the earth in advance, and preferably with the first irrigation with Propamocard solution (Magnicur Energy or Energodar (4-5 g per 1 liter of water).
Varieties and hybrids of cabbage resistant to root rot:
Akira F1, Ankoma F1, Valentina F1.
Downy mildew or downy mildew of cabbage
Description
The second name is downy or fake powdery mildew. It affects white cabbage, cauliflower, Savoy, Beijing, broccoli, kohlrabi.
A dangerous disease of cabbage seedlings, also the greatest threat to the testes. It spreads quickly, like other diseases in the open field, as a result of which the plant dies, affected by rot. nine0005
Downy mildew can also form on cabbages already in storage, causing the stalk to rot and making the heads unsuitable for further use.
Favorable conditions for the development of cabbage disease: high humidity, too thick seedlings.
Signs of downy mildew/downy mildew: yellow or brownish spots on the top of the leaf, gray coating on the underside of the leaves.
Control methods:
Agrotechnics:
General agrotechnical control measures for the cultivation of cabbage .
Agrochemistry:
To prevent the disease, seedlings can be treated with Bordeaux liquid.
If there are signs of downy mildew in seedlings, the fungicide Ridomil Gold can be used.
Agronomist's comment: Alternate change of fungicides during crops will prevent fungus pathogens from developing immunity to drugs.
Downy mildew resistant varieties and hybrids:
Pushma F1, Reima F1.
Fusarium wilt of cabbage (fusarium, jaundice)
Description
Fungal disease of cabbage, leading to the death of most of the crop plants in the area. Its main purpose is seedlings and adult plants of cabbage, savoy, cauliflower and broccoli. nine0005
Its main purpose is seedlings and adult plants of cabbage, savoy, cauliflower and broccoli. nine0005
The optimal conditions for the development of Fusarium wilt are hot and dry weather.
Symptoms of cabbage disease:
In seedlings. Yellowing of leaves. When cut, there are noticeable brown rings on the petiole.
On mature plants. Leaves fall off, turn yellow. Brown, dark rings on sections of leaves and stems.
Control methods
Agrotechnics:
General agrotechnical control measures for the cultivation of cabbage .
Agrochemistry:
An effective prevention against diseases of cabbage seedlings will be treatment with Fitosporin (paste). Before transplanting seedlings, you can put their roots in the solution for 2 hours.
Agronomist's comment: A very effective way for vegetable growing to combat Fusarium wilt is the use of the drug Fundazol.
nine0005
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Kolobok, Valentina F1, Bronco F1, Megaton F1.
Fusarium irradiationCabbage blight
Description
It is also dry rot. The spectrum of damage to this disease is quite wide: testes, seedlings and adult plants of all types of cabbage. But most severely this disease affects the white-headed. Even on heads of cabbage placed in storage, it continues to develop, leading to their rotting. nine0005
Develops more intensively in high humidity and warm climate. Entirely affected heads of cabbage disease completely rot, partially infected ones slow down in development, lose their presentation.
Signs of the disease: darkening of the bottom of the stem on seedlings. In adult plants, it can be seen by brown spots with a dark dot in the middle. Dry rot on the roots and yellowing are also characteristic. Maybe be similar in appearance to root rot (blackleg), but different from it color. nine0005
nine0005
Control methods
Agrotechnics
General agrotechnical control measures in the cultivation of cabbage 905 .
To avoid the formation of dry rot in heads of storage, it is necessary to sort the harvested crop and organize the optimal temperature regime. Heads with mechanical damage to cabbage are very vulnerable to this disease, so you should avoid them. nine0005
Agrochemistry
Improving the resistance of cabbage heads to cabbage disease is facilitated by treatment with a mixture of trichodermin and phytocide P (10 ml of each of the preparations), preferably in conjunction with an adhesive or liquid soap. Seedlings are treated immediately after transplanting into open ground, and then every three to three and a half weeks.
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Langedijker, Turkis, Kraft F1.
Alternaria
Description
A.k.a. black spot. A fungal disease that can spread through seeds, soil, wind. It affects both seedlings and adult plants. Spoils the appearance of heads of cabbage, makes them unsuitable for sale and consumption.
Signs of Alternaria: cracking at the end of the pod, dark spots on the leaves with a yellow border.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
General agrotechnical control measures for the cultivation of cabbage .
Agrochemistry
For prevention, folk remedies such as Bordeaux liquid and copper oxychloride are used.
Also increases the resistance of plants Fundazol, sprayed in the vegetation phase.
The fungicide Quadris is used to prevent early blight in cabbage or after early symptoms appear.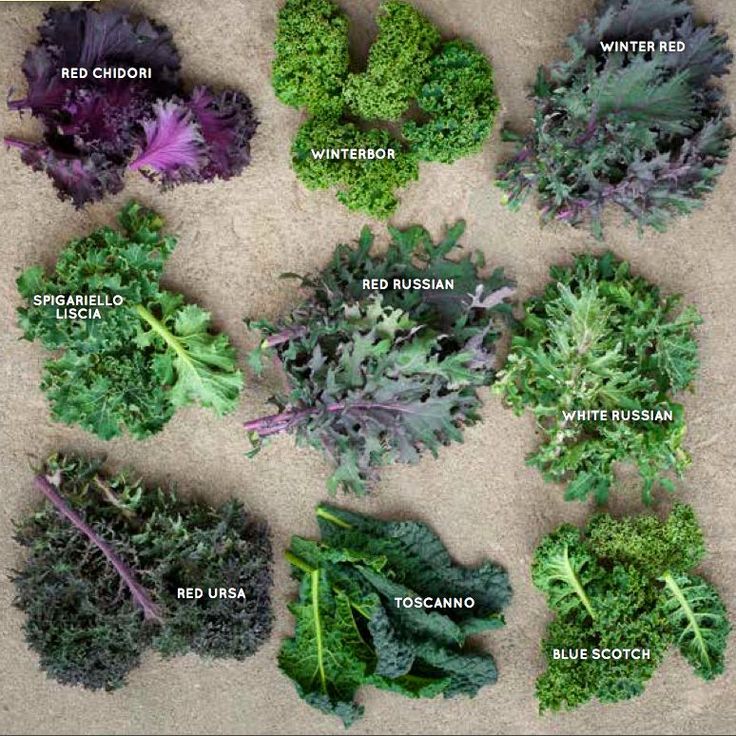 nine0005
nine0005
Agronomist's comment: for prevention preparations Champion, Quadris, for treatment Switch, Speed.
Resistant varieties and hybrids :
Supermarket F1, Galaxy F1, Arles F1, Nozomi F1.
Cabbage late blight
Description
A fungus that causes cabbage to slowly die, enters the plant from the soil. More dangerous for tomatoes or cucumbers, but sometimes affects some types of cabbage. Favorable conditions for the development of late blight are rainy weather before harvesting and during harvesting. nine0005
Signs of the disease: browning of leaves, plant tissues turn gray and die.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
Agrochemistry
Preventive treatment with Quadris.
Agronomist's comment: Ridomil or Acrobat can be used to counteract. Be sure to pay attention to the concentration (100 ml per 10 liters of water) . An excellent choice would be fungicide Charivnyk, which is a mixture of Ridomil and Acrobat.
Gray rot (Botrytis)
Description
Fungus affecting cabbage and other cruciferous plants. The cabbage disease spreads from the bottom of the plants, initiating rotting of the roots and the heads themselves, from which the plants most often die.
Favorable conditions for the formation of gray rot - rainy weather, frost and mechanical damage to plants. nine0005
Gray rot is especially dangerous for heads of cabbage placed in a cellar / storeroom / warehouse, reducing their shelf life to 2-3 years, or even completely destroying them.
Signs of gray rot:
Harvested: gray coating, slime on leaves. In field , gray mold rarely develops, usually recognized by brown spots on the leaves.
In field , gray mold rarely develops, usually recognized by brown spots on the leaves.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
General agrotechnical control measures for cabbage cultivation .
Proper irrigation system (warm and infused water). Optimal top dressing mode (complex fertilizer). Fruit picking at the optimum time (dry weather).
Agrochemistry
Preventive treatment with Fitosporin M. Dilute 10 ml of fungicide into a 10-liter container. That's enough for about a hundred. nine0005
Treat seedlings for the first time 10 days after transplanting, and a second time after 14-21 days.
Spraying plants with Bordeaux liquid solution.
Agronomist's comment: When cabbage is affected by gray and white rot, Switch, Skor, Blue Bordeaux will help.
They are used as a prophylaxis against these diseases, already affected heads of cabbage should be thrown away to avoid the spread of the fungus to the remaining crop.
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Amtrak F1, Galaxy F1, Akira F1.
White rot (sclerotinia)
Description
A disease of cabbage that mainly affects mature plants in the open field. Dangerous for all types of cabbage.
In greenhouses and other shelters, sometimes affects seedlings. It actively begins to manifest itself before harvesting, further provoking rotting of heads of cabbage in storage. Conditions for intensive development: frost and high humidity. nine0005
Signs of the disease: mucus on the outer leaves, on the head and leaf apparatus, white mycelium is formed, similar to cotton wool, dark-colored structures (sclerotia) appear on the upper side of the head.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
Heads already affected will have to be discarded .
Agronomist's comment: When cabbage is affected by gray and white rot, Switch, Skor, Blue Bordeaux will help. They are used as a prophylaxis against these diseases, already affected heads of cabbage should be thrown away to avoid the spread of the fungus to the remaining crop.
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Kraft F1, Akira F1.
Powdery mildew
Description
A disease of cabbage that acts very quickly and is transmitted very easily. Its main targets are seedlings and seedlings, sometimes it infects heads of cabbage in storage. It is dangerous for seedlings in greenhouses and greenhouses, sometimes it infects plants in open ground.
Like many other diseases of white cabbage, powdery mildew progresses with high levels of humidity and too dense crops. It is also dangerous for Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi and broccoli. nine0005
Causes dropping of seedlings, deterioration of seed development, rotting and death of plants in storage.
Signs of the disease: yellow spots on the top of the leaf, gray bloom on the underside.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
Organization of proper watering. Irrigation is carried out under the root, so as not to overmoisten the leaves, thereby creating favorable conditions for the development of the disease. nine0005
Agrochemistry
For the prevention and treatment of powdery mildew, Phytosporin can be used, which is applied by spraying.
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Slava, Amager, Jetodor F1.
White rust
Description
Great danger for open ground. Conditions for the intensive development of the disease: high humidity, lingering fogs, heavy dew. Because of this fungus, plants lose their marketable appearance, develop poorly. It affects all major types of cabbage. nine0005
It affects all major types of cabbage. nine0005
Signs of cabbage disease: white cavities with pus on the leaves and stem, deformation of the leaves, violation of their structure, twisting of the tips.
Methods of struggle
Agricultural technician
General agricultural control measures when growing cabbage .
Agronomist's comment: Topaz fungicide will help well (0.125–0.15 per hundred square meters). nine0005
Agrochemistry
When symptoms of the disease appear, spraying with Ridomil can be used.
Cabbage Turnip Mosaic
Description
The disease often occurs outdoors. It affects both seedlings and mature plants. It infects all types of cabbage (most often white-headed, broccoli and cauliflower). It negatively affects the marketable appearance of the crop, causes growth retardation, renders healthy heads unusable for further use. nine0005
It negatively affects the marketable appearance of the crop, causes growth retardation, renders healthy heads unusable for further use. nine0005
Actively progresses in warm and arid climates, a large number of weeds and pests.
Signs of the disease:
Light green spots on the bottom of the cabbage leaves, then the tissue begins to die in these places, black spots are observed on the surface of the leaves. Leaf deformation, mosaic, slow development and swelling are also observed.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
General agrotechnical control measures for cabbage cultivation .
Continuous prevention and control of aphids, the main vector of the disease.
Agrochemistry
Agronomist's comment: Turnip mosaic cannot be cured. Therefore, prevention is very important.
For example, treatment with Farmayod.
Vascular bacteriosis of cabbage
Description
Bacterial disease mainly affecting cabbage seedlings after transplanting into the field. It provokes a strong growth retardation, does not allow a head of cabbage to form. Progresses rapidly in hot weather and humid environments. Distributed among the main varieties of cabbage
Signs of the disease: yellowing of cabbage leaves along the edges, then it progresses to the middle, the veins darken, darkening is found on the cut of the stem and stalk. nine0005
Control methods
Agronomist's comment: Kazumin – is an excellent antibiotic for plants. There is also a more affordable way - treatment with metronidazole, available at any pharmacy, (in liquid form, 0.
5-1 l per 1 ha)
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Bruno F1, Zoltan F1, Transam F1, Succesor F1.
Mucous bacteriosis of cabbage
Description
Bacterial disease, mainly affects adult plants, testes rarely get sick. May progress further in heads of cabbage in storage. It leads to the fact that the middle of the head becomes soft, exudes a pungent odor. Dangerous for almost all types of cabbage.
Begins active development with heavy precipitation, high moisture levels. nine0005
Symptoms: on rot, mucus, and an unpleasant odor form in infected places.
Control methods
Agrotechnics
Control of disease-carrying pests (cabbage fly, bed bugs).
Agronomist's comment: I recommend treatment with metronidazole, you can buy it at any pharmacy (liquid, 0.
5-1 l per 1 ha). nine0005
Resistant varieties and hybrids:
Cossack F1, Dijon F1, Typhoon F1.
As a conclusion, it can be said that in order to counteract cabbage diseases, it is enough to adhere to the basic rules of agricultural technology: crop rotation, weeding, removal of old plant residues from the site, use of healthy seed, optimal thickening and watering.
It is possible to treat a certain disease, but it is much easier and more effective to use both agrotechnical measures and fungicides as a preventive measure, preventing infection. nine0005
Cabbage diseases by growth phase (seeds, seedlings, transplanted plants, heads in storage)
Some cruciferous diseases appear only at a certain growth stage, others can infect it at any growth phase. This block will show a list of popular diseases by cabbage growth phases, both mature plants and cabbage seedlings, photo description and treatment are indicated in the list above.
Cabbage seedling diseases
- Mucous bacteriosis
Table Cabbage diseases Treatment
| The name of the drug | Disease, against which is treated | The rate of consumption of the drug (l/ha, kg/ha) | 9103 9005 FASK 9101 Kila Fusarium wilt Powdery mildew | 3 g per 1 liter of water | 200 g | |||||||
| Bordeaid liquid | Black leg False powder dew | 1 % solution | gNOVECHIC | COMPLIA ml per 10 l of water | 10 ml, 60 ml, 500 ml, 1 l, 5 l | |||||||
| Trichodermin | Black leg Phomosis | 100 ml per 10 l of water 1030 | ||||||||||
| RIDOMIL GOLD | False powder dew | 2.5 | 25 g, 50 g, 5 kg | |||||||||
| Foundation | alternariosis Fuzario vehicle 4-5 .  kv. kv. | 10 g, 50 g | ||||||||||
| Quadris | Phytophrosis White rot Gray rot | 0.6 g | 6 ml, 100 ml, 300 ml, 1 l | |||||||||
| 40 g | ||||||||||||
| Energodar | False powder dew | 2.5-3.0 L | 30 ml, 500 ml | |||||||||
| Magneck Garda (Teldor) 50% | Seed Gnil | 0 8-1.0 | 8 g, 5 kg | |||||||||
| Salto | Fusarious wilting Fomoz Fulture Rosa Gray and white rot | 15-20 ml per 1 hundredth | 30 ml0056 To prevent the appearance of diseases on cabbage, first of all, it is necessary to choose healthy seeds or seedlings.
a) Weather and climatic conditions in your area. nine0085 For example, in the southern regions of Ukraine (Nikolaev, Kherson, Odessa regions), the soil will warm up faster, which will allow sowing earlier. b) Seed germination time. The period from planting to when the seed hatches to the surface is often not taken into account, and therefore errors in the calculations occur. c) Vegetation phase of the selected variety or hybrid. It is important for a gardener to know how long it will take from germination to picking ripe heads of cabbage. nine0005 Approximate calculation scheme: Taking into account the climate, we determine the date when the seedlings will need to be transplanted to the site. From this day, we calculate the right moment for planting seedlings, taking as a basis the ripening period of the variety / hybrid.
Stability of varieties and cabbage hybrids to diseases
|
 nine0016
nine0016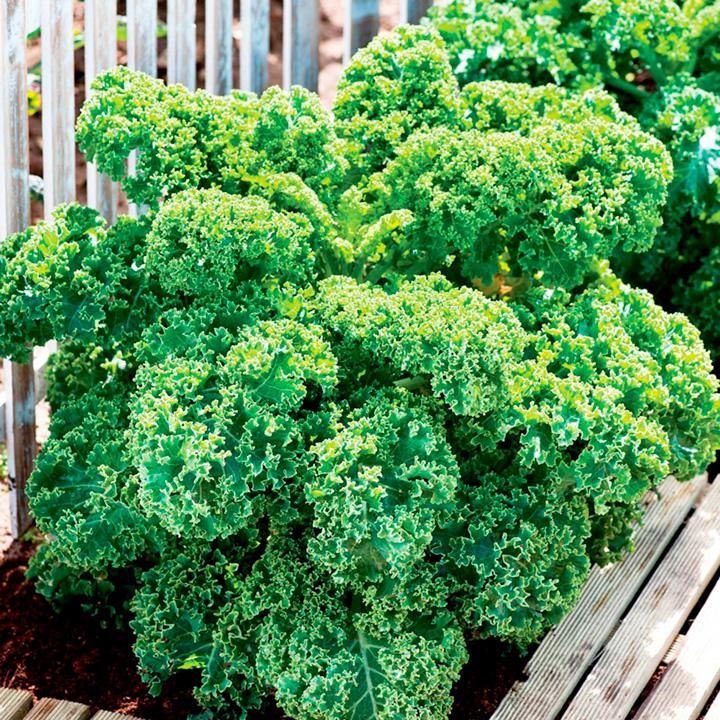  This directly depends on the choice of variety / hybrid and planting time.
This directly depends on the choice of variety / hybrid and planting time.  Minus the number of days it takes for the seeds to germinate and we have an approximate sowing date.
Minus the number of days it takes for the seeds to germinate and we have an approximate sowing date. 
 It is necessary to maintain the optimal amount of moisture, without drought and waterlogging.
It is necessary to maintain the optimal amount of moisture, without drought and waterlogging.  Preparing the future storage for the harvest - cleaning and disinfection, organizing the correct temperature (0-1 C © ).
Preparing the future storage for the harvest - cleaning and disinfection, organizing the correct temperature (0-1 C © ).  Since the larvae or eggs of pests are small (it is easier to detect them with a magnifying glass), sometimes such a pale color is mistaken for a lack of nitrogen. And urgent measures are needed, otherwise you can be left without a harvest. nine0005
Since the larvae or eggs of pests are small (it is easier to detect them with a magnifying glass), sometimes such a pale color is mistaken for a lack of nitrogen. And urgent measures are needed, otherwise you can be left without a harvest. nine0005  Moreover, the use of this drug eliminates the need to apply under the root or give out through the drip tape Bazudin, a rather dangerous substance that poisons the soil microflora in the fight against cabbage fly larvae. nine0005
Moreover, the use of this drug eliminates the need to apply under the root or give out through the drip tape Bazudin, a rather dangerous substance that poisons the soil microflora in the fight against cabbage fly larvae. nine0005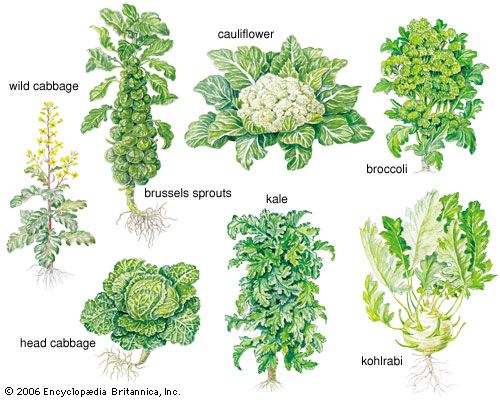  And this is very little. And the content of microelements in them is a fraction of a percent. As a result, the practical vegetable grower is not always satisfied with the result of such treatments. nine0085
And this is very little. And the content of microelements in them is a fraction of a percent. As a result, the practical vegetable grower is not always satisfied with the result of such treatments. nine0085  nine0005
nine0005  This is achieved by increasing the concentration of working solutions up to 300% or more of those recommended by the manufacturer. Naturally, such concentrations significantly increase the insecticidal effectiveness of treatments. nine0005
This is achieved by increasing the concentration of working solutions up to 300% or more of those recommended by the manufacturer. Naturally, such concentrations significantly increase the insecticidal effectiveness of treatments. nine0005 
 This is especially important in hot climates. nine0005
This is especially important in hot climates. nine0005