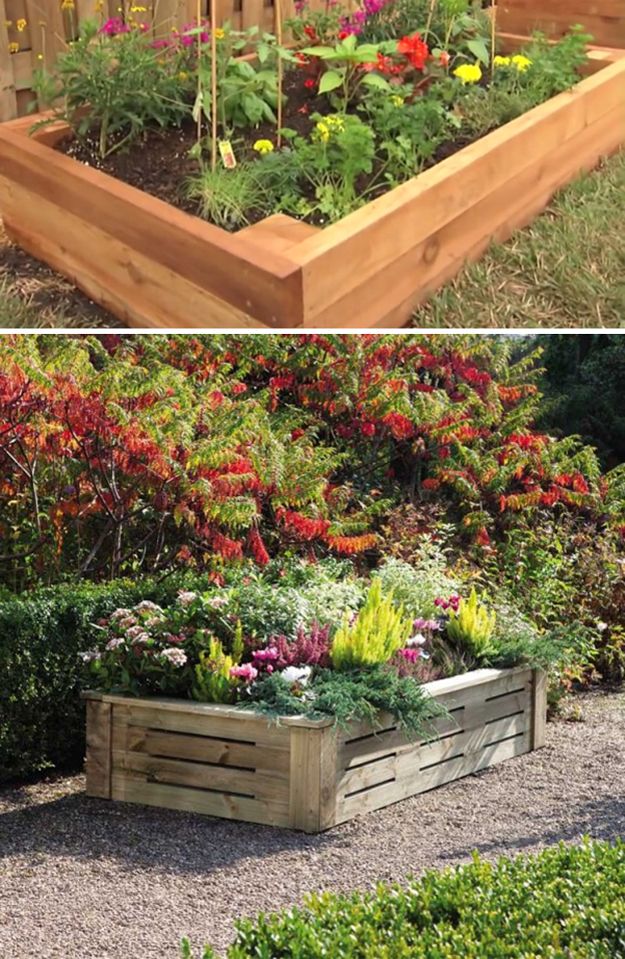
How deep should a raised flower bed be
How Deep Should A Raised Garden Bed Be? – Vego Garden
When deciding on a raised garden bed, one of the major factors is the depth requirements of the raised garden bed. If you’re placing your raised bed on a patio or a terrain where the soil underneath is not conducive to growth, then it is important to grow your plants within the parameters of the bed itself. A raised bed should be able to blend in well with its surroundings as well as adequately support the roots of your plants. The required soil depth depends on the types of plants grown, the soil conditions, and desired aesthetic. Other important considerations include the shape, size, and material chosen for the raised garden bed. Since there are a dazzling array of designs available worldwide, choosing one can be a tough decision to make.
However, the large variety of patterns available guarantees that there is a match for every type of landscape, budget and style. A raised bed can either be informal or formal, depending on your preference and garden situation. We recommend displaying vegetable gardens in modern, industrial metal beds, which can prove to be an attractive focal point of your garden, and significantly brighten up dull spaces or outdoor dining areas. It is important to keep in mind that the size of the bed should be proportional to the space around it. If you have limited space, it is best to buy modular raised garden kits, which will allow you to customize your beds based on your available space. This article examines the soil depth requirements for various types of yards and plants.
Drainage: Whether it be an irregularly-shaped perennial border garden that sits behind a dry-stone wall, or a metal raised bed in a vegetable garden, one should always consider the depth of the raised bed carefully. A raised bed does not always require a significant depth for it to be effective. They should have at least 8 inches of soil depth to accommodate the root systems of plants, because the majority of plant roots require 6 – 8 inches of soil for healthy root growth.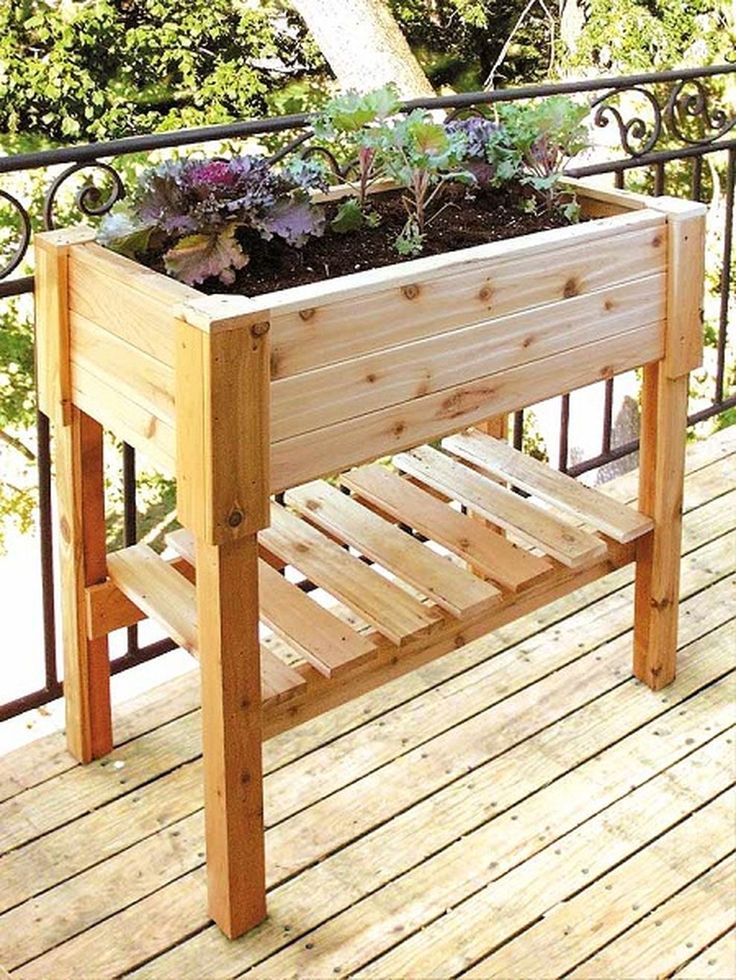 A depth of 8 – 12 inches will suffice for most gardening situations.
A depth of 8 – 12 inches will suffice for most gardening situations.
Because of the excellent drainage properties of raised beds, it is possible to grow an abundance of vegetables in a limited amount of space. In cases where drainage is an issue, or if the plants that you are planning to grow prefer an environment with drier soil, then the depth of your raised garden bed can be taller, which can then be filled up with a porous growing medium.
Material: The material you use for a particular raised bed should be durable, attractive and stable. It is important to consider the material of your garden bed, which determines how well it blends in with the landscape. The sides of the bed lend structural support to the and help contain the soil in a particular space. The sides of raised garden beds can be metal panels, wood, or brick and stone. While it is important to consider the depth of your raised garden beds when browsing for raised garden bed designs, it is also important to consider the material of your garden bed.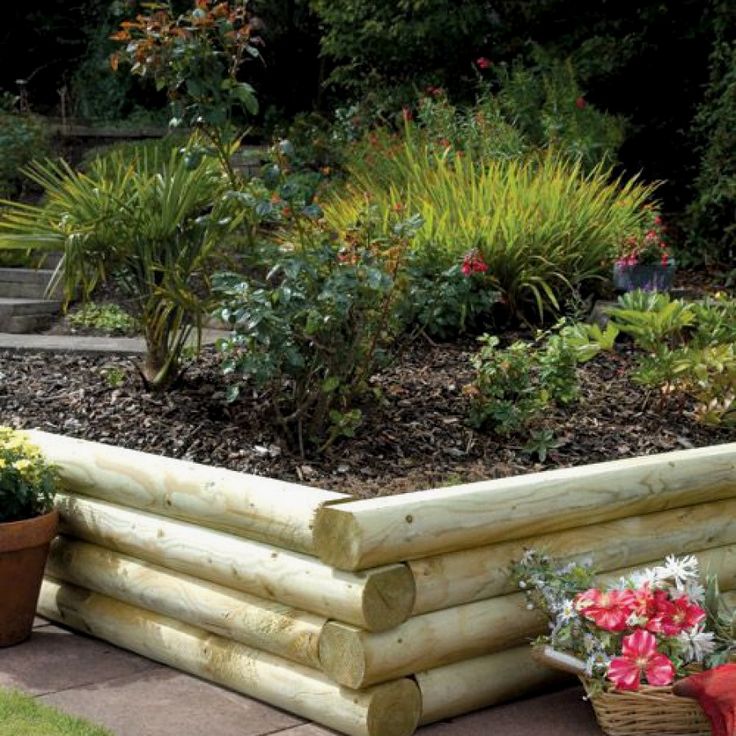
Traditional metal panels, while easy to install, can rust over time, diminishing its attractiveness and usefulness. Wood will rot in as little as one season. Stone and concrete blocks can be expensive to install. Also, many gardeners do not want the hassle of buying raw material and assembling them for a DIY raised garden bed project. We recommend Vego Garden beds for an easy solution. Vego raised garden beds are made of a specialized rust and corrosion resistant metal and lend a clean, modern aesthetic to your garden. Our kits are easy to assemble, and complete with heavy duty rubber edging along the top to ensure a safe and fun experience.
Double Digging: Some gardeners choose to dig below the ground using their shovel to create more space for their roots, especially if they have a crowded or shallow garden bed. This process, known as double digging, can be time consuming and arduous. Vego Garden beds are tall enough that you don’t have to dig into the ground. You can simply place your raised bed anywhere in your yard after clearing the ground of debris.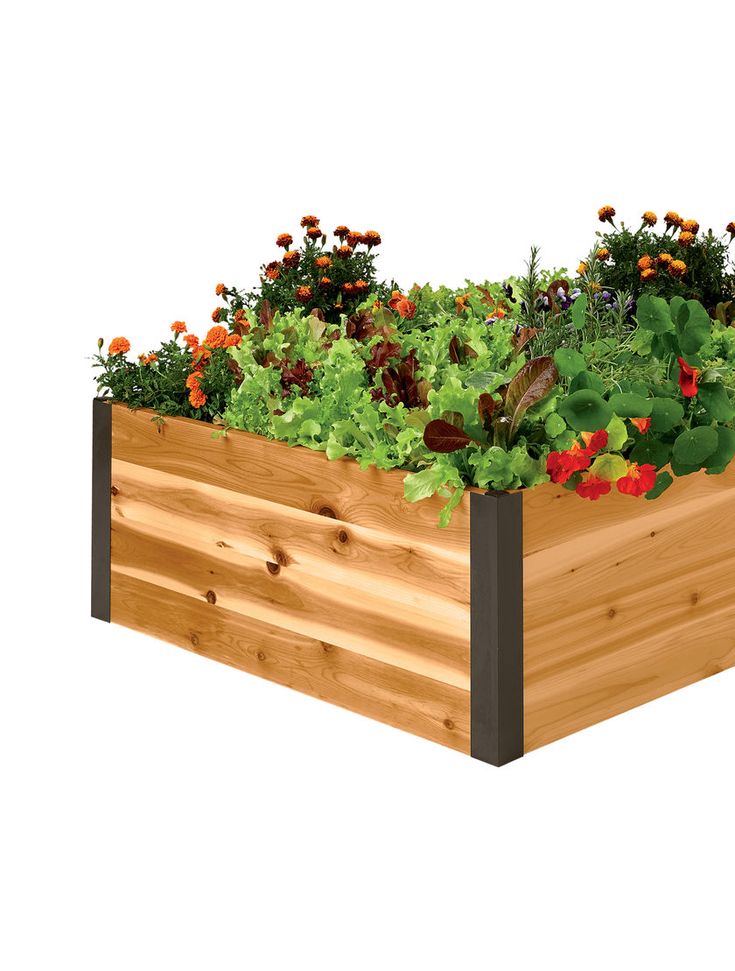
Gardeners should slightly overfill their gardening beds, because the soil will compact over time with watering. As a tip, you should add an extra 2 inches of soil over your garden bed, and water the soil to see how much it compresses.
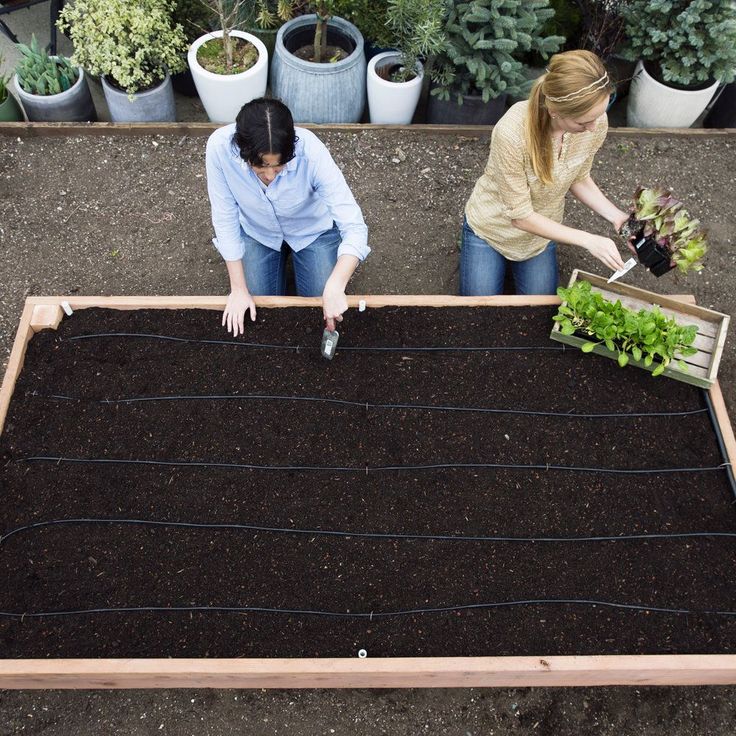
Vegetable Beds: On the other hand, when it comes to vegetable beds, the bed must be approximately 12 to 18 inches deep to ensure adequate depth for the roots of your plants. This is especially important if your raised bed is placed on cement or the patio, which will inhibit roots from growing deeper into the ground. Below are the root depth requirements of a few common garden plants. Since our garden beds are 17″ and 32″ deep, they are deep enough to cultivate a medley of vegetables, including those with deep root systems. A deeper bed also allows for more moisture retention, leading to less watering and chance of drying out.
The following plants have 12 - 18″ roots
- Garlic, onions, chives
- Lettuce, brussels sprouts, spinach
- Corn, cabbage, radishes
- Strawberries
The following plants have 18 - 24″ roots
- Beans, peas
- Cantaloupes, squash, eggplants
- Carrots, turnips, beets
- Potatoes
Below are plants with deeper systems of 24 - 36″ roots
- Artichokes, asparagus
- Parsnips, rhubarb
- Sweet potatoes, pumpkins
- Watermelons
When planning out the components of your raised garden bed, it is important to orient your crops so that taller plants don’t block shorter plants from receiving sunlight. Beds should face South horizontally, which optimizes sun exposure across the bed and prevents neighboring plants from shading each other as the sun moves from East to West. If you are growing a variety of plants, you can orient your bed vertically (North to South), positioning the taller plants in the back to prevent them from shading shorter plants. Do not situate your garden bed in windy locations or near wet and marshy areas.
Beds should face South horizontally, which optimizes sun exposure across the bed and prevents neighboring plants from shading each other as the sun moves from East to West. If you are growing a variety of plants, you can orient your bed vertically (North to South), positioning the taller plants in the back to prevent them from shading shorter plants. Do not situate your garden bed in windy locations or near wet and marshy areas.
It is important to know the height of each crop at maturity in order to plan out your planting arrangements. To illustrate, shorter plants such as lettuce and radishes should be planted on the south side, while the tallest plants should be planted on the northern side of the area. If you have a trellis, it is important to keep it near the rear wall, as those plants can block out a large amount of light. Below are the heights of some popular vegetables at maturity:
| Vegetable | Size at Maturity | Vegetable | Size at Maturity |
| Artichokes | 4' - 5' | Leeks | 12" – 24" |
| Arugula | 8" - 10" | Lettuce | 6" – 12" |
| Garlic | 12" – 24" | Onions | 8" – 24" |
| Corn | 4' – 8' | Peas | 2' – 6' |
| Beans (lima) | 24" – 36" | Watermelon | 12" – 36" |
| Beans (pole) | 8' – 12' | Parsnips | 6" – 18" |
| Tomatoes | 2' – 8' | Potatoes | 12" – 30" |
| Cabbage | 12" – 18" | Turnips | 6" – 12" |
If you experience mobility issues, back strain, or simply dislike bending over, a taller raised garden bed will improve your gardening experience.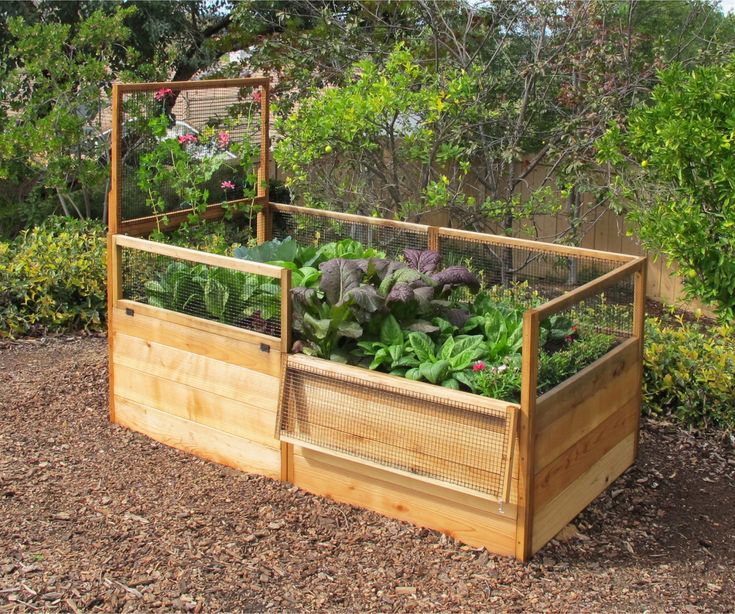 Our extra tall 32″ garden bed kits significantly reduce back strain when you are tending or harvesting your garden. Whether you are a more experienced gardener or a beginner, we definitely recommend you invest in a raised garden bed to reduce the toll that straining your back can have on your health.
Our extra tall 32″ garden bed kits significantly reduce back strain when you are tending or harvesting your garden. Whether you are a more experienced gardener or a beginner, we definitely recommend you invest in a raised garden bed to reduce the toll that straining your back can have on your health.
32" Extra Tall 9 In 1 Modular Metal Raised Garden Bed Kit
$369.95 $319.95
Our extra tall 32" height eliminates bending and strain on your back when you tend to your garden, as well as creates plenty of space for healthy roots. …
About Vego
At Vego Garden, our goal is to redefine Raised Garden Beds. The company was founded with the goal of launching a modular metal garden bed system with a 20+ year life expeclancy, utilizing eco- friendly metal materials instead of cutting down trees. We emphasize innovative design and high quality with our products. The name vego carries the spirit of DIY modular raised beds suitable for growing vegetables.
Read More >>
Featured Posts
What is Mulch? Here's Everything You Need to Know
July 31.2022
Watermelon 101: What to Grow & When to Harvest
July 27.2022
Get A $15 OFF + Free Shipping*
Be the first to know about our discounts, and get $15 off your next order of $199 + free shipping
How Deep Should Your Raised Garden Beds Be? • Gardenary
kitchen garden design
Published May 19, 2022 by Nicole Burke
Filed Under:
raised gardens
raised kitchen garden
raised vegetable garden
garden design
Raised garden beds allow us to maximize our growing space, improve drainage, increase productivity, and tend our plants with greater ease. If you're new to the idea of growing in raised beds, explore three reasons raised beds are better for gardening.
My six main beds (pictured above) are two feet tall, as are the majority of the raised beds my Houston-based company Rooted Garden designs.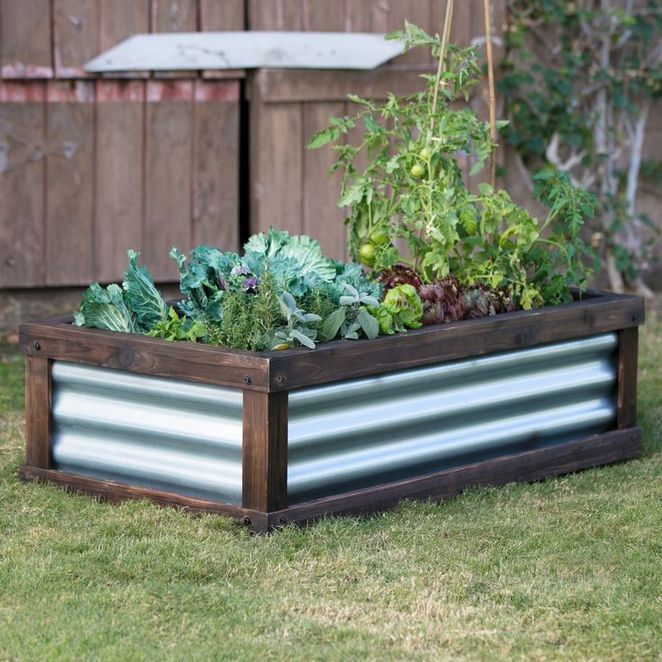 While two-foot beds aren't required to have a beautiful and productive garden, you do need at least 18 inches to grow certain plants.
While two-foot beds aren't required to have a beautiful and productive garden, you do need at least 18 inches to grow certain plants.
Ideal raised bed depth based on the plants you want to grow
Let's look at how deep vegetable plant roots grow and how deep a raised bed would therefore need to be to accommodate the root balls of those plants.
- herbs - 6 inches deep
- lettuce - 6 inches deep
- carrots - 12 inches deep
- radishes - 12 inches deep
- peppers - 12 inches deep
- tomatoes - 18 inches deep
- cucumbers - 18 inches deep
- squash/zucchini - 18 inches deep
- kale - 18 inches deep
Now, let's break down each of these raised bed heights, and then I'll explain why I converted to two-feet-tall raised beds.
What can you grow in a six-inch-deep garden bed?
Six inches is the minimum height I’d recommend. The very first raised bed my family ever put together was only four inches tall, and that height just didn't hold enough good soil we could grow in.
Six inches is enough to grow lettuce greens, herbs, and plants with very shallow root structures.
If you're not quite ready to commit to building a full raised bed, try grabbing a six-inch deep container that's at least a foot wide, and try growing your own lettuce plants. Here are my picks for the best containers to grow salad greens.
What can you grow in a 12-inch-deep garden bed?
One-foot-tall beds are pretty standard in the gardening world. You'll be able to grow plants with deeper roots like carrots, radishes, celery, and peppers, though you might struggle with things like tomatoes, kale, and eggplants, which have really deep root structures.
Personally, I find this height of raised bed hard to tend since you have to bend over more from the waist to reach down.
learn how to build Gardenary-style raised beds
What can you grow in an 18-inch-deep garden bed?
Eighteen inches is the minimum height needed for plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, zucchini, and kale—plants that have a bigger root base and need more nutrients and space to spread out.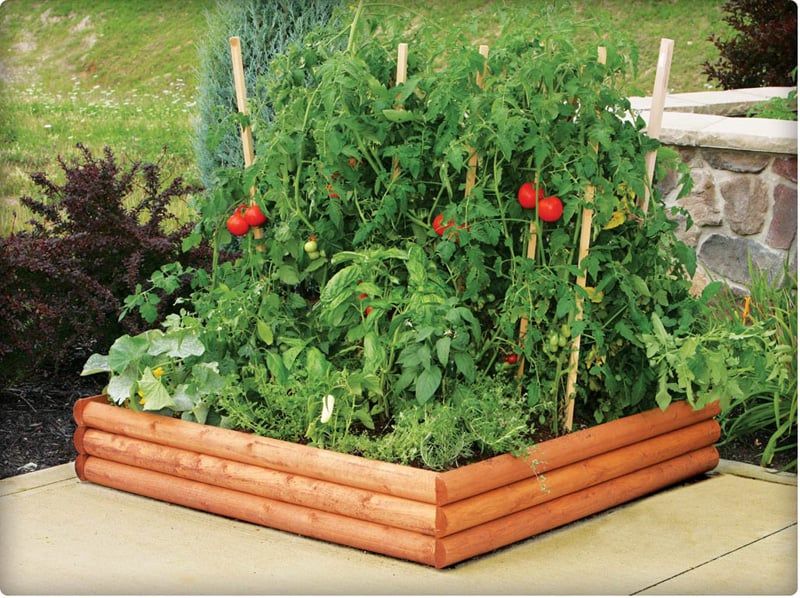
This height also allows for better drainage. Most edible plants hate having their roots stay wet. In-ground plants are more likely to sit in water for longer than plants in a raised bed structure because the soil allows for faster draining, even when there's heavy rain.
What can you grow in a two-foot-deep garden bed?
You can grow just about anything you want in a two-foot-tall raised kitchen garden bed. Few plants really need two feet of depth for their roots, so the extra height is mostly just for the ease and convenience of the gardener. I find the closer a bed is to two feet, the easier it is to tend and harvest from your plants. You bend over from the waist and are at the plant’s level. Garden work should be an enjoyable part of your daily routine, not a chore that hurts your knees and back.
I also prefer this height for aesthetic reasons. Two feet of stone, brick, Corten steel, or cedar planks adds beauty and way more vertical interest to a landscape.
It’s not necessary to have anything over two feet, unless you have a specific reason, like a dog you want to keep out of your beds.
What do you put in the bottom of a raised garden bed?
I get asked this question a lot. The answer is new soil.
This is your opportunity to start fresh with clean, nutrient-rich soil and organic matter. I've seen suggestions to add plastic bottles or trash bags as filler to the bottom of raised beds to save money on soil, but that kind of defeats the purpose of giving your plants' roots all the growing room they need. We want to make sure we're filling up our raised beds from the bottom all the way to the top with great organic matter that will feed our plants, not something that will break down slowly and contaminate your soil with plastic particles.
Before you shovel your new soil in, add some weed barrier cloth to the bottom of your bed to keep weeds out and to prevent your soil from washing out of your bed with the first heavy rain. If you have pests that like to burrow from the ground and eat your plants, add an extra barrier with hardware cloth, as well.
Discover your own gardening strengths and find inspiration to grow your self further with our fun and brief Green Thumb Quiz.
take the quiz
How much soil do I need to fill a raised bed?
Here's a simple soil calculator to add up exactly how much soil you need to fill up your raised bed garden:
STEP 1
Calculate the total width of your garden in feet = W
STEP 2
Calculate the total length of your garden in feet = L
STEP 3
Calculate the total height of your garden in feet = H
STEP 4
Multiply all three together: W x L x H
The answer for this equation is the TOTAL CUBIC FEET of soil you need for your raised beds.
Example
Let's practice with my own six raised garden beds, each measuring 2.5' x 7' x 2'.
To calculate the cubic feet of each bed, we'll use our soil calculator: 2.5 x 7 x 2 = 35 cubic feet for each bed.
Because this setup includes six gardens that all have the same measurement, the total calculation for the full amount of soil needed for these raised beds is: 6 x (2.5 x 7 x 2) or 6 x (35) = 210 cubic feet.
Read our full directions on how to calculate soil for raised beds, plus whether you should buy soil bags or order a truck delivery to fill your total soil requirement.
shop Gardenary's raised garden beds
Not only are raised beds more practical, but they add another layer of beauty as you step into your kitchen garden day after day. I'm confident that you're going to love having raised beds if you choose to install them in your outdoor space, and we've got tons of resources to help you build your own gardening haven and start growing!
Gardenary 365
Gardenary 365 includes full access to our complete Gardenary content library, including Intensive Planting, Herb Garden Guide, Salad Garden School, Microgreens, and Seed Starting Indoors. You'll also learn how to design and build your own raised beds with comprehensive step-by-step guides.
start your 1st lesson
Previous
Next
The Author
NB
Nicole Burke
As founder of Rooted Garden, I've consulted with hundreds of new and experienced gardeners and designed all kinds of kitchen gardens from large to small and everything in between.
Raised flowerbeds in landscape design, photo
Raised flowerbed is one of the ways to change the landscape of the site, make it more original and memorable.
In addition to the design side, there are several practical advantages to creating a tall flower garden.
The size of the flower garden depends on the availability of free space in the yard, and the design can be changed at the request of the owner of the house, you just need to plant different plants every season.
Clean Yard
Raised flowerbed with high sides to keep soil from washing out during rain or irrigation. Thanks to this, the earth does not fall outside the fence, and the paving of the yard always remains clean.
So that the soil does not really get behind the parapet, its level inside the flower bed should not reach the edges by at least 7 cm.
The higher the fence, the more difference can be made between the edge of the parapet and the surface of the flower bed.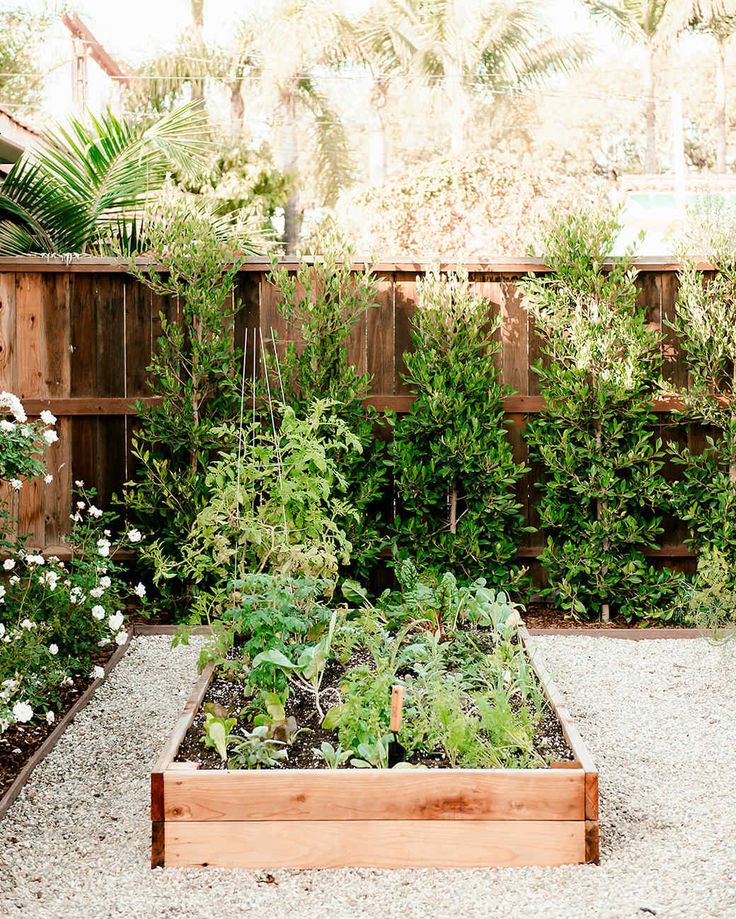 Hence, it is easier to keep the yard clean, so it looks more tidy.
Hence, it is easier to keep the yard clean, so it looks more tidy.
Easy maintenance of the flower garden
Since the surface inside the fence is at least 30 cm higher than the paving level of the yard, the flower garden is easier to care for. You can perform weeding and loosening the soil without leaning too low to the ground. This is especially true for older people suffering from hypertension and heart disease.
The frequency of weeding also decreases, as weed grass settles less often inside the flower bed.
Raised bed reduces water use as the number of irrigations is reduced. This is due to the fact that all the moisture remains inside the bowl, and only decorative plantings receive it.
Expressiveness of the landscape
One of the main advantages of a high flower bed is to create a stylish design. A tall flower garden is visible from afar, therefore it dominates the landscape of the garden.
If an ordinary flower bed, broken in the back of the yard, is visually lost, then a raised flower bed attracts attention, being at a great distance.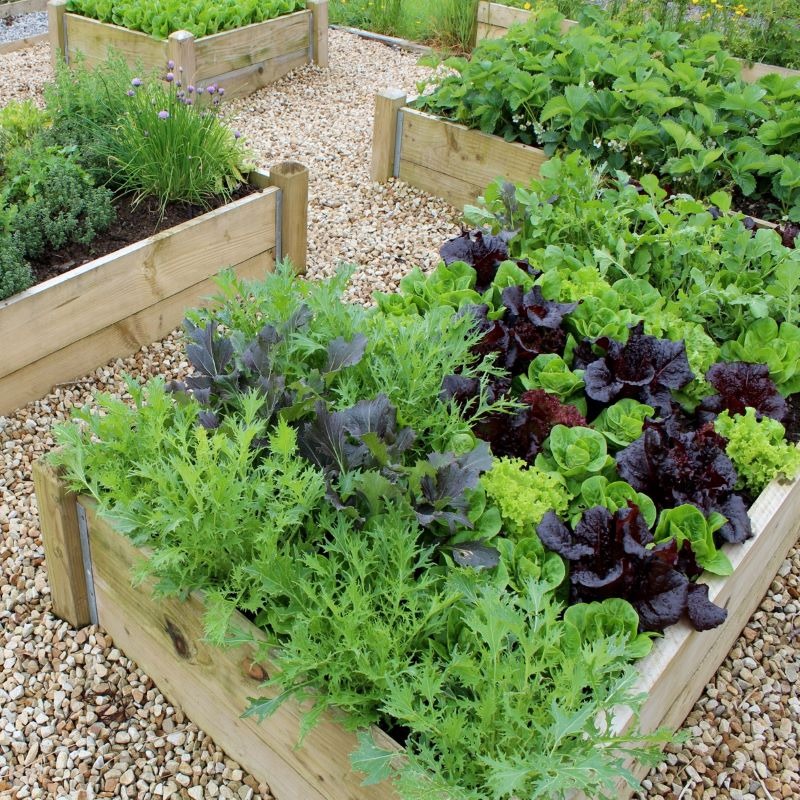 It makes the site more expressive, it is easier to view.
It makes the site more expressive, it is easier to view.
Depending on the area of the yard, you can arrange a small flower bed, only 1 m2, or take up a large space by building a multi-tiered flower garden.
Any vegetation is planted inside the bowl, from annual flowers to shrubs and trees: spruces, junipers, arborvitae.
Do-it-yourself stone flower bed
To create a flower garden, you do not need to invite specialists: it is not difficult to make it yourself from improvised materials. If bricks, blocks or stone remain after the construction of the house, a high curb is laid out of them, and the internal space is filled with fertile soil.
For the installation of parapet walls, processed wood remaining after construction, such as planed boards, round timber trimmings, is also suitable. As a result, excess materials do not litter the yard, but serve to improve it.
Zoning the yard
With the help of a tall flower bed, it is easy to separate areas of different functionality. Most often, a recreation area is separated from outbuildings or a garden. You can also separate a children's or sports ground with a high curb.
Most often, a recreation area is separated from outbuildings or a garden. You can also separate a children's or sports ground with a high curb.
A bowl of the required length is laid out of stone, tall plants are planted in it and cover part of the yard.
In this way, you can not only zone the site, but also disguise an old fence or a building in need of repair.
Flower bed on a retaining wall
On a site with uneven terrain, a flower bed is arranged on a retaining wall. In this case, its height is determined by the degree of difference in soil levels.
The high wall is a protection from the wind, so you can arrange a cozy summer patio near it. Climbing plants are planted inside the bowl, the lashes of which hang picturesquely down, and then the resting place becomes even more picturesque.
Thanks to this approach, natural irregularities turn into dignity, a kind of highlight of the landscape.
DIY flowerbed. How to choose the right flowers and make a chic flower bed
Article content:
- Where to make a flower bed
- Flower bed size
- Preparing the soil for planting flowers
- Selection of plants for flower beds
- Example of a continuous flowering bed
- How to make a colorful annual flower bed
Who among us, leafing through glossy magazines on gardening and landscaping, has not dreamed of creating something like this in our garden? For example, to build a flower bed with your own hands to the envy of all neighbors and to your own joy. A flower bed, like any composition in a garden, must fit into the surrounding landscape, but we will not argue about whether a designer and, in general, a professionally trained person is needed to create a flower garden. Let's try to create a charming flower bed with our own hands.
A flower bed, like any composition in a garden, must fit into the surrounding landscape, but we will not argue about whether a designer and, in general, a professionally trained person is needed to create a flower garden. Let's try to create a charming flower bed with our own hands.
Where to make a flower bed
Looking for a free place for a flower bed
The first thing an unprepared but fascinated by beauty and stubborn in his desire flower grower should do is to go to his site and decide where the flower bed will be located. Since the flower garden will have to be done with your own hands, then you need to choose the right place for it.
If the site is new and you have already swept away all the obstacles on it with a grader, then there will be no special problems with the location of the flower garden. It is much more difficult to "shove" another mixborder where everything is there: paths, flower beds, a garden, berry fields and other related buildings.
In modern dachas and suburban areas, which are devoid of the rustic charm of beds and orchards, you can create a flower bed anywhere. Actually, flower beds and compositions of ornamental trees and shrubs occupy almost the entire area of such plots.
But if you want to make a small flower garden at your grandmother's dacha, and the best place is already occupied by carrots and cabbage, you will have to limit yourself to the front area at the gate or under the window. Well, this is a very good solution for a flower bed.
Choose places to create a flower bed that are as protected from the wind as possible, with deep groundwater and quite fertile.
Determining the illumination
If the selected area for the flower bed is in the sun, then this is very good. You can easily pick up plants for such a site. But if your flower garden will be located in partial shade or shade, do not worry, now you can create charming compositions from plants that prefer partial shade to the sun.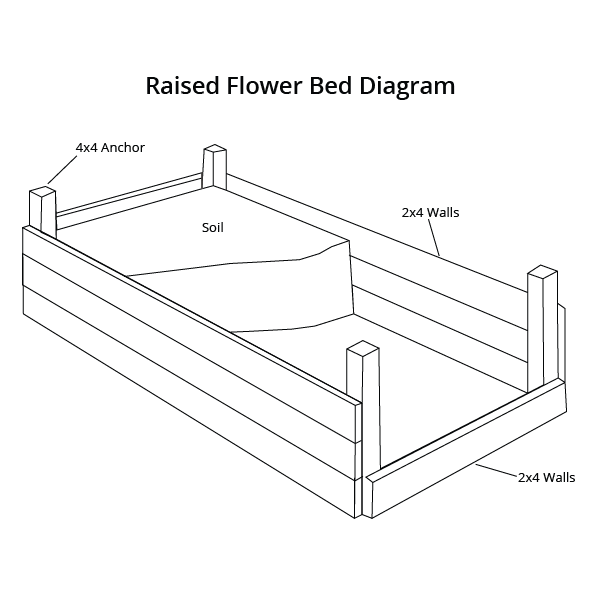 Flowers in a shady flower bed will be brighter, and their flowering will last longer.
Flowers in a shady flower bed will be brighter, and their flowering will last longer.
Depending on the illumination, we select an assortment of flowers for the flower bed - shade-loving or "sun-loving".
Flower bed size
If you have never planted flowers and this is your first flower garden, then you should not break a huge flower bed. Ornamental plants for a large flower bed will require a lot, and caring for them will take you a lot of time. In order not to be disappointed, it is better to break a small flower garden.
The shape of a flower bed can be of a regular geometric shape or an arbitrary landscape (natural) shape. In addition, a flower garden can be arranged from an old car, a rusty watering can, a broken cart, and even from a stump from a sawed apple tree.
Preparing the soil for planting flowers
You have determined the place for the flower bed, now you need to prepare the soil. Cut off the bumps and level the desired area. Dig the ground to a depth of 30-35 cm and select all the weeds. If the soil at the site of the future flower bed is clayey and heavy, sanding should be carried out (apply 1 sq.m per liter jar of coarse sand). If there are a lot of horsetail, horse sorrel, couch grass among the weeds that you removed, the earth needs to be limed. Add 100-200 g of lime per 1 sq.m of soil.
Dig the ground to a depth of 30-35 cm and select all the weeds. If the soil at the site of the future flower bed is clayey and heavy, sanding should be carried out (apply 1 sq.m per liter jar of coarse sand). If there are a lot of horsetail, horse sorrel, couch grass among the weeds that you removed, the earth needs to be limed. Add 100-200 g of lime per 1 sq.m of soil.
Fertilize the soil for the flower bed - per 1 sq. m 100g of complex mineral fertilizer, 3 kg of compost and 5 kg of rotted manure. Do not forget about green fertilizers - green manure.
Selection of plants for the flower bed
Making flower gardens from plants is not as easy as it seems. When choosing plants for a flower bed, consider:
- The shape, size and color of flowers, inflorescences and leaves.
- Terms and duration of flowering of different plant species.
- Growth rates of shoots and root system, as well as the possibility of oppression of one flower by another.

- Plant resistance to diseases and pests.
There are a lot of different flower beds. Let's see what flower beds are depending on the number of plant species and their location:
- traditional (flower beds of regular geometric shape with a variety of bright colors, decorative throughout the summer season)
- regular (plants in such beds form a certain pattern)
- irregular (landscape - most often mixborders of perennials, the flowering of which varies depending on the month. In mixborders, many plants are planted not for their bright colors, but because of the openwork decorative foliage)
- raised beds (beds located on retaining walls and stairs).
annuals, biennials, perennials, creepers, bulbous, aquatic flowers, as well as trees and shrubs can be used to decorate the flower bed.
Remember! The easiest way is to make a mono-flower with one type of plant with your own hands.
For example, a monoklumba from marigolds.
For such compositions, unpretentious and long-flowering plants are chosen: tagetis, calendula, kosmeya, petunias, viola, alissum, etc.
You can make a flower bed from annuals. Such a composition will be decorative during the planting season, unlike a perennial flower garden, which takes time to grow.
If you want to make a flower bed of several types of flowers, then the easiest way is not to select the plants yourself, but to take a ready-made scheme. There are a lot of such schemes now. They are easy to find on the Internet and special magazines for flower growers. In the scheme, you will already be given the dimensions of the flower bed, the color scheme, as well as the required number of flower specimens.
Depending on the view, the flower beds are divided into:
- round (look good from any angle),
- one-sided (show themselves at their best on one side only).

In round beds, consider the position of the plants in height. So the tallest flowers should be planted in the center of the flower bed, and the low ones at the edges.
In one-sided beds, tall plants are planted in the background (closer to the fence), and the rest of the flowers line up in height from medium to ground cover.
Taking into account the color scheme of the flower bed when choosing plants
When choosing plants for your flower bed, think about how the corolla colors of different plants will be combined.
Basic colors: red, yellow and blue. Harmoniously combined:
- blue/orange,
- yellow with purple,
- red with green.
If you have nearby plants with an incongruous color, then between them it is worth planting flowers with white corollas.
Selecting plants by flowering time or creating a continuous flowering bed
The most beautiful flowerbeds are obtained if the assortment of plants is selected so that the flowering of some is replaced by others from spring to late autumn.
April - white flowers, crocuses, muscari, snowdrops, primrose, chionodoxes, forget-me-nots.
May - pansies, daffodils, tulips, doronicum, daisies, periwinkle, gravilate, lilies of the valley, dicentra.
June - decorative onion, peonies, aquilegia, irises, poppy, geyhera, delphinium, foxglove, carnations, calendula, roses, evening primrose.
July - nasturtium, lavatera, hydrangea, astilba, mallow, cornflowers, gladiolus, phlox, chrysanthemum, dahlia, coreopsis, lily, etc.
August - gaillardia, asters, gelenium, marigolds.
When creating a flower bed that will bloom from spring to autumn, select plants not only for the color of the corolla, but also for the shape and appearance of the leaves. Blooming plants are well decorated with chic peony leaves, aquilegia, asparagus panicles, colored geyhera and, of course, cereal herbs.
Example of a continuous flowering bed
This flower bed is corner, but you can get creative with the planting process.
Do not think that multicolor is the best option. Flower beds made in one color look very original and chic. You can read about such a flower bed in our article - Scheme of a flower bed in white
How to make a colorful annual flower bed
If you want to make a bright flower bed of annuals, you should not choose many types of plants for it.
1 - tree heliotrope
2 - Sander tobacco with scarlet flowers
3 - terry bright orange marigolds
4- pink balsam New Guinea
In the center of the flower bed, you should always place the tallest and most luxurious flowers. They will be the most important viewpoint. The rest of the plants will complement the tapeworm.
Plants for your flower bed you can grow from seeds or buy ready-made seedlings.
When planting in a flower bed, consider the distance between neighboring plants.
Seedlings of flowers are watered abundantly before planting, so that the earthen lump is not disturbed and the flowers take root well.










