Growing basil seed
Growing Basil From Seed: A Step-by-Step Guide
Growing basil from seed should be on every gardeners to-do list. Why? Basil is easy to grow from seed and when you buy seeds instead of transplants you can choose from dozens of types and varieties available through seed catalogs. There are two ways to start basil seeds: indoors in a window or beneath a growlight, or by direct seeding outdoors. Keep reading to learn more about the simple steps of growing basil from seed.
Most gardeners start their basil seeds indoors to get a jump on the growing season. Sow seeds 6 to 8 weeks before the last expected spring frost.What is basil?
Basil (Ocimum basilicum) is a tender annual herb grown for its aromatic leaves that are added to fresh and cooked dishes. Sweet basil, also called Genovese basil is the most widely grown due to its delicious anise clove flavor. There are many other types of basil available through seed catalogs including lemon basil, Greek basil, cinnamon basil, and Thai basil. Each one offers a variety of flavors, forms, leaf sizes, and even colors. Basil is often planted with tomatoes and peppers because they have similar growing conditions – well draining soil and 8 to 10 hours of sunlight. Basil is also used in companion planting as the mid to late summer flowers attract bees and beneficial insects to the garden.
Why you should be growing basil from seed
Wondering if it’s worth your time to grow basil from seed? It absolutely is! Here are my four reasons for starting basil from seeds:
- Basil is easy to grow from seed – It’s true! I’ve been growing basil from seed for over 25 years and it’s generally a fuss-free herb that goes from seed to garden in under two months. You don’t need special equipment either. I start my seeds under grow lights but you can also use a sunny windowsill.
- Save money – I grow a lot of basil each summer so we have plenty of fresh basil and basil leaves for pesto, as well as for the freezer and to dry.
 With individual basil plants costing $3.00 to $4.00 each at my local nursery, growing basil from seed is a budget-friendly way to get a lot of basil plants for your garden.
With individual basil plants costing $3.00 to $4.00 each at my local nursery, growing basil from seed is a budget-friendly way to get a lot of basil plants for your garden. - Variety – There are a lot of different types and varieties of basil available through seed catalogs. It’s fun to try new ones each year, but growing basil from seed was also a game changer in my garden when downy mildew wiped out almost all of my basil plants. The plants that weren’t affected? They were Rutgers Devotion DMR, a downy mildew-resistant variety I grew from seed. It can be hard to find disease-resistant basil transplants at garden centres, but they’re easy to source as seeds from seed catalogs.
- Succession planting – I plant basil several times over the course of the growing season to ensure a non-stop supply of high quality leaves. It’s hard to find healthy basil seedlings in mid-summer but starting a few pots of seeds under my grow lights ensures I’ll have basil for successive crops.

Growing basil from seed
There are two ways to grow basil from seed. First, you can start the seeds indoors on a sunny windowsill or beneath grow lights. Eventually the young plants are transplanted into the garden. The second method is to direct sow basil seeds in garden beds or containers. Let’s look closer at each method so you can figure out which one is right for you.
Growing basil from seed indoors
Most gardeners start their basil seeds indoors to get a jump on the growing season. Success begins with sowing the seeds at the right time, 6 to 8 weeks before the last frost date. In my zone 5 garden that’s late May so I start my basil seeds indoors in late March. Sowing the seeds indoors even earlier doesn’t necessarily give you a head start on the basil harvest. It just means you’ll have bigger plants that need to be re-potted into larger containers. And they’ll take up a lot of space on a windowsill or beneath grow lights. Plus, transplanting mature basil plants into the garden often results in bolted plants that begin to flower instead of pushing out lots of fresh leaves. This reduces the overall harvest. Younger seedlings adapt better to transplanting and should be moved to the garden when they’re 6 to 8 weeks old.
And they’ll take up a lot of space on a windowsill or beneath grow lights. Plus, transplanting mature basil plants into the garden often results in bolted plants that begin to flower instead of pushing out lots of fresh leaves. This reduces the overall harvest. Younger seedlings adapt better to transplanting and should be moved to the garden when they’re 6 to 8 weeks old.
The best containers for growing basil from seed
Now that we know when to sow basil seeds indoors, we can consider containers. I typically use 10 by 20 trays with cell pack inserts to start most of my vegetable, flower, and herb seeds. They offer an efficient use of space under my grow lights and I re-use them from year to year. However, you can start basil seeds in pretty much any type of container as long as it’s clean and offers good drainage. If you’re up-cycling items like salad containers for seed starting be sure to pole holes in the bottom for excess water to drain away.
To cut down on plastic use I’ve recently bought a soil blocker for seed starting. A soil blocker forms lightly compressed cubes of soil – no container needed. I have several sizes and look forward to experimenting with starting basil seeds this way.
The best soil for growing basil from seed
When starting seeds indoors a lightweight seed starting or potting mix is essential. These mixes are typically made up of materials like peat moss, coconut coir, compost, vermiculite, perlite, and fertilizers. The ideal growing medium for seed starting is one that retains water, but is also quick draining to promote healthy root growth. You can make your own (check out our DIY potting mix recipes here) or buy a bag online or from your local garden centre.
You can use a variety of containers to start basil seeds including soil blocks. Soil blockers form loosely compacted cubes of soil ideal for seed starting.Starting basil seeds indoors
Once you’ve gathered your supplies, it’s time to get planting. Fill your containers with the pre-moistened potting mix. When sowing basil seeds in cell packs, plant 2 to 3 seeds per cell. If starting basil seeds in 4 inch pots, plant 6 to 8 seeds per pot. Whatever type of container you are using for the basil seeds, sow each seed about an inch apart. Plant the seeds a quarter of an inch deep. The exception to this is holy basil whose seeds need light to germinate. Instead of covering holy basil seeds, gently press them into the moist potting mix to ensure good soil-seed contact.
Fill your containers with the pre-moistened potting mix. When sowing basil seeds in cell packs, plant 2 to 3 seeds per cell. If starting basil seeds in 4 inch pots, plant 6 to 8 seeds per pot. Whatever type of container you are using for the basil seeds, sow each seed about an inch apart. Plant the seeds a quarter of an inch deep. The exception to this is holy basil whose seeds need light to germinate. Instead of covering holy basil seeds, gently press them into the moist potting mix to ensure good soil-seed contact.
After the seeds have been planted place a clear dome or a piece of plastic wrap on top of the trays or pots. This keeps humidity high to promote good germination. Once the seeds sprout, remove any plastic coverings so air can circulate.
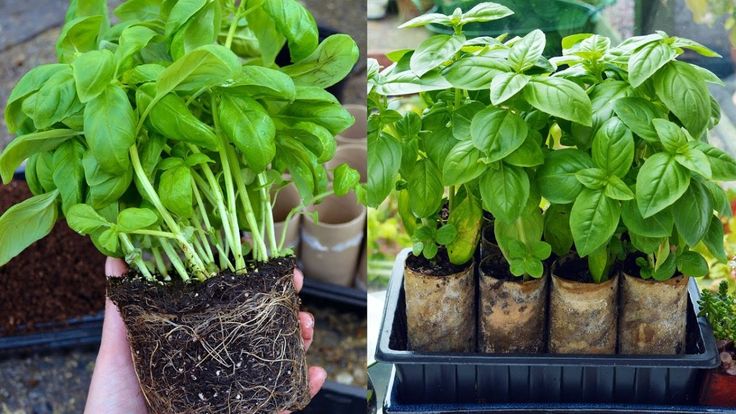
When the young plants have developed two sets of true leaves, thin them to one plant per cell, or three to four plants per 4 inch pot. You can carefully prick the surplus seedlings from their containers and transplant them into more pots. Let’s be honest, you can never have too much basil!
Let’s be honest, you can never have too much basil!
How much light do basil seedlings need?
Providing sufficient light is perhaps the biggest challenge when starting seeds indoors. Most types of vegetables, flowers, and herbs need plenty of light to form strong, stocky seedlings. Relying on natural sunlight from a window can be a challenge, especially for those who live in Northern climates. Seedlings grown in insufficient light are tall, leggy, and tend to flop over. The solution is to use a grow light to start seeds like basil.
I have two types of grow lights: LED grow lights and fluorescent grow lights. I leave my grow lights on for 16 hours each day using an inexpensive timer to turn them on and off. You can DIY a grow light set up or buy one from a garden supply store. When I’m not starting seeds I use my grow lights to provide light to succulents, culinary herbs, and other indoor plants.
The ideal temperature for basil
Basil is a heat-loving herb and the seeds germinate best in warm soil. The ideal temperature for basil seed germination is 70 to 75F (21 to 24C) with the seeds emerging in about 5 to 10 days. If you have a seedling heat mat you can use it provide bottom heat to both speed up germination and increase germination rates.
As basil seedlings grow thin them to one plant per cell pack. Also keep an eye on soil moisture aiming to maintain a lightly moist, but not wet soil.Watering and fertilizing basil seedlings
Basil seedlings can be prone to damping off, a soil-borne fungal disease that affects the stems and roots of young seedlings. I’ve found the two best ways to reduce damping off is to water the seedlings properly and provide good air circulation. First, let’s talk watering. Basil seedlings grow best in lightly moist, not wet soil. Water when the soil is dry to the touch, checking seedlings every day to gauge soil moisture. The other consideration for preventing damping off is air movement. I keep a small oscillating fan in the room near my grow lights. Good air circulation helps strengthen the seedlings, reduces mold growth on the soil surface (a sign of overwatering), and dries the leaves after watering.
I keep a small oscillating fan in the room near my grow lights. Good air circulation helps strengthen the seedlings, reduces mold growth on the soil surface (a sign of overwatering), and dries the leaves after watering.
When basil seedlings have developed their first set of true leaves I begin to fertilize. I use a liquid organic fertilizer diluted to half strength every 14 days. This promotes healthy growth and plenty of bright green leaves.
These basil seedlings are ready to be hardened off and moved to the garden.Hardening off basil seedlings
Hardening off seedlings is the final step when growing basil from seed. This is a step you don’t want to skip. The hardening off process acclimatizes seedlings to the sun, wind, and weather of the outdoor garden. Because basil is sensitive to heat don’t move the plants outside while there is still a risk of cold weather. I begin the hardening off process, which takes about five days, after the last expected date has passed.
Start by moving the seedlings outside on a mild day, placing the trays or containers in a shady spot. Cover them with row cover that night or bring them back indoors. On day two, give the plants some early morning or late afternoon sun, but shade during from mid-morning to mid-afternoon when the sun is most intense. Again, cover them up at night or bring them back inside the house. On days three to five continue to gradually introduce the plants to more light until by day five they are ready for full sun.
Cover them with row cover that night or bring them back indoors. On day two, give the plants some early morning or late afternoon sun, but shade during from mid-morning to mid-afternoon when the sun is most intense. Again, cover them up at night or bring them back inside the house. On days three to five continue to gradually introduce the plants to more light until by day five they are ready for full sun.
Do you want to learn more about growing basil from seed? Watch this video:
How and when to transplant basil
Hardened off basil seedlings can be moved into garden beds or containers once the risk of frost has passed and the weather has warmed. Don’t rush basil outside, however, as cold damage can occur when the day or night temperatures fall below 50F (10C). Once the conditions are right, transplant seedlings into a site with direct sunlight and well-draining fertile soil. I add all purpose compost to my beds or containers before transplanting. Space basil plants 8 to 10 inches apart. When the plants have five to six sets of true leaves you can start to harvest basil.
When the plants have five to six sets of true leaves you can start to harvest basil.
Growing basil from seed outdoors
The other technique for growing basil from seed is to direct sow seeds outdoors. Because I live in a cold climate, I start my basil seeds indoors to give the plants a head start. Gardeners who live in zones 6 and above, however, can direct sow basil seeds outdoors in a garden bed or container. Choose a sunny site and amend the soil with a thin layer of compost. Plant the seeds in late spring or early summer, about a week or two after the last spring frost. The soil temperature should be at least 70F (21C). Sow the seeds a quarter of an inch deep and one inch apart.
Once the seeds are planted, water the seedbed often with a hose nozzle on a gentle setting. You don’t want a hard jet of water which could dislodge or wash away the seeds or young seedlings. Don’t let the soil dry out as the seeds are germinating. Once the basil seedlings have developed two to three sets of true leaves, thin them 8 to 10 inches apart.
Don’t let the soil dry out as the seeds are germinating. Once the basil seedlings have developed two to three sets of true leaves, thin them 8 to 10 inches apart.
For further reading on growing basil, be sure to check out these articles:
- Types of basil to grow
- The secrets of growing great basil
- How to grow basil from cuttings
- How to trim basil for bushy plants
- 7 reasons for basil leaves turning yellow
Are you growing basil from seed this spring?
Growing Basil From Seed - The Ultimate Guide
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Read full disclosure here.
Growing basil from seed is pretty easy to do, especially when you know all of the secrets for success! In this post, I’m going to show you everything you need to know about how to grow basil seeds, step by step.
Basil is one of my favorite herbs, and I grow several varieties in my garden every year. It might seem like it would be hard to grow from seed, but it’s actually pretty darn easy!
It might seem like it would be hard to grow from seed, but it’s actually pretty darn easy!
This is a complete guide to growing basil from seed, and it covers everything from start to finish! Including the best method to use and when to start.
Plus you’ll find step-by-step planting instructions, expected germination time, seedling identification and care, transplanting to your garden, fixing common problems, faqs, and more!
Table of Contents
Growing Basil From Seed
The best part is that, once you learn how to grow basil seeds, you’ll be able to start any variety you want! The steps outlined in this guide work for all types.
Types Of Basil Seeds To Grow
It’s easy to grow basil from seed, and there are lots of varieties to choose from. Some of my personal favorites are Genovese, lemon basil, Italian large leaf, Thai basil, and purple leaf.
The color and flavor may vary between the different varieties, but the seed planting instructions are the same for all!
Different types of basil seed packetsWhat Do Basil Seeds Look Like?
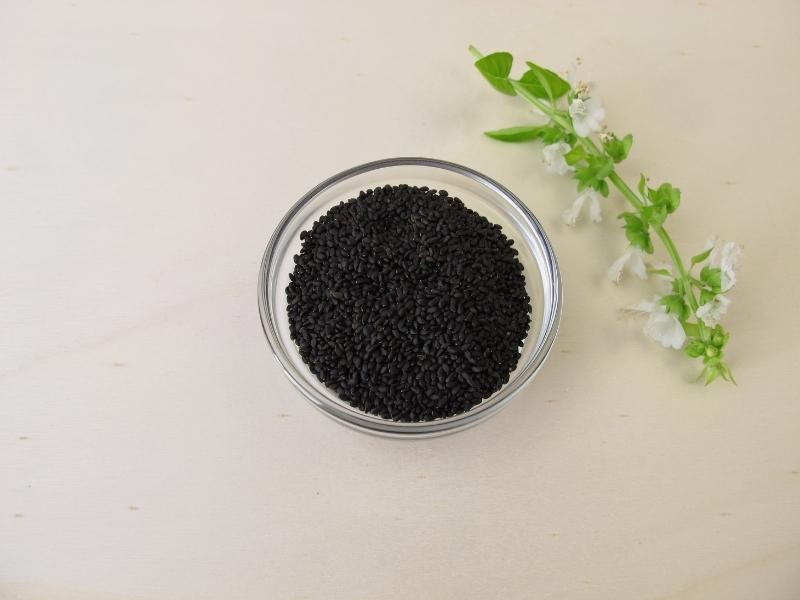
Basil seeds are pretty small, but not super tiny. They are oval shaped, hard but very lightweight, and can range in color from dark brown to black.
They are oval shaped, hard but very lightweight, and can range in color from dark brown to black.
Recommended Basil Seed Starting Methods
People who live in a warm climate can plant basil seeds directly into their garden in early spring. But, the seeds need warm soil in order to germinate.
So, if you live in a cold climate like I do, it’s best to start them indoors, rather than direct seeding outdoors or winter sowing them.
Related Post: 3 Seed Starting Methods That Every Gardener Should Try
When To Plant Basil Seeds
You should plan to start them indoors 6-8 weeks before your average last frost date. The exact timing will depend on where you live.
Here in zone 4b, our average last frost date is May 15th. So, I start basil seeds indoors sometime in late March.
If you live in a warm climate, you can plant them outdoors in your garden 1-2 weeks after last frost, when the soil temperature is warm.
Related Post: How To Propagate Basil – A Step By Step Guide
Planting Basil Seeds
While it’s true that it’s pretty easy to grow basil from seed, there are a few steps you can take to ensure your seeds will germinate.
In this section, I’ll talk about how to prepare the seeds, and then show you how to plant them step-by-step.
Preparing For Planting
You don’t need to do anything special to prepare basil seeds for planting. But soaking them in warm water overnight will give them a good head start, and help to speed up germination.
How To Plant Basil Seeds Step-By-Step
The good news is that you don’t need any fancy equipment to grow basil from seed. If you’ve ever done any seed starting before, then you probably already have everything you need on hand.
Supplies Needed:
- Seedling flat with a lid
- Pre-moistened seed starting soil or peat pellets
- Seeds
- Water
- Heat mat (optional)
Step 1: Fill the trays with soil – Start by filling the planting cells to the top with seed starting medium. Or you can use seed pellets in your trays, if you prefer.
Or you can use seed pellets in your trays, if you prefer.
Step 2: Figure out how many seeds to plant – If you’re using old seeds with a low germination rate, then you should plant 2-3 seeds per hole. Otherwise, if your seeds are fresh, then you can plant one seed per cell/pellet.
Sowing basil seeds indoorsStep 3: Plant the seeds – Since they are so tiny, I find it easier to place the seeds on top of the dirt, and gently work them into the soil. But if you prefer, you can make a shallow hole, and the drop them in.
Step 4: Cover the seeds with soil – If you laid the seeds on top of the dirt, then gently press them down, or use your finger to work them into the soil. Basil seeds are tiny, and should only be planted 1/4″ deep.
Step 5: Add water to the seed trays – Since the seeds are so tiny, don’t try to water your flats by pouring it over the top.
Doing that will likely displace the seeds. Instead, pour water into the tray, and allow the soil to soak it up from the bottom. Dump out any water that hasn’t been absorbed after 20 minutes.
Dump out any water that hasn’t been absorbed after 20 minutes.
Step 6: Cover the trays with plastic – Cover the seedling tray with the plastic lid to keep the soil moist and warm during germination.
Related Post: How To Grow Seeds: The Ultimate Seed Starting Guide
Covered tray after planting basil seedsBasil Germination Time
In the right conditions, basil seeds germinate pretty quickly. On average, germination takes about 5-10 days. But sometimes they can be much slower.
If yours seem to be taking forever, then it’s probably too cold for them. They need warm soil to germinate, so be sure to use a seedling heat mat to speed things up.
What Does Basil Look Like When It Sprouts?
The first two leaves that grow are called the “seed leaves” (aka: cotyledons). Those look like two half circles on either side of the stem. All of the leaves that grow after the first two are called the “true leaves”.
The true leaves look like tiny baby basil leaves (they’re so cute!). They usually start to grow within a few days after the seed leaves have opened.
They usually start to grow within a few days after the seed leaves have opened.
Basil Seedling Care Tips
When you first start to see the seedlings emerging from the soil, it’s very exciting!! But soon after you may think… uh oh, now what!?!
Yep, growing basil from seed indoors is one thing, but keeping the seedlings alive can be a whole different ballgame. Well, I’ve got you covered!
Below you’ll find detailed basil seedling care tips. You can read all about general seedling care here if you want even more details.
Light
Basil seedlings growing indoors need a lot of light to keep them from getting too tall and leggy. As soon as the first seed has sprouted, position your grow light a few inches above the tray.
If you’re a DIYer, you can make your own grow lights using an inexpensive fluorescent light fixture and plant grow light bulbs.
Keep the light 1-2 inches above the seedlings at all times. Leave it on for 14-16 hours a day, and adjust the height of the light as the seedlings get taller.
Use an inexpensive outlet timer to make it easy to give your basil seedlings the perfect amount of light.
Related Post: A Beginner’s Guide To Grow Lights For Seedlings
Water
Basil seedlings need consistently moist soil in order to grow their best. So always keep the soil damp, and never allow it to dry out completely.
They don’t like to be sitting in soggy soil though, so make sure you don’t overwater them. To protect the delicate seedlings, and help prevent mold growth, water the trays from the bottom rather than over the top.
Fertilizer
Once the true leaves start to grow, you can begin feeding basil seedlings with a weak dose of liquid fertilizer. Then slowly increase it to full strength as they get larger.
Be sure to use organic fertilizers though, because chemicals can damage the tiny seedlings. I use an organic compost solution, or brew my own with compost tea bags. Or you could use a plant start fertilizer that is specially made for seedlings.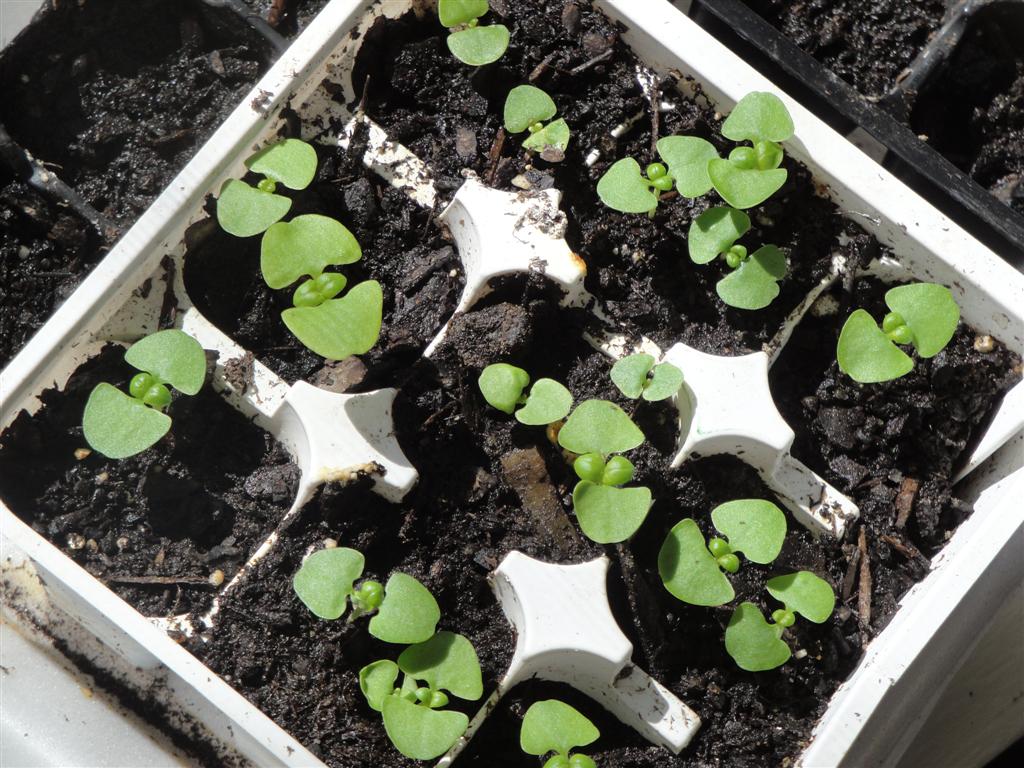
Once they’re outside, I switch to fish emulsion, which seedlings absolutely love. But it can be a bit stinky, so that’s why I wait until they’re outside to use it.
Seed tray full of basil seedlingsAir Circulation
Once most of the seeds in a tray have germinated, then it’s time to give them some fresh air. This will prevent mold growth, and also help to strengthen the seedlings.
Remove the lid, and then run an oscillating fan set on low over them. Start by doing this for a little while every day, and gradually add more time until you finally plug the fan into the same timer your lights are running on.
Just be aware that once the lids are off, the soil will dry out much faster. So check the moisture level at least once per day to make sure it’s not getting too dry.
Thinning
If you planted more than one basil seed per hole, cell or pellet, then you’ll need to thin them out. Once they have grown to be a few inches tall, choose the strongest looking one, and thin the rest.
Don’t pull them out when thinning though, or it could damage the tender roots of the one you’re keeping. Instead, use a sharp pair of micro-tip snips or bonsai shears to cut them off at the base.
Repotting Basil Seedlings
Once they get going, basil seedings grow fast, and can quickly outgrow their starter trays. When this happens, it’s best to pot them up to give them plenty of room to grow.
I like to use plantable pots to make transplanting them easier (and lower the risk of transplant shock). If you don’t like using peat, and prefer a more sustainable option, coco coir and cow pots are both really great.
Of course, you could also use plastic seedling pots (which are reusable) instead of plantable ones. Whatever you prefer.
Related Post: How To Prune Basil The Right Way
Transplanting Basil Seedlings Into Your Garden
Once the weather starts warming up in the spring, we all get antsy to plant our seedlings outside! But, getting them ready for planting into the garden is a delicate process.
It’s super important to transplant them at the right time, or all of the work you put into growing basil from seed will be lost. You don’t want that, so be sure to follow these transplanting tips…
When To Transplant
Basil won’t tolerate cold weather or cold soil, so make sure you wait to transplant your seedlings into the garden until both have warmed up in the spring.
I know it’s hard to wait, but it is best to plant a little later in the spring than transplanting too early, and risk losing your seedlings to a late frost. Plus, if the soil is too cold, it will stunt basil seedling growth.
Find out how to figure out the exact timing for when to transplant seedlings into the garden here.
Hardening Off
But before you can transplant them, you must first get them used to living outside. You can’t plant basil seedlings grown indoors directly into the garden, or they will most likely die from the shock.
So make sure that you harden them off first, and do not be tempted to skip this step! Slowly transition them to life outside over a couple of weeks.
Start by placing them in a protected, shady spot for a few hours a day. Then slowly expose them to more sun, and leave them outside a little longer every day. They’ll be ready to go into the garden once they’re used to being in full sun all day.
Where To Plant
Basil grows best in a warm, sunny location. You can either plant it in the ground or in containers, it does very well either way.
They aren’t super picky about the soil, but make sure it has good drainage. Amend poor quality garden soil with compost or worm castings, or use a good container potting mix.
I like to mix an organic granular fertilizer into the soil before planting my basil seedlings, which will give them the nutrients they need to grow strong and healthy.
Basil seedlings transplanted into the gardenSpacing
Though it can grow to be tall and bushy, it doesn’t need a ton of room. But ideally, you should space basil seedlings 6-12 inches apart.
Giving the plants plenty of room to grow will allow for ample airflow, and help to prevent diseases like powdery mildew.
How Deep To Plant
You can plant basil seedlings slightly deeper than they were in their container. Don’t plant them super deep, but deep enough to ensure their tender roots are completely covered.
How Long To Harvest Basil From Seed
Since we eat the leaves, rather than having to wait for them to develop fruit, you can harvest at any time. The more you harvest and pinch the tops, the bushier the plants will grow.
Never remove all of the leaves from the plant though, or it may not survive. If it starts to bolt, simply pinch out the flowers, and your basil will keep producing all summer long.
Learn all about when and how to harvest basil here.
Mature basil plant ready for harvestingTroubleshooting Common Problems
Growing basil from seed is fun… until you start having problems, and don’t how to fix it! It can be super frustrating, that’s for sure.
So in this section, I’m going to address some of the most common problems you may have, and how to fix them. You can read more about how to fix common seedling problems here.Basil seeds not germinating – If your seeds aren’t germinating, then it’s either too cold, too wet, or the seeds weren’t viable (old seeds). Use a heat mat and fresh seeds for the best success, and make sure the soil is never soggy.
You can read more about how to fix common seedling problems here.Basil seeds not germinating – If your seeds aren’t germinating, then it’s either too cold, too wet, or the seeds weren’t viable (old seeds). Use a heat mat and fresh seeds for the best success, and make sure the soil is never soggy.
Seedlings Falling Over & Dying
When seedlings suddenly flop over at the base and die, it’s caused by a disease called seedling blight, and is usually from using dirty equipment. Unfortunately, there’s nothing you can do to save the ones that have already toppled over. Be sure to clean and disinfect the flats before using them again.
Tall, Leggy Seedlings
The seedlings will grow tall and leggy when they aren’t getting enough light. So if this is happening with yours, add a grow light.
Basil Seedlings Not Growing
If your seedlings are slow to grow, that usually means it’s too cold for them, or the soil moisture level is inconsistent. Move them to a warmer location, and make sure to keep the soil evenly moist (never saturated or dried out).
Move them to a warmer location, and make sure to keep the soil evenly moist (never saturated or dried out).
Related Post: How To Preserve & Store Basil (Leaves Or Stems)
FAQs About Growing Basil Seeds
In this section, I will answer some of the most frequently asked questions about growing basil from seed. If you can’t find the answer to your question after reading through all of this, then ask it in the comments below.
Should I soak basil seeds before planting?
You certainly can, but it is an optional step. Soaking basil seeds before planting will soften them up, and can help to speed up germination.
How deep do you plant basil seeds?
The general rule of thumb is to plant a seed twice as deep as it is wide. Since basil seeds are so small, they should only be planted 1/4″ deep.
How long does it take to grow basil from seed?
It takes 65-70 days to grow basil from seed to harvest. You may be able to start harvesting sooner than that, but make sure to wait until the plant has several mature leaves.
How many basil seeds should I plant per hole?
If you’re using brand new seeds, then you can just plant one per hole, seed cell, or pellet. If the seeds are old, or have a low viability rate, then plant 2-3 seeds per hole, and thin out the weakest once they’re 3-4″ tall.
Do basil seeds need light to germinate?
No, basil seeds do not need light in order to germinate. But you should only cover them with a thin layer of soil, and don’t bury them too deep.
How can I speed up basil seed germination?
Since basil seeds need warmth in order to sprout, adding bottom heat is the best way to speed up germination. Placing them on a heat mat will help them germinate faster. Soaking the seeds before planting can also speed things up.
Growing basil from seed is easy, and doesn’t take much time. Plus, once you know how, you’ll be able to plant any variety that you want! Simply follow the instructions in this guide, and you’ll have the best success.
Up Next: Learn how to care for basil plants in my ultimate guide.
If you want to learn how to easily grow all of your garden plants from seed, check out my Seed Starting Course. This is a comprehensive, self-paced online course that will give you step-by-step guidance and support for growing any plant you want from seed. Sign up and get started right now!
Otherwise, if you’r e just looking for a quick-start guide to growing seeds indoors, or refresher to get you going, then you should grab a copy of my Starting Seeds Indoors eBook.
More Posts About Growing Seeds
- How To Grow Parsley From Seed: Step-By-Step
- How To Grow Lavender From Seed & When To Plant
- How To Make Your Own DIY Seed Starting Mix (with recipe!)
Share your tips for how you grow basil from seed in the comments section below.
growing from seeds in the open field, seedlings on the windowsill, photo
Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/en/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden plants Reissued: Last edited:
Contents
- Planting and caring for basil
- Basil plant - description 0 seedlings
- planting 0011 When to sow basil for seedlings
- Growing basil from seed
- How to grow basil at home
- Watering basil
- Feeding basil
- Planting basil in the ground
- Growing basil in the ground soil
- Watering basil
- Top dressing basil
- What to plant after basil
- Diseases of basil
- Pests of basil
- Useful properties of basil
- Basil - contraindications
Plant fragrant basil ( lat. Ocimum basillicum), or camphor, or garden, or common, is a herbaceous annual of the Basil species of the subfamily Kotovnikovye family Lamiaceae. In the wild, basil herb grows in China, Iran, India, Africa, southern Asia, the tropics of the American continent, Central Asia and the Caucasus. It is assumed that basil originated from Africa, and was brought to Europe by the soldiers of the army of Alexander the Great.
Ocimum basillicum), or camphor, or garden, or common, is a herbaceous annual of the Basil species of the subfamily Kotovnikovye family Lamiaceae. In the wild, basil herb grows in China, Iran, India, Africa, southern Asia, the tropics of the American continent, Central Asia and the Caucasus. It is assumed that basil originated from Africa, and was brought to Europe by the soldiers of the army of Alexander the Great.
Our ancestors used basil primarily as a medicinal plant. Today, this herb is grown all over the world as a food spice.
Planting and caring for basil
- Flowering: late July or early August.
- Planting: sowing seeds for seedlings - at the end of March or in the first half of April, transplanting seedlings into open ground - in the second half of May. Sowing seeds in the ground - not earlier than the beginning of June.
- Lighting: bright sunlight.

- Soil: light, fertile, rich in humus, well-drained, breathable.
- Water: when the topsoil dries.
- Top dressing: once a month. The first time - 2 weeks after planting the seedlings in the ground with a solution of 2 tablespoons of Nitrophoska in 12 liters of water, spending 3-4 liters of solution for each m².
- Propagation: seeds.
- Pests: aphids, field bugs, spider mites.
- Diseases: blackleg, gray mold, fusariosis.
Read more about growing basil below
Basil plant - description petioles. Both stems and leaves are covered with hairs. Axillary pale pink or white, and sometimes purple flowers are collected in irregular whorls. The fruit of the plant consists of nuts that separate from each other after ripening. Basil seeds remain viable for about five years.
- Hyssop: growing in the garden from seeds, properties
Purple varieties of basil have a sharper aroma and are popular in Asia and the Caucasus, while green basil is preferred in Europe - it is one of the most sought after spices in Mediterranean cuisine. The strongest aroma of basil exudes before flowering.
The strongest aroma of basil exudes before flowering.
In our article we will tell you how to grow basil from seeds, when to sow basil for seedlings, how to grow basil at home, how to plant basil in open ground, what can be the benefits of basil, and what can be harmful basil - in general, everything that may be needed for those who decide to grow basil at home or in the garden.
Planting basil for seedlings
When to sow basil for seedlings
Basil can be grown both in seedlings and without seedlings, but it will be more reliable to grow seedlings from seeds first, and then transplant seedlings into open ground. In the article "Planting vegetables for seedlings in April" we described in detail how this process is carried out. For those who have not had time to read the article, we will tell you about it right now.
So, when to sow basil seedlings? Best in the first half of April.
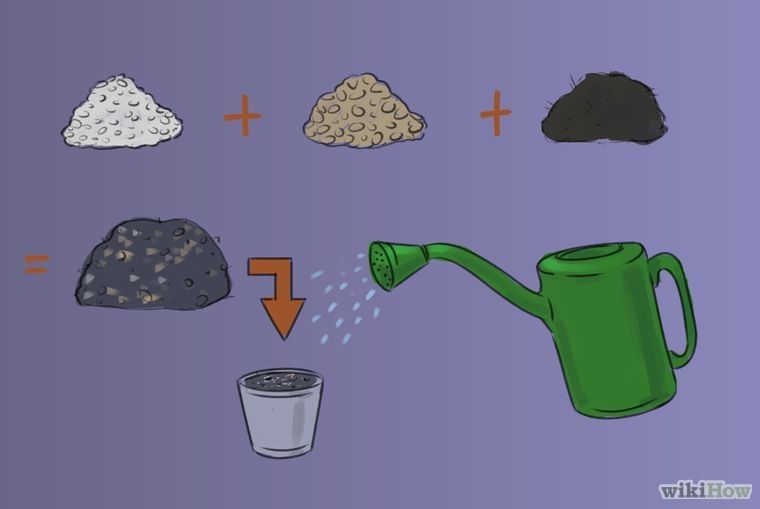
Planting basil for seedlings is carried out in a prepared soil mixture of four parts of rotted compost, two parts of humus and one part of washed river sand, which must be sifted and steamed for an hour in a water bath. Gardeners who prefer a mixture for seedlings sold in stores will need to shed the substrate with Fitosporin solution or a strong solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
Gardeners who prefer a mixture for seedlings sold in stores will need to shed the substrate with Fitosporin solution or a strong solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
You can grow basil seeds in a box, but then you will have to dive seedlings after some time, or you can sow basil in 5-7 cm deep cassettes. Sowing basil is carried out in well-moistened soil at a depth of about 1 cm. Distance between rows there should be about 5 cm in the box. After sowing, the container is covered with glass or plastic wrap and kept in a warm, bright place at a temperature of 20-25 ºC. After about a week or two, the first shoots of basil will appear.
- Mint: growing from seeds at home and in the garden
Growing basil from seeds
After the seeds have germinated, the transparent cover can be removed from the box and the temperature should be lowered to 15-20 ºC. Caring for basil seedlings does not require any extra effort: water the plants as needed, preventing the soil from drying out, however, waterlogging should not be allowed, otherwise the seedlings may be affected by the black leg, a fungal disease that can destroy all crops. If you notice the symptoms of this disease, treat the seedlings with a solution of a teaspoon of copper sulfate in 2 liters of water or spill the substrate with a strong solution of potassium permanganate.
If you notice the symptoms of this disease, treat the seedlings with a solution of a teaspoon of copper sulfate in 2 liters of water or spill the substrate with a strong solution of potassium permanganate.
Seedlings growing in a common container dive at the stage of development of the first pair of true leaves into a larger container with the same substrate, in which a spoonful of complex mineral fertilizer and a couple of spoons of wood ash are added to 5 liters of the mixture. The depth of planting seedlings in a new container should remain the same.
When the basil seedlings are established and growing, pinch them over the 6-8th leaf to stimulate the growth of side shoots. Two weeks before planting the seedlings in the ground, they begin to harden them, taking them out onto the balcony or into the yard, first for an hour, the next day for two, and so on, until the seedlings can be in the fresh air for a whole day. Planting basil in open ground is carried out when the return frosts have passed - in the second half of May.
Growing basil on the windowsill
How to grow basil at home
Growing basil from seeds at home starts in late February or early March in the same way as growing seeds for seedlings, only you need to sow a few seeds in a peat humus pot or peat tablet. Before planting basil, the seeds are poured for a couple of hours with a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate. The crops are covered with a transparent airtight material and kept under the conditions described in the previous section. Keep in mind that basil should be in the sun for at least 3-4 hours a day.
When the seedlings develop the first pair of leaves, they are transplanted together with a tablet or a pot into a large container - a liter pot, on the bottom of which a drainage layer 2-3 cm high is placed from expanded clay, broken brick or pieces of foam. The substrate for home basil should be fertile, but light and permeable. For example, a soil mixture of one part humus and two parts coconut fiber. You can cut off the first fragrant leaves for salads in a month and a half.
You can cut off the first fragrant leaves for salads in a month and a half.
Watering basil
Basil loves moisture, so the soil in the pot should always be slightly damp. You will have to water the basil almost daily, and you yourself will understand this when one day, due to your forgetfulness, its leaves will hang like sails in calm weather. However, make sure that waterlogging of the soil does not occur, which can result in root rot. After watering once every 2-3 days, carefully loosen the soil in the pot.
Basil dressing
If you have planted basil in not very fertile soil, you will need to correct this with regular feeding. The plant responds well to universal fertilizers based on humates or compost, which are applied to the soil at a concentration indicated by manufacturers, no more than once a month.
- Marjoram: growing in the garden, properties, varieties
Growing basil outdoors
Planting basil outdoors
Planting basil outdoors is carried out only in the second half of May, when the return frosts have passed.
Basil loves open sunny areas, protected from strong cold winds. Some gardeners successfully grow basil in the near-stem circles of young fruit trees, which give almost no shade, which does not prevent the basil from absorbing the sun's rays, and its strong spicy smell repels harmful insects from seedlings. Here is such a successful symbiosis.
The soil for Basil should be light and rich in humus, and most importantly - permeable. The site is dug up with humus, peat or compost a month before planting at the rate of 2 kg of organic matter per m² of area. For planting, choose an evening or a cloudy day, dig holes at a distance of 15-20 cm from one another and plant basil seedlings in them. The interval between rows should be at least 30 cm. Water the planted seedlings well with warm settled water.
Growing basil in the ground
Growing basil is a series of routine activities for every gardener: watering, weeding, loosening the plot, top dressing, protection from insects and diseases. Freshly planted, still weak basil seedlings cover the first two weeks with a film at night in case it gets colder at night. Until the basil begins to grow, weeds are regularly removed from the site. You will have to loosen the soil quite often - 7-8 times per season before watering. As soon as flower stalks begin to appear, carefully break them off to encourage branching in the basil.
Freshly planted, still weak basil seedlings cover the first two weeks with a film at night in case it gets colder at night. Until the basil begins to grow, weeds are regularly removed from the site. You will have to loosen the soil quite often - 7-8 times per season before watering. As soon as flower stalks begin to appear, carefully break them off to encourage branching in the basil.
Watering basil
Frequent watering of basil has a positive effect on the appearance of new leaves, so moisten the area as the soil dries. However, do not over-moisturize, as both under-watering and over-watering basil are harmful. Water for irrigation should be warm (about 25 ºC) and settled for at least a day. For settling and heating water, you can use a capacious dish (barrel, old bathtub), setting it in the garden in a sunny place.
Basil top dressing
Basil top dressing to stimulate the growth of green mass is carried out once a month. The first time fertilizers in the form of a solution of 2 tablespoons of Nitrophoska in 12 liters of water are applied two weeks after the seedlings are planted in open ground. Solution consumption - 3-4 liters per m².
Solution consumption - 3-4 liters per m².
What to plant after basil
It is undesirable to grow basil in one place for many years, you need to alternate different crops on the plot. Rotation of crops is one of the main principles of success in agriculture. It is possible to return the culture to the place where it grew for 2-3 years only after 4-5 years. After basil, the area should be planted with basil-resistant crops, such as legumes, carrots, cucumbers, zucchini, squash, pumpkins, early potatoes, and tomatoes. For the basil itself, siderats, tomatoes, onions, cauliflower and early white cabbage, beets, strawberries and green crops are good predecessors.
- Fennel: growing in the garden, types, properties
Pests and diseases of basil
Diseases of basil
Basil plant is extremely resistant to pathogens, but sometimes health problems occur. Most often, basil is affected by:
Black leg - a fungal disease of basil seedlings that develops in conditions of high acidity, poor aeration of the soil and too frequent and abundant watering. The fungus infects the root neck of seedlings, as a result, the vessels that feed the plant become clogged, the stem and its base become soft, blacken, thinner, the plant turns yellow and dies;
The fungus infects the root neck of seedlings, as a result, the vessels that feed the plant become clogged, the stem and its base become soft, blacken, thinner, the plant turns yellow and dies;
Fusarium - this fungal disease also affects the vessels of the plant, releasing toxins into its nutrient juices. In young plants, the stem becomes brown and thin, in adults the top dries up, they gradually wither and die. Contribute to the development of the disease is too high temperature against the background of high humidity;
Gray mold is more likely to harm plants in greenhouses and greenhouses, but outdoor basil can also become sick. The disease manifests itself first on the lower, dying leaves, then covers the entire plant: dry spots of light brown color form on the affected areas, which gradually become watery and covered with a gray fluff.
As a treatment for gray mold and fusariosis, treat basil at the initial stage of the disease with an infusion of onion peel: pour one volume of the peel with four volumes of water and infuse for a day, then strain the infusion and spray it on the basil. The black leg is treated by spilling the soil in seedlings with a solution of potassium permanganate. Remove diseased plants together with an earthen clod, and pour the remaining hole after that with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. But if the disease has come into force, it is unlikely that you will be able to do without fungicides - Fundazol, Fitosporin, Topaz, Toivita Jet and others.
The black leg is treated by spilling the soil in seedlings with a solution of potassium permanganate. Remove diseased plants together with an earthen clod, and pour the remaining hole after that with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. But if the disease has come into force, it is unlikely that you will be able to do without fungicides - Fundazol, Fitosporin, Topaz, Toivita Jet and others.
In order not to have to resort to pesticides, observe the agricultural practices of the crop: do not grow basil in one place for more than three years, do not sow it too thickly, dust the surface of the soil with wood ash once a week, observe the water balance of the soil in the area, loosen it and remove weeds from the garden in a timely manner.
Pests of basil
Aphids and field bugs are dangerous insects for basil.
- Lovage: cultivation, properties, types
Aphid is the most harmful of pests, sucking the juice from the leaves and stems of basil, as a result of which the leaves curl up, the stems stop developing, the plant dries out. The sugary secretions of aphids are a beneficial environment for the soot fungus that covers the plant with a dark coating. In addition, aphids carry viral diseases for which there is no cure. You need to get rid of aphids as soon as you discover their presence. To combat aphids, decoctions of wormwood, tansy, hot pepper, dandelion, yarrow, onion, garlic, tomato or potato tops, mustard are used. It is necessary to process basil in the ground two or three times with an interval of 7-10 days. A good remedy for aphids is a solution of 100 g of grated tar soap in 10 liters of water or an ash solution prepared according to this recipe: 300 g of ash is poured with boiling water and boiled for half an hour, after which it is settled, filtered and topped up with water to a volume of 10 liters. In especially severe cases, when natural formulations do not help, treat the basil with Karbofos solution in accordance with the instructions - this insecticide has no taste and smell. They cope well with the pest Akarin, Bankol, Aktellik.
The sugary secretions of aphids are a beneficial environment for the soot fungus that covers the plant with a dark coating. In addition, aphids carry viral diseases for which there is no cure. You need to get rid of aphids as soon as you discover their presence. To combat aphids, decoctions of wormwood, tansy, hot pepper, dandelion, yarrow, onion, garlic, tomato or potato tops, mustard are used. It is necessary to process basil in the ground two or three times with an interval of 7-10 days. A good remedy for aphids is a solution of 100 g of grated tar soap in 10 liters of water or an ash solution prepared according to this recipe: 300 g of ash is poured with boiling water and boiled for half an hour, after which it is settled, filtered and topped up with water to a volume of 10 liters. In especially severe cases, when natural formulations do not help, treat the basil with Karbofos solution in accordance with the instructions - this insecticide has no taste and smell. They cope well with the pest Akarin, Bankol, Aktellik.
Meadow, or field bug like aphids, feeding on basil cell sap, deforms its leaves, they become covered with whitish spots, then turn brown and die. Damage to the plant is caused by both adults and bug larvae. These pests hibernate in fallen leaves and in the upper layer of soil. Ways to deal with field bugs are the same as aphids.
Types and varieties of basil
In cultivation, the most commonly grown types of basil are camphor (or fragrant), Mexican (or cinnamon), purple (common or regan) and lemon (Thai). Numerous varieties of basil vary:
- according to the shades of smell. They are cold, tart, warm or sweet. The main flavors of basil are: cinnamon, anise, pepper, lemon, vanilla, caramel, clove and menthol. Varieties with caramel, lemon, vanilla and cinnamon flavors are used to prepare dessert dishes and drinks. Those that have an anise smell are needed for cooking fish dishes, and clove and pepper flavors are needed for meat dishes;
- by color: basil purple and basil green.
 Purple varieties of basil have a more pungent odor and are more commonly used in Caucasian cuisine and in Central Asian dishes. Green varieties are more popular in Europe, in particular in the Mediterranean;
Purple varieties of basil have a more pungent odor and are more commonly used in Caucasian cuisine and in Central Asian dishes. Green varieties are more popular in Europe, in particular in the Mediterranean; - according to the size and shape of the bush varieties of basil are erect, sprawling, semi-spreading, compact, although there are intermediate forms. By height, low-growing varieties are known from a height of 18 to 30 cm, varieties of medium height - from 30 to 60 cm and tall varieties - from 60 to 85 cm. At home, it is more convenient to grow low-growing varieties;
- by maturity – early, medium and late varieties.
The best varieties of basil are:
- Mauritanian is a productive fragrant mid-season variety of purple color with an upright sprawling bush up to 65 cm high;
- Table is an upright shrub up to 60 cm high with large, light green, egg-shaped leaves with delicate texture.
 This is one of the most fragrant mid-late varieties, characterized by good productivity;
This is one of the most fragrant mid-late varieties, characterized by good productivity; - Fantazer - one of the most productive varieties of rich green color with a massive sprawling bush, branched stem and lanceolate-oval leaves;
- Balconstar is a low growing variety with small fragrant leaves of excellent taste, suitable for salads. It grows well in pots on the windowsill;
- Genoa - this productive variety has large, glossy, dark green leaves, fragrant and pleasant to the taste. Genoese basil leaves are consumed fresh and dried, sometimes it is put in soft drinks instead of mint;
- Carnation Gourmet is a productive variety with a medium height, massive upright shrub with green elliptical leaves of medium size. This basil perfectly complements the taste of fish, meat, potato dishes, as well as rice and cheese dishes;
- Basilisk is a compact indoor and outdoor variety with a clove-pepper aroma.
 The bush is upright, up to 20 cm high, densely leafy with small, green leaves, the shoots are semi-raised;
The bush is upright, up to 20 cm high, densely leafy with small, green leaves, the shoots are semi-raised; - Yerevan is one of the most common productive varieties with a clove-pepper aroma. Bush of medium height, purple leaves, ovoid, medium size;
- Troll is a mid-season, high-yielding, small-leaved and compact variety for growing indoors, resistant to sudden changes in temperature. The leaves of the plants of this variety are dark purple. The bush looks very attractive;
- Magic Mountain is a variety of Israeli selection, characterized by endurance to high and low temperatures and lack of moisture. Its neat round bush with purple-green leaves looks great in the garden and as an ornamental plant;
- Red Ruby is an American variety of mahogany-purple color, in which not only the leaves, devoid of bitterness of green varieties, are edible, but also the buds, which in America are customary to add to omelettes.
The following varieties of basil have also proved to be excellent: Charm, Marquis, Ararat, Velvet, Violet, Greek, Robin Hood, Dragon, Gigolo, Fragrant Green, Orion, Pepper aroma, Tempter, Baku, Enchanter, Lemon, Dwarf, Curly, Philosopher , Broad-leaved and others.
Properties of basil - harm and benefits
Useful properties of basil
The aroma of basil is due to the presence in its ground part of an essential oil of complex composition, which has a bactericidal effect. Contains basil vitamins C, B2, PP, provitamin A, carotene, sugar, phytoncides, rutin. Basil protects the body from infections by stimulating the immune system. It even inhibits the growth of HIV and cancer cells. Basil has antipyretic, bactericidal, antioxidant, tonic and tonic effects.
The use of basil is indicated for viral, bacterial and fungal infections, respiratory and pulmonary diseases. It helps to get rid of excess mucus in the nasal passages, excess gases in the rectum, improves memory, strengthens the nervous tissue.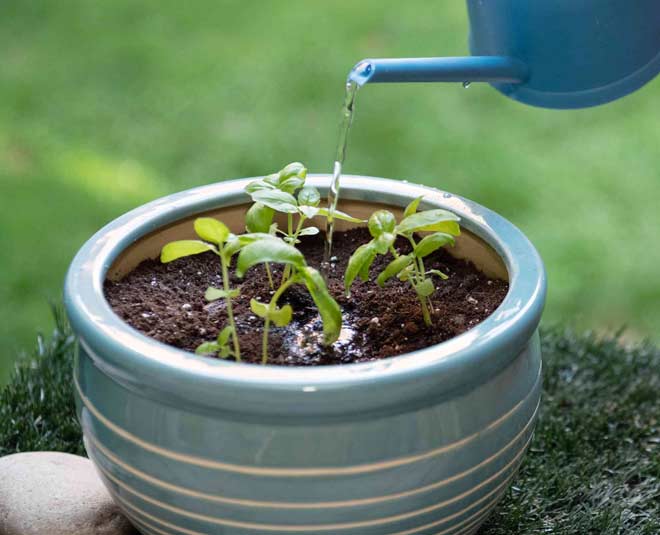
- Rosemary: growing in the garden and at home, varieties
Basil easily copes with inflammation of the oral cavity - caries, ulcers, tartar, plaque and bad breath. Having an astringent effect, it strengthens the gums, preventing premature tooth loss.
Basil helps the body cope with flatulence and gastrointestinal problems. Enzymes contained in it accelerate the breakdown and burning of fats in the body, and estragole and evenol stimulate mental activity.
Basil essential oil successfully heals wounds, relieves spasms of various nature, is used for inhalation of the upper respiratory tract. Basil leaf juice is used in the fight against fungal infections of the skin, water extracts from the plant give good results in the treatment of gastritis and food poisoning.
Dried basil is used to make tea or compresses to relieve headaches and eczema. Alcoholic infusion of basil treats colitis, pyelitis, whooping cough, neurosis, bronchial asthma, low blood pressure, inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, flatulence and the common cold.
Basil - contraindications
Since basil has a tonic effect, it is contraindicated for those suffering from diseases of the vascular-cardiac system - hypertension and hypertension, and especially for those who have suffered a myocardial infarction. Basil is also dangerous for patients with thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, thrombophlebitis, vegetative-vascular dystonia and diabetes mellitus. Hypotonic patients can use basil without fear.
Basil is not recommended in large quantities during pregnancy, especially for purple varieties of the plant, but it is indicated for nursing mothers as a good lactagon agent, and if your baby is not confused by the strange taste and aroma of your milk, you can not refuse basil during breastfeeding .
Basil contains a small amount of mercury, so it is better not to consume it in large quantities, even for absolutely healthy people.
- Broccoli: growing in the garden, varieties
Literature
- Read related topics on Wikipedia
- Peculiarities and other plants of the Lamiaceae family
- List of all species on The Plant List
- More information on World Flora Online
Basil: 15 wonders
Eggplant: growing from seeds in the garden
Sections: Lamiaceae (Lamiaceae) Spicy plants Plants on B Leafy Garden plants
People usually read after this article
Add a comment
growing from seeds, planting in open ground, properties of basil
Herbaceous annual plant fragrant basil (Ocimum basillicum), also called garden, or camphor, or ordinary, is a member of the Basil species of the subfamily Kotovnikovye of the Lamiaceae family. In the wild, such a plant can be found in Iran, Africa, the tropical regions of the American continent, the Caucasus, China, India, southern Asia and Central Asia. There is an opinion that Africa is the birthplace of the basilica, and it came to Europe thanks to the soldiers of the army of A. Macedonian. Previously, such a culture, as a rule, was used as a medicinal plant. To date, it is cultivated in almost all countries as a food spice.
There is an opinion that Africa is the birthplace of the basilica, and it came to Europe thanks to the soldiers of the army of A. Macedonian. Previously, such a culture, as a rule, was used as a medicinal plant. To date, it is cultivated in almost all countries as a food spice.
Contents
- 1 Features of basil
- 2 Planting basil seedlings
- 2.1 When to sow
- 2.2 Growing basil from seed
900 010 - 3.1 Rules for growing at home
- 3.2 How to water
- 3.3 Fertilizer
- 4.1 Planting outdoors
- 4.2 Growing
- 4.3 How to water
- 4.4 Fertilizer
- 4.5 What can be planted after basil
- 5.1 Diseases 1 21
- 6.1 Best varieties
- 7.1 Useful properties of basil
- 7.
 2 Contraindications
2 Contraindications
Features of basil
Basil has a branching and superficial root system. The straight tetrahedral stem reaches a height of 0.5–0.7 m, it is leafy and branched. Rarely toothed, oblong-ovate leaf blades are short-petiolate. On the surface of foliage and shoots there are villi. Irregular whorls consist of axillary flowers of white, pinkish or purple color. The composition of the fruit includes nuts, which, after full ripening, are easily separated from each other. Seeds remain viable for 5 years.
Purple varieties of this plant have the strongest odor and are very popular in the Caucasus and Asia. Green basil is the most sought after in Europe, and this plant is also considered the most popular spice in Mediterranean cuisine. Before the bush begins to bloom, it begins to exude the most pungent smell.
Basil. A new effective way of planting. (02/19/2016)
Watch this video on YouTube
Planting basil seedlings
When to sow
Basil can be grown from seedlings or sown directly into open ground. However, most gardeners choose the first method, as it is the most reliable.
However, most gardeners choose the first method, as it is the most reliable.
Seeds for seedlings are sown in spring, it is recommended to do this from early to mid-April. For sowing, you will need a special soil mixture. To prepare it, you need to combine humus, rotted compost and washed river sand, which should be taken in a ratio of 2: 4: 1. This substrate must be sieved, and then it is subjected to steaming in a water bath for 60 minutes. If you use a ready-made soil mixture for sowing, which is sold in a store, then it will also need to be disinfected. To do this, it is shed with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or Fitosporin. For sowing basil, you can choose boxes, but in this case you need to be prepared for the fact that the plants will need a pick in individual containers. Therefore, experts advise using cassettes for growing such seedlings, the depth of which should be 50–70 mm.
Sowing seeds is carried out in a moist substrate, while deepening them by only 10 mm. The row spacing when sowing in a common box should be about 50 centimeters. Crops from above must be covered with polyethylene or glass, after which they are removed to a well-lit and warm (from 20 to 25 degrees) place. The first seedlings can be seen 7-15 days after sowing.
The row spacing when sowing in a common box should be about 50 centimeters. Crops from above must be covered with polyethylene or glass, after which they are removed to a well-lit and warm (from 20 to 25 degrees) place. The first seedlings can be seen 7-15 days after sowing.
Growing basil from seeds
As soon as the first seedlings appear, the cover is removed from the container, and the plants themselves are moved to a cooler place (from 15 to 20 degrees). It is very easy to care for such seedlings. Watering should be carried out as needed, while remembering that the substrate should not dry out, however, it is necessary to ensure that it is not waterlogged, as in this case a fungal disease such as a black leg may develop, due to which all seedlings die. At the first signs of this disease, the plants will need treatment with a solution of copper sulphate (1 tsp per 2 liters of water) or you can shed the earth with a strong solution of potassium manganese.
If the basil was planted in a box, then during the growth of the first pair of true leaf blades, it will need to be dived. For this, a larger container is taken, which is filled with the same soil mixture, but only it will need to be fertilized. To do this, pour 2 tbsp into 5 liters of substrate. l. wood ash and 1 tbsp. l. complex mineral fertilizer. Planting seedlings in a new container should be at the same depth that they grew before. After the seedlings take root and begin to grow, they should be pinched over a 6–8 leaf plate to stimulate the growth of side shoots. Plants begin to harden off about 15 days before transplanting them into open soil. To do this, they must be taken out to fresh air every day. The duration of such a procedure should be increased gradually, so you need to start from one hour, and at the end, the seedlings will have to be on the street around the clock. Landing in open soil is carried out from mid to late May, but it should be noted that return spring frosts should be left behind.
For this, a larger container is taken, which is filled with the same soil mixture, but only it will need to be fertilized. To do this, pour 2 tbsp into 5 liters of substrate. l. wood ash and 1 tbsp. l. complex mineral fertilizer. Planting seedlings in a new container should be at the same depth that they grew before. After the seedlings take root and begin to grow, they should be pinched over a 6–8 leaf plate to stimulate the growth of side shoots. Plants begin to harden off about 15 days before transplanting them into open soil. To do this, they must be taken out to fresh air every day. The duration of such a procedure should be increased gradually, so you need to start from one hour, and at the end, the seedlings will have to be on the street around the clock. Landing in open soil is carried out from mid to late May, but it should be noted that return spring frosts should be left behind.
Growing basil on a windowsill
Rules for growing at home
If you decide to grow basil on your windowsill, then it should be sown in the last days of February or the first - March. For sowing, you need to use peat tablets or peat pots. It should also be noted that several seeds must be sown at once in 1 tablet or pot.
For sowing, you need to use peat tablets or peat pots. It should also be noted that several seeds must be sown at once in 1 tablet or pot.
In this case, the seeds should be subjected to pre-sowing preparation. To do this, they are immersed in a solution of potassium manganese of a dark pink color, where they must stay for 2 hours. Crops should be covered with a material that should be transparent and breathable. They need to be kept in the same conditions as basil grown for seedlings (see above). It should be noted that such a plant needs sunlight for at least 3-4 hours a day. After the plants develop their first pair of true leaf blades, they must be transplanted. To do this, a 1 liter pot is taken, at its bottom a layer of drainage is laid out from broken brick, expanded clay or small pieces of foam, its thickness should be from 20 to 30 mm. Basil should be planted together with a pot or a tablet. The soil mixture for planting is used nutritious, it should also pass water well and be light. For example, you can use this composition: combine coconut fiber and humus (2: 1). It will be possible to start picking the first leaves after 6 weeks.
For example, you can use this composition: combine coconut fiber and humus (2: 1). It will be possible to start picking the first leaves after 6 weeks.
How to water
Basil belongs to moisture-loving plants. In this regard, it is necessary to ensure that the substrate is always slightly moist. Watering should be arranged almost every day. If you forget to water the bush in time, then its leaves will very quickly lose their turgor. But in watering it is also very important not to overdo it, because due to the stagnation of liquid in the substrate, rot can appear on the root system. When the plant is watered, it is necessary to loosen the surface of the substrate in the container, do this with a frequency of 1 time in 2-3 days.
WE GROW BASIL ON THE WINDOW SILL. Simply and easily.
Watch this video on YouTube
Fertilizer
If a medium that is not very fertile was used for planting this plant, then in this case it will need to be systematically fed. For top dressing, it is recommended to use universal fertilizers based on compost or humates, they must be applied to the substrate in the concentration indicated in the instructions attached to the preparation. You need to feed the bush no more than 1 time in 4 weeks.
For top dressing, it is recommended to use universal fertilizers based on compost or humates, they must be applied to the substrate in the concentration indicated in the instructions attached to the preparation. You need to feed the bush no more than 1 time in 4 weeks.
Growing basil outdoors
Planting outdoors
As mentioned above, it is imperative to plant basil seedlings outdoors from mid to late May, but you need to make sure that spring return frosts are behind. For landing, you should choose an open, well-lit area, which should be reliably protected from cold, strong winds. Some gardeners advise planting basil in the trunk circle of a young fruit tree, there is practically no shade from it, so the plant receives a sufficient amount of light, while its powerful spicy aroma can scare away various pests from the seedling.
The soil on the site should be light and saturated with humus, and it should also pass water well. 4 weeks before planting, the site should be digged, while peat, humus or compost should be added to the soil (2 kilograms of organic fertilizer per 1 square meter of the site).
Landing should be done in the evening or on a cloudy day. Prepare the holes, the distance between them should be from 15 to 20 centimeters. In them, the grown seedlings should be planted. Planted plants need abundant watering, for this they use tepid, well-settled water.
Growing
Growing basil in open soil is relatively easy. To do this, it needs to be watered in a timely manner, weeded, fed, loosened the soil surface, and also protected from pests and diseases. Planted plants that did not have time to take root should be covered with a film for the first 15 days at night in case of a sudden cold snap. Until the plant gets stronger and starts to grow, it is recommended to systematically weed. During the season, it will be necessary to loosen the surface of the soil 7 or 8 times before watering. To stimulate branching, it is necessary to carefully break out the newly appeared peduncles.
How to water
Watering the basil frequently will cause new leaf blades to grow much faster. Watering should be done immediately after the topsoil dries out. However, it should be remembered that excessive watering is just as unacceptable as insufficient watering, as it causes severe damage to the plant. It should be watered with tepid water (about 25 degrees), while it should stand for 24 hours (longer possible). To make it more convenient to prepare water for irrigation, it is necessary to install a large container on the site in a well-lit place, for example, an unnecessary bath or barrel.
Watering should be done immediately after the topsoil dries out. However, it should be remembered that excessive watering is just as unacceptable as insufficient watering, as it causes severe damage to the plant. It should be watered with tepid water (about 25 degrees), while it should stand for 24 hours (longer possible). To make it more convenient to prepare water for irrigation, it is necessary to install a large container on the site in a well-lit place, for example, an unnecessary bath or barrel.
Fertilizer
To stimulate the growth of the green mass of basil, you need regular top dressing, which is carried out once every 4 weeks. The first top dressing is arranged half a month after planting the seedlings on the site, for this they use a solution of Nitrofoska (a couple of large spoons of fertilizer per 12 liters of water). On 1 square meter of the site should go from 3 to 4 liters of nutrient mixture.
Planting basil seedlings in a bed
Watch this video on YouTube
What can be planted after basil
Experts advise against planting basil in the same area every year. It is necessary to rotate crops, which is the main principle of successful farming. If the basil was grown in the same area for 2 or 3 seasons in a row, then it will be possible to plant it in the same place only after 4 or 5 years. The area where basil was previously grown is suitable for planting plants that are resistant to diseases of this crop, for example, you can plant carrots, zucchini, pumpkins, tomatoes, legumes, cucumbers, squash and early potatoes. Basil is recommended to be planted after tomatoes, early and cauliflower, strawberries, green manure, onions, beets and greens.
It is necessary to rotate crops, which is the main principle of successful farming. If the basil was grown in the same area for 2 or 3 seasons in a row, then it will be possible to plant it in the same place only after 4 or 5 years. The area where basil was previously grown is suitable for planting plants that are resistant to diseases of this crop, for example, you can plant carrots, zucchini, pumpkins, tomatoes, legumes, cucumbers, squash and early potatoes. Basil is recommended to be planted after tomatoes, early and cauliflower, strawberries, green manure, onions, beets and greens.
Pests and diseases of basil
Diseases
Basil is highly resistant to various diseases. However, sometimes he still gets sick. Below will be described those diseases that this culture suffers from most often.
Blackleg
Blackleg - Basil seedlings are susceptible to this fungal disease. Its development provokes increased acidity, insufficient aeration of the substrate, as well as excessively frequent and abundant watering.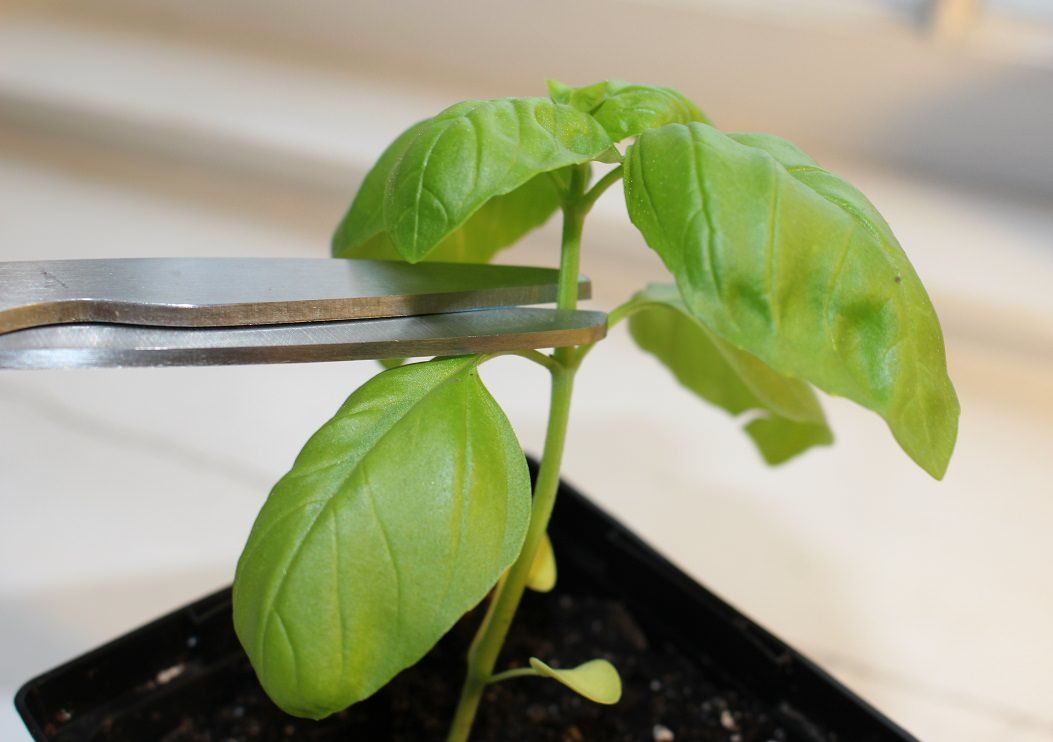 The root neck of the seedlings is affected by the fungus, due to which the vessels that are involved in the nutrition of the plant become clogged, the stem, as well as its base, soften, become black and thin, after which the bush begins to turn yellow and dies.
The root neck of the seedlings is affected by the fungus, due to which the vessels that are involved in the nutrition of the plant become clogged, the stem, as well as its base, soften, become black and thin, after which the bush begins to turn yellow and dies.
Fusarium
Fusarium is also a fungal disease. Toxins are released into the nutrient juice of a diseased bush, as a result of which its vessels are affected. If a young bush is affected, then its shoots turn brown and gradually become thinner. In diseased adult plants, the top dries up, after which they wither and die. The disease actively develops at high temperatures, while the humidity of the air should be increased.
Gray mold
Gray rot - it most often affects plants grown in greenhouses or greenhouses. However, bushes grown in open soil can also be affected by this disease. At first, the disease manifests itself on the leaf plates located below, which have already begun to die. After that, the disease gradually captures the entire bush. Dry brownish spots appear on the infected parts of the plant, which eventually become watery and covered with a gray fluff.
After that, the disease gradually captures the entire bush. Dry brownish spots appear on the infected parts of the plant, which eventually become watery and covered with a gray fluff.
If the bush is affected by gray rot or fusarium, then at the initial stage of development of such a disease, it should be sprayed with an infusion of onion peel. To prepare it, it is necessary to combine the husk with water in a ratio of 1: 4, the mixture must be infused for 24 hours. Before processing, the infusion should be filtered. If the seedlings are affected by the black leg, then the substrate in which it grows must be shed with a solution of potassium permanganate. At the same time, diseased plants must be removed from the container along with a clod of earth and destroyed, and the resulting hole must be shed with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. If the disease has already gained strength, then in this case treatment with fungicidal preparations will be required, for example: Fitosporin, Toivita Jet, Fuedazole, Topaz and others of similar action.
To prevent basil from getting sick, certain preventive measures should be taken:
- this crop should not be grown in the same area for more than three years;
- crops should not be too thick;
- Once every 7 days, the surface of the area should be dusted with wood ash;
- water the plant on time, without watering it or letting the soil dry out;
- Loosen the area regularly;
- Remove weeds as soon as they appear.
Pests
This plant is also very resistant to pests, however, field bugs and aphids can settle on it.
Aphids
Aphids are a very dangerous pest that can severely damage the basil. It sucks the juice from the shoots and foliage, due to which the folding of the leaf plates is observed, the development of the shoots stops, and the bush itself begins to dry out. Such a pest leaves sugary secretions on the surface of the plant, on which the sooty fungus prefers to settle, which is why the bush is covered with a touch of dark color.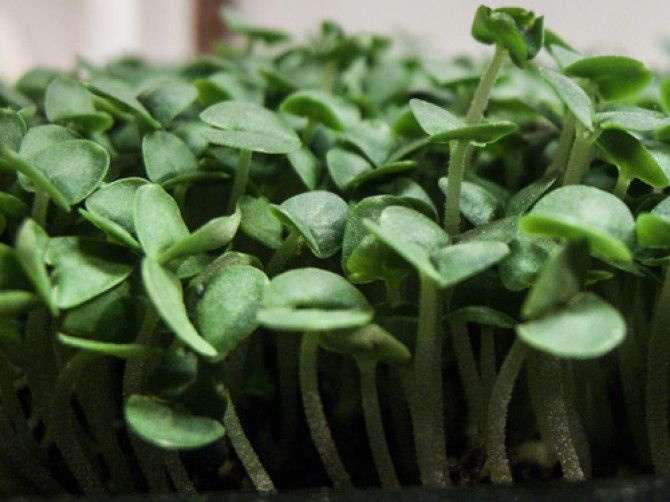 In addition, this pest is considered the main carrier of viral diseases that are not currently being treated. To start the fight against aphids should be immediately after its discovery. You can fight it with folk remedies, for example, decoctions of wormwood, tansy, hot pepper, dandelion, yarrow, onion, garlic, tomato or potato tops, mustard. It will take 2-3 treatments with an interval of 1-1.5 weeks if this crop is grown in open ground. A remedy prepared from 100 grams of tar soap, crushed with a grater, and 1 bucket of water is considered quite effective. Ash solution also shows good results, for its preparation it is necessary to mix 300 grams of wood ash with freshly boiled water, the mixture should boil for 30 minutes. When it settles, it is filtered, then so much water is added to the solution so that its volume becomes equal to 10 liters. If there are a lot of pests, then folk remedies may be powerless, in this case the bushes are treated with Karbofos, while the solution must be done in accordance with the instructions.
In addition, this pest is considered the main carrier of viral diseases that are not currently being treated. To start the fight against aphids should be immediately after its discovery. You can fight it with folk remedies, for example, decoctions of wormwood, tansy, hot pepper, dandelion, yarrow, onion, garlic, tomato or potato tops, mustard. It will take 2-3 treatments with an interval of 1-1.5 weeks if this crop is grown in open ground. A remedy prepared from 100 grams of tar soap, crushed with a grater, and 1 bucket of water is considered quite effective. Ash solution also shows good results, for its preparation it is necessary to mix 300 grams of wood ash with freshly boiled water, the mixture should boil for 30 minutes. When it settles, it is filtered, then so much water is added to the solution so that its volume becomes equal to 10 liters. If there are a lot of pests, then folk remedies may be powerless, in this case the bushes are treated with Karbofos, while the solution must be done in accordance with the instructions. It should be noted that this insecticidal preparation is odorless and also tasteless. So, Bankol, Akarin and Aktellik are best suited for processing.
It should be noted that this insecticidal preparation is odorless and also tasteless. So, Bankol, Akarin and Aktellik are best suited for processing.
Meadow or field bug
Field or meadow bug is also a sucking insect that feeds on plant sap of this crop. As a result of its vital activity, the leaf plates are deformed, whitish spots form on their surface, then they turn brown and gradually die off. Both larvae and adults of this insect can harm the basil. For wintering, such a bug settles in the upper layer of soil or in leaves that have flown around. Bedbugs should be dealt with in the same way as with aphids.
Types and varieties of basil
The following types of basil are most commonly cultivated: camphor (or fragrant), Mexican (or cinnamon), purple (common or regan) and lemon (Thai). There are many varieties of this plant, which are distinguished by the following features:
- Shades of smell . The aroma is tart, sweet, cold and warm.
 The main aromas of this culture are cinnamon, anise, pepper, lemon, vanilla, caramel, clove and menthol. For the preparation of drinks, as well as desserts, those varieties are used that have a lemon, cinnamon, caramel and vanilla smell. Varieties with anise flavor are good for fish dishes, and basil with peppery and clove flavors is suitable for meat dishes.
The main aromas of this culture are cinnamon, anise, pepper, lemon, vanilla, caramel, clove and menthol. For the preparation of drinks, as well as desserts, those varieties are used that have a lemon, cinnamon, caramel and vanilla smell. Varieties with anise flavor are good for fish dishes, and basil with peppery and clove flavors is suitable for meat dishes. - Color . There is green basil and purple basil. Varieties with a purple color have a stronger aroma and are most often used in Central Asian and Caucasian cuisine. And green varieties are most popular in Europe, and in particular in the Mediterranean.
- Size and shape of bush . Basil is divided into sprawling, compact, erect and semi-spreading. There are also intermediate forms. In terms of height, tall (0.6–0.85 m), medium-sized (0.3–0.6 m), as well as undersized (0.18–0.3 m) varieties are distinguished. For growing indoors, it is recommended to choose low-growing varieties.

- Maturity dates . Varieties are divided into late, middle and early.
How to choose a basil variety
Watch this video on YouTube
Best varieties
- Moorish . This medium ripening variety is distinguished by its productivity and aroma. The color of the sprawling upright bush is purple. Plant height about 0.65 m.
- Table . The height of an upright bush is about 0.6 m. The ovoid large leaf plates are painted greenish in color and have a delicate texture. This productive variety is the most fragrant of all mid-late varieties.
- Dreamer . This variety is among the most productive. Spreading massive bush has a bright green color. The shoots are branched, and the shape of the leaf plates is oval-lanceolate.
- Balconstar . This variety is undersized. Small fragrant leaf plates have excellent taste, they are great for salads.
 It is often grown in pots on a windowsill.
It is often grown in pots on a windowsill. - Genoese . This variety is distinguished by its productivity. Large shiny dark green leaf plates are quite fragrant and have a pleasant taste. Leaves are used both dried and fresh. In some cases, they replace mint, adding to soft drinks.
- Clove Gourmet . The variety is distinguished by its productivity. The bush is medium tall, upright and massive. Green leaf plates are medium in size and elliptical in shape. This variety is recommended for use as a seasoning for meat, fish, cheese, rice and potatoes.
- Basilisk . This compact variety grows well both in open soil and indoors. It has a peppery-clove scent. The height of an upright densely leafy bush is about 0.2 m. Small leaf plates are green in color. The stems are semi-raised.
- Yerevan . This variety is one of the most popular fruit varieties. The smell of such a basil is clove-pepper.
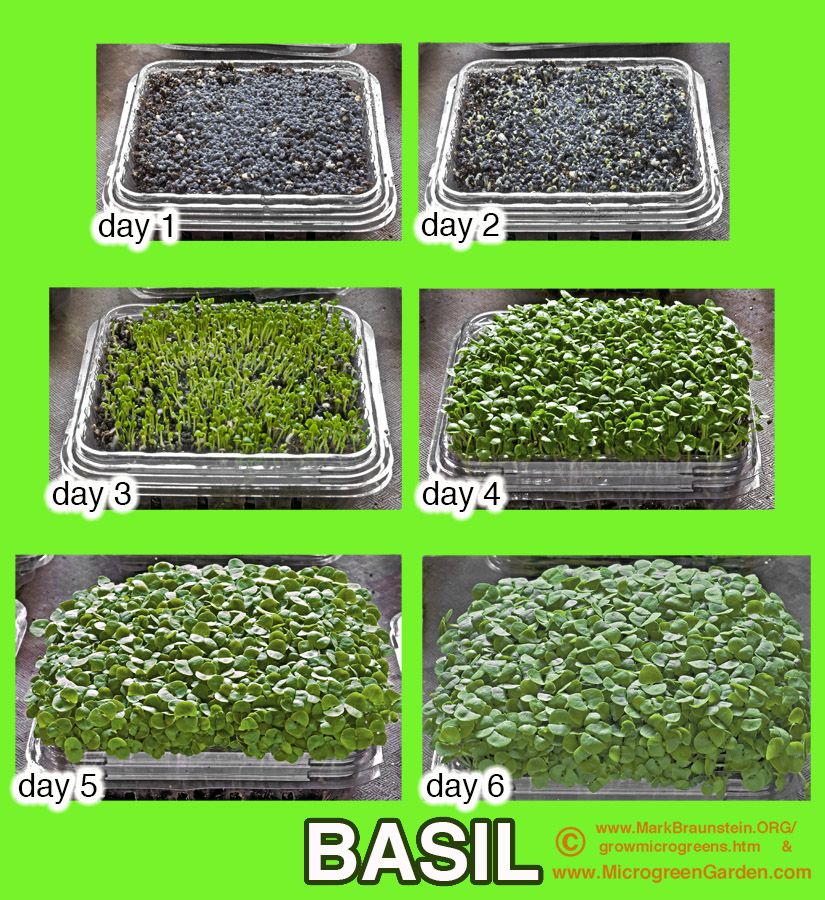 On a medium-sized bush there are medium-sized leaf plates of an ovoid shape and purple color.
On a medium-sized bush there are medium-sized leaf plates of an ovoid shape and purple color. - Troll . This mid-season small-leaved variety is compact and productive. Great for growing indoors. Such a plant is not afraid of sudden changes in temperature. The foliage has a dark purple color. The plant looks very impressive.
- Magic Mountain . This Israeli variety is resistant to both low and high temperatures, and it is also drought tolerant. A neat bush has a round shape. Green leaf plates have a purple tint. Such a plant looks good in the garden as an ornamental.
- Red Ruby . The variety was created by American breeders. The color of the bush is mahogany-purple. These plants eat both foliage, which does not have the bitterness characteristic of green varieties, and buds (they are added to omelettes).
The following varieties of basil are also quite popular: Charm, Marquis, Ararat, Velvet, Violet, Greek, Robin Hood, Dragon, Gigolo, Fragrant green, Orion, Pepper aroma, Tempter, Baku, Wizard, Lemon, Dwarf, Curly, Philosopher, Shirokolistny, etc.
Properties of basil: harm and benefits
Useful properties of basil
Basil has a specific smell, which is due to the presence of essential oil in the aerial part of the bush, which has a complex composition and antibacterial properties. Basil contains vitamins C, B2, PP, provitamin A, carotene, sugar, phytoncides, rutin.
It helps to strengthen the immune system, thereby increasing the resistance of the human body to infections. This plant has been proven to be able to restrain the growth of HIV as well as cancer cells. It has an antibacterial, tonic, antipyretic, antioxidant and tonic effect. Basil is recommended to be included in your diet for bacterial, viral and fungal infections, as well as pulmonary and respiratory diseases.
This spicy herb will help get rid of excess gas in the rectum, excess mucus in the nose, and it also helps to strengthen the nervous tissue and improve memory. It shows high efficiency in the fight against inflammatory processes in the oral cavity: ulcers, plaque, caries, tartar and bad breath. Also, basil has an astringent effect, it strengthens the gums, which helps prevent tooth loss. It will help get rid of flatulence, as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Also, basil has an astringent effect, it strengthens the gums, which helps prevent tooth loss. It will help get rid of flatulence, as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
It contains enzymes that accelerate the breakdown and burning of fats in the human body. And the evengol and estragol contained in it contribute to the stimulation of mental activity. This culture contains an essential oil, which has a wound healing effect, it also eliminates spasms of a diverse nature and is used for inhalation of the upper respiratory tract. The juice obtained from the foliage is used to treat fungal skin lesions, and water extracts are used during the treatment of food poisoning and gastritis. Dried grass is used to make tea, as well as to make compresses that eliminate pain in the head and eczema. A tincture is prepared from this herb, which is used to treat colitis, pyelitis, whooping cough, neurosis, bronchial asthma, low blood pressure, inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, flatulence and colds.










