Diy insect repellent for plants
6 bug sprays for plants |
(Image credit: Getty Images)
While insects are a valuable part of our gardens' ecosystems, sometimes they end up tucking into our vegetable harvests or eating their way through our flower buds before they bloom.
These moments can have us reaching for the insecticides. However, filled with toxic chemicals, commercial insecticides often stand at odds with the sustainable garden ideas that we want our plots to embody.
This is where homemade insect sprays and deterrents come into their own. Created from items you would find in your store cupboard, they are quick and effective ways to ward bugs off your prized plants.
‘Homemade garlic, nettle, soap, tomato and basil sprays are effective against aphids, mites and thrips. The aim is not to kill off all the insects in your garden, but rather aim for a healthy ecosystem,’ says garden expert Leigh Clapp.
Bug sprays – 6 homemade recipes for plants
Homemade bug sprays should only be used as a short term solution – at the same time as treating pests, think of adding other plants to your garden that will encourage insects and animals that prey on the problem bug.
‘Disaster-proof your garden through plant diversity. The wider the range of plants, the less they are plagued by pests, so that if a disease or pest occurs only a limited number of susceptible plants will be affected,’ continues Leigh.
For example, if you want to get rid of slugs, can you attract more birds? If you need to get rid of aphids, could you plant angelica, fennel and dill nearby to attract ladybirds? There are lots of different companion planting ideas that will help you to reduce pests in your plot. By creating a balanced garden, you will find that you have less and less need for bug sprays.
Before using any of these bug sprays on your plants, always do a patch-test. Spray a small amount onto a few leaves of the plant and wait 24 hours to see if there is any damage. Avoid using any foliar sprays during the heat of the day as the exposure to the sun can cause leaf burn.
1. Insecticidal soap
(Image credit: Getty Images)
A popular bug spray for treating a wide range of pests, homemade insecticidal soap, consists of soap, oil and water. Homemade insecticidal soap is often the first port of call for many gardeners as the ingredients are all store cupboard essentials.
Homemade insecticidal soap is often the first port of call for many gardeners as the ingredients are all store cupboard essentials.
To create insecticidal soap combine one cup of vegetable oil with one tablespoon of dishwashing soap or pure Castile liquid soap. For this method, as well as any others that call for dishwashing soap, avoid those that contain a degreaser or bleach as these can cause more harm than good. Use this oil and soap mixture as a concentrate and dilute one teaspoon with two cups of warm water into a spray bottle. Once mixed with water, the solution’s efficacy will only last for a day.
Insecticidal soap is one of the best ways of getting rid of aphids, as well as lacebugs, leafhoppers, mealybugs and thrips.
2. Neem oil bug spray
(Image credit: Getty Images)
An organic insecticide, neem oil has seen a rise in popularity as a method to treat everything from insects through to fungi.
‘Neem oil has been used in India for thousands of years and is a trusted method to keep on top of pests, without any of the nasties,’ explains John Maree, co-owner of OxyPlants . ‘A spray of Neem oil on the tops and undersides of your plant’s leaves will help remove several pests, including mites, whitefly, aphids, thrip, and mealybugs, at every stage in their life cycle. Using neem oil also helps to get rid of powdery mildew, too.’
‘A spray of Neem oil on the tops and undersides of your plant’s leaves will help remove several pests, including mites, whitefly, aphids, thrip, and mealybugs, at every stage in their life cycle. Using neem oil also helps to get rid of powdery mildew, too.’
To use neem oil as a homemade bug spray mix one to two tablespoons of pure, cold-pressed neem oil with a gallon of water. You can also add one to two teaspoons of dish soap to the mix to help the neem oil adhere to the plants.
Alternatively, you can use neem oil as a root soak to treat root rot. Mix one gallon of water with two tablespoons of neem oil and one teaspoons of pure Castile liquid soap (to help the neem oil adhere). Apply a small amount as a test and wait 24 hours. If all is well, then apply two or three cups to the soil around the plant, then continue the treatment as a replacement to the watering cycle.
A benefit of using neem oil over other pesticides is that it doesn't harm birds, pets or beneficial insects. This is because neem oil gets absorbed into the plant’s tissue rather than just sitting on the surface and so only affects any insects that ingest the plant.
This is because neem oil gets absorbed into the plant’s tissue rather than just sitting on the surface and so only affects any insects that ingest the plant.
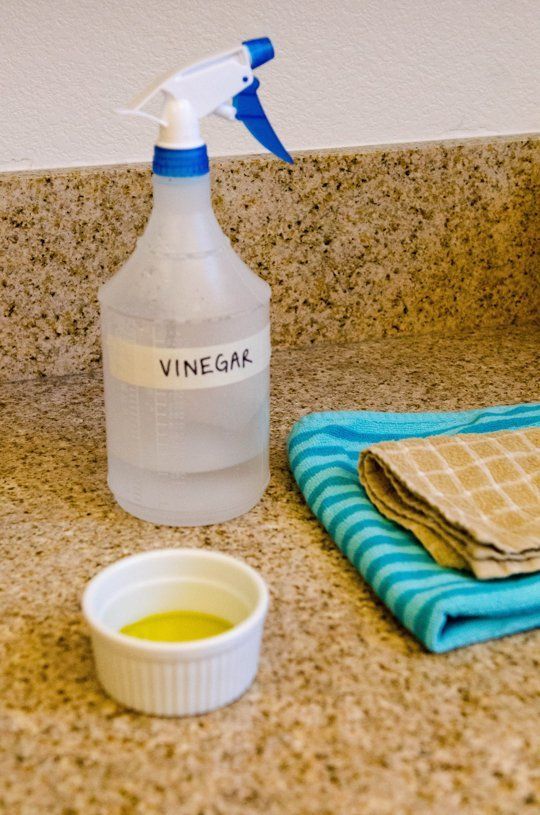
3. Vinegar spray
(Image credit: Getty Images)
It seems that there is no end to the abilities of vinegar, especially when you take into account the numerous ways of cleaning with vinegar, but did you know that it can also be used as a bug spray?
One of the easiest homemade bug sprays, simply mix one cup of white vinegar with three cups of water. You can also add half a teaspoon of dishwashing soap to help the solution adhere. Shake thoroughly and apply to the affected areas.
The acetic acid in the vinegar will treat a wide range of garden pests but it requires contact. If you have whitefly eggs be sure to spray under the leaves. Furthermore, white vinegar has a strong odor which has been reported to repel ants and other scent driven pests.
'If you are wanting to treat houseplants with a vinegar spray, try adding a few drops of essential oil or some slices of lemon peel or rosemary sprigs to help temper the vinegar smell,' advises Period Living editor Melanie Griffiths.
4. Garlic spray
(Image credit: Future)
You may have heard that onions and garlic make good companion plants as the scent of their foliage helps to repel aphids, slugs and carrot fly. This spray takes it to the next level.
‘Puree two garlic bulbs with one tablespoon of vegetable oil, let it sit overnight, strain, add one teaspoon of mild liquid soap and four cups of water to fill the spray container,’ recommends Leigh Clapp.
Store this mixture in the fridge until needed. In the evening, spray both sides of the leaves with the spray and then reapply every few days when your plants are suffering with infestation. Alternatively, use every one to two weeks as a deterrent.
If you want to be even more sustainable, why not learn how to grow garlic so that you can have an endless supply of garlic spray – plus extra cloves that you can add to your favorite meals?
5. Tomato leaf spray
(Image credit: merlinpf / Getty Images)
If you’ve ever tried growing tomatoes, you will be familiar with the characteristic scent of their leaves, but did you know that these leaves contain a compound called alkaloid which can be used to create a spray that is toxic to aphids and mites? To make a tomato leaf spray, mix equal quantities of chopped up tomato leaf with water and leave to steep overnight. Let this steep overnight, before straining into a spray bottle and applying to the plant’s leaves.
Let this steep overnight, before straining into a spray bottle and applying to the plant’s leaves.
This is a great way to recycle tomato leaves once you've pruned them – you can learn how to prune tomato plants for a maximum yield.
6. Cinnamon spray
(Image credit: Getty Images)
If you’ve ever grown plants in pots, you’ll be familiar with the problem of stray mushrooms. However, this can be easily resolve with a simple cinnamon spray. Mix two teaspoons cinnamon powder into four cups of warm water. Allow this to steep overnight and then strain through a coffee filter and then pour into a spray bottle. Mist the potting soil and plants.
Cinnamon spray is also reported to be an effective treatment to get rid of ants. If you have an ant problem in your pots or want to keep ants away from dining or patio areas, try applying cinnamon oil or powdered cinnamon to create an effective barrier.
What is a natural bug killer for plants?
Vinegar is a really effective natural bug killer for plants. Dilute it 1:1 with water in a spray bottle and spray it over and under the leaves of affected plants. You can also use it around the house to deter bugs inside; the vinegary smell will quickly dissipate.
Dilute it 1:1 with water in a spray bottle and spray it over and under the leaves of affected plants. You can also use it around the house to deter bugs inside; the vinegary smell will quickly dissipate.
You can also use a hydrogen peroxide and water solution, which is great when trying to get rid of bugs from houseplant soil.
Which homemade bug spray is best for repelling mosquitoes?
The best homemade bug sprays for repelling mosquitoes are those with a strong smell that mosquitoes hate. Other than citronella, which you are probably already familiar with as a mosquito repellent, they include the following essential oils:
- Catnip
- Cinnamon bark
- Geranium
- Lavender
- Lemon eucalyptus
- Peppermint
- Pine
- Rosemary
Having graduated with a first class degree in English Literature four years ago, Holly started her career as a features writer and sub-editor at Period Living magazine, Homes & Gardens' sister title. Working on Period Living brought with it insight into the complexities of owning and caring for period homes, from interior decorating through to choosing the right windows and the challenges of extending. This has led to a passion for traditional interiors, particularly the country-look. Writing for the Homes & Gardens website as a content editor, alongside regular features for Period Living and Country Homes & Interiors magazines, has enabled her to broaden her writing to incorporate her interests in gardening, wildlife and nature.
Working on Period Living brought with it insight into the complexities of owning and caring for period homes, from interior decorating through to choosing the right windows and the challenges of extending. This has led to a passion for traditional interiors, particularly the country-look. Writing for the Homes & Gardens website as a content editor, alongside regular features for Period Living and Country Homes & Interiors magazines, has enabled her to broaden her writing to incorporate her interests in gardening, wildlife and nature.
5 Homemade Pesticides: Soap Sprays for Plants
There is no magic bullet for keeping your garden and indoor plants free from insect pests. Some tricks I have learned over the years are ways to cope with bugs without resorting to nasty chemicals. Here are my tips, including homemade insecticidal sprays (soap sprays).
Pay Attention to Your Plants
Before resorting to using pesticides (even organic ones), consider the following techniques to discourage insect pests from attacking your plants:
- Nourish your plants with organic amendments such as aged compost.
 Strong plants don't attract as many insects and can withstand their assault better than weak ones. If you're using fertilizer, follow instructions closely. Over-fertilized plants will attract pests to eat their lush new growth.
Strong plants don't attract as many insects and can withstand their assault better than weak ones. If you're using fertilizer, follow instructions closely. Over-fertilized plants will attract pests to eat their lush new growth. - Use companion planting to repel insects naturally. Some plants thrive together; some do not. See our Companion Planting Guide.
- Use barriers like row covers to block pests from attacking your plants, especially tender transplants. (Remove the covers when plants are established and in bloom to allow for insect pollination.) Additionally, "collars" (paper towel or toilet paper cardboard rolls) inserted around the small transplants (1 to 2 inches into the soil) will prevent insects such as cutworms from eating the young stems.
- Time plantings to avoid peak insect populations. For example, plant squash as early as possible to avoid squash vine borers, which lay eggs in early to mid-summer. Plant carrots after June 1 and harvest by early September to avoid the carrot fly.

- Select varieties that are naturally resistant to some pests. I grow a lot of butternut squash because it is highly resistant to attack from the squash vine borer.
- Make your garden welcoming to beneficial insects and they will do a lot of the work for you by keeping the bugs they feed on in check. For example, lady beetles are an effective biological control of many insect pests. If you see a tomato hornworm with white cocoons on his back (above photo), leave him alone. A parasitic wasp has laid her eggs on him and soon her babies will eat him from the inside out. A fitting death for such a gruesome pest!
- Learn to identify the bugs in your garden. You can't beat them if you don't know who is friend and who is foe. Learn what their larvae and eggs look like to head them off before they become adults.
These aphids have done some damage, but don't spray if you see the black and orange alligator-like ladybug larvae attacking them. He will do the dirty work for you by eating up to 50 aphids a day!
5 Organic Pesticide Sprays for Insects
If you have exhausted all these methods and feel you must resort to using a spray, don't reach for harsh chemicals. They will do more harm than good by polluting the watershed, killing good and bad bugs alike, and eventually the insects you are trying to kill may grow resistant to those chemicals requiring you to use even stronger ones! They can also harm birds, animals, you, and your children!
They will do more harm than good by polluting the watershed, killing good and bad bugs alike, and eventually the insects you are trying to kill may grow resistant to those chemicals requiring you to use even stronger ones! They can also harm birds, animals, you, and your children!
Try a more natural approach by making one of these homemade insecticidal sprays. Bear in mind that although they are less toxic they are not totally harmless. Keep them away from kids and pets. Test them on a few leaves before you go all in to make sure they won't injure your plants. Be sure never to spray them on your plants during the sunny, hot part of the day or they will definitely cause foliar damage. Spray in the evening, when bees and other pollinators are not active.
- Dish Soap Spray: Dissolve 1 tablespoon of a mild liquid soap such as a pure dish soap (no bleach, degreaser, or detergents added) or castile soap in 1 quart of water. Dr. Bronner's soap may be expensive, but it uses no animal fats, which makes it a good choice for vegans.
 Insecticidal soaps are good for killing soft-bodied insects. Be sure to cover the whole plant—both sides of the leaves and on the stems. Soap sprays only work when wet, so they will need to be reapplied every 4-7 days or until you notice that populations have decreased. After a few applications, if rain hasn't done this for you, spray the plants with plain water to rinse off any soapy residue.
Insecticidal soaps are good for killing soft-bodied insects. Be sure to cover the whole plant—both sides of the leaves and on the stems. Soap sprays only work when wet, so they will need to be reapplied every 4-7 days or until you notice that populations have decreased. After a few applications, if rain hasn't done this for you, spray the plants with plain water to rinse off any soapy residue.
- Oil Spray: Mix 1 cup of vegetable oil with 1 tablespoon of mild liquid soap. Add 2-8 teaspoons of this mixture to 1 quart of water and spray your plants as above. The oil in this spray smothers the insects so it is effective on aphids, thrips, mites, and scale.
- Tomato Leaves Insecticide: The leaves of tomatoes contain solanine and tomatine and can be used as an insecticide. Soak 2 cups of fresh leaves in 1 quart of water overnight. Strain and spray. It kills aphids and many types of chewing insects, but also attracts beneficials. Don't use it on other nightshades like eggplants, peppers, or potatoes because it could spread disease from plant to plant.

- Garlic Repellent Spray: Despite all you've read, garlic acts as more of a repellent than a killer. Puree 2 bulbs of garlic with 1 cup of water and let sit overnight. Strain the liquid into a quart jar, add 1/2 cup vegetable oil, 1 teaspoon liquid soap, and fill the jar the rest of the way with water. Put one cup in a 1 quart sprayer, fill with water and apply to your affected plants. It is good for repelling aphids, cabbage worms, leaf hoppers, squash bugs, and whiteflies.
- Hot Pepper Repellent Spray: Hot pepper is also a good repellent and works on rabbits and deer as well as many insects. Mix 1 tablespoon dried chile powder, 1 quart of water, and 1 teaspoon of mild soap. Spray full strength on the plants under attack.
If you have lots of hot peppers growing in your garden, you can make a fresh concoction from 1/2 cup chopped peppers pureed in 1 cup of water. Add the puree to 1 quart of water and bring to a boil. Let sit until cool and then strain. Add 1 teaspoon mild soap and spray full strength on plants. You might want to wear gloves when working with this spray and be sure not to get it into your eyes!
Add 1 teaspoon mild soap and spray full strength on plants. You might want to wear gloves when working with this spray and be sure not to get it into your eyes!
Many other plants have been reported to have insecticidal qualities, including hyssop, lettuce leaves, onions, pennyroyal, peppermint, and radish leaves.
There is no one-size fits all when it comes to pest management. At best we can try to maintain a healthy balance of good guys and bad guys and still get some decent produce for us!
Now that we've learned how to minimize insect pests, let's tackle weeds. Here are tips on coping with weeds, including 5 Homemade Herbicides.
How to protect flowers from diseases and pests
Gardeners with great love grow a variety of flower crops. But even in the most experienced of them, plants sometimes get sick, they are inhabited by numerous pests that worsen the appearance of flowers. They damage leaves, buds, stems and roots. If no action is taken, the affected flower may die. But timely and competent actions taken to combat ailments and harmful insects will help plants recover and maintain their decorative properties. An important task of gardeners is preventive measures, which consist in strictly following the agricultural technology developed for each crop. Strong and powerful plants are much less affected by diseases.
But timely and competent actions taken to combat ailments and harmful insects will help plants recover and maintain their decorative properties. An important task of gardeners is preventive measures, which consist in strictly following the agricultural technology developed for each crop. Strong and powerful plants are much less affected by diseases.
Preventive measures include:
- Deep soil digging - flower beds with annual plants should be dug up annually after the end of the season. Autumn digging of the soil of flower beds contributes to the destruction of various caterpillars, as well as gnawing scoops, wireworm larvae and moths.
- Autumn destruction of plant residues - this should be done before digging. It is necessary to collect after the end of the gardening season all plant residues, decontaminate them and place them in a compost heap. Such work leaves no room for the survival of pests, almost 75% of which overwinter on the soil surface, hiding under dead plant parts.

- Selection for planting disease-resistant varieties - healthy seeds are selected, dressed with effective protective drugs, as well as growth stimulants.
- Soil liming - this procedure disinfects the soil, namely, it worsens the conditions for the development of pest larvae, such as wireworm. Liming also gives good results in the fight against Fusarium dahlias and nematodes on phlox.
In addition, timely disposal of weeds helps to maintain the ideal condition of the flower garden.
The most common flower diseases
There are many diseases that affect flowers. Some of them are rare, others can be found in almost every garden. The most common "ailments" of flowers include:
- powdery mildew;
- rust;
- gray mold;
- spotting.
Powdery mildew
It is manifested by the appearance on the leaves of a white, ashy or grayish coating, which can subsequently turn into a brown color. First, mild whitish spots appear, then the affected area increases and gradually covers the entire diseased plant. In leaves, the upper side is more affected. It causes a similar disease a number of varieties of the fungus. It develops more actively during periods of inclement wet weather, but can appear on flowers and at air humidity of 70% or less. From flower crops, phloxes and chrysanthemums, lupins and levkoy, as well as geraniums, delphinium, calendula and many other species often suffer from powdery mildew.
First, mild whitish spots appear, then the affected area increases and gradually covers the entire diseased plant. In leaves, the upper side is more affected. It causes a similar disease a number of varieties of the fungus. It develops more actively during periods of inclement wet weather, but can appear on flowers and at air humidity of 70% or less. From flower crops, phloxes and chrysanthemums, lupins and levkoy, as well as geraniums, delphinium, calendula and many other species often suffer from powdery mildew.
Ways to deal with powdery mildew of flowers:
- We mentioned prevention above - it is necessary to cut off plants that have faded in a timely manner, as well as cut off and destroy stained leaves or stems.
- In autumn or at the very beginning of spring, after removing diseased stems and harvesting dead leaves, perennials should be sprayed until leaves appear with a 1-2% solution of iron or copper sulphate. For those perennials that overwinter with leaves, treatment with 1% Bordeaux liquid is suggested.

- During the growing season, except for the period when flowers bloom, if characteristic signs of powdery mildew are found, the plant is sprayed with Topaz or Skor. Effective treatment is also provided by the use of fungicides such as Fundazol and Raek. They are recommended to be used alternately, mixing water-soluble fertilizers into the solutions of the products in order to immediately perform foliar top dressing.
Rust
This disease can spread in some types of flowers exclusively on leaves, while in others it affects both shoots and buds. Small pads are formed on them, the color of which varies. This is what pustules look like containing spores of the fungus, provoking the appearance of rust on plants. If no action is taken, the pustules will spread over most of the leaves and stems of the plant, the color around the pustules will turn pale green, yellow or brown. The leaves will eventually fall off, the stems are deformed, the plant will die. Mallow and carnation are most susceptible to rust, white phloxes are resistant flower varieties.
You need to fight this disease in the following way:
- Choose planting varieties that are resistant to this scourge.
- Remove diseased leaves and shoots, remove leafless ones, destroy parts of diseased plants by burning.
- For the purpose of prevention, spray plantings with Abiga-Peak or other copper-containing preparation - for example, 1% Bordeaux mixture, Ordan or Hom, copper oxychloride, etc. - during the beginning of growth of two-year or perennial flowers that were rusty last season. Such treatment should be periodically repeated throughout the growing season when rust foci are detected, changing preparations.
- Flowers are recommended to be fed with fertilizers with a high content of potassium, this increases the immunity of plants.
Gray mold
The disease is caused by fungi that colonize all parts of many flower crops, including their roots, and begin to parasitize them, causing a change in color to brown, softening and decay. Plants are covered with a characteristic thick coating of gray color, consisting of colonies of the fungus. Because of this plaque, the disease got its name. It occurs at different stages of the growing season, but in the second half of summer it is found more often.
Plants are covered with a characteristic thick coating of gray color, consisting of colonies of the fungus. Because of this plaque, the disease got its name. It occurs at different stages of the growing season, but in the second half of summer it is found more often.
First of all, gray rot appears on weak shoots, but if you do not fight it, it quickly covers the entire area.
Almost all types of flower crops are susceptible to this disease. The pathogen successfully overwinters on the remains of affected flowers. It develops at almost any positive temperature. Dry weather slows its spread. Increased air humidity, excessive density of flower beds contribute to the intensification of the spread of the disease.
Flower crops such as tulips and lilies, dahlias and gladioli, lupins, peonies, geraniums, roses, chrysanthemums, etc. are especially susceptible to the causative agent of gray rot. These types of flowers do not have varieties with increased resistance to gray rot.
In the fight against this disease, the emphasis is on creating unfavorable conditions for the life of the pathogen fungus. Measures taken include:
- Thinning dense plantings to ensure good ventilation.
- Careful care of flowers, preventing accidental mechanical damage to all parts of plants.
- Carefully dosed watering without waterlogging the soil.
- Top dressing with fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. These elements increase the resistance of flowers to disease.
- Periodic loosening of the soil.
- Timely removal and destruction of diseased leaves and stems. When pruning from the last border of the lesion, it is necessary to recede 5-10 cm lower; with extensive distribution, the plant is completely removed.
- Preventive spraying of flowers with a frequency of 10-12 days with any preparations containing copper - for example, "Abiga-Peak", "Oxyhom" or "Ordan". During flowering, preventive spraying is not carried out.
 If during this period foci of the disease were found, the flowers can be watered with Profit Gold, diluted to a concentration of 5 g per bucket of water. For each affected bush, 0.2 liters of working solution are consumed.
If during this period foci of the disease were found, the flowers can be watered with Profit Gold, diluted to a concentration of 5 g per bucket of water. For each affected bush, 0.2 liters of working solution are consumed.
Planting material must be treated with a growth stimulator, this will increase resistance to disease.
Spotting
It begins with the appearance of mild spots on the leaves, gradually they increase, the disease covers all parts of the plants. The form of the formed spots can be any, the color is predominantly brown or brown, often with a bright border. Often the leaves look perforated. With the further development of the disease, the flowers dry and fall off. Individual fungi and a number of bacteria cause spotting. Unfavorable conditions in which flowers are grown contribute to its development. The disease spreads with water, air currents moved by the wind, and is carried by insects. Most often, spots of fungal and bacterial origin affect irises and chrysanthemums, peonies and lupins, delphiniums and primroses.
How to deal with flower spotting:
- take preventive measures - alternation of flower species in the garden, competent destruction of diseased plants and weeds, elimination of insects that carry pathogens;
- to carry out active treatment - spraying flowers with such means as "Skor", Hom, oxychloride and copper oxychloride, "Ordan" or "Fundazol".
Garden pest control
In addition to diseases, flowers in our garden are threatened by various insect pests. The most frequent uninvited guests are:
- aphids;
- spider mite;
- wireworm;
- thrips.
Aphids and how to deal with them
This small insect pest infects almost all flower plants, settling in colonies on young tender leaves and shoots, and sucks the juice. As a result, the leaves curl, and pathological growth of shoots and flowers is observed. There is no longer any talk of decorativeness, you need to save the plant.
How to destroy these small oval insects 0.1-0.7 in size, which secrete honeydew, attracting ants to flowers, which carry viral plant diseases? When the first signs of aphids appear, you need to spray the flowers with such effective insecticides as Zubr and Tanrek, Alatpar and Biotplin, Fufanon and Aktpellik, as well as Inta-Vir and various types of Iskra acting in accordance with the instructions. If all insects cannot be destroyed, a second spraying should be carried out after two weeks, using a different preparation.
Insecticide against aphids and whiteflies Tanrek 12ml
Spider mite
Small, almost invisible to the naked eye, the tick especially loves the combination of heat and low humidity. It settles on the underside of the leaves, damaging them, entangling them with cobwebs, changing color to marble, then yellow. Then the leaves dry up and fall off prematurely. The tick - its adult females - winters well in the bark, in fallen leaves. In the spring, it begins to multiply first on weeds, then goes on to flowers.
In the spring, it begins to multiply first on weeds, then goes on to flowers.
It is possible to protect flower beds from spider mites only with an integrated approach. It is necessary to constantly remove weeds from flower plantings, destroy the remains of plants from the diseased area. Spraying flowers from a tick can be especially effective for combating these pests with Fufanon and Iskra-M. In extreme heat, use "Thiovit Jet" or colloidal sulfur, diluting the working solution at the rate of 40 g per half a bucket of water. Processing is carried out every ten days.
Broad-spectrum insecticide Fufanon-Nova 2ml
Wire rope
This is the name of the larvae of the click beetle, which develop in the ground and damage the roots, flower bulbs, and gnaw through the stems. Distributed in all regions. The larvae look like long and hard to the touch yellow worms. The wireworm lives in the ground, some even hibernate in the larval phase. Flowers affected by it either die or lag far behind in development from healthy plants. If 10-12 individuals live on each square meter, this poses a real threat to the flower garden.
If 10-12 individuals live on each square meter, this poses a real threat to the flower garden.
It is necessary to fight the wireworm by destroying weeds, especially the wheatgrass he loves, and treating the flower garden with effective preparations - Provotox, Bazudin, Initiation or Zemlin (consumption of only 10 g per 30 m2). If a perennial flower garden is being laid, one of these preparations is mixed with sand and added to the grooves or pits for planting.
Insecticide against wireworm, cabbage fly, soil pests Zemlin 100g
Thrips
Another species of insect pests, numerous, very small (from 0.5 to 3.0 mm), with an elongated body, most often choosing flowers for life. They suck the juices from plants, damage the stamens and pistils, preventing the pollination process. Flowers lose their decorative qualities and do not produce viable seeds, their leaves become ugly and colorless. Adult thrips are able to fly to neighboring plants.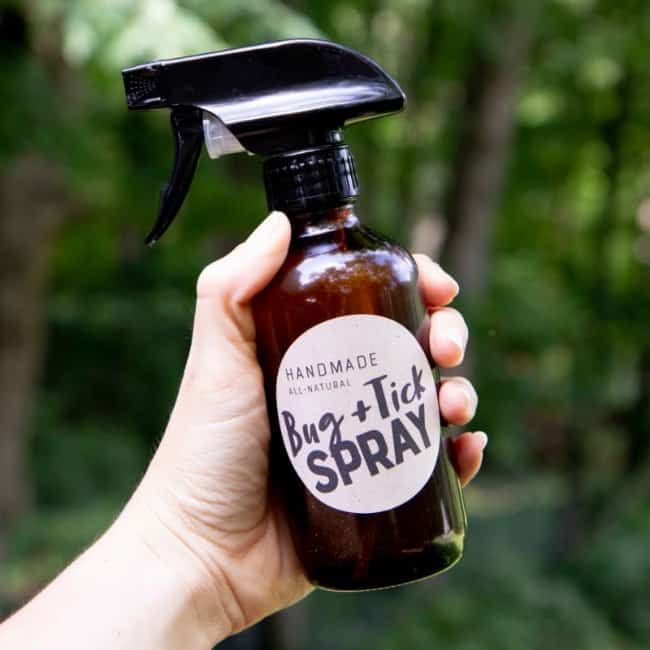 They lay their eggs here, the generation of insects develops in two weeks, they overwinter in plant debris or in the upper soil layer. Some of these insect species carry viral and bacterial diseases of cultivated plants grown in our gardens.
They lay their eggs here, the generation of insects develops in two weeks, they overwinter in plant debris or in the upper soil layer. Some of these insect species carry viral and bacterial diseases of cultivated plants grown in our gardens.
How to deal with thrips, protecting your flower beds from them? First of all, be careful and start taking action when you find the first foci where pests have appeared. You can destroy insects by spraying the affected plants with effective insecticides, the list of which is similar to those used in the fight against aphids. Processing of the flower garden is carried out every 8-10 days, it is recommended to alternate the preparations.
Plant protection products - Fertilizers, fungicides, herbicides, insecticides, plant care products.
Destroying annual, perennial grass and dicotyledonous weeds, including cow parsnip, trees and shrubs
Destruction of a wide range of annual and perennial dicotyledonous weeds, including wild thistle, sow thistle
To combat any weeds, including the most difficult to eradicate ( wheatgrass, sow thistle, plantain, dandelion, hogweed, nettle, etc. )
)
To combat all types of weeds, including the most malicious (wheatgrass, thistle, bindweed and others), more than 155 species of weeds
Against spider mites
Has a lightning-fast effect on insects (flies, midges, fruit flies, mosquitoes, moths)
leaf beetles, false scale insects, mining flies, centipedes, moths, flies, spider mites, sawflies, scoops, aphids, thrips, tubeworms, earwigs, color
For the destruction of flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, moths, as well as cockroaches, bedbugs, fleas, ants ,os
For the extermination of flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, moths, as well as cockroaches, bugs, fleas, ants
Crawling and flying insects (flies, cockroaches, ants, bugs, fleas, etc.)
fleas, ants, skin beetles)
For the extermination of flying (flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, moths) and non-flying (cockroaches, ants, bugs, fleas) and treatment of landing sites of flies
, ants, bugs, fleas)
For the destruction of larvae of the May and other types of cockchafers, wireworms and false wireworms
For the destruction of all types of ants
From the Colorado potato beetle, aphids, whiteflies, thrips and scale insects
From bugs, ants, ants slugs, snails, Colorado potato beetle, bears
Against mosquitoes, midges, mosquitoes, midges, horseflies, fleas
To protect people from ticks and fleas, flying blood-sucking insects
soil, as well as the suitability of potting soil for certain indoor plants
For vegetable and fruit crops
Intended for garden, garden, indoor, greenhouse plants
For flowers, indoor and greenhouse plants
For all crops
For all types of plants, crops
Means for rooting seedlings of fruit, berry, ornamental and flower crops, improving the survival of seedlings
Kit for preparing a tank mix. Three active components enhance the effect and ensure the destruction of persistent weeds: hogweed, goutweed, nettle, couch grass, sow thistle
Three active components enhance the effect and ensure the destruction of persistent weeds: hogweed, goutweed, nettle, couch grass, sow thistle
More than 100 species of weeds - clover, dandelion, thistle, bindweed, plantain, quinoa
Biological snake repeller based on special blends of essential oils
For the extermination of wasps and wasp nests, as well as for the extermination of flying (flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, moths) and non-flying (cockroaches, bugs, fleas, ants, skin beetles) indoor insects
Universal remedy against all types of rodents and insects on any territory
Bait for the fight against mole cricket. Effective against garden ants, wireworms and other soil pests
Bait from mole crickets and wireworms
0003
From moths and skin beetles. Destroys not only adults, but also their larvae
For the destruction of ants indoors and in their immediate vicinity (on terraces, in gazebos, patios, under awnings adjacent to buildings, etc. )
)
Against house and garden ants
For the extermination of all types of cockroaches, ants, bugs, fleas, flies (in places of breeding)
For the control of garden and house ants, as well as cockroaches
For the extermination of cockroaches and ants inside residential premises , private house areas, at objects of various categories, as well as in the garden and vegetable garden
Against all types of garden and house red ants
For the extermination of cockroaches
For the control of household insects (cockroaches, ants, bugs, fleas, flies)
For the control of all harmful insects: cockroaches, bugs, ants, flies , flies
Against all flying and crawling pests
Means for the destruction of caterpillars on vegetables, fruit crops and grapes
For the control of larvae and adults of the Colorado potato beetle
Pests: spider mites, fruit and other mites, moths, leafworms, whiteflies, scoops, moths, thrips
To combat a complex of pests: mites, aphids, thrips, spider mites, Colorado potato beetle, leaf-eating caterpillars
To destroy a wide range of pests pests, including mites, aphids, thrips, weevils, codling moths, leafworms, suckers, sawflies, scale insects, false scale insects, flies, whiteflies, raspberry beetles, whiteflies, scoops, moths, gall midges, moths, scale insects, moths on
Fights insect pests (aphid, sucker, codling moth, weevil, flea beetle, caterpillars, etc. ) sawflies, caterpillars, scale insects, spider mites, aphids and other sucking pests)
) sawflies, caterpillars, scale insects, spider mites, aphids and other sucking pests)
Against most insect pests, including soil midges
Natural growth and development stimulator of various crops based on succinic acid
Means for changing the color of hydrangea inflorescences with pink petals to light blue
For all types of crops
Used for soaking and germinating seeds, root feeding of seedlings during their development, for healthy plant nutrition throughout their life
For all types of orchids
For feeding vegetables, fruit and berries and ornamental crops
For pre-sowing treatment and feeding vegetables, berries, flowers and houseplants, for soaking seeds, tillage and plants
Food bait to control moles, shrews, mice and rats
Control rats and house mice
Control rats, house mice, field mice
gerbils, bank voles and ground squirrels (small mountain, long-tailed)
For the control of house mice
For the destruction of black and gray rats, voles, ground squirrels, as well as house mice
Against moles
For killing mice
For accelerating natural processes in compost pits
For latrines
Biological preparation for toilets and latrines of fast action
For country toilets, septic tanks, pit latrines
preparation of compost
Preparation for combating fungal diseases: root and fruit rot, blackleg, macrosporiosis, fusarium, late blight, anthracnose, wilt, etc.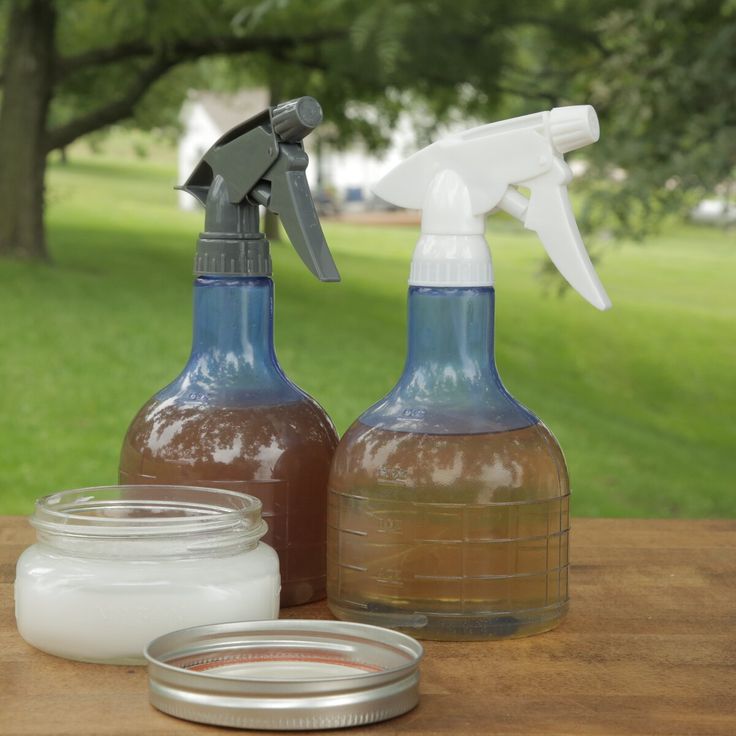
Against powdery mildew, gray mold, anthracnose, goblet rust, columnar rust, leaf septoria, purple spot, leaf rust
For treatment and healing of wounds of ornamental and fruit trees after pruning, grafting, wind damage, as well as wounds caused by sunburn
For healing wounds of fruit and ornamental trees caused by grafting, budding or pruning, sunburn
To prevent infection of seedlings with soil infections (rot, scab, fusarium, mold)
From late blight, macrosporiosis, peronosporosis, septoria, black bacterial spot, mildia.
To combat pathogens of late blight and peronosporosis resistant to other drugs, as well as mildew
Used to combat a complex of fungal and bacterial diseases
From various diseases - moniliosis, various rot, penicillosis
Against gray and white rot, downy mildew, early blight, late blight, peronosporosis, black spot
Against diseases (scab, powdery mildew, phytophthora, rust, etc.) thrips, sawflies, suckers and other suckers)
To protect trees from insects, from fungal and bacterial infections, from lichens, from frost and temperature extremes,
shrub vegetation. hogweed, dandelion, sow thistle, couch grass, goutweed, nettle, ragweed
hogweed, dandelion, sow thistle, couch grass, goutweed, nettle, ragweed
Designed for the destruction of annual and perennial grasses and dicotyledonous weeds, herbaceous and tree-shrub vegetation
For the destruction of flying and crawling insects (cockroaches, ants, wood lice, moths, flies, mosquitoes, etc.)
For the destruction of non-flying insects (ants, bugs, cockroaches, fleas, skin beetles) and flying (flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, moths) insects
For the destruction of crawling insects (cockroaches, ants, bedbugs, etc.) and flying insects (flies, mosquitoes)
For the destruction of flying and non-flying insects - flies, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, butterflies, moths, cockroaches, bed bugs, fleas, ants
For the destruction of all flying and crawling insects
Universal agent for the destruction of any flying and crawling insects
For protection against the attack of midges
beetle, aphids and moths
Bait against mole cricket, wireworm, Colorado potato beetle
Bait powder for fighting garden and house ants, as well as other crawling parasitic insects
Means for fighting flying insects: flies, midges, wasps, etc. in the form of a trap on sticky tape
in the form of a trap on sticky tape
Activates growth processes, accelerates flowering and ripening, increases yield, normalizes soil microflora, and also helps plants to endure stress more easily, as well as recover after transplantation or adverse conditions
Increases seed germination, strengthens the root system and bushiness, increases resistance to diseases and weather stresses
Bait for rats, mice, voles and other mouse-like
For the destruction of rodents: rats, house mice, voles
To prevent overgrowth of seedlings ( inhibits the growth of the plant in length, but increases the growth in width)
For the destruction of annual and perennial grasses and dicotyledonous weeds, as well as unwanted trees and shrubs in personal subsidiary plots. Destroys more than 155 species of weeds, incl. bindweed, thistle, wheatgrass and others
For the destruction of ixodid ticks in home gardens, summer cottages and garden plots
It is used to control pests: thrips, aphids, caterpillars, leafworms, cabbage, apple and fruit moths, onion flies, spider mites, whiteflies, slugs, suckers, etc. e
e
Designed to improve the appearance of ornamental and flowering indoor plants, enhance their growth, increase resistance to diseases and pests
Designed to increase the yield of vegetable, fruit, berry and flower crops, stimulate the growth and development of plants, increase germination and seed germination
For use in storage cisterns of dry closets, cottage sewage systems
Used to combat powdery mildew, scab, late blight and other fungal diseases of plants burns
It is used to combat scab, powdery mildew, leaf curl, white, perforated and brown spotting, clasterosporiasis, coccomycosis, moniliosis, late blight, cercosporosis
Plant protection against aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, wireworms, mites, whiteflies, midges, moths, flies, leaf beetles, cutworms, cockroaches, fleas, wasps, mosquitoes, Maybugs), as well as an auxiliary agent that increases the effectiveness of chemical protection products
Means for treating non-residential basements, cellars, greenhouses, greenhouses, from diseases, insects, rodents (hogweed)
For seedlings of vegetable, flower crops, pot plants, garden plants, shrubs
From bedbugs, fleas, cockroaches, ants, leather beetles, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, midges
whiteflies, spiders, carrot flies, Colorado beetles, aphids and mothsFor the control of insects, pests and the protection and disinfection of trees
Against all types of ants, in particular against black, garden and red house ants and cockroaches
For the control of red house and black garden ants, bed bugs, fleas, basement mosquito larvae and houseflies fleas and flies (larvae and adults)
Preparation for complex protection of potatoes against diseases, Colorado potato beetle, wireworm and weather stresses
For the destruction of mice, gray and black rats with a mummifying effect
For control of gray and black rats, house mice, voles, other mouse-like rodents
For control of house mice, field mice, gray and black rats
Used to get rid of moles and red house ants, against cockroaches
Suitable for both treatment and prevention of late blight, alternariosis, peronosporosis and other diseases, on potatoes and tomatoes in open ground, on onions (on turnips) and cucumbers in open ground
From diseases (rhizoctoniosis, common scab) and pests (Colorado potato beetle, aphids), including those living in the soil (wireworm) etc. , and as a fertilizer, pouring into the soil before digging in spring or autumn
, and as a fertilizer, pouring into the soil before digging in spring or autumn
To protect people from the attack of blood-sucking insects (midges, mosquitoes, midges, mosquitoes, horseflies, fleas), forest and taiga ticks
Against the Colorado potato beetle and leaf-eating caterpillars for use in agriculture and in personal subsidiary plots
Destroy most common pests: apple flower beetle, various types of scale insects, aphids, thrips, leafworms, scoops, whites, moths, cruciferous fleas, weevils, etc.
Effectively fights against a complex of pests: whitefly, aphid, thrips, codling moth, leafworm, apple flower beetle, mites, sprout fly, Colorado potato beetle, raspberry-strawberry weevil, etc.
For the destruction of nests of garden and house ants, cockroaches, fleas, flies, wood lice, earwigs, crickets and other insects , bugs, sawflies, caterpillars, aphids and other sucking pests
Intended for the destruction of cockroaches, bugs, fleas, flies, ants (red house and various garden species) and rat mites
For treatment of cesspools, septic tanks, sewer systems
For protection against pests of most horticultural and horticultural crops - cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, apple trees, currants, raspberries, flowers, etc.
mealybug, spider mite, whitefly, Colorado potato beetle, tortoise bug, wireworm, thrips, cabbage butterfly
Restores soil balance in microelement composition, prevents a number of fungal and viral diseases. Designed for pre-sowing (pre-planting) treatment of seeds and planting material, fertilizing vegetables, fruits, berries, flowers cult
For indoor and garden plants
For country toilets, septic tanks, bio-toilets, latrines
Means for fighting slugs, snails on flowers, fruit and berry crops food, in the practice of medical disinfestation by specialists of organizations that have the right to engage in disinfection activities, and the population in everyday life
Means for combating flying insects: flies, midges, wasps, etc.
For quick and effective extermination of cockroaches
Against all types of rodents - gray and black rats, mice, voles, moles and ground squirrels for the destruction of synanthropic insects (cockroaches, ants and winged flies)
For the prevention of plant diseases. Warns, destroys and repels pests: aphids, mites, butterflies, beetles and even rodents
Warns, destroys and repels pests: aphids, mites, butterflies, beetles and even rodents
For home ornamental flowers and plants in the garden
Natural, environmentally friendly product with a specific smell for protecting garden plants from pests and rodents
Stimulates the growth and development of plants, maintains leaf elasticity (turgor), reduces dust settling, strengthens plant immunity
For the prevention of infection by insect pests and for giving shine to leaves
Designed to protect vegetable, berry, ornamental, fruit crops from a wide range of soil pests (bearworm, beetle, wireworm, weevil, onion fly, etc. .)
Mineral-oil emulsion of vaseline oil to control wintering stages of insect pests: Scale insects, false scale insects, mites, aphids, mealybugs, as well as eggs of insect pests
Used to change and maintain the blue color of large-leaved hydrangeas
Highly effective preparation with a triple combination active substances for the destruction of the Colorado potato beetle and its larvae on potatoes during the growing season.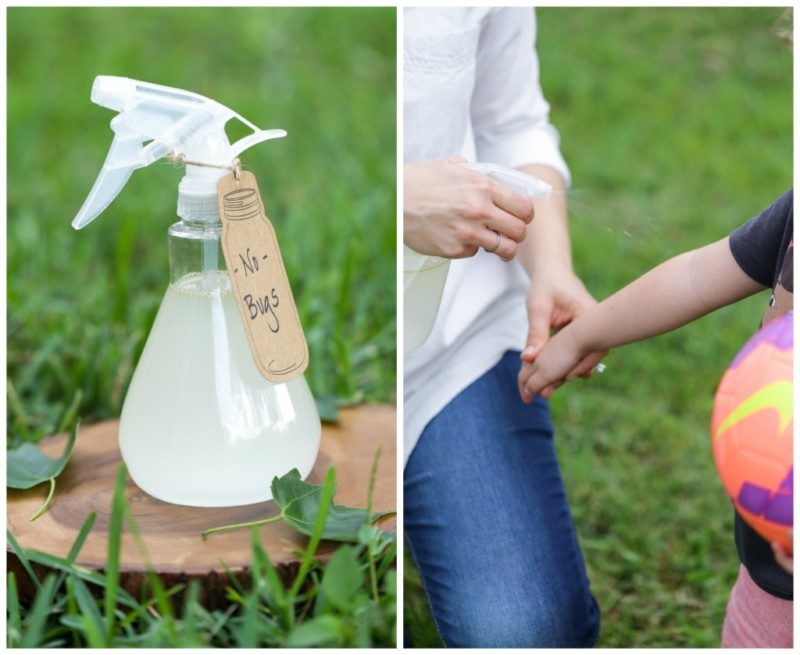
To protect wool, fur, felt and felt products from moths
The drug has an intestinal mechanism of action and is effective against insects of any age. For the fight against insect caterpillars moths, silkworms, scoops, nuns, meadow moths, leafworms, hawthorn, butterflies, moths, etc. for the protection of coniferous crops from a wide range of pests: hermes, aphids, sawflies, scale insects, etc.
For prolonged protection of coniferous and deciduous trees, as well as perennial flowers from diseases: snow, brown, gray, ordinary shute (shedding needles), rust on conifers
Used on garden paths and paths, along fences and hedges, on the blind areas of houses, foundation cracks, near greenhouses and between ridges
To control snails and slugs on plants
To kill wasps and various types of flies
To kill ants (domestic and garden), as well as flies, wood lice, fleas, cockroaches, crickets
flies, centipedes, moths, flies, spider mites, sawflies, cutworms, aphids, thrips, tubeworm, earwigs,
Ready-to-use grain bait with a mummifying effect for the destruction of house mice, voles and other mouse-like rodents, as well as gray and black rats
Used to combat various crop diseases: late blight, coccomycosis, scab, rust, leaf curl, black rot , mildew, anthracnose, various types of leaf spot and needles
Designed for the treatment of agricultural products from fungal infections (fusarium, phomosis, or gangrene, oosporosis, dry rot, all types of clamp rot, gray rot, etc.