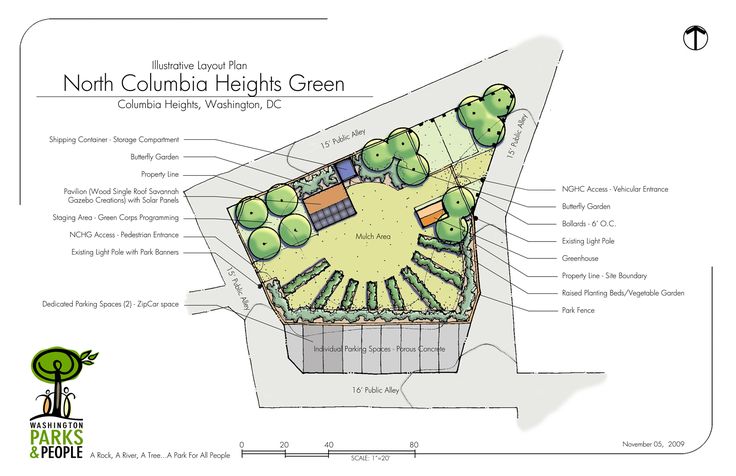
Container vegetable garden layout
22 Stunning Container Vegetable Garden Design Ideas & Tips
Search
Follow these
Container Vegetable Garden Design Ideas to maximize harvest and make your edible garden less boring.Growing a vegetable garden doesn’t mean it has to be boring, dull, and less interesting. On the contrary, it can be very enjoyable and attractive. If you want to know how? Just follow the tips below!
Here are the best vegetables for containers1. Grow Climbers and Vines
shutterstockSupport climbing vegetables and vines and direct them upward with the help of a trellis or a cage or in any other way.
Such plants use vertical space and are abundant in production. Bitter melon (a unique tropical gourd known for its health benefits), gourds, cucumber, pole beans and other beans, Malabar spinach, vine tomatoes, squashes, peas, if you want to try– pumpkin and melons.
2. Choose Colorful Containers
You can brighten up your container vegetable garden by choosing colorful containers to grow your favorite vegetable and herbs.
3. Use Hanging Baskets
Image Credit: HGTVDon’t cast out the idea of growing herbs and vegetables in hanging baskets. Tomatoes, strawberries, many other vegetables, and herbs can be grown in hanging baskets successfully. It also creates space!
Learn more about the best-hanging basket vegetables here4. Start One Pot Vegetable Garden
This one-pot vegetable garden idea is perfect if you don’t have space to set up a container garden. It is also useful for those who have a small balcony or open window that receives full sun. We picked up this idea from the Sunset; read more there!
5. Try this Vertical Lettuce Planter Idea
We love this project done by Bonnie Plants, and why not? You can grow fresh herbs and greens easily in a limited space by following this idea. They have a step-by-step DIY article on this for you to look at, check out!
They have a step-by-step DIY article on this for you to look at, check out!
6. Grow Edible Flowers
To add some interest, color, and beauty, it’s a good idea to grow some edible flowers. You can use them in salads to garnish your meal or make sharbat.
Flowers like marigolds, calendula, viola, and nasturtiums can be tried. The list is long, and you can discover more names here.
7. Give Space to Herbs
Your container vegetable garden may look incomplete if you don’t grow some herbs. Fresh herbs can enhance the taste of your meal always, so it’s a great idea.
You don’t need to grow all the herbs. Consider adding 2-3 plants that you like most and suit your location: Parsley, thyme, mint, sage, oregano, cilantro, and much more to choose from. A window box, a few small containers, and hanging baskets can also be used.
8. Tomatoes are Must!
Tomatoes are a wonderful and the most important addition to a container vegetable garden. They look beautiful too. Choose 2-3 varieties and grow a few plants to get a bountiful harvest of homegrown tomatoes. Learn about the best tomato varieties for the container in this post.
They look beautiful too. Choose 2-3 varieties and grow a few plants to get a bountiful harvest of homegrown tomatoes. Learn about the best tomato varieties for the container in this post.
9. Add Colorful Varieties
Vegetables and herbs with different textures, attractive foliage, and colors can be an excellent addition to your container vegetable garden; they can add visual interest to it.
Red hot pepper, red-stemmed swiss chard, round midnight basil, fine leaf rosemary with other herbs like lemongrass or thyme can make it look appealing. Here’s an interesting post on colorful vegetables for you to see!
10. Use Unique Planters
Use unique planters to provide virtual interest to your container vegetable garden. You can recycle and DIY your own planters or buy a few in unusual shapes and sizes. There are a lot of DIY ideas available on our website for help.
11. Play with the Height
If you don’t want your vegetable garden to look boring, play with the height. Don’t use planters of similar size and height. Instead, group large and small containers together; this will create a visual appeal.
Don’t use planters of similar size and height. Instead, group large and small containers together; this will create a visual appeal.
Tip: Group plants according to their height to create a garden-like surrounding effect. To do this, place tall plants in the back and short and low-growing plants like herbs and greens in front.
12. Grow a Citrus Tree
Growing a lemon tree in a pot is not difficult and is probably an intelligent addition to your container vegetable garden. Here’s our step-by-step post on it!
13. Take the Help of Vertical Gardening
Lettuces in the window boxes in a balconyThe biggest challenge of limited space gardening is limited space itself. To beat this, take the help of Vertical Gardening. Use shoe racks, bookshelves, and plant holders to keep more pots.
If you’re a balcony gardener, railing planters and hanging planters are a must. Besides, there are many other unique vertical gardening ideas available here.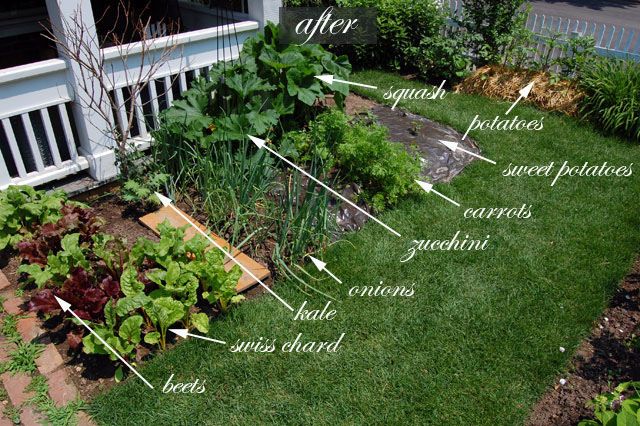
14. Start with the Productive and Easiest Container Vegetables
Try succession planting for continuous harvest and grow the most productive and easiest container vegetables for a successful harvest. Here’s our article on it.
15. Try this One Pot Herb Garden Idea
Image Credit: Southern LivingGrowing herbs is easy to grow along with other vegetables you’re growing. We found this One-pot herb garden idea on Southern Living fascinating for urban gardeners. See the full post here!
16. Stake ’em Up!
Staking and caging are also good ways to grow vegetables like tomatoes easily in containers in a compact spot. You can train the plant to grow vertically, saving a lot of space.
If you have a sunny balcony, patio, or rooftop, all you need is a large container to grow multiple plants together and enjoy a fresh, homegrown harvest.
17. Make a Salad Table Garden
gardenersA Salad Table is an ingenious way to grow plants like spinach and lettuce.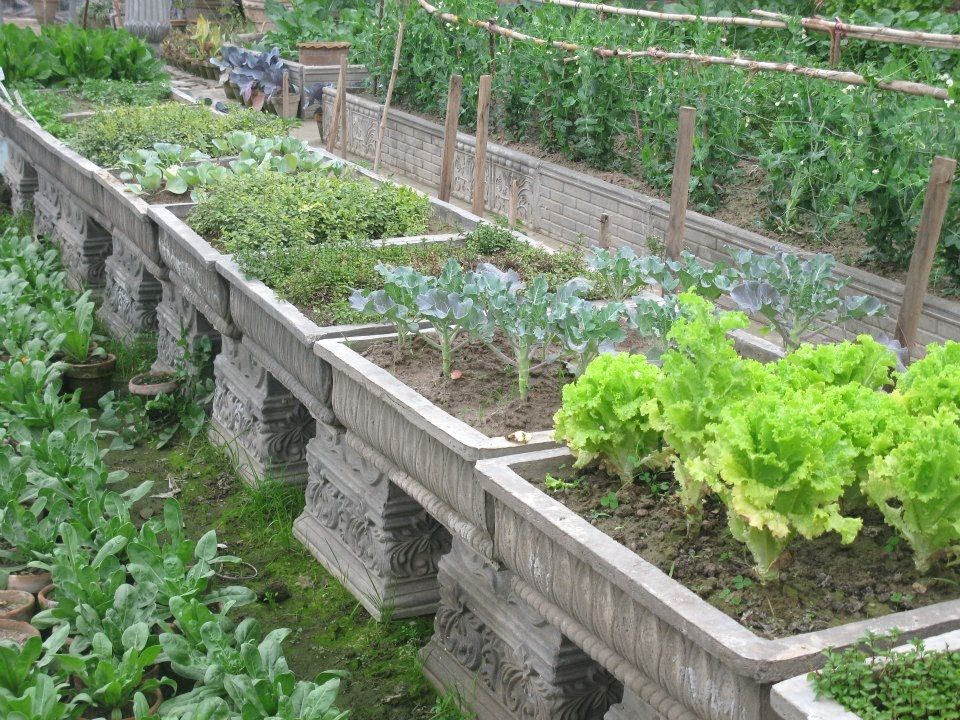 Just find a sunny spot and keep the table there, simple! You can easily get them ready-made from the market or make one for yourself at home.
Just find a sunny spot and keep the table there, simple! You can easily get them ready-made from the market or make one for yourself at home.
18. Try Raised Beds
Instead of growing veggies on the ground, you can grow them in raised beds instead. They are easy to maintain this way, compared to a traditional garden–If you have a back problem, want to control the quality of the soil, or looking to improve the drainage.
Here’s everything you need to know about making Raised Beds19. Go the Hydroponic Way
Want to grow vegetables hydroponically? Check out some of the best DIYs here. You can also use PVC pipes for this purpose. One similar DIY is here to watch on YouTube.
View these hydroponic vertical garden ideas here20. Grow Exotic Vegetables
Finding fresh, exotic veggies like Black tomatoes, Romanesco Broccoli, Mexican Sour Gherkin, Dragon Carrot, Red Perilla, and Thai Basil can be a tough job at the supermarket–so why not grow them at your home?
21.
 Make a Movable Garden
Make a Movable GardenIf your garden doesn’t get all the sunlight it needs, DIY a movable garden, which is basically a raised bed on wheels. This way, you can grow vegetables and move them around accordingly, where they get the right sun exposure to thrive well.
Check out some amazing movable garden ideas here22. Save Space by Making a Herb Tower
Yes! You read that right! You can grow not just herbs but some leafy greens as well in a tower form to save space and plant multiple of them together.
Have a look at some impressive herb tower ideas hereJoin our 2.8 Million Followers
Social Followers
2.5MFollowers
219kFans
36kSubscribers
YouTube
Container Vegetable Gardening - Designing Your Container Vegetable Garden
If you do not have adequate space for a vegetable garden, consider growing these crops in containers.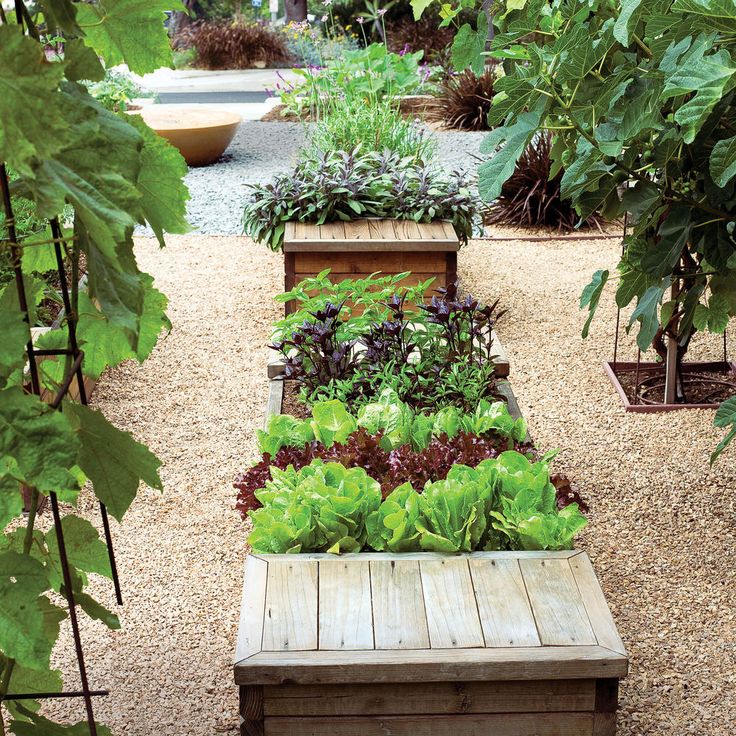 Let’s take a look at growing vegetables in containers.
Let’s take a look at growing vegetables in containers.
Container Gardening Vegetables
Almost any vegetable that can be grown in a garden will work well as a container-grown plant. Vegetables normally suited for growing in containers include:
- tomatoes
- peppers
- eggplant
- potatoes
- beans
- lettuce
- carrots
- radishes
Most vine crops, such as squash and cucumbers, also do well in containers. Generally, compact varieties are the better choices for growing in containers. Bush beans, for example, thrive well in this type of environment and look quite attractive when arranged with other container crops.
Containers for Vegetable Gardening
Nearly any type of container can be used for growing vegetable plants. Old wash tubs, wooden boxes or crates, gallon-sized (4 L.) coffee cans, and even five-gallon buckets (19 L.) can be implemented for growing crops as long as they provide adequate drainage.
Regardless of the type or size of your container, drainage is vital for successful growth and the overall health of vegetables. If the container you have chosen does not provide any outlets for drainage, you can easily drill a few holes in the bottom or lower sides. Placing gravel or small stones in the bottom of the container will help improve drainage as well. You may also consider raising the container an inch or two (2.5-5 cm.) off the ground with blocks.
Depending on the crops you selected, the size of the container will vary. Most plants require containers that allow at least 6 to 8-inch (15-20.5 cm.) depths for adequate rooting.
- Smaller-sized containers, like coffee cans, are generally ideal for crops such as carrots, radishes, and herbs.
- Use medium-sized containers, such as five-gallon (19 L.) buckets, to grow tomatoes or peppers.
- For larger crops, such as vine growers, beans, and potatoes, you want to implement something more suitable to their needs, such as a large wash tub.

The spacing requirements for most vegetables are usually found on the seed packet or you can find them in gardening resource books. Once the seeds have sprouted, you can thin the plants to the desired number suitable to the container.
Fill containers with peat moss and a suitable potting mix. Compost or manure should be worked in to achieve healthier plant growth. Do not add more than the recommended amounts of fertilizer; however, doing so can burn the plants.
Where to Put Your Container Vegetable Garden
Once you have taken care of the basics, you’ll have to decide where to place your container garden. You want to situate the containers in an area that is close to a water source with sufficient sunlight, usually at least five hours. Excessive wind can quickly dry container plants out, so you should consider this factor as well when choosing a site.
Set the larger pots furthest back or in the center, if your design permits, with the medium-sized containers placed in front or around the larger ones. Always place the smallest containers in the very front.
Always place the smallest containers in the very front.
With containers, there is also the option of growing vegetables in windowsills or hanging baskets that can be placed right on the porch or balcony. Ornamental peppers and cherry tomatoes look good in hanging baskets, as do trailing plants such as the sweet potato vine. Keep them watered daily; however, since hanging baskets are more prone to drying out, especially during hot spells.
Watering Container Gardening Vegetables
Generally, you should water container plants every few days unless it is quite hot; more frequent watering will then be required. Check containers at least once a day and feel the soil to determine whether or not it is damp. You also might consider sitting containers on trays or lids. Doing so will help retain moisture by holding excess water and allowing the roots to slowly pull it up as needed.
Check these plants often to make sure that they are not continually sitting in water. If sitting water becomes a problem, fill the trays with some type of mulching material, such as chips, to help soak it up.
Apply water with a watering can or sprayer attachment on a garden hose. Also, check that the water is reasonably cool beforehand, as hot water may cause damage to root development. During the hottest part of the day or when severe weather is expected, you can move the containers for additional protection.
Garden planning: how to do it right
What is about? A well-thought-out plan will help you effectively use the potential of your site and ensure that you get the most out of every vegetable crop.
What to pay attention to ? To properly plan your garden, you must first determine how much space you will have for growing each type of plant. Then, when you calculate the area, you can outline the size of the beds and their shape.
The article describes:
- Choosing a place for a vegetable garden
- How to plan a garden for beds
- Features of the location of the beds in the garden
- Calculation of the number of beds
- Zoning when planning orchards and berries
- Features of garden planning
- How to organize a vegetable garden in a small area
- Crop rotation procedure
Choosing a place for a vegetable garden
All gardeners know that almost all plants love sunlight, which they need for normal growth and reproduction.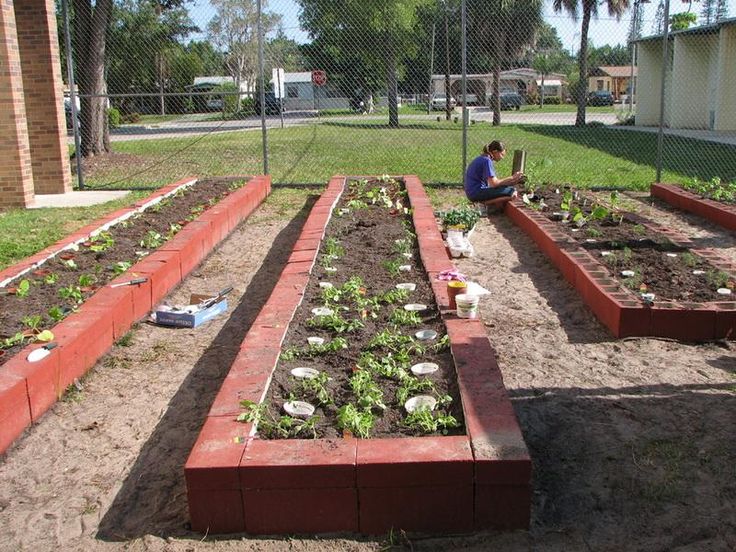 If you plan to arrange a garden in your summer cottage, then be sure to consider this circumstance.
If you plan to arrange a garden in your summer cottage, then be sure to consider this circumstance.
A site that receives a sufficient amount of sunlight is especially important for areas located in the middle lane and in the northern regions of our country. Proper planning of the garden not only allows you to make your site attractive in appearance, but also creates a favorable environment for a good harvest.
Before you plan a place for your yet future vegetable garden, pay attention to what kind of shade there is on your site during the day. It appears not only because of the buildings, but from a solid fence, trees and bushes. The area of your territory can be illuminated throughout the day, until noon, shade for the whole day.
If you live in a northern area with a cool climate, then choose a place for the garden where the sun shines all day. If you are a resident of the south, then a site where there is sunlight only in the morning hours is suitable for you, and in the afternoon your plants are in partial shade. In shaded areas, only those plantings that do not like light can be planted. There are few such garden crops, but for a flower bed this is ideal, since there are many shade-loving flowers or decorative crops.
In shaded areas, only those plantings that do not like light can be planted. There are few such garden crops, but for a flower bed this is ideal, since there are many shade-loving flowers or decorative crops.
How to plan a garden for beds
There is more than one system for dividing the soil into beds. It depends on the width, length of your planting and row spacing. The garden will bear fruit regularly if you use the following layouts.
- Narrow beds.
This means beds 45 cm wide, and the distance between them should be no less than 90 cm. Why is this necessary? If your plants are located on a regular bed, then the extreme ones are usually stronger and larger than the others, as they receive more light. Therefore, the bed is made 45 cm wide, and only two rows of plants are planted on it. This allows the gardener to have a higher yield, especially in the northern regions and in the middle lane, since even plants that love sunlight will ripen in this way.
But here you can also note a big drawback: if you make the aisles wide, then you have a smaller working part of the garden, and the areas between the rows must be often weeded so that they do not overgrow with weeds.
- Standard width beds .
These are normal beds that gardeners make most often. Their width: 50 - 90 cm, and sometimes up to 1 meter. Row spacing in width: 40 - 60 cm. The beds can be flush with the soil or raised, that is, not have walls, but at the same time, the place for sowing should be higher than the row spacing area. The height can be adjusted by adding soil purchased or taken from other parts of your site.
Featured Products
Brand: OrganicMix
AminoRost 12 gr
Organic growth stimulator
390 rub. 390 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
BioRoot 50 gr
Organic root
690 r. 690 r.
690 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Anti-vertex 25 g
Treatment and prevention
of blossom end rot
1200 r. 445 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Soil for seedlings 4 l.
Organic soil
for seedlings
570 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Soil for seeds and cuttings 4 l.
Premium Soil Mix
$485
Brand: OrganicMix
Fertilizer for strawberries and berries 800 gr.
Granular fertilizer
485 rub.
- Raised beds.
You can make walls from any material at hand: boards, slate, etc. Pour humus, a layer of soil into the resulting box. These beds are convenient in that they warm up well with sunlight and do not suffer from flooding during rains or autumn floods. They are easy to care for, as they are easy to handle, no need to lean down much. But to arrange them, you will spend a lot of time.
They are easy to care for, as they are easy to handle, no need to lean down much. But to arrange them, you will spend a lot of time.
- Warm beds.
Their difference from the tall ones is in the “stuffing” of branches, foliage, which are laid out in a box, mixed with humus and earth, where plants are planted later. They are up to 1 meter wide. On the positive side, the foliage inside rots, which warms the ground, and this makes it possible to plant your plants earlier. This is more relevant if you live in the north, and is not very important in the southern areas, but it gives excellent results, since your plants grow quickly in the prepared land.
You can do any planning for your summer cottage by choosing the right gardening device for you. Normal - no more than a meter, but you can use less. It is important for you that you can easily reach the middle, as this is the center of your landing, processing which you should not feel uncomfortable.
Features of the arrangement of beds in the garden
Once you've decided to start a garden, decide what your garden beds will look like.
If you plan them correctly, then any obstacle will not be important and will not interfere with you.
When landing, certain difficulties arise, but they are easily solved:
- Growing sun-loving plants in a dimly lit home garden. For those who want to grow sun-loving vegetables but don't have a place in your area that gets at least six hours of sunshine a day, plant potted vegetables.
- Growing shade-loving plants in the sun. It's easy as there are many options to make your green spaces feel great. First, we can plant large or bushy plants around those that like to grow in the shade. For example, peas and beans grow quickly and provide shade, which is good for growing juicy lettuce or cabbage. Legumes are also useful because they fix nitrogen in the soil. Laurel and fruit trees are great for creating shade.

- Growing vegetables on unsuitable land . This applies to sandy or waterlogged soil. If you don't have the time or patience to improve the soil, then raised beds that can be filled with compost and topsoil will work for you. Their advantage is that they provide good drainage, the ground warms up quickly after the spring snowmelt, and they are easy to care for.
- You have a small garden . The size of the plot does not matter, as even a tiny area can be quite productive for any plant, even the demanding ones like sweet corn and potatoes. Fences and walls surrounding the space, and related plants in your room or on the site, can provide useful service in this matter. This joint planting of vegetables and plants allows you to use your space wisely, and even scare away harmful insects.
Calculation of the number of beds
To properly plan your garden, you must first determine how much space you will have for growing each type of plant.
Then, when you calculate the area, you can outline the size of the beds and their shape. How to do it right?
- First you need to understand what crops you will grow in the garden and what kind of crop you want to get from each of them. It is better to enter such information in a table with which it will be convenient for you to work further.
- After that, you need to find information on the level of yield that is realistically possible from each acre of your land, and for all your types of plants. Regional data may vary. Such information will be useful for the first calculations. As you get your first harvest, you can change the numbers.
- Ask your neighbors what vegetables they grow and how much they get annually.
Zoning when planning garden and berry plantings
If you plan to plant horticultural and vegetable crops in the same area, then clearly label the functional parts. At the main entrance, a lawn, low trees, shrubs and benches will look best.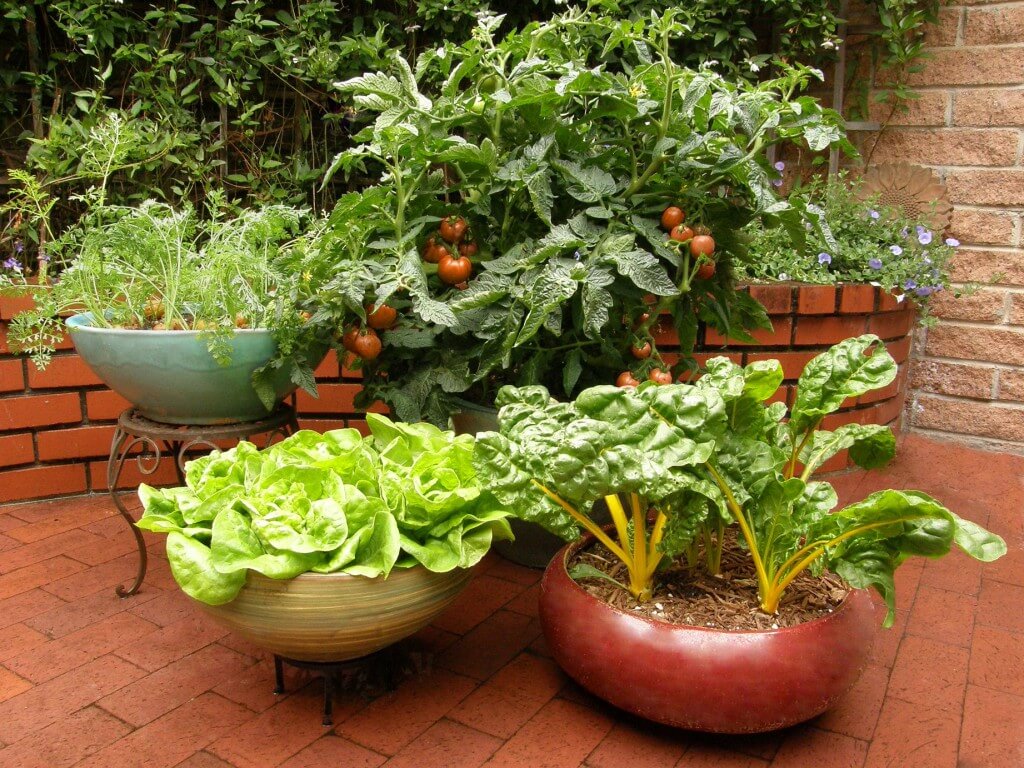 The correct layout of the garden should not be limited only to the beds. On your territory, there must be zones for planting, storing crops and equipment, and, of course, recreation.
The correct layout of the garden should not be limited only to the beds. On your territory, there must be zones for planting, storing crops and equipment, and, of course, recreation.
Plants
Shrubs are planted on the borders between the garden and the vegetable garden, hedges of gooseberries, raspberries and currants look especially good. They need to be trimmed to keep an attractive appearance. Also suitable are large vases and pots with large plants. Climbing crops will look good on fences and hedges.
Download 3 instructions from Organic Mix experts and learn how to harvest 1.5-3 times more
Organic Mix Team
We have prepared for you TOP 3 instructions from Organic Mix experts, with which you will prepare garden by spring and get 1.5-3 times more yield, without chemicals!
Let's tell you what to plant at home in order to enjoy your harvest in winter
We will analyze how to choose the right variety for seedlings, planting time and how to properly feed seedlings in order to avoid problems
Simple instructions for spring dressing beds
Already downloaded 13 197
Crops such as thuja, boxwood and juniper are ideal for low open fences up to 40 cm in height.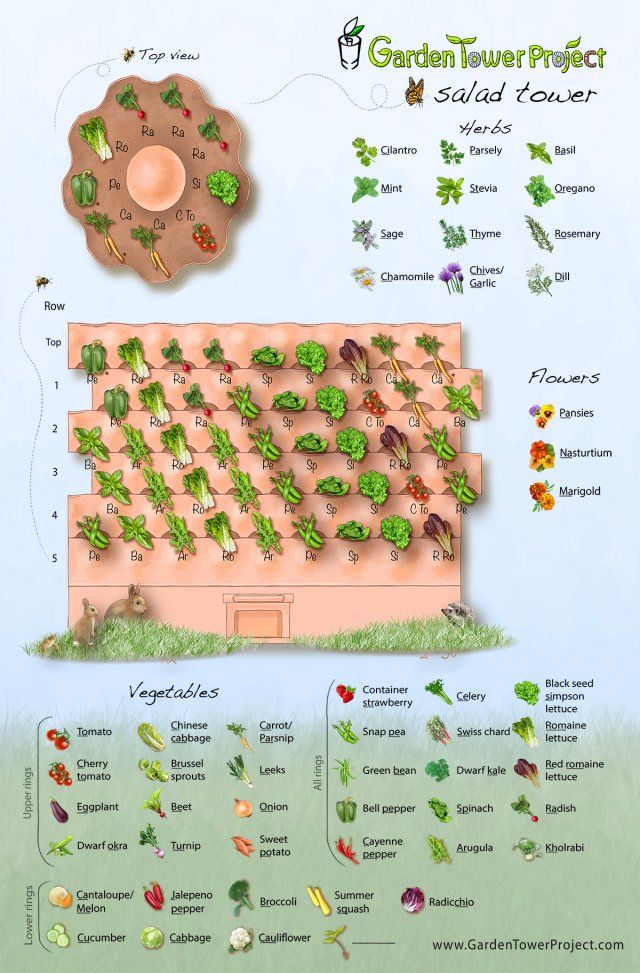 This is a suitable border that separates a playground, vegetable garden or garden from everything else. A solid wall up to 1.5 m high can be built from low trees and shrubs:
This is a suitable border that separates a playground, vegetable garden or garden from everything else. A solid wall up to 1.5 m high can be built from low trees and shrubs:
- barberry;
- Japanese quince;
- steppe almonds.
Sunflowers and thorns grow quickly, so they are well suited for creating a high border between different zones. Flowers with large inflorescences will form a beautiful green fence. Perennial plants with trailing stems (such as roses or clematis) are suitable for trellises and arches. Decorative beans and nasturtiums will grow during the year so that they will hide a screen or some other partition from prying eyes.
Colors
Landscape design experts advise zoning using different colors in your interior. If you have kids, then bright and cheerful colors that children love so much are suitable for the children's area. For places of rest, pastel colors are good, which set you up for peace. A cheerful combination of red and green colors improves mood.
A cheerful combination of red and green colors improves mood.
Tracks
Paths give your yard a neat and finished look, and not only serve to connect its various parts and delimit zones. Paths from the gate to the house are best made of paving stones or tiles with a clear geometric pattern. Openwork looks great in a park or garden, and colored gravel looks great on ridges and flower beds.
Read also!
18 ways to make your garden beautiful
More details
All the shortcomings in your territory can be hidden by winding paths.
Height
Height differences are a great solution for any site, especially a small one. Arrange flower beds, lawns and beds from above and below. The space between them can be decorated with stone, tiles or mosaics. If you have a pond or waterfall on your site, arrange a recreation area next to the reservoirs. In the evenings, at the place of your rest, you can use the backlight, which will create romance and set you up for relaxation after a hard day's work.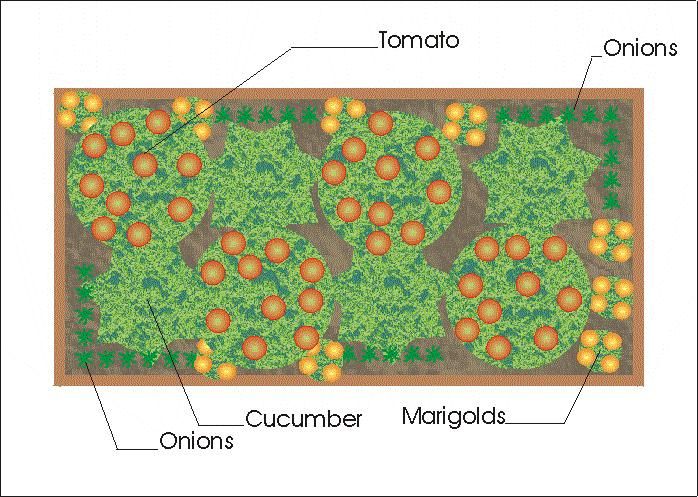
Features of the garden layout
Landscape designers recommend not placing plants of different waters in a random order, as this will not create an overall harmonious picture of your site. All crops in your garden should be planted in a rectangular or checkerboard pattern. The color and size of the fruit, the shape of the foliage matter. The best combination of green is with yellow and red.
For planting fruit trees and berry bushes, a place well lit by the sun, which will also be easy to water, is suitable. In a small area of \u200b\u200bculture, it is better to plant in vertical beds. Containers are good for growing strawberries, and barrels are good for growing raspberries. Mobile plants can be placed in any corner.
Trees are the largest component in a garden, so their roots can damage other plants and buildings. To prevent growing roots from creating such inconvenience, place trees at a distance of at least 3 m from structures. In recreation areas, alleys of fruit crops, pergolas, vine arches will look good.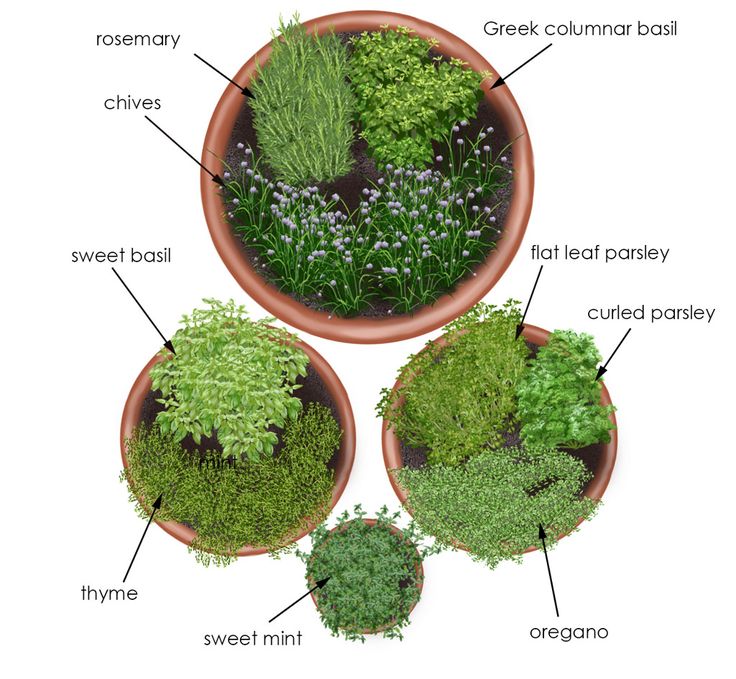
To create beautiful flower beds, various flowers, vegetables and berries are suitable. In the central part of the flower bed, install a vertical bed for strawberries. Ornamental cabbage, lettuce and carrots are planted on the sides. For borders, marigolds, calendula and mint are good.
How to organize a vegetable garden in a small area
Not everyone has a large garden in their backyard. Some of the summer residents like to relax, not work, since the cottage is intended mainly for a pleasant pastime. Many are currently making two or three ridges for greenery and a small amount of vegetable crops on their site. There are many different solutions for organizing your personal plot, the choice is yours.
Vertical beds
Some people like to use vertical beds for their plantings, and this type of planting has many ways. The main thing in this method: your cultures are located on top of each other, some are higher, some are lower.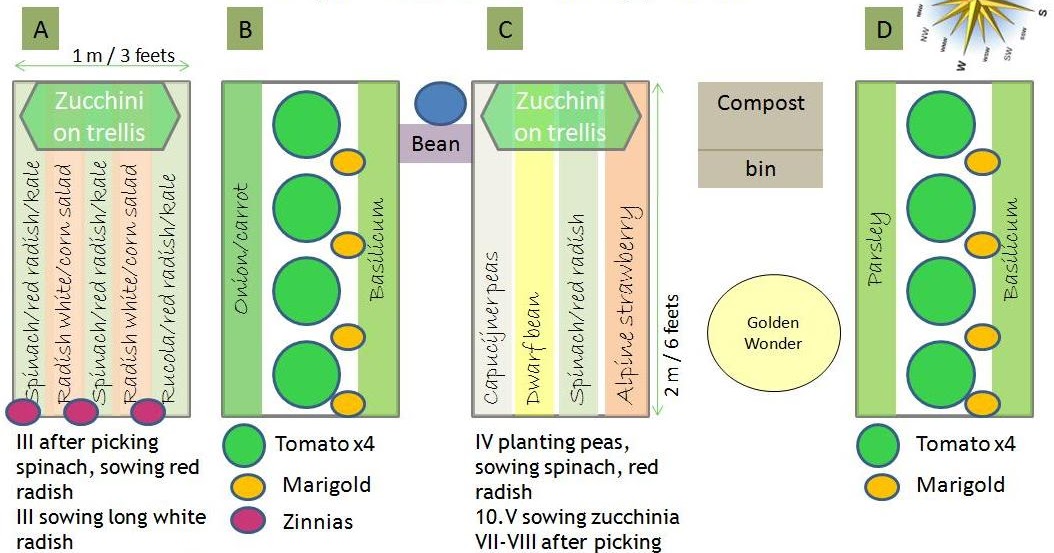 They can be placed in different ways, but they all tend to the top and save space.
They can be placed in different ways, but they all tend to the top and save space.
Featured Products
Brand: OrganicMix
AminoRost 12 gr
Organic Growth Stimulant
RUB 390 390 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
BioRoot 50 gr
Organic root
690 r.690 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Anti-Top Rot 25 g
Treatment and prevention
blossom end rot
1200 r. 445 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Soil for seedlings 4 l.
Organic soil
for seedlings
570 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Soil for seeds and cuttings 4 l.
Premium soil mixture
485 r.
Brand: OrganicMix
Fertilizer for strawberries and berries 800 gr.
Granular fertilizer
$485
First, you can arrange a wall for the garden. Trays or boxes with earth are hung on a wall or fence, in which already mature plants or seeds can be planted for their growth. It is good for growing greens and different herbs, especially those with curly or weaves. They will look very beautiful if they grow together with support from a grid or a wooden lattice.
Plant boxes hanging on the wall are not suitable for everyone, as the wall can be damaged by water that will flow due to excessive watering. Therefore, it is better to make a rack for containers, which can be located on your site to your liking, not necessarily next to a wall or fence, but at the border between the garden and the garden, to serve as a cover for a toilet, a shed or a compost pit.
An original solution would be vertical or horizontal plastic pipes with a large diameter, in which holes for plants are cut. It is suitable for strawberries, herbs and aromatic plants.
It is suitable for strawberries, herbs and aromatic plants.
Garden along the fence
Not under every fence you can arrange beds. This applies to corrugated fences in the southern regions. The metal structure heats up under the sun so much that your plants risk not only getting burned, but also burned. For areas of the northern regions, this will not create any particular inconvenience, since such hedges will only additionally warm the plants.
The layout of the garden should be arranged taking into account such factors: groundwater level, soil type and rainfall. In high-quality soil, water does not stagnate even after heavy rain, you can easily allocate a part for plants. The optimal width of the beds is 50-60 cm, dig it up and put up a fence.
If there is little land, a lot of moisture in it, or you want your site to look neater, make high beds. Arrange partitions, and you will have space for greens and vegetables. Or plant your plants in a box if you do not want to use open ground for this purpose. Wrap it inside with geotextile. Lay on the bottom
Wrap it inside with geotextile. Lay on the bottom
fine-mesh metal mesh, which will save your crops from moles.
The width of such a bed is 50-60 cm, which will help you easily reach the farthest edge. You will not get very tired if you stand in this position, but you will do several things at once: planting, weeding, watering. You can make the height, as well as the material of the walls, according to your taste.
Crop rotation
Simple rules of agricultural technology, for example, the correct crop rotation, as well as other techniques used on your site, will give you plant health in the future. Do not plant vegetables in the same place two years in a row, this will reduce your yield, and may even cause an invasion of harmful insects and dangerous diseases.
Different types of plants absorb nutrients in different ways. There must be a system in the cultivation of crops, otherwise, if you plant at random, you will quickly deplete the soil. The roots of cucumbers, onions and cereals take potassium and phosphorus from the upper layer of the earth, and carrots and beets - from the lower parts of the soil.
The roots of cucumbers, onions and cereals take potassium and phosphorus from the upper layer of the earth, and carrots and beets - from the lower parts of the soil.
A reasonable option is to change places for all plants every season. Before planting a vegetable garden, make a list of the plants you want to have in your garden so you don't spontaneously plant them later. Vegetable crops can be divided into 4 groups:
- Leafy: all varieties of cabbage, onion feathers, lettuce and spinach.
- Forming fruits: pumpkin, cucumbers, marrows, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants.
- Root vegetables: potatoes, carrots, radishes and beets.
- Legumes: beans, peas.
For the next season, take each group one step further. It is better to leave one of the beds for rest (for steam). To ensure that the soil is not empty, sow green manure. Yellow sweet clover, lupine and clover will not only decorate the flower bed, but also nourish the soil with useful components.
Neighborhood rules
The layout of the garden on a plot of a small area will give you the opportunity to conveniently and correctly arrange plantings and harvest a large crop. As landscape designers advise, the neighbors in the garden must be selected correctly, then the cultivation will be useful for all plants, as this will allow them not only to grow and multiply quickly, but also to get rid of pests and protect against diseases.
The neighborhood of bush beans is useful for eggplant and cabbage, as it scares away Colorado potato beetles from the first crop and fleas from the second. Beans get along well with cucumbers, potatoes and corn, as they enrich the soil with nitrogen. Close planting of peas is useful for carrots and turnips, but planting wormwood and marigolds next to them is not worth it, this will spoil the taste of root crops.
Potatoes are ideally grown along with horseradish, tansy, nasturtium, spinach and beans, which will drive away dangerous insects such as Colorado potato beetles.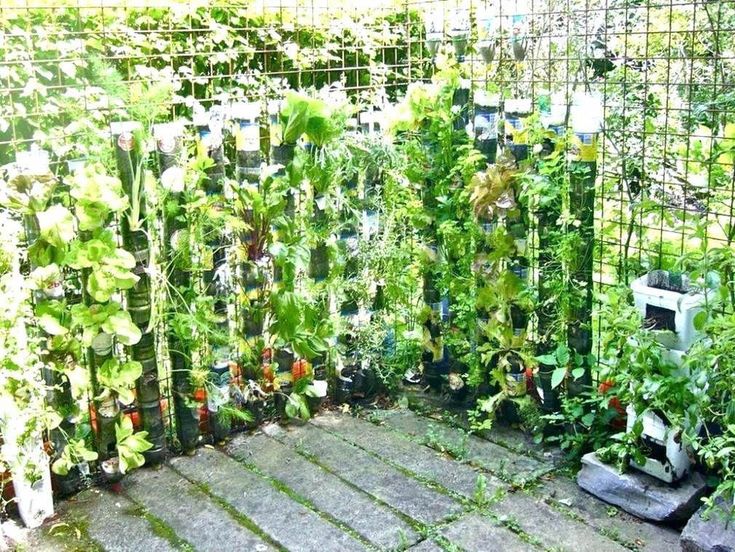 Celery is unsuitable for neighborhood with potatoes and other root crops.
Celery is unsuitable for neighborhood with potatoes and other root crops.
Read also!
Landscape design of a garden plot: styles, zoning rules, useful tips
Read more
Strawberries will not harm other crops, so they can be planted next to any others. Parsley is useful for this juicy berry, which will save it from damage by slugs. You will improve the taste of your crop by planting sage and borage. Garlic is good for strawberries, but will depress grapes. For tomatoes, it is not recommended to plant kohlrabi nearby. Turnips make great friends with peas, but not with mustard and bird knotweed.
Corn is very capricious, it will not grow with beets and celery. In its native region, in Latin America, this plant is planted next to pumpkin and beans. Pepper will take root well with basil, but such a neighbor as fennel is destructive for it.
Author of article
OrganicMix site editors
Like this article? Share:
Correct way: Make an ornamental garden
Just a couple of decades ago, the garden was a great help for the family budget. But now gardening is more of a hobby. Growing your own vegetables is unprofitable, labor intensive, hectic and responsible. However, it is very interesting! I will tell you what is important to know about creating an ornamental garden.
But now gardening is more of a hobby. Growing your own vegetables is unprofitable, labor intensive, hectic and responsible. However, it is very interesting! I will tell you what is important to know about creating an ornamental garden.
► About the author: Oksana Razumovskaya, the chief landscape architect of our studio, has been professionally caring for gardens for over 27 years.
BUGAEV Parks & Gardens
What is the difference between an ordinary vegetable garden and an ornamental one
A vegetable garden is a relatively small piece of land that is primarily used for growing vegetables. It may also contain berry bushes and fruit trees. In the village and garden associations, the garden is usually located in the immediate vicinity of a residential building.
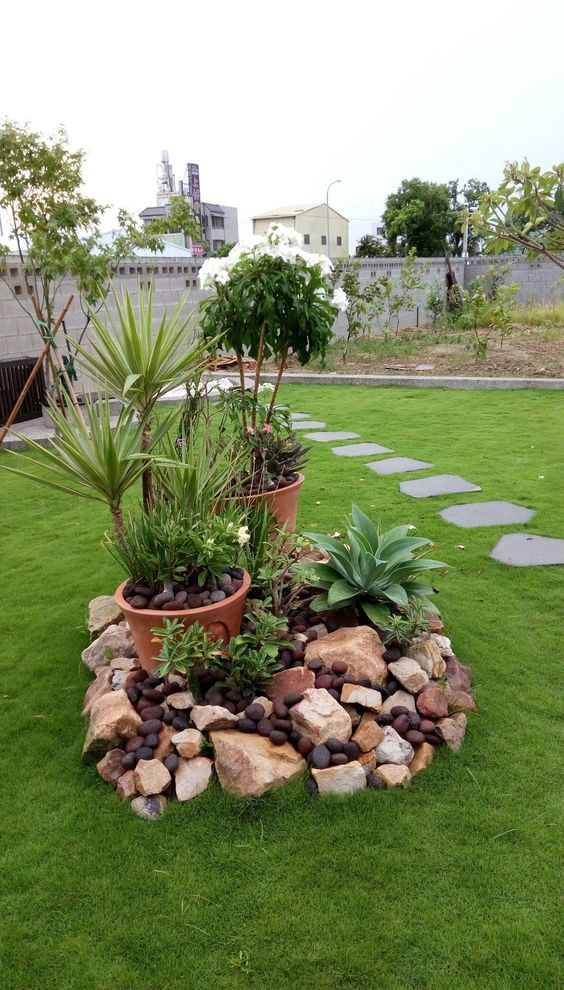
A vegetable garden can be utilitarian: rows of beds, above them arcs with a film (greenhouse). And sometimes the garden is decorative. For example, container, when vegetables are planted in beautiful containers and decorate terraces and patios in the manner of flower pots. Or in the form of a rockery, using stones and gravel from backfilling - herbs are usually grown on this.
For example, container, when vegetables are planted in beautiful containers and decorate terraces and patios in the manner of flower pots. Or in the form of a rockery, using stones and gravel from backfilling - herbs are usually grown on this.
Reasonable garden
The photo: garden with spicy herbs In a container of boards decorated with copper plates
Reasonable garden
In the photo 9000 9000 9000 9000 What is an ornamental garden
Most often, by “decorative” we mean a garden with a high level of improvement: paved paths, “capital” beds with borders, original planting layout. Another important condition is the presence of annual and perennial flowers in the amount of up to 5–10% of the total number of plants in the garden. These are vegetables and other plants that are grown not for food, but for their beauty. For example, decorative sunflowers, corn, tomatoes, some types of lettuce, etc.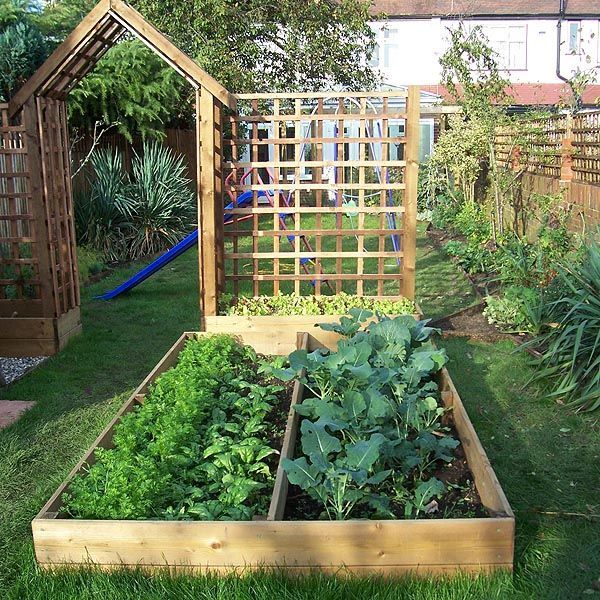 Gardening stores offer a wide range of such plants - for every taste and color.
Gardening stores offer a wide range of such plants - for every taste and color.
Important: I strongly do not recommend planting ornamental plants with inedible fruits on the beds! The fact that they grow in the garden can be misleading not only for children, but also for adults.
Reasonable garden
A sunny place for a vegetable garden
In central Russia, it is important to place any vegetable garden on a well-lit part of the site. Watch for a while how exactly the sun illuminates your allotment at different times of the day. Consider the transparency of fences on the border with neighbors.
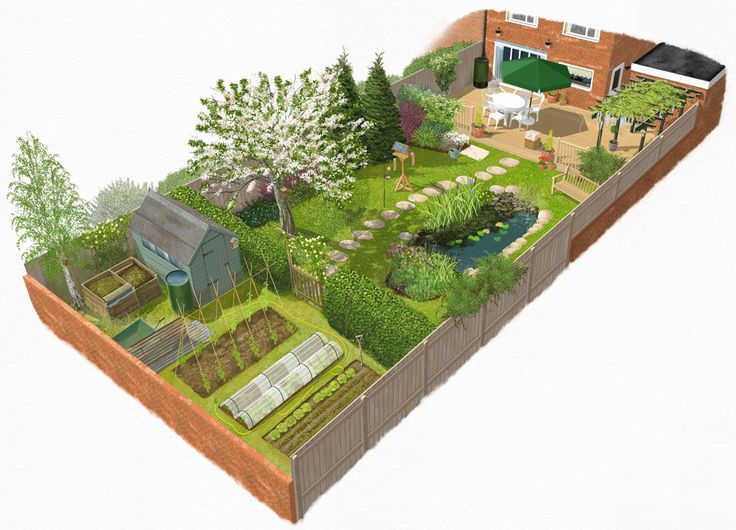
If you plan to combine a vegetable garden and an orchard, it is better to arrange trees and shrubs in tiers, focusing on the south (as in the figure above). The tallest fruit trees should be in the background, and the garden - the lowest element - in front. Fruit bushes and low trees can be placed between them. This will allow all tiers of the garden and vegetable garden to receive their share of sunlight and heat.
This will allow all tiers of the garden and vegetable garden to receive their share of sunlight and heat.
RELATED…
- How to: Mark a vegetable garden in a garden
- How to do it right: Create a vegetable garden in an “uncomfortable” place
Smart garden
Despite the fact that our vegetable garden also has a decorative function, stylistically it belongs to the economic zone of the site. Therefore, you should not place it on the main house adjoining territory. Not the best option would be the location of the garden in the center of the site, glade or lawn - this will lead to division and, as a result, a visual reduction in the site as a whole.
Dimensioning
The basis of any garden is a garden bed: a strip of dug up land allocated for planting. During the season, gardeners spend more than one hour in the beds - they dig and loosen the ground, sow seeds or plant seedlings, weed and water the plants. To work comfortably, you need to create comfortable conditions in advance. Based on many years of experience, we have determined the following parameters for ourselves.
To work comfortably, you need to create comfortable conditions in advance. Based on many years of experience, we have determined the following parameters for ourselves.
LLC "SUCCESSFUL PROJECT"
- The maximum bed width is 80–100 cm.
- The height of the bed depends on the age and physical capabilities of gardeners. It will be more convenient for the elderly and inactive people to work on raised beds. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the soil in such beds freezes faster in winter than in those located directly on the ground, and in summer it will require additional watering.
- Most vegetable crops require 20 cm of fertile soil.
Smart Garden
- The minimum width between beds is 40 cm.0016
- We advise you to frame all beds with boards - it is much more convenient to carry out agrotechnical work with them and water loose fertile soil.
 The material of the boards must be moisture resistant and environmentally friendly - a board with a thickness of 30 mm is suitable.
The material of the boards must be moisture resistant and environmentally friendly - a board with a thickness of 30 mm is suitable.
Intelligent garden
Ornamental garden is a combination of beds and paths. It would seem that it's easier. However, the development of a garden plan is a complex creative work that takes into account a number of restrictions, both technical and decorating.
The most common mistake is to create beds more than a meter wide for the sake of a “beautiful layout”: in the future, this will not allow you to carry out agricultural work on them accurately. It is important to adhere to a rational balance: the area of \u200b\u200bthe beds should significantly exceed the area of \u200b\u200bthe tracks.
In the picture: options for a compositional solution for planning an ornamental garden
What else can be placed on an ornamental garden
Fence. This is not about fencing each garden bed, but about making it difficult for pets - dogs, chickens, rabbits, etc. to enter the garden. After all, they can damage the landing. The main requirements for the fence are light transmission (should not interfere with the access of sunlight to the beds) and compliance with the style of the design of the entire small garden.
This is not about fencing each garden bed, but about making it difficult for pets - dogs, chickens, rabbits, etc. to enter the garden. After all, they can damage the landing. The main requirements for the fence are light transmission (should not interfere with the access of sunlight to the beds) and compliance with the style of the design of the entire small garden.
Outbuildings and outbuildings - greenhouse, greenhouse, compost heap, tanks for heating and settling water used for watering plants, and others. An orchard, together with a vegetable garden, can become the core of the economic zone of a small garden.
Smart Garden
Tip: The dimensions of the greenhouse, its length and width, should be in proportion to the size of the garden. Consider the agricultural technology of growing vegetables (cucumbers and tomatoes are grown separately). Conduct electricity to the greenhouse - for the possible connection of ground heating and lighting.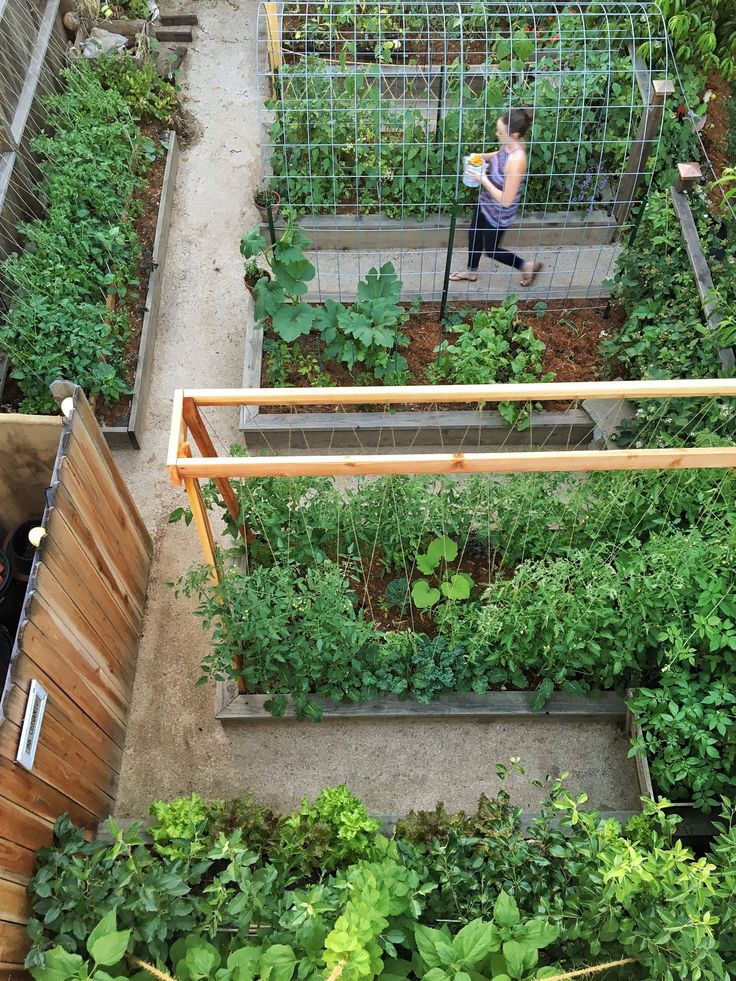 It is advisable to orient the greenhouse with an elongated side from east to west - to obtain maximum sunlight.
It is advisable to orient the greenhouse with an elongated side from east to west - to obtain maximum sunlight.
RELATED…
Sunny house: A greenhouse can be beautiful
Staab & Olmsted LLC - Landscape Architecture and F
What to plant
Indoor varieties should be selected with self-pollination. For example, tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplants, etc. are suitable for the Moscow region. For open ground, the assortment of seedlings can be supplemented with cabbage, zucchini, squash and many others.
Lettuces, onions, parsley, dill, cilantro and other plants are suitable for sowing in the ground. Moreover, sowing and repetition frequency depend on the germination time. For example, parsley and carrots sprout for a long time and are sown one-time and early. And dill, cilantro and various salads - several times with an interval of 2-3 weeks. Cucumbers can also be grown at intervals.
A good option for early planting is radishes, which can withstand surface frosts and cold nights. And crops such as cucumber should be planted in the ground when the nights become warmer. To preserve crops during surface frosts, seedlings are covered with spunbond.
Smart Garden
Ornamental Garden Step-by-Step Plan
1. Examine the scale garden design in detail. When transferring the project to the planned territory, determine in advance the area and boundaries of the beds and paths. It is convenient to make markings with pegs, to mark the lines of the sides with a stretched twine or tape.
2. Install the bead bases at the junction of beds and paths. If the bases are made of boards, pre-treat them with an antiseptic or coated waterproofing.
3. Dig a "trough" under the base of the tracks. Fill it in layers with sand and gravel. Crushed stone is drainage, rainwater and excess water during irrigation will drain into it.