Best runner beans to grow
Five of the Best Runner Beans to Grow
Runner beans (Phaseolus coccineus) are one of the easiest crops to grow, bearing masses of long, sweet-tasting beans all summer long. While they can reach 2-3m tall, they don't take up much ground space - grow them on the veg plot or scrambling up a wigwam in a border. You can even grow them a large container.
Find out all you need to know about growing runner beans in our runner bean Grow Guide.
The pretty red, white or bi-coloured flowers are edible and have a beany flavour - use them as a garnish or to decorate salads.
There's a wide range of runner bean to choose from - here are five of the best.
1
'Scarlet Emperor'
Runner bean 'Scarlet Emperor' is an old favourite - a heritage variety that has been grown in Britain for centuries. It has bright red flowers and produces heavy crops of long, smooth, dark-green pods with an great flavour.
Handful of 'Scarlet Emperor' runner beans
2
'Painted Lady'
Runner bean 'Painted Lady' is a Victorian variety that is grown as much for its pretty bicoloured red and white flowers as for its large crops of tender, medium length, well-flavoured beans.
Red and white flowers of runner bean 'Painted Lady'
3
'Red Rum'
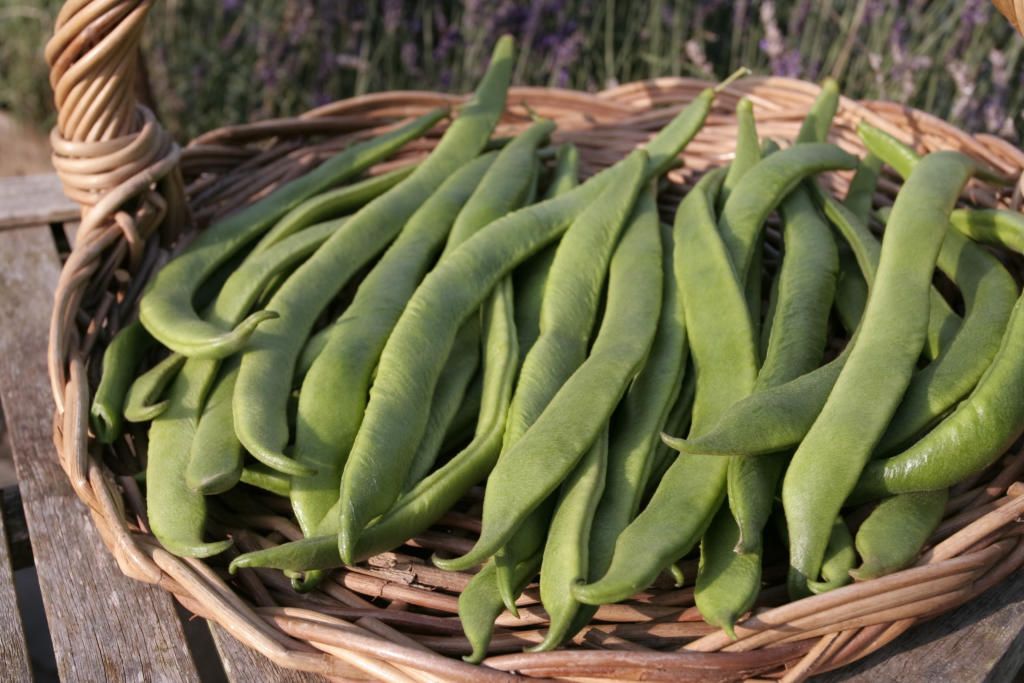
Runner bean 'Red Rum' is a self-fertile, which means that it doesn't need cross pollination from other bean plants nearby. So even if you grew one plant, you would enjoy a tasty crop. 'Red Rum' starts cropping early in summer and carries on producing heavy crops of medium-length beans throughout the season. Its ability to set beans even in poor weather means it outcrops many other varieties.
Picked 'Red Rum' runner beans, lying on hessian
4
'White Lady'
Runner bean 'White Lady' bears pretty, pure white flowers and long, mid-green, stringless, tender pods with white seeds. It's a reliable and heavy cropper, and is more tolerant of dry, hot conditions than some other varieties.
A wooden trug full of 'White Lady' runner beans
5
'Polestar'
British bred, 'Polestar' is a is a reliable runner bean that bears heavy crops of stringless and smooth, fleshy pods. They have a good flavour. It's early to flower and the flowers set easily; it crops over a long season.
They have a good flavour. It's early to flower and the flowers set easily; it crops over a long season.
'Polestar' runner beans, placed on hessian
Try growing sweet peas alongside your runner beans - not only does the combination look pretty, it will help to attract beneficial pollinators, too.
Harvesting runner beans into a saucepan
- Sow seeds under cover from mid-April and plant out from late May.
- Alternatively sow in mid- to late May, outdoors. Sow two per support.
- Grow in a sheltered, sunny position and dig in plenty of organic matter into the soil before planting.
- Protect seedlings from slugs and squash blackfly as soon as they appear on shoot tips.
- Keep plants well-watered.
- Pick beans regularly, as leaving pods on the plant will stop production and shorten the season.
Varieties Growing Guide, Problems, and Harvesting
Until recently, you’d typically only find runner beans in British gardens, but now, they claimed spaces in gardens all over the world. It’s easy to see why. These tall vines produce colorful flowers and beans, acting as an edible and ornamental plant in your garden. If you’ve ever had green beans in your garden, then growing runner beans will be a piece of cake.
It’s easy to see why. These tall vines produce colorful flowers and beans, acting as an edible and ornamental plant in your garden. If you’ve ever had green beans in your garden, then growing runner beans will be a piece of cake.
This last growing season was the first time I grew runner beans. I opened a gardening catalog to a gorgeous photo of vines draping an arch with red flowers and green pods dangling downward. I knew I needed to give them a try if only to add a unique look to my garden.
I learned that runner beans are easy to grow and attract plenty of attention. Nearly every person who stopped by my garden asked about them.
Are you ready to learn how to grow runner beans? I thought so! Keep reading.
Runner Beans vs. Green BeansTaking a look at them side-by-side, it might be hard to notice a difference between runner beans and green beans – and don’t forget pole beans, soybeans, and string beans! That’s a lot of beans, each with their own unique characteristics.
Runner beans look like a larger version of green beans. There are a few other differences besides the size, though.
- Runner beans are a perennial plant, and green beans are annuals.
- When a runner bean seed starts to grow, the stem and first set of leaves emerge from the ground first. When green beans grow, the two halves of the seed appear first.
- The vines on a runner bean plant twist clockwise, but green bean vines rotate counterclockwise.
- From a gardening point of view, runner beans double as an ornamental plant, producing flowers that are an inch long, typically in an orange or red color, with 20 or more flowers to a stalk.
- Runner bean pods measure anywhere from 6-12 inches long with 6-10 beans inside. Each bean is an inch long.
Some people might tell you that runner beans aren’t edible, but they’re wrong. Runner beans are not only something you can eat, but they’re delicious. They were a customary food in the early American colonies and Britain, so plant and eat away!
They were a customary food in the early American colonies and Britain, so plant and eat away!
Runner beans differ in the color of flowers they produce. Most varieties grow either scarlet-colored or white flowers. The scarlet runner beans look more orange than red.
Here are a few varieties you might want to try.
- Scarlet Emperor: This variety is similar to the scarlet runner, producing orange-red flowers, but the pods are fatter.
- Scarlet Runner: This is the most common variety – it produces bright red flowers. It’s a vigorous vine that reaches over 10 feet tall and produces enormous seeds.
- Sunset Runner Beans: This variety produces blooms that are peach to shell-pink. The vines reach 6 feet tall and are packed with pods.
- Black Coat: This is an heirloom runner bean dating back to the 1600s. The blooms range from tangerine to cherry red, and the pods are shorter than other varieties.

These beans are native to Central and South America, but they grow well in a variety of climates. Many gardeners find that they germinate better in cool soil rather than the hot soils found in their native lands. Remember that these plants are perennials, but they’re usually grown as annuals. If you live in an area with mild climates, they can over-winter.
Here is what you need to know about growing runner beans in your garden.
The Right Location for Runner BeansMake sure that you pick a site with full sun, and you need a location that offers some type of support for the plants to climb on. Trellis or teepees are options, along with metal arches.
An even bigger bonus is if you pick a spot that has plenty of pollinating insects, which are essential for the plants to set pods.
Preparing the Soil to Grow Runner BeansThese beans require the same soil as green beans.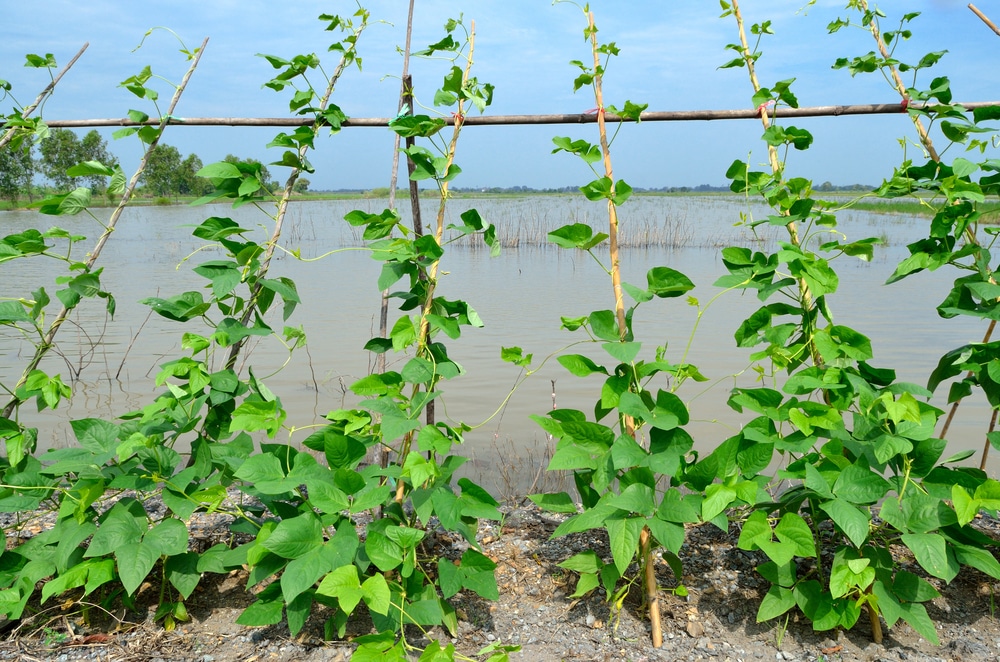 You want to plant them in moderately fertile soil that is amended with plenty of organic matter. Mix in some compost or well-rotted manure several weeks before you sow your beans.
You want to plant them in moderately fertile soil that is amended with plenty of organic matter. Mix in some compost or well-rotted manure several weeks before you sow your beans.
Runner bean flowers set better in alkaline soil. If your ground is neutral or acidic, try adding some lime.
When to Plant Runner BeansYou have two options. First, you can direct-sow the beans outside after the damage of frost passes. The second option is to start the seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before you plan to move them out. Most importantly, remember that runner beans are a tender plant and don’t like the frost.
Starting Runner Beans InsideTypically, most gardeners opt to direct sow beans because they grow fast and don’t transplant well. Beans don’t like their roots to be disturbed, but if you have a short growing season, starting the plants inside gives you a head start.
If you decide to start them indoors, plant the beans in peat or paper pots. Use a seed starting soil and keep them well watered until it’s time to set them outside. These seeds need warm conditions to germinate, around 54℉, and they take 7-10 days to germinate.
Use a seed starting soil and keep them well watered until it’s time to set them outside. These seeds need warm conditions to germinate, around 54℉, and they take 7-10 days to germinate.
Make sure you harden the seedlings off for a week before transplanting them outside. The seedlings should be around 3 inches tall, and you have to wait until any danger of frost passes.
Planting Runner Beans in the GardenDirect sowing the beans into your garden is the easiest choice. Wait until the ground warms up before planting outside. Plant two or three seeds at the corner of each teepee or space the seeds six inches apart along a trellis or an arch.
Runner beans germinate quickly, so you need to train them to grow along the support system as soon as you see the tendrils appear. Direct them to the support system and soon, they’ll figure it out and climb on their own. All you need to do is loosely tie the plants to their supports. Simple, right?
How to Care for Runner BeansWateringRunner bean vines need to stay well-watered. Make sure you don’t let them dry out by watering them throughout the week. Otherwise, they’ll die.
Make sure you don’t let them dry out by watering them throughout the week. Otherwise, they’ll die.
One of the best was to ensure these plants stay well-watered is by mulching around the roots. Not only does mulch keep the roots cool, but it also helps to reduce how many times you need to water your plants each week.
FertilizingTypically, runner beans don’t require too much fertilization. You can apply a side dressing of compost mid-season to help give them a boost throughout the growing season. That can help give them the final push needed to produce a bountiful harvest.
Common Pests and Diseases for Runner BeansHere are a few pests and diseases you might encounter.
Black Bean AphidThese are sap-sucking aphids that destroy and disfigure your plants, stunting the growth of the leaves and stems. Typically, if you have an aphid infestation, you need to knock them off of the plant with a strong jet of water. You can pinch off the infested parts of the plant as well. Then, spray plants with neem oil to keep the pests from returning.
You can pinch off the infested parts of the plant as well. Then, spray plants with neem oil to keep the pests from returning.
These pests love to feed on young seedlings. You’ll find a slime trail on the soil around your crops, as well as the leaves. Gardeners can try many ways to control slugs and snails, such as barriers, copper tape, and sawdust.
Bean RustAt first, bean rust might appear as small yellow or white spots on the leaves, and then the spots enlargen. Raised brick-red pustules develop, surrounded by a yellow halo, and you might have premature leaf drop in severe cases.
This fungus can be hard to treat, so you need to remove and destroy the infected crop debris. Use crop rotation to help decrease the fungus. In severe cases, you might need to spray a fungicide.
Bacterial BlightIf you notice water-soaked spots on the growing runner bean leaves that become necrotic, you might have bacterial blight. These spots might be surrounded by yellow discoloration. Eventually, the leaves die.
These spots might be surrounded by yellow discoloration. Eventually, the leaves die.
Make sure you only use certified seeds and treat seeds with appropriate antibiotics beforehand to kill off bacteria. You could spray the plants with a protective copper-based fungicide as well.
Harvesting Runner BeansYou can start harvesting when the pods are 6-8 inches long before the beans inside begin to swell. Those beans can get huge, so you don’t want to wait too long.
You must regularly pick to stop any pods from reaching maturity. Once that happens, the plants will stop flowering, and no more pods are set. If you pick pods regularly, you can expect the plants to produce a crop for eight or more weeks.
Before you cook these beans, you do need to make sure you boil them. Cut off the ends of the pods and bring water to a boil. Put the beans into the boiling water and cook for 2-3 minutes. Remove and place into cold water instantly, a process called blanching.
If you’ve never heard of runner beans before, now is the chance to add them to your garden. Not only are they ornamental, but they are a delicious veggie to put on your dinner table. Learning how to grow runner beans is worth it because you’ll love the flowers that cover the support system all summer long.
Was this article helpful?
Yes NoTop 10 varieties of beans
Beans originate from Central and South America and South Asia (India, China, Japan), where they have been cultivated for several millennia. How to choose the best varieties of green and grain beans will be discussed in our review.
Most of the bean varieties grown in Russia and in the world belong to the species Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean). In addition to the common bean, several other types of beans have been cultivated (lima beans, multi-flowered or fiery red beans, etc.), but they are much less common. nine0003
In addition to the common bean, several other types of beans have been cultivated (lima beans, multi-flowered or fiery red beans, etc.), but they are much less common. nine0003
Bean is a self-pollinating plant with long flowering. The response to the length of daylight hours is weak or absent. In the conditions of the middle lane, all varieties of beans grow and ripen well. Beans are more thermophilic, unlike peas, so they are sown after the threat of frost, along with cucumber. She is also very light-loving.
Varieties of beans differ in shape, size and color of the bean; in size. seed shape and color. According to consumer qualities, bean varieties are divided into vegetable (green beans, asparagus) and grain (shelling). grain beans only seeds that have ripened to a dry state have consumer value. In green beans , immature beans and seeds are consumed in milky ripeness or after full ripeness. The wings of such varieties are devoid of coarse fibers and a parchment layer, juicy and fleshy.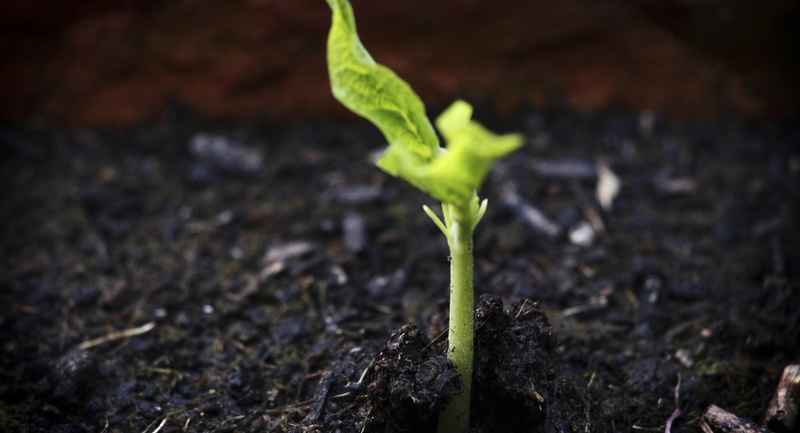 In fact, vegetable beans have a universal purpose, since they give both "shoulders" and seeds. Only the size of beans is significantly inferior to grain varieties. A separate group includes semi-sugar varieties of vegetable beans with a late development of the parchment layer and with coarse fibers only along the seams. Their beans are consumed before coarsening, for this the collection is carried out every 2 to 3 days. nine0009 Attention! Raw beans in milky ripeness contain toxic substances - lectins. They are destroyed only after heat treatment.
In fact, vegetable beans have a universal purpose, since they give both "shoulders" and seeds. Only the size of beans is significantly inferior to grain varieties. A separate group includes semi-sugar varieties of vegetable beans with a late development of the parchment layer and with coarse fibers only along the seams. Their beans are consumed before coarsening, for this the collection is carried out every 2 to 3 days. nine0009 Attention! Raw beans in milky ripeness contain toxic substances - lectins. They are destroyed only after heat treatment.
According to the characteristics of growth, both green beans and grain beans are divided into curly, semi-curly and bush beans. Lianoid varieties require support, are decorative and have a high yield per unit area. Bush - compact and easy to care for. Ornamental beans are also grown - multi-flowered. Its seeds are edible, but ripen for a long time and the yield is very low. nine0003
Description, photos of the best varieties of beans, reviews of popular varieties are presented in our rating.
Rating of the best varieties of beans
| Category | Location | Designation | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green beans, or asparagus: the best sugar varieties nine0036 | 1 | Bluehilda (Germany) | 9.9 / 10 |
| 2 | nine0037 Supernano Yellow (Russia) 9.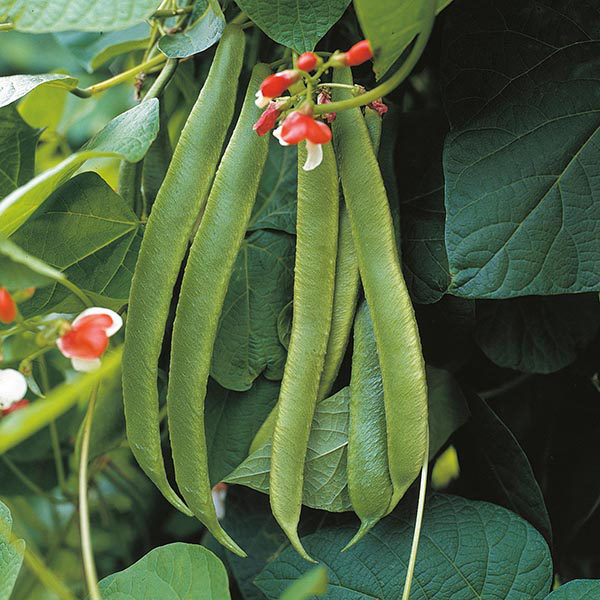 9 / 10 9 / 10 | ||
| 3 | Matilda (Russia) | nine0037 9.9 / 10||
| 4 | Saks without fiber 615 (Russia) | 9.8 / 10 | nine0033|
| 5 | Sugar shovel (Russia) | 9. 8 / 10 8 / 10 | |
| Green beans, or asparagus: the best semi-sugar varieties nine0036 | 1 | Gribovskaya 92 (Russia) | 9.8 / 10 |
| 2 | nine0037 Dream hostess (Russia)9.7 / 10 | ||
| Grain beans, or shelling: the best varieties | nine0037 1Lastochka (Russia) | 9. 8 / 10 8 / 10 | |
| 2 | Rubin (Russia) nine0036 | 9.8 / 10 | |
| 3 | Little Red Riding Hood (Russia) | 9.8 / 10 nine0036 |
Green beans or asparagus: the best sugar varieties
|
Bluehilda (Germany)nine0002 Opens our rating of the best varieties of Bluechild green beans - a mid-season high-yielding climbing variety for an amateur garden.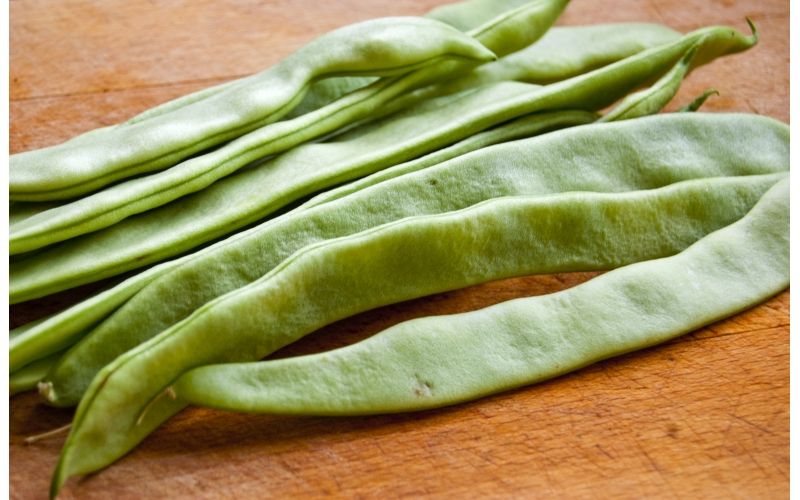 Gives shoots up to 3 meters long. Technical ripeness occurs 70 days after germination. If you do not pluck the first set beans, they will soon be harvested for seeds. This will ensure that germinating seeds are obtained, even in cold and rainy summers. Beans up to 25 cm long, 1-1.5 cm wide, slightly curved, dark purple, flat at the beginning of ripening, after filling the grains are rounded, without a parchment layer and coarse fibers. The seeds are beige, medium in size, tender and sweetish when boiled. nine0003 Gives shoots up to 3 meters long. Technical ripeness occurs 70 days after germination. If you do not pluck the first set beans, they will soon be harvested for seeds. This will ensure that germinating seeds are obtained, even in cold and rainy summers. Beans up to 25 cm long, 1-1.5 cm wide, slightly curved, dark purple, flat at the beginning of ripening, after filling the grains are rounded, without a parchment layer and coarse fibers. The seeds are beige, medium in size, tender and sweetish when boiled. nine0003 Bluechild beans are grown for shoulder beans and grains. The collection period is extended, as the shoulder blades grow, with an interval of 3-4 days. After harvesting the blades, the beans are left to ripen in order to peel the grain. Cultivated in all regions of Russia. In the Moscow region, some summer residents sow seeds first for seedlings in individual cups, so that they can then be transferred to open ground. This measure is sometimes forced - if the germinated seeds cannot be planted in the ground due to bad weather. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9.9 / 10 Rating Reviews A very good variety of green beans. The beans are very beautiful and tasty, they turn green when cooked. |
|
Supernano Yellow (Russia) nine0129 Early ripe string beans. Consumer ripeness occurs at 55 - 65 days. The plant forms a compact shrub 30 - 45 cm high, with large purple flowers. Main advantages:
| 9. Rating Reviews I pluck the shoulder blades before the seeds are released. The more often you cut off, the more it gives new beans - a very productive bean variety. In any dish, green beans are tasty and sweet, good in pickled form and for freezing. |
| nine0036 | |
|
Matilda (Russia) Mid-early asparagus curly bean variety. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews Vigorous curly beans with large and numerous beans of sweet taste. I use everything on the shoulder blades, I leave only a few beans for seeds (I mark them with a ribbon at the beginning of fruiting). nine0003 |
|
Saks without fiber 615 (Russia) nine0129 Continues our rating of the best varieties of green beans, the old early-ripening bush variety of asparagus beans, included in the state register in 1943. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews Productivity is not the highest, but it produces fruit even in rainy summers near St. Petersburg. This variety of green beans is proven and reliable. If you want tender pods, you need to harvest the beans often. |
| nine0036 | |
|
Sugar shovel (Russia) Mid-early asparagus bean variety of bush type. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews Sugar shovel - the best variety of green beans for pickling. These beans are truly versatile - large sweet pods and large tender grains. I advise summer residents of the "weekend", as the shoulder blades do not overripe for a long time and do not coarsen. nine0003 |
Green beans or asparagus: the best semi-sugar varieties
nine0002 Gribovskaya 92 (Russia) Continues our rating of the best varieties of beans Gribovskaya 92 - an old mid-early bush variety. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews An excellent variety of green beans for those who do not eat a lot of shoulder blades. I don’t freeze his shoulder blades, but preserve them - they turn out sweet and crispy. If the beans are plucked on time, there are no fibers. Therefore, it is necessary to clean it every other day. nine0003 |
|
Dream hostess (Russia) nine0129 Mid-season bush variety of green beans. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews I pick the beans often until the seeds appear - then they are juicy and tender. When we are full of pods, I leave the beans for grain. nine0036 |
Grain or shell beans: best varieties
|
Lastochka (Russia) nine0129 Next in our ranking of the best varieties of beans, Swallow is an early ripe grain bean of the bush type. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews I have been growing the Swallow variety for a long time, the beans are very bright and large. Ripens well, does not get sick. | nine0033
|
Rubin (Russia) nine0129 Mid-season corn bean bush type. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews Beans are very tasty and tender. Yield every year pleases. I grow without support, in one row. nine0036 |
|
Little Red Riding Hood (Russia) nine0129 Mid-late corn bean variety of bush type. Main advantages:
Cons:
| 9. Rating Reviews I use standard care when growing beans. I like it very much in cooking: it is tasty and cooks quickly, even without long soaking. |
| nine0033 | |
Growing beans
Beans grow best in fertile soils. On poor soils, organic, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, and ash are applied in autumn.
In the middle lane, bean seeds are sown directly into the ground in late May - early June (simultaneously with cucumbers, that is, when the threat of frost has passed).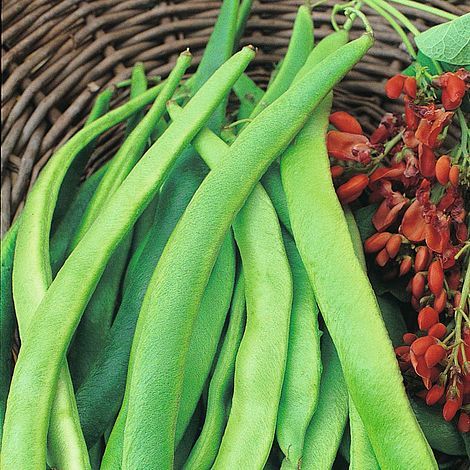 Seedlings appear after 5-7 days, they are very sensitive to frost. With the threat of a cold snap, the seedlings are covered with spunbond or other covering material. Mature plants can withstand short light frosts. The optimum temperature for plant growth and development is 20–25 °C. nine0003
Seedlings appear after 5-7 days, they are very sensitive to frost. With the threat of a cold snap, the seedlings are covered with spunbond or other covering material. Mature plants can withstand short light frosts. The optimum temperature for plant growth and development is 20–25 °C. nine0003
Growing beans from seedlings gives good results. Seedlings are planted at a soil temperature of 10 ° -12 ° (end of May, June).
Beans are a heat-resistant plant. But at the same time it loves moist soils, in hot and dry weather it needs to be watered. To keep watering and weeding to a minimum, the soil can be mulched.
Like all legumes, nodule bacteria reside on the roots of beans, which fix nitrogen from the air and enrich the soil with it. Therefore, peas and beans are not pulled out, but cut off with scissors at the root. The roots remain in the ground, the green mass can be chopped with a shovel and buried. nine0003
Growing beans is not troublesome and even exciting. There are really many good and productive varieties.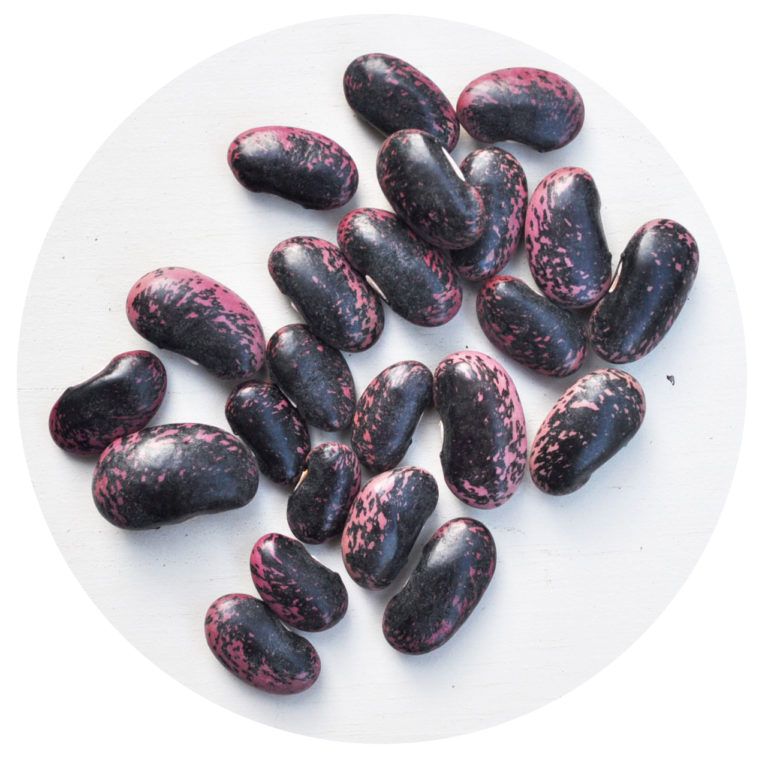 All of them differ in color and shape of both beans and grains. Previously, beans were grown without irrigation and received excellent yields. Modern varieties are more spoiled, but they also have a good return with minimal care. We wish you a good harvest!
All of them differ in color and shape of both beans and grains. Previously, beans were grown without irrigation and received excellent yields. Modern varieties are more spoiled, but they also have a good return with minimal care. We wish you a good harvest!
Rate the article
4.3 / 5 nine0003
Total votes - 23, rating - 4.3
Updated on 10/27/2020 is subjective and is not an advertisement
The best varieties of beans, top 10 rating of good varieties of beans
Subscribe to our VK community!
Beginning gardeners in most cases prefer crops that do not require special care and at the same time are able to give quite a decent harvest. These plants include beans - this vegetable has been known to mankind for many millennia.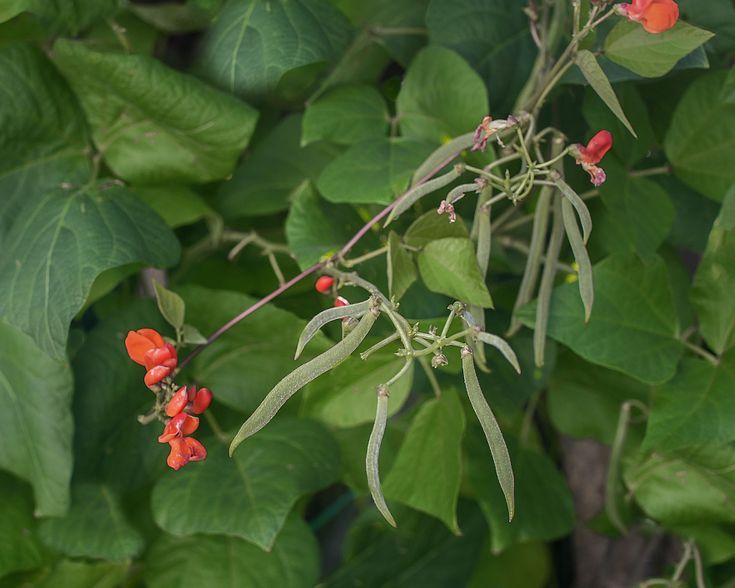 Most of the varieties that exist today are self-pollinating, flowering is long, so the crop can be harvested for several months at once. nine0003
Most of the varieties that exist today are self-pollinating, flowering is long, so the crop can be harvested for several months at once. nine0003
Another important advantage of this crop is the lack of reaction to the length of daylight hours, but the beans are very fond of sunny areas, they do not tolerate frost. For this reason, this crop should be planted after the last spring frosts have passed.
Vegetables can vary greatly in shape, size and color. In general, all existing varieties can be divided into two large groups - leguminous and peeling or grain. The latter is suitable for eating only when ripe to a dry state. Leguminous breeds can be eaten at the stage of milky ripeness and in an unripe form. According to the characteristics of cultivation, beans are divided into three types - curly, semi-curly and bush. nine0003
In our review of the best varieties of beans, we tried to tell as much as possible about the most popular breeds. We chose varieties for this rating based on feedback from experienced gardeners, so low-yielding and fastidious options did not make it into our article.
Summary of the rating: (hide/show)
Top 10 best bean varieties in 2022-2023
10. Laura properties. The breed perfectly resists the most common diseases - anthracnose and bacteriosis. From one square meter you can get up to 2 kg of finished products. It can be eaten as food after heat treatment, in canned form, often housewives freeze beans for the winter. This is a bush variety, it is distinguished by its compact size - it can be no more than half a meter in height. From the moment the first shoots appear to the harvest, about two months pass. Harvesting beans is easy and convenient, as most of the pods ripen at the same time. The pods themselves are yellow in color, they are cylindrical, about 12 cm long and about 2 cm in diameter. nine0003
Each pod contains about 6-10 beans, they have a dense white skin, the average weight is 5 grams. The fruits contain a high concentration of vegetable protein, mineral salts, B vitamins, iron and calcium. When cooked, they practically do not boil. The variety does not need special preparation for planting, but it is afraid of hypothermia, so the seeds are planted in the ground towards the end of May, they will first need to be soaked for a couple of days. nine0003
When cooked, they practically do not boil. The variety does not need special preparation for planting, but it is afraid of hypothermia, so the seeds are planted in the ground towards the end of May, they will first need to be soaked for a couple of days. nine0003
Benefits:
- Fairly high yield;
- Excellent resistance to most common diseases;
- Shrubs low;
- Do not collapse under the weight of the pods.
Disadvantages:
- Although not a high variety, but very sprawling - such beans will have to be planted sparsely.
Beans Laura
9. Lima Sweet Bean
The main distinguishing quality of this breed is that its fruits are distinguished by a very pleasant aftertaste of natural butter. This is a fairly tall plant - it reaches 1.6 meters in height, so the beans will definitely need support. The fruits are in large curved pods, they grow up to 11 cm in length, but there are usually few seeds in them - about 5.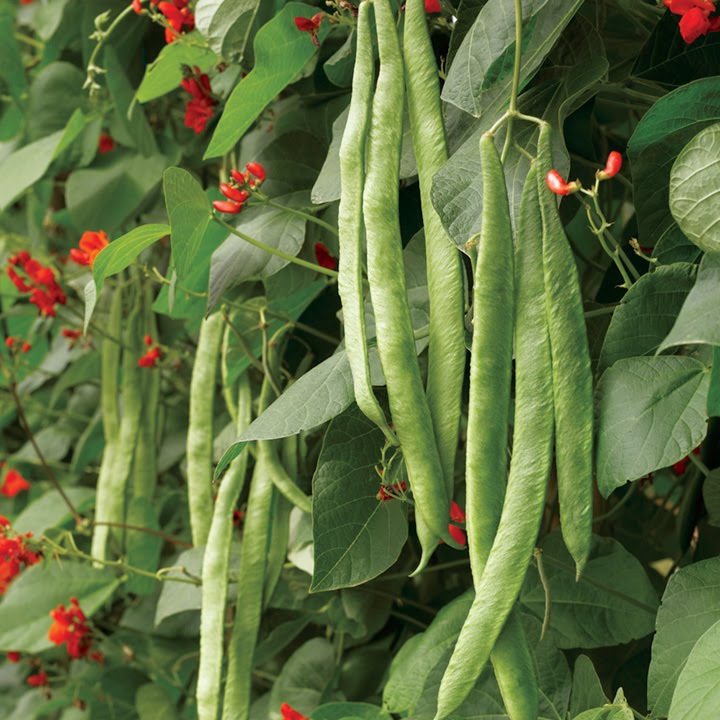 They have a pale greenish or white-green color. The beans are round in shape, but slightly flattened. The skin is quite thin, and the flesh is fleshy. nine0003
They have a pale greenish or white-green color. The beans are round in shape, but slightly flattened. The skin is quite thin, and the flesh is fleshy. nine0003
The products can be eaten from the period of milky ripeness, while the fruits have not yet had time to harden. The protein obtained in this case will be well absorbed by the body. For long-term storage, it is best to use a crop of biological ripeness. Beans are suitable for frying, stewing, freezing, preservation. It has a high calorie content, so you can quickly get enough of it.
Benefits:
- Excellent performance;
- Can be consumed both fresh and after heat treatment;
- Fruit does not crack or fall out of the pod;
- High content of nutrients.
Weaknesses:
- Poorly withstands lack of moisture in the soil.
Sweet Bean Lima Bean
8. Royal Grain
The breed belongs to the late-ripening group. The variety is distinguished by very large pods: they can grow up to 16 cm in length, one bean contains about 4 beans with a delicate white skin.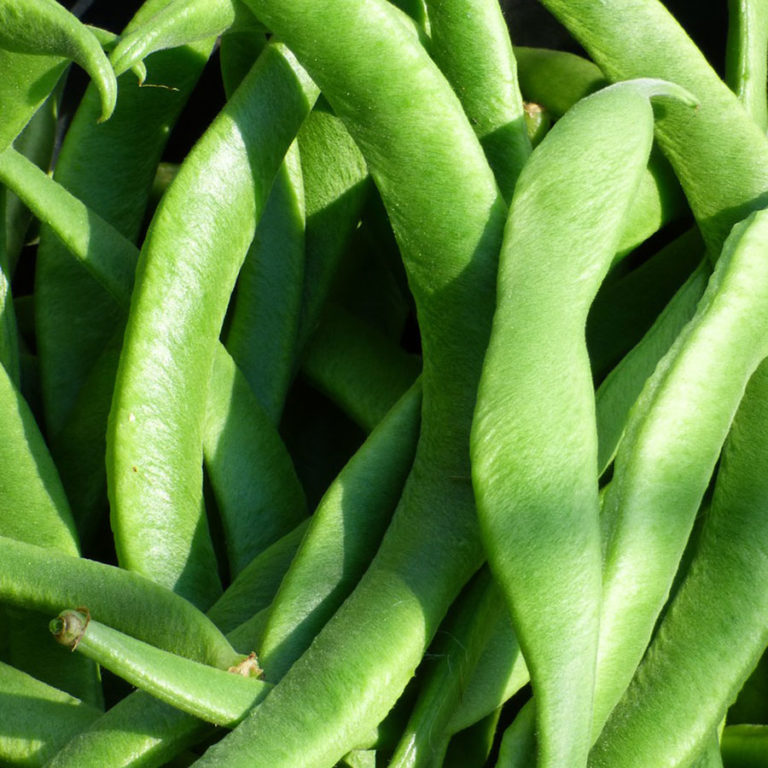 The plant belongs to climbing - the length of the whip can reach 3.5 meters, so it is often planted along the hedge in order not to install supports. Beans bloom very beautifully, which also gives it certain decorative properties. nine0003
The plant belongs to climbing - the length of the whip can reach 3.5 meters, so it is often planted along the hedge in order not to install supports. Beans bloom very beautifully, which also gives it certain decorative properties. nine0003
Very fast growing, high yield, high quality, must be harvested consistently as it matures. It practically does not resist frost, therefore this variety is planted in the ground in the case when the average daily temperature is in the range of 12-15 degrees. Feels best in light soils, but in clay soils or with close-lying groundwater, it feels depressed. Before planting, the seeds must be soaked until the sprouts hatch. It is easy to care for the variety - the soil is watered as needed, loosened and certain fertilizers are applied. nine0003
Advantages:
- Excellent performance;
- Tolerates drought quite well;
- Easy care;
- Allows you to get a fairly high quality and plentiful harvest.
Weaknesses:
- The plant is climbing, so you need to think in advance about how it will grow;
- This bean simply cannot survive frosts;
- Sensitive to soil type.

King beans
7. Xera
This plant produces green pods that are perfectly acceptable to eat. Their length reaches 13 cm, they are usually no more than 9 mm in diameter, according to these parameters, the entire crop is approximately the same. Bush type beans - no need to think through the installation of supports. When growing, to obtain a fairly plentiful harvest, it is quite enough to follow fairly simple agricultural practices. The plant belongs to the class of heat-loving, it also needs regular, fairly abundant watering. The best harvest can be obtained in light soil structure. It grows poorly in heavy soils, mainly due to the fact that they warm up slowly and poorly. nine0003
This variety is planted in open ground only after it warms up to at least 16 degrees - in the conditions of the middle lane, this happens around the end of May - beginning of June. Pre-sowing preparation (in other words, soaking) is not required, because in this case the seeds can simply fall apart. It is much better to disinfect them in a weak solution of potassium permanganate - they are placed there for no more than 15 minutes before direct planting. The variety is medium early, so the harvest can be harvested somewhere in two and a half months. This variety does not require special care. nine0003
It is much better to disinfect them in a weak solution of potassium permanganate - they are placed there for no more than 15 minutes before direct planting. The variety is medium early, so the harvest can be harvested somewhere in two and a half months. This variety does not require special care. nine0003
Advantages:
- Universal grade;
- Higher yield;
- Drought tolerant and generally unpretentious;
- Excellent resistance to various diseases and pests;
- Grows compactly in the field.
Faults:
- Both the beans and the pods themselves coarsen rather quickly.
Xera Bean
6. Yin-Yang
This variety lives up to its name - the skin of the bean has a black and white pattern, which very much resembles the most famous symbol in Chinese philosophy. Beans belong to the bush group. It is a grain variety, that is, it should be eaten in a purified form, without a pod. The maximum height of the plant is no more than 45 cm. For such growth, the variety is considered super-yielding. In particular, during the fruiting period, the plant is literally invisible because of the pods. nine0003
For such growth, the variety is considered super-yielding. In particular, during the fruiting period, the plant is literally invisible because of the pods. nine0003
Before planting, the seeds are soaked and planted in holes no deeper than 7 cm, with a distance of 15 cm between plants. The lightest and most fertile soil is best suited for beans. It is best if the bed is protected from the wind and is under the sun for most of the daylight hours. The variety is planted in late May-early June, depending on climatic conditions. Water the variety as needed, loosen the soil, feed it well with mineral fertilizers before flowering. The fruits contain a significant amount of fiber and many other useful substances. nine0003
Benefits:
- Adapts well to all soils, but prefers light soils;
- Easily tolerates high temperatures;
- Shrubs compact and low growing;
- Harvest is very early and abundant.
Faults:
- Bean shells begin to coarsen very quickly.

Yin-Yang beans
5. Swallow
Shelling breed, which is very easy to store for several years, but it can also be consumed fresh. It contains a high percentage of nutrients that help the human body fight a number of infections and diseases. This is a short breed, the bush is quite strong, but not too sprawling, it belongs to early ripening varieties. The pods are up to 15 cm long. The grains are white in color with a small but bright pattern, the taste is excellent. During heat treatment, the fruits quickly begin to boil soft. Beans thrive in moist soil, but tolerate drought with ease. Even in canned form, it retains about 80% of useful substances. nine0003
Seeds are planted in the ground around the middle of May - the first half of June. At this time, there are practically no frosts, and the soil warms up to a temperature of 15 degrees and above. Seeds are soaked overnight before planting.
Benefits:
- Easy care variety;
- Adapts well to all climates;
- Excellent disease resistance;
- Compact plant size.
Faults:
- Coarse fibers appear on overripe fruits;
- If plants are planted too close to each other, bacteriosis is likely to occur.
Swallow beans
4. Borlotto
An asparagus variety that can be eaten both with the pods and in a peeled form. In addition, the breed is well suited for eating at different stages of ripeness. This bean belongs to early ripening varieties - about 60 days pass from the moment the first sprouts appear until the crop is fully ripe, although unripe pods can be harvested much earlier. In order to collect completely dried seeds, you will have to wait about 80 days. The plants themselves are not very whimsical in relation to weather conditions, do not need special care. Fully ripe beans are large in size, and there are burgundy stains on the skin. nine0003
It tastes delicate and slightly sweet. The yield is very high, the pods are about 15 cm long, about 2 cm in diameter, each of them contains up to 5 grains. The latter are perfect not only for fresh consumption, but also for freezing, preservation, and cooking various culinary dishes. The variety perfectly resists viruses, fungi and pests.
The latter are perfect not only for fresh consumption, but also for freezing, preservation, and cooking various culinary dishes. The variety perfectly resists viruses, fungi and pests.
Benefits:
- Gives a bountiful harvest over time;
- Shrubs are very compact, low growing; nine0139
- The beans themselves look very attractive.
Faults:
- Fully ripe seeds have a very hard skin.
Borlotto beans
3. Gerda
The crop obtained from this variety is used in cooking together with the pods, because they do not contain hard fibers, and there is no parchment layer. The breed is considered early ripe, since only about 50 days pass from the moment of emergence to the collection of the first pods. The pods are quite long - up to 30 cm, their diameter reaches 3 cm. They have a pale yellow color. Climbing plant: reaches a height of 3 m, the lower pods grow at a distance of about half a meter from the root. Beans need a vertical support, instead of which you can easily use a fence, an arbor, and even a tree. nine0003
Beans need a vertical support, instead of which you can easily use a fence, an arbor, and even a tree. nine0003
The variety is unpretentious, even a novice gardener can grow it. Best of all, the breed will feel in a well-lit, calm area. The soil should be sandy or loamy. Such soil warms up perfectly, moisture will not stagnate in it. Seeds are planted in mid-May, when the probability of spring frosts is minimal.
Advantages:
- High productivity of the variety;
- Adapts well to any climate; nine0139
- Actively resists any disease;
- Does not overripe for a long time.
Drawbacks:
- Needs supports;
- Does not tolerate heat and drought well.
Gerda Beans
2. Snegurochka
In second place in our ranking of the best varieties of beans is another strongly curly asparagus variety. It belongs to the early ripening options in terms of ripening speed - the crop can be harvested approximately 50 days after the appearance of the first shoots. There are quite a lot of leaves, so this variety is often used as a green hedge. The skin of the beans has a light yellow color, the fruits are slightly curved, the parchment layer and fibrous pods are not noticed. The latter can grow up to 17 cm in length, their diameter reaches 1.2 cm. Up to 3 kg of crop can be harvested from one square meter of plantings. nine0003
There are quite a lot of leaves, so this variety is often used as a green hedge. The skin of the beans has a light yellow color, the fruits are slightly curved, the parchment layer and fibrous pods are not noticed. The latter can grow up to 17 cm in length, their diameter reaches 1.2 cm. Up to 3 kg of crop can be harvested from one square meter of plantings. nine0003
The fruits contain a significant concentration of protein and mineral salts, there is a whole complex of vitamins - group B, as well as C, E, A and many others. Ideal for any cooking method, the vegetable can be frozen or canned.
Benefits:
- Quite decent yields;
- Unpretentious in terms of fertilizers, humidity, sunlight;
- Versatile cooking grade;
- Highly decorative. nine0139
Faults:
- The plant is sensitive to various diseases;
- Needs high supports.
Beans Snegurochka
1. Butter king
There is nothing surprising in the fact that this breed of beans is the most popular not only among beginner gardeners, but also among experienced summer residents.
 nine0003
nine0003  I freeze a lot of blades and still remain for grain. The bushes do not get sick, it ripens well - I leave it for seeds. nine0003
I freeze a lot of blades and still remain for grain. The bushes do not get sick, it ripens well - I leave it for seeds. nine0003  The beans are straight, 10 - 15 cm long, 1 - 1.2 cm wide, flat, with a long "nose", when fully ripe, the green color turns into yellow, without a parchment layer and coarse fibers along the seam. Seeds are large, black, shiny, with a smooth surface, chocolate-colored in milky ripeness. Unripe shoulder blades, seeds in milky ripeness and ripened grain are used. The variety is grown everywhere, according to generally accepted agricultural practices, often by sowing swollen seeds directly into the ground. nine0003
The beans are straight, 10 - 15 cm long, 1 - 1.2 cm wide, flat, with a long "nose", when fully ripe, the green color turns into yellow, without a parchment layer and coarse fibers along the seam. Seeds are large, black, shiny, with a smooth surface, chocolate-colored in milky ripeness. Unripe shoulder blades, seeds in milky ripeness and ripened grain are used. The variety is grown everywhere, according to generally accepted agricultural practices, often by sowing swollen seeds directly into the ground. nine0003  9 / 10
9 / 10  The pods grow 55-60 days after germination. A plant of unlimited growth, with a medium leafy shoot up to 3 meters long and small purple flowers. The beans are straight, 18–20 cm long, up to 1.5 cm wide, light purple in the unripe state and beige in biological ripeness, flat, blunt, with a “nose” of medium length, without a parchment layer and coarse fiber. Seeds are gray with brown strokes, reniform. In freezing, both blades and seeds in milky ripeness are used. In the Moscow region and in the North-West region, it is recommended to grow under temporary shelter to ensure seed maturation in the cold and rainy season. The appearance of the beans and the taste are similar to Bluechild. nine0003
The pods grow 55-60 days after germination. A plant of unlimited growth, with a medium leafy shoot up to 3 meters long and small purple flowers. The beans are straight, 18–20 cm long, up to 1.5 cm wide, light purple in the unripe state and beige in biological ripeness, flat, blunt, with a “nose” of medium length, without a parchment layer and coarse fiber. Seeds are gray with brown strokes, reniform. In freezing, both blades and seeds in milky ripeness are used. In the Moscow region and in the North-West region, it is recommended to grow under temporary shelter to ensure seed maturation in the cold and rainy season. The appearance of the beans and the taste are similar to Bluechild. nine0003  9 / 10
9 / 10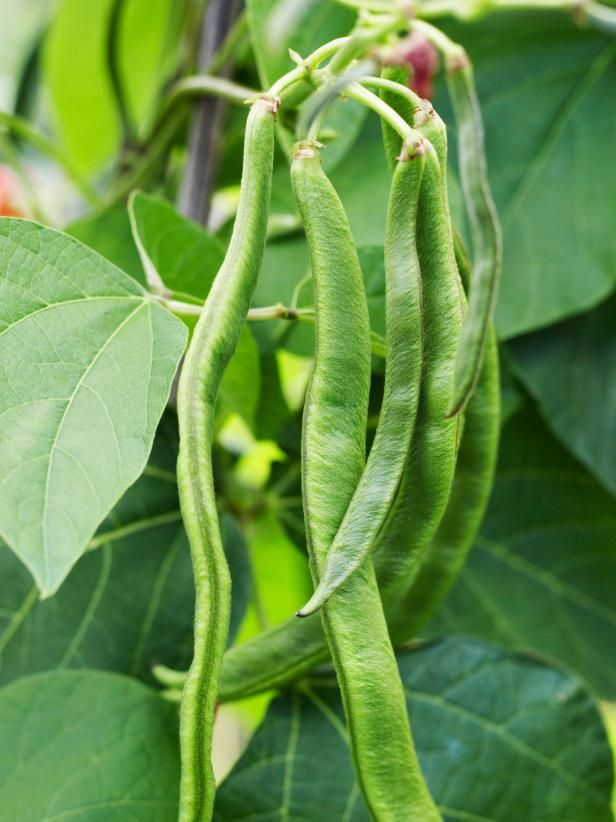  The blades are eaten 50-60 days after full germination. The height of the bush is 35 - 40 cm. The beans are 10 - 12 cm long, narrow, slightly curved, rounded, light green, devoid of a parchment layer and coarse fiber. The grain is greenish-yellow, round-elongated, of medium size. The blades are recommended to be plucked every 2-3 days, preventing overripe. Zoned in all regions of Russia. Grown by direct sowing in the ground. Differs in high vitality and stability. nine0003
The blades are eaten 50-60 days after full germination. The height of the bush is 35 - 40 cm. The beans are 10 - 12 cm long, narrow, slightly curved, rounded, light green, devoid of a parchment layer and coarse fiber. The grain is greenish-yellow, round-elongated, of medium size. The blades are recommended to be plucked every 2-3 days, preventing overripe. Zoned in all regions of Russia. Grown by direct sowing in the ground. Differs in high vitality and stability. nine0003  8 / 10
8 / 10  The beans are harvested 60-65 days after germination. Forms bushes 30 - 40 cm high. Beans 14 - 16 cm long, slightly curved, flat, up to 2 cm wide, green in color, with juicy thick valves, devoid of parchment layer and fibers. Seeds are white and large. Gives a lot of blades and grain. Beans Sugar shovel ripens well even in the Central and North-Western regions. Fruiting is extended and plentiful. If you regularly pick unripe beans, the yield increases significantly. nine0003
The beans are harvested 60-65 days after germination. Forms bushes 30 - 40 cm high. Beans 14 - 16 cm long, slightly curved, flat, up to 2 cm wide, green in color, with juicy thick valves, devoid of parchment layer and fibers. Seeds are white and large. Gives a lot of blades and grain. Beans Sugar shovel ripens well even in the Central and North-Western regions. Fruiting is extended and plentiful. If you regularly pick unripe beans, the yield increases significantly. nine0003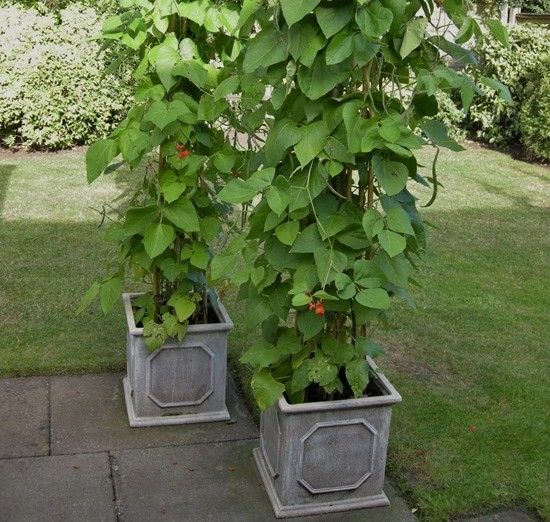  8 / 10
8 / 10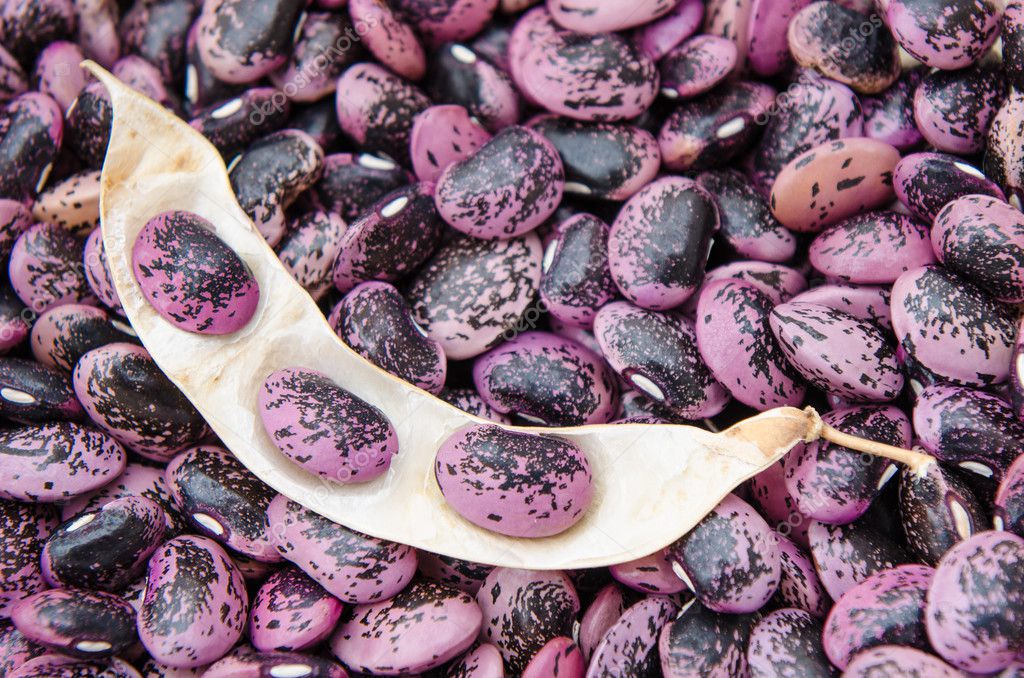  From germination to consumer ripeness, 50-60 days pass. The plant forms a medium-branched shrub 30–40 cm high. The beans are straight, 12–15 cm long, xiphoid, slightly curved, green, with a slightly pronounced parchment layer and fibers that appear when ripe. Seeds are white, oval, flattened. It has a universal use: at the very beginning of the fruiting of the shoulder, later - grain. Beans Gribovskaya in the registry for the North-Western, Central, North Caucasian and West Siberian regions. This variety of beans bears fruit well even in unfavorable years, and is distinguished by good disease resistance. nine0003
From germination to consumer ripeness, 50-60 days pass. The plant forms a medium-branched shrub 30–40 cm high. The beans are straight, 12–15 cm long, xiphoid, slightly curved, green, with a slightly pronounced parchment layer and fibers that appear when ripe. Seeds are white, oval, flattened. It has a universal use: at the very beginning of the fruiting of the shoulder, later - grain. Beans Gribovskaya in the registry for the North-Western, Central, North Caucasian and West Siberian regions. This variety of beans bears fruit well even in unfavorable years, and is distinguished by good disease resistance. nine0003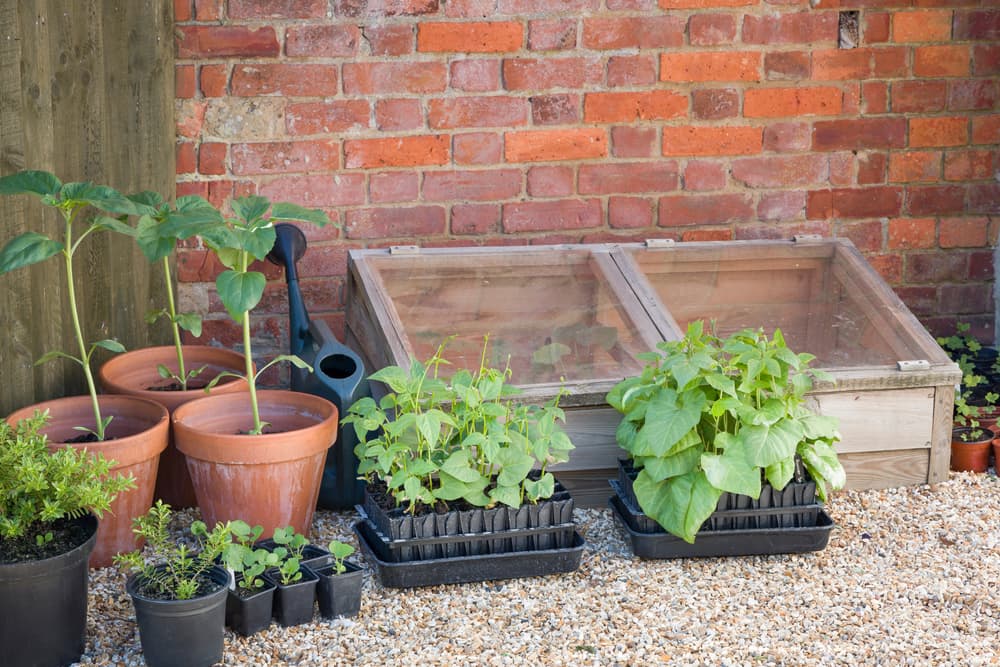  8 / 10
8 / 10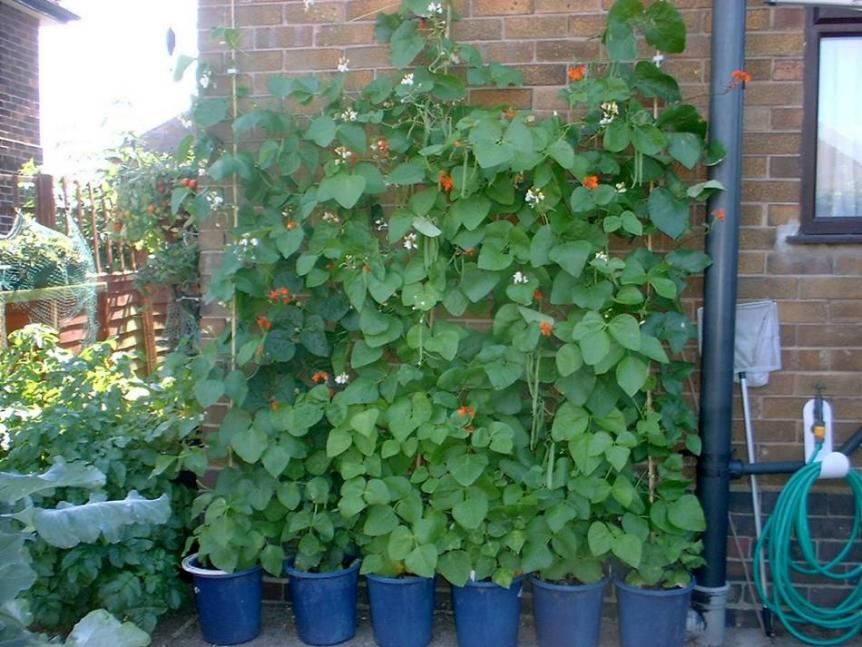  It ripens for shoulder blades in 60-65 days, for grain - in 86-90 days after germination. The plant forms a medium-sized bush with a height of 30 - 50 cm. In the North Caucasus region it has industrial importance, in the middle lane it is grown in household plots. The beans are straight, flat, 16 - 18 cm long, wide, green when unripe and bright yellow when ripe, with a medium beak, with a partial parchment layer and late appearing fibers. Seeds are oval, white, large. Designed for early production of blades and high yield of grain, including in the phase of milky-wax ripeness for freezing and canning. Zoned in all regions. If you leave the beans until fully ripe, they do not burst and the grain does not crumble. The variety is weakly susceptible to ascochitosis and anthracnose. nine0003
It ripens for shoulder blades in 60-65 days, for grain - in 86-90 days after germination. The plant forms a medium-sized bush with a height of 30 - 50 cm. In the North Caucasus region it has industrial importance, in the middle lane it is grown in household plots. The beans are straight, flat, 16 - 18 cm long, wide, green when unripe and bright yellow when ripe, with a medium beak, with a partial parchment layer and late appearing fibers. Seeds are oval, white, large. Designed for early production of blades and high yield of grain, including in the phase of milky-wax ripeness for freezing and canning. Zoned in all regions. If you leave the beans until fully ripe, they do not burst and the grain does not crumble. The variety is weakly susceptible to ascochitosis and anthracnose. nine0003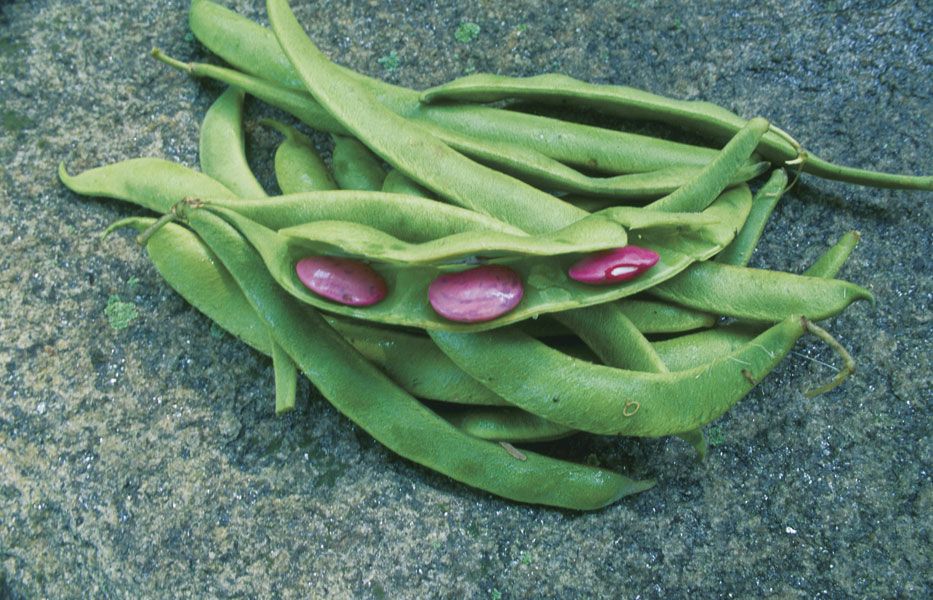  7 / 10
7 / 10  Beans ripen 65 - 75 days after germination. The plant forms a short, slightly sprawling bush, 30–40 cm high. Beans 15 cm long, straight, without voids, green with frequent red-pink strokes. The seeds are oval, oblong, large, white with a maroon pattern on ½ beans in the form of a large spot and inclusions, quickly boil soft and do not require soaking. The variety is unpretentious in care and resistant to adverse factors, including major crop diseases. Grown in all regions. nine0003
Beans ripen 65 - 75 days after germination. The plant forms a short, slightly sprawling bush, 30–40 cm high. Beans 15 cm long, straight, without voids, green with frequent red-pink strokes. The seeds are oval, oblong, large, white with a maroon pattern on ½ beans in the form of a large spot and inclusions, quickly boil soft and do not require soaking. The variety is unpretentious in care and resistant to adverse factors, including major crop diseases. Grown in all regions. nine0003  8 / 10
8 / 10  Ripens in 75 - 87 days. The plant is medium-sized, forms a bush 50 - 60 cm high and bright pink flowers. The beans are straight, medium length (10 - 12 cm), narrow, with a long "beak". Seeds are round-oval, deep cherry color, medium size. The garnish is tender, with a thin and inconspicuous skin. The variety was bred in the Oryol region and zoned in all regions. Suitable for intensive agricultural cultivation. For the full realization of potential productivity, top dressing with mineral fertilizers and complexes of microelements is required. Given the height of the bush, it is better to let the shoots along the support. This is not necessary, but will greatly simplify watering and weeding. nine0003
Ripens in 75 - 87 days. The plant is medium-sized, forms a bush 50 - 60 cm high and bright pink flowers. The beans are straight, medium length (10 - 12 cm), narrow, with a long "beak". Seeds are round-oval, deep cherry color, medium size. The garnish is tender, with a thin and inconspicuous skin. The variety was bred in the Oryol region and zoned in all regions. Suitable for intensive agricultural cultivation. For the full realization of potential productivity, top dressing with mineral fertilizers and complexes of microelements is required. Given the height of the bush, it is better to let the shoots along the support. This is not necessary, but will greatly simplify watering and weeding. nine0003  8 / 10
8 / 10  Grain ripens in 95 - 100 days after full shoots. The plant forms a spreading, medium-branched shrub 35-40 cm high, with numerous white flowers. Beans 10 - 12 cm long, contain 8 - 12 grains, pale yellow when ripe. The beans are round-oval, slightly flattened, with a smooth surface, white with a large blurred red spot, of medium size. During heat treatment, the grains retain their shape, do not fall apart, but are tender and without a hard skin. Widespread bean variety with good adaptation. In the northern regions, to obtain dry ripened grain, it is necessary to take into account the growing season. Early landings under covering material or film are justified. nine0003
Grain ripens in 95 - 100 days after full shoots. The plant forms a spreading, medium-branched shrub 35-40 cm high, with numerous white flowers. Beans 10 - 12 cm long, contain 8 - 12 grains, pale yellow when ripe. The beans are round-oval, slightly flattened, with a smooth surface, white with a large blurred red spot, of medium size. During heat treatment, the grains retain their shape, do not fall apart, but are tender and without a hard skin. Widespread bean variety with good adaptation. In the northern regions, to obtain dry ripened grain, it is necessary to take into account the growing season. Early landings under covering material or film are justified. nine0003  8 / 10
8 / 10